Terahertz Spectroscopy for Food Quality Assessment: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
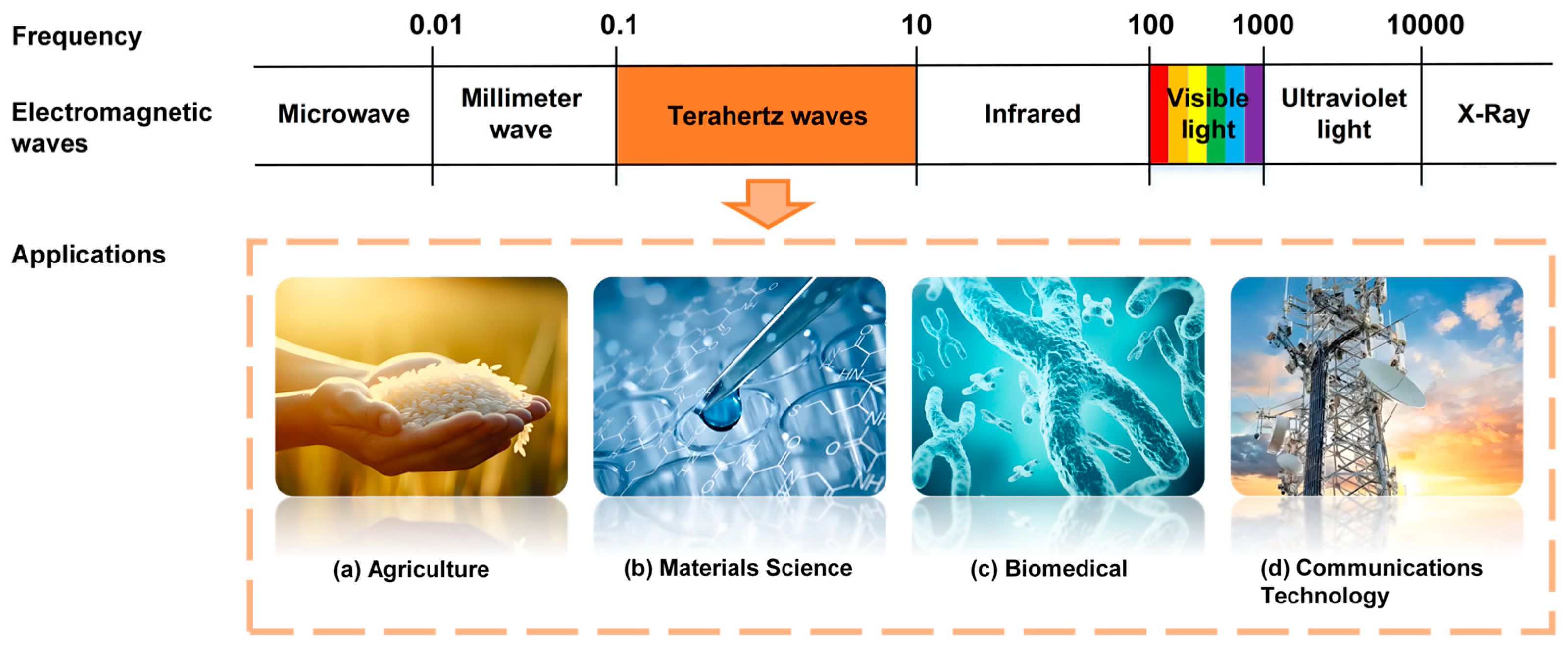
1. Introduction
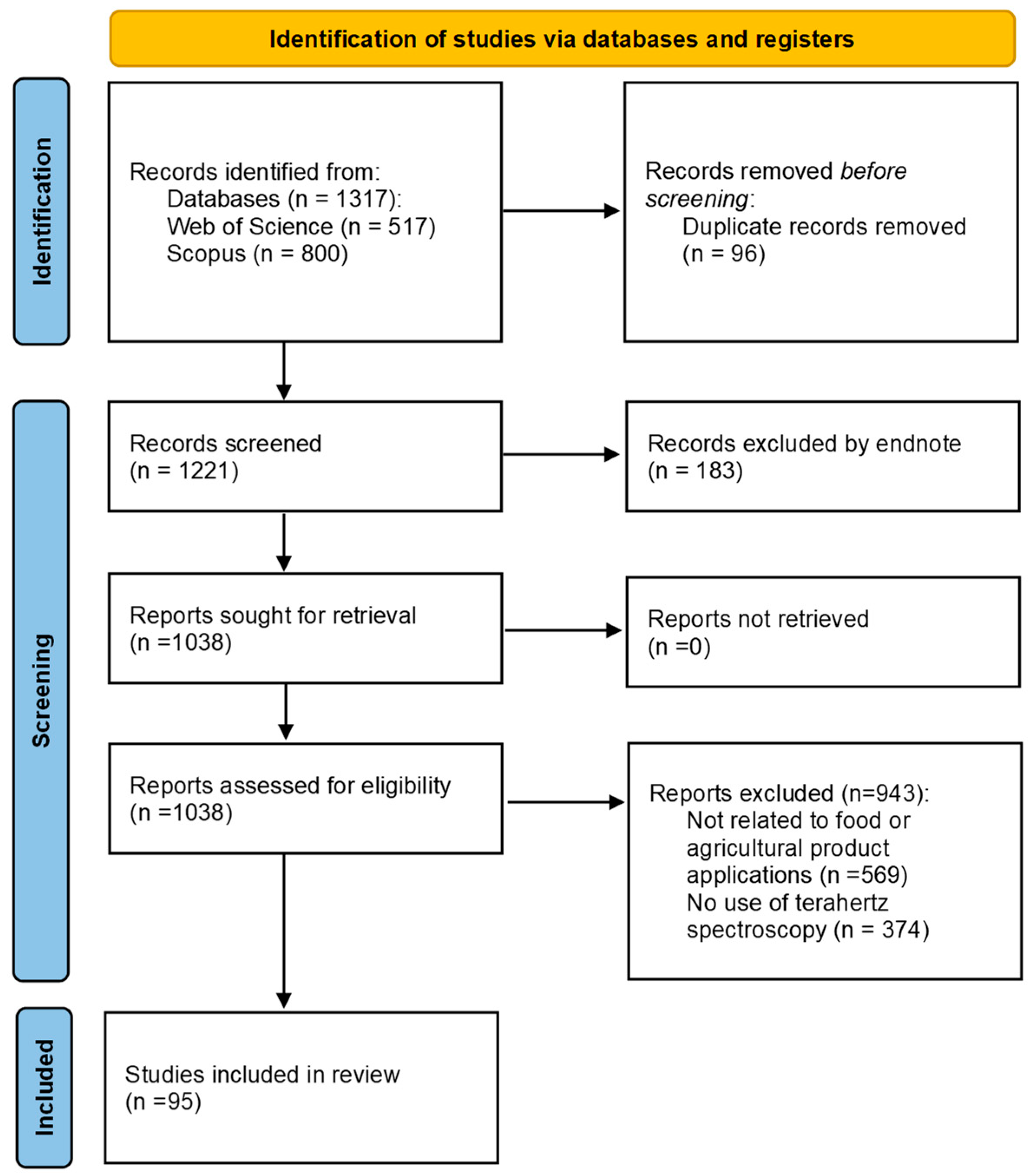
Review Methodology
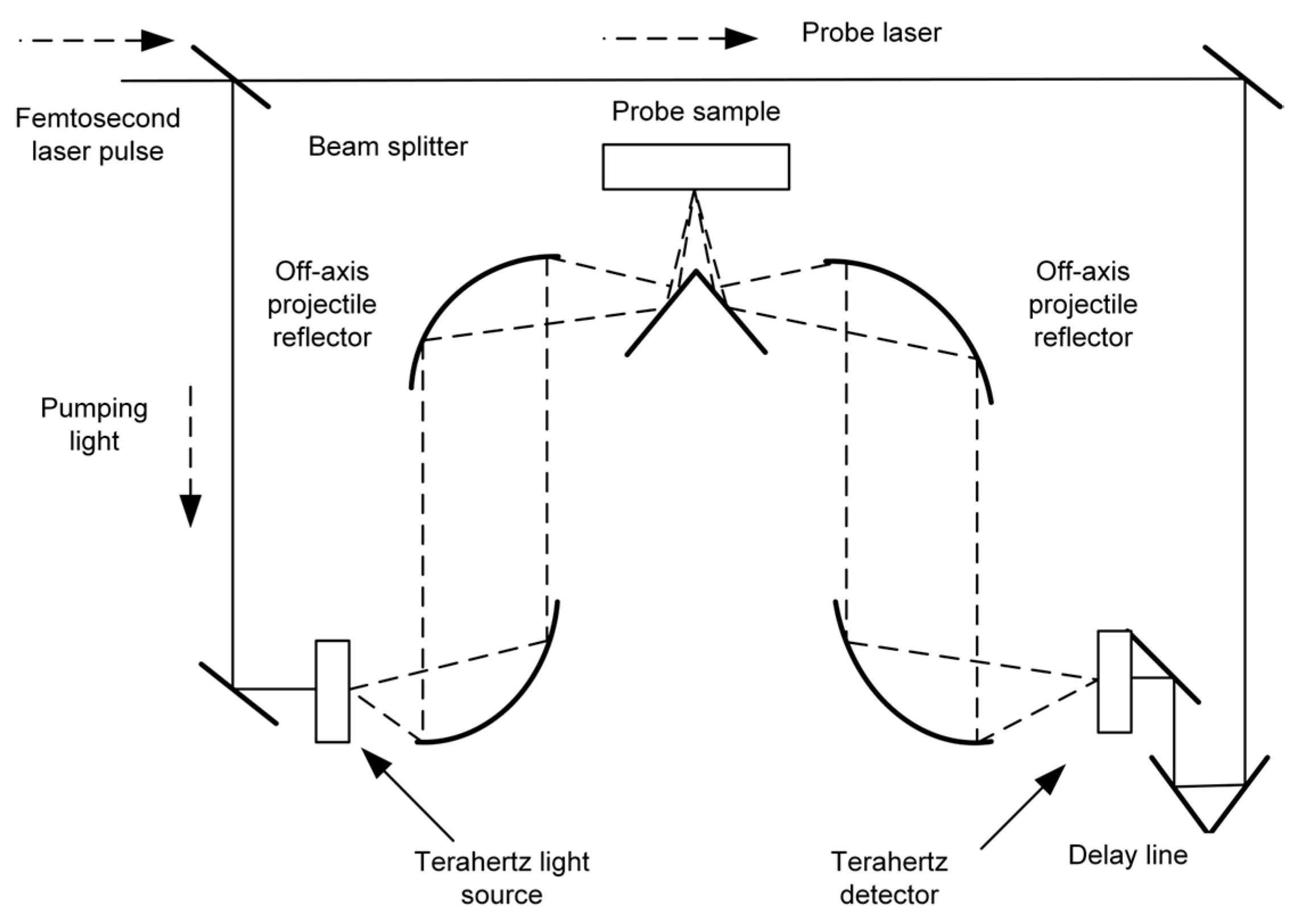
2. Terahertz Spectroscopy
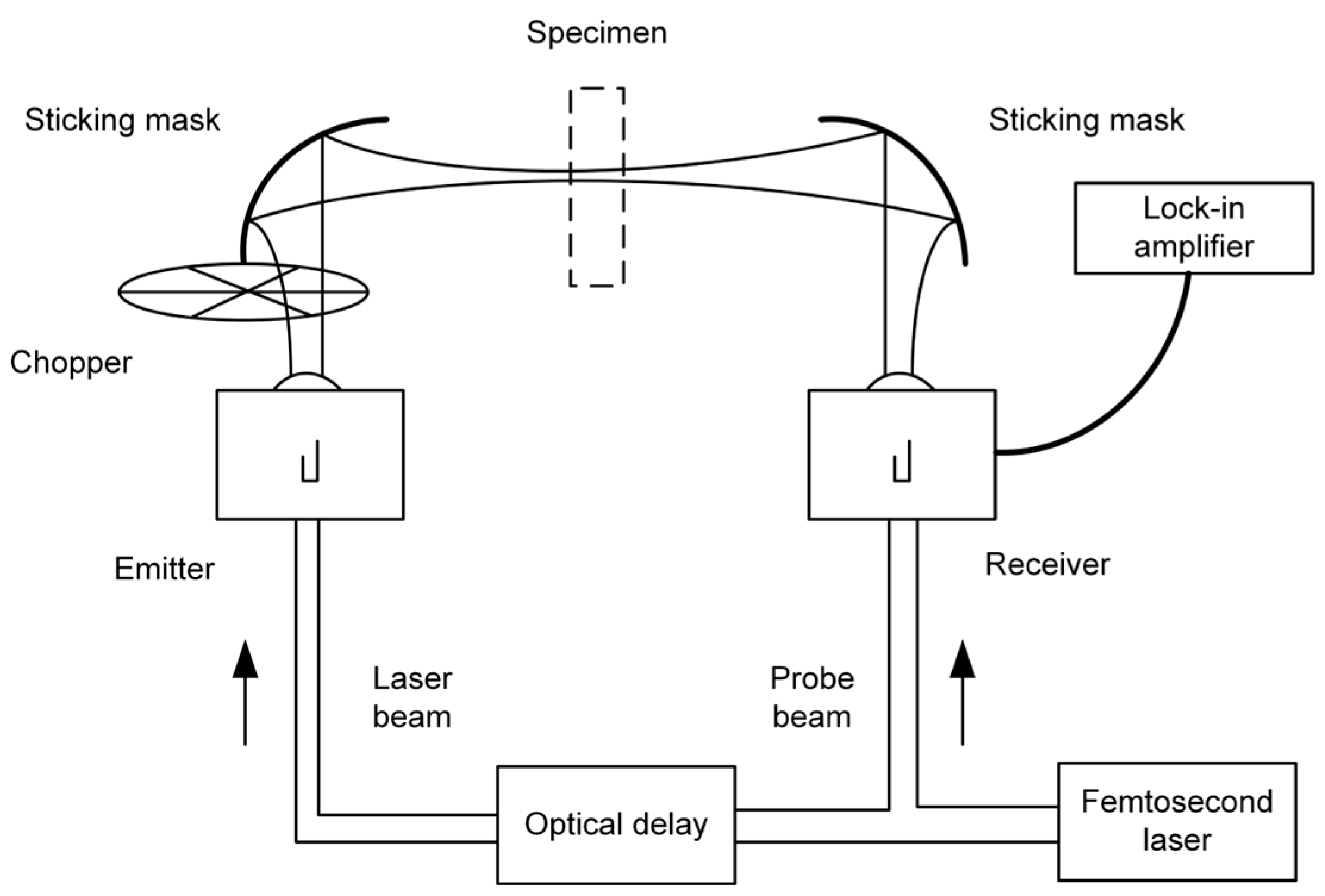
2.1. Principles
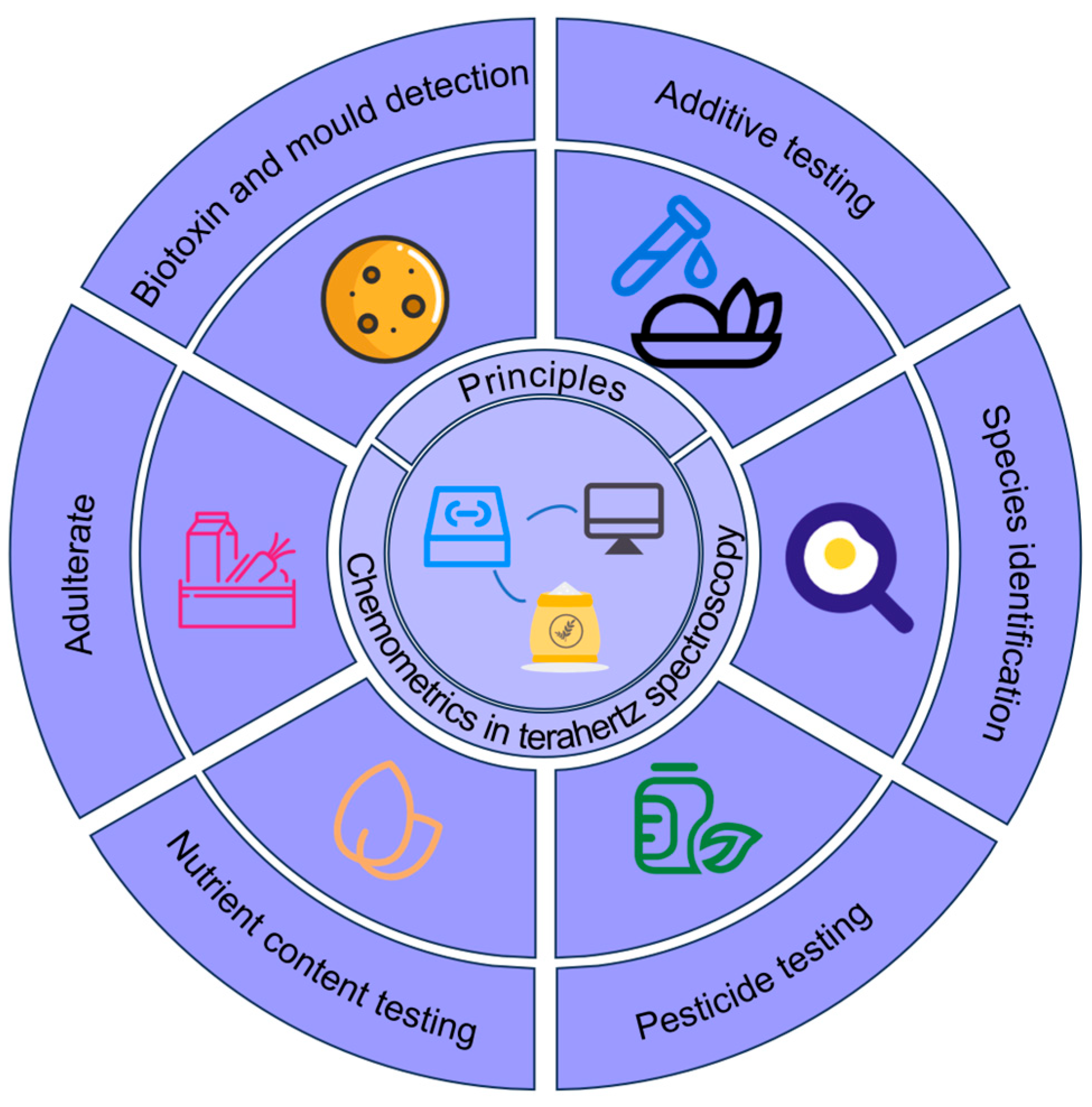
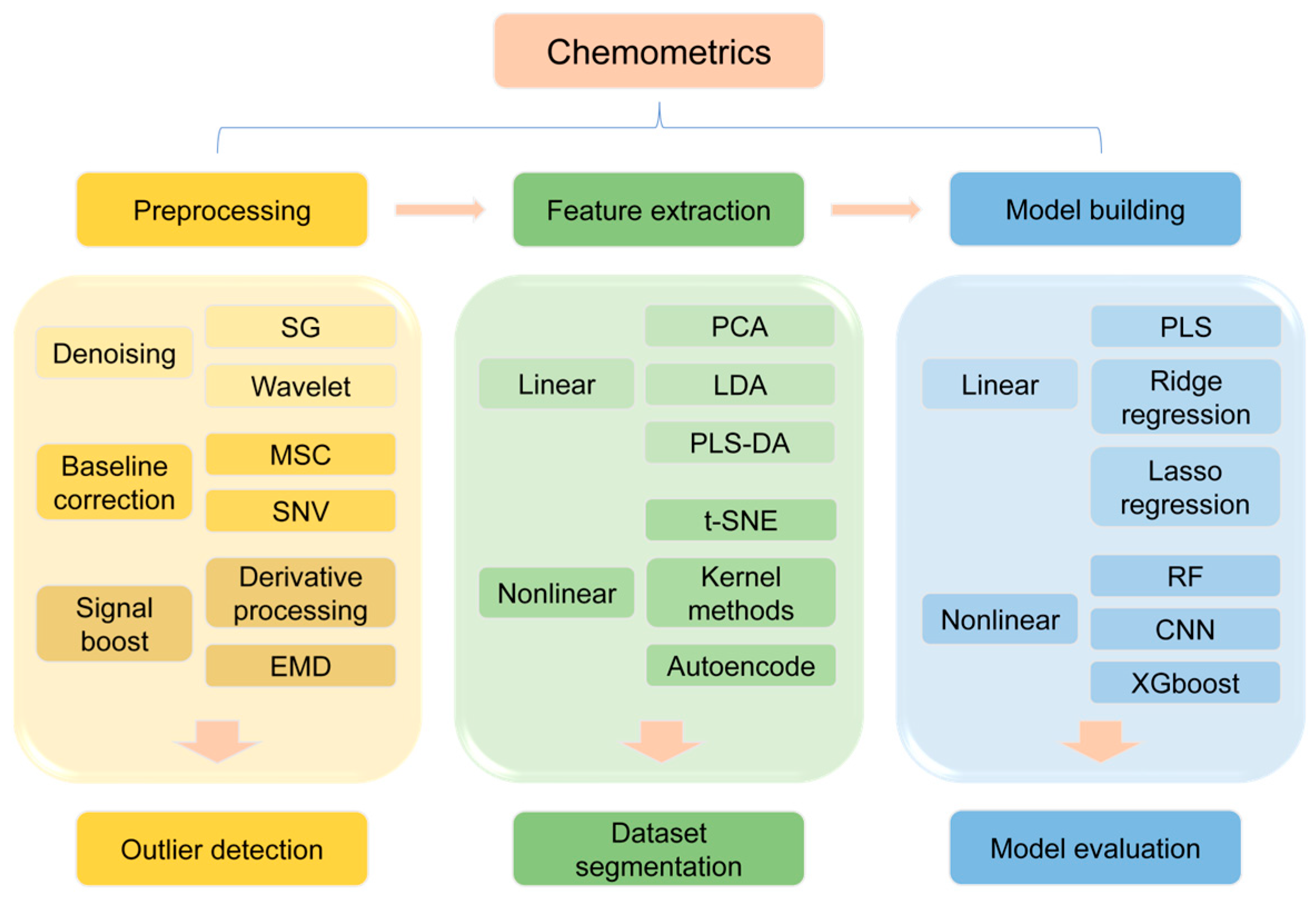
2.2. Chemometrics in Terahertz Spectral Analysis
2.3. Comparative Analysis with Other Detection Techniques
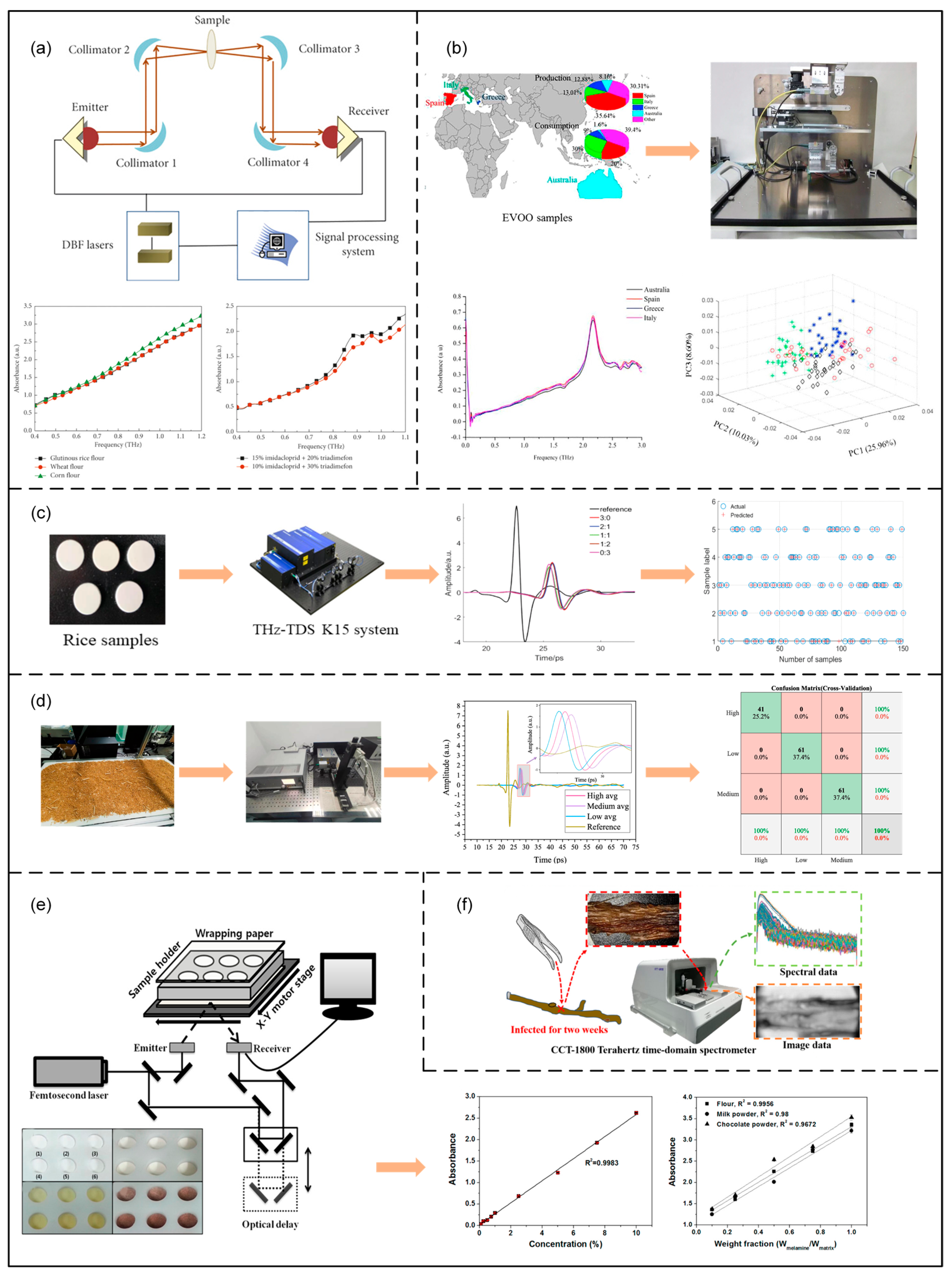
3. Application of Terahertz Spectroscopy in Food Quality Testing
3.1. Pesticide Testing
3.2. Additive Testing
3.3. Biotoxin and Mold Detection
3.4. Adulteration
3.5. Identification of Varieties
3.6. Nutrient Testing
4. Challenges and Future Developments
4.1. Physical and Technical Limitations in Complex Matrices
4.2. Barriers to Industrial Implementation
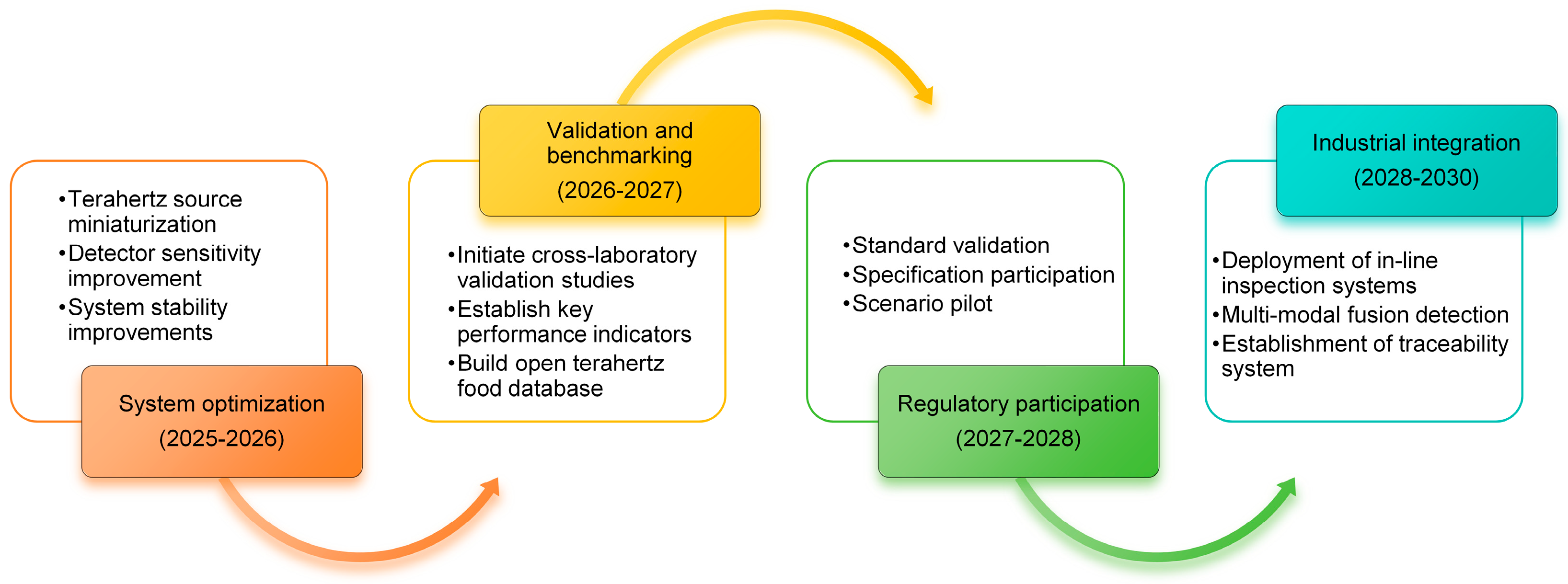
4.3. Future Development Strategy
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khairi, M.T.M.; Ibrahim, S.; Yunus, M.A.M.; Faramarzi, M. Noninvasive techniques for detection of foreign bodies in food: A review. J. Food Process Eng. 2018, 41, e12808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raki, H.; Aalaila, Y.; Taktour, A.; Peluffo-Ordonez, D.H. Combining AI Tools with Non-Destructive Technologies for Crop-Based Food Safety: A Comprehensive Review. Foods 2024, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sindhu, S.; Manickavasagan, A. Nondestructive testing methods for pesticide residue in food commodities: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 1226–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.H.; Zhao, X.K.; Luo, W.F.; Bai, X.; Xu, L.J.; Jiang, H. Microwave detection technique combined with deep learning algorithm facilitates quantitative analysis of heavy metal Pb residues in edible oils. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 6005–6015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambropoulou, D.A.; Albanis, T.A. Methods of sample preparation for determination of pesticide residues in food matrices by chromatography-mass spectrometry-based techniques: A review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 1663–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Deng, J.H.; Jiang, H. Markov Transition Field Combined with Convolutional Neural Network Improved the Predictive Performance of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Models for Determination of Aflatoxin B1 in Maize. Foods 2022, 11, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Q.; Deng, J.H.; Chen, Q.S.; Jiang, H. Near-infrared spectroscopy based on colorimetric sensor array coupled with convolutional neural network detecting zearalenone in wheat. Food Chem.-X 2024, 22, 101322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, N.; Gan, Y.; Kong, L. Emerging non-invasive microwave and millimeter-wave imaging technologies for food inspection. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 65, 3302–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelali, M.; Papadopoulos, K. Inline Inspection of Packaged Food Using Microwave/Terahertz Sensing-An Overview with Focus on Confectionery Products. Processes 2024, 12, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, S.J.; Bampidis, V.; Benford, D.; Bragard, C.; Hernandez-Jerez, A.; Bennekou, S.H.; Halldorsson, T.I.; Koutsoumanis, K.P.; Lambre, C.; Machera, K.; et al. Guidance Document on Scientific criteria for grouping chemicals into assessment groups for human risk assessment of combined exposure to multiple chemicals. Efsa J. 2021, 19, e07033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, L.C.; Di Piazza, G.; Dujardin, B.; Marchese, E.; Pastor, P.M.; European Food Safety Authority, E. The 2023 European Union report on pesticide residues in food. Efsa J. 2025, 23, e9398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetherington, D. New Era of Smarter Food Safety FDA’s Blueprint for the Future; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.X.; Wang, C.; Qin, J.Y.; Xu, W.D.; Chen, M.; Du, J.X.; Xie, L.J.; Ying, Y.B. Feasibility Study on Rapid Analysis of Doxycycline Hydrochloride Aqueous Solution by Terahertz Time-Domain Spectroscopy. Trans. Asabe 2019, 62, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olakanmi, S.J.; Bharathi, V.S.K.; Jayas, D.S.; Paliwal, J. Innovations in nondestructive assessment of baked products: Current trends and future prospects. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, M.; Mujumdar, A.S. Terahertz Spectroscopy: A Powerful Technique for Food Drying Research. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 1733–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Ruan, C.; Chen, K.; Wu, Y.; He, W. Investigating the Molecular Rearrangement of Polar Liquid Mixtures Using Terahertz Frequency Domain Reflection Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. A 2023, 127, 5502–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Bao, H.; Peng, A.; Shao, Y. Real-time and accurate calibration detection of gout stones based on terahertz and Raman spectroscopy. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1218927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, L.; Cai, N. Study of Application of Thz Time Domainspectroscopy in Food Safet. In Proceedings of the Computer and Computing Technologies in Agriculture II; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; Volume 3, pp. 1691–1697. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Asante, E.A.; Duan, H.; Hu, Y. Quantitative Assessment of Cold Injury in Tea Plants by Terahertz Spectroscopy Method. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, H.; Yu, J.; Sun, D.-W.; Wei, Q.; Wang, Z. Feature construction methods for processing and analysing spectral images and their applications in food quality inspection. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 138, 726–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Martínez, M.; González, J.A.M.; García, G.R.; Bugallo, A.D.; Guerrero, M.A.J.; Strupiechonski, E.C. Enhancing Sensitivity and Selectivity in Pesticide Detection: A Review of Cutting-Edge Techniques. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2024, 43, 1468–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, G.; Ge, H.; Wang, F.; Li, L.; Chen, X.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Y. Machine Learning and Application in Terahertz Technology: A Review on Achievements and Future Challenges. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 53761–53776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Deng, J.H.; Ding, Z.D.; Chen, Q.S. Quantitative detection of heavy metal Cd in vegetable oils: A nondestructive method based on Raman spectroscopy combined with chemometrics. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 8054–8065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, M.; Zhang, Z.; Song, W.; Qiu, J. Food safety application of Terahertz spectroscopy based on metamaterials: A review. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 139, 107034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Chen, X.; Xie, D.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Guo, M.; Song, Y.; Guo, J.; Feng, Y.; et al. Identification and detection of frozen-thawed muscle foods based on spectroscopy and machine learning: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 155, 104797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Li, S.; Zhu, S.; Zheng, W.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, S.; Hu, M.; Miao, Y.; Ma, L.; Wu, W.; et al. Terahertz spectroscopy combined with data dimensionality reduction algorithms for quantitative analysis of protein content in soybeans. Spectrochim. Acta Part A-Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 253, 119571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Ying, Y.; Xie, L. The Detection of Agricultural Products and Food Using Terahertz Spectroscopy: A Review. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2013, 48, 439–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.-H.; Otani, C. Terahertz spectroscopy technology as an innovative technique for food: Current state-of-the-Art research advances. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 2523–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Lei, T.; Sun, D.-W. Analysis and detection using novel terahertz spectroscopy technique in dietary carbohydrate-related research: Principles and application advances. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 1793–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Guo, Y.; Liang, X.; Lu, H. Intelligent Rapid Detection Techniques for Low-Content Components in Fruits and Vegetables: A Comprehensive Review. Foods 2024, 13, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhan, C.; Shi, H.; Qiao, P.; He, Y.; Liu, Y. Rapid non-destructive detection of foreign bodies in fish based on terahertz imaging and spectroscopy. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2023, 131, 104448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Fan, M. Quantitative Analyses of Tartaric Acid based on Terahertz Time Domain Spectroscopy. In Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Advanced Optical Manufacturing and Testing Technologies—Optical Test and Measurement Technology and Equipment, Dalian, China, 26–29 April 2010; pp. 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Kawase, M. Application of Terahertz Waves to Food Science. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2012, 18, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Yang, S.; Zhan, C.; Liu, Y. Application of terahertz time-domain spectroscopy and chemometrics-based crested porcupine algorithm in identification of different medicinal parts of Angelica sinensis. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2024, 143, 105584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Xie, L. A Preliminary Study of Aflatoxin B1 Detection in Peanut Oil by Terahertz Time-Domain Spectroscopy. Trans. Asabe 2014, 57, 1793–1799. [Google Scholar]
- Dinovitser, A.; Valchev, D.G.; Abbott, D. Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy of edible oils. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 170275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, Z. The terahertz spectrum detection of transgenic food. Optik 2014, 125, 6867–6869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.H.; Sun, J.; Yao, K.S.; Xu, M.; Dai, C.X. Multi-task convolutional neural network for simultaneous monitoring of lipid and protein oxidative damage in frozen-thawed pork using hyperspectral imaging. Meat Sci. 2023, 201, 109196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pu, H.; Li, Q.; Sun, D.-W. Discrimination of Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae in different years using Terahertz Time-Domain spectroscopy combined with convolutional neural network. Spectrochim. Acta Part A-Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 286, 122035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, D.W.; Erkintalo, M.; Leonhardt, R.; IEEE. Terahertz frequency domain spectroscopy using Hilbert transformation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics Europe/European Quantum Electronics Conference (CLEO/Europe-EQEC), Munich, Germany, 23–27 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, S.; Hill, K.; Vogt, D.W.; Puppe, T.A.; Mayzlin, Y.; Wilk, R. Ultra-high precision comb-locked terahertz frequency-domain spectroscopy of whispering-gallery modes. APL Photonics 2024, 9, 076109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Feng, C.; Zhao, X. Recent developments in terahertz quantum cascade lasers for practical applications. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2023, 12, 20230115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Liu, B.; Lu, P.; Peng, Y. Rapid Determination of Ochratoxin A in Black Tea Using Terahertz Ultrasensitive Biosensor. Photonics 2024, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Sun, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, X.; Jia, Z.; Cui, G.; Zhang, Y. Recent Advances in THz Detection of Water. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Deng, J.H.; Chen, Q.S. Olfactory sensor combined with chemometrics analysis to determine fatty acid in stored wheat. Food Control 2023, 153, 109942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; He, Y.C.; Xu, W.D.; Chen, Q.S. Quantitative Detection of Acid Value During Edible Oil Storage by Raman Spectroscopy: Comparison of the Optimization Effects of BOSS and VCPA Algorithms on the Characteristic Raman Spectra of Edible Oils. Food Anal. Methods 2021, 14, 1826–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Lee, S.D.; Moon, J.H.; Kim, K.B.; Lee, D.K.; IEEE. Terahertz Technology for the Detection of Food Contaminants. In Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves (IRMMW-THz), Wollongong, Australia, 23–28 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, F.; Ying, Y.-B. Applications of Terahertz Spectroscopy and Imaging Techniques in Food Safety Inspection. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2009, 29, 1445–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Fan, F.; Shi, W.; Zhang, T.; Chang, S. Terahertz circular polarization sensing for protein denaturation based on a twisted dual-layer metasurface. Biomed. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, J.B.; Guglietta, G.W. Terahertz Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 4342–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, D.; Li, M.; Zheng, J.; Jiang, L.; Li, R.; Wang, S. Developing a two-stage strategy in the dehydration treatment of fresh apple slices: Combined freeze and radio frequency-vacuum drying. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2024, 92, 103596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.S.; Sun, J.; Tang, N.Q.; Xu, M.; Cao, Y.; Fu, L.H.; Zhou, X.; Wu, X.H. Nondestructive detection for Panax notoginseng powder grades based on hyperspectral imaging technology combined with CARS-PCA and MPA-LSSVM. J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 44, e13718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bec, K.B.; Grabska, J.; Huck, C.W. Chemometric methods in analytical spectroscopy technology. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 2147–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirere, A.; Sun, J.; Atindana, V.A.; Hussain, A.; Zhou, X.; Yao, K. A comparative analysis of hybrid SVM and LS-SVM classification algorithms to identify dried wolfberry fruits quality based on hyperspectral imaging technology. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e16320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.H.; Ni, L.H.; Bai, X.; Jiang, H.; Xu, L.J. Simultaneous analysis of mildew degree and aflatoxin B1 of wheat by a multi-task deep learning strategy based on microwave detection technology. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 184, 115047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Kang, Y.; Long, T.; Yi, H.; Wang, F.; Chen, C. Rapid quality evaluation of moutan cortex (Paeonia suffruticosa Andrews) by near-infrared spectroscopy and bionic swarm intelligent optimization algorithm. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2025, 260, 116822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Liu, T.; He, P.H.; Ding, Y.H.; Chen, Q.S. Rapid measurement of fatty acid content during flour storage using a color-sensitive gas sensor array: Comparing the effects of swarm intelligence optimization algorithms on sensor features. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 127828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, G.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, Y. Fingerprinting of Boletus bainiugan: FT-NIR spectroscopy combined with machine learning a new workflow for storage period identification. Food Microbiol. 2025, 129, 104743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Chen, R.; Yang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Huang, J.; Luo, L.; Liu, H.; Xu, J.; Chen, W.; Ding, Y.; et al. Application of back propagation neural network model optimized by particle swarm algorithm in predicting the risk of hypertension. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2022, 24, 1606–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charron, D.M.; Ajito, K.; Kim, J.-Y.; Ueno, Y. Chemical Mapping of Pharmaceutical Cocrystals Using Terahertz Spectroscopic Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 1980–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, H.E.; Arslan, M.; Mahunu, G.K.; Mariod, A.A.; Hashim, S.B.H.; Xiaobo, Z.; Jiyong, S.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Musa, T.H. The use of analytical techniques coupled with chemometrics for tracing the geographical origin of oils: A systematic review (2013–2020). Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Yan, J.; Chu, J.W.; Qi, H.; Xu, P.; Liu, S.Q.; Zhou, L.; Gao, J.L. Accurate prediction of wood moisture content using terahertz time-domain spectroscopy combined with machine learning algorithms. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 227, 120771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y. Detection technologies, and machine learning in food: Recent advances and future trends. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Pu, H.; Sun, D.-W. Stacked long and short-term memory (SLSTM)- assisted terahertz spectroscopy combined with permutation importance for rapid red wine varietal identification. Talanta 2025, 291, 127650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, C.; Mei, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, R.; Chen, W.; Han, D.; Xu, K. Discrimination of corn variety using Terahertz spectroscopy combined with chemometrics methods. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 2021, 252, 119475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mesery, H.S.; Mao, H.; Abomohra, A.E.-F. Applications of Non-destructive Technologies for Agricultural and Food Products Quality Inspection. Sensors 2019, 19, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Yang, X.; Xue, S.; Zhou, R.; Wang, C.