The Psychosocial Resonance of Food Safety Risk: A Space-Time Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Diffusion Mechanism of Psychosocial Resonance of Food Safety Risk
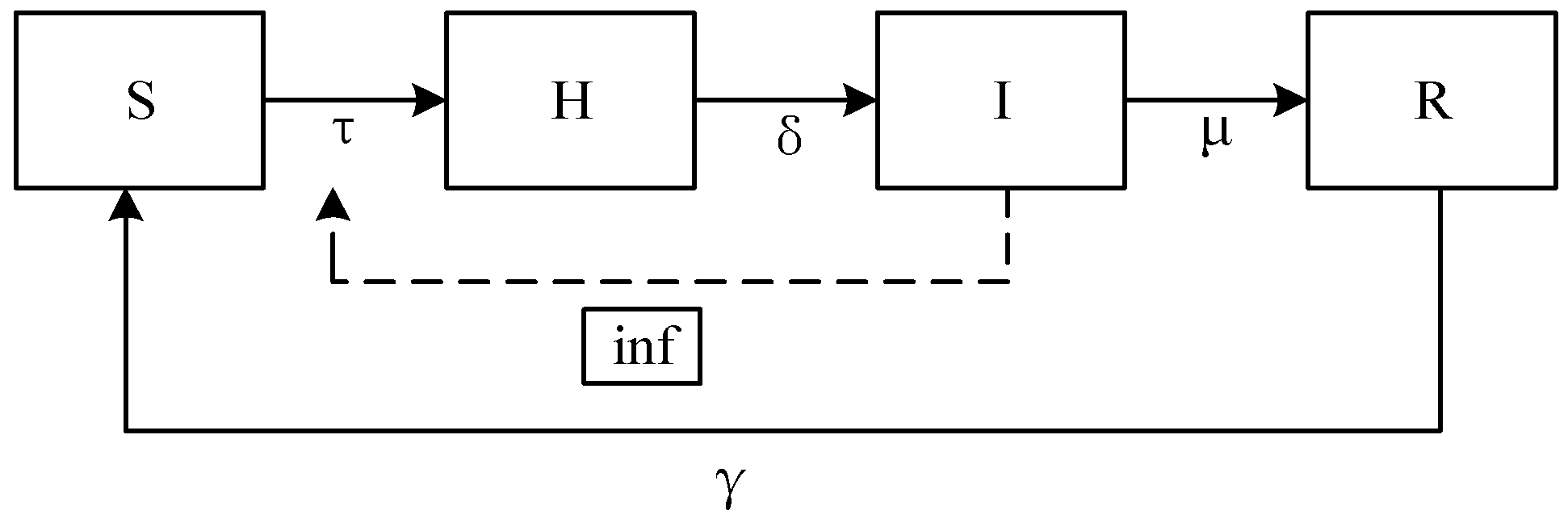
2.2. CA-SHIRS Model of Psychosocial Resonance Diffusion of Food Safety Risk
2.2.1. Cellular State Setting
2.2.2. Dynamical Evolution Rule
2.2.3. Threshold Analysis of Psychosocial Resonance Diffusion of Food Safety Risk
2.2.4. Theory Analysis of Psychosocial Resonance Diffusion of Food Safety Risk
3. Results
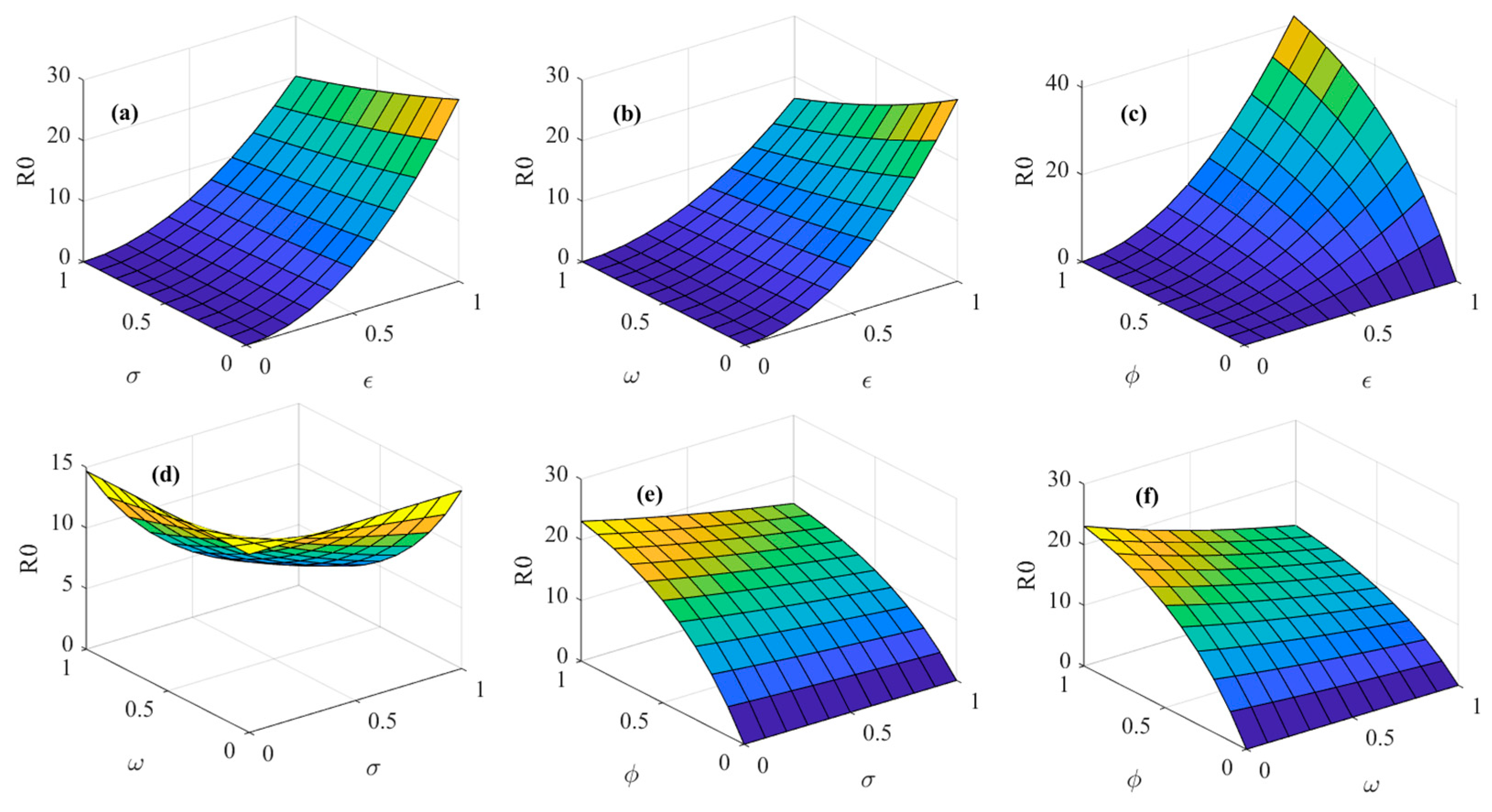
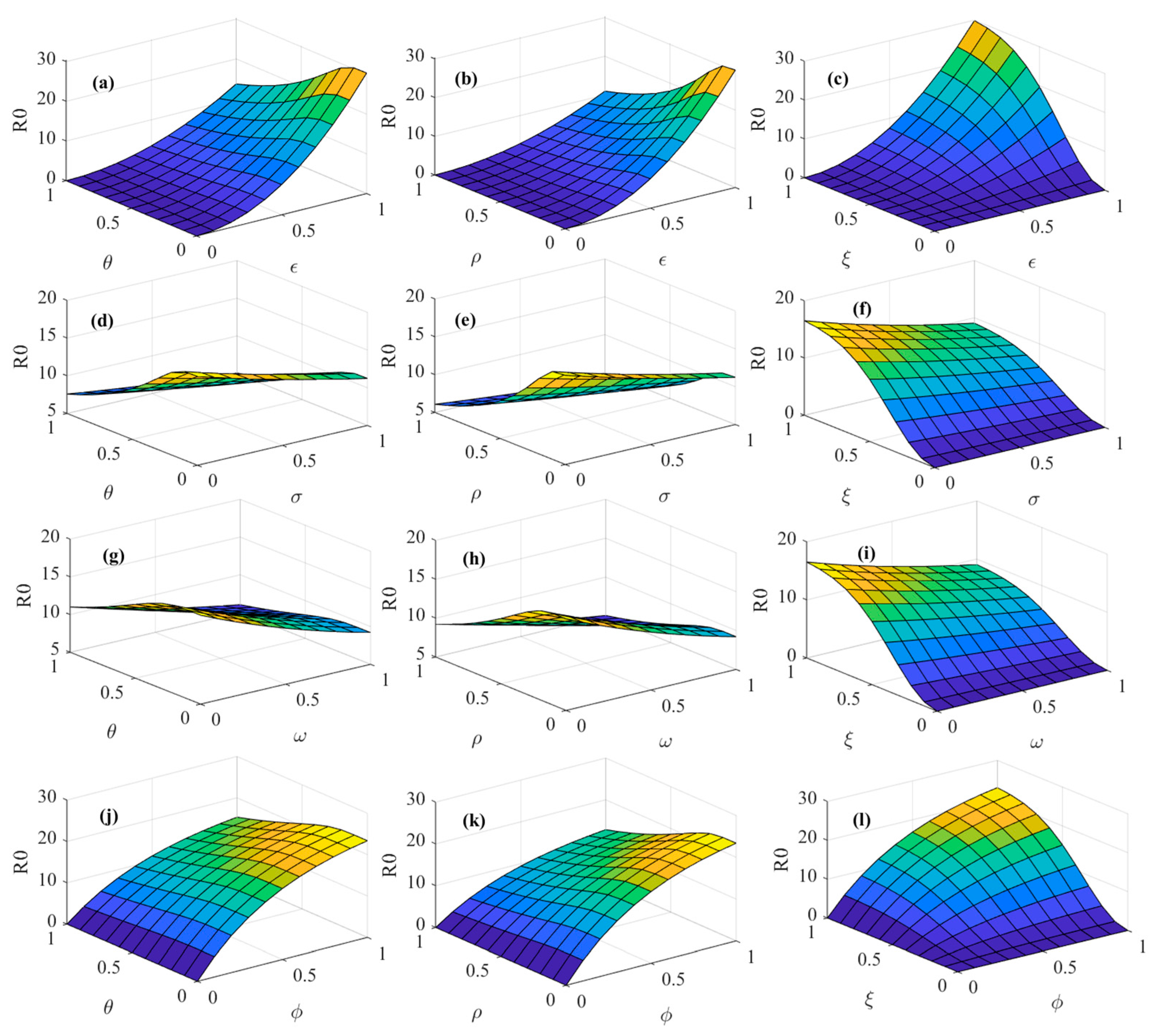
3.1. Analysis of Diffusion Equilibrium Point of Psychosocial Resonance of Food Safety Risk
3.2. Spatial–Temporal Evolutionary Characteristics of Psychosocial Resonance Diffusion of Food Safety Risk
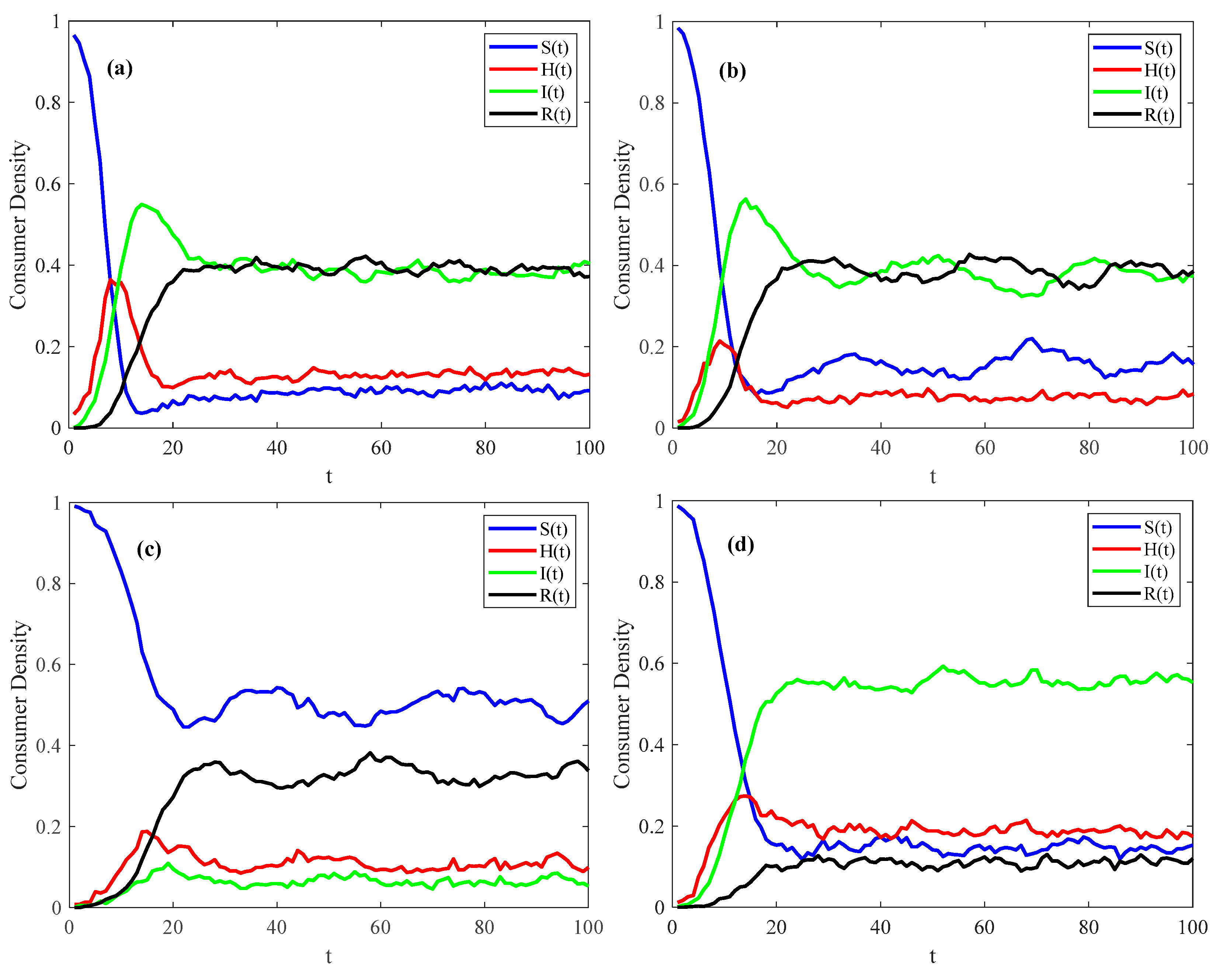
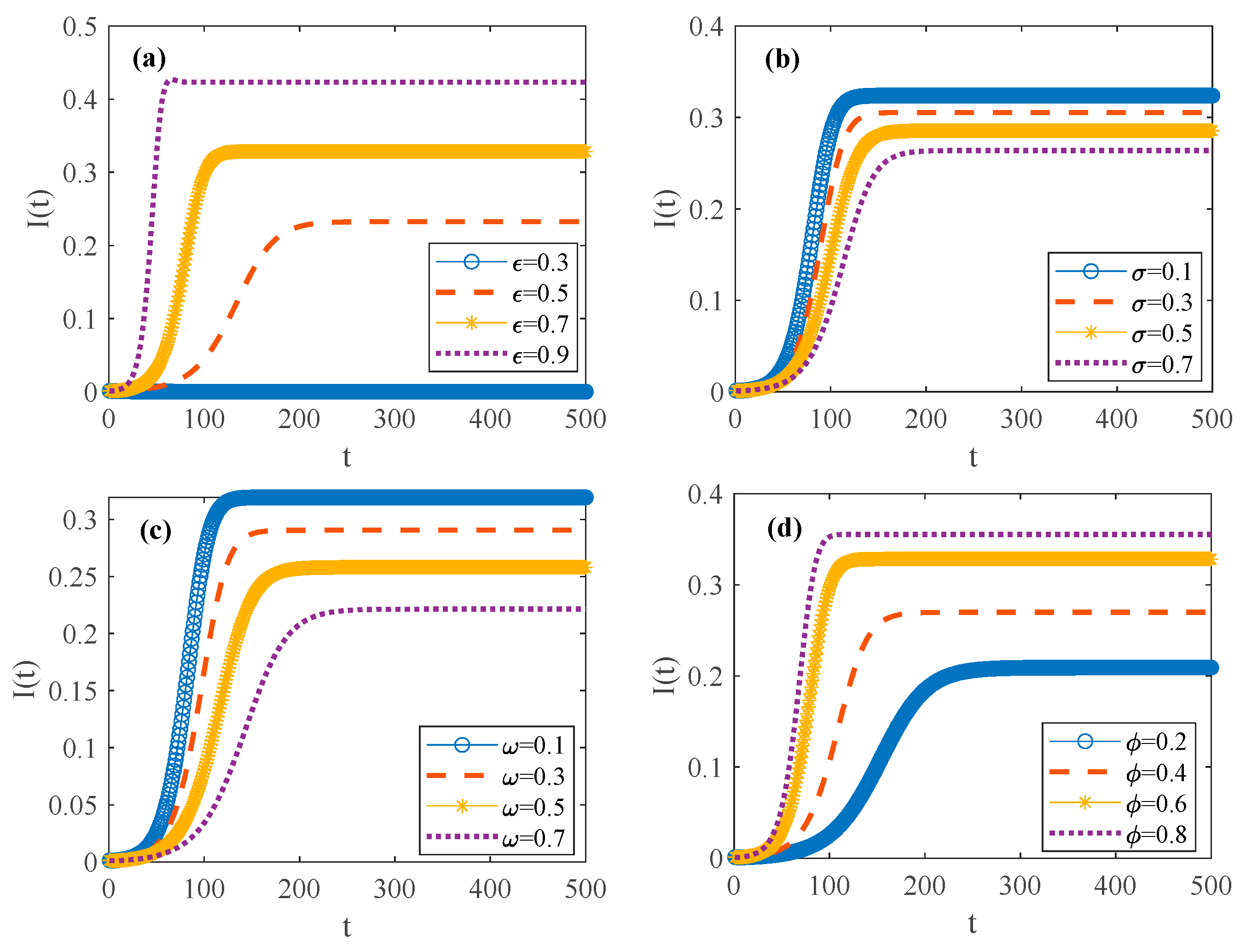
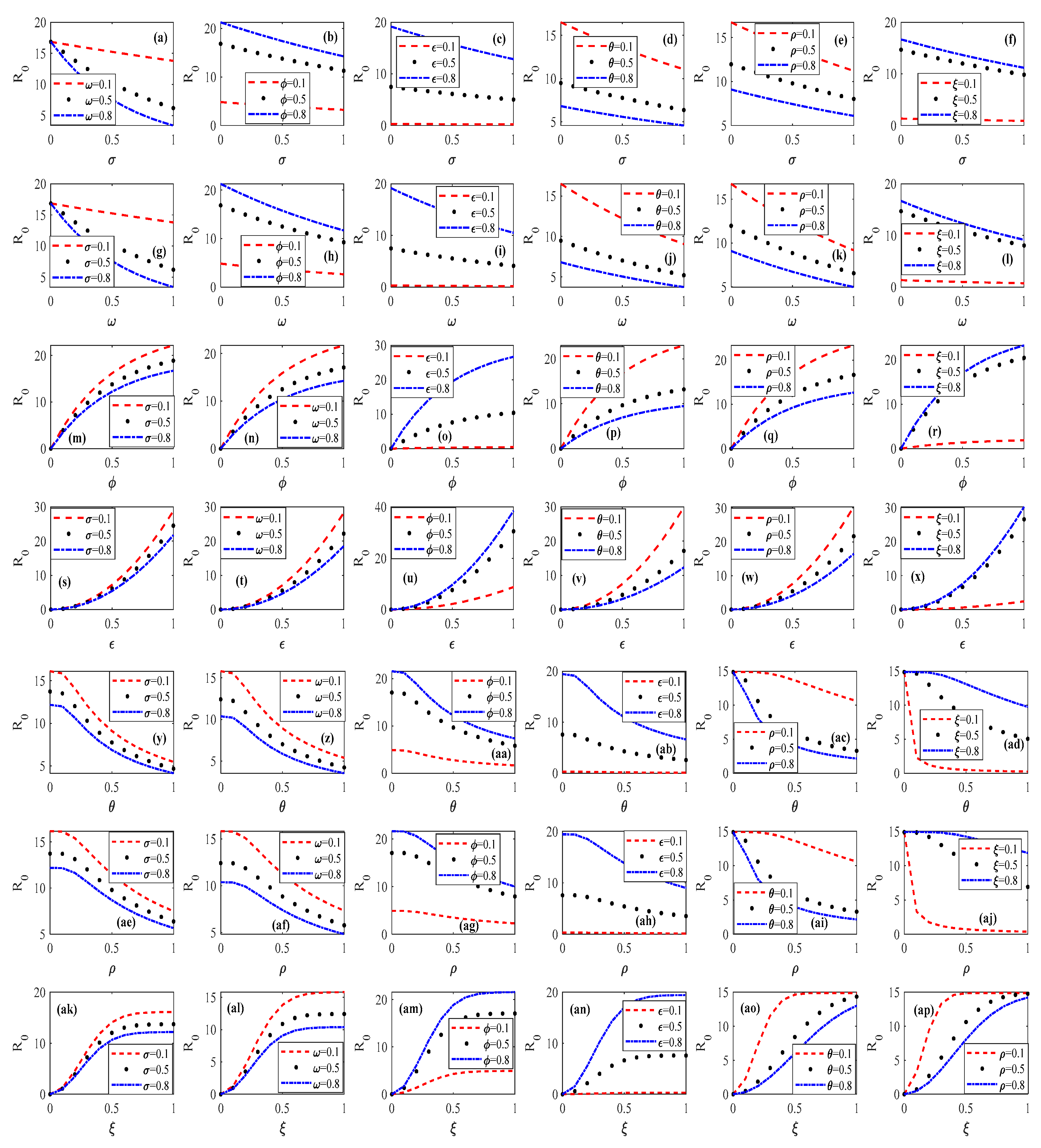
3.2.1. Spatial–Temporal Evolutionary Characteristics of Psychosocial Resonance Diffusion of Food Safety Risk Under Influence of Consumer Heterogeneity
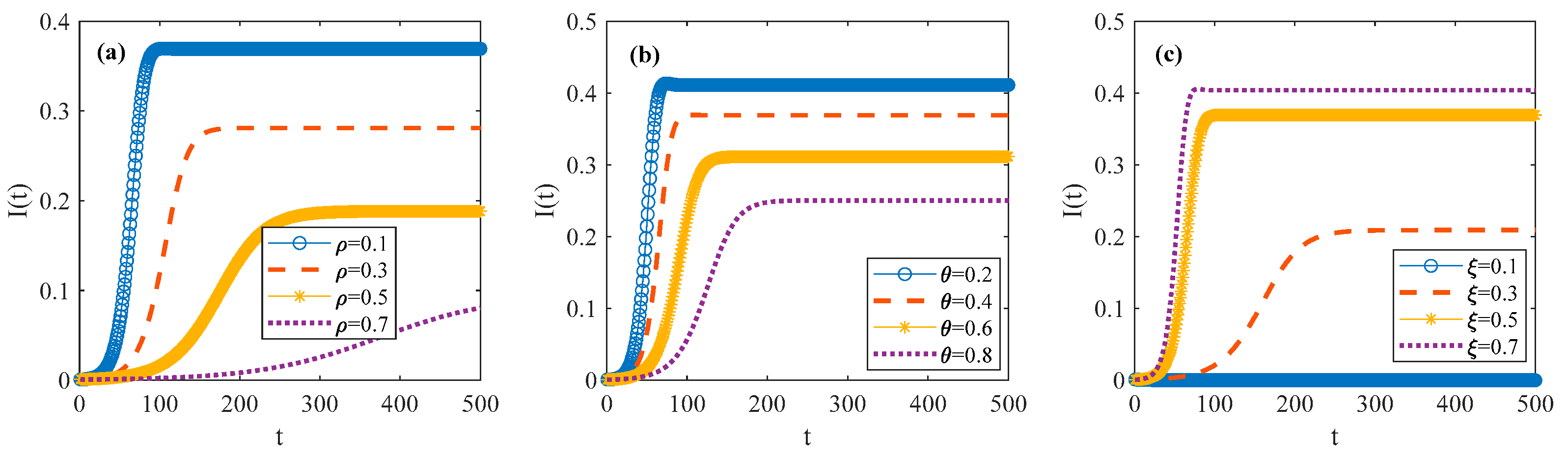
3.2.2. Spatial–Temporal Evolutionary Characteristics of Psychosocial Resonance Diffusion of Food Safety Risk Under Influence of Media Communication Strategies
3.2.3. Spatial–Temporal Evolutionary Characteristics of Psychosocial Resonance Diffusion of Food Safety Risk Under Interaction of Consumer Heterogeneity and Media Communication Strategies
3.3. Robustness Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vergis, J.; Pollumahanti, N.; Sahu, R.; Rawool, D.B.; Barbuddhe, S.B. Ensuring food safety: Microbiological risk assessment strategies. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2025, 62, 101272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-X.; Baker, L.M. Impact of reliable news information on consumers’ perceptions and information seeking intentions from a food safety risk. Br. Food J. 2024, 126, 3805–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Wu, L. The impact of capitalist profit-seeking behavior by online food delivery platforms on food safety risks and government regulation strategies. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2023, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Adewoye, L.; Dupouy, E.; Er, J.C.; Geraghty, F.; Hallman, W.K.; Healy, M.; Jiang, Y.; de Leon-Lim, E.; Narrod, C.; et al. Principles and Practices of Effective Food Safety Risk Communication—Introducing the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation Food Safety Risk Communication Framework. Eur. J. Nutr. Food Saf. 2023, 15, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y. Correction: Basis for fulfilling responsibilities, behavior, and professionalism of government agencies and effectiveness in public–public collaboration for food safety risk management. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2023, 10, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Ma, B.; Liang, J.; Jin, S. Price response to government disclosure of food safety information in developing markets. Food Policy 2024, 123, 102602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wen, X.; Chu, M.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X. Consumers’ Food Safety Risk Communication on Social Media Following the Suan Tang Zi Accident: An Extended Protection Motivation Theory Perspective. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djekic, I.; Nikolic, A.; Mujcinovic, A.; Blazic, M.; Herljevic, D.; Goel, G.; Trafiałek, J.; Czarniecka-Skubina, E.; Guiné, R.; Gonçalves, J.C.; et al. How do consumers perceive food safety risks?—Results from a multi-country survey. Food Control. 2022, 142, 109216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, H.-C.; Chen, L.; Su, Y. Effect of social media use on food safety risk perception through risk characteristics: Exploring a moderated mediation model among people with different levels of science literacy. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 963863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravec, V.; Hynek, N.; Gavurova, B.; Kubak, M. Perceptions of food safety in a post-communist context: The role of disinformation and regulatory trust. Br. Food J. 2025, 127, 1305–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Sun, Z.; Chen, Q. Discussion on food safety risk monitoring problems and solutions. Forum Res. Innov. Manag. 2024, 2, 55–57. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Dou, Y.; Ohuru, R.; de By, R.; Jin, X.; Feng, S.; Meng, F.; Zhou, Y. Local food system resilience in China integrating supply and demand. Glob. Food Secur. 2025, 44, 100830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yin, S.; Chen, Y. Analysis of Cross-Regional Transfer of Food Safety Risks and Its Influencing Factors—An Empirical Study of Five Provinces in East China. Foods 2023, 12, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, K.; Zhang, J.; Qian, H.; Wu, L. Risk evaluation, spatiotemporal evolution, and driving factors of provincial food safety in China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.; Zhong, G.