Effect of a 6-Month Functional Food Intervention on the Microbiota of Stunted Children in East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia—A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Parallel Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Study Design
2.3. DNA Isolation and Sequencing of the V3–V4 Region of the 16S rRNA Gene
2.4. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Anthropometric Measures
3.2. Microbiota Composition
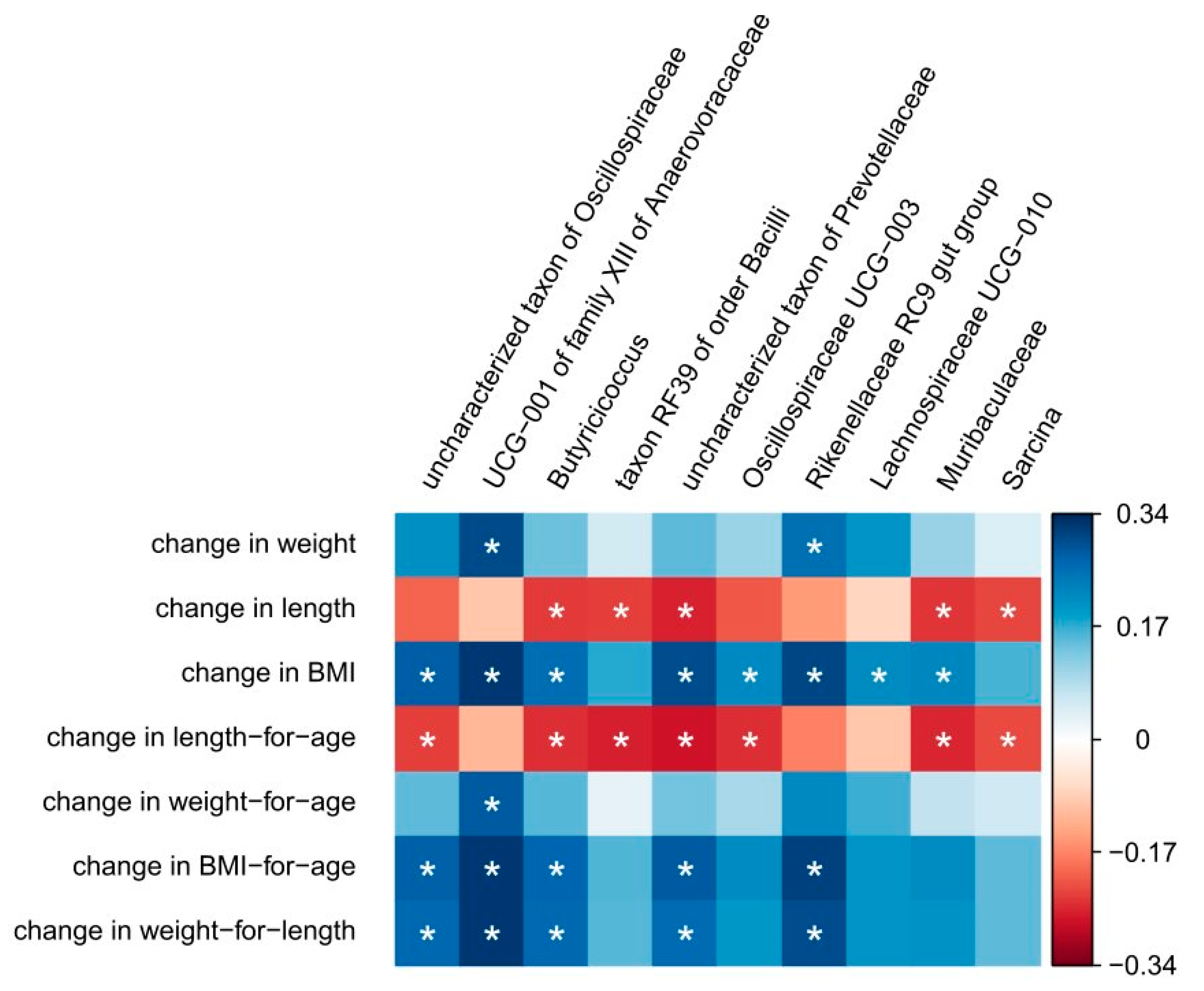
3.3. Correlation Between Anthropometric Measures and Changes in Microbiota Composition
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASVs | Amplified sequence variants |
| CFUs | Colony-forming units |
| ENT | East Nusa Tenggara |
| FDR | False discovery rate |
| SCFAs | Short-chain fatty acids |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| zbmi | BMI for age |
| zlen | Height-for-age Z-score |
| zwei | Weight for age |
| zwfl | Weight for length |
References
- World Health Organization. WHO Child Growth Standards and the Identification of Severe Acute Malnutrition in Infants and Children—A Joint Statement by the World Health Organization and the United Nations Children’s Fund; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241598163 (accessed on 11 January 2024).
