The Effects of Tea Polyphenols on the Emulsifying and Gelling Properties of Minced Lamb After Repeated Freeze–Thaw Cycles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
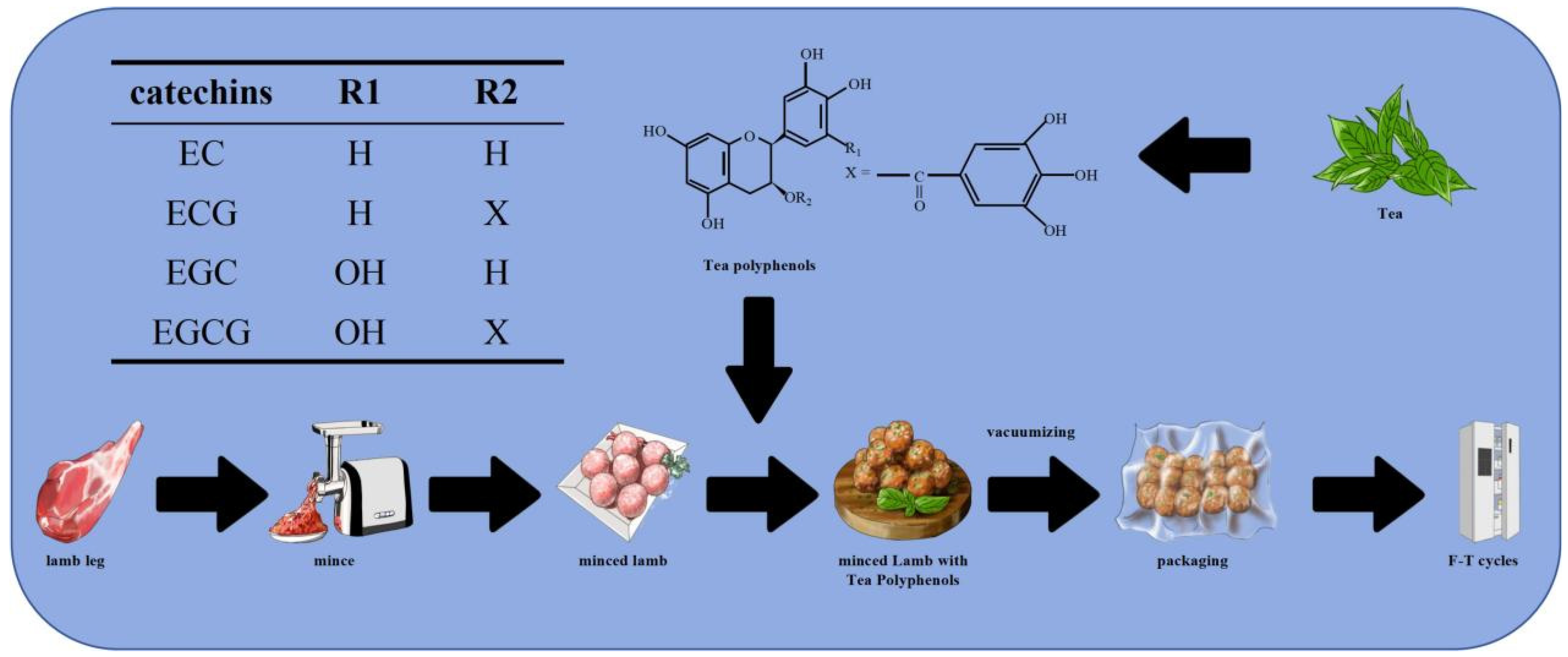
2.2. Preparation of Minced Meat
2.3. Freeze–Thaw Treatment
2.4. Preparation of Minced Meat Gel
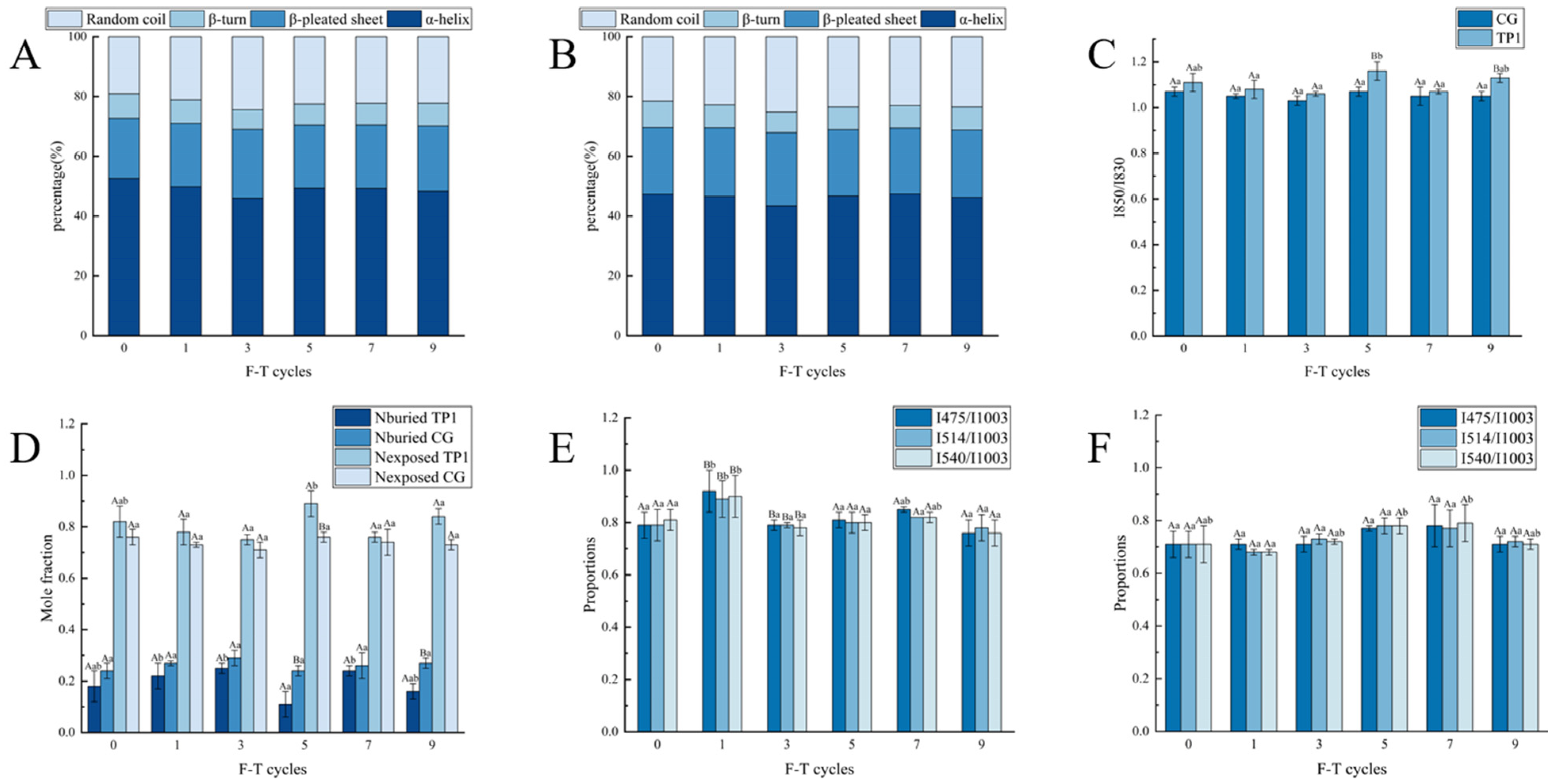
2.5. Raman Spectroscopy
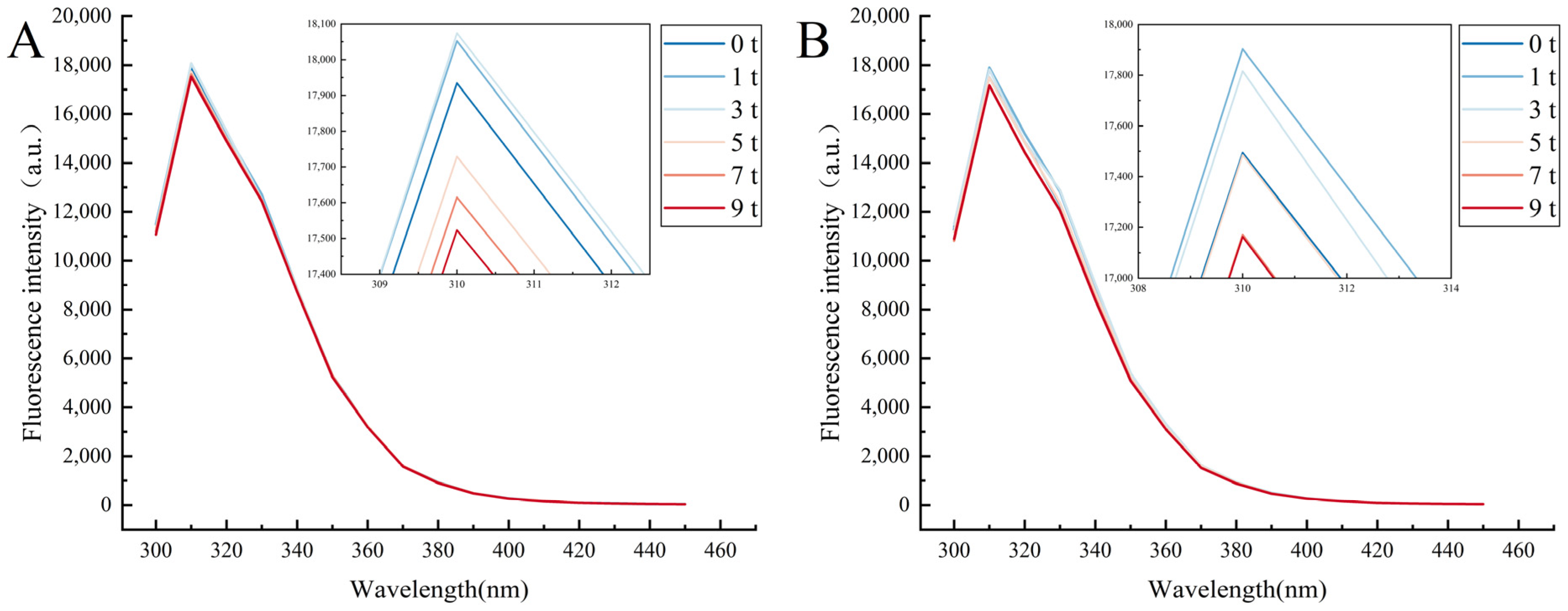
2.6. Fluorescence Scan
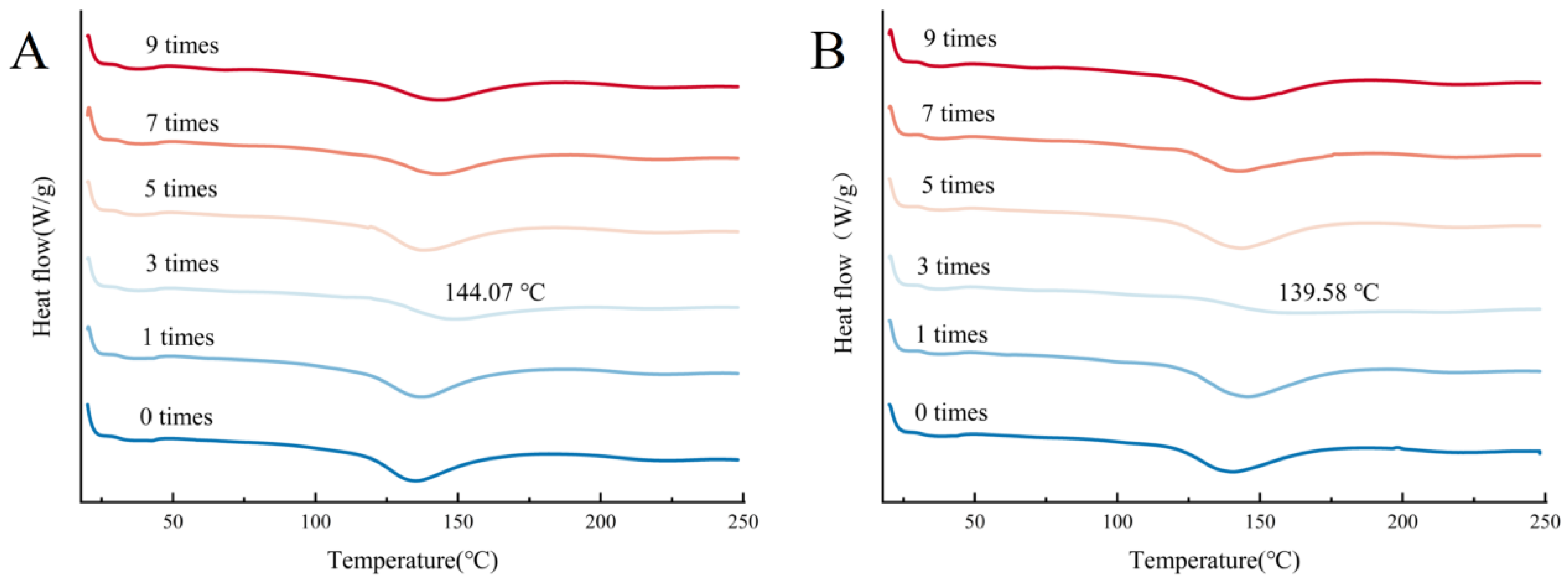
2.7. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.8. Low Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF-NMR) Measurement
2.9. Protein Properties
2.9.1. Protein Solubility
2.9.2. Emulsion Stability
2.9.3. Surface Hydrophobicity
2.10. Gel Properties
2.10.1. Microstructure Analysis
2.10.2. Determination of Textural Properties and Gel Strength
2.10.3. Cooking Loss
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Raman Spectral Analysis
3.2. Fluorescence Spectral Analysis
3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Analysis
3.4. Low Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF-NMR) Analysis
3.5. Changes in the Nature of Proteins in Minced Lamb
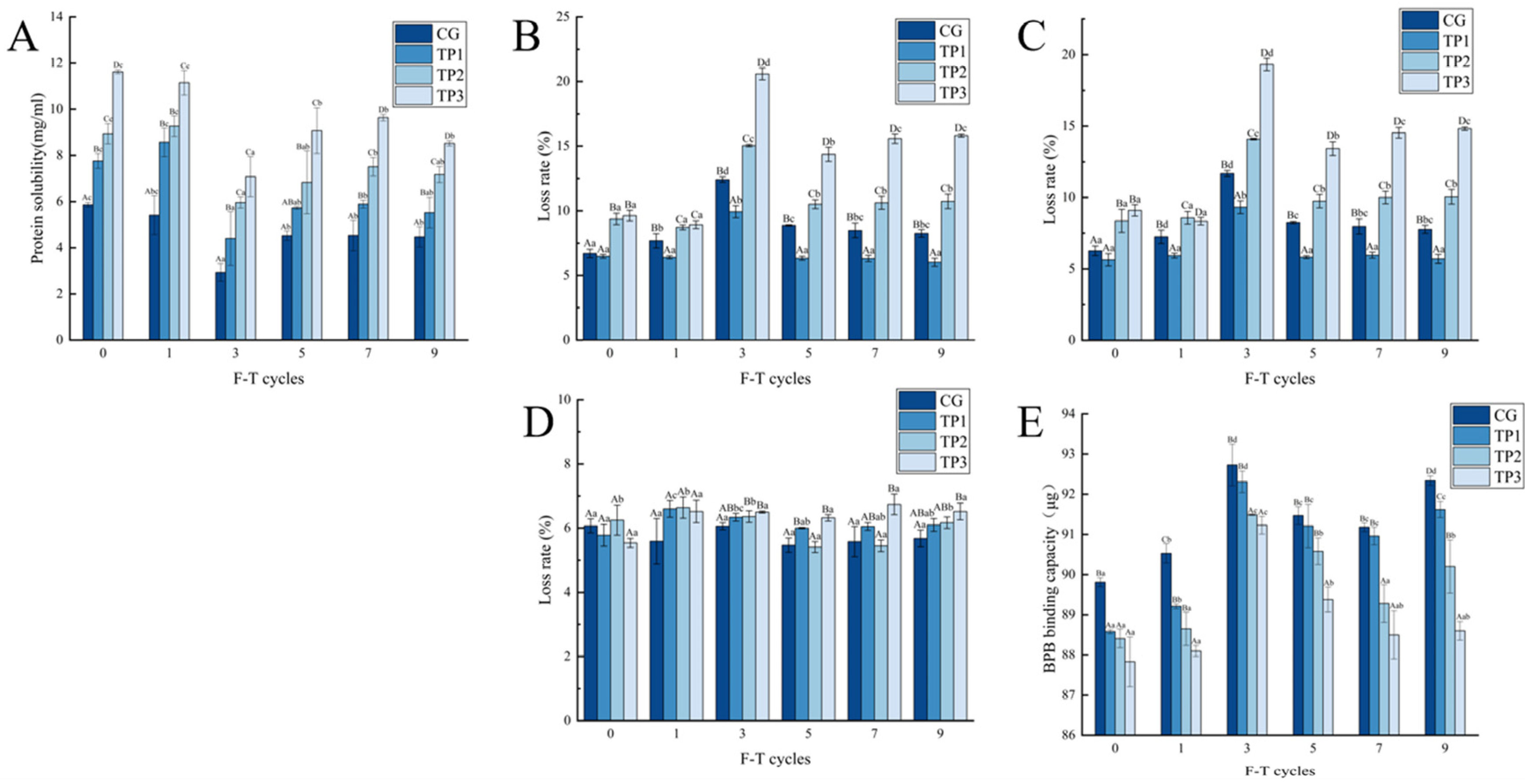
3.5.1. Changes in Protein Solubility of Minced Lamb
3.5.2. Changes in the Emulsion Stability of Minced Lamb
3.5.3. Changes in Surface Hydrophobicity
3.6. Changes in Gel Properties of Minced Lamb
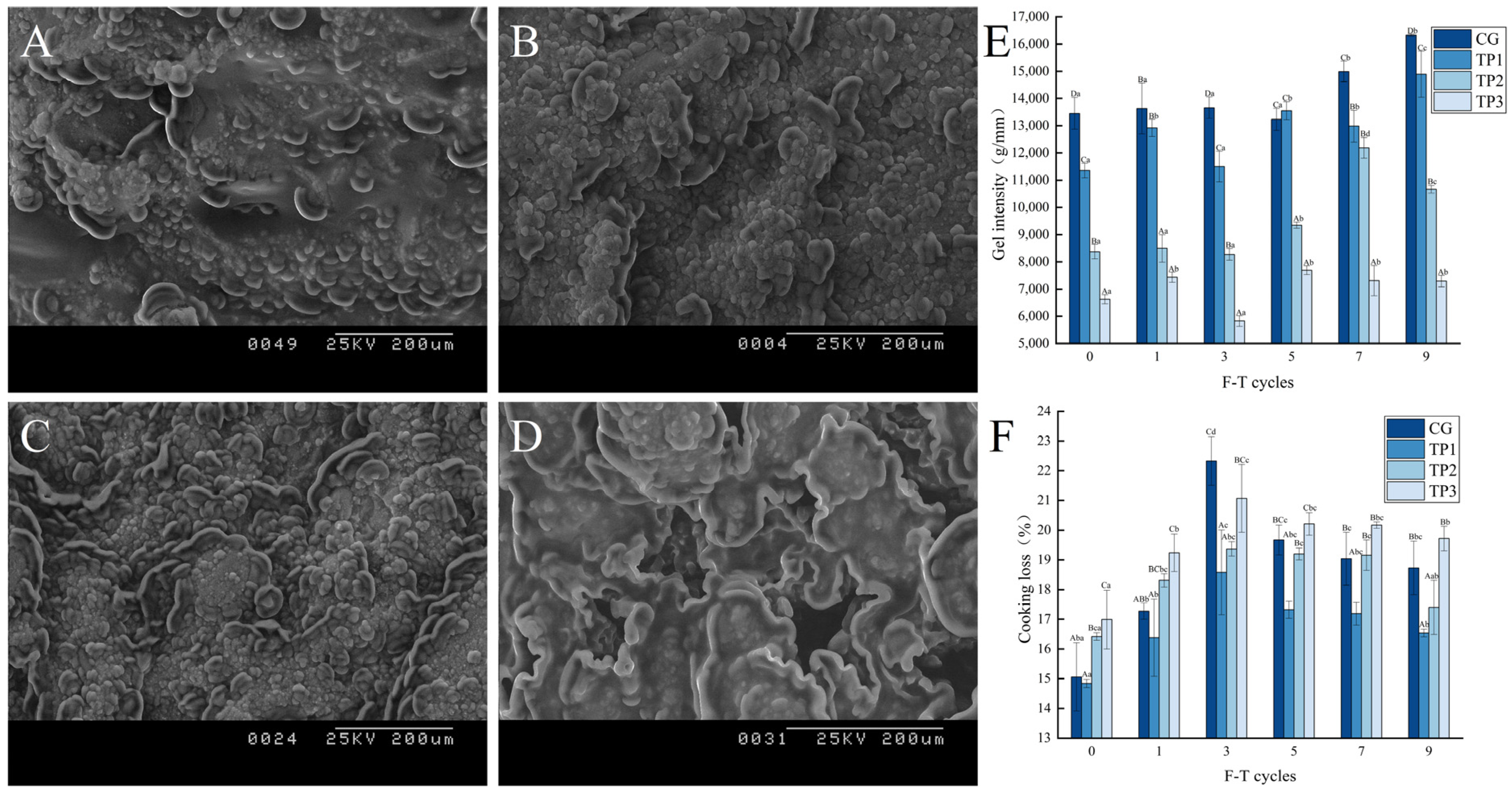
3.6.1. Changes in Gel Microstructure
3.6.2. Changes in Gel Textural Properties
3.6.3. Changes in Gel Strength
3.6.4. Changes in Cooking Loss
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Witte, F.; Sawas, E.; Berger, L.M.; Gibis, M.; Weiss, J.; Röser, A.; Upmann, M.; Joeres, E.; Juadjur, A.; Bindrich, U.; et al. Influence of Finely Chopped Meat Addition on Quality Parameters of Minced Meat. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouafo, H.T.; Mbawala, A.; Tanaji, K.; Somashekar, D.; Ndjouenkeu, R. Improvement of the shelf life of raw ground goat meat by using biosurfactants produced by lactobacilli strains as biopreservatives. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 133, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.F.; Kong, B.H.; Xiong, Y.L.; Ren, Y.M. Decreased gelling and emulsifying properties of myofibrillar protein from repeatedly frozen-thawed porcine longissimus muscle are due to protein denaturation and susceptibility to aggregation. Meat Sci. 2010, 85, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.D.; Jung, E.Y.; Lim, H.J.; Yang, H.S.; Joo, S.T.; Jeong, J.Y. Influence of meat exudates on the quality characteristics of fresh and freeze-thawed pork. Meat Sci. 2013, 95, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.W.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Sun, D.W. Measuring and controlling ice crystallization in frozen foods: A review of recent developments. