What We Know About per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Contamination Levels in Milk. A Review from the Last Decade
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
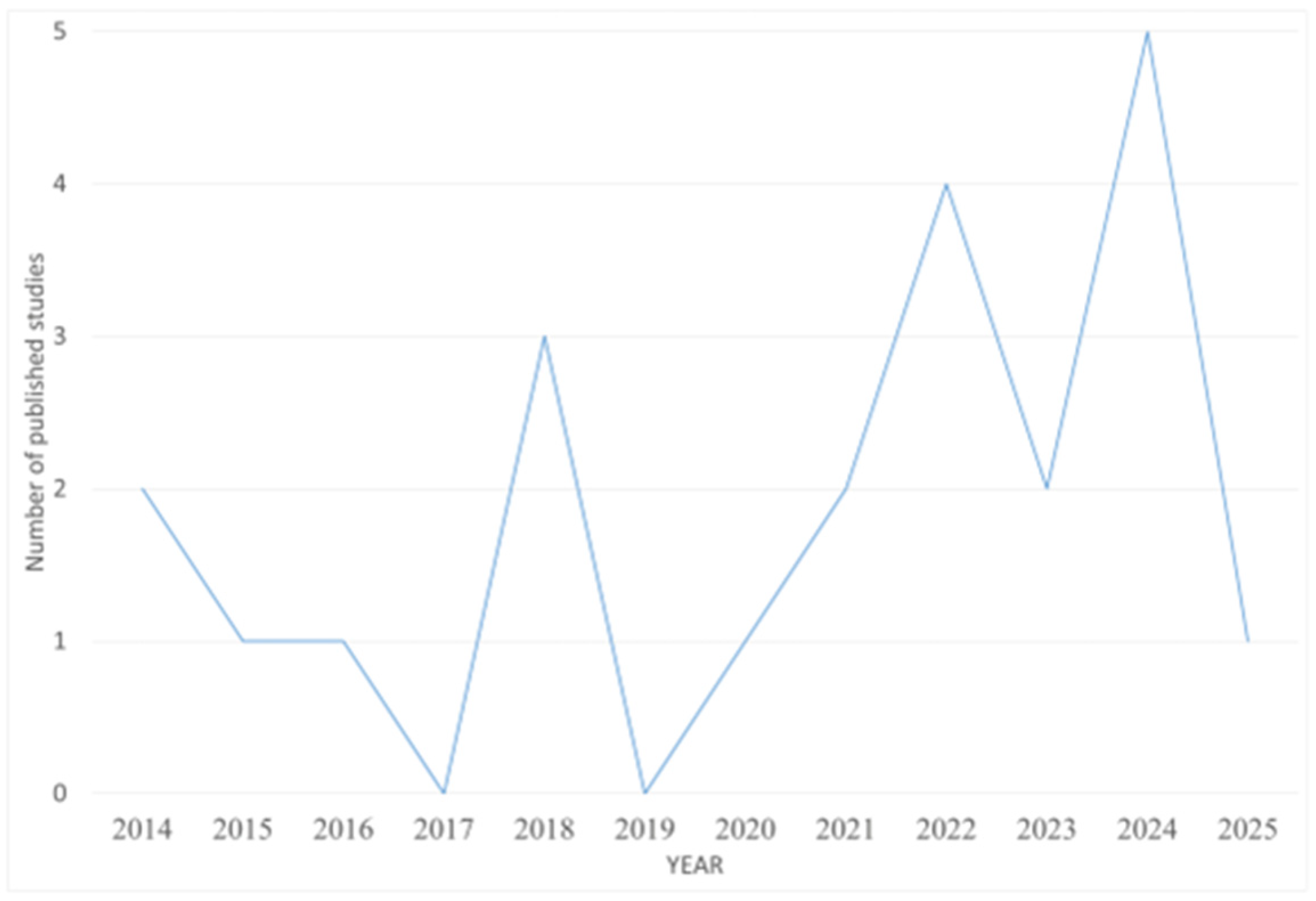
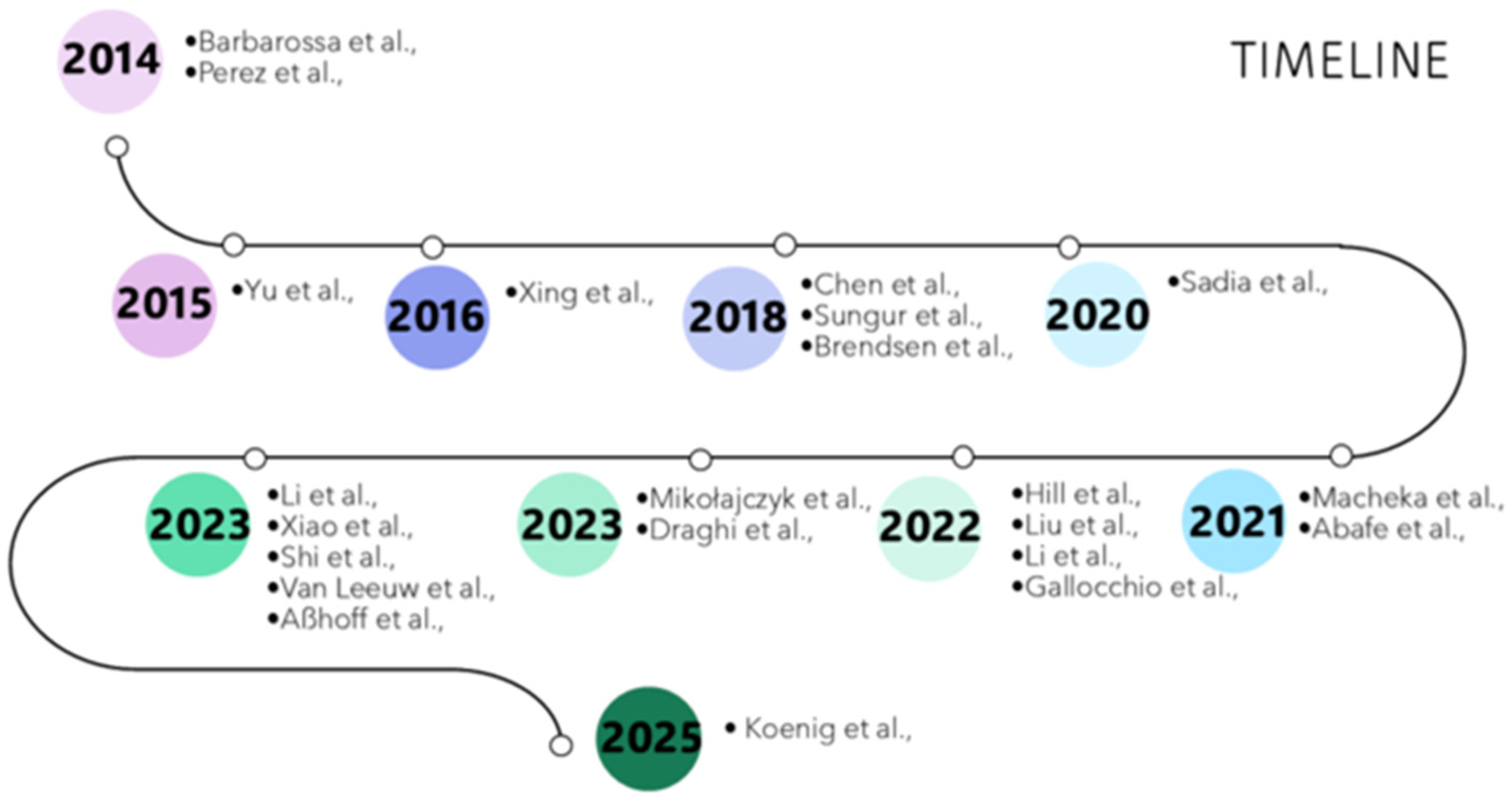
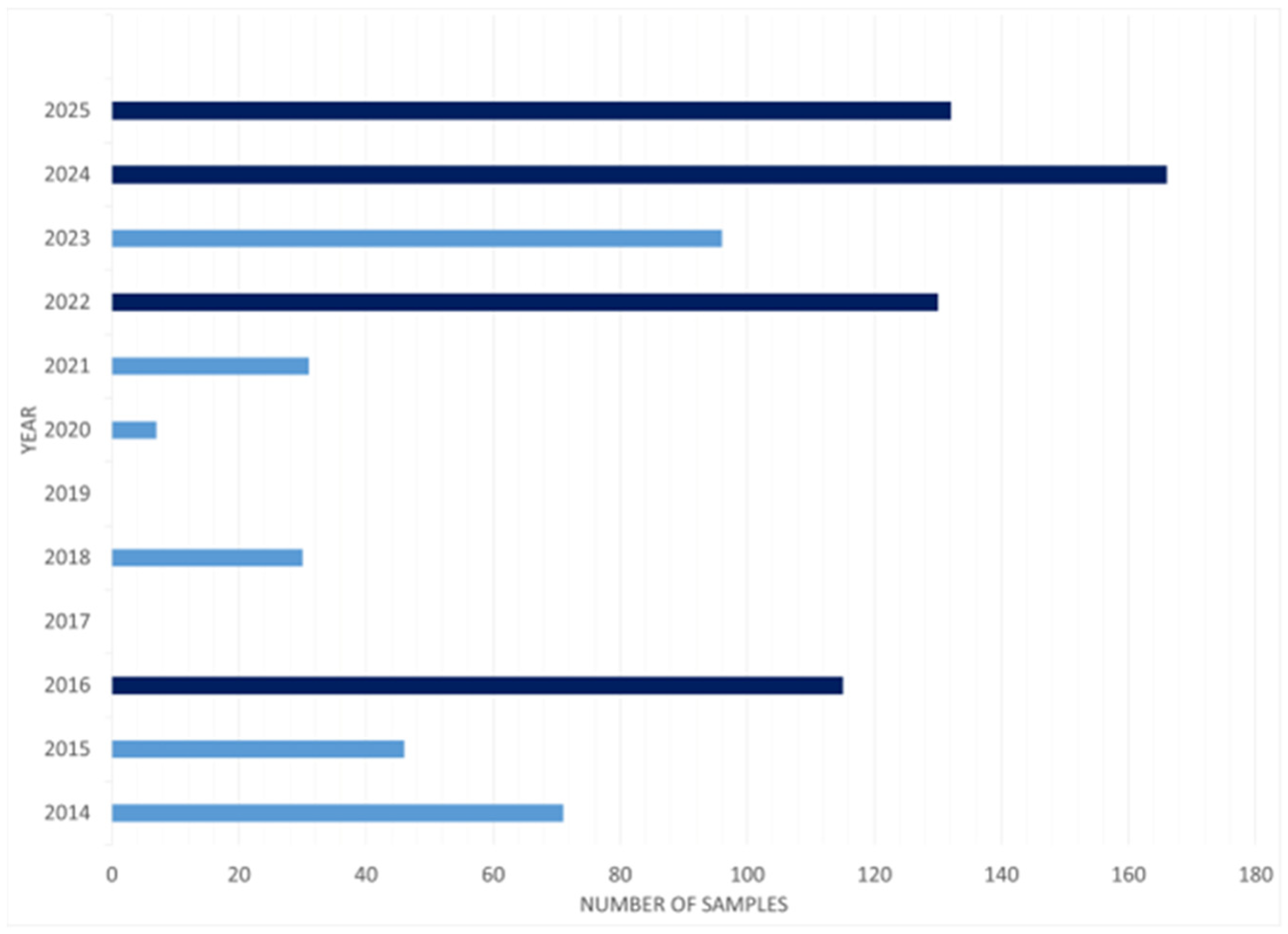
3.1. Literature Overview
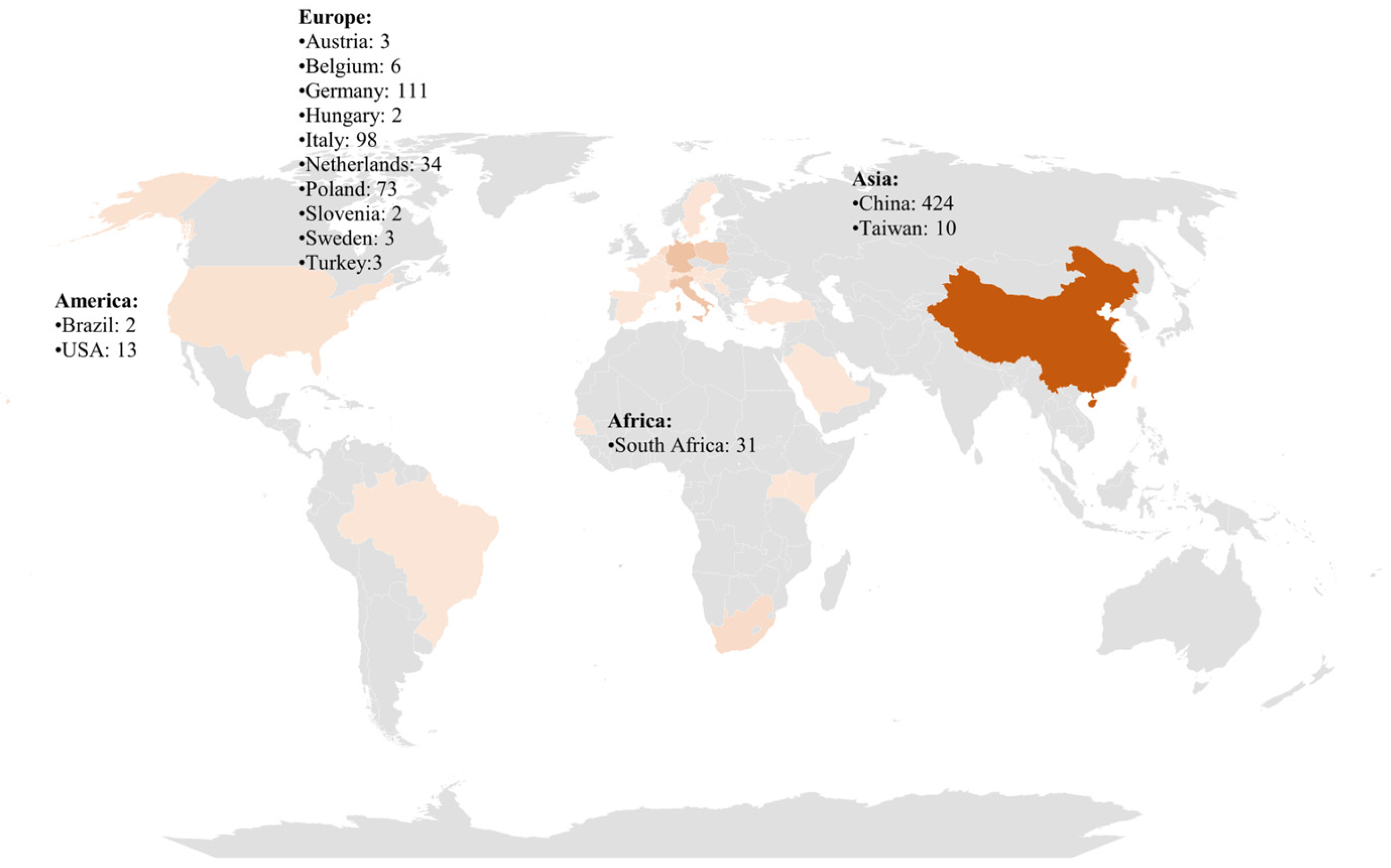
3.2. Incidence of PFASs in Milk Around the World
3.2.1. Africa
3.2.2. America
3.2.3. Asia
3.2.4. Europe
3.2.5. Others
4. Discussion
4.1. Understudied Exposure: PFAS in Milk Amid Widespread Consumption
4.2. PFAS Contamination: Regional and Analytical Disparities
4.3. PFAS Contamination in Non-Cow Milk Species
4.4. Risk Characterization
4.5. Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 10:2 FTCA | 10:2 Fluorotelomer carboxylic acid |
| 10:2 FTUCA | 10:2 Fluorotelomer unsaturated carboxylic acid |
| 11H-PFUnDA | 11H-Perfluoroundecanoic acid |
| 3:3 FTCA | 3:3 Fluorotelomer carboxylic acid |
| 5:1:2 FTB | 5:1:2 Fluorotelomer betaine |
| 5:3 FTB | 5:3 Fluorotelomer betaine |
| 5:3 FTCA | 5:3 Fluorotelomer carboxylic acid |
| 6:2 Cl PFESA | 6:2 chlorinated polyfluoroalkyl ether sulfonate |
| 6:2 FTCA | 6:2 fluorotelomer carboxylic acid |
| 6:2 FTUCA | 6:2 Fluorotelomer unsaturated carboxylic acid |
| 7:3 FTCA | 7:3 Fluorotelomer carboxylic acid |
| 7H-PFHpA | 7H Perfluoroheptanoic acid |
| 8:2 ClPFESA | 8:2 chlorinated polyfluoroalkyl ether sulfonate |
| 8:2 FTCA | 8:2 Fluorotelomer carboxylic acid |
| 8:2 FTUCA | 8:2 Fluorotelomer unsaturated carboxylic acid |
| 8:3 FTCA | 8:3 Fluorotelomer carboxylic acid |
| Cl-PFOS | Chlorinated perfluorooctanesulfonate |
| FBSA | Perfluoro-1-butanesulfonamide |
| FDSA | Perfluorodecanesulfonamide |
| FHxSA | Perfluoro-1-hexanesulfonamide |
| FOSA | Perfluorooctane sulfonamide |
| l-PFHxS | Perfluorohexanesulfonic acid |
| NaDONA | Sodium dodecafluoro-3H-4,8-dioxanonanoate |
| N-AP-FHxSA | N-(3-dimethylaminopropan-1-yl)perfluoro-1-hexane-sulfonamide |
| N-CMAmP 6:2FOSA | N-(carboxymethyl)-N,N-dimethyl-N-[3-(1H,1H,2H,2H- perfluoro-1-octanesulfonamido)propan-1-yl]ammonium (6:2 FTAB) |
| N-TAmP-FHxSA | N-[3-(perfluoro-1-hexanesulfonamido)propan-1-yl]-N,N,N-trimethylammonium |
| N-EtFOSA | N-ethyl perfluorooctane sulfonamide |
| N-EtFOSAA | N-ethyl perfluorooctanesulfonamido acetic acid |
| N-MeFBSA | N-Methylperfluoro-1-butanesulfonamide |
| N-MeFOSA | N-methyl perfluorooctane sulfonamide |
| N-MeFOSAA | N-methyl perfluorooctanesulfonamido acetic acid |
| PF4OPeA | Perfluoro-4-oxapentanoic acid |
| PF5OHxA | Perfluoro-5-oxahexanoic acid |
| PFBA | Perfluorobutanoic acid |
| PFBS | Perfluorobutanesulfonic acid |
| PFDA | Perfluorodecanoic acid |
| PFDoDA | Perfluorododecanoic Acid |
| PFDoS | Perfluorodecane Sulfonic Acid |