- Lefebo, B.K.; Kassa, D.H.; Tarekegn, B.G. Factors associated with stunting: Gut inflammation and child and maternal-related contributors among under-five children in Hawassa City, Sidama Region, Ethiopia. BMC Nutr. 2023, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibuye, M.; Mende, D.R.; Spijker, R.; Simuyandi, M.; Luchen, C.C.; Bosomprah, S.; Chilengi, R.; Schultsz, C.; Harris, V.C. Systematic review of associations between gut microbiome composition and stunting in under-five children. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beal, T.; Tumilowicz, A.; Sutrisna, A.; Izwardy, D.; Neufeld, L.M. A review of child stunting determinants in Indonesia. Matern. Child Nutr. 2018, 14, e12617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siramaneerat, I.; Astutik, E.; Agushybana, F.; Bhumkittipich, P.; Lamprom, W. Examining determinants of stunting in Urban and Rural Indonesian: A multilevel analysis using the population-based Indonesian family life survey (IFLS). BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Central Bureau of Statistics-Ministry of Health Indonesia. Report on Integration of Economic Social Survey (Susenas) Implementation, March 2019 and Nutritional Status of Children Younger than Five Study in Indonesia (SSGBI). Available online: https://www.bps.go.id/en/statistics-table/2/MTYxNCMy/prevalensi-balita-sangat-pendek-dan-pendek-pada-kabupaten-kota-ssgbi.html (accessed on 11 January 2024).
- Hardjo, J.; Selene, N.B. Stunting and Gut Microbiota: A Literature Review. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2024, 27, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadia, B.M.; Ramsteijn, A.S.; Dasi, T.; Fahmida, U.; Kulkarni, B.; Faye, B.; Htet, M.K.; Sow, D.; Kalashikam, R.R.; Sharma, R.; et al. Assessment of the role of gut health in childhood stunting in a multisite, longitudinal study in India, Indonesia and Senegal: A UKRI GCRF Action Against Stunting Hub protocol. BMJ Paediatr. Open 2024, 8 (Suppl. S1), e001637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinanda, T.; Riani, C.; Artarini, A.; Sasongko, L. Correlation between gut microbiota composition, enteric infections and linear growth impairment: A case–control study in childhood stunting in Pidie, Aceh, Indonesia. Gut Pathog. 2023, 15, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surono, I.S.; Popov, I.; Verbruggen, S.; Verhoeven, J.; Kusumo, P.D.; Venema, K.; Carbonero, F. Gut microbiota differences in stunted and normal-lenght children aged 36–45 months in East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0299349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadia, B.M.; Otiti, M.I.; Ramsteijn, A.S.; Sow, D.; Faye, B.; Heffernan, C.; Hall, L.J.; Webster, J.P.; Walker, A.W.; Allen, S. Modulating the early-life gut microbiota using pro-, pre-, and synbiotics to improve gut health, child development, and growth. Nutr. Rev. 2024, 82, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiten, D.J.; Bremer, A.A. Exploring the Nutritional Ecology of Stunting: New Approaches to an Old Problem. Nutrients 2020, 12, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, I.; Hibberd, M.C.; Hartman, S.J.; Rahman, H.H.; Mahfuz, M.; Hasan, S.T.; Ashorn, P.; Barratt, M.J.; Ahmed, T.; Gordon, J.I. A microbiota-directed complementary food intervention in 12–18-month-old Bangladeshi children improves linear growth. EBioMedicine 2024, 104, 105166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibberd, M.C.; Webber, D.M.; Rodionov, D.A.; Henrissat, S.; Chen, R.Y.; Zhou, C.; Lynn, H.M.; Wang, Y.; Chang, H.-W.; Lee, E.M.; et al. Bioactive glycans in a microbiome-directed food for children with malnutrition. Nature 2024, 625, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roediger, R.; Hendrixson, D.T.; Manary, M.J. A roadmap to reduce stunting. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112 (Suppl. S2), 773S–776S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijjar, J.K.; Stafford, D. Undernutrition and growth in the developing world. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2019, 26, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, M.J.; Nuzhat, S.; Ahsan, K.; Frese, S.A.; Arzamasov, A.A.; Alam Sarker, S.; Islam, M.M.; Palit, P.; Islam, R.; Hibberd, M.C.; et al. Bifidobacterium infantis treatment promotes weight gain in Bangladeshi infants with severe acute malnutrition. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabk1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umanets, A.; Surono, I.S.; Venema, K. I am better than I look: Genome based safety assessment of the probiotic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum IS-10506. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surono, I.S.; Pato, U.; Koesnandar; Hosono, A. In vivo antimutagenicity of dadih probiotic bacteria towards Trp-P1. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 22, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulyaningsih, T.; Mohanty, I.; Widyaningsih, V.; Gebremedhin, T.A.; Miranti, R.; Wiyono, V.H.; Metwally, A.M. Beyond personal factors: Multilevel determinants of childhood stunting in Indonesia. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wibowo, S.A.; Surono, I.S. Phenolic content and antioxidant activity of formulated biscuits with banana, tempeh and moringa flours. Braz. J. Food Technol. 2024, 27, e2023068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surono, I.; Verhoeven, J.; Verbruggen, S.; Venema, K. Microencapsulation increases survival of the probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum IS-10506, but not Enterococcus faecium IS-27526 in a dynamic, computer-controlled in vitro model of the upper gastrointestinal tract. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 1604–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.A.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassambara, A. ggpubr: “ggplot2” Based Publication Ready Plots. Available online: https://rpkgs.datanovia.com/ggpubr/ (accessed on 11 January 2024).
