Modulatory Effects of Tetraselmis chuii Gastrointestinal Digests on Human Colonic Microbiota
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biomass and Reagents
2.2. INFOGEST Gastrointestinal Digestion
2.3. Static Colonic Fermentation and Microbial Plate Counting
2.4. Extraction and Quantification of Microbial DNA
2.5. 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene Sequencing
2.6. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.7. Chemical Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
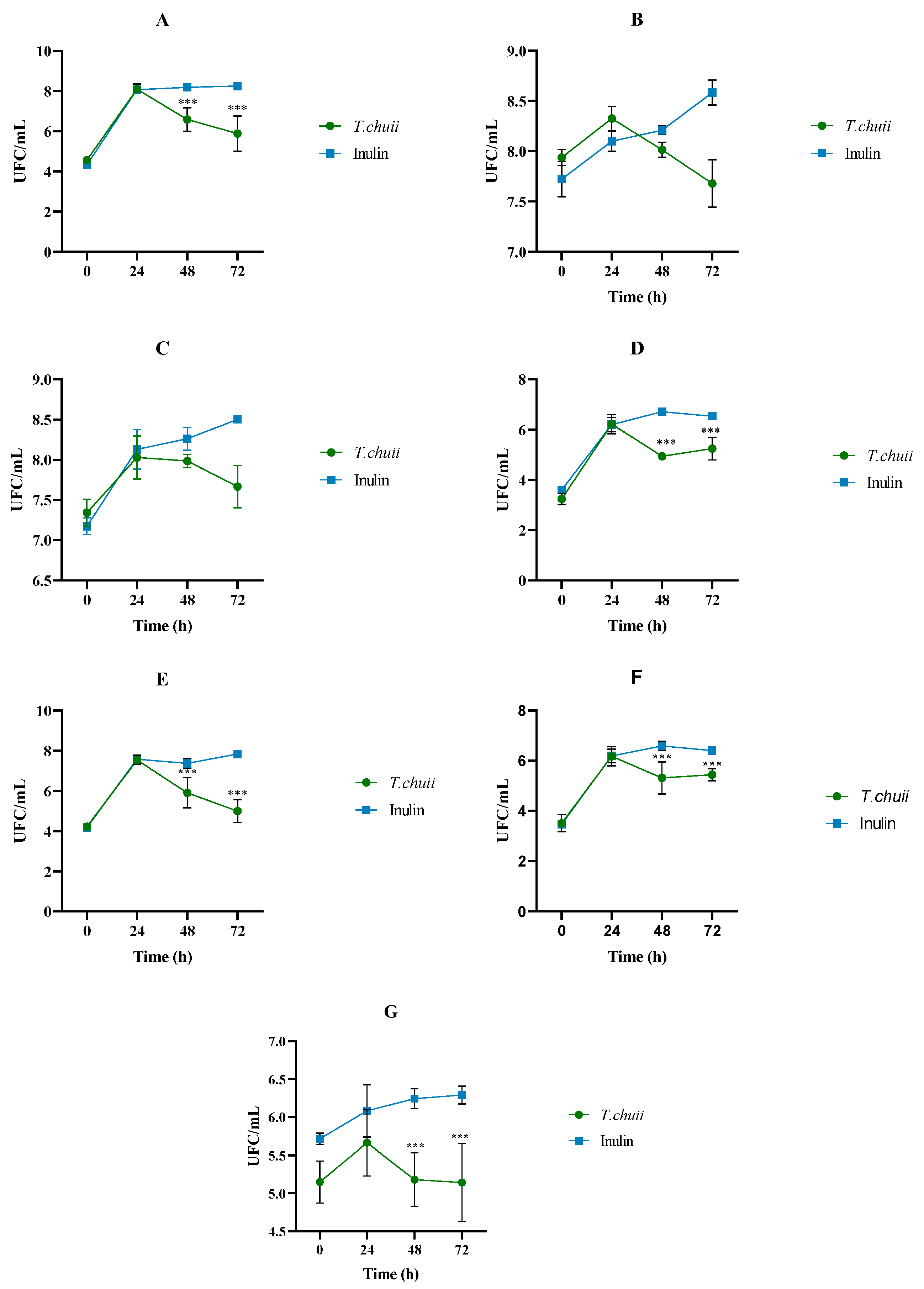
3.1. Effects of T. chuii on the Intestinal Bacterial Populations During Colonic Fermentation: Plate Counting
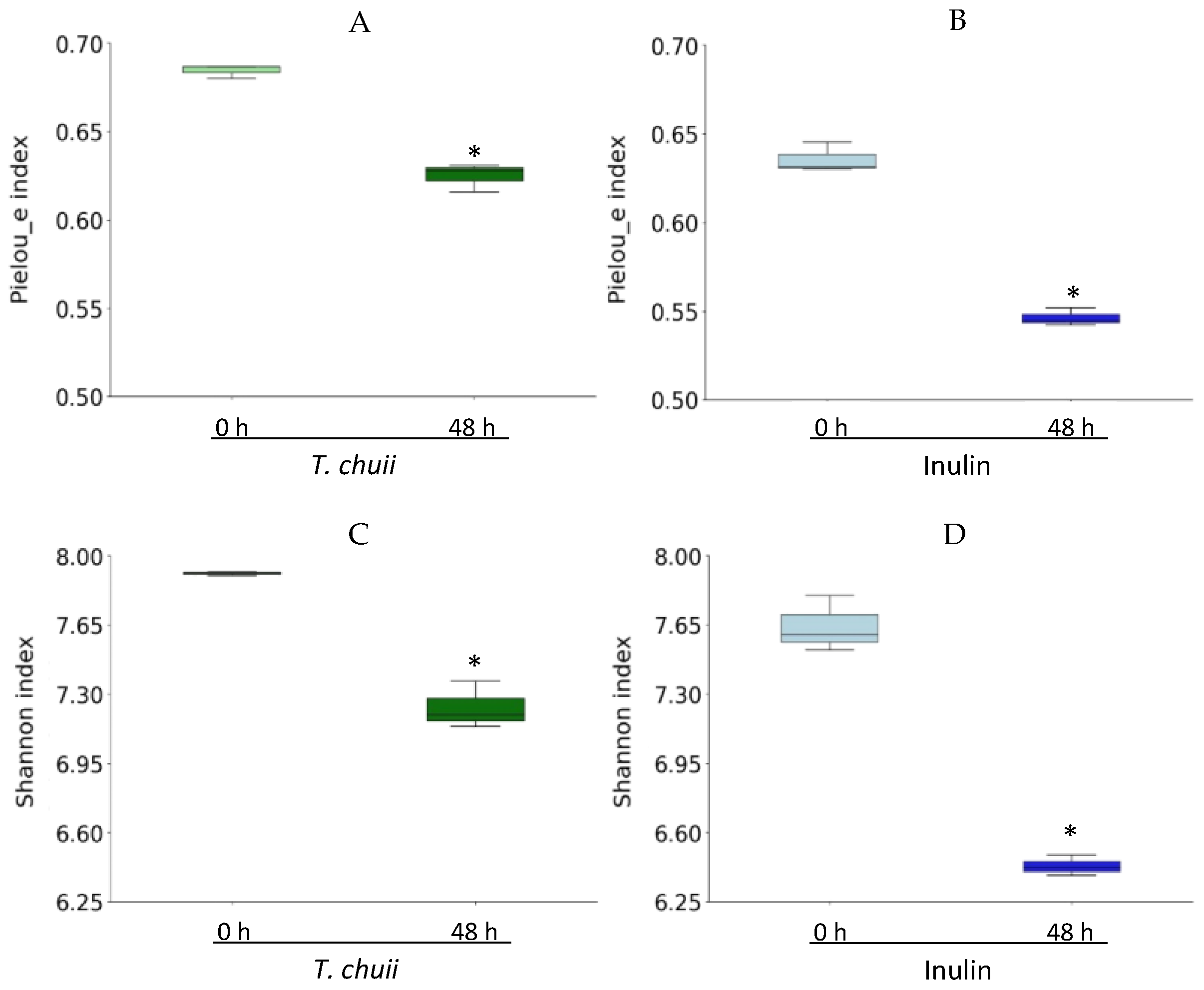
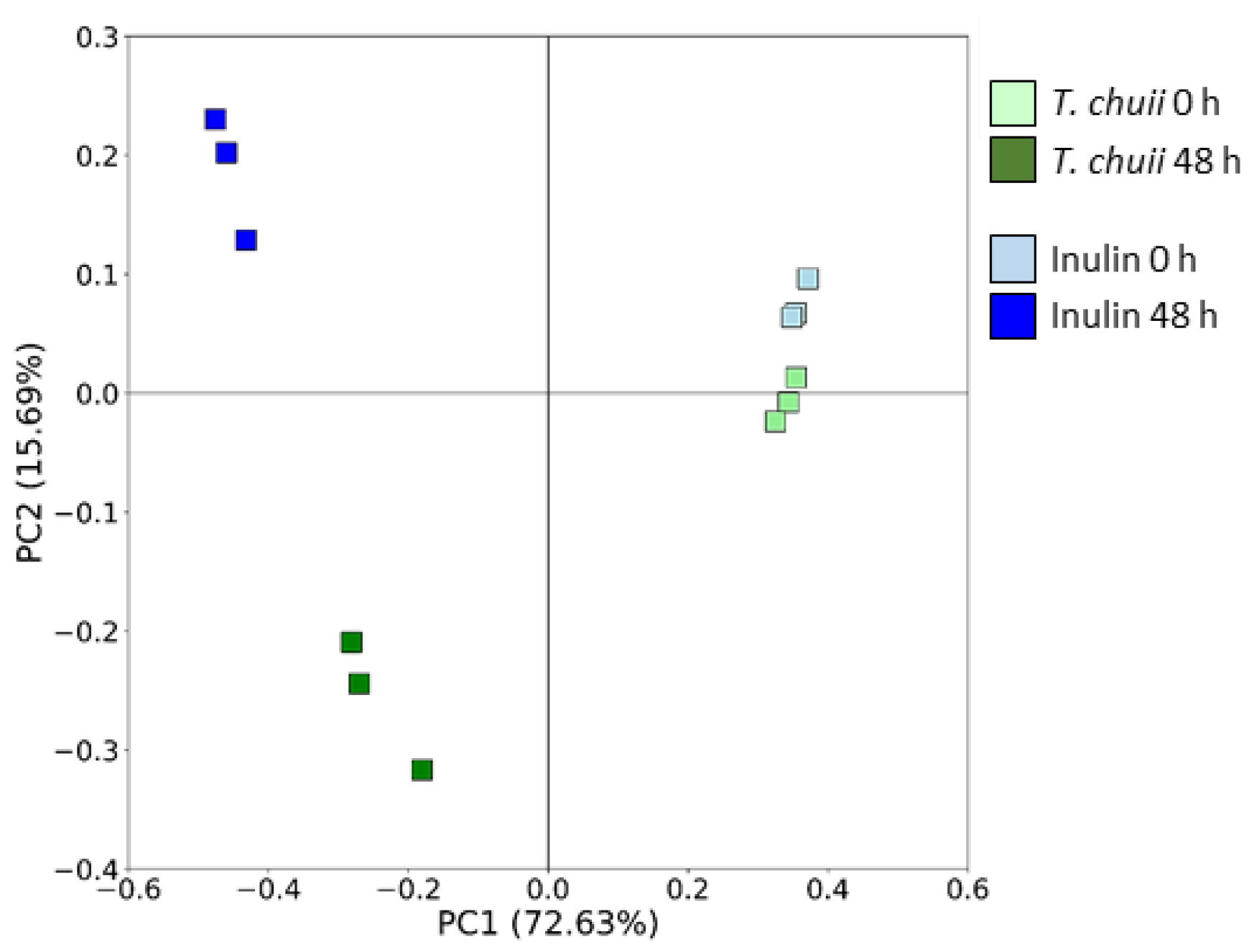
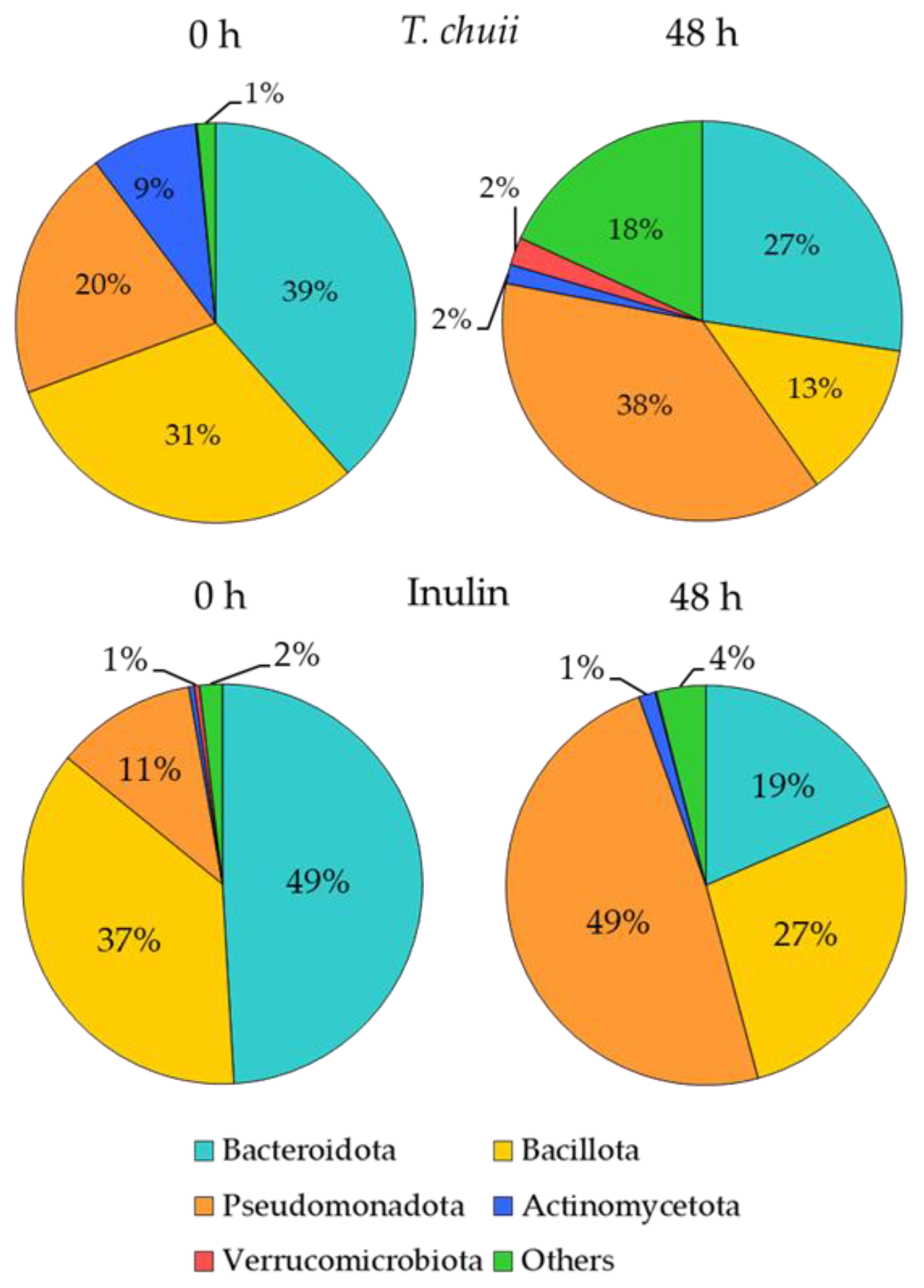
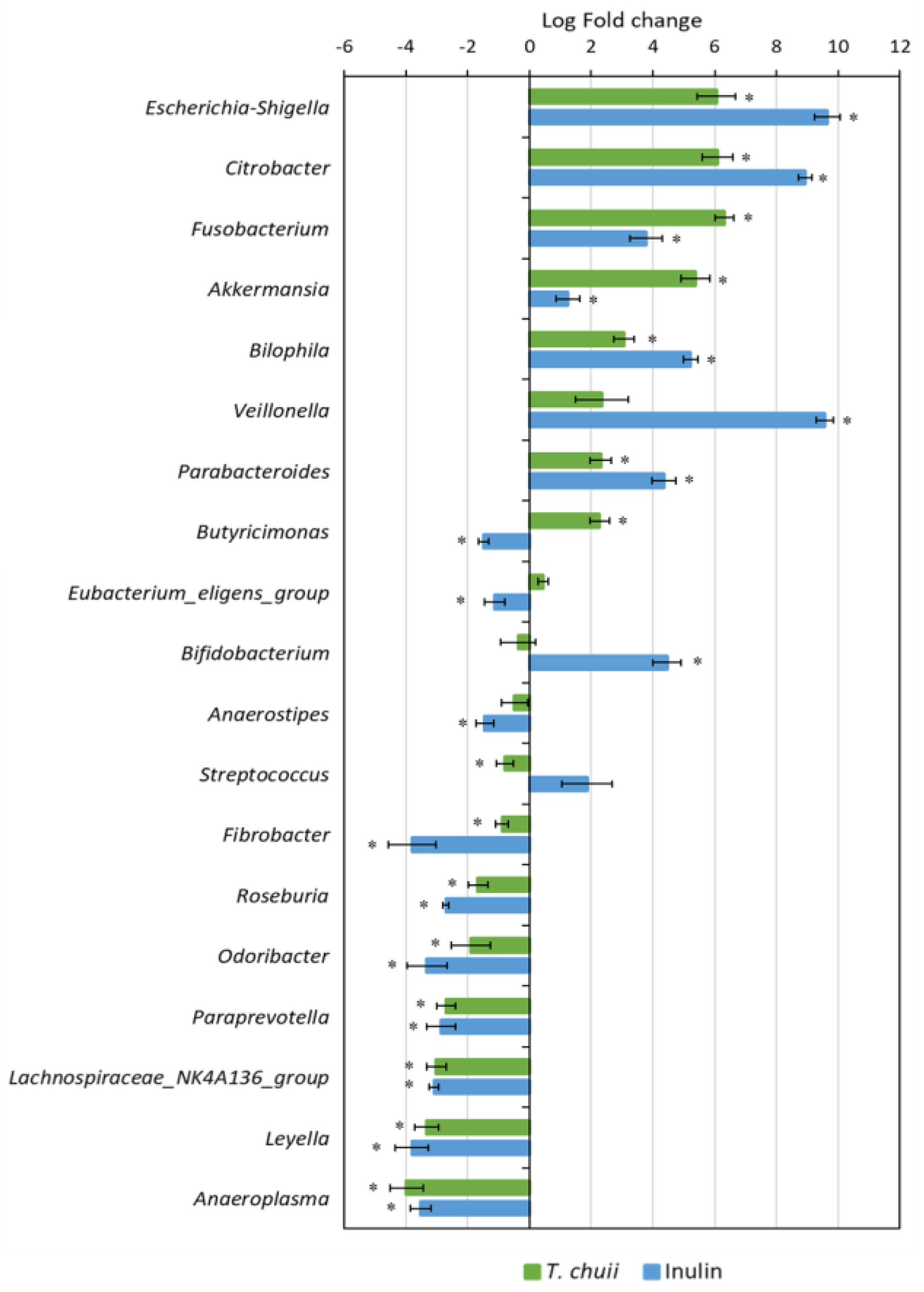
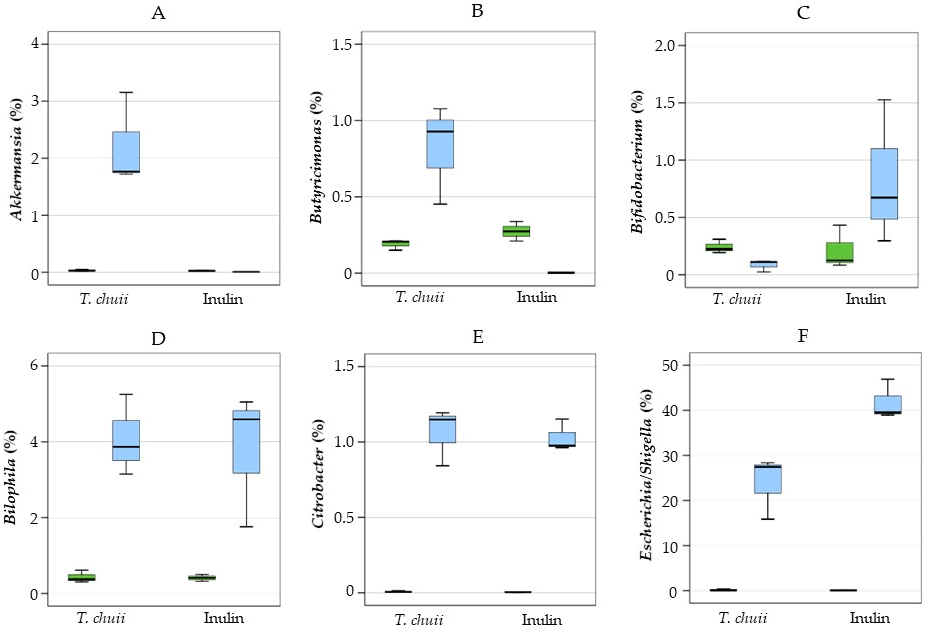
3.2. Effects of T. chuii on the Intestinal Bacterial Populations During Colonic Fermentation: Sequencing of Bacterial 16S rRNA