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cai, J. “Raman plus X” dual-modal spectroscopy technology for food analysis: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2025, 24, e70102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhlaei, R.; Babadi, A.A.; Sun, C.; Ariffin, N.M.; Khatib, A.; Selamat, J.; Xiaobo, Z. Application, challenges and future prospects of recent nondestructive techniques based on the electromagnetic spectrum in food quality and safety. Food Chem. 2024, 441, 138402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Ren, Y.; Sun, D.-W. Novel analysis of food processes by terahertz spectral imaging: A review of recent research findings. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 147, 104463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonouchi, M. Sate-of-the-Art of Terahertz Science and Technology. In Frontiers in Optical Methods: Nano-Characterization and Coherent Control; Shudo, K.-I., Katayama, I., Ohno, S.-Y., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 153–166. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, T.; Luo, Q.; Yang, L.; Gao, C.L.; Ling, C.J.; Wu, W.B. Research Review on Quality Detection of Fresh Tea Leaves Based on Spectral Technology. Foods 2024, 13, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.-H.; Otani, C.; Ogawa, Y. Innovatively identifying naringin and hesperidin by using terahertz spectroscopy and evaluating flavonoids extracts from waste orange peels by coupling with multivariate analysis. Food Control 2022, 137, 108897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, F.; Xu, D.; Fu, M.; Ge, H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Identification of Transgenic Ingredients in Maize Using Terahertz Spectra. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.T.; Gao, J.H.; Tan, L.; Zheng, L.; Wang, L.J. Research on the Application of Terahertz Technology in Detecting Additives in Milk Powder. Food Anal. Methods 2025, 18, 398–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Meng, T.; Wu, M.; Hu, W.; Yang, D.; Wu, W. Nucleobase discrimination based on terahertz spectroscopy using multi-scale convolutional neural network with convolutional block attention module and long short-term memory. Sens. Actuators A-Phys. 2025, 387, 116434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhlaei, R.; Babadi, A.A.; Ariffin, N.M.; Zou, X. Development of FTIR-ATR spectra and PLS regression combination model for discrimination of pure and adulterated acacia honey. Food Control 2025, 169, 110996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wu, X.; Wu, B.; Dai, C.; Fu, H. Rapid authentication of the geographical origin of milk using portable near-infrared spectrometer and fuzzy uncorrelated discriminant transformation. J. Food Process Eng. 2022, 45, e14040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Fu, Y.; Cui, T.J. Applications of Terahertz Spectroscopy in the Detection and Recognition of Substances. Front. Phys. 2022, 10, 869537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Jia, S.; Qin, J.; Du, Y.; Zhao, Z. A Feasible Approach to Detect Pesticides in Food Samples Using THz-FDS and Chemometrics. J. Spectrosc. 2020, 2020, 3859076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, C.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, L. Discrimination of geographical origin of extra virgin olive oils using terahertz spectroscopy combined with chemometrics. Food Chem 2018, 251, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhao, P.; Shi, Y.; Liu, C.; Zheng, L. Rapid Determination of Peroxide Value of Peanut Oils During Storage Based on Terahertz Spectroscopy. Food Anal. Methods 2021, 14, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, B.; Ye, D. Analysis and Identification of Rice Adulteration Using Terahertz Spectroscopy and Pattern Recognition Algorithms. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 26839–26850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Wei, S.; Zhang, G.; Xiong, X.; Ai, M.; Li, X.; Shen, Y. Discrimination of wheat gluten quality utilizing terahertz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS). Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2025, 328, 125452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.H.; Lim, H.B.; Chun, H.S. Detection of melamine in foods using terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 5403–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, K.; Han, C.; Guan, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Feasibility and potential of terahertz spectral and imaging technology for Apple Valsa canker detection: A preliminary investigation. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2025, 327, 125308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuefang, H.; Hongjian, Z. Qualitative and Quantitative Detection of Pesticides With Terahertz Time-Domain Spectroscopy. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2010, 58, 2064–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, W.; Mei, C.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Q. Rapid Diagnosis of Normal and Abnormal Conditions in Solid-State Fermentation of Bioethanol Using Fourier Transform Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 12959–12964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Han, D.; Liu, W. Determination of invert syrup adulterated in acacia honey by terahertz spectroscopy with different spectral features. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 1913–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, B.; Li, H.; Cai, E.; Fan, M. Determination of Pesticides in Flour by Terahertz Time-Domain Spectroscopy (THz-TDS) with Voigt Function Fitting and Partial Least Squares (PLS) Analysis. Anal. Lett. 2020, 54, 830–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Huang, Q.; Fu, Z.; Lu, Y. Analysis of Flavonoid Compounds by Terahertz Spectroscopy Combined with Chemometrics. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 18134–18141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Li, H.; Fan, M.; Wang, W.; Wang, M. Determination of pesticides in a flour substrate by chemometric methods using terahertz spectroscopy. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 5097–5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.; Wang, J.; Zhu, H.; Liao, Q.; Hu, L.; Wang, H. Relationship between the characteristic temperature and terahertz permittivity of different rank coals considering FeS2 content. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2023, 135, 104995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Teng, Y.; Li, C.; Jiang, L. Simultaneous quantitative determination of low-concentration ternary pesticide mixtures in wheat flour based on terahertz spectroscopy and BPNN. Food Chem. 2022, 377, 132030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.F.; Deng, J.H.; Li, C.X.; Jiang, H. Quantitative Analysis of Peanut Skin Adulterants by Fourier Transform Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Chemometrics. Foods 2025, 14, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qin, J.Y.; Xu, W.D.; Chen, M.; Xie, L.J.; Ying, Y.B. Terahertz Imaging Applications in Agriculture and Food Engineering: A Review. Trans. Asabe 2018, 61, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Deng, H.; Wei, X.; Zhang, J. Progress in application of terahertz time-domain spectroscopy for pharmaceutical analyses. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1219042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Sun, X.; Li, B. Optimization of quantitative detection model for benzoic acid in wheat flour based on CARS variable selection and THz spectroscopy. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 14, 2549–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Ma, L.; Tang, Z.; Yu, L.X. Identification of coumarin-based food additives using terahertz spectroscopy combined with manifold learning and improved support vector machine. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, C.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.; Tuo, S.; Guan, H. On ALIF-WT-GDA-based Terahertz spectral method for identification of transgenic cotton seeds. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2022, 127, 104476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.C.; Jiang, H. Monitoring of Chlorpyrifos Residues in Corn Oil Based on Raman Spectral Deep-Learning Model. Foods 2023, 12, 2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.H.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Q.S. Characteristic wavelengths optimization improved the predictive performance of near-infrared spectroscopy models for determination of aflatoxin B1 in maize. J. Cereal Sci. 2022, 105, 103474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.Y.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Q.S. High Precisive Prediction of Aflatoxin B1 in Pressing Peanut Oil Using Raman Spectra Combined with Multivariate Data Analysis. Foods 2022, 11, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, X.; Zhang, W. A toxin-free enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the analysis of aflatoxins based on a VHH surrogate standard. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 6019–6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.J.; Chen, Z.S.; Bai, X.; Deng, J.H.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, H. Determination of aflatoxin B1 in peanuts based on millimetre wave. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, H.; Sun, J.; Zhou, X.; Yao, K.; Nirere, A. Nondestructive determination of the total mold colony count in green tea by hyperspectral imaging technology. J. Food Process Eng. 2020, 43, e13570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Ding, L.; Han, K.; Zou, X.; Wang, S.; Wen, Z.; Ye, Y.; Ren, X. Detection of carbendazim in oranges with metal grating integrated microfluidic sensor in terahertz. Food Addit. Contam. Part A-Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2022, 39, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, H.; Jiang, Y.; Lian, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, S. Quantitative determination of aflatoxin B1 concentration in acetonitrile by chemometric methods using terahertz spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2016, 209, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Sun, J.; Fu, L.; Xu, M.; Tang, N.; Cao, Y.; Yao, K.; Jing, J. Identification of red jujube varieties based on hyperspectral imaging technology combined with CARS-IRIV and SSA-SVM. J. Food Process Eng. 2022, 45, e14137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhan, C.; Wang, Q.; Shi, H.; He, Y.; Ouyang, A. Research on highly sensitive quantitative detection of aflatoxin B2 solution based on THz metamaterial enhancement. Spectrochim. Acta Part A-Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 300, 122809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hao, H. Determination of the SSC in oranges using Vis-NIR full transmittance hyperspectral imaging and spectral visual coding: A practical solution to the scattering problem of inhomogeneous mixtures. Food Chem. 2025, 474, 143239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Tu, B.; Zeng, L.; Yin, C.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, X.; He, D.-P.; Qi, P. Classification of Edible Vegetable Oils by Laser Near-infrared Spectra. In Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE International Conference on Progress in Informatics and Computing (PIC), Shanghai, China, 16–18 May 2014; pp. 123–127. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Lin, H.; Wang, L.; Gao, L.; Sui, J.; Wang, K. Optical sensing techniques for rapid detection of agrochemicals: Strategies, challenges, and perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Wang, S.; Han, K.; Song, X.; Zhang, W.; Ye, Y.; Ren, X. Development of a Novel Metal Grating and Its Applications of Terahertz Spectroscopic Detection of CuSO4 in Fruit (Mar, 10.1007/s12161-021-01999-1, 2021). Food Anal. Methods 2021, 14, 1590–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Sun, Z.; Yuan, T.; Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Du, Y. Trace determination of dimethyl phthalate based on double F-type multi-frequency resonant metamaterial sensor. Opt. Commun. 