Beyond Meat Substitution: A Multifaceted Review of Plant-Based and Alternative Proteins, from Environmental Impact to Analytical Technologies
Abstract
1. Introduction
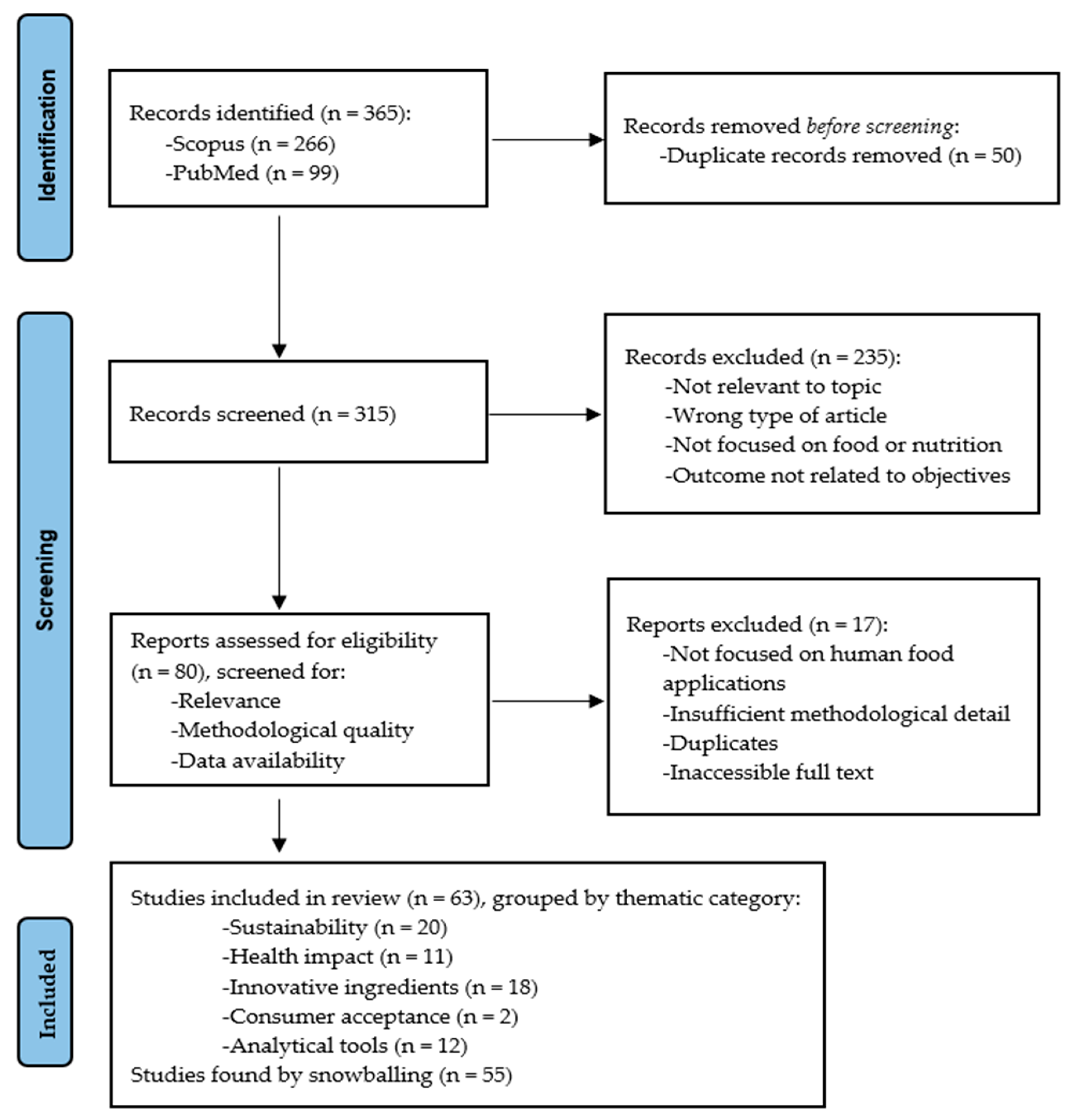
2. Methodology for Literature Selection
3. Results of PRISMA Search
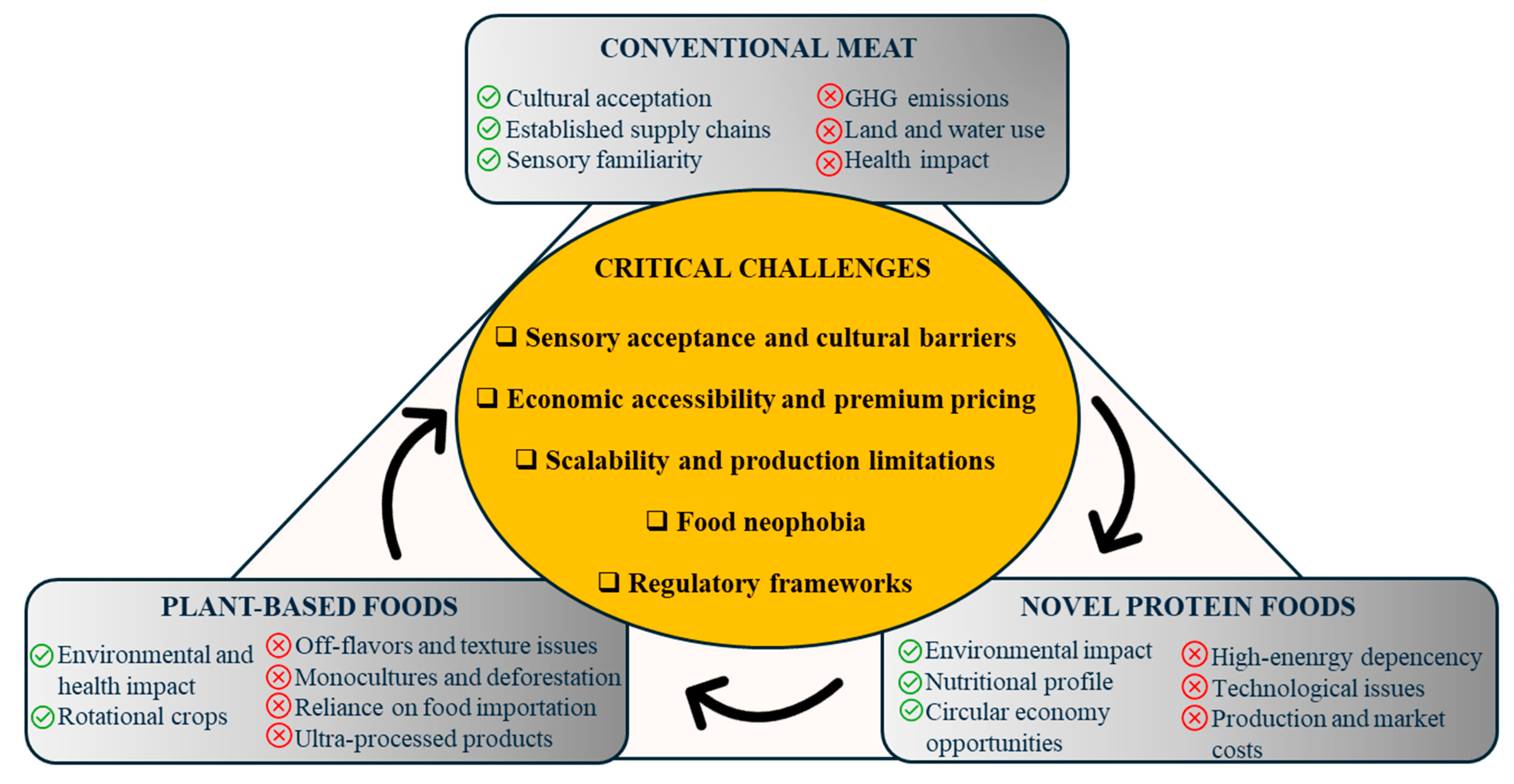
3.1. Sustainability and the Environmental Impact of PBF Versus Meat
3.1.1. Favorable Environmental Impacts of Plant-Based Diets
3.1.2. Challenges and Critiques of PBFs
3.1.3. Synthesis of Perspectives
3.2. Plant-Based Dietary Pattern Impact on Health
3.2.1. All-Cause Mortality
3.2.2. Cause-Specific Disease
3.3. Innovative Ingredients and Their Environmental Impact: Feasibility of Future Meat Alternatives
3.3.1. Edible Insects
3.3.2. Cultured Meat
3.3.3. Mycoprotein
3.3.4. Microalgae
3.3.5. Comparison of Meat-Alternative Foodstuffs
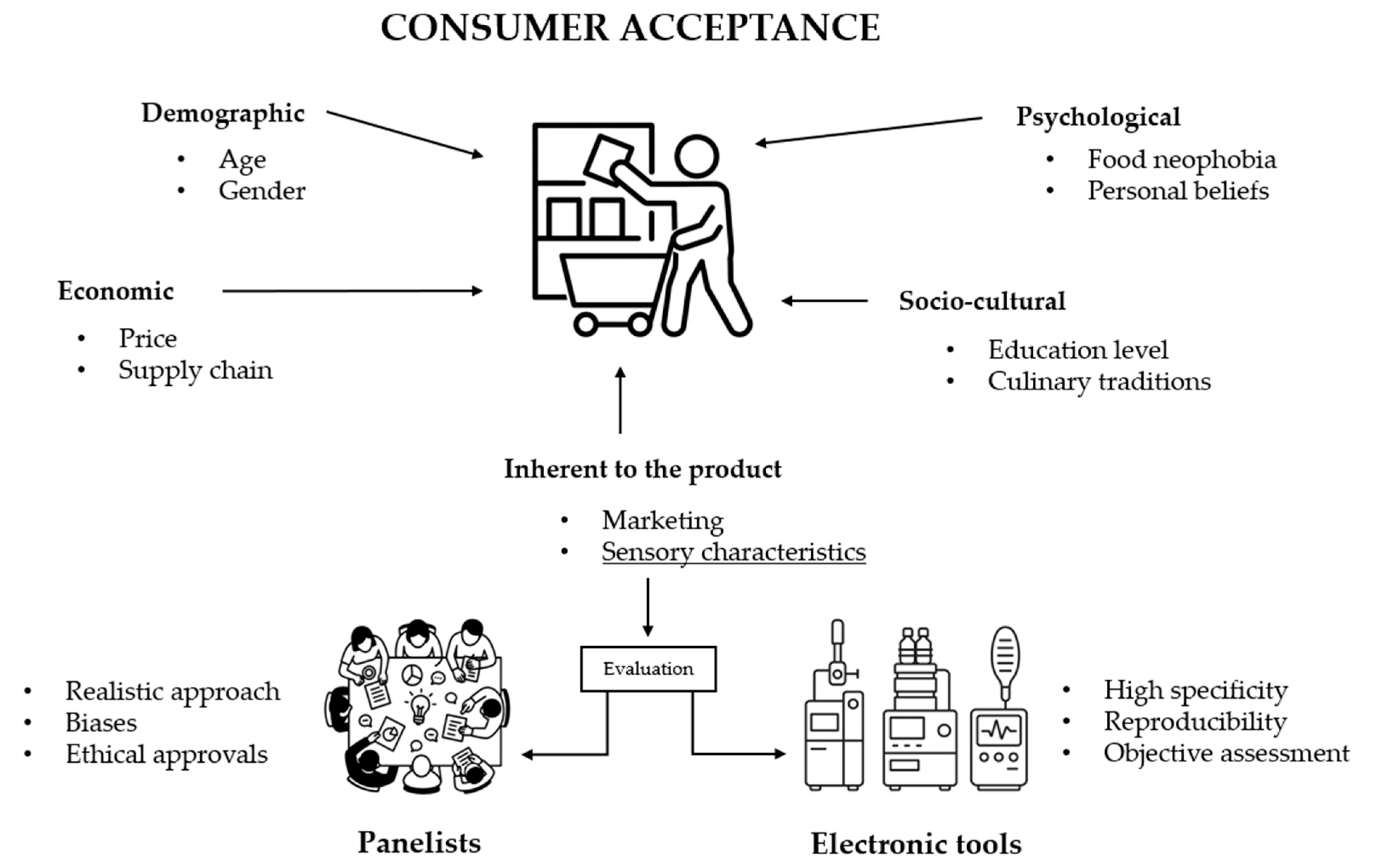
3.4. Consumer Sensory Acceptance Analysis of MS
3.4.1. Sensory Perception
3.4.2. Factors Affecting Acceptance
3.5. Analytical Evaluation of MSs and PBFs Through Electronic Sensors
3.5.1. MA Electronic Sensory Analysis
3.5.2. Other PBF Electronic Sensory Analysis
3.6. Strengths and Limitations
3.7. Critical Perspectives and Future Trends
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PBF | Plant-Based Food |
| MS | Meat Substitute |
| MA | Meat Analogue |
| GHG | Greenhouse Gas |
| LCA | Life Cycle Assessment |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| SSPs | Shared Socioeconomic Pathways |
| FFQ | Food Frequency Questionnaire |
| HR | Hazard Ratio |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| PDI | Plant-Based Diet Index |
| oPDI | Overall Plant-Based Diet Index |
| hPDI | Healthy Plant-Based Diet Index |
| uPDI | Unhealthy Plant-Based Diet Index |
| HPF | Healthy Plant-Based Foods Index |
| uHPF | Unhealthy Plant-Based Foods Index |
| AF | Animal-Based Foods Index |
| oPVG | Overall Pro-Vegetarian Dietary Pattern |
| hPVG | Healthy Pro-Vegetarian Dietary Pattern |
| uPVG | Unhealthy Pro-Vegetarian Dietary Pattern |
| HEI-2015 | Healthy Eating Index–2015 |
| PVD | Pro-Vegetarian Diet Index |
| DQI | Diet Quality Index |
| aDQI | Animal-Based Diet Quality Index |
| cDQI | Comprehensive Diet Quality Index |
| pDQI | Plant-Based Diet Quality Index |
| EPA | Eicosapentaenoic Acid |
| DHA | Docosahexaenoic Acid |
| SFA | Saturated Fatty Acid |
| MUFA | Monounsaturated Fatty Acid |
| PUFA | Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid |
| e-nose | Electronic Nose |
| e-tongue | Electronic Tongue |
| e-eye | Electronic Eye |
| GC-MS | Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry |
| SPC | Sustainable Production and Consumption (journal context) |
| AFW | Agri-Food Waste |
References
- Szenderák, J.; Fróna, D.; Rákos, M. Consumer Acceptance of Plant-Based Meat Substitutes: A Narrative Review. Foods 2022, 11, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crippa, M.; Solazzo, E.; Guizzardi, D.; Monforti-Ferrario, F.; Tubiello, F.N.; Leip, A. Food Systems Are Responsible for a Third of Global Anthropogenic GHG Emissions. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.; Rudy, M.; Duma-Kocan, P.; Stanisławczyk, R.; Krajewska, A.; Dziki, D.; Hassoon, W.H. Sustainability of Alternatives to Animal Protein Sources, a Comprehensive Review. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.A.; Domingo, N.G.G.; Colgan, K.; Thakrar, S.K.; Tilman, D.; Lynch, J.; Azevedo, I.L.; Hill, J.D. Global food system emissions could preclude achieving the 1.5° and 2 °C climate change targets. Science 2020, 370, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlich, M.J.; Sabaté, J.; Mashchak, A.; Fresán, U.; Jaceldo-Siegl, K.; Miles, F.; Fraser, G.E. Ultra-Processed Food Intake and Animal-Based Food Intake and Mortality in the Adventist Health Study-2. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 115, 1589–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.D.; Giromini, C.; Givens, D.I. Animal-derived foods: Consumption, composition and effects on health and the environment: An overview. Front. Anim. Sci. 2024, 5, 1332694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, A.; Ponnuchamy, M.; Kumar, P.S.; Kapoor, A.; Nguyen Vo, D.-V.; Rangasamy, G. Digitalization of the Agro-Food Sector for Achieving Sustainable Development Goals: A Review. Sustain. Food Technol. 2023, 1, 783–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbour, L.; Lindberg, R.; Woods, J.; Charlton, K.; Brimblecombe, J. Local Urban Government Policies to Facilitate Healthy and Environmentally Sustainable Diet-Related Practices: A Scoping Review. Public Health Nutr. 2022, 25, 471–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordelle, S.; Redl, A.; Schlich, P. Sensory Acceptability of New Plant Protein Meat Substitutes. Food Qual. Pref. 2022, 98, 104508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentini, M.; Kinchla, A.J.; Nolden, A.A. Role of Sensory Evaluation in Consumer Acceptance of Plant-Based Meat Analogs and Meat Extenders: A Scoping Review. Foods 2020, 9, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrell, E.L. Reinventing the Meal: A Genealogy of Plant-Based Alternative Proteins. Agric. Hum. Values 2024, 41, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Moreno, M.; Kraselnik, A. The Impact of Plant-Based Proteins on Muscle Mass and Strength Performance: A Comprehensive Review. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2025, 14, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, S.R.K.; Kok, C.W.; Kunasegaran, T.; Ramadas, A. Effect of Plant-Based Diets on Gut Microbiota: A Systematic Review of Interventional Studies. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowski, A.C.; Miller, A.C.; Miller, M.E.; Xiao, H.; Wu, X. Potential Health Benefits of Edible Insects. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 3499–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kustar, A.; Patino-Echeverri, D. A Review of Environmental Life Cycle Assessments of Diets: Plant-Based Solutions are Truly Sustainable, Even in the Form of Fast Foods. