Oat Protein Isolate Mitigates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Rats Through Gut Microbiota, Glucose, and Lipid Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of OPI
2.3. Animal Experimental Design
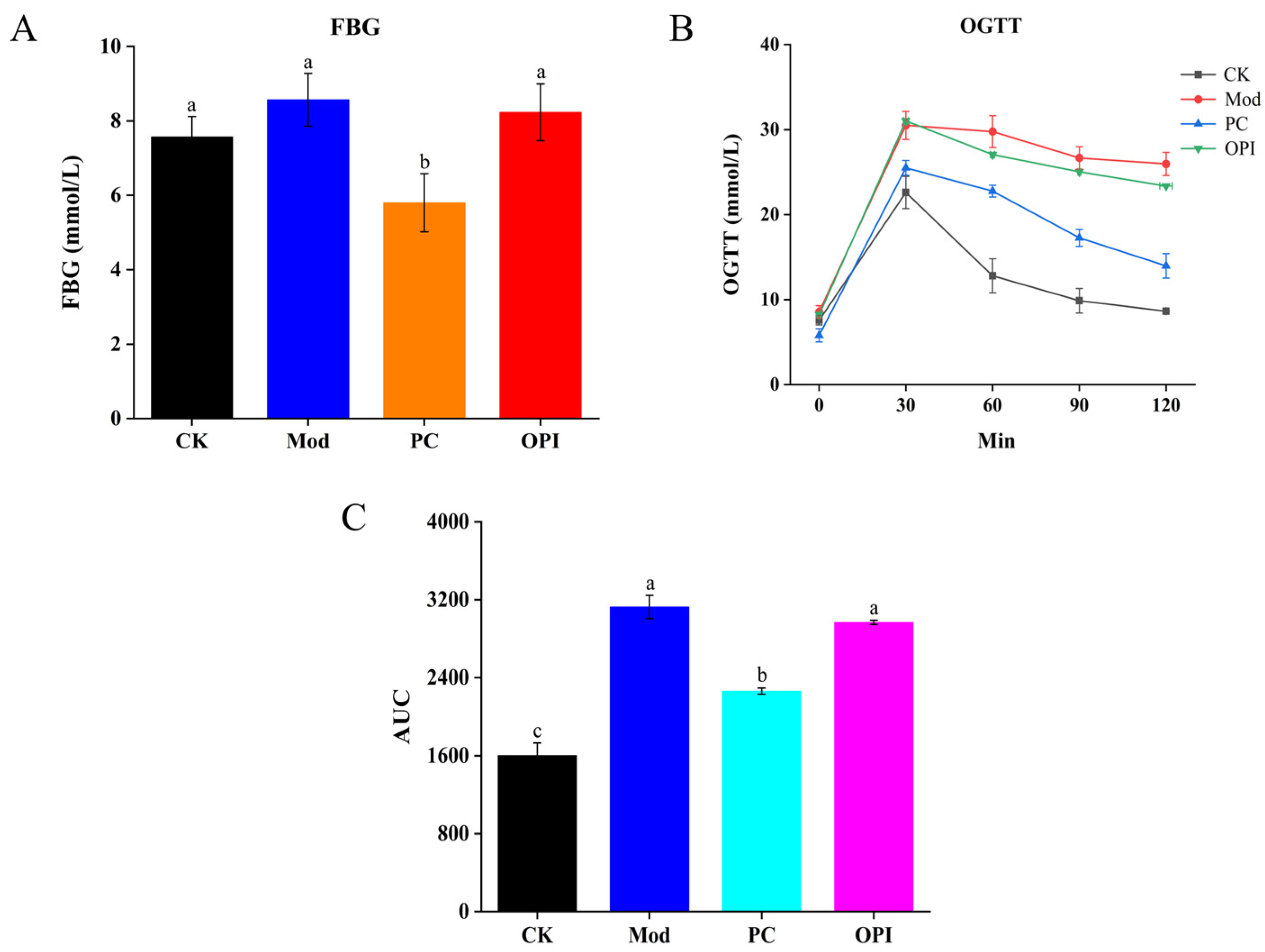
2.4. Fasting Blood Glucose (FBG) and Oral Glucose Tolerance (OGTT)
2.5. Histological Examination
2.6. Biochemical Analysis
2.7. Determination of Oxidative Stress Levels and Proinflammatory Cytokines
2.8. Immunofluorescence Assessment
2.9. Analysis of Gut Microbiota
2.10. Determination of Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
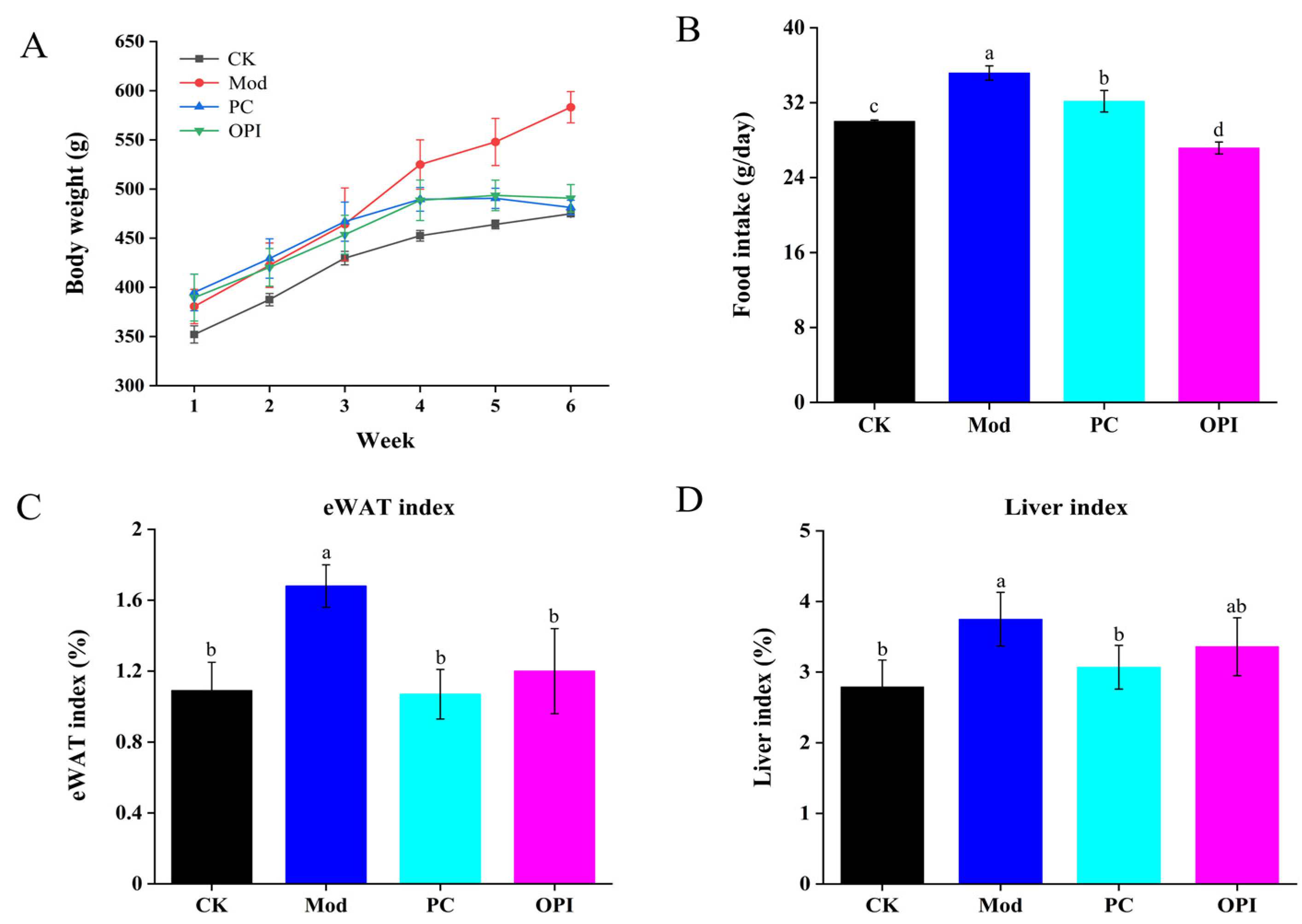
3.1. Effect of OPI on Body Weight, Food Intake, eWAT, and Liver Indices of HFD-Induced Rats
3.2. Effect of OPI on Lipid Levels in Serum of HFD-Induced Rats
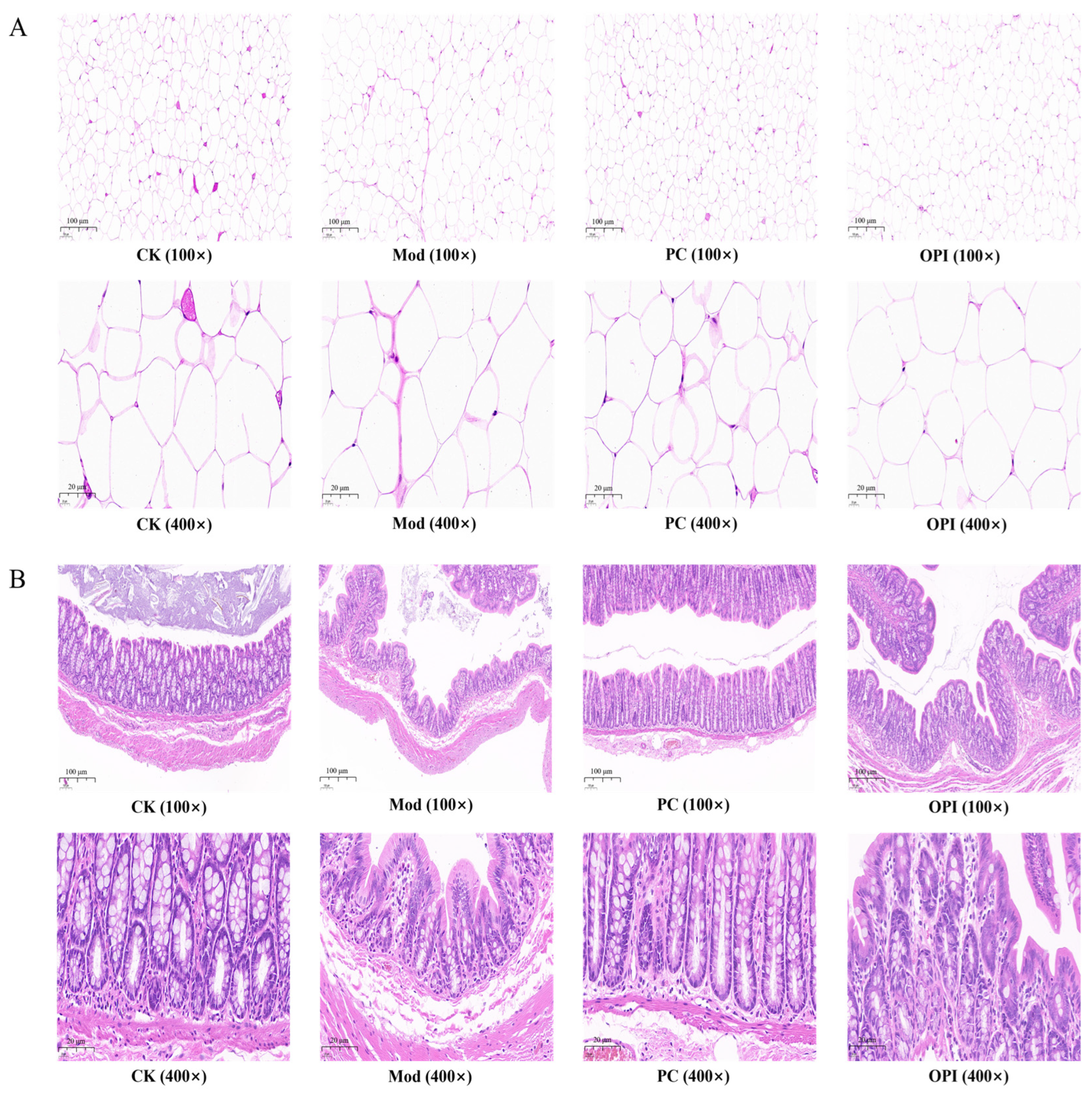
3.3. Histologic Analysis of HFD-Induced Rats Affected by OPI
3.4. Effect of OPI on Liver Biochemical Parameters and Histopathological Features in HFD-Induced Rats
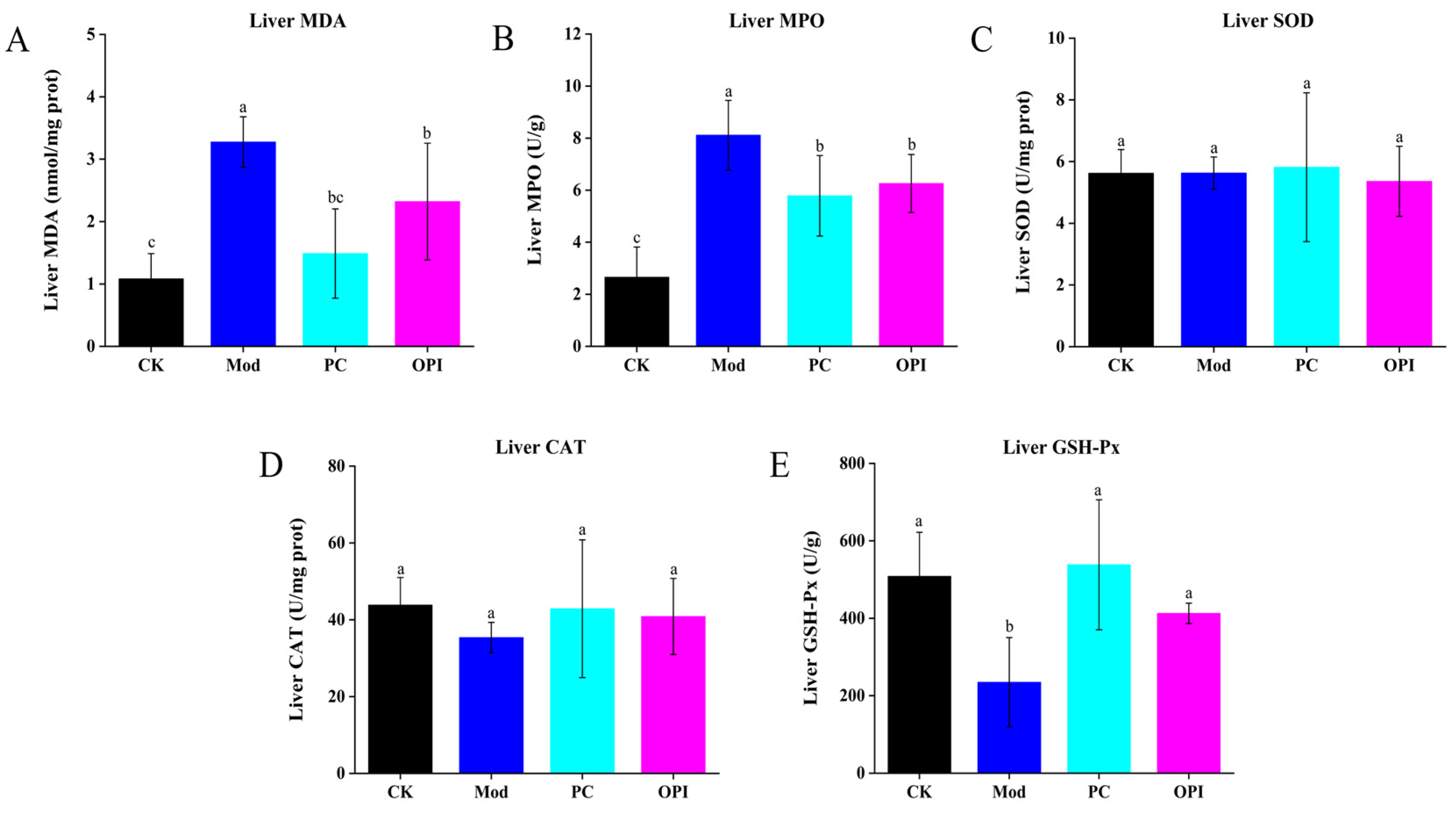
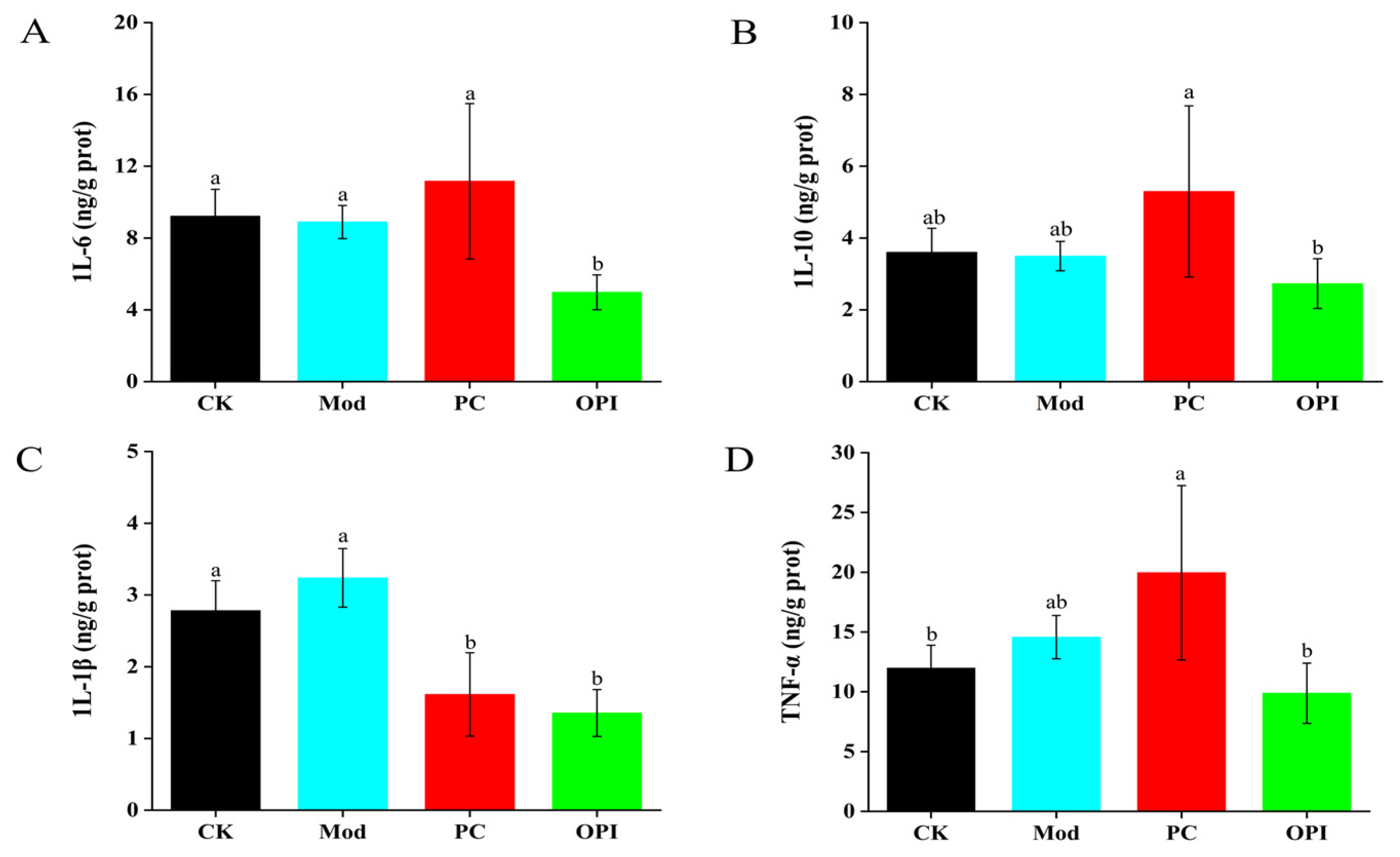
3.5. Effects of OPI on Liver Antioxidant Ability and Inflammatory Response of HFD-Induced Rats
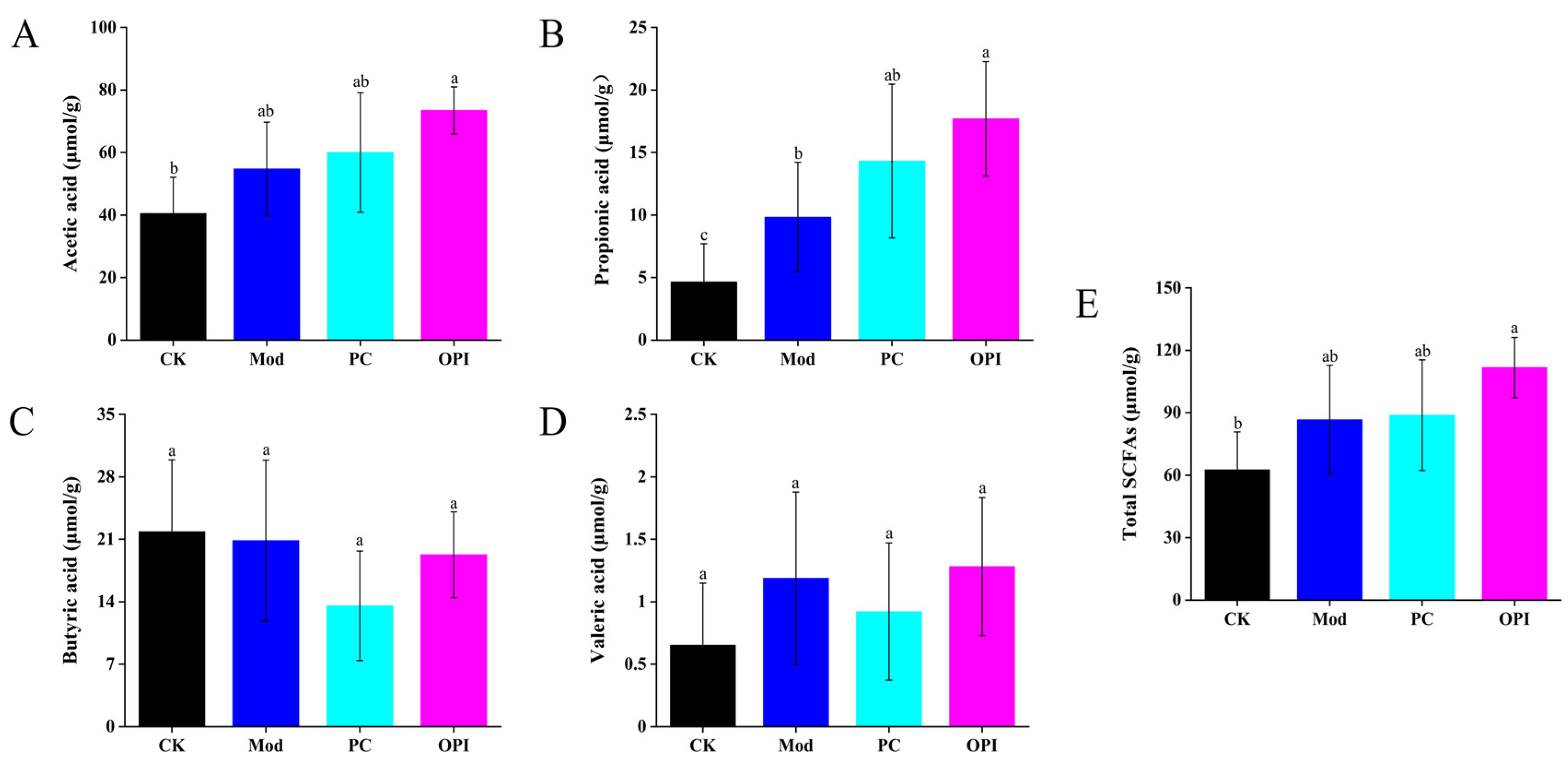
3.6. Effect of OPI on SCFA Levels in HFD-Induced Rats
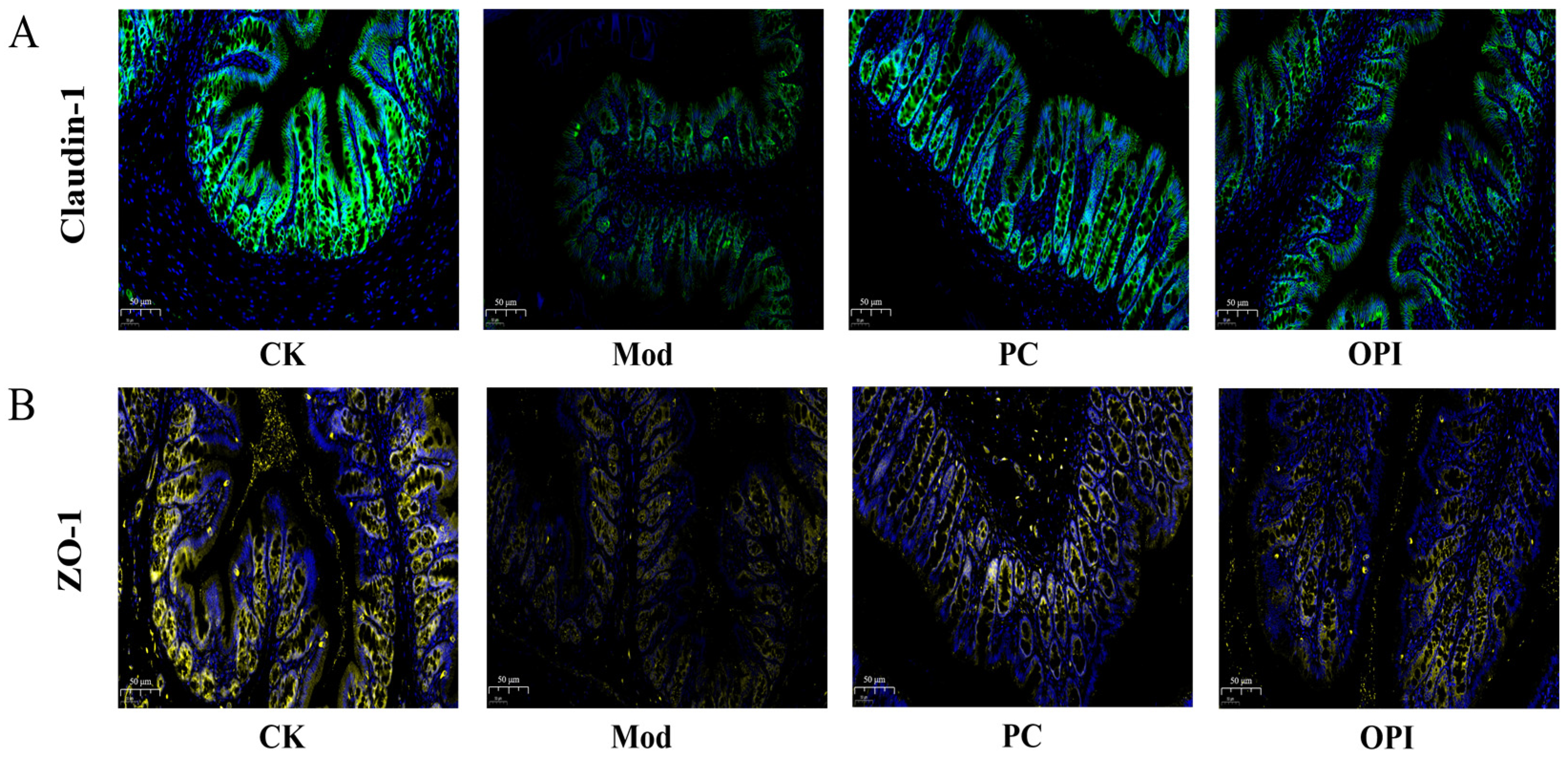
3.7. Effects of OPI on Expression of Tight-Junction Proteins in Colonic Tissues of HFD-Induced Rats
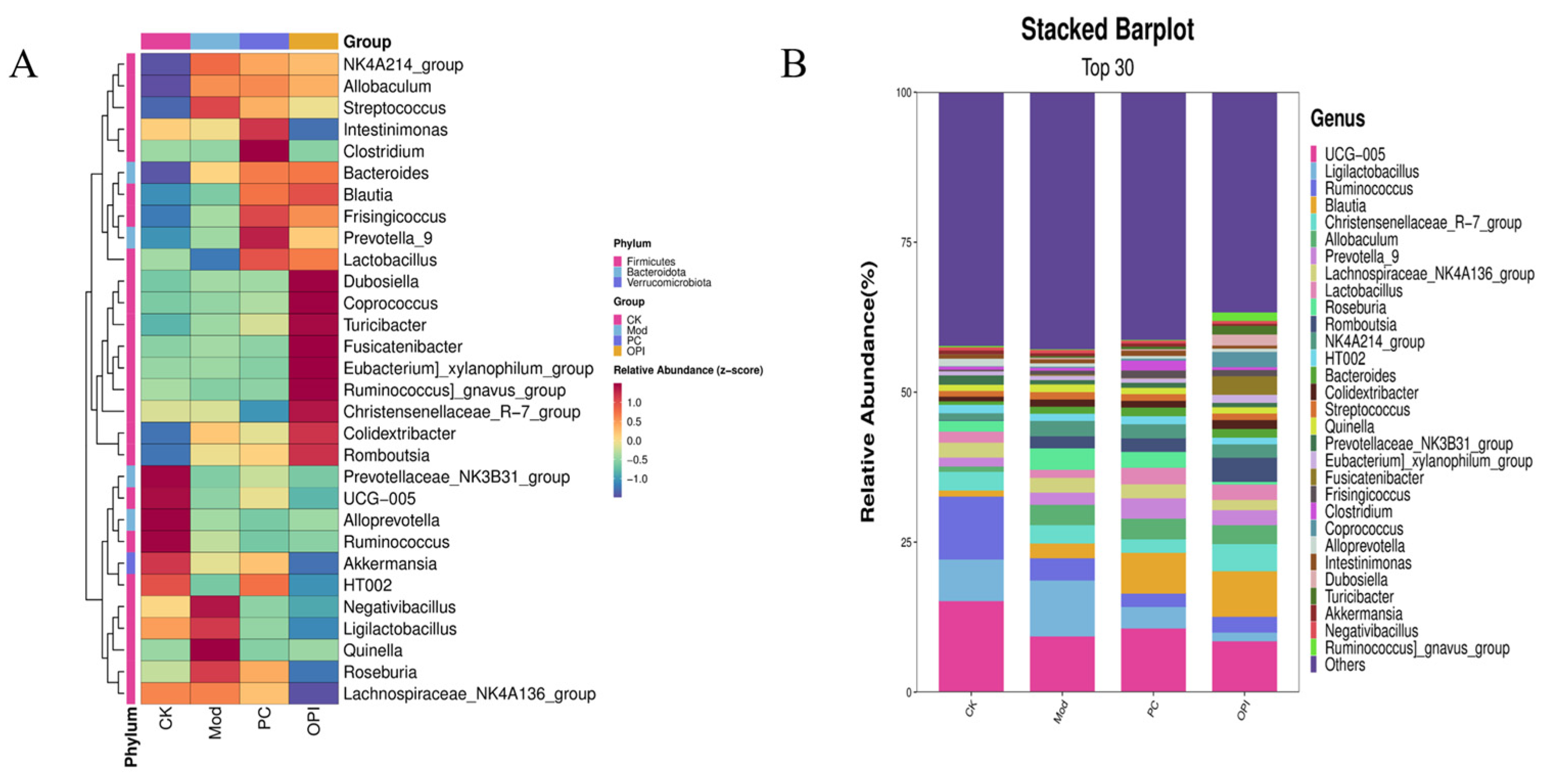
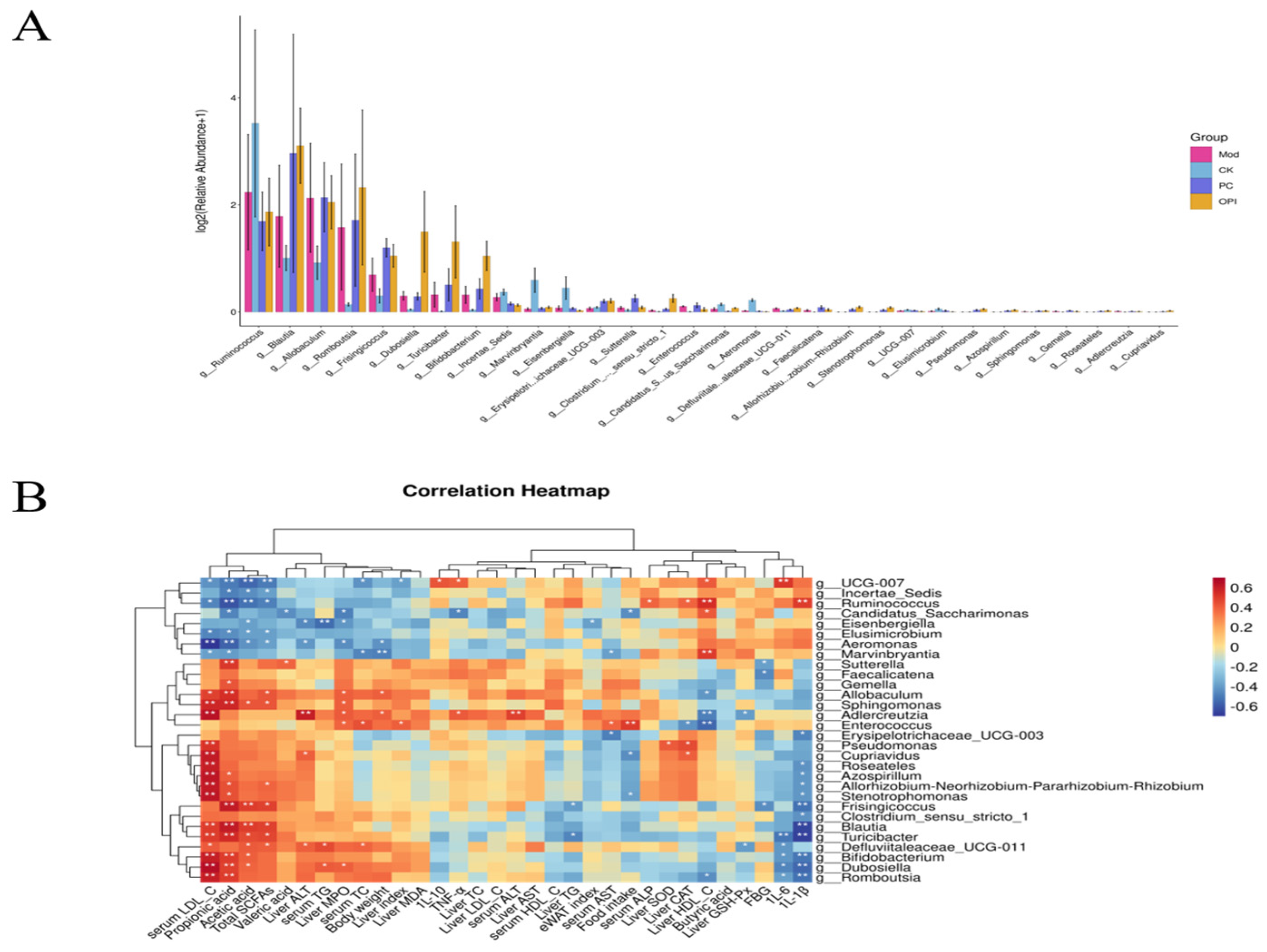
3.8. Effects of OPI Intervention on Gut Microbiota in HFD-Induced Rats
3.9. Correlation Between Intestinal Bacteria and Obesity-Related Indicators
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Endalifer, M.L.; Diress, G. Epidemiology, Predisposing Factors, Biomarkers, and Prevention Mechanism of Obesity: A Systematic Review. J. Obes. 2020, 2020, 6134362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, B.; Zhao, X.; Ao, T.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Gao, X.; Liu, L.; Hu, X.; Yu, Q. The role of bound polyphenols in the anti-obesity effects of defatted rice bran insoluble dietary fiber: An insight from multi-omics. Food Chem. 2024, 459, 140345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Wang, Q.; Han, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, N.; Huang, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhang, R.; Meng, K. In