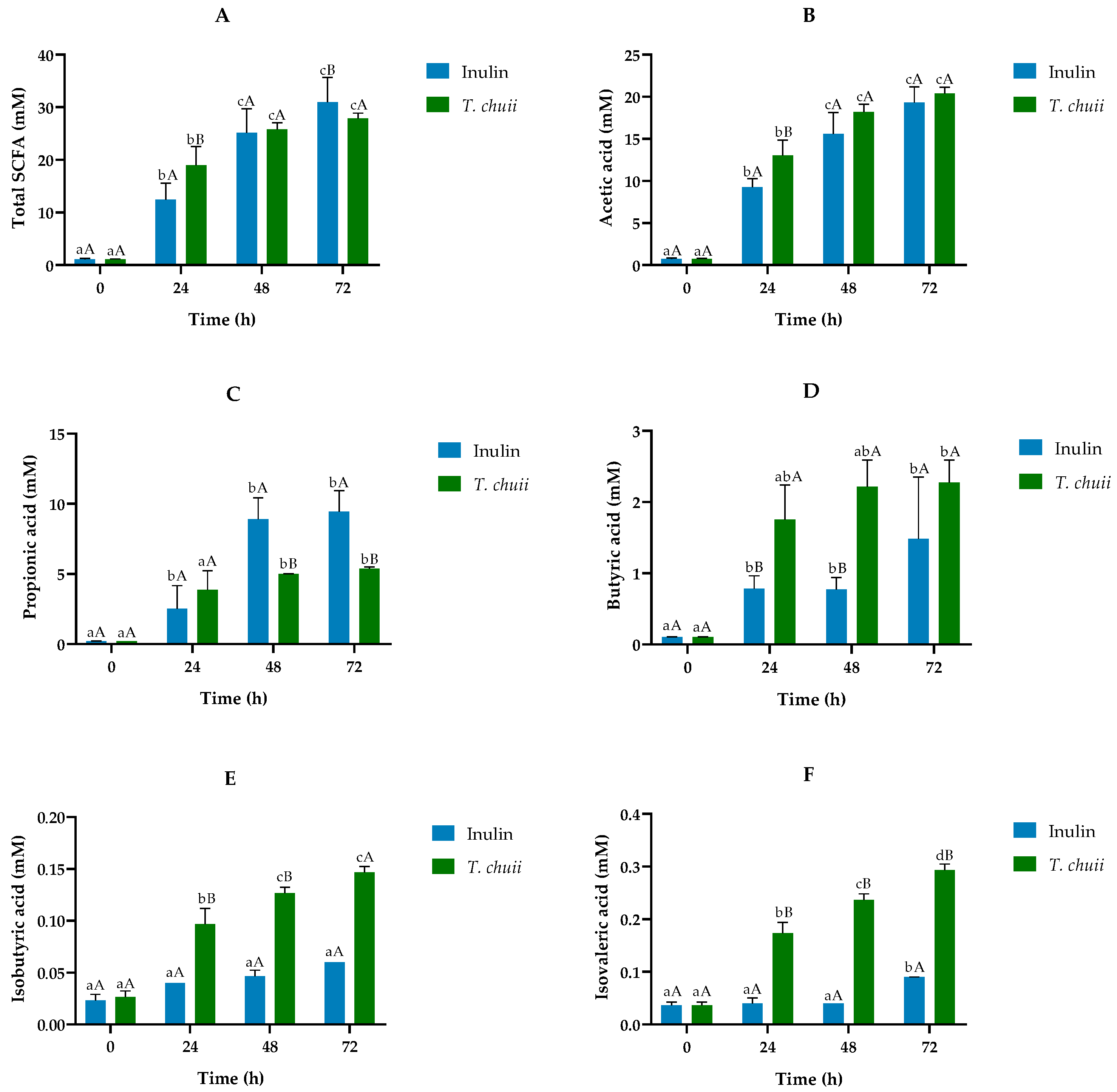
3.3. Short-Chain Fatty Acid Profiles from In Vitro Human Colonic Fermentation Samples
3.4. Evolution of the Proteolytic Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Levasseur, W.; Perré, P.; Pozzobon, V. A review of high value-added molecules production by microalgae in light of the classification. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 41, 107545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros de Medeiros, V.P.; da Costa, W.K.A.; da Silva, R.T.; Pimentel, T.C.; Magnani, M. Microalgae as source of functional ingredients in new-generation foods: Challenges, technological effects, biological activity, and regulatory issues. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 4929–4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero Montarelo, L.B.; Gómez Vázquez, M.D.; Teruel Muñoz, V.J. New regulation on novel foods in the European Union. AECOSAN Sci. Commun. J. 2015, 27, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- AECOSAN. Report of the scientific Committee of the Spanish Agency for Consumer Affairs, Food Safety and Nutrition (AECOSAN) on a request for initial assessment for marketing of the dried marine microalgae Tetraselmis chuii in food supplements under regulation (EC) no 258/97 on novel foods and novel food ingredients. AECOSAN Sci. Commun. J. 2017, 25, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- FDA. Gras Notice Inventory; US Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2016; p. 26.