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 90, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, D.V.S.; Bastarrachea, L.J.; Martini, S.; Matarneh, S.K. Crystallization Behavior and Quality of Frozen Meat. Foods 2021, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.J.; Bakry, A.M.; Zeng, S.W.; Xiong, S.B.; Yin, T.; You, J.; Fan, M.C.; Huang, Q.L. Effect of phosphates on gelling characteristics and water mobility of myofibrillar protein from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Food Chem. 2019, 272, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliwan, P.; Wangtueai, S.; Yarnpakdee, S.; Katekhong, W.; Klinmalai, P. Role of Skipjack Tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) Blood Protein Hydrolysate as a Natural Cryoprotectant on Threadfin Bream Surimi Protein During Repeated Freeze–Thaw Stability. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2025, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.L.; Yang, W.E.; Wei, H.M.; Deng, S.G.; Yu, X.X.; Huang, T. The mechanisms and applications of cryoprotectants in aquatic products: An overview. Food Chem. 2023, 408, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karre, L.; Lopez, K.; Getty, K.J.K. Natural antioxidants in meat and poultry products. Meat Sci. 2013, 94, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Peñalver, D.; Alemán, A.; Montero, P.; Gómez-Guillén, M.C. Gelling properties of hake muscle with addition of freeze-thawed and freeze-dried soy phosphatidylcholine liposomes protected with trehalose. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 98, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Yu, Q.Y.; Liu, Y.Y.; Sun, X.Y.; Li, Q.; Fan, H.B.; Benjakul, S.; Tan, Y.Q.; Luo, Y.K.; Hong, H. Dual cryoprotective and antioxidant effects of young apple polyphenols on myofibrillar protein degradation and gelation properties of bighead carp mince during frozen storage. J. Food Sci. 2023, 88, 4560–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lima, S.N.; de Oliveira, C.C.; Castilho, E.A.; Damasceno, K.A.; de Almeida, P.L.; de Oliveira, S.C.; Campagnol, P.C.B. Effect of Marcela Extract (Achyroclines satureiodes) on the Shelf Life of Minced Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Sausages. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2017, 26, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Z.; Axelsson, J.; Kuhlin, M.; Fristedt, R.; Undeland, I. Pilot-Scale Antioxidant Dipping of Herring (Clupea harengus) Co- products to Allow Their Upgrading to a High-Quality Mince for Food Production. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 4727–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.M.; Zhong, Y.Z.; Duan, Y.H.; Chen, Q.H.; Li, F.N. Antioxidant mechanism of tea polyphenols and its impact on health benefits. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 6, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lei, Y.T.; Tan, Y.Q.; Zhang, J.B.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y.K. Efficacy of freeze-chilled storage combined with tea polyphenol for controlling melanosis, quality deterioration, and spoilage bacterial growth of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Food Chem. 2022, 370, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, L.L.; Fu, S.L.; Yuan, C.H.; Ishimura, G.; Chen, S.G.; Chen, J.C.; Hu, Y.Q. Combined effect of superchilling and tea polyphenols on the preservation quality of hairtail (Trichiurus haumela). Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, S992–S1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walayat, N.; Wei, R.; Su, Z.C.