2025, 578, 131482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, H.; Fang, T.; Wu, Z.; Sun, D.-W. Advancements in recyclable photocatalytic semiconductor substrates for SERS detection in food safety applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 138, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhlaei, R.; Selamat, J.; Khatib, A.; Razis, A.F.A.; Sukor, R.; Ahmad, S.; Babadi, A.A. The Toxic Impact of Honey Adulteration: A Review. Foods 2020, 9, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Zhou, W. A Review of Recent Advances for the Detection of Biological, Chemical, and Physical Hazards in Foodstuffs Using Spectral Imaging Techniques. Foods 2023, 12, 2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Zhang, Z.-T.; Bai, L.; Chen, L.; Yuan, D.; Liu, W.; Chen, P.; Shi, Z.; Hu, C.; Xue, M.; et al. Multi-spectra combined with Bayesian optimized machine learning algorithms for rapid and non-destructive detection of adulterated functional food Panax notoginseng powder. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 133, 106412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.H.; Sun, J.; Shi, L.; Dai, C.X. An effective method fusing electronic nose and fluorescence hyperspectral imaging for the detection of pork freshness. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 103880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.-Q.; Yin, X.-L.; Gu, H.-W.; Sun, W.; Ding, B.; Hu, X.-C.; Ma, L.-A.; Wei, S.-D.; Liu, Z.; Ye, S.-Y. HPLC-DAD fingerprints combined with chemometric techniques for the authentication of plucking seasons of Laoshan green tea. Food Chem. 2021, 347, 128959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Luo, B.; Liu, Y.-D.; Wu, J. Detection of adulteration of kudzu powder by terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 4380–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yin, H.; Yang, A.K.; Ouyang, A.-G.; Cozzolino, D. Detection of Adulteration of Panax Notoginseng Powder by Terahertz Technology. J. Spectrosc. 2022, 2022, 7247941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Chen, C.; Tang, J.; Lv, X.; Ma, C. Rapid and efficient screening of human papillomavirus by Raman spectroscopy based on GA-SVM. Optik 2020, 210, 164514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Solomon Adade, S.Y.-S.; Rong, Y.; Zhao, S.; Han, Z.; Gong, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, J.; Huang, C.; Lin, H. Online System for Monitoring the Degree of Fermentation of Oolong Tea Using Integrated Visible-Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Image-Processing Technologies. Foods 2024, 13, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, M.; Tang, S.; Tong, M. Identification of edible oils using terahertz spectroscopy combined with genetic algorithm and partial least squares discriminant analysis. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 2794–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.H.; Yan, Y.L.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Jiang, H. Classification of Tea Quality Levels Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Based on CLPSO-SVM. Foods 2022, 11, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Shen, Y.; Li, G.; Ai, M.; Wang, L.; Ma, H.; He, W. Classification of wheat grain varieties using terahertz spectroscopy and convolutional neural network. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 129, 106060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.H.; Chen, Z.Y.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Q.S. High-precision detection of dibutyl hydroxytoluene in edible oil via convolutional autoencoder compressed Fourier-transform near-infrared spectroscopy. Food Control 2025, 167, 110808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Lang, W.; Liu, W.; Xu, X.; Yang, J.; Zheng, L. A Non-destructive Terahertz Spectroscopy-Based Method for Transgenic Rice Seed Discrimination via Sparse Representation. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2017, 38, 980–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Mao, L.; Ku, J.; Peng, H.; Lao, Z.; Chen, D.; Yang, B. Using terahertz spectroscopy to identify transgenic cottonseed oil according to physicochemical quality parameters. Optik 2017, 142, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, M.; Hu, B.; Jiang, Q.; Shi, Z.; He, Y.; Peng, J. Desert Soil Salinity Inversion Models Based on Field In Situ Spectroscopy in Southern Xinjiang, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Terahertz spectroscopy and chemometrics classification of transgenic corn oil from corn edible oil. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2017, 59, 654–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liu, M.; Li, B.; Chitrakar, B.; Duan, X. Terahertz Spectroscopic Identification of Roast Degree and Variety of Coffee Beans. Foods 2024, 13, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Qu, B.; Liao, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Hu, L.; Gao, R. Study on the effects of oxidation temperature and ambient humidity on the terahertz spectroscopy characteristics of lignite. Fuel 2023, 349, 128693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; Chen, P.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Liu, D.; Chu, X. Commentary on the review articles of spectroscopy technology combined with chemometrics in the last three years. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2024, 59, 423–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Ge, H.; Zhang, Y. Quantitative analysis of wheat maltose by combined terahertz spectroscopy and imaging based on Boosting ensemble learning. Food Chem. 2020, 307, 125533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Detection Method for Tomato Leaf Mildew Based on Hyperspectral Fusion Terahertz Technology. Foods 2023, 12, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Lei, T.; Cheng, Y.; Wei, X.; Sun, D.W. Predicting wheat gluten concentrations in potato starch using GPR and SVM models built by terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2024, 432, 137235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Lv, H.; Qiao, P.; Shi, H.; He, Y.; Liu, Y. Research on Rice Seed Fullness Detection Method Based on Terahertz Imaging Technology and Feature Extraction Method. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2023, 44, 407–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, H.; Yu, J.; Sun, D.-W.; Wei, Q.; Li, Q. Distinguishing pericarpium citri reticulatae of different origins using terahertz time-domain spectroscopy combined with convolutional neural networks. Spectrochim. Acta Part A-Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 299, 122771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Li, S.; Zhu, S.; Zheng, W.; Zhou, S.; Wu, W.; Xie, Z. Quantitative analysis of soybean protein content by terahertz spectroscopy and chemometrics. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2021, 208, 104199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Qu, F.; Wang, X.; Zhai, X.; Li, J.; Yu, K.; Zhao, Y. Terahertz Spectroscopy and Imaging Techniques for Herbal Medicinal Plants Detection: A Comprehensive Review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2024, 54, 2485–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yan, F.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, Z. Wide angle microfluidic terahertz sensor in aqueous environment. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 172, 110405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, J.; Tang, Y. Preliminary investigation of Terahertz spectroscopy to predict pork freshness non-destructively. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 39, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joerdens, C.; Koch, M. Detection of foreign bodies in chocolate with pulsed terahertz spectroscopy. Opt. Eng. 2008, 47, 037003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau-Noguer, E.; Rodriguez-Sanz, M.; Suppi, R.; Serratosa, J.; Lunden, J.; Bolao, A.; Cedano, D.; Portana, S. Effectiveness of official food safety control in Barcelona city: Digital and traditional inspections. Food Control 2024, 165, 110655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Wu, W.; Yu, Q.; Ruiz-Garcia, L.; Xiang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Shi, Y.; Duan, Y.; Yang, P. Filling the trust gap of food safety in food trade between the EU and China: An interconnected conceptual traceability framework based on blockchain. Food Energy Secur. 2020, 9, e249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsah-Hejri, L.; Hajeb, P.; Ara, P.; Ehsani, R.J. A Comprehensive Review on Food Applications of Terahertz Spectroscopy and Imaging. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1563–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, S.H.; Garner, J.P.; Wuerbel, H. Environmental standardization: Cure or cause of poor reproducibility in animal experiments? Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latha, A.M.; Ranjan, R. Development of a Compact and Portable Terahertz Imaging System for Industrial Applications. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Microwaves, Antennas, and Propagation Conference (MAPCON), Hyderabad, India, 9–13 December 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Han, J.; Raghavan, V.; Wang, J. Portable sensor devices based on multifunctional framework materials: Recent advances for food safety assurance by on-site detection. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 159, 104965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonouchi, M. Cutting-edge terahertz technology. Nat. Photonics 2007, 1, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sensale-Rodriguez, B.; Yan, R.; Liu, L.; Jena, D.; Xing, H.G. Graphene for Reconfigurable Terahertz Optoelectronics. Proc. IEEE 2013, 101, 1705–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organisation for Standardisation. Nature 1947, 160, 389. [CrossRef]
- Khushbu, S.; Yashini, M.; Rawson, A.; Sunil, C.K. Recent Advances in Terahertz Time-Domain Spectroscopy and Imaging Techniques for Automation in Agriculture and Food Sector. Food Anal. Methods 2022, 15, 498–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, M.A.; Rather, M.Y.; Singh, P.; Hassan, S.; Hussain, N. Advances in smart food authentication for enhanced safety and quality. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 155, 104800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, R.; Singha, P.; Singh, S.K. Spectroscopic food adulteration detection using machine learning: Current challenges and future prospects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 146, 104377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porep, J.U.; Kammerer, D.R.; Carle, R. On-line application of near infrared (NIR) spectroscopy in food production. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 46, 211–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Lovett, D.; Morris, J. Process analytical technologies and real time process control a review of some spectroscopic issues and challenges. J. Process Control 2011, 21, 1467–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimidou, M.Z.; Ordoudi, S.A.; Mantzouridou, F.T.; Nenadis, N.; Stelzl, T.; Rychlik, M.; Belc, N.; Zoani, C. Strategic Priorities of the Scientific Plan of the European Research Infrastructure METROFOOD-RI for Promoting Metrology in Food and Nutrition. Foods 2022, 11, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Detection Technology | Technical Characteristics | Detection Time | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPLC | Highly efficient separation | Minutes to tens of minutes | High sensitivity for multi-component analysis | High cost and complex pre-treatment |
| GC | Volatility analysis | Minutes to 20 min | High sensitivity to volatile components, clear structural information | Requires derivatization and cumbersome sample pretreatment |
| ELISA | Bioimmune recognition | 1–3 h | Highly specific, rapid screening for low concentration indicators | High antibody quality dependence and risk of cross-reactivity |
| PCR | Molecular detection | 2–4 h | High specificity for microbial/transgenic testing | Complex process, strict control of contamination, specialized equipment required |
