Nondestructive Detection and Quality Grading System of Walnut Using X-Ray Imaging and Lightweight WKNet
Abstract
1. Introduction
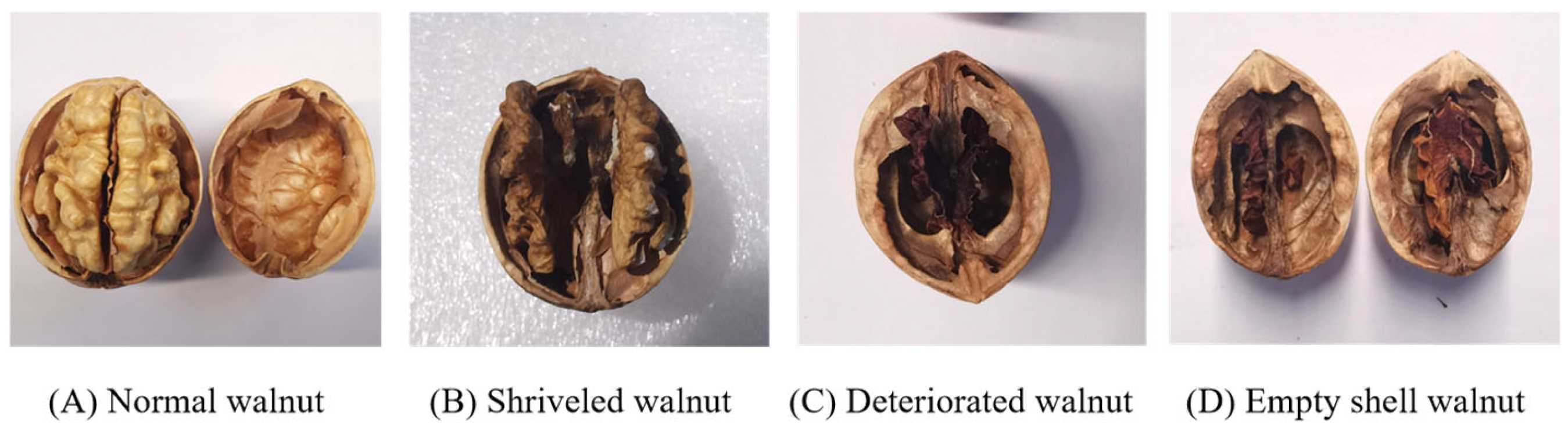
- An X-ray imaging system and a walnut kernel detection (WKD) dataset including 1756 images with 8472 bounding boxes are constructed.
- A novel rapid and lightweight WKNet is proposed by employing the efficient Transformer, GhostNet, and criss-cross attention (CCA) module to the advanced YOLO v5s deep learning model, aiming to solve the problem of poor feature extraction ability, parameter redundancy, and computing time consuming.
- A comprehensive investigation ranging from qualitative and quantitative evaluations of WKNet model are carried out to obtain best performance using the self-built WKD dataset.