- Wei, T.; Simko, V. R package “corrplot”: Visualization of a Correlation Matrix. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/ggcorrplot/index.html (accessed on 11 January 2024).
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Christensen, R.H.B. lmerTest Package: Tests in Linear Mixed Effects Models. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 82, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolker, B.; Robinson, D. broom.mixed: Tidying Methods for Mixed Models. Available online: https://github.com/bbolker/broom.mixed (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aphalo, P. ggpmisc: Miscellaneous Extensions to “ggplot2”. Available online: https://github.com/aphalo/ggpmisc (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Surono, I.S.; Widiyanti, D.; Kusumo, P.D.; Venema, K.; Carbonero, F. Gut microbiota profile of Indonesian stunted children and children with normal nutritional status. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Ji, B.; Babaei, P.; Das, P.; Lappa, D.; Ramakrishnan, G.; Fox, T.E.; Haque, R.; Petri, W.A.; Bäckhed, F.; et al. Gut microbiota dysbiosis is associated with malnutrition and reduced plasma amino acid levels: Lessons from genome-scale metabolic modeling. Metab. Eng. 2018, 49, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, R.C.; Edens, T.J.; Carr, L.; Mutasa, K.; Gough, E.K.; Evans, C.; Geum, H.M.; Baharmand, I.; Gill, S.K.; Ntozini, R.; et al. The gut microbiome and early-life growth in a population with high prevalence of stunting. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfora, E.E.; Feitelson, M.A.; Arzumanyan, A. Editorial: Microbiome metabolites in health and disease. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1270001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaak, E.E.; Canfora, E.E.; Theis, S.; Frost, G.; Groen, A.K.; Mithieux, G.; Nauta, A.; Scott, K.; Stahl, B.; Van Harsselaar, J.; et al. Short chain fatty acids in human gut and metabolic health. Benef. Microbes 2020, 11, 411–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwami, C.S.; Godfrey, S.; Gavilan, H.; Lakhanpaul, M.; Parikh, P. Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene: Linkages with Stunting in Rural Ethiopia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batool, M.; Saleem, J.; Zakar, R.; Butt, M.S.; Iqbal, S.; Haider, S.; Fischer, F. Relationship of stunting with water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) practices among children under the age of five: A cross-sectional study in Southern Punjab, Pakistan. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumming, O.; Cairncross, S. Can water, sanitation and hygiene help eliminate stunting? Current evidence and policy implications. Matern. Child Nutr. 2016, 12 (Suppl. S1), 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglatzi, L.; Gavrili, S.; Stamouli, K.; Zachaki, S.; Favre, L.; Pecquet, S.; Benyacoub, J.; Costalos, C. Effect of Infant Formula Containing a Low Dose of the Probiotic Bifidobacterium lactis CNCM I-3446 on Immune and Gut Functions in C-Section Delivered Babies: A Pilot Study. Clin. Med. Insights Pediatr. 2016, 10, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Hacini-Rachinel, F.; Gosoniu, M.L.; Bourdeau, T.; Holvoet, S.; Doucet-Ladeveze, R.; Beaumont, M.; Mercenier, A.; Nutten, S. Immune-modulatory effect of probiotic Bifidobacterium lactis NCC2818 in individuals suffering from seasonal allergic rhinitis to grass pollen: An exploratory, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depommier, C.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Plovier, H.; Van Hul, M.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Falony, G.; Raes, J.; Maiter, D.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Supplementation with Akkermansia muciniphila in overweight and obese human volunteers: A proof-of-concept exploratory study. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokol, H.; Pigneur, B.; Watterlot, L.; Lakhdari, O.; Bermúdez-Humaran, L.G.; Gratadoux, J.-J.; Blugeon, S.; Bridonneau, C.; Furet, J.-P.; Corthier, G.; et al. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is an anti-inflammatory commensal bacterium identified by gut microbiota analysis of Crohn disease patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16731–16736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quévrain, E.; Maubert, M.A.; Michon, C.; Chain, F.; Marquant, R.; Tailhades, J.; Miquel, S.; Carlier, L.