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abi-Rizk, H.; Jouan-Rimbaud Bouveresse, D.; Chamberland, J.; Cordella, C.B.Y. Recent Developments of E-Sensing Devices Coupled to Data Processing Techniques in Food Quality Evaluation: A Critical Review. Anal. Methods 2023, 15, 5410–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harwatt, H.; Benton, T.G.; Bengtsson, J.; Birgisdóttir, B.E.; Brown, K.A.; van Dooren, C.; Erkkola, M.; Graversgaard, M.; Halldorsson, T.; Hauschild, M.; et al. Environmental sustainability of food production and consumption in the Nordic and Baltic region—a scoping review for Nordic Nutrition Recommendations 2023. Food Nutr. Res. 2024, 68, 10539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Vega, D.; Dumas, P.; Prudhomme, R.; Kremen, C.; Aubert, P.-M. A safe agricultural space for biodiversity. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1328800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakstad, M.M.; Danaei, G.; Tadesse, A.W.; Damerau, K.; Bellows, A.L.; Canavan, C.R.; Bliznashka, L.; Zack, R.; Myers, S.S.; Berhane, Y.; et al. Life expectancy and agricultural environmental impacts in Addis Ababa can be improved through optimized plant and animal protein consumption. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Xie, B.; Wan, C.; Song, R.; Zhong, W.; Xin, S.; Song, K. Enhancing Soil Health and Plant Growth through Microbial Fertilizers: Mechanisms, Benefits, and Sustainable Agricultural Practices. Agronomy 2024, 14, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, S.G.; Joyce, P.J.; Rigarlsford, G.; Dötsch-Klerk, M.; van Elk, K.; Doelman, J.; Daioglou, V.; Huijbregts, M.A.J.; Sim, S. Prospective life cycle assessment of climate and biodiversity impacts of meat-based and plant-forward meals: A case study of Indonesian and German meal options. J. Ind. Ecol. 2024, 28, 1598–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Parajuli, R.; Thoma, G. Life Cycle Assessment of Dietary Patterns in the United States: A Full Food Supply Chain Perspective. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auclair, O.; Colombo, P.E.; Milner, J.; Burgos, S.A. Partial substitutions of animal with plant protein foods in Canadian diets have synergies and trade-offs among nutrition, health and climate outcomes. Nat. Food 2024, 5, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazac, R.; Järviö, N.; Tuomisto, H.L. Environmental and nutritional Life Cycle Assessment of novel foods in meals as transformative food for the future. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 876, 162796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nájera Espinosa, S.; Hadida, G.; Jelmar Sietsma, A.; Alae-Carew, C.; Turner, G.; Green, R.; Pastorino, S.; Picetti, R.; Scheelbeek, P. Mapping the Evidence of Novel Plant-Based Foods: A Systematic Review of Nutritional, Health, and Environmental Impacts in High-Income Countries. Nutr. Rev. 2024, 83, e1626–e1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daba, A.K.; Murimi, M.; Abegaz, K.; Hailu, D. Determinants and constraints to household-level animal source food consumption in rural communities of Ethiopia. J. Nutr. Sci. 2021, 10, e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haileselassie, M.; Redae, G.; Berhe, G.; Henry, C.J.; Nickerson, M.T.; Tyler, B.; Mulugeta, A. Why are animal source foods rarely consumed by 6–23 months old children in rural communities of Northern Ethiopia? A qualitative study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enahoro, D.; Kozicka, M.; Pfeifer, C.; Jones, S.K.; Tran, N.V.; Chan, C.Y.; Sulser, T.B.; Gotor, E.; Rich, K.M. Linking ecosystem services provisioning with demand for animal-sourced food: An integrated modeling study for Tanzania. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2023, 23, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, M.C.; Walchale, A.; Heard, B.R.; Hoey, L.; Khoury, C.K.; De Haan, S.; Burra, D.D.; Duong, T.T.; Osiemo, J.; Trinh, T.H.; et al. Environmental analyses to inform transitions to sustainable diets in developing countries: Case studies for Vietnam and Kenya. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2020, 25, 1183–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, C.N.; Paquette, M.; Sahye-Pudaruth, S.; Dadvar, A.; Dinh, D.; Khodabandehlou, K.; Liang, F.; Mishra, E.; Sidhu, M.S.; Brown, R.; et al. The Environmental Sustainability of Plant-Based Dietary Patterns: A Scoping Review. J. Nutr. 2023, 153, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrens, P.; Kiefte-de Jong, J.C.; Bosker, T.; Rodrigues, J.F.D.; de Koning, A.; Tukker, A. Evaluating the environmental impacts of dietary recommendations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 13412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodirsky, B.L.; Dietrich, J.P.; Martinelli, E.; Stenstad, A.; Pradhan, P.; Gabrysch, S.; Mishra, A.; Weindl, I.; Mouël, C.L.; Rolinski, S.; et al. The ongoing nutrition transition thwarts long-term targets for food security, public health and environmental protection. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeles-Agdeppa, I.; Sun, Y.; Tanda, K.V. Dietary pattern and nutrient intakes in association with non-communicable disease risk factors among Filipino adults: A cross-sectional study. Nutr. J. 2020, 19, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, E.M.; Fischer, C.G.; Aguiar, S.; Geri, M.; Fernández, R.J.; Coquet, J.B.; Scavuzzo, C.M.; Rieznik, A.; León, A.; González, A.D.; et al. The Health, Environmental, and Economic Dimensions of Future Dietary Transitions in Argentina. Sustain. Sci. 2022, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachie, C.; Nwachukwu, I.D.; Aryee, A.N.A. Trends and innovations in the formulation of plant-based foods. Food Prod. Proc. Nutr. 2023, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimutis, W.R.; Shirwaiker, R. A perspective on the environmental impact of plant-based protein concentrates and isolates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2319003121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuin, V.G.; Araripe, E.; Zanotti, K.; Stahl, A.M.; Gomes, C.J.C. Alternative Products Selling Sustainability? A Brazilian Case Study on Materials and Processes to Produce Plant-Based Hamburger Patties. Sust. Chem. 2022, 3, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, K.R.G.; Anton, A.; Ventura, M.U.; Andrade, E.P.; Ralisch, R. Using the available indicators of potential biodiversity damage for Life Cycle Assessment on soybean crop according to Brazilian ecoregions. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 127, 107809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, A.d.S.; Barbero, R.P.; Romanzini, E.P.; Teobaldo, R.W.; Ongaratto, F.; Fernandes, M.H.M.R.; Ruggieri, A.C.; Reis, R.A. Intensification: A Key Strategy to Achieve Great Animal and Environmental Beef Cattle Production Sustainability in Brachiaria Grasslands. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chandio, A.A.; Yang, F.; Tang, Y.; Ankrah Twumasi, M.; Sargani, G.R. Modeling the Impact of Climatological Factors and Technological Revolution on Soybean Yield: Evidence from 13-Major Provinces of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán, A.M.; Scheel, C.N.; Fitton, N.; Schmidt, J.; Kløverpris, J. Assessing life cycle environmental impacts of inoculating soybeans in Argentina with Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2021, 26, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, F.R.; Zanon, A.J.; Monzón, J.P.; Andrade, J.F.; Silva, E.H.F.M.d.; Richter, G.L.; Antolin, L.A.S.; Ribeiro, B.S.M.R.; Ribas, G.G.; Battisti, R.; et al. Protecting the Amazon forest and reducing global warming via agricultural intensification. Nat. Sustain. 2022, 5, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.B.; Freddi, O.d.S.; Matos, E.d.S.; Tavanti, R.F.R.; Wruck, F.J.; de Lima, J.P.; Marchioro, V.; Franchini, J.C. Integrated Production Systems: An Alternative to Soil Chemical Quality Restoration in the Cerrado-Amazon Ecotone. Catena 2020, 185, 104279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznar-Sánchez, J.A.; Velasco-Muñoz, J.F.; López-Felices, B.; Román-Sánchez, I.M. An Analysis of Global Research Trends on Greenhouse Technology: Towards a Sustainable Agriculture. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucić, R.; Raposo, M.; Chervinska, A.; Domingos, T.; Teixeira, R.F.M. Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Land Use Impacts of Soybean Production: Systematic Review and Analysis. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, S.L.; D’Adamo, C.R.; Holton, K.F.; Ortiz, S.; Overby, N.; Logan, A.C. Beyond Plants: The Ultra-Processing of Global Diets is Harming the Health of People, Places and Planet. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO) European Office for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases. Plant-Based Diets and Their Impact on Health, Sustainability and the Environment: A Review of the Evidence; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2021; Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/349086/WHO-EURO-2021-4007-43766-61591-eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 7 April 2025).
- Schorr, K.A.; Agayn, V.; de Groot, L.C.P.G.M.; Slagboom, P.E.; Beekman, M. A plant-based diet index to study the relation between diet and disease risk among adults: A narrative review. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2024, 28, 100272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keaver, L.; Ruan, M.; Chen, F.; Du, M.; Ding, C.; Wang, J.; Shan, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, F.F. Plant- and animal-based diet quality and mortality among US adults: A cohort study. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 125, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Shen, J.; Xuan, J.; Zhu, A.; Ji, J.S.; Liu, X.; Cao, Y.; Zong, G.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Plant-based dietary patterns in relation to mortality among older adults in China. Nat. Aging 2022, 2, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zeng, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, A.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, W. A prospective study of healthful and unhealthful plant-based diet and risk of overall and cause-specific mortality. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, L.J.; Kim, H.; Talegawkar, S.A.; Tucker, K.L.; Correa, A.; Rebholz, C.M. Plant-based diets and incident cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality in African Americans: A cohort study. PLoS Med. 2022, 19, 1003863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.B.; Page, A.J.; Gill, T.K.; Melaku, Y.A. The association between diet quality, plant-based diets, systemic inflammation, and mortality risk: Findings from NHANES. Eur. J. Nutr. 2023, 62, 2723–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, R.; Yang, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Maimaitiyiming, M.; Lin, J.; Ma, Y.; et al. Association of plant-based diets with total and cause-specific mortality across socioeconomic deprivation level: A large prospective cohort. Eur. J. Nutr. 2024, 63, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Jiang, Q.; Zhai, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hu, F.; Qian, Y.; Sun, J. Association between Plant-based Diet and Risk of Chronic Diseases and All-Cause Mortality in Centenarians in China: A Cohort Study. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2024, 8, 102065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Wilkens, L.R.; Haiman, C.A.; Le Marchand, L.; Park, S.-Y. Plant-based dietary patterns and mortality from all causes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer: The Multiethnic Cohort Study. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 43, 1447–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abris, G.P.; Shavlik, D.J.; Mathew, R.O.; Butler, F.M.; Oh, J.; Sirirat, R.; Sveen, L.E.; Fraser, G.E. Cause-specific and all-cause mortalities in vegetarian compared with those in nonvegetarian participants from the Adventist Health Study-2 cohort. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 120, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oncina-Cánovas, A.; Torres-Collado, L.; García-de-la-Hera, M.; Compañ-Gabucio, L.M.; González-Palacios, S.; Signes-Pastor, A.J.; Vioque, J. Pro-vegetarian dietary patterns and mortality by all-cause and specific causes in an older Mediterranean population. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2024, 28, 100239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Lou, Y.; Wang, S.; You, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Cao, S. Association of changes in plant-based diet consumption with all-cause mortality among older adults in China: A prospective study from 2008 to 2019. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2024, 28, 100027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufingerl, N.; Eilander, A. Nutrient Intake and Status in Adults Consuming Plant-Based Diets Compared to Meat-Eaters: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2025 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee. Scientific Report of the 2025 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee: Advisory Report to the Secretary of Health and Human Services and Secretary of Agriculture; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (USDHHS): Washington, DC, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.dietaryguidelines.gov/2025-advisory-committee-report (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- AESAN Scientific Committee (Working Group); Martínez, J.A.; Cámara, M.; Giner, R.; González, E.; López, E.; Mañes, J.; Portillo, M.P.; Rafecas, M.; Gutiérrez, E.; et al. Report from the Scientific Committee of the Spanish Agency for Food Safety and Nutrition (AESAN) on the revision and updating of the Dietary Recommendations for the Spanish population. AESAN Scientific Comm. J. 2020, 32, 11–58. Available online: https://www.aesan.gob.es/en/AECOSAN/web/publicaciones/aecosan_comite_cientifico.htm (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Cutroneo, S.; Angelino, D.; Tedeschi, T.; Pellegrini, N.; Martini, D.; SINU Young Working Group; Dall’Asta, M.; Russo, M.D.; Nucci, D.; Moccia, S.; et al. Nutritional Quality of Meat Analogues: Results From the Food Labelling of Italian Products (FLIP) Project. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 852831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2021/882. Off. J. Eur. Union L. 2023, 194, 16–20. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32021R0882 (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- European Union. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2021/1975. Off. J. Eur. Union L. 2021, 402, 10–16. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32021R1975 (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- European Union. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2022/169. Off. J. Eur. Union L. 2022, 27, 10–16. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32022R0169 (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- European Union. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2022/188. Off. J. Eur. Union L. 2022, 30, 1–4. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32022R0188 (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- European Union. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2023/5. Off. J. Eur. Union L. 2023, 2, 9–14. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32023R0005 (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- European Union. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2023/58. Off. J. Eur. Union L. 2023, 8, 10–15. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32023R0058 (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Vinci, G.; Prencipe, S.A.; Masiello, L.; Zaki, M.G. The Application of Life Cycle Assessment to Evaluate the Environmental Impacts of Edible Insects as a Protein Source. Earth 2022, 3, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyer, M.; Hörtenhuber, S.; Zollitsch, W.; Jäger, H.; Schaden, L.-M.; Gronauer, A.; Kral, I. Environmental life cycle assessment of yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) production for human consumption in Austria—a comparison of mealworm and broiler as protein source. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2021, 26, 2232–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.; Rinaldi, R.; Giglio, F.; Ianniciello, D.; Boschi, A.; Scieuzo, C.; Salvia, R.; Falabella, P. Edible insects: An overview on farming, from processing procedures to environmental impact, with a glimpse to traditional recipes and to future cultured meat. Entomol. Gen. 2024, 44, 813–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Huis, A.; Klunder, J.V.I.H.; Merten, E.; Halloran, A.; Vantomme, P. Edible Insects: Future Prospects for Food and Feed Security; Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2013; Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/i3253e/i3253e.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Francis, A.; Ghnimi, S.; Smetana, S. Development of a regionalized dynamic weighting method for the environmental impact of alternative protein sources. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1294390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macwan, S.; de Souza, T.S.P.; Dunshea, F.R.; DiGiacomo, K.; Suleria, H.A.R.; Morgan, N. Black soldier fly larvae (Hermetica illucens) as a sustainable source of nutritive and bioactive compounds, and their consumption challenges. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2023, 64, AN23192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smetana, S.; Ristic, D.; Pleissner, D.; Tuomisto, H.L.; Parniakov, O.; Heinz, V. Meat substitutes: Resource demands and environmental footprints. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 190, 106831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smetana, S.; Profeta, A.; Voigt, R.; Kircher, C.; Heinz, V. Meat substitution in burgers: Nutritional scoring, sensorial testing, and Life Cycle Assessment. Future Foods 2021, 4, 100042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spykman, R.; Hossaini, S.M.; Peguero, D.A.; Green, A.; Heinz, V.; Smetana, S. A modular environmental and economic assessment applied to the production of Hermetia illucens larvae as a protein source for food and feed. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2021, 26, 1959–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, L.; Rueda, O.; Smetana, S. Chapter 14—Environmental impacts of meat and meat replacements. In Meat and Meat Replacements; Meiselman, E.H.L., Lorenzo, J.M., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2023; pp. 365–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeone, M.; Scarpato, D. Consumer Perception and Attitude toward Insects for a Sustainable Diet. Insects 2022, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranga, L.; Panagiotou, M.; Noci, F.; Charalampidou, M.; Gkatzionis, K.; Dermiki, M. Cross-Cultural Perspectives on Insect-Based Foods: Insights from Consumers in Greece and Ireland. Foods 2025, 14, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, I.; Peterson, A.; Madden, J.; Huang, E.; Amin, S.; Lammert, A. Will It Cricket? Product Development and Evaluation of Cricket (Acheta domesticus) Powder Replacement in Sausage, Pasta, and Brownies. Foods 2022, 11, 3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresciani, A.; Cardone, G.; Jucker, C.; Savoldelli, S.; Marti, A. Technological Performance of Cricket Powder (Acheta domesticus L.) in Wheat-Based Formulations. Insects 2022, 13, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, E.; Pankiewicz, U.; Sujka, M. Nutritional, Physiochemical, and Biological Value of Muffins Enriched with Edible Insects Flour. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldkamp, T.; Belghit, I.; Chatzfiotis, S.; Mastoraki, M.; Jansman, A.J.M.; Radhakrishnan, G.; Schiavone, A.; Smetana, S.; Gasco, L. The Role of Insects in Novel Sustainable Animal Production Systems. In Sustainable Use of Feed Additives in Livestock; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 137–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heines, W.; Ristic, D.; Rosenberger, S.; Coudron, C.; Gai, F.; Schiavone, A.; Smetana, S. Eggs or meat? Environmental impact and efficiency assessment of chicken protein production with potential of Hermetia illucens use in feed. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. Adv. 2022, 16, 200121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagtap, S.; Garcia-Garcia, G.; Duong, L.; Swainson, M.; Martindale, W. Codesign of Food System and Circular Economy Approaches for the Development of Livestock Feeds from Insect Larvae. Foods 2021, 10, 1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikołajczak, Z.; Mazurkiewicz, J.; Rawski, M.; Kierończyk, B.; Józefiak, A.; Świątkiewicz, S.; Józefiak, D. Black Soldier Fly Full-Fat Meal in Atlantic Salmon Nutrition—Part B: Effects on Growth Performance, Feed Utilization, Selected Nutriphysiological Traits and Production Sustainability in Pre-Smolts. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2023, 23, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, S.; Ott, D.; Liebscher, J.; Höfling, D.; Müller, A.; Dautz, J.; Gutzeit, H.O.; Schmidt, D.; Reuss, R. Sustainability Analysis of Fish Feed Derived from Aquatic Plant and Insect. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desaulniers Brousseau, V.; Goldstein, B.P.; Leroux, D.; Giguère, T.; MacPherson, S.; Lefsrud, M. Estimating the global warming potential of animal waste-based organic liquid fertilizer for urban hydroponic farms. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 472, 143434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasnetti, E.; Sadeqi, H.; Lamastra, L. Integrating insects into the agri-food system of northern Italy as a circular economy strategy. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2023, 43, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Klammsteiner, T.; Dregulo, A.M.; Kumar, V.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Awasthi, M.K. Black soldier fly larvae for organic manure recycling and its potential for a circular bioeconomy: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orkusz, A. Edible Insects versus Meat—Nutritional Comparison: Knowledge of Their Composition Is the Key to Good Health. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udomsil, N.; Imsoonthornruksa, S.; Gosalawit, C.; Ketudat-Cairns, M. Nutritional Values and Functional Properties of House Cricket (Acheta domesticus) and Field Cricket (Gryllus bimaculatus). Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2019, 25, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, V.J.; Finer, E.; Bergmans, R.S.; Febvre, H.P.; Longhurst, C.; Manter, D.K.; Patz, J.A.; Weir, T.L. Impact of Edible Cricket Consumption on Gut Microbiota in Healthy Adults, a Double-blind, Randomized Crossover Trial. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateti, T.; Laha, A.; Shenoy, P. Artificial Meat Industry: Production Methodology, Challenges, and Future. JOM 2022, 74, 3428–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Wali, M.; Golroudbary, S.R.; Kraslawski, A.; Tuomisto, H.L. Transition to cellular agriculture reduces agriculture land use and greenhouse gas emissions but increases demand for critical materials. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soccol, C.R.; Molento, C.F.M.; Reis, G.G.; Karp, S.G. (Eds.) Cultivated Meat: Technologies, Commercialization and Challenges; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, K.; Huaccho Huatuco, L.; Dyke, A.; Green, J. The Environmental Impacts of Cultured Meat Production: A Systematic Literature Review. In Sustainable Design and Manufacturing 2023; Scholz, S.G., Howlett, R.J., Setchi, R., Eds.; Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies; Springer: Singapore, 2024; Volume 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q. The contribution of artificial meat in reducing carbon emission and mitigating climate change. E3S Web Conf. 2025, 606, 03008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risner, D.; Negulescu, P.; Kim, Y.; Nguyen, C.; Siegel, J.B.; Spang, E.S. Environmental Impacts of Cultured Meat: A Cradle-to-Gate Life Cycle Assessment. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 5, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Wali, M.; Karinen, H.; Rønning, S.B.; Skrivergaard, S.; Dorca-Preda, T.; Rasmussen, M.K.; Young, J.F.; Therkildsen, M.; Mogensen, L.; Ryynänen, T.; et al. Life cycle assessment of culture media with alternative compositions for cultured meat production. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2024, 29, 2077–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinke, P.; Swartz, E.; Sanctorum, H.; van der Giesen, C.; Odegard, I. Ex-ante life cycle assessment of commercial-scale cultivated meat production in 2030. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2023, 28, 234–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomisto, H.L.; Allan, S.J.; Ellis, M.J. Prospective life cycle assessment of a bioprocess design for cultured meat production in hollow fiber bioreactors. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Escobar, M.I.; Cadena, E.; Nhu, T.T.; Cooreman-Algoed, M.; De Smet, S.; Dewulf, J. Analysis of the Cultured Meat Production System in Function of Its Environmental Footprint: Current Status, Gaps and Recommendations. Foods 2021, 10, 2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, C.; Barnett, J. Consumer Acceptance of Cultured Meat: An Updated Review (2018–2020). Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broucke, K.; Van Pamel, E.; Van Coillie, E.; Herman, L.; Van Royen, G. Cultured meat and challenges ahead: A review on nutritional, technofunctional and sensorial properties, safety and legislation. Meat Sci. 2023, 195, 109006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upcraft, T.; Tu, W.