| PFDS | Perfluorodecanesulfonic Acid |
| PFECHS | Perfluoro-4-ethylcyclohexane |
| PFEESA | Perfluoro(2-ethoxyethane)sulfonic acid |
| PFHpA | Perfluoroheptanoic acid |
| PFHpS | Perfluoroheptanesulfonic acid |
| PFHxA | Perfluorohexanoic acid |
| PFHxDA | Perfluoro-n-hexadecanoic acid |
| PFHxS | Linear perfluorohexanesulfonic acid |
| PFNA | Perfluorononanoic acid |
| PFNS | Perfluorononanesulfonic acid |
| PFOA | Perfluorooctanoic acid |
| PFOcDA | Perfluorooctadecanoic acid |
| PFOS | Perfluorooctanesulfonic acid |
| PFPeA | Perfluoropentanoic acid |
| PFPeS | Perfluoropentanesulfonic acid |
| PFTeDA | Perfluorotetradecanoic acid |
| PFTrDA | Perfluorotridecanoic Acid |
| PFUnDA | Perfluoroundecanoic acid |
| 10:2 FTS | 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorododecane sulfonate |
| 4:2 FTS | 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluoro-1-hexanesulfonate |
| 6:2 FTS | 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluoro-1-octanesulfonate |
| 8:2 FTS | 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluoro-1-decanesulfonate |
| ADONA | Dodecafluoro-3H-4,8-dioxanonanoate |
| br PFOS | Branched Perfluorooctanesulfonic acid |
| C6O4 | Perfluoropolyether carboxylic acid |
| FDEA | 2-Perfluorodecyl ethanoic acid |
| FHEA | 2-Perfluorohexyl ethanoic acid |
| FOEA | 2-Perfluorooctyl ethanoic acid |
| FOUEA | 2H-perfluoro-2-decenoic acid |
| HFPO-DA (Gen X) | Hexafluoropropylene oxide dimer acid |
| l PFDOS | Linear Perfluorodecane Sulfonic Acid |
| l PFHpS | Linear Perfluoroheptanesulfonic acid |
| l PFNS | Linear Perfluorononanesulfonic acid |
| l PFOS | Linear Perfluorooctanesulfonic acid |
| l-PFBS | Linear Perfluorobutanesulfonic acid |
| l-PFDS | Linear Perfluorodecanesulfonic Acid |
| PFDoA | Perfluorododecanoic acid |
| PFDoDS | Perfluoro-1-dodecanesulfonate |
| PFODA | 4,4′-((perfluorocyclobutane-1,2-diyl)bis(oxy))dianiline |
| PFOSA | Perfluorooctane sulfonamide |
| PFPA | Pentafluoropropionic anhydride |
| PFPrS | Perfluoropropanesulfonic acid |
| PFTeA | Perfluorotetradecanoic acid |
| PFTrA | Perfluorotridecanoic acid |
| PFTrDS | Perfluoro-1-tridecanesulfonate |
| PFTriDA | Pentacosafluorotridecanoic acid |
| PFUdA | Perfluoroundecanoic acid |
| PFUnA | Perfluoroundecanoic acid |
| PFUnDS | Perfluoroundecane sulfonate |
References
- Danesi, L.; Nobile, M.; Fontana, M.; Tirloni, E.; Chiesa, L.M.; Savini, F.; Villa, R.E.; Panseri, S. Preliminary Investigation towards the Use of Infrared Technology for Raw Milk Treatment. Foods 2024, 13, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clal.it. Available online: https://www.clal.it/ (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Nobile, M.; Panseri, S.; Curci, D.; Chiesa, L.M.; Ghidini, S.; Arioli, F. Prevalence of perfluoroalkyl substances in paired batches of precooked and canned bovine meat and their implication on consumer safety. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2024, 192, 114910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, N.I.; Becanova, J.; Lohmann, R. A sensitive method for the detection of legacy and emerging per- and polyfluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS) in dairy milk. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, G.; Kankarla, V.; McLennon, E.; Pal, S.; Sihi, D.; Dari, B.; Diaz, D.; Nocco, M. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Integrated Crop–Livestock Systems: Environmental Exposure and Human Health Risks. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, J.L.; Nadal, M. Human exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) through drinking water: A review of the recent scientific literature. Environ. Res. 2019, 177, 108648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobile, M.; Arioli, F.; Curci, D.; Ancillotti, C.; Scanavini, G.; Chiesa, L.M.; Panseri, S. Incidence of Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Commercial Eggs and Their Impact on Consumer’s Safety. Foods 2023, 12, 3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macheka, L.R.; Olowoyo, J.O.; Mugivhisa, L.L.; Abafe, O.A. Determination and assessment of human dietary intake of per and polyfluoroalkyl substances in retail dairy milk and infant formula from South Africa. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunderland, E.M.; Hu, X.C.; Dassuncao, C.; Tokranov, A.K.; Wagner, C.C.; Allen, J.G. A review of the pathways of human exposure to poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and present understanding of health effects. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, W.M.; South, P.; Begley, T.H.; Diachenko, G.W.; Noonan, G.O. Determination of Perfluorochemicals in Cow’s Milk Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1652–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahm, S.; Bonde, J.P.; Chiu, W.A.; Hoppin, J.; Kanno, J.; Abdallah, M.; Blystone, C.R.; Calkins, M.M.; Dong, G.-H.; Dorman, D.C.; et al. Carcinogenicity of perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid. Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, 16–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavone, C.; Portesi, C. PFAS: A Review of the State of the Art, from Legislation to Analytical Approaches and Toxicological Aspects for Assessing Contamination in Food and Environment and Related Risks. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission Regulation (EU). Regulation (Eu) 2019/1021 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 June 2019 on Persistent Organic Pollutants; EU: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS), perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and their salts Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Contaminants in the Food chain. EFSA J. 2008, 6, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM). Risk to human health related to the presence of perfluorooctane sulfonic acid and perfluorooctanoic acid in food. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (EFSA CONTAM Panel). Risk to human health related to the presence of perfluoroalkyl substances in food. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e06223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EU). 2023/915 on Maximum Levels for Certain Contaminants in Food and Repealing Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006; EU: Brussels, Belgium, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Commission Recommendation (EU). 2022/1431 of 24 August 2022 on the Monitoring of Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Food; EU: Brussels, Belgium, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ropers, M.H.; Durand, S.; Veyrand, B.; Beaumal, V.; Marchand, P.; Anton, M.; Le Bizec, B. Contamination of food by fluorinated surfactants—Distribution in emulsions and impact on the interfacial protein behaviour. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shi, Y.; Pan, Y.; Cai, Y. Perfluorinated compounds in milk, milk powder and yoghurt purchased from markets in China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, J.; Ehlers, S.; Oberhausen, A.; Tischer, M.; Fürst, P.; Schafft, H.; Lahrssen-Wiederholt, M. Absorption, Distribution, and Milk Secretion of the Perfluoroalkyl Acids PFBS, PFHxS, PFOS, and PFOA by Dairy Cows Fed Naturally Contaminated Feed. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 2903–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Asselt, E.D.; Kowalczyk, J.; Van Eijkeren, J.C.H.; Zeilmaker, M.J.; Ehlers, S.; Fürst, P.; Lahrssen-Wiederholt, M.; van der Fels-Klerx, H.J. Transfer of perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) from contaminated feed to dairy milk. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 1489–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarossa, A.; Gazzotti, T.; Zironi, E.; Serraino, A.; Pagliuca, G. Short communication: Monitoring the presence of perfluoroalkyl substances in Italian cow milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 3339–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, F.; Llorca, M.; Köck-Schulmeyer, M.; Škrbić, B.; Oliveira, L.S.; Martinello, K.d.B.