- Hurtado, M.C.; Pilar, M.; Moreno, C.; Daschner, Á.; Riba, R.E.; María, R.; Pons, G.; Fandos, E.G.; Arnau, S.G.; Gallego, J.; et al. Section of Food Safety and Nutrition Report Approved by the Section of Food Safety and Nutrition of the Scientific Committee in Its Plenary Session, 2017; Volume 25.
- Mantecón, L.; Moyano, R.; Cameán, A.M.; Jos, A. Safety assessment of a lyophilized biomass of Tetraselmis chuii (TetraSOD®) in a 90 Day feeding study. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 133, 110810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Cardoso, K.; Del Bas, J.M.; Caimari, A.; Lama, C.; Torres, S.; Mantecón, L.; Infante, C. TetraSOD®, a unique marine microalgae ingredient, promotes an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory status in a metabolic syndrome-induced model in rats. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cokdinleyen, M.; Alvarez-Rivera, G.; Tejera, J.L.G.; Mendiola, J.A.; Valdés, A.; Kara, H.; Ibáñez, E.; Cifuentes, A. Tetraselmis chuii edible microalga as a new source of neuroprotective compounds obtained using fast biosolvent extraction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, V.; Siquier-Coll, J.; Bartolomé, I.; Robles-Gil, M.C.; Rodrigo, J.; Maynar-Mariño, M. Effects of Tetraselmis chuii microalgae supplementation on ergospirometric, haematological and biochemical parameters in amateur soccer players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, M.; Sahin, K.; Stefan, M.; Orhan, C.; Gheith, R.; Reber, D.; Sahin, N.; Tuzcu, M.; Lowery, R.; Durkee, S.; et al. Phytoplankton supplementation lowers muscle damage and sustains performance across repeated exercise bouts in humans and improves antioxidant capacity in a mechanistic animal. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, Á.; Toro-Román, V.; Siquier-Coll, J.; Bartolomé, I.; Muñoz, D.; Maynar-Mariño, M. Effects of Tetraselmis chuii microalgae supplementation on anthropometric, hormonal and hematological parameters in healthy young men: A double-blind study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, S.; Gómez-Cortés, P.; de la Fuente, M.A.; Hernández-Ledesma, B. Bioactivity and digestibility of microalgae Tetraselmis sp. and Nannochloropsis sp. as basis of their potential as novel functional foods. Nutrients 2023, 15, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peredo-Lovillo, A.; Romero-Luna, H.E.; Jiménez-Fernández, M. Health promoting microbial metabolites produced by gut microbiota after prebiotics metabolism. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Medeiros, V.P.B.; de Souza, E.L.; de Albuquerque, T.M.R.; da Costa Sassi, C.F.; dos Santos Lima, M.; Sivieri, K.; Pimentel, T.C.; Magnani, M. Freshwater microalgae biomasses exert a prebiotic effect on human colonic microbiota. Algal Res. 2021, 60, 102547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodkorb, A.; Egger, L.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Assunção, R.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Boutrou, R.; Carrière, F.; et al. INFOGEST static in vitro simulation of gastrointestinal food digestion. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 991–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, S.; Majchrzak, M.; Alexandru, D.; Di Bella, S.; Fernández-Tomé,, S.; Arranz, E.; de la Fuente, M.A.; Gómez-Cortés, P.; Hernández-Ledesma, B. Impact of the biomass pretreatment and simulated gastrointestinal digestion on the digestibility and antioxidant activity of microalgae Chlorella vulgaris and Tetraselmis chuii. Food Chem. 2024, 453, 139686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamargo, A.; de Llano, D.G.; Cueva, C.; del Hierro, J.N.; Martin, D.; Molinero, N.; Bartolomé, B.; Victoria Moreno-Arribas, M. Deciphering the interactions between lipids and red wine polyphenols through the gastrointestinal tract. Food Res. Int. 2023, 165, 112524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.B.; Cha, J.W.; Shin, I.S.; Jeon, J.Y.; Cha, K.H.; Pan, C.H. Supplementation with Chlorella vulgaris, Chlorella protothecoides, and Schizochytrium sp. increases propionate-producing bacteria in in vitro human gut fermentation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 2938–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiel, S.; Bindels, L.B.; Pachikian, B.D.; Kalala, G.; Broers, V.; Zamariola, G.; Chang, B.P.I.; Kambashi, B.; Rodriguez, J.; Cani, P.D.; et al. Effects of a Diet Based on Inulin-Rich Vegetables on Gut Health and Nutritional Behavior in Healthy Humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 1683–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamargo, A.; Cueva, C.; Alvarez, M.D.; Herranz, B.; Bartolome, B.; Moreno-Arribas, M.V.; Laguna, L. Influence of viscosity on the growth of human gut microbiota. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Arroyo, C.; Tamargo, A.; Molinero, N.; Moreno-Arribas, M.V. The gut microbiota, a key to understanding the health implications of micro(nano)plastics and their biodegradation. Microb. Biotechnol. 