-Y.; Li, J.-C. Dynamic correlation and risk resonance among industries of Chinese stock market: New evidence from time–frequency domain and complex network perspectives. Phys. A: Stat. Mech. its Appl. 2023, 614, 128558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, Y.; Shi, Y.; Xiong, X.; Yi, S. Time-frequency extreme risk spillovers between COVID-19 news-based panic sentiment and stock market volatility in the multi-layer network: Evidence from the RCEP countries. Int. Rev. Financial Anal. 2024, 94, 103339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Jin, Y.; Yang, J.; Cong, G. Identifying emergence process of group panic buying behavior under the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2022, 67, 102970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; Liu, C. Assessing food safety risks based on a geospatial analysis: Toward a cross-regional food safety management. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 6654–6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Ren, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, K.; Song, R. Heterogeneous impacts and spillover effects of green innovation network and environmental regulation on water use efficiency: A spatiotemporal perspective from 269 cities in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 90, 104361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Deng, X.; Gao, Y.; Chen, J. Does regional economic development drive sustainable grain production growth in China? Evidence from spatiotemporal perspective on low-carbon total factor productivity. Socio-Economic Plan. Sci. 2025, 98, 102129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Jiang, X.; Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wu, J. Revealing the sentiment propagation under the conscious emotional contagion mechanism in the social media ecosystem: For public opinion management. Phys. D: Nonlinear Phenom. 2024, 469, 134327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Zhang, G.; Hong, X.; Lu, D. Panic emotional contagion in emergencies: The role of safety and hazard information diffusion. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2025, 116, 105146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, G.; Guo, Z. Stability behavior of a two-susceptibility SHIR epidemic model with time delay in complex networks. Nonlinear Dyn. 2021, 106, 1083–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Wei, Y. Dynamical analysis and optimal control of an SIVS epidemic model with nonmonotone incidence rate on complex network. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2025, 142, 108531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, D. Layered SIRS model of information spread in complex networks. Appl. Math. Comput. 2021, 411, 126524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Shen, S.; Zhu, L. Spatio-temporal pattern formation mechanism of an epidemic-like information propagation model with diffusion behavior. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2025, 16, 103244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Sun, S.; Liu, Q. The capital flow of stock market studies based on epidemic model with double delays. Phys. A: Stat. Mech. its Appl. 2019, 526, 120733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozhidarova, M.; Ball, F.; van Gennip, Y.; O’dEa, R.D.; Stupfler, G. Describing financial crisis propagation through epidemic modelling on multiplex networks. Proc. R. Soc. A: Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2024, 480, 20230787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Ma, B.; Wang, J. SIRS contagion model of food safety risk. J. Food Saf. 2017, 38, e12410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, T.; Brodka, P. Scare Behavior Diffusion Model of Health Food Safety Based on Complex Network. Complexity 2018, 2018, 5902105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, S.; Mathur, K.S.; Das, K.P. Optimal control of deterministic and stochastic Eco-epidemic food adulteration model. Results Control. Optim. 2024, 14, 100336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biernacki, S.; Malarz, K. Does Social Distancing Matter for Infectious Disease Propagation? An SEIR Model and Gompertz Law Based Cellular Automaton. Entropy 2022, 24, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, D.; Nidhi; Chaturvedi, R.; Prakash, S.; Yang, T.; Rathore, R.S.; Wang, L.; Tahir, S.; Bakhsh, S.T. Revolutionizing load harmony in edge computing networks with probabilistic cellular automata and Markov decision processes. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Fang, T.; Rong, X.; Xu, X. Nonlinear behavior of tail risk resonance and early warning: Insight from global energy stock markets. Int. Rev. Financial Anal. 2024, 93, 103162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Dai, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, J.; Hu, W. Food safety risk behavior and social Co-governance in the food supply chain. Food Control. 