- Some insights are given by our evaluation and analysis for walnut internal quality detection by deploying the WKNet to walnut quality control equipment.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Principle of X-Ray Technology and Images Acquisition
2.1.1. The Principle of X-Ray Imaging Technology
2.1.2. X-Ray Image Acquisition
2.1.3. X-Ray Images Preprocessing
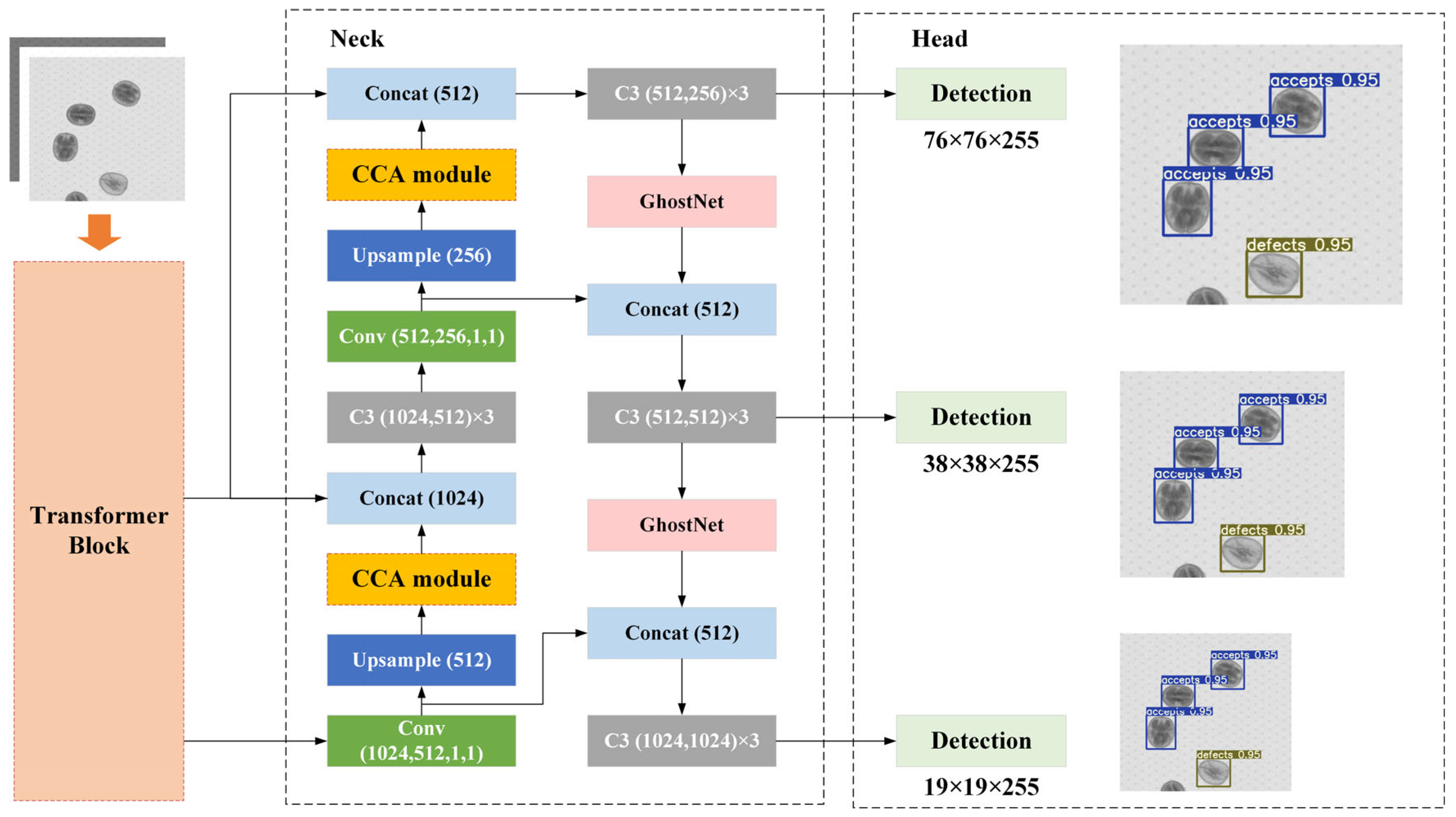
2.2. The Proposed WKNet
2.2.1. Overview
2.2.2. Transformer Block
2.2.3. GhostNet Makes Model Lightweight
2.2.4. Criss-Cross Attention Mechanism
3. Experiment Results and Discussion
3.1. WKNet Model Experiment Platform and Evaluation Metrics
3.2. WKNet Experiment Results and Analysis
3.2.1. Training and Validation Results of WKNet
3.2.2. Walnut Quality Detection Result Based on WKNet
3.2.3. Feature Visualization Analysis
3.2.4. Ablation Experiments of WKNet
3.2.5. Comparison Experiments to SOTA Methods
3.3. Walnut On-Line Detection and Quality Grading Test
3.3.1. Walnut On-Line Detection and Grading System Structure
3.3.2. Working Parameters and Evaluation Metrics
3.3.3. The On-Line Detection and Grading Test Result
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, J.; Shi, H.; Zhan, C.; Qiao, P.; He, Y.; Liu, Y. Study on the identification and detection of walnut quality based on terahertz maging. Foods 2022, 11, 3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, L.; Ji, W.; Guo, J.; Wang, J. Study on a novel energy-saving cryogenic pre-treatment equipment for walnut kernel peeling. Food Control 2021, 121, 107650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Peng, X.; Pei, H.; Chen, Y.; Meng, H.; Yuan, J.; Xing, H.; Wu, Y. An overview of walnuts application as a plant-based. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1083707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, M.; Chen, H.; Zhao, M.; Wang, X.; Yang, B.; Ren, J.; Su, G. Identification of antioxidant peptides released from defatted walnut (juglans sigillata dode) meal proteins with pancreatin. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 60, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, T.; Fang, L.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Shi, J.; Li, M.; Min, W. Anti-diabetic effect by walnut (Juglans mandshurica maxim.)-Derived peptide lpllr through inhibiting α-glucosidase and α-amylase, and alleviating insulin resistance of hepatic hepg2 cells. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 69, 103944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wu, L.; Du, Q.; Ren, J.; Chen, Q.; Li, D.; Mao, R.; Liu, X.; Li, Y. Small molecule oligopeptides isolated from walnut (Juglans regia L.). Their Anti-Fatigue Eff. Mice. Mol. 2019, 24, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Lu, Z.; Xiao, X.; Xu, M.; Lin, Y.; Dai, H.; Liu, X.; Pi, F.; Han, D. Non-destructive determination of internal defects in chestnut (Castanea mollissima) during postharvest storage using X-ray computed tomography. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 196, 112185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, L.; Guo, Y.; Mu, Q.; Wang, S. Advances in machine learning and hyperspectral imaging in the food supply chain. Food Eng. Rev. 2022, 14, 596–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wei, W.; Cui, Q.; Xie, W. The prospects for china’s food security and imports: Will china starve the world via imports? J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 2933–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, A.; Jagtap, S.; Garcia-Garcia, G.; Trollman, H.; Pateiro, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Trif, M.; Rusu, A.V.; Aadil, R.M.; Šimat, V.; et al. Food quality 4.0: From traditional approaches to digitalized automated analysis. J. Food Eng. 2023, 337, 111216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Bian, Y.; Wang, F.; Huang, T.; Wang, Z. A novel method for detection of internal quality of walnut kernels using low-field magnetic resonance imaging. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 217, 108546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Dai, D.; Zheng, J.; Li, L.; Kang, H.; Zheng, X. WT-YOLOM: An Improved Target Detection Model Based on YOLOv4 for Endogenous Impurity in Walnuts. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.; Jin, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, R. Machine learning for detection of walnuts with shriveled kernels by fusing weight and image information. J. Food Process Eng. 2020, 43, 13562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, D.; Wang, H.; Xie, L.; Ying, Y.; Zhang, Y. Impurity detection of juglans using deep learning and machine vision. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 178, 105764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugraha, B.; Verboven, P.; Janssen, S.; Wang, Z.; Nicolaï, B.M. Non-destructive porosity mapping of fruit and vegetables using X-ray ct. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 150, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Hu, Y.; Ali Buttar, N.; Mahmood, A. X-ray computed tomography for quality inspection of agricultural products: A review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 3146–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Wang, N.; Ding, X.; Qi, Z.; Hu, N.; Duan, S.; Yang, Z.; Bi, X. Detection of pear freezing injury by non-destructive X-ray scanning technology. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 190, 111950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunakaran, C.; Jayas, D.S.; White, N.D.G. X-ray image analysis to detect infestations caused by insects in grain. Cereal Chem. 2003, 80, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves Pereira, L.F.; Janssens, E.; Cavalcanti, G.D.C.; Tsang, I.R.; Van Dael, M.; Verboven, P.; Nicolai, B.; Sijbers, J. Inline discrete tomography system: Application to agricultural product inspection. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 138, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Yang, W.; Niu, Z.; Huang, C. Non-destructive detection of wheat tiller morphological traits based on X-ray ct technology. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 196–201. [Google Scholar]
- Raju Ahmed, M.; Yasmin, J.; Wakholi, C.; Mukasa, P.; Cho, B. Classification of pepper seed quality based on internal structure using X-ray ct imaging. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 179, 105839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Zhang, S.; Sun, H.; Ren, R. Mass detection of walnut based on X-ray imaging technology. J. Food Process Eng. 2022, 45, 14034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Looverbosch, T.; Rahman Bhuiyan, M.H.; Verboven, P.; Dierick, M.; Van Loo, D.; De Beenbouwer, J.; Sijbers, J.; Nicolaï, B. Nondestructive internal quality inspection of pear fruit by X-ray ct using machine learning. Food Control 2020, 113, 107170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Yang, L.; Zhu, Z.; Cui, K. Detection and Grading Method of Walnut Kernel Quality Based on Hyperspectral Image. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2020, 48, 1737–1746. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, S.; Qiao, J.; Wang, R.; Yu, H.; Wang, C.; Taylor, K.; Pan, H. Intelligent diagnosis of northern corn leaf blight with deep learning model. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 1094–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, G.; Li, X. Yolox-dense-ct: A detection algorithm for cherry tomatoes based on yolox and densenet. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2022, 16, 4788–4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, O.M. Real-time cucurbit fruit detection in greenhouse using improved yolo series algorithm. Precis. Agric. 2024, 25, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempelaere, A.; Van De Looverbosch, T.; Kelchtermans, K.; Verboven, P.; Tuytelaars, T.; Nicolai, B. Synthetic data for X-ray ct of healthy and disordered pear fruit using deep learning. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 200, 112342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhou, D.; Li, J. Application of lightweight yolov5 for walnut kernel grade classification and endogenous foreign body detection. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 127, 105964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Wang, J.; Nie, Z.; Yang, H.; Yu, S. A lightweight yolov8 tomato detection algorithm combining feature enhancement and attention. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Qian, S.; Niu, Y. Visual recognition and location algorithm based on optimized yolov3 detector and rgb depth camera. Vis. Comput. 2024, 40, 1965–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Hameed, S.; Xie, L.; Ying, Y. Non-destructive quality control detection of endogenous contaminations in walnuts using terahertz spectroscopic imaging. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 14, 2453–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 20398-2021; Grade of Walnut. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Guan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chai, X.; Chai, X.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, J.; Sun, T. Visual learning graph convolution for multi-grained orange quality grading. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 22, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Cheng, M.; Huang, S.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, H. A deep learning approach incorporating yolo v5 and attention mechanisms for field real-time detection of the invasive weed Solanum rostratum Dunal seedlings. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 199, 107194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenggang, S.; Yunlu, W.; Peng, L.; Xudong, Z.; Xiude, C.; Zhijun, W. Identification of apple fruit diseases using improved yolov5s and transfer learning. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 171–179. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, L.; Su, J.; He, R.; Song, L.; Huang, R.; Fang, Y.; Song, Y.; Su, B. Real-time tracking and counting of grape clusters in the field based on channel pruning with yolov5s. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 206, 107662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.03762. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Guo, J.; Liu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Xiao, A.; Xu, C.; Xu, Y.; et al. A survey on vision transformer. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Guo, J.; Xu, C.; Xu, C. Ghostnet: More features from cheap operations. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1577–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; He, G.; Deng, H.; Fan, W.; Xu, L.; Cao, L.; Feng, D.; Li, J.; Wu, H.; Lv, J.; et al. Pigeon cleaning behavior detection algorithm based on light-weight network. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 199, 107032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Zhong, G.; Yu, H. A review on the attention mechanism of deep learning. Neurocomputing 2021, 452, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wei, Y.; Huang, L.; Shi, H.; Liu, W.; Huang, T.S. Ccnet: Criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 6896–6908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Han, X.; Yang, H. Fast and accurate wheat grain quality detection based on improved yolov5. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 202, 107426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Environmental Attribute | Environment Configuration |