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Nawaz, A. Effect of tea polysaccharides on fluctuated frozen storage impaired total sulfhydryl level and structural attributes of silver carp surimi proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 157, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Xu, Q.D.; Chen, N.; He, Q.; Sun, Q.; Yu, Z.L.; Zeng, W.C. Effects of tea polyphenols on the quality of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) meat during the freezing process and its action mechanism. J. Food Process Preserv. 2022, 46, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Di, Z.; Li, C.; Yue, X.; Shao, J.H. Raman spectroscopy and low-field nuclear magnetic resonance used to monitor the relationship between protein conformation and water retention in the formation for process of gel. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, e14225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.Y.; Li, M.Y.; Tian, G.; Zhang, T.H.; Ren, H.; Quek, S.Y. Effects of ultrasonic pretreatment on the structure and functionality of chicken bone protein prepared by enzymatic method. Food Chem. 2019, 299, 125103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Xiong, Y.L. Interaction of whey proteins with phenolic derivatives under neutral and acidic pH conditions. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, J.-H.; Deng, Y.-M.; Song, L.; Batur, A.; Jia, N.; Liu, D.-Y. Investigation the effects of protein hydration states on the mobility water and fat in meat batters by LF-NMR technique. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 66, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, N.; Qiu, K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Yin, J. The coordination of dietary valine and isoleucine on water holding capacity, pH value and protein solubility of fresh meat in finishing pigs. Meat Sci. 2020, 163, 108074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cofrades, S.; Serrano, A.; Ayo, J.; Carballo, J.; Jiménez-Colmenero, F. Characteristics of meat batters with added native and preheated defatted walnut. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 1506–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, J.; Li, X.; Shao, J.-H. The study of protein conformation and hydration characteristics of meat batters at various phase transition temperatures combined with Low-field nuclear magnetic resonance and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2019, 280, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, P.; Toldrà, M.; Saguer, E.; Carretero, C.; Parés, D. Microstructure–function relationships of heat-induced gels of porcine haemoglobin. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1654–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, X.; Li, A.; Li, F. Effect of recombinant buckwheat trypsin inhibitor on gel properties of chicken meat emulsion. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.C.; Niu, H.L.; Chen, Q.; Xia, X.F.; Kone, B.H. Influence of ultrasound-assisted immersion freezing on the freezing rate and quality of porcine longissimus muscles. Meat Sci. 2018, 136, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.C.; Li, F.F.; Diao, X.P.; Kong, B.H.; Xia, X.F. Moisture migration, microstructure damage and protein structure changes in porcine longissimus muscle as influenced by multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Meat Sci. 2017, 133, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.Y.