2023, 152, 109832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabási, A.-L.; Albert, R. Emergence of Scaling in Random Networks. Science 1999, 286, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onnela, J.-P.; Saramäki, J.; Hyvönen, J.; Szabó, G.; Lazer, D.; Kaski, K.; Kertész, J.; Barabási, A.-L. Structure and tie strengths in mobile communication networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7332–7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauset, A.; Shalizi, C.R.; Newman, M.E.J. Power-Law Distributions in Empirical Data. SIAM Rev. 2009, 51, 661–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornholdt, S.; Ebel, H. World Wide Web scaling exponent from Simon’s 1955 model. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 64, 035104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, W.-C.; Zhu, W.; Huang, C.-L.; Hsu, T.-Y.; Liu, Z.; Tan, S.-Y. A New BAT and PageRank Algorithm for Propagation Probability in Social Networks. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porciúncula, G.G.; Sena-Junior, M.I.; Pereira, L.F.C.; Vilela, A.L. Consensus effects of social media synthetic influence groups on scale-free networks. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2025, 197, 116479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y. Risk contagion and decision-making evolution of carbon market enterprises: Comparisons with China, the United States, and the European Union. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 99, 107036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.H.; El-Azab, T.; AlNemer, G.; Sohaly, M.A.; El-Metwally, H. Analysis Time-Delayed SEIR Model with Survival Rate for COVID-19 Stability and Disease Control. Mathematics 2024, 12, 3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F.; Schimit, P.; Bezerra, F. A deep learning based surrogate model for the parameter identification problem in probabilistic cellular automaton epidemic models. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 205, 106078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugnaine, M.; Gabrick, E.C.; Protachevicz, P.R.; Iarosz, K.C.; de Souza, S.L.; Almeida, A.C.; Batista, A.M.; Caldas, I.L.; Jr, J.D.S.; Viana, R.L. Control attenuation and temporary immunity in a cellular automata SEIR epidemic model. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2022, 155, 111784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Arif, R.; Fahmy, M.A.; Sohail, A. Self organizing maps for the parametric analysis of COVID-19 SEIRS delayed model. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 150, 111202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, B.A.; Stern, R.; Paré, P.E. Analysis and Applications of Population Flows in a Networked SEIRS Epidemic Process. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2024, 11, 6664–6677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, S.; Chen, T. Investor behavior, information disclosure strategy and counterparty credit risk contagion. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2019, 119, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, M.; Drewitt, C.M. An empirical study on Green values of consumers, their level of awareness about environmental issues, green products and practices carried out in Tiruchirappalli district. Int. J. Mark. Technol. 2020, 10, 9–22. [Google Scholar]
- Van Fossen, J.A.; Ropp, J.W.; Darcy, K.; Hamm, J.A. Comfort with and willingness to participate in COVID-19 contact tracing: The role of risk perceptions, trust, and political ideology. Soc. Sci. Med. 2022, 306, 115174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabija, D.-C.; Pocol, C.-B.; Mititean, P.; Semeniuc, C.A.; Omara, T. Consumers’ Perception of Biopolymer Films for Active Packaging: From Aesthetic Appeal to Nutritional Value and Experiential Consumption. J. Food Qual. 2024, 2024, 1255122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, U.; Kayani, U.N.; Khan, S.; Polat, A.; Hussain, M.; Aysan, A.F. Investor sentiment and stock price crash risk: The mediating role of analyst herding. Comput. Hum. Behav. Rep. 2024, 13, 100371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, A.; Dogot, T.; Yin, C. How to enhance agricultural plastic waste management in China? Insights from public participation. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 23, 2127–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, E.R.T.; Pimentel, T.C.; Silva, R.; Praxedes, C.I.S.; Oliveira, J.M.S.; Prudêncio, E.S.; Felix, P.H.C.; Neta, M.T.S.; Silva, P.H.F.; Mársico, E.T.; et al. Inulin or xylooligosaccharide addition to dulce de leche affects consumers’ sensory experience and emotional response. Food Res. Int. 2024, 200, 115492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.D.; Tran, G.T.; Simonne, A. Explaining Consumers’ Intention for Traceable Pork regarding Animal Disease: The Role of Food Safety Concern, Risk Perception, Trust, and Habit. Int. J. Food Sci. 2020, 2020, 8831356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Gao, Z.; Snell, H.A.; Ma, H. Food safety concerns and consumer preferences for food safety attributes: Evidence from China. Food Control. 