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Antić, I.; Farré, M.; Barceló, D. Assessment of perfluoroalkyl substances in food items at global scale. Environ. Res. 2014, 135, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Xu, D.; Lu, M.; Zhou, S.; Peng, T.; Yue, Z.; Zhou, Y. QuEChERs Combined with Online Interference Trapping LC-MS/MS Method for the Simultaneous Determination of 20 Polyfluoroalkane Substances in Dietary Milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 4087–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Lu, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, G.; Wang, X. Occurrence of Perfluorooctanoic Acid and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate in Milk and Yogurt and Their Risk Assessment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.L.; Bai, F.Y.; Chang, Y.C.; Chen, P.C.; Chen, C.Y. Concentrations of perfluoroalkyl substances in foods and the dietary exposure among Taiwan general population and pregnant women. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sungur, Ş.; Köroğlu, M.; Turgut, F. Determination of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) in food and beverages. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, B.J.A.; Lakraoui, F.; Leenders, L.; Van Leeuwen, S.P.J. The analysis of perfluoroalkyl substances at ppt level in milk and egg using UHPLC-MS/MS. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2020, 37, 1707–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadia, M.; Yeung, L.W.; Fiedler, H. Trace level analyses of selected perfluoroalkyl acids in food: Method development and data generation. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 113721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abafe, O.A.; Macheka, L.R.; Olowoyo, J.O. Confirmatory Analysis of Per and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Milk and Infant Formula Using UHPLC–MS/MS. Molecules 2021, 26, 3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallocchio, F.; Moressa, A.; Zonta, G.; Angeletti, R.; Lega, F. Fast and Sensitive Analysis of Short- and Long-Chain Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Foods of Animal Origin. Molecules 2022, 27, 7899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Wan, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Sun, X.; Pi, F.; Chen, X. A novel analytical strategy for the determination of perfluoroalkyl acids in various food matrices using a home-made functionalized fluorine interaction SPME in combination with LC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Hao, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, P.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, T.; et al. Occurrence of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in raw milk and feed from nine Chinese provinces and human exposure risk assessment. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikołajczyk, S.; Warenik-Bany, M.; Pajurek, M. Occurrence of perfluoroalkyl substances in cow’s, goat’s and sheep’s milk—Dietary intake and risk assessment. J. Vet. Res. 2023, 67, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draghi, S.; Pavlovic, R.; Pellegrini, A.; Fidani, M.; Riva, F.; Brecchia, G.; Agradi, S.; Arioli, F.; Vigo, D.; Di Cesare, F.; et al. First Investigation of the Physiological Distribution of Legacy and Emerging Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Raw Bovine Milk According to the Component Fraction. Foods 2023, 12, 2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Shi, L.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Q. Efficient Online TurboFlow Method for Simultaneous Determination of 60 Emerging Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 24857–24865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, K.; Li, X.; Xu, N.; Wang, X.; Hao, L.; Bao, H.; Zhang, L.; Shi, Y.; Cai, Y. Carry-over rate of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances to raw milk and human exposure risks in different regions of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 944, 173902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuw, V.; Malysheva, S.V.; Fosseprez, G.; Murphy, A.; Aarab, C.E.A.; Andjelkovic, M.; Waegeneers, N.; Van Hoeck, E.; Joly, L. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in food and beverages: Determination by LC-HRMS and occurrence in products from the Belgian market. Chemosphere 2024, 366, 143543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Di, S.; Qi, P.; Wang, X. Integrated QuEChERS combined with LC–MS/MS for high-throughput analysis of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in milk. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aßhoff, N.; Bernsmann, T.; Esselen, M.; Stahl, T. A sensitive method for the determination of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in food and food contact material using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2024, 1730, 465041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, P.; Brand, B.; Hamscher, G.; Stahl, T. Development, optimization and validation of a highly sensitive and selective method for the determination of PFAS in animal-based food. Chemosphere 2025, 372, 144123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/environmental-contaminants-food/analytical-results-testing-food-pfas-environmental-contamination (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- González, N.; Domingo, J.L. PFC/PFAS concentrations in human milk and infant exposure through lactation: A comprehensive review of the scientific literature. Arch. Toxicol. 2025, 99, 1843–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livestock Production. Available online: https://www.fao.org/4/Y4252E/y4252e07.htm?utm_source (accessed on 6 June 2025).