Vitro Evaluation of Probiotic Activities and Anti-Obesity Effects of Enterococcus faecalis EF-1 in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Foods 2024, 13, 4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henney, A.E.; Wilding, J.P. Obesity: Medical management. Medicine 2023, 51, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, P.; Zhang, P.; Chang, Y.; Cui, M.; Duan, J. Protein-Bound β-glucan from Coriolus Versicolor has Potential for Use Against Obesity. Mol. Nutr. Food. Res. 2019, 63, 1801231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Harahap, I.A.; Suthar, P.; Wu, Y.S.; Ghosh, N.; Castro-Muñoz, R. A Comprehensive Review of Phytonutrients as a Dietary Therapy for Obesity. Foods 2023, 12, 3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Hamady, M.; Yatsunenko, T.; Cantarel, B.L.; Duncan, A.; Ley, R.E.; Sogin, M.L.; Jones, W.J.; Roe, B.A.; Affourtit, J.P.; et al. A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 2009, 457, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhao, M.; Yang, M.; Xiao, N.; Wang, J.; Feng, F. Mulberry leaf extract ameliorates high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice by regulating the gut microbiota and metabolites. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indiani, C.M.D.S.P.; Rizzardi, K.F.; Castelo, P.M.; Ferraz, L.F.C.; Darrieux, M.; Parisotto, T.M. Childhood Obesity and Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio in the Gut Microbiota: A Systematic Review. Child. Obes. 2018, 14, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, H.; Xia, Q.; Lu, S. Ougan (Citrus suavissima Hort. ex Tanaka) pomace dietary fibers alleviate high fat diet-induced obesity in mice by regulating intestinal microbiota. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 104997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Yu, P.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Ren, D. Structural characterization and alleviative effects of novel polysaccharides from Artemisia sphaerocephala Krasch seed on obese mice by regulating gut microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 310, 143407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, K.; Niu, M.; Zhao, S. Wheat β-glucan reduces obesity and hyperlipidemia in mice with high-fat and high-salt diet by regulating intestinal flora. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 288, 138754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce-España, E.; Cruz-Chamorro, I.; Santos-Sánchez, G.; Álvarez-López, A.I.; Fernández-Santos, J.M.; Pedroche, J.; Millán-Linares, M.C.; Bejarano, I.; Lardone, P.J.; Carrillo-Vico, A. Anti-obesogenic effect of lupin-derived protein hydrolysate through modulation of adiposopathy, insulin resistance and gut dysbiosis in a diet-induced obese mouse. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 178, 117198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Tao, H.; Peng, Y.; Huang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Tian, W.; Chang, Y.; Zhou, Y. Amur linden honey and its principal polyphenols alleviate obesity and regulate gut microbiota in high-fat diet-induced mice. Food. Chem. X. 2025, 27, 102368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, H.; Dong, R.; Wang, X.; Alim, A.; Aadil, R.M.; Li, L.; Zou, L.; Hu, X. Dietary-Nutraceutical Properties of Oat Protein and Peptides. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 950400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mel, R.; Malalgoda, M. Oat protein as a novel protein ingredient: Structure, functionality, and factors impacting utilization. Cereal Chem. 2022, 99, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLauchlan, J.; Tyler, A.I.I.; Chakrabarti, B.; Orfila, C.; Sarkar, A. Oat protein: Review of structure-function synergies with other plant proteins. Food Hydrocolloid 2024, 154, 110139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, H.; Peng, P.; Hu, X.; Saeed, K.; Khalid, M.Z.; Khalid, W.; Morya, S.; Alsulami, T.; Mugabi, R.; Nayik, G.A. Ultrasound-assisted modification of oat protein isolates: Structural and functional enhancements. Ultrason. Sonochem 2025, 112, 107204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.B.; Liu, X.R.; Liu, S.Q.; Mao, R.X.; Hou, C.; Zhu, N.; Liu, R.; Ma, H.J.; Li, Y. Hypoglycemic Effects of Oat Oligopeptides in High-Calorie Diet/STZ-Induced Diabetic Rats. Molecules 2019, 24, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baakdah, M.M.; Tsopmo, A. Identification of peptides, metal binding and lipid peroxidation activities of HPLC fractions of hydrolyzed oat bran proteins. J. Food. Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 3593–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, L.T.; Guo, L.; Zhou, X.; Qiu, J.; Liu, L.; Zhong, K.; Zhou, S. Effects of dietary oat proteins on cholesterol metabolism of hypercholesterolaemic hamsters. J. Sci. Food. Agr. 2016, 96, 1396–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesh, R.; Srinivasan, K.; Singh, S.A. Effect of arginine:lysine and glycine:methionine intake ratios on dyslipidemia and selected biomarkers implicated in cardiovascular disease: A study with hypercholesterolemic rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 91, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, J.; Raj, P.; Yu, L.; Sobhi, B.; Malalgoda, M.; Malunga, L.; Netticadan, T.; Thandapilly, S.J. Oat protein modulates cholesterol metabolism and improves cardiac systolic function in high fat, high sucrose fed rats. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2024, 49, 738–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litson, L.; Cai, W.; Yang, J.; Prado, C.M.; Chen, L. Identifying peptides from oat protein with potential hypocholesterolemic and satiety effects. J. Funct. Foods. 2025, 128, 106793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; An, Y.; Du, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, Y. Effects of short-chain fatty acids on blood glucose and lipid levels in mouse models of diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 199, 107041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ma, C.M.; Bian, X.; Ren, L.K.; Liu, B.X.; Ai, L.Z.; Zhang, N. The improvement of the oxidative oat (Avena sativa L.) protein based on ultrasound treatment: Study of structural, emulsifying, and rheological properties. Food Hydrocolloid 2023, 144, 109047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Han, X.; Chen, M.; Lu, X.; Zhou, W.; Li, R. Fabrication of tannins and oat protein non-covalent complexes: Effect on the structure and in vitro digestion properties of oat proteins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 304, 140481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Xiang, Q.; Mao, B.; Tang, X.; Cui, S.