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G.; Pigneur, B.; et al. Identification of an anti-inflammatory protein from Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, a commensal bacterium deficient in Crohn’s disease. Gut 2016, 65, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Q.X.; Lim, Y.L.; Yaow, C.Y.L.; Ng, W.K.; Thumboo, J.; Liew, T.M. Effect of Probiotic Supplementation on Gut Microbiota in Patients with Major Depressive Disorders: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, M.E. Probiotics and microbiota composition. BMC Med. 2016, 14, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mörschbächer, A.P.; Pappen, E.; Henriques, J.A.P.; Granada, C.E. Effects of probiotic supplementation on the gut microbiota composition of adults: A systematic review of randomized clinical trials. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2023, 95, e20230037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athiyyah, A.F.; Brahmantya, H.; Dwiastuti, S.; Darma, A.; Puspitasari, D.; Husada, D.; Ranuh, R.; Endaryanto, A.; Surono, I.; Sudarmo, S.M. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum IS-10506 on blood lipopolysaccharide level and immune response in HIV-infected children. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2019, 11, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumo, P.; Bela, B.; Wibowo, H.; Munasir, Z.; Surono, I. Lactobacillus plantarum IS-10506 supplementation increases faecal sIgA and immune response in children younger than two years. Benef. Microbes 2019, 10, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakoeswa, C.; Herwanto, N.; Prameswari, R.; Astari, L.; Sawitri, S.; Hidayati, A.; Indramaya, D.; Kusumowidagdo, E.; Surono, I. Lactobacillus plantarum IS-10506 supplementation reduced SCORAD in children with atopic dermatitis. Benef. Microbes 2017, 8, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakoeswa, C.R.S.; Bonita, L.; Karim, A.; Herwanto, N.; Umborowati, M.A.; Setyaningrum, T.; Hidayati, A.N.; Surono, I.S. Beneficial effect of Lactobacillus plantarum IS-10506 supplementation in adults with atopic dermatitis: A randomized controlled trial. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2022, 33, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surono, I.S.; Martono, P.D.; Kameo, S.; Suradji, E.W.; Koyama, H. Effect of probiotic L. plantarum IS-10506 and zinc supplementation on humoral immune response and zinc status of Indonesian pre-school children. J. Trace Elements Med. Biol. 2014, 28, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendergast, A.J.; Humphrey, J.H. The stunting syndrome in developing countries. Paediatr. Int. Child Health 2014, 34, 250–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanitsuwan, W.; Pahumunto, N.; Surachat, K.; Thananimit, S.; Wonglapsuwan, M.; Laohawiriyakamol, S.; Teanpaisan, R. Comparison of the effects of postbiotics and live-probiotics containing Lacticaseibacillus paracasei SD1 and Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus SD11 in patients with previous colorectal cancer: A randomized controlled trial. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 123, 106576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
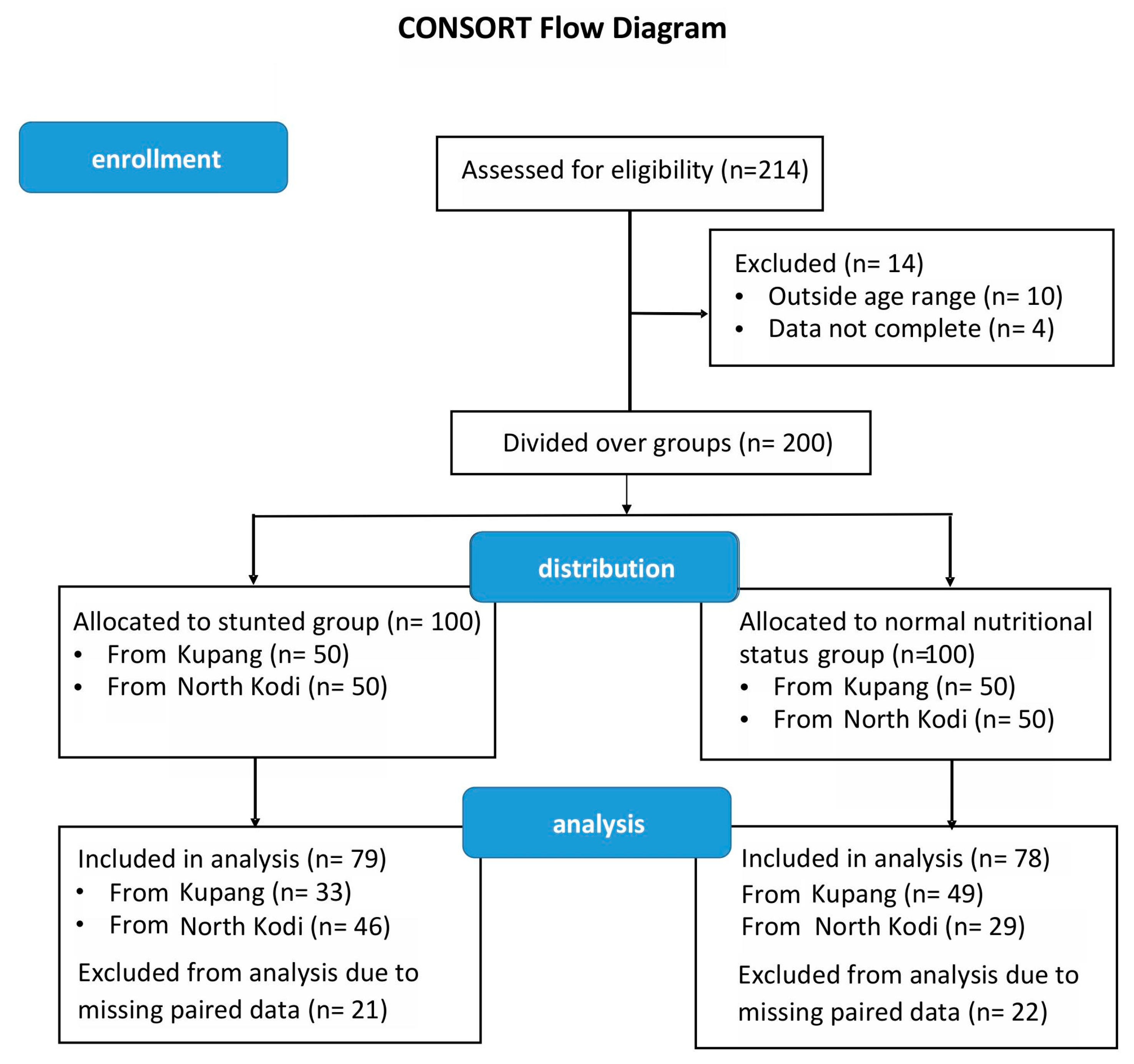
| Baseline | After Intervention | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stunted | Non-Stunted | p-Value | Stunted | Non-Stunted | p-Value | |
| n = 79 | n = 78 | n = 79 | n = 78 | |||
| M/F (%) | 47/53 | 46/54 | 1 † | 47/53 | 46/54 | 1 † |
| age (months) | 46.76 ± 4.82 | 44.43 ± 5.07 | 0.004 | 52.76 ± 10.82 | 50.43 ± 11.07 | 0.004 |
| weight (kg) | 11.79 ± 1.09 | 13.13 ± 1.50 | <0.0001 | 12.93 ± 1.23 | 14.60 ± 1.85 | <0.0001 |
| length (cm) | 91.01 ± 3.20 | 96.11 ± 4.05 | <0.0001 | 94.56 ± 3.53 | 99.17 ± 3.98 | <0.0001 |
| BMI (kg/cm2) | 14.22 ± 1.00 | 14.20 ± 1.17 | 0.91 | 14.46 ± 1.05 | 14.80 ± 1.16 | 0.056 |
| zlen | −2.67 ± 0.51 | −1.12 ± 0.80 | <0.0001 | −2.18 ± 0.60 | −0.80 ± 0.81 | <0.0001 |
| zwei | −2.39 ± 0.63 | −1.36 ± 0.84 | <0.0001 | −1.89 ± 0.66 | −0.79 ± 0.89 | <0.0001 |
| zbmi | −0.90 ± 0.81 | −0.98 ± 0.98 | 0.63 | −0.68 ± 0.83 | −0.44 ± 0.89 | 0.087 |
| zwfl | −1.20 ± 0.80 | −1.05 ± 0.98 | 0.3 | −0.87 ± 0.83 | −0.47 ± 0.90 | 0.005 |
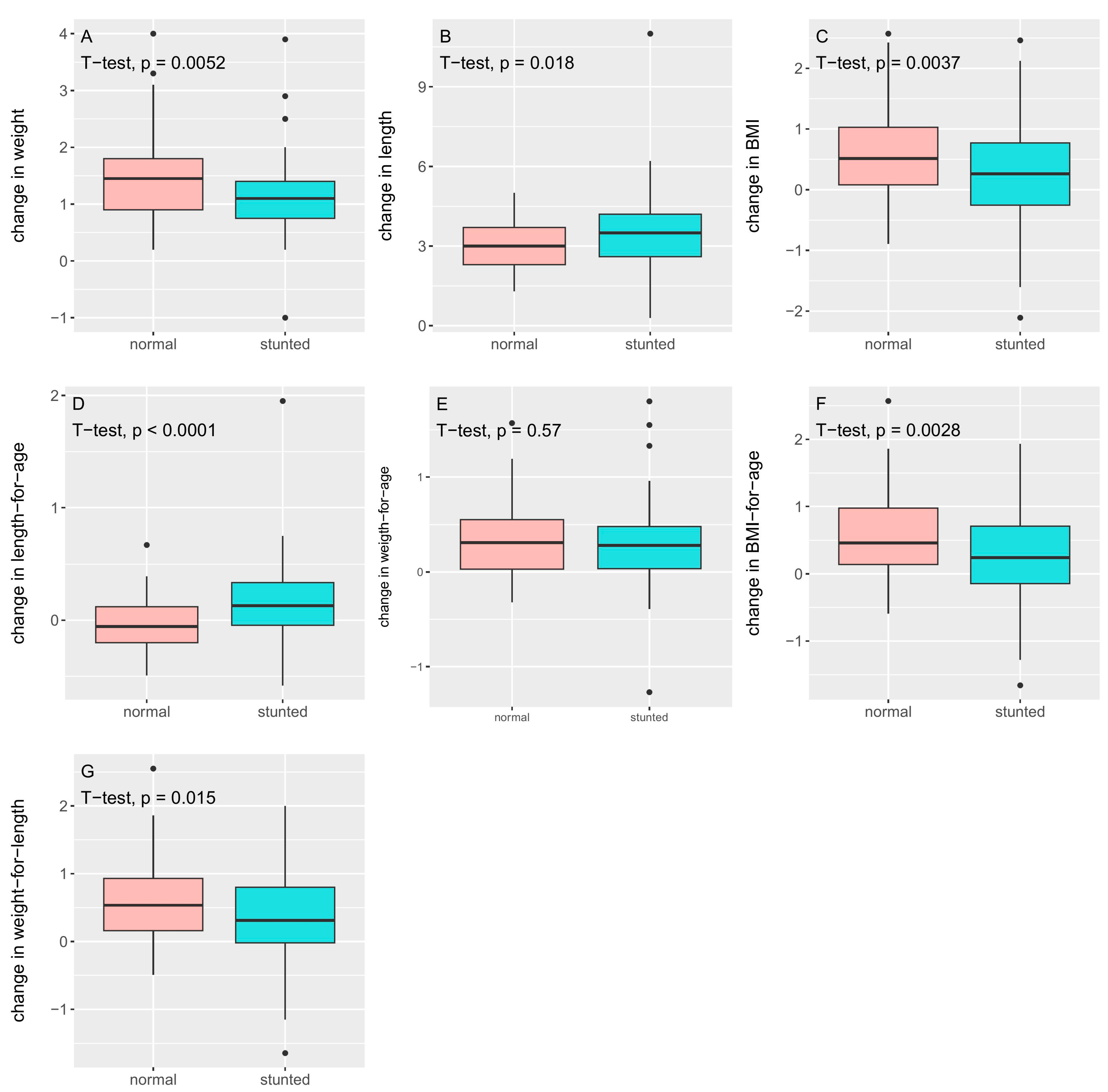
| Stunted | Non-Stunted | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n = 79 | n = 78 | ||
| Δ weight (kg) | 1.15 ± 0.66 | 1.46 ± 0.74 | 0.005 |
| Δ length (cm) | 3.55 ± 1.51 | 3.06 ± 0.93 | 0.018 |
| Δ BMI (kg/cm2) | 0.24 ± 0.80 | 0.60 ± 0.72 | 0.004 |