2023, 16, 34–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, D.W.; Garrison, E.K.; Quinlan, A.R.; Strömberg, M.P.; Marth, G.T. BamTools: A C++ API and Toolkit for analyzing and managing BAM files. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1691–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modrego, J.; Ortega-Hernández, A.; Sánchez-González, S.; Corbatón-Anchuelo, A.; Gómez-Garre, D. Analysis of the gut microbiota profile targeted to multiple hypervariable regions of 16S rRNA in a hypertensive heart failure rat model. Methods Cell Biol. 2024, 188, 183–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Villalba, R.; Giménez-Bastida, J.A.; García-Conesa, M.T.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Carlos Espín, J.; Larrosa, M. Alternative method for gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of short-chain fatty acids in faecal samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 1906–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterson, S.; Fernández-Tomé, S.; Galvez, A.; Hernández-Ledesma, B. Evaluation of the multifunctionality of soybean proteins and peptides in immune cell models. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, M.; Bäuerl, C.; Cortés-Macías, E.; Calvo-Lerma, J.; Carmen Collado, M.; Barba, F.J. The impact of liquid-pressurized extracts of Spirulina, Chlorella and Phaedactylum tricornutum on in vitro antioxidant, antiinflammatory and bacterial growth effects and gut microbiota modulation. Food Chem. 2023, 401, 134083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanchi, H.; Mottawea, W.; Sebei, K.; Hammami, R. The genus Enterococcus: Between probiotic potential and safety concerns-an update. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, C. Modulation of gut microbiota and immune system by probiotics, pre-biotics, and post-biotics. Front. Nutr. 2022, 8, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Zhou, D.D.; Gan, R.Y.; Huang, S.Y.; Zhao, C.N.; Shang, A.; Xu, X.Y.; Li, H.-B. Effects and mechanisms of probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and postbiotics on metabolic diseases targeting gut microbiota: A narrative review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Pan, L.; Wang, B.; Zou, X.; Zhang, A.; Zhou, Z.; Han, Y. Simulated digestion and fecal fermentation behaviors of levan and its impacts on the gut microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 1531–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bañares, C.; Paterson, S.; Gómez-Garre, D.; Ortega-Hernández, A.; Sánchez-González, S.; Cueva, C.; de la Fuente, M.Á.; Hernández-Ledesma, B.; Gómez-Cortés, P. Modulation of gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acid production by simulated gastrointestinal digests from microalga Chlorella vulgaris. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjiwani, M.I.D.; Aryadi, I.P.H.; Semadi, I.M.S. Review of literature on Akkermansia muciniphila and its possible role in the etiopathogenesis and therapy of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. ASEAN Fed. Endocr. Soc. 2022, 37, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, V.F.; Elias-Oliveira, J.; Pereira, Í.S.; Pereira, J.A.; Barbosa, S.C.; Machado, M.S.G.; Carlos, D. Akkermansia muciniphila and gut immune system: A good friendship that attenuates inflammatory bowel disease, obesity, and diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 934695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, K.; Venugopal, S.K.; Lorenzo Pisarello, M.J.; Gradilone, S.A. The role of gut microbiome-derived short-chain fatty acid butyrate in hepatobiliary diseases. Am. J. Pathol. 2023, 193, 1455–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivière, A.; Selak, M.; Lantin, D.; Leroy, F.; De Vuyst, L. Bifidobacteria and butyrate-producing colon bacteria: Importance and strategies for their stimulation in the human gut. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leimbach, A.; Hacker, J.; Dobrindt, U. E. coli as an all-rounder: The thin line between commensalism and pathogenicity. Curr. Topics Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 358, 3–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, I.; Islam, S.; Hassan, A.K.M.I.; Tasnim, Z.; Shuvo, S.R. A brief insight into Citrobacter species—A growing threat to public health. Front. Antib. 2023, 2, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, S.C.; Denger, K.; Burrichter, A.; Irwin, S.M.; Balskus, E.P.; Schleheck, D. A glycyl radical enzyme enables hydrogen sulfide production by the human intestinal bacterium Bilophila wadsworthia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 3171–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natividad, J.M.; Lamas, B.; Pham, H.P.; Michel, M.-L.; Rainteau, D.; Bridonneau, C.; da Costa, G.; van Hylckama Vlieg, J.; Sovran, B.; Chamignon, C.; et al. Bilophila wadsworthia aggravates high fat diet induced metabolic dysfunctions in mice. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, H.; Silva, J.; Santos, T.; Gangadhar, K.N.; Raposo, A.; Nunes, C.; Coimbra, M.A.; Gouveia, L.; Barreira, L.; Varela, J. Nutritional potential and toxicological evaluation of Tetraselmis sp. CTP4 microalgal biomass produced in industrial photobioreactors. Molecules 2019, 24, 3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bastard, Q.; Chapelet, G.; Javaudin, F.; Lepelletier, D.; Batard, E.; Montassier, E. The effects of inulin on gut microbial composition: A systematic review of evidence from human studies. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaak, E.E.; Canfora, E.E.; Theis, S.; Frost, G.; Groen, A.K.; Mithieux, G.; Nauta, A.; Scott, K.; Stahl, B.; van Harsselaar, J.; et al. Short chain fatty acids in human gut and metabolic health. Benef. Microbes 2020, 11, 411–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Lee, G.D.; Son, H.W.; Koh, H.; Kim, E.S.; Unno, T.; Shin, J.H. Butyrate producers, “The Sentinel of Gut”: Their intestinal significance with and beyond butyrate, and prospective use as microbial therapeutics. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1103836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, N.; González, S.; De los Reyes Gavilan, C.G.; Rios-Covian, D. Branched short-chain fatty acids as biological indicators of microbiota health and links with anthropometry. In Biomarkers in Nutrition, Biomarkers in Disease: Methods, Discoveries and Applications; Patel, V.B., Preedy, V.R., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaskiewicz, J.; Zhao, Y.; Hawes, J.W.; Shimomura, Y.; Crabb, D.W.; Harris, R.A. Catabolism of Isobutyrate by Colonocytes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1996, 327, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakeney, B.A.; Crowe, M.S.; Mahavadi, S.; Murthy, K.S.; Grider, J.R. Branched short-chain fatty acid isovaleric acid causes colonic smooth muscle relaxation via CAMP/PKA pathway. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 64, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimann, E.; Nyman, M.; Pålbrink, A.K.; Lindkvist-Petersson, K.; Degerman, E. Branched short-chain fatty acids modulate glucose and lipid metabolism in primary adipocytes. Adipocyte 2016, 5, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandgruber, F.; Gielsdorf, A.; Baur, A.C.; Schenz, B.; Müller, S.M.; Schwerdtle, T.; Stangl, G.I.; Griehl, C.; Lorkowski, S.; Dawczynski, C. Variability in macro- and micronutrients of 15 commercially available microalgae powders. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Medeiros, V.P.B.; Salgaço, M.K.; Pimentel, T.C.; da Silva, T.C.R.; Sartoratto, A.; Lima, M.D.S.; da Costa Sassi, C.F.; Mesa, V.; Magnani, M.; Sivieri, K. Spirulina platensis biomass enhances the proliferation rate of Lactobacillus acidophilus 5 (La-5) and combined with La-5 impact the gut microbiota of medium-age healthy individuals through an in vitro gut microbiome model. Food Res. Int. 2022, 154, 110880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Protein (µg/mL) | Ammonium (mg/L) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Tetraselmis chuii | 0 h | 3056 ± 171 bB | 31.92 ± 2.18 cA |
| 24 h | 1934 ± 74 aB | 269.20 ± 25.38 bA | |
| 48 h | 1922 ± 106 aA | 309.02 ± 16.83 abA | |
| 72 h | 2003 ± 39 aA | 324.03 ± 12.48 aA | |
| Inulin | 0 h | 3362 ± 215 cA | 33.88 ± 7.52 dA |
| 24 h | 2490 ± 103 bA | 105.31 ± 9.94 cB | |
| 48 h | 1930 ± 85 aA | 131.56 ± 3.10 bB | |
| 72 h | 2062 ± 108 aA | 200.16 ± 11.54 aB |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Majchrzak, M.; Paterson, S.; Gutiérrez-Corral, J.; Gómez-Garre, D.; Ortega-Hernández, A.; de la Fuente, M.Á.; Hernández-Ledesma, B.; Gómez-Cortés, P. Modulatory Effects of Tetraselmis chuii Gastrointestinal Digests on Human Colonic Microbiota. Foods 2025, 14, 2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122106
Majchrzak M, Paterson S, Gutiérrez-Corral J, Gómez-Garre D, Ortega-Hernández A, de la Fuente MÁ, Hernández-Ledesma B, Gómez-Cortés P. Modulatory Effects of Tetraselmis chuii Gastrointestinal Digests on Human Colonic Microbiota. Foods. 2025; 14(12):2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122106
Chicago/Turabian StyleMajchrzak, Marta, Samuel Paterson, Javier Gutiérrez-Corral, Dulcenombre Gómez-Garre, Adriana Ortega-Hernández, Miguel Ángel de la Fuente, Blanca Hernández-Ledesma, and Pilar Gómez-Cortés. 2025. "Modulatory Effects of Tetraselmis chuii Gastrointestinal Digests on Human Colonic Microbiota" Foods 14, no. 12: 2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122106
APA StyleMajchrzak, M., Paterson, S., Gutiérrez-Corral, J., Gómez-Garre, D., Ortega-Hernández, A., de la Fuente, M. Á., Hernández-Ledesma, B., & Gómez-Cortés, P. (2025). Modulatory Effects of Tetraselmis chuii Gastrointestinal Digests on Human Colonic Microbiota. Foods, 14(12), 2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122106