-C.; Johnson, R.; Finnigan, T.; Hung, N.V.; Hallett, J.; Guo, M. Protein from renewable resources: Mycoprotein production from agricultural residues. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 5150–5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Shah, P.; Mach, K.; Rodgers-Hunt, B.; Finnigan, T.; Frost, G.; Neal, B.; Hadjikakou, M. The environmental impact of mycoprotein-based meat alternatives compared to plant-based meat alternatives: A systematic review. Future Foods 2024, 10, 100410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamarra-Castillo, O.; Echeverry-Montaña, N.; Marbello-Santrich, A.; Hernández-Carrión, M.; Restrepo, S. Meat Substitute Development from Fungal Protein (Aspergillus oryzae). Foods 2022, 11, 2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakman, T.; Hoffmann, B.S.; Portugal-Pereira, J. A recipe for change: Analyzing the climate and ecosystem impacts of the Brazilian diet shift. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 930, 172568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smetana, S.; Mathys, A.; Knoch, A.; Heinz, V. Meat alternatives: Life cycle assessment of most known meat substitutes. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2015, 20, 1254–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.I.; Farooq, S.; Alhamoud, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, H. A review on mycoprotein: History, nutritional composition, production methods, and health benefits. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 121, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporgno, M.P.; Mathys, A. Trends in microalgae incorporation into innovative food products with potential health benefits. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tseng, J.; Tang, D.; Yong, Y.; Sun, L.; Huo, Y.-X. Upcycling C1 gas-derived resources in future food system. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 210, 107827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawky, E.; Gibbons, S.; Selim, D.A. Bio-sourcing from byproducts: A comprehensive review of bioactive molecules in Agri-Food Waste (AFW) streams for valorization and sustainable applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 431, 132640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramandani, A.A.; Sun, Y.-M.; Lan, J.C.-W.; Chen, W.-H.; Chang, J.-S.; Rachmadona, N.; Lim, J.W.; Khoo, K.S. Upcycling nutrients derived from food waste via microalgae cultivation: A review on impacts on cellular compounds, economy and environment analyses for achieving circular bioeconomy. Biochem. Eng. J. 2024, 211, 109454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, K.; Abinandan, S.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Megharaj, M. Synergy of eco-innovation with on-farm practices enhances circularity beyond conventional nutrient recovery framework. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 208, 107735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ro, J.W.; Yothers, C.; Kendall, A.; Franz, A.; Zhang, R. Economic and environmental performance of microalgal energy products—A case study exploring circular bioeconomy principles applied to recycled anaerobic digester waste flows. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 358, 120802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, M.; Liang, Q.; Yang, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Mou, H.; Sun, H. Upcycling food waste into biorefinery production by microalgae. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 484, 149532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Z.; Abdullah, M.; Yasin, M.T.; Amanat, K.; Ahmad, K.; Ahmed, I.; Qaisrani, M.M.; Khan, J. Organic waste-to-bioplastics: Conversion with eco-friendly technologies and approaches for sustainable environment. Environ. Res. 2024, 244, 117949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielemann, A.K.; Smetana, S.; Pleissner, D. Cultivation of the heterotrophic microalga Galdieria sulphuraria on food waste: A Life Cycle Assessment. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 340, 125637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josa, I.; Garfí, M. Social life cycle assessment of microalgae-based systems for wastewater treatment and resource recovery. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 407, 137121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arashiro, L.T.; Josa, I.; Ferrer, I.; Van Hulle, S.W.H.; Rousseau, D.P.L.; Garfí, M. Life cycle assessment of microalgae systems for wastewater treatment and bioproducts recovery: Natural pigments, biofertilizer and biogas. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julius Pahmeyer, M.; Anusha Siddiqui, S.; Pleissner, D.; Gołaszewski, J.; Heinz, V.; Smetana, S. An automated, modular system for organic waste utilization using heterotrophic alga Galdieria sulphuraria: Design considerations and sustainability. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 348, 126800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, K.; Abinandan, S.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Megharaj, M. Acid-tolerant microalgae-based winery wastewater treatment: Performance evaluation and techno-economic analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 383, 125335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moglie, M.; Biancini, G.; Cioccolanti, L. Environmental and economic analysis of an olive mill wastewater treatment system integrated with microalgae production. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2024, 29, 1000–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, C.J.; McDonnell, A.; Rollins, K.S.; Hiibel, S.R.; Cornejo, P.K. Assessing the environmental impact of resource recovery from dairy manure. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 330, 117150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadaki, S.; Tricha, N.; Panagiotopoulou, M.; Krokida, M. Innovative Bioactive Products with Medicinal Value from Microalgae and Their Overall Process Optimization through the Implementation of Life Cycle Analysis—An Overview. Mar. Drugs. 2024, 22, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, G.; Venditti, P.; Agnisola, C.; Quartucci, S.; Fasciolo, G.; Muscari Tomajoli, M.T.; Geremia, E.; Catone, C.M.; Ulgiati, S. Towards sustainable aquaculture systems: Biological and environmental impact of replacing fishmeal with Arthrospira platensis (Nordstedt) (spirulina). J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 374, 133978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smetana, S. Life cycle assessment of bio-based nitrogen upcycling approaches. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2023, 43, 100853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalermthai, B.; Nootong, K.; Olsen, B.D.; Assabumrungrat, S.; Charoensuppanimit, P. Cradle-to-gate life cycle assessment of Spirulina bioplastic produced via plasticization with glycerol. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Al-Tohamy, R.; Al-Zahrani, M.; Schagerl, M.; Kornaros, M.; Sun, J. Advancements and challenges in microalgal protein production: A sustainable alternative to conventional protein sources. Microb. Cell Fact. 2025, 24, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutra, D.A.; Deprá, M.C.; Dias, R.R.; Zepka, L.Q.; Jacob-Lopes, E. Ensuring nutrition and food safety within planetary boundaries: The role of microalgae-based ingredients in sustainable food chain. J. Appl. Phycol. 2024, 36, 2635–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ríos, A.; Laso, J.; Aldaco, R.; Margallo, M. Environmental implications and hidden costs of artisanal spirulina (Arthrospira platensis) production and consumption. EIA Rev. 2024, 108, 107579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baune, M.-C.; Januschewski, E.; Bussa, M.; Van De Walle, S.; Gifuni, I.; Rodrigues, A.M.C.; Cardoso, M.H.; Van Royen, G.; Juadjur, A.; Jungbluth, N.; et al. Innovative vs. classical methods for drying heterotrophic Chlorella vulgaris: Impact on the nutritional properties, safety, sustainability and costs. Algal Res. 2025, 86, 103913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ríos, A.; Butnar, I.; Margallo, M.; Laso, J.; Borrion, A.; Aldaco, R. Carbon accounting of negative emissions technologies integrated in the life cycle of spirulina supplements. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 890, 164362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKuin, B.; Kapuscinski, A.R.; Sarker, P.K.; Cheek, N.; Lim, J.; Sabarsky, M. Comparative life cycle assessment of marine microalgae, Nannochloropsis sp. And fishmeal for sustainable protein ingredients in aquaculture feeds. Elem. Sci. Anth. 2023, 11, 00083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; An, S.; Yao, R.; Fu, W.; Han, Y.; Du, M.; Chen, Z.; Lei, A.; Wang, J. Life cycle assessment of auto-tropically cultivated economic microalgae for final products such as food, total fatty acids, and bio-oil. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 990635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartek, L.; Strid, I.; Henryson, K.; Junne, S.; Rasi, S.; Eriksson, M. Life cycle assessment of fish oil substitute produced by microalgae using food waste. Sust. Prod. Consum. 2021, 27, 2002–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niimi, J.; Sörensen, V.; Mihnea, M.; Valentin, D.; Bergman, P.; Collier, E.S. Does cooking ability affect consumer perception and appreciation of plant-based protein in Bolognese sauces? Food Qual. 2022, 99, 104563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, A.C.; Luning, P.A.; Weijzen, P.; Engels, W.; Kok, F.J.; De Graaf, C. Replacement of meat by meat substitutes. A survey on person- and product-related factors in consumer acceptance. Appetite 2011, 56, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, F.; Kataria, M.; Lampi, E. How much does it take? Willingness to switch to meat substitutes. Ecol. Econ. 2022, 193, 107329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laureati, M.; De Boni, A.; Saba, A.; Lamy, E.; Minervini, F.; Delgado, A.M.; Sinesio, F. Determinants of Consumers’ Acceptance and Adoption of Novel Food in View of More Resilient and Sustainable Food Systems in the EU: A Systematic Literature Review. Foods 2024, 13, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Khan, S.; Ullah Farooqi, M.Q.; Singh, P.; Fernando, I.; Nagdalian, A. Consumer behavior towards cultured meat: A review since 2014. Appetite 2022, 179, 106314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwezen, M.C.; Dagevos, H. A meta-review of consumer behaviour studies on meat reduction and alternative protein acceptance. Food Qual. Prefer. 2024, 114, 105067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Singh, A.; Kumar, N. Electronic panel for sensory assessment of food: A review on technologies integration and their benefits. J. Food Sci. 2025, 90, e70128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keum, D.H.; Han, J.H.; Kwon, H.C.; Park, S.M.; Kim, H.Y.; Han, S.G. Enhancing the flavor of plant-based meat analogues using flavor-capturing alginate/β-cyclodextrin hydrogel beads. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 309, 142930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zang, M.; Chen, J.; Zhang, K.; Wang, S.; Li, D.; Li, X.; Liu, M.; Pan, X. Effect of the mycelium of oyster mushrooms on the physical and flavor properties of a plant-based beef analogue. LWT 2024, 198, 116029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, X. Effects of Haematococcus pluvialis Addition on the Sensory Properties of Plant-Based Meat Analogues. Foods 2023, 12, 3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zang, M.; Zhang, K.; Wang, S.; Li, D.; Li, X. Effect of two types of thermal processing methods on the aroma and taste profiles of three commercial plant-based beef analogues and beef by GC-MS, E-nose, E-tongue, and sensory evaluation. Food Control. 2023, 146, 109551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhsh, A.; Lee, E.-Y.; Bakry, A.M.; Rathnayake, D.; Son, Y.-M.; Kim, S.-W.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Joo, S.-T. Synergistic effect of lactoferrin and red yeast rice on the quality characteristics of novel plant-based meat analog patties. LWT 2022, 171, 114095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, S.; Rondoni, A.; Bari, R.; Smith, R.; Mansilla, N. Effect of information on consumers’ sensory evaluation of beef, plant-based and hybrid beef burgers. Food Qual. 2022, 96, 104417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhsh, A.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, E.-Y.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Joo, S.-T. Characteristics of Beef Patties Substituted by Different Levels of Textured Vegetable Protein and Taste Traits Assessed by Electronic Tongue System. Foods 2021, 10, 2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeter, A.K.; Farkas, D.; Király, M.; Kovács, Z.; Ludányi, K.; Antal, I.; Kállai-Szabó, N. Study on Lyophilised Orodispersible Tablets from Plant-Based Drinks as Bulking Agents. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, Z.; Nemeth, L.G.; Nzetchouang Siyapndjeu, S.; Bufa, A.; Marosvölgyi, T.; Gyöngyi, Z. Classification of Plant-Based Drinks Based on Volatile Compounds. Foods 2024, 13, 4086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tian, W.; Xie, B.; Sun, Z. Insight into the Influence of Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermentation on the Variations in Flavor of Chickpea Milk. Foods 2022, 11, 2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; Dai, T.; Huang, S.; Wu, K.; Wang, M.; Tan, C.; Zhang, F.; Sheng, J.; Zhao, C. Physical and Chemical Properties, Flavor and Organoleptic Characteristics of a Walnut and Purple Rice Fermented Plant Drink. Foods 2024, 13, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pointke, M.; Albrecht, E.H.; Geburt, K.; Gerken, M.; Traulsen, I.; Pawelzik, E. A Comparative Analysis of Plant-Based Milk Alternatives Part 1: Composition, Sensory, and Nutritional Value. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reference | n | Data Collection | Diet Classification | Follow-Up Years | Participant Age |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Keaver et al. [50] | 36,825 | 24 h dietary recall | Comprehensive diet quality index: | 8.3 | 47.1 ± 0.2 (average) |
| Overall (cDQI) | |||||
| Animal-based (aDQI) | |||||
| Plant-based (pDQI) | |||||
| Chen et al. [51] | 13,154 | Food frequency questionnaire | Plant-based index: | 5.7 | 86.9 ± 11.4 (average) |
| Overall (oPDI) | |||||
| Healthy (hPDI) | |||||
| Unhealthy (uPDI) | |||||
| Li et al. [52] | 40,074 | 24 h dietary recall | Plant-based index: | 7.8 | 47.3 ± 19.4 (average) |
| oPDI | |||||
| hPDI | |||||
| uPDI | |||||
| Weston et al. [53] | 3635 | Food frequency questionnaire | Plant-based index: | 15 | 21–95 |
| oPDI | |||||
| hPDI | |||||
| uPDI | |||||
| Wang et al. [54] | 11,939 | 24 h dietary recall | Plant-based index: | 11.2 | 49 (average) |
| oPDI | |||||
| hPDI | |||||
| uPDI | |||||
| Healthy eating index (HEI-2015) | |||||
| Pro-vegetarian diet index (PVD) | |||||
| Zhou et al. [55] | 189,003 | 24 h dietary recall | Plant-based index: | 9.6 | 55.99 ± 7.95 (average) |
| oPDI | |||||
| hPDI | |||||
| uPDI | |||||
| Yuan et al. [56] | 2675 | Food frequency questionnaire | Plant-based index: | 10 | 102.33 (average) |
| oPDI | |||||
| hPDI | |||||
| uPDI | |||||
| Healthy plant-based foods index (HPF) | |||||
| Unhealthy plant-based foods index (uHPF) | |||||
| Animal-based foods index (AF) | |||||
| Kim et al. [57] | 144,729 | Food frequency questionnaire | Plant-based index: | 21 | 45–75 |
| oPDI | |||||
| hPDI | |||||
| uPDI | |||||
| Abris et al. [58] | 88,400 | Food frequency questionnaire | Vegetarians: | 11.07 | ≥30 |
| Vegans | |||||
| Pescovegetarians | |||||
| Lacto-ovovegetarians | |||||
| Non-vegetarians | |||||
| Oncina-Cánovas et al. [59] | 597 | Food frequency questionnaire | Pro-vegetarian dietary pattern: | 12 | ≥65 |
| Overall (oPVG) | |||||
| Healthy (hPVG) | |||||
| Unhealthy (uPVG) | |||||
| Huang et al. [60] | 7843 | Food frequency questionnaire | Plant-based index: | 11 | 82.2 ± 10 (average) |
| oPDI | |||||
| hPDI | |||||
| uPDI |
| Reference | Dietary Pattern Classification | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| oPDI | hPDI | uPDI | oPVG | hPVG | uPVG | AF | uHPF | HPF | Veg. | Non-Veg. | cDQI | aDQI | pDQI | PVD | HEI-2015 | |
| Keaver et al. [50] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.75 | n.a. | 0.66 | - | - |
| Chen et al. [51] | 0.92 | 0.81 | 1.17 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Li et al. [52] | 0.80 | 0.86 | 1.33 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Weston et al. [53] | 1.07 | 0.94 | 1.15 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Wang et al. [54] | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | n.a. | 0.87 |
| Zhou et al. [55] | 0.87 | 0.92 | 1.29 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Yuan et al. [56] | 0.81 | 0.79 | 1.10 | - | - | - | 1.17 | 0.95 | 0.81 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Kim et al. [57] | 0.85 (male) 0.89 (female) | 0.88 (male) 0.86 (female) | 1.03 (male) 1.11 (female) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Abris et al. [58] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.89 | 1 (reference) | - | - | - | - | - |
| Oncina-Cánovas et al. [59] | - | - | - | 0.85 | 0.90 | 1.53 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Huang et al. [60] | 1.10 (highest increase) 1.32 (highest decrease) | 0.96 (highest increase) | 1.13 (highest increase) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1.21 (highest decrease) | 0.90 (highest decrease) | |||||||||||||||
| Food Type | GHG Emissions (kg CO2 eq/kg) | Land Use (m2/kg) | Water Use (L/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beef | 27.0 | 326 | 15,415 |
| Pork | 12.0 | 70 | 5988 |
| Chicken | 6.9 | 12 | 4325 |
| Soy | 2.0 | 4 | 2145 |
| Lentils | 0.9 | 2.5 | 1250 |
| Vegetables | 0.6 | 1.5 | 500 |
| Insects | 5.7 | 1.9 | 247 |
| Mycoprotein | 5.3 | 1.5 | 4996 |
| Cultured meat | 5.7 | 1.9 | 414 |
| Microalgae | 81.6 | 3.1 | 53,944 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Navarré, A.; Musto, L.; Nazareth, T. Beyond Meat Substitution: A Multifaceted Review of Plant-Based and Alternative Proteins, from Environmental Impact to Analytical Technologies. Foods 2025, 14, 2312. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132312
Navarré A, Musto L, Nazareth T. Beyond Meat Substitution: A Multifaceted Review of Plant-Based and Alternative Proteins, from Environmental Impact to Analytical Technologies. Foods. 2025; 14(13):2312. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132312
Chicago/Turabian StyleNavarré, Abel, Leonardo Musto, and Tiago Nazareth. 2025. "Beyond Meat Substitution: A Multifaceted Review of Plant-Based and Alternative Proteins, from Environmental Impact to Analytical Technologies" Foods 14, no. 13: 2312. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132312
APA StyleNavarré, A., Musto, L., & Nazareth, T. (2025). Beyond Meat Substitution: A Multifaceted Review of Plant-Based and Alternative Proteins, from Environmental Impact to Analytical Technologies. Foods, 14(13), 2312. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132312