| TA | Stoichiometry | Manual: 5~20 min Automatic: 3~10 min | Simple instrument, low cost, suitable for acid-base, salinity and other routine testing | High human error and lower accuracy than instrumental methods |
| UV–Vis | Absorbance measurement | 5–30 min | Fast, low equipment cost, easy to use for color and characterization quantification | Sensitive to sample matrix interference, not suitable for complex systems |
| Detection Technology | Wavelength/ Frequency | Brief Outline of Principle | Detection Limit | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NIR | 780–2500 nm | Molecular vibration absorption | % | Fast, non-destructive, simultaneous measurement of components | Sensitive to complex matrices, model-dependent |
| THz | 3 mm–30 µm | Low-frequency resonance absorption | ppm | Wearable packaging, identifies adulteration, non-ionizing and harmless | Heavy water interference, limited sensitivity and penetration |
| Raman | 532–1064 nm (excitation light) | Molecular vibration induced scattered radio frequency shifts | ppm | Highly sensitive, resistant to water interference, rapid detection | Fluorescence interference, high equipment cost |
| X-ray | 0.01–10 nm | Penetration and absorption imaging | µg–mg | Industrially proven, efficient identification of hard foreign objects | Weak recognition of low-density foreign objects such as mixed plastics |
| CV | Visible light 400–700 nm | Visual feature extraction and recognition | µm | Real-time online sorting at low cost | Vulnerable to light and background |
| UT | 16 kHz–20 MHz | Echo detection of sound waves | mm | Detects sealing defects, internal tissue structure | Requires coupling agent, fast signal attenuation, poor results with complex samples |
| MW | 30–300 GHz | Dielectric response to EM waves | % | Secure, low cost, penetrating packaging, suitable for online | Low resolution, difficult to identify small particles or trace adulteration |
| NMR | 43–100 MHz | Nuclear spin resonance detection | % | Non-destructive quantification, suitable for water/lipid analysis | Expensive equipment, insufficient sensitivity for trace adulteration detection |
| HSI | 400–2500 nm | Combined spectral and spatial analysis | ppm | Graphically rich, detects spoilage, adulteration, spotting | Large data volumes, complex models, expensive equipment |
| Food | Target of Detection | Typology | Arithmetic | Outcome | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene and glutinous rice flour | Imidacloprid | Pesticide detection | PLS | Relative error of prediction < 5.00% RMSEP = 0.70% | [86] |
| Flour | Imidacloprid Carbendazim | Pesticide detection | MSBC-PLS-Voigt | RP = 0.9914 RC = 0.9957 | [89] |
| Wheat flour | 6-BA 2,6-D Imidacloprid | Pesticide detection | BPNN | RP = 0.9913 RP = 0.9948 RP = 0.9923 | [93] |
| Food | Target of Detection | Typology | Arithmetic | Outcome | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat flour | Benzoic acid | Additive detection | CARS-PCA-LS-SVM | RP = 0.9956 RMSEP = 0.64% | [97] |
| Coumarin-based food additives | Coumarin-based food additives | Additive detection | P-t-SNE-DEGWO-SVM | RP = 0.9861 | [98] |
| Food | Target of Detection | Typology | Arithmetic | Outcome | Reference |
| Acetonitrile solution | AFB1 | Toxins and mildew | PLSR (High concentration) RBF-SVM (low concentration) | R = 0.9780 | [107] |
| R = 0.9376 RMSE = 0.0779 | |||||
| Peanut oil | AFB1 | Toxins and mildew | Second derivative-SMLR | RCV = 0.9309 RC = 0.9639 | [35] |
| Black tea | OTA | Toxins and mildew | / | RMSEC = 0.2800 RMSEP = 0.3500 | [112] |
| Food | Target of Detection | Typology | Arithmetic | Outcome | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice | Different mixed proportions of rice | Adulteration | 1st derivative-PCA-SVM | Accuracy = 97.33% | [82] |
| Kudzu powder | Lotus root powder and potato powder | Adulteration | UVE-LS-SVM-RBF-DA | Misjudgment rate = 6.70% | [121] |
| Panax notoginseng powder | Zedoary turmeric powder Wheat flour | Adulteration | LS-SVM | RP = 0.9015 RMSEP = 0.0723 RP = 0.9305 RMSEP = 0.0677 | [122] |
| Rice flour | PLS | RP = 0.9424 RMSEP = 0.0601 |
| Food | Target of Detection | Typology | Arithmetic | Outcome | Reference |
| Wheat grain | Strong-gluten Medium-gluten Weak-gluten | Variety identification | SNV-CNN | Misjudgment rate = 2.20% | [127] |
| Rice seeds | Gene | Variety identification | SR-RF | Accuracy = 95.00% | [129] |
| Cottonseed oil | Gene | Variety identification | PLS-DA | Accuracy = 97.00% | [130] |
| Corn oil | Gene | Variety identification | PLS-DA | Accuracy = 98.70% | [132] |
| Coffee beans | Degree of baking | Variety identification | PCA-LD | Accuracy = 100.00% | [133] |
| Food | Target of Detection | Typology | Arithmetic | Outcome | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat | Maltose | Nutrient content | PCA-Boosting-LS-SVM | R2 > 0.9600 RMSEC = 0.1200 RMSEP = 0.1500 | [136] |
| Potato starch | Wheat gluten | Nutrient content | GPR | R2 = 0.8590 RMSE = 0.0700 | [138] |
| Soybeans | Protein | Nutrient content | SNV-second derivative- ABC-SVR | RP = 0.9659 RMSEP = 1.31% RSD = 3.53% | [141] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Bai, X.; Wei, M.; Jiang, H.; Xu, L. Terahertz Spectroscopy for Food Quality Assessment: A Comprehensive Review. Foods 2025, 14, 2199. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132199
Yang J, Bai X, Wei M, Jiang H, Xu L. Terahertz Spectroscopy for Food Quality Assessment: A Comprehensive Review. Foods. 2025; 14(13):2199. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132199
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jie, Xue Bai, Mingji Wei, Hui Jiang, and Leijun Xu. 2025. "Terahertz Spectroscopy for Food Quality Assessment: A Comprehensive Review" Foods 14, no. 13: 2199. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132199
APA StyleYang, J., Bai, X., Wei, M., Jiang, H., & Xu, L. (2025). Terahertz Spectroscopy for Food Quality Assessment: A Comprehensive Review. Foods, 14(13), 2199. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132199