| Δ zlen | 0.18 ± 0.36 | −0.04 ± 0.23 | <0.0001 |
| Δ zwei | 0.31 ± 0.44 | 0.34 ± 0.38 | 0.57 |
| Δ zbmi | 0.25 ± 0.66 | 0.65 ± 0.60 | 0.003 |
| Δ zwfl | 0.33 ± 0.66 | 0.58 ± 0.58 | 0.015 |
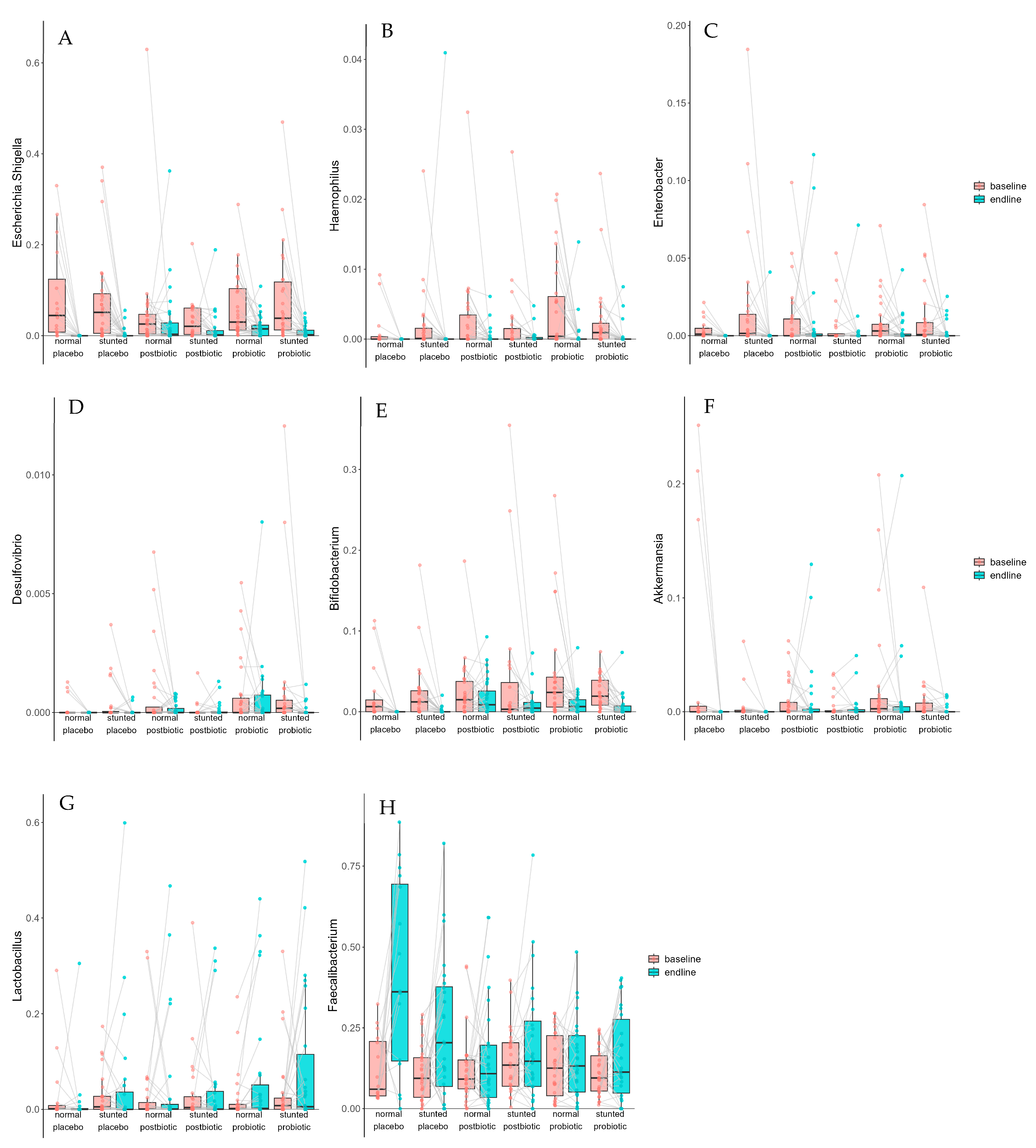
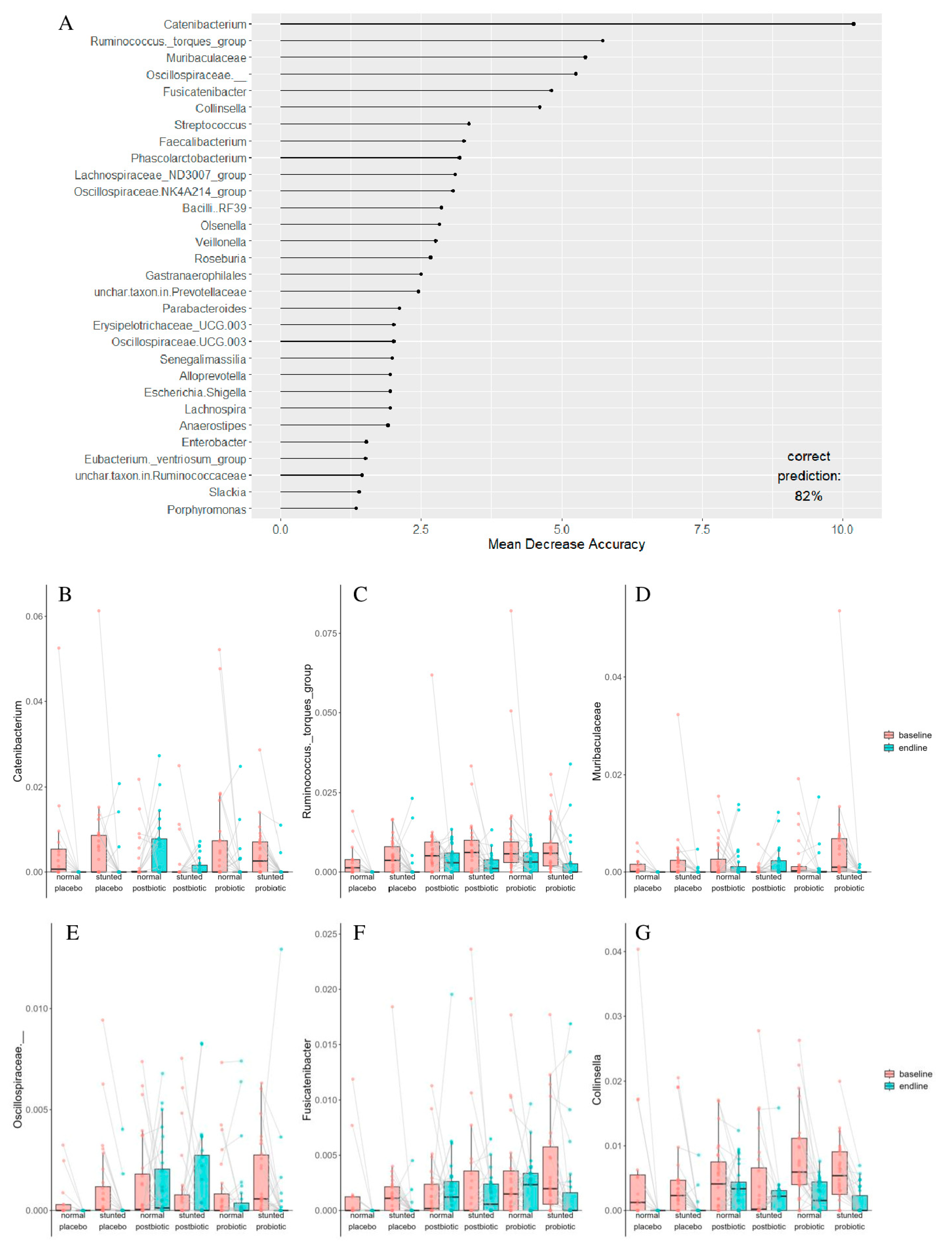
| Taxon | Term | Estimate | Std. Error | Statistic | p. Value | p. Adjusted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| unchar. taxon in Lachnospiraceae | baseline–endline | −0.0037 | 0.0012 | −3.1932 | 0.0017 | 0.0222 |
| Enterobacter | baseline–endline | −0.0066 | 0.0023 | −2.8849 | 0.0042 | 0.0414 |
| Haemophilus | baseline–endline | −0.0020 | 0.0005 | −3.7275 | 0.0002 | 0.0053 |
| Olsenella | baseline–endline | −0.0003 | 0.0001 | −2.9117 | 0.0041 | 0.0414 |
| Faecalibacterium | baseline–endline | 0.0850 | 0.0177 | 4.7982 | 2.53 × 10−6 | 0.0002 |
| Escherichia/Shigella | baseline–endline | −0.0492 | 0.0084 | −5.8807 | 1.09 × 10−8 | 1.51 × 10−6 |
| Butyricicoccus | baseline–endline | −0.0020 | 0.0006 | −3.5221 | 0.0005 | 0.0098 |
| Christensenellaceae R-7 group | baseline–endline | −0.0036 | 0.0011 | −3.1749 | 0.0017 | 0.0222 |
| Bifidobacterium | baseline–endline | −0.0216 | 0.0043 | −5.0126 | 1.50 × 10−6 | 0.0001 |
| Oscillospiraceae UCG-003 | baseline–endline | −0.0007 | 0.0002 | −3.0814 | 0.0025 | 0.0271 |
| Senegalimassilia | baseline–endline | −0.0008 | 0.0002 | −3.8557 | 0.0002 | 0.0052 |
| Fusicatenibacter | baseline–endline | −0.0011 | 0.0004 | −2.9348 | 0.0039 | 0.0410 |
| Muribaculaceae | baseline–endline | −0.0015 | 0.0005 | −2.8291 | 0.0050 | 0.0474 |
| Alistipes | baseline–endline | −0.0061 | 0.0015 | −4.1678 | 5.19 × 10−5 | 0.0021 |
| Catenibacterium | baseline–endline | −0.0028 | 0.0009 | −3.1177 | 0.0022 | 0.0252 |
| Collinsella | baseline–endline | −0.0038 | 0.0005 | −6.9461 | 1.09 × 10−10 | 3.00 × 10−8 |
| Turicibacter | baseline–endline | −0.0013 | 0.0004 | −3.1566 | 0.0019 | 0.0232 |
| Barnesiella | baseline–endline | −0.0012 | 0.0003 | −3.6632 | 0.0003 | 0.0073 |
| Monoglobus | baseline–endline | −0.0022 | 0.0007 | −3.2575 | 0.0014 | 0.0222 |
| Eubacterium hallii group | baseline–endline | −0.0057 | 0.0015 | −3.7308 | 0.0002 | 0.0053 |
| Ruminococcus torques group | baseline–endline | −0.0044 | 0.0009 | −4.6511 | 4.97 × 10−6 | 0.0003 |