|---|---|
| Operation system | Ubuntu 20.04 |
| CPU | Intel(R) Core (TM) i7-9750H |
| GPU | RTX 2060 |
| Memory | 32G DDR4 |
| Programs language | Python 3.8.5 |
| Dataset Attribute | Performance Metrics Statistics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP_0.5 | P | R | F1 | Infer Time (ms) | |
| Original background | 0.9716 | 0.9665 | 0.9600 | 0.9632 | 13.4 |
| Removing background | 0.9869 | 0.9779 | 0.9875 | 0.9827 | 11.9 |
| Value changing | +0.0153 | +0.0114 | +0.0275 | +0.0195 | −1.5 |
| Model Type | mAP_0.5 | P | R | F1 | Infer Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLO v5s | 0.9349 | 0.9412 | 0.9283 | 0.9347 | 26.2 |
| YOLO v5s (Trans) | 0.9613 | 0.9647 | 0.9618 | 0.9624 | 21.4 |
| YOLO v5s (Ghost) | 0.9625 | 0.9651 | 0.9622 | 0.9636 | 20.6 |
| YOLO v5s (CCA) | 0.9627 | 0.9649 | 0.9631 | 0.9640 | 22.1 |
| YOLO v5s (Ghost + CCA) | 0.9774 | 0.9782 | 0.9746 | 0.9764 | 16.5 |
| YOLO v5s (Trans + Ghost) | 0.9669 | 0.9673 | 0.9658 | 0.9665 | 18.7 |
| YOLO v5s (Trans + CCA) | 0.9742 | 0.9727 | 0.9719 | 0.9723 | 20.3 |
| WKNet (Trans + Ghost + CCA) | 0.9869 | 0.9779 | 0.9875 | 0.9827 | 11.9 |
| Model | mAP_0.5 | F1 | Inference Time/ms | Parameters/M | Model Size/M | FLOPs/G |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSD | 0.8172 | 0.8113 | 274.7 | 34.4 | 69.1 | 98.7 |
| Faster R-CNN | 0.9247 | 0.9233 | 362.3 | 137.2 | 245.7 | N/A |
| YOLO v4-tiny | 0.9108 | 0.8972 | 37.8 | 52.4 | 108.6 | 216.4 |
| YOLO v5s | 0.9349 | 0.9347 | 26.2 | 7.1 | 14.2 | 16.3 |
| YOLO v5m | 0.9558 | 0.9471 | 39.4 | 21.1 | 40.6 | 59.3 |
| YOLO v5l | 0.9774 | 0.9785 | 44.9 | 46.6 | 89.2 | 171.8 |
| YOLO v5x | 0.9316 | 0.9264 | 76.1 | 87.3 | 166.9 | 241.9 |
| YOLO v6 | 0.9322 | 0.9247 | 56.7 | 15.4 | 20.3 | 36.8 |
| YOLO v7 | 0.9418 | 0.9252 | 54.5 | 37.9 | 72.8 | 106.1 |
| YOLO v8n | 0.9459 | 0.9328 | 18.1 | 3.3 | 6.3 | 8.7 |
| YOLO v8s | 0.9531 | 0.9436 | 34.4 | 11.2 | 22.6 | 28.4 |
| YOLO v9s | 0.9627 | 0.9549 | 21.8 | 7.3 | 16.1 | 27.6 |
| RT-DETR | 0.9562 | 0.9477 | 15.6 | 41.7 | 81.4 | 27.2 |
| YOLO v10s | 0.9578 | 0.9556 | 13.4 | 7.2 | 14.3 | 21.7 |
| Our WKNet | 0.9869 | 0.9827 | 11.9 | 3.1 | 6.1 | 6.9 |
| Walnut Variety. | (%) | Take-Sorting Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Wen 185 | 98.50 | 53.96 |
| Xin 2 | 96.81 | 46.5 |
| Xinfeng | 98.34 | 53.95 |
| Three mixed varieties | 96.65 | 49.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, X.; Zhou, J. Nondestructive Detection and Quality Grading System of Walnut Using X-Ray Imaging and Lightweight WKNet. Foods 2025, 14, 2346. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132346
Fan X, Zhou J. Nondestructive Detection and Quality Grading System of Walnut Using X-Ray Imaging and Lightweight WKNet. Foods. 2025; 14(13):2346. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132346
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Xiangpeng, and Jianping Zhou. 2025. "Nondestructive Detection and Quality Grading System of Walnut Using X-Ray Imaging and Lightweight WKNet" Foods 14, no. 13: 2346. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132346
APA StyleFan, X., & Zhou, J. (2025). Nondestructive Detection and Quality Grading System of Walnut Using X-Ray Imaging and Lightweight WKNet. Foods, 14(13), 2346. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132346