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Protective Effects of Microbiome-Derived Inosine on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Liver Damage and Inflammation in Mice via Mediating the TLR4/NF-κB Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 7619–7628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.C.; Wu, Q.; Cao, Y.J.; Lin, Y.C.; Guo, W.L.; Rao, P.F.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.T.; Ai, L.Z.; Ni, L. Ganoderic acid A from Ganoderma lucidum protects against alcoholic liver injury through ameliorating the lipid metabolism and modulating the intestinal microbial composition. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 5820–5837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Yu, H.; Han, B.; Lv, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z. Exploring the liver fibrosis induced by deltamethrin exposure in quails and elucidating the protective mechanism of resveratrol. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Perez, W.; Martinez-Lopez, E. Effects of short chain fatty acids on metabolic and inflammatory processes in human health. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2021, 1866, 158900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vourakis, M.; Mayer, G.; Rousseau, G. The Role of Gut Microbiota on Cholesterol Metabolism in Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Wu, Q.; Yao, Q.; Jiang, K.; Yu, J.; Tang, Q. Short-chain fatty acid metabolism and multiple effects on cardiovascular diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 81, 101706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, M. The critical role of short-chain fatty acids in health and disease: A subtle focus on cardiovascular disease-NLRP3 inflammasome-angiogenesis axis. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 238, 109013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jiang, Q.; Lu, H.; Jiang, C.; Hu, W.; Liu, H.; Xiang, X.; Tan, C.P.; Zhou, T.; Shen, G. Effects of Tea Seed Oil Extracted by Different Refining Temperatures on the Intestinal Microbiota of High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Foods 2024, 13, 2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.-L.; Deng, J.-C.; Pan, Y.-Y.; Xu, J.-X.; Hong, J.-L.; Shi, F.-F.; Liu, G.-L.; Qian, M.; Bai, W.-D.; Zhang, W.; et al. Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic activities of Grifola frondosa polysaccharides and their relationships with the modulation of intestinal microflora in diabetic mice induced by high-fat diet and streptozotocin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Song, C.; Feng, X.; Wang, Y.; Meng, T.; Li, S.; Bai, Y.; Du, B.; Sun, Q. Isolation and hypoglycemic effects of water extracts from mulberry leaves in Northeast China. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 3112–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, T.; He, J.; Cui, J.; Wang, J.; Cheng, X.; Fan, J. Oat globulin peptides regulate antidiabetic drug targets and glucose transporters in Caco-2 cells. J. Funct. Foods. 2018, 42, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, A.A.; Ahmed, W.E.; Algonaiman, R.; Alhomaid, R.M.; Almujaydil, M.S.; Althwab, S.A.; Elhassan, A.E.M.; Mousa, H.M. Hypolipidemic, Hypoglycemic, and Ameliorative Effects of Boiled Parsley (Petroselinum crispum) and Mallow (Corchorus olitorius) Leaf Extracts in High-Fat Diet-Fed Rats. Foods 2023, 12, 4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Kang, J.; Chen, B.; Zhong, Y.; Abudurexiti, A.; Zhang, R.; Tan, H.; Ma, X. Effects of Cichorium glandulosum on hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia and intestinal flora in db/db mice. J. Funct. Foods. 2022, 97, 105240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandi, R.; Willmore, W.G.; Tsopmo, A. Peptidomic analysis of hydrolyzed oat bran proteins, and their in vitro antioxidant and metal chelating properties. Food Chem. 2019, 279, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandi, R.; Willmore, W.G.; Tsopmo, A. Antioxidant and Anti-Apoptotic Properties of Oat Bran Protein Hydrolysates in Stressed Hepatic Cells. Foods 2019, 8, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, C.J. Lipid Metabolism in Inflammation and Immune Function. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghikia, A.; Zimmermann, F.; Schumann, P.; Jasina, A.; Roessler, J.; Schmidt, D.; Heinze, P.; Kaisler, J.; Nageswaran, V.; Aigner, A.; et al. Propionate attenuates atherosclerosis by immune-dependent regulation of intestinal cholesterol metabolism. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 43, 518–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poll, B.G.; Xu, J.; Jun, S.; Sanchez, J.; Zaidman, N.A.; He, X.; Laeben, L.; Berkowitz, D.E.; Nazareno, P.; Wei Dong, G.; et al. Acetate, a Short-Chain Fatty Acid, Acutely Lowers Heart Rate and Cardiac Contractility Along with Blood Pressure. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2021, 377, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shen, G.; Lu, H.; Jiang, C.; Hu, W.; Jiang, Q.; Xiang, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L. Psidium guajava Seed Oil Reduces the Severity of Colitis Induced by Dextran Sulfate Sodium by Modulating the Intestinal Microbiota and Restoring the Intestinal Barrier. Foods 2024, 13, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasim, S.A.; Opulencia, M.J.C.; Ramírez-Coronel, A.A.; Abdelbasset, W.K.; Abed, M.H.; Markov, A. The emerging role of microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids in immunometabolism. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 110, 108983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.J.; Sears, C.L.; Maruthur, N. Gut microbiome and its role in obesity and insulin resistance. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2020, 1461, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yang, M.; Liu, C.; Du, Z. Egg white-derived peptides co-assembly-reinforced zein/chondroitin sulfate nanoparticles for orally colon-targeted co-delivery of quercetin in colitis mitigation. Food Biosci. 2025, 65, 106161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Wu, Q.; Li, W.; Tang, K.; Zhang, J. Effects of Lactobacillus supplementation on glycemic and lipid indices in overweight or obese adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 1787–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, B.; Hu, J.; Nie, S.; Xiong, T.; Xie, M. Intervention of five strains of Lactobacillus on obesity in mice induced by high-fat diet. J. Funct. Foods. 2020, 72, 104078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozato, N.; Saito, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Katashima, M.; Tokuda, I.; Sawada, K.; Katsuragi, Y.; Kakuta, M.; Imoto, S.; Ihara, K.; et al. Blautia genus associated with visceral fat accumulation in adults 20–76 years of age. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2019, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, R.; Li, P. MNAM enhances Blautia abundance and modulates Th17/Treg balance to alleviate diabetes in T2DM mice. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 230, 116593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Qi, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Hu, C.; Zhao, L.; Zhan, H.; Bian, H.; Ma, Y. Anti-obesity and gut microbiota modulation effects of chondroitin sulfate on obese mice induced by high-fat diet. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 298, 139968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Groups | TC (mmol/L) | TG (mmol/L) | LDL-C (mmol/L) | HDL-C (mmol/L) | AST (U/L) | ALT (U/L) | AST/ALT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.64 ± 0.11 c | 1.19 ± 0.39 b | 0.33 ± 0.08 b | 1.27 ± 0.22 a | 134.57 ± 15.15 b | 56.00 ± 9.09 a | 2.50 ± 0.52 a |
| Mod | 1.68 ± 0.08 a | 2.30 ± 0.38 a | 0.95 ± 0.42 a | 1.46 ± 0.30 a | 236.43 ± 45.35 a | 74.43 ± 15.41 a | 3.30 ± 0.89 a |
| PC | 0.71 ± 0.06 bc | 1.34 ± 0.46 b | 0.74 ± 0.24 a | 1.41 ± 0.28 a | 144.86 ± 23.86 b | 60.29 ± 15.50 a | 2.50 ± 0.70 a |
| OPI | 0.79 ± 0.10 b | 1.98 ± 0.41 a | 1.11 ± 0.23 a | 1.30 ± 0.39 a | 138.86 ± 46.91 b | 62.14 ± 26.49 a | 2.33 ± 0.51 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Han, X.; Chen, M.; Li, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, R. Oat Protein Isolate Mitigates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Rats Through Gut Microbiota, Glucose, and Lipid Control. Foods 2025, 14, 2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122047
Chen X, Han X, Chen M, Li J, Zhou W, Li R. Oat Protein Isolate Mitigates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Rats Through Gut Microbiota, Glucose, and Lipid Control. Foods. 2025; 14(12):2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122047
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xi, Xue Han, Mianhong Chen, Jihua Li, Wei Zhou, and Ruyi Li. 2025. "Oat Protein Isolate Mitigates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Rats Through Gut Microbiota, Glucose, and Lipid Control" Foods 14, no. 12: 2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122047
APA StyleChen, X., Han, X., Chen, M., Li, J., Zhou, W., & Li, R. (2025). Oat Protein Isolate Mitigates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Rats Through Gut Microbiota, Glucose, and Lipid Control. Foods, 14(12), 2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122047