| Erysipelotrichaceae UCG-003 | group postbiotic | 0.0025 | 0.0007 | 3.7791 | 0.0002 | 0.0053 |
| unchar. taxon in Lachnospiraceae | group probiotic | 0.0064 | 0.0018 | 3.4943 | 0.0006 | 0.0115 |
| Faecalibacterium | group probiotic | −0.0696 | 0.0220 | −3.1552 | 0.0018 | 0.0222 |
| Butyricicoccus | group probiotic | 0.0023 | 0.0007 | 3.1835 | 0.0016 | 0.0222 |
| Fusicatenibacter | group probiotic | 0.0018 | 0.0006 | 3.2622 | 0.0014 | 0.0222 |
| Eubacterium hallii group | group probiotic | 0.0073 | 0.0019 | 3.8433 | 0.0001 | 0.0051 |
| Erysipelotrichaceae UCG-003 | group probiotic | 0.0028 | 0.0007 | 4.1647 | 5.26 × 10−5 | 0.0021 |
| Ruminococcus torques group | group probiotic | 0.0037 | 0.0012 | 3.1970 | 0.0015 | 0.0222 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Surono, I.S.; Venema, K.; Martosudarmo, S.; Kusumo, P.D. Effect of a 6-Month Functional Food Intervention on the Microbiota of Stunted Children in East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia—A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Parallel Trial. Foods 2025, 14, 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132218
Surono IS, Venema K, Martosudarmo S, Kusumo PD. Effect of a 6-Month Functional Food Intervention on the Microbiota of Stunted Children in East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia—A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Parallel Trial. Foods. 2025; 14(13):2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132218
Chicago/Turabian StyleSurono, Ingrid S., Koen Venema, Subijanto Martosudarmo, and Pratiwi D. Kusumo. 2025. "Effect of a 6-Month Functional Food Intervention on the Microbiota of Stunted Children in East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia—A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Parallel Trial" Foods 14, no. 13: 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132218
APA StyleSurono, I. S., Venema, K., Martosudarmo, S., & Kusumo, P. D. (2025). Effect of a 6-Month Functional Food Intervention on the Microbiota of Stunted Children in East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia—A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Parallel Trial. Foods, 14(13), 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132218