- Skapetas, B.; Kalaitzidou, M. Current status and perspectives of sheep sector in the world. LRRD 2017, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Sahoo, A. Importance of sheep milk: ‘dairy sheep’ a perspective avenue. In Donkey & Non-Bovine Milk; ILRI-NRCC Publication: Bikaner, India, 2023; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Pignotti, E.; Casas, G.; Llorca, M.; Tellbüscher, A.; Almeida, D.; Dinelli, E.; Farré, M.; Barceló, D. Seasonal variations in the occurrence of perfluoroalkyl substances in water, sediment and fish samples from Ebro Delta (Catalonia, Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellani, F.; Galletti, M.; Charavgis, F.; Cingolani, A.; Renzi, S.; Nucci, M.; Protano, C.; Vitali, M. Perfluorinated Compounds (PFCs) in River Waters of Central Italy: Monthly Variation and Ecological Risk Assessment (ERA). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2023, 84, 332–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Reference | Year | Analytes | Extraction Protocol | Instrumental Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [23] | 2014 | PFOA; PFOS | L-L extraction followed by two purification steps performed by SPE cartridges | UPLC-MS/MS |
| [24] | 2014 | PFBA, PFBS, PFPeA, PFHxA, PFHxS, PFHpA, FHEA, PFOA, PFOS, PFOSA, FOEA, PFNA, PFDA, PFDS, PFUdA, PFDoA, FDEA, PFTrA, PFTeDA, PFHxDA, PFODA | Alkaline digestion followed by a purification step performed by turbulent flow chromatography | LC-QqQ-MS |
| [25] | 2015 | PFBA, PFPA, PFHxA, PFHpA, PFOA, PFNA, PFDA, PFUnDA, PFDoDA, PFTrDa, PFTeDA, PFHxDA, PFOcDA, PFBS, PFPS, PFPS, L-PFHxS, L-PFHpS, L-PFOS, L-PFNS, L-PFDS | Extraction and clean up performed using a QuEChERS method | LC-MS/MS |
| [26] | 2016 | PFOA; PFOS | Ultrasonic extraction followed by a purification step performed by SPE cartridges | HPLC-MS/MS |
| [27] | 2018 | PFHxA, PFOA, PFDA, PFUnDA, PFDoDA, PFHxS, PFOS | Acidification and then purification by SPE cartridges | UPLC-MS/MS |
| [28] | 2018 | PFOA, PFOS | Liquid extraction | LC-MS/M |
| [29] | 2018 | PFOA, HFPO-DA | Liquid extraction followed by a purification step performed by SPE cartridges | LC-MS/MS |
| [30] | 2020 | L- and br-PFOS, PFOA, PFHxS | Alkaline digestion followed by SPE clean-up steps | LC-MS/MS |
| [8] | 2021 | PFBA, PFPeA, PFBS, PFHxA, PFHpA, PFHxS, PFOA, PFNA, PFOS, PFDA, PFUdA, PFDS, PFDoA, PFTrDA, PFTeDA | Extraction and clean up performed using a QuEChERS method | UHPLC-MS/MS |
| [31] | 2021 | L-PFBS, PFBA, PFDA, PFDoA, PFDS, PFHpA, PFHxA, PFHxS, PFNA, PFOA, PFOS, PFPeA, PFTeDA, PFTrDA, PFuDA | Extraction and clean up performed using a QuEChERS method | UHPLC-MS/MS |
| [4] | 2022 | PFBA, PFPeA PFHxA, PFHpA PFOA, PFNA PFDA, PFUnDA PFDoDA, PFTriDA PFTeDA, PFBS, PFPeS, PFHxS PFHpS, PFOS PFNS, PFDS, PFECHS, FBSA FOSA, N-MeFOSA N-EtFOSA, N-MeFOSAA, N-EtFOSAA, 4:2 FtS, 6:2 FtS, 8:2 FtS | Liquid extraction followed by SPE clean up step | LC-MS/MS |
| [32] | 2022 | PFBA, PFPeA, PFHxA, PFHpA, PFOA, PFNA, PFDA, PFUnA, PFDoA, PFBS, PFHxS, PFOS, GenX, C6O4 | Extraction and clean up performed using a QuEChERS method | LC-MS/MS |
| [33] | 2022 | PFPeA, PFHpA PFOA, PFNA PFDA, PFHxS PFOS | Direct immersion SPME (DI-SPME) | LC-MS/MS |
| [34] | 2022 | PFBA, PFBS, PFPeA, PFHxA, PFHxS, PFHpA, PFOA, PFOS, PFNA, PFDA, PFUnDA, PFDoDA, PFTrDA, PFTeDA, PFHxDA, PFODA | Liquid extraction followed by SPE clean-up step | UPLC-MS/MS |
| [35] | 2023 | PFBS, PFPeS, PFHxS, PFHpS, l-PFOS and br-PFOS, PFHxA, PFHpA, PFOA, PFNA, PFDA, PFUnDA, PFDoA, PFTrDA, PFTeDA | Liquid extraction followed by SPE clean-up step | LC-MS/MS |
| [36] | 2023 | PFBA, PFPeA, PFHxA, PFHpA, PFOA, PFNA, PFDA, FOUEA, NADONA, PFBS, PFHxS, PFOS, NmetFOSAA, 6-2FTS | Liquid extraction followed by SPE clean-up step | UPLC-HRMS |