2020, 112, 107157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jiang, X. China’s Stock Market under COVID-19: From the Perspective of Behavioral Finance. Int. J. Financial Stud. 2024, 12, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazoe, T.; Sato, S. The Authenticity of Digital News Coverage in the Mainstream Media in Japan. SN Comput. Sci. 2022, 3, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucundorfeanu, M.; Balaban, D.C.; Mauer, M. Exploring the effectiveness of digital manipulation disclosures for Instagram posts on source credibility and authenticity of social media influencers. Int. J. Advert. 2025, 44, 131–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.; Samarasinghe, A.; Skully, M. Watchdogs or Petdogs: The role of media freedom on banking system stability. Pac.-Basin Financ. J. 2024, 87, 102499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenova, M.; Sokolov, V.; Benov, A. Bank runs and media freedom: What you don’t know won’t hurt you? J. Financial Stab. 2024, 74, 101323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Xiong, X.; Li, X. The role of media coverage in measuring the systemic risk of Chinese financial institutions. Appl. Econ. 2021, 53, 6138–6152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q. Impact of sentiment tendency of media coverage on corporate green total factor productivity: The moderating role of environmental uncertainty. Finance Res. Lett. 2024, 65, 105637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabb, N.; Cowen, L.; de Ruiter, J.P.; Scheutz, M.; Cremonini, M. Cognitive cascades: How to model (and potentially counter) the spread of fake news. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0261811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.; Bhamra, R.; Liu, Z.; Pan, Y. Risk Propagation and Supply Chain Health Control Based on the SIR Epidemic Model. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroga, C.d.L.; Schimit, P.H.T. A multi-city epidemiological model based on cellular automata and complex networks for the COVID-19. Comput. Appl. Math. 2023, 42, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascante-Vega, J.; Torres-Florez, S.; Cordovez, J.; Santos-Vega, M. How disease risk awareness modulates transmission: Coupling infectious disease models with behavioural dynamics. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2022, 9, 210803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | Descriptions | Baseline Values | Value Ranges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infection probability | 0.2 | [0, 1] | |
| Conversion probability | 0.3 | [0, 1] | |
| Immune probability | 0.1 | [0, 1] | |
| Immune failure probability | 0.1 | [0, 1] | |
| Total quantity of consumers in the network | 1000 | Positive Integer | |
| Number of edges connected when each new node joins | 3 | Positive Integer | |
| Number of connections of the initial node | 3 | Positive Integer | |
| Consumer risk perception level | 0.3 | [0, 1] | |
| Consumer sentiment | 0.4 | [0, 1] | |
| Consumer risk attention | 0.2 | [0, 1] | |
| Market noise | 0.7 | [0, 1] | |
| Media report authenticity | 0.2 | [0, 1] | |
| Media freedom | 0.3 | [0, 1] | |
| Media report tendency | 0.5 | [0, 1] |
| Parameter Variation | Trend Chart | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | Remain unchanged | Figure 3 |
| 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | Increase infection probability | Figure 4a |
| 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.1 | Increase conversion probability | Figure 4b |
| 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.1 | Increase immune probability | Figure 4c |
| 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.5 | Increase immune failure probability | Figure 4d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Sun, H.; Chen, T. The Psychosocial Resonance of Food Safety Risk: A Space-Time Perspective. Foods 2025, 14, 2260. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132260
Wang L, Sun H, Chen T. The Psychosocial Resonance of Food Safety Risk: A Space-Time Perspective. Foods. 2025; 14(13):2260. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132260
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lei, Han Sun, and Tingqiang Chen. 2025. "The Psychosocial Resonance of Food Safety Risk: A Space-Time Perspective" Foods 14, no. 13: 2260. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132260
APA StyleWang, L., Sun, H., & Chen, T. (2025). The Psychosocial Resonance of Food Safety Risk: A Space-Time Perspective. Foods, 14(13), 2260. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132260