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Mehmood, W.; Zhong, M.; Zhang, C.H.; Blecker, C. Effects of low voltage electrostatic field thawing on the changes in physicochemical properties of myofibrillar proteins of bovine Longissimus dorsi muscle. J. Food Eng. 2019, 261, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.P.; Liu, C.K.; Wang, J.X.; Li, W.X.; Lin, B.Y.; Zhu, W.H.; Xu, Y.X.; Yi, S.M.; Mi, H.B.; Li, J.R. Tea Polyphenols Affect Oxidative Modification and Solution Stability of Myofibrillar Protein from Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Food Biophys. 2020, 15, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, L.; Zhu, X.; Ning, C.; Cai, K.; Zhou, C. Conformational and charge changes induced by L-arginine and L-lysine increase the solubility of chicken myosin. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asquith, T.N.; Butler, L.G. Interactions of condensed tannins with selected proteins. Phytochemistry 1986, 25, 1591–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutilangi, W.A.M.; Panyam, D.; Kilara, A. Functional Properties of Hydrolysates from Proteolysis of Heat-denatured Whey Protein Isolate. J. Food Sci. 1996, 61, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdal, T.; Capanoglu, E.; Altay, F. A review on protein–phenolic interactions and associated changes. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 954–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, P.; Winterbourn, C.C. Chapter 6—Redox Chemistry of Biological Thiols. In Advances in Molecular Toxicology; Fishbein, J.C., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 4, pp. 183–222. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.Y.; Xu, Y.S.; Yu, D.W.; Wang, B. Effects of freeze-thaw cycles and heat treatment on the odor-binding properties of myofibrillar protein to key fishy compounds. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, J.; Rawel, H.M. Reactions of Plant Phenols with Myoglobin: Influence of Chemical Structure of the Phenolic Compounds. J. Food Sci. 2001, 66, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.P.; Gao, Y.F.; Solangi, I.; Liu, S.C.; Zhu, J. Effects of tea polyphenols on the conformational, functional, and morphological characteristics of beef myofibrillar proteins. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 154, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.H.; Chen, Q.L.; Wang, X.W.; Chen, Z.J. Effect of Freezing on Soybean Protein Solution. Foods 2023, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.G.; Xiong, Y.L.L. Chlorogenic acid-mediated gel formation of oxidatively stressed myofibrillar protein. Food Chem. 2015, 180, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, A.Q.; Xiong, Y.L.L. Glucose oxidase promotes gallic acid-myofibrillar protein interaction and thermal gelation. Food Chem. 2019, 293, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.X.; Chen, Q.; Xia, X.F.; Kong, B.H.; Diao, X.P. Effects of ultrasound-assisted freezing at different power levels on the structure and thermal stability of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) proteins. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 54, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.-b.; Zhang, W.-g.; Dai, C.; Li, H.-x.; Xu, X.-l.; Zhou, G.-h. Identification and quantification of adducts between oxidized rosmarinic acid and thiol compounds by UHPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap and MALDI-TOF/TOF tandem mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.G.; True, A.D.; Chen, J.; Xiong, Y.L.L. Dual Role (Anti- and Pro-oxidant) of Gallic Acid in Mediating Myofibrillar Protein Gelation and Gel in Vitro Digestion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 3054–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.S.; Wang, X.H.; Li, R.R.; Yang, H.M.; Wang, H.H.; Wang, H.T.; Tan, M.Q. Influence of multiple freeze-thaw cycles on quality characteristics of beef semimembranous muscle: With emphasis on water status and distribution by LF-NMR and MRI. Meat Sci. 2019, 147, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balange, A.; Benjakul, S. Enhancement of gel strength of bigeye snapper (Priacanthus tayenus) surimi using oxidised phenolic compounds. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.L.; Xie, T.Y.; Cheng, W.W.; Ding, Y.; Xu, B.C. Characterization and mechanism of thermally induced tea polyphenols and egg white proteins gel system and its 3D printing. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 205, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff-Lonergan, E.; Lonergan, S.M. Mechanisms of water-holding capacity of meat: The role of postmortem biochemical and structural changes. Meat Sci. 2005, 71, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, H.C.; Andersen, H.J.; Karlsson, A.H. Comparative study of low-field NMR relaxation measurements and two traditional methods in the determination of water holding capacity of pork. Meat Sci. 2001, 57, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazeddinova, D.; Rahman, M.R.; Bin Hamdan, S.; Matin, M.M.; Bin Bakri, M.K.; Rahman, M.M. Plant Based Polyphenol Associations with Protein: A Prospective Review. Bioresources 2022, 17, 7110–7134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornberg, E.; Wahlgren, M.; Brøndum, J.; Engelsen, S.B. Pre-rigor conditions in beef under varying temperature- and pH-falls studied with rigometer, NMR and NIR. Food Chem. 2000, 69, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.M.; Xia, M.Q.; Zhou, Y.H.; Wang, X.; Ma, J.; Xiong, G.Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.J.; Sun, W.Q. Gel properties of grass carp myofibrillar protein modified by low-frequency magnetic field during two-stage water bath heating. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 107, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.B.; Liu, D.Y.; Zhou, G.H.; Xu, X.L.; Qi, J.; Shi, P.L.; Xia, T.L. Meat quality and cooking attributes of thawed pork with different low field NMR T21. Meat Sci. 2012, 92, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Bhandari, B.; Gao, Z.X. Effects of malondialdehyde-induced protein modification on water functionality and physicochemical state of fish myofibrillar protein gel. Food Res. Int. 2016, 86, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xiong, Y.L.L.; Sato, H.; Kurnazawa, Y. Controlled Cross-Linking with Glucose Oxidase for the Enhancement of Gelling Potential of Pork Myofibrillar Protein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 9523–9531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, Z.; He, Z.; Wang, Z.; Qin, F.; Zeng, M.; Chen, J. Effect of freeze-thaw cycles on the oxidation of protein and fat and its relationship with the formation of heterocyclic aromatic amines and advanced glycation end products in raw meat. Molecules 2021, 26, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, Z.P.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.F. The effect of non-covalent interaction of chlorogenic acid with whey protein and casein on physicochemical and radical-scavenging activity of in vitro protein digests. Food Chem. 2018, 268, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, C.S.; Li, L.H.; Yang, X.Q.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhou, W.G. Improved physicochemical properties and product characteristics of tilapia surimi by tea polyphenols during chilled storage. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 167, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorba, Ö.; Kurt, Ş.; Gençcelep, H. The effects of different levels of skim milk powder and whey powder on apparent yield stress and density of different meat emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2005, 19, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Xu, D.; Liu, G.; Xiao, J.; Cao, Y.; Sun, B. Influence of unadsorbed emulsifiers on the rheological properties and structure of heteroaggregate of whey protein isolate (WPI) coated droplets and flaxseed gum (FG) coated droplets. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 80, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Sun, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, G.Z.; Luo, P.; Tang, D.B.; Huang, Q. Study on the mechanism of mulberry polyphenols inhibiting oxidation of beef myofibrillar protein. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, X.; Gong, Y.; Wang, N.; Meng, X. Preparation and characterization of edible myofibrillar protein-based film incorporated with grape seed procyanidins and green tea polyphenol. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Do, M.D.; Casey, P.; Sulistio, A.; Qiao, G.G.; Lundin, L.; Lillford, P.; Kosaraju, S. Chemical Cross-Linking Gelatin with Natural Phenolic Compounds as Studied by High-Resolution NMR Spectroscopy. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L.; Lin, S.; Liu, D. The beneficial effects of rutin on myofibrillar protein gel properties and related changes in protein conformation. Food Chem. 2019, 301, 125206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.F.; Yang, X.Q.; Jin, Z.; Han, L.; Li, K.; Prakash, S.; Dong, X.P. Effect of tea polyphenols on the quality of Mackerel puree (Scomber scombrus) during refrigerated storage: Color, oxidative stability and microstructure. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongberg, S.; Terkelsen, L.D.; Miklos, R.; Lund, M.N. Green tea extract impairs meat emulsion properties by disturbing protein disulfide cross-linking. Meat Sci. 2015, 100, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, F.F.; Pan, N.; Kong, B.H.; Xia, X.F. Effect of ice structuring protein on the quality of quick-frozen patties subjected to multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Meat Sci. 2021, 172, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattaya, S.; Benjakul, S.; Prodpran, T. Properties of fish skin gelatin film incorporated with seaweed extract. J. Food Eng. 2009, 95, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.; Wang, Y.; Tang, S.; Huang, C.; Jackson, M.G. Role of ferulic acid in preparing edible films from soy protein isolate. J. Food Eng. 2005, 70, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
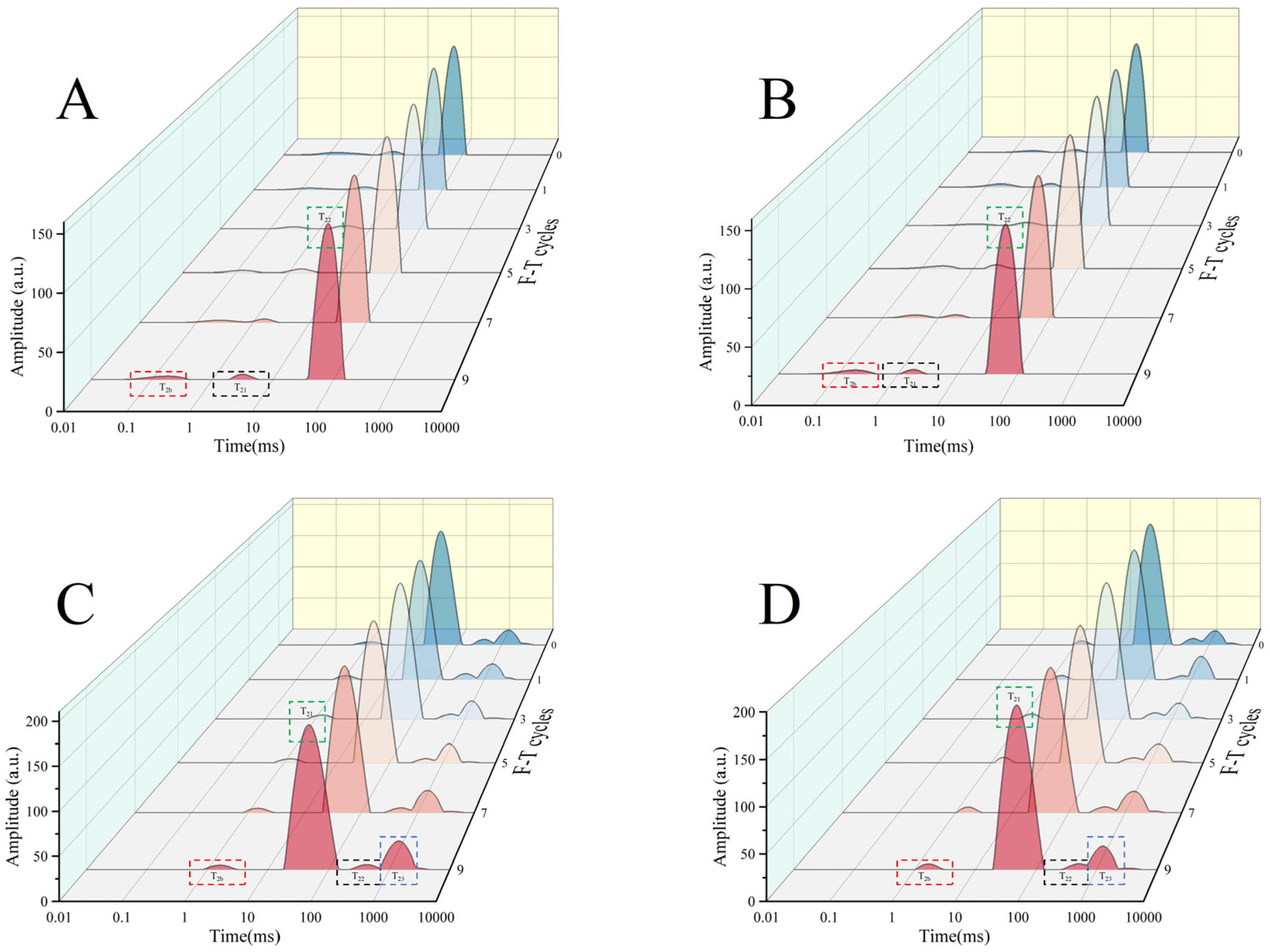
| F-T Cycles | Groups | T2b/ms | T21/ms | T22/ms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | CG | 0.17 ± 0.02 Aa | 2.20 ± 0.07 Aa | 60.84 ± 2.11 Aa |
| TP1 | 0.27 ± 0.03 Bb | 2.71 ± 0.09 Bab | 65.21 ± 2.26 Ba | |
| 1 | CG | 0.18 ± 0.03 Aa | 3.19 ± 0.70 Ab | 72.50 ± 5.03 Ab |
| TP1 | 0.33 ± 0.02 Bc | 3.47 ± 0.63 Ab | 75.29 ± 7.81 Ab | |
| 3 | CG | 0.26 ± 0.03 Ab | 2.79 ± 0.32 Aab | 70.24 ± 7.29 Aab |
| TP1 | 0.26 ± 0.01 Ab | 2.84 ± 0.25 Aab | 68.13 ± 9.40 Aab | |
| 5 | CG | 0.22 ± 0.01 Aab | 2.31 ± 0.15 Aab | 67.64 ± 4.69 Aab |
| TP1 | 0.25 ± 0.02 Ab | 2.64 ± 0.09 Bab | 67.64 ± 4.69 Aab | |
| 7 | CG | 0.26 ± 0.00 Bb | 2.20 ± 0.48 Aa | 64.08 ± 1.96 Aab |
| TP1 | 0.18 ± 0.03 Aa | 2.87 ± 0.77 Aab | 62.95 ± 0.00 Aa | |
| 9 | CG | 0.20 ± 0.04 Aab | 2.44 ± 0.41 Aab | 73.02 ± 10.07 Ab |
| TP1 | 0.19 ± 0.01 Aa | 2.06 ± 0.18 Aa | 62.95 ± 0.00 Aa |
| F-T Cycles | Groups | T2b/ms | T21/ms | T22/ms | T23/ms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | CG | 1.40 ± 0.19 Aa | 46.09 ± 1.60 Aa | 457.76 ± 47.50 Aa | 1431.46 ± 0.00 Ba |
| TP1 | 1.49 ± 0.10 Aa | 47.69 ± 0.00 Ab | 490.67 ± 50.91 Aa | 1335.45 ± 0.00 Aab | |
| 1 | CG | 1.61 ± 0.49 Aa | 53.72 ± 9.23 Ab | 588.30 ± 178.04 Aa | 1589.52 ± 55.15 Ab |
| TP1 | 1.83 ± 0.13 Ab | 58.73 ± 0.00 Ac | 622.26 ± 0.00 Ab | 1703.80 ± 59.12 Ad | |
| 3 | CG | 1.67 ± 0.29 Aa | 51.11 ± 0.00 Bab | 541.59 ± 0.00 Ba | 1431.46 ± 0.00 Aa |
| TP1 | 1.54 ± 0.05 Aa | 47.69 ± 0.00 Ab | 488.32 ± 16.94 Aa | 1383.46 ± 48.00 Ab | |
| 5 | CG | 1.62 ± 0.33 Aa | 51.11 ± 0.00 Bab | 506.48 ± 35.11 Aa | 1383.46 ± 48.00 Aa |
| TP1 | 1.76 ± 0.06 Ab | 47.69 ± 0.00 Ab | 488.32 ± 16.94 Aa | 1482.91 ± 51.45 Ac | |
| 7 | CG | 1.79 ± 0.31 Aa | 51.11 ± 0.00 Bab | 523.43 ± 18.16 Aa | 1431.46 ± 0.00 Aa |
| TP1 | 1.76 ± 0.06 Ab | 47.69 ± 0.00 Ab | 472.51 ± 32.75 Aa | 1383.46 ± 48.00 Ab | |
| 9 | CG | 1.90 ± 0.20 Aa | 47.69 ± 0.00 Aab | 439.76 ± 0.00 Aa | 1431.46 ± 0.00 Ba |
| TP1 | 1.76 ± 0.06 Ab | 46.09 ± 1.60 Aa | 488.32 ± 16.94 Aa | 1290.67 ± 44.78 Aa |
| Textural Property | F-T Cycles | CG | TP1 | TP2 | TP3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hardness/g | 0 | 10,608.04 ± 518.54 Dbc | 9375.32 ± 121.02 Cabc | 8507.81 ± 496.25 Ba | 5551.66 ± 383.60 Ac |
| 1 | 10,357.29 ± 957.30 Cbc | 9160.55 ± 324.84 Ba | 9155.21 ± 253.74 Bb | 5842.65 ± 302.10 Acd | |
| 3 | 11,109.69 ± 267.40 Dc | 10,618.35 ± 54.13 Cd | 10,063.29 ± 67.57 Bc | 6026.25 ± 95.95 Ad | |
| 5 | 9337.44 ± 167.32 Ca | 9784.76 ± 291.76 Cbc | 8412.92 ± 358.35 Ba | 4590.79 ± 143.41 Ab | |
| 7 | 10,516.25 ± 263.52 Dbc | 9820.79 ± 191.80 Cc | 8533.88 ± 193.97 Ba | 3513.73 ± 157.36 Aa | |