| [37] | 2024 | PFPrS, PFBS, PFPeS, PFHxS, PFHpS, PFOS, PFNS, PFDS, PFDoS, PFBA, PFPeA, PFHxA, PFHpA, PFOA, PFNA, PFDA, PFUnDA, PFDoDA, PFTrDA, PFTeDA, PFHxDA, PFOcDA, 4:2FTS, 6:2FTS, 8:2FTS, 10:2FTS, PFEESA, PFECHS, Cl-PFOS, 6:2ClPFESA, 8:2ClPFESA, 3:3FTCA, 5:3FTCA, 7:3FTCA, 8:3FTCA, 6:2FTCA, 8:2FTCA, 10:2 FTCA, 6:2FTUCA, 8:2FTUCA, 10:2FTUCA, PF4OPeA, PF5OHxA, 7H-PFHpA, 11H-PFUnDA, NaDONA, FBSA, FHxSA, FOSA, FDSA, N-MeFBSA, N-MeFOSA, N-EtFOSA, N-MeFOSAA, N-EtFOSAA, N-AP-FHxSA, N-CMAmP 6:2FOSA N-TAmP-FHxSA, 5:1:2FTB, 5:3FTB | pH-dependent cold-induced liquid–liquid extraction as pre-clean-up step | HPLC-MS/MS |
| [38] | 2024 | PFBA, PFPeA PFHxA, PFHpA PFOA, PFNA PFDA, PFUnDA PFDoDA, PFTrDA, PFTeDA, PFBS, PFPeS, PFHxS PFHpS, PFOS | Liquid extraction followed by SPE clean-up step | HPLC-MS/MS |
| [39] | 2024 | PFBA, PFPeA PFHxA, PFHpA PFOA, PFNA PFDA, PFUnDA PFDoDA, PFTrDA PFTeDA, PFBS PFPeS, PFHxS PFHpS, PFOS PFNS, PFDS PFUnDS, PFDoDS PFTrDS, HFPO-DA DONA | QuEChERS method followed by two clean up steps performed by SPE | LC-HRMS |
| [40] | 2024 | PFBA, PFHxA, PFHpA PFOA, PFNA PFDA, PFUnDA PFDoDA, PFTrDA PFTeDA, N-MeFOSAA, N-EtFOSAA, PFBS PFHxS, PFHpS PFOS, PFDS 4:2 FTS, 6:2 FTS 8:2 FTS, L-PENS L-PFDoS | Extraction and clean up performed using a QuEChERS method | LC–MS/MS |
| [41] | 2024 | PFBS, PFHxA PFPeS, PFHpA, PFHxS, PFOA, PFHpS, PFNA PFOS, PFDA, PFNS, PFUnDA, PFDS, PFDoDA, PFTrDA, PFDoDS, PFTeA, 4:2 FTS, 6:2 FTS, 8:2 FTS, NaDONA, HFPO-DA | Liquid extraction followed by SPE clean-up step | HPLC-MS/MS |
| [42] | 2025 | PFBA, PFPeA PFHxA, PFHpA PFOA, PFNA PFDA, PFUnDA PFDoA, PFTrDA PFTeA, ADONA HFPO-DA (GenX) PFBS, PFPeS PFHxS, PFHpS PFOS, PFNS PFDS, PFDoS 4:2 FTS, 6:2 FTS 8:2 FTS | Liquid extraction followed by a QuEChERS step and then two purification steps performed by SPE | LC-MS/MS |
| Analytes | Frequency (%) |
|---|---|
| PFOA | 100 |
| PFOS | 100 |
| PFHxS | 77 |
| PFHpA | 77 |
| PFDA | 77 |
| PFHxA | 73 |
| PFNA | 73 |
| PFBS | 64 |
| PFBA | 59 |
| PFPeA | 55 |
| PFUnDA | 55 |
| PFTrDA | 50 |
| PFTeDA | 50 |
| PFDS | 41 |
| PFDoDA | 41 |
| PFHpS | 36 |
| PFPeS | 32 |
| PFDoA | 27 |
| 6:2 FtS | 27 |
| l PFOS | 23 |
| br PFOS | 23 |
| PFNS | 23 |
| HFPO-DA (Gen X) | 23 |
| 4:2 FtS | 23 |
| 8:2 FtS | 23 |
| PFHxDA | 18 |
| NaDONA | 14 |
| N-MeFOSAA | 14 |
| N-EtFOSAA | 14 |
| PFUdA | 14 |
| PFDoS | 9 |
| PFOcDA | 9 |
| PFECHS | 9 |
| FBSA | 9 |
| FOSA | 9 |
| N-MeFOSA | 9 |
| N-EtFOSA | 9 |
| PFODA | 9 |
| PFPS | 9 |
| PFTeA | 9 |
| PFDoDS | 9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Curci, D.; Sundaram, T.S.; Ghidini, S.; Arioli, F. What We Know About per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Contamination Levels in Milk. A Review from the Last Decade. Foods 2025, 14, 2274. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132274
Curci D, Sundaram TS, Ghidini S, Arioli F. What We Know About per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Contamination Levels in Milk. A Review from the Last Decade. Foods. 2025; 14(13):2274. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132274
Chicago/Turabian StyleCurci, Dalia, Tamil Selvi Sundaram, Sergio Ghidini, and Francesco Arioli. 2025. "What We Know About per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Contamination Levels in Milk. A Review from the Last Decade" Foods 14, no. 13: 2274. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132274
APA StyleCurci, D., Sundaram, T. S., Ghidini, S., & Arioli, F. (2025). What We Know About per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Contamination Levels in Milk. A Review from the Last Decade. Foods, 14(13), 2274. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132274