| 9 | 9722.12 ± 75.11 Cab | 9299.54 ± 428.30 Cab | 8290.09 ± 364.57 Ba | 3637.52 ± 117.60 Aa | |
| resilience | 0 | 0.89 ± 0.01 Ba | 0.90 ± 0.02 Ba | 0.88 ± 0.00 Ba | 0.83 ± 0.01 Ad |
| 1 | 0.90 ± 0.01 Bbc | 0.90 ± 0.03 Ba | 0.89 ± 0.00 Ba | 0.83 ± 0.00 Ad | |
| 3 | 0.92 ± 0.01 Cc | 0.91 ± 0.01 Ca | 0.89 ± 0.01 Ba | 0.75 ± 0.02 Ac | |
| 5 | 0.90 ± 0.02 Bbc | 0.91 ± 0.02 Ba | 0.87 ± 0.05 Ba | 0.71 ± 0.01 Ab | |
| 7 | 0.91 ± 0.02 Bbc | 0.91 ± 0.00 Ba | 0.87 ± 0.01 Ba | 0.70 ± 0.03 Ab | |
| 9 | 0.92 ± 0.01 Cc | 0.91 ± 0.02 Ca | 0.86 ± 0.01 Ba | 0.65 ± 0.01 Aa | |
| cohesiveness | 0 | 0.69 ± 0.01 Cb | 0.73 ± 0.00 Dd | 0.68 ± 0.03 Bb | 0.61 ± 0.00 Ad |
| 1 | 0.70 ± 0.00 Cb | 0.72 ± 0.00 Dc | 0.68 ± 0.00 Bb | 0.60 ± 0.00 Ad | |
| 3 | 0.69 ± 0.00 Cb | 0.72 ± 0.00 Dc | 0.65 ± 0.00 Ba | 0.56 ± 0.01 Ac | |
| 5 | 0.67 ± 0.01 B Ca | 0.70 ± 0.00 Cb | 0.64 ± 0.00 Ba | 0.51 ± 0.03 Ab | |
| 7 | 0.66 ± 0.00 Ca | 0.69 ± 0.00 Da | 0.64 ± 0.02 Ba | 0.48 ± 0.00 Aa | |
| 9 | 0.70 ± 0.00 Cb | 0.70 ± 0.00 Cb | 0.63 ± 0.00 Ba | 0.46 ± 0.00 Aa | |
| chewiness/g | 0 | 6958.15 ± 42.03 Db | 6225.65 ± 54.88 Cb | 4914.27 ± 351.05 Bbc | 3090.02 ± 192.16 Ae |
| 1 | 6977.87 ± 455.21 Db | 5929.07 ± 190.35 Cab | 5158.12 ± 382.81 Bc | 2822.79 ± 18.19 Ad | |
| 3 | 6240.97 ± 676.08 Ca | 5746.30 ± 22.08 B Ca | 5164.81 ± 110.80 Bc | 2269.00 ± 114.38 Ac | |
| 5 | 6140.44 ± 197.18 Ca | 6030.01 ± 193.83 Cab | 4529.69 ± 81.73 Bab | 1562.00 ± 65.53 Ab | |
| 7 | 5820.34 ± 190.08 Ca | 5843.48 ± 266.69 Ca | 4872.54 ± 222.29 Bbc | 1631.54 ± 101.57 Ab | |
| 9 | 6093.82 ± 147.47 Ca | 5855.64 ± 197.45 Ca | 4332.49 ± 37.24 Ba | 1089.77 ± 56.10 Aa | |
| responsiveness | 0 | 0.29 ± 0.00 Dc | 0.33 ± 0.00 Cb | 0.24 ± 0.01 Ba | 0.21 ± 0.00 Ad |
| 1 | 0.32 ± 0.01 Cd | 0.34 ± 0.01 Db | 0.28 ± 0.00 Bc | 0.22 ± 0.00 Ad | |
| 3 | 0.29 ± 0.00 Cbc | 0.33 ± 0.00 Db | 0.25 ± 0.00 Bab | 0.19 ± 0.00 Ac | |
| 5 | 0.28 ± 0.01 Cab | 0.30 ± 0.00 Da | 0.26 ± 0.01 Bb | 0.15 ± 0.01 Ab | |
| 7 | 0.27 ± 0.00 Ca | 0.31 ± 0.00 Da | 0.24 ± 0.01 Bab | 0.14 ± 0.01 Aa | |
| 9 | 0.29 ± 0.01 Cc | 0.31 ± 0.01 Da | 0.25 ± 0.00 Bab | 0.13 ± 0.00 Aa |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yun, X.; Yang, G.; Li, L.; Wu, Y.; Yang, X.; Gao, A. The Effects of Tea Polyphenols on the Emulsifying and Gelling Properties of Minced Lamb After Repeated Freeze–Thaw Cycles. Foods 2025, 14, 2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132259
Yun X, Yang G, Li L, Wu Y, Yang X, Gao A. The Effects of Tea Polyphenols on the Emulsifying and Gelling Properties of Minced Lamb After Repeated Freeze–Thaw Cycles. Foods. 2025; 14(13):2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132259
Chicago/Turabian StyleYun, Xueyan, Ganqi Yang, Limin Li, Ying Wu, Xujin Yang, and Aiwu Gao. 2025. "The Effects of Tea Polyphenols on the Emulsifying and Gelling Properties of Minced Lamb After Repeated Freeze–Thaw Cycles" Foods 14, no. 13: 2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132259
APA StyleYun, X., Yang, G., Li, L., Wu, Y., Yang, X., & Gao, A. (2025). The Effects of Tea Polyphenols on the Emulsifying and Gelling Properties of Minced Lamb After Repeated Freeze–Thaw Cycles. Foods, 14(13), 2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132259




