Effects of Aqueous Extracts from Wheat Bran Layers on the Functional Properties of Wheat Starch and Gluten
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.2.1. Separation of AL and Non-AL Fractions
2.2.2. Preparation of Extracts from WB Layers
2.2.3. Separation of Major Components in WB-E
2.2.4. Extraction of Starch and Gluten Proteins
2.2.5. Preparation of Blended Flour
2.3. Chemical Composition Analysis
2.4. Microscopic Observation
2.5. Thermal Properties
2.6. Dynamic Rheological Properties
2.7. Pasting Characteristics
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
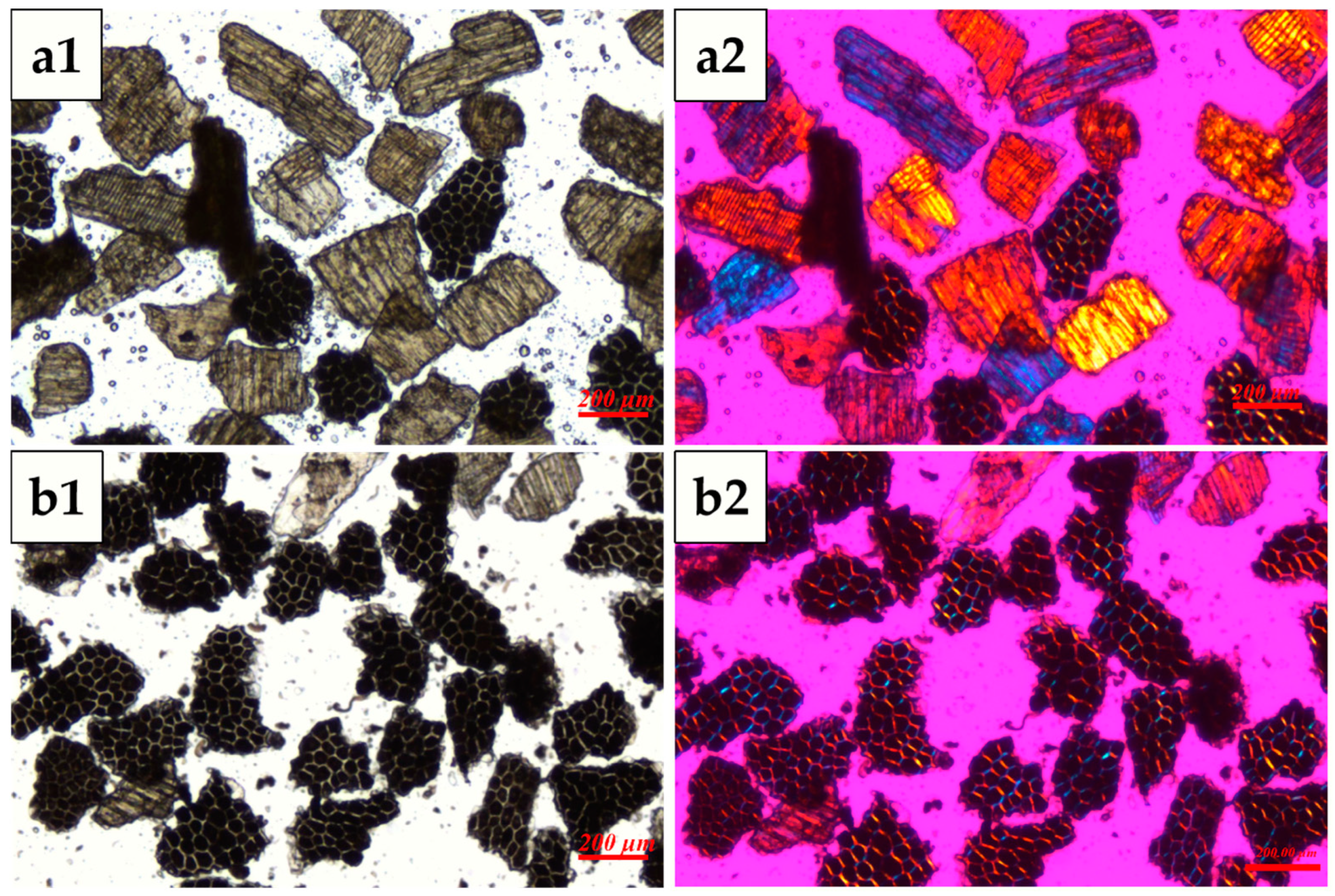
3.1. Microstructure and Chemical Composition of WB Fractions Before Water Extraction
3.2. Composition of Aqueous Extracts and Residuals from Different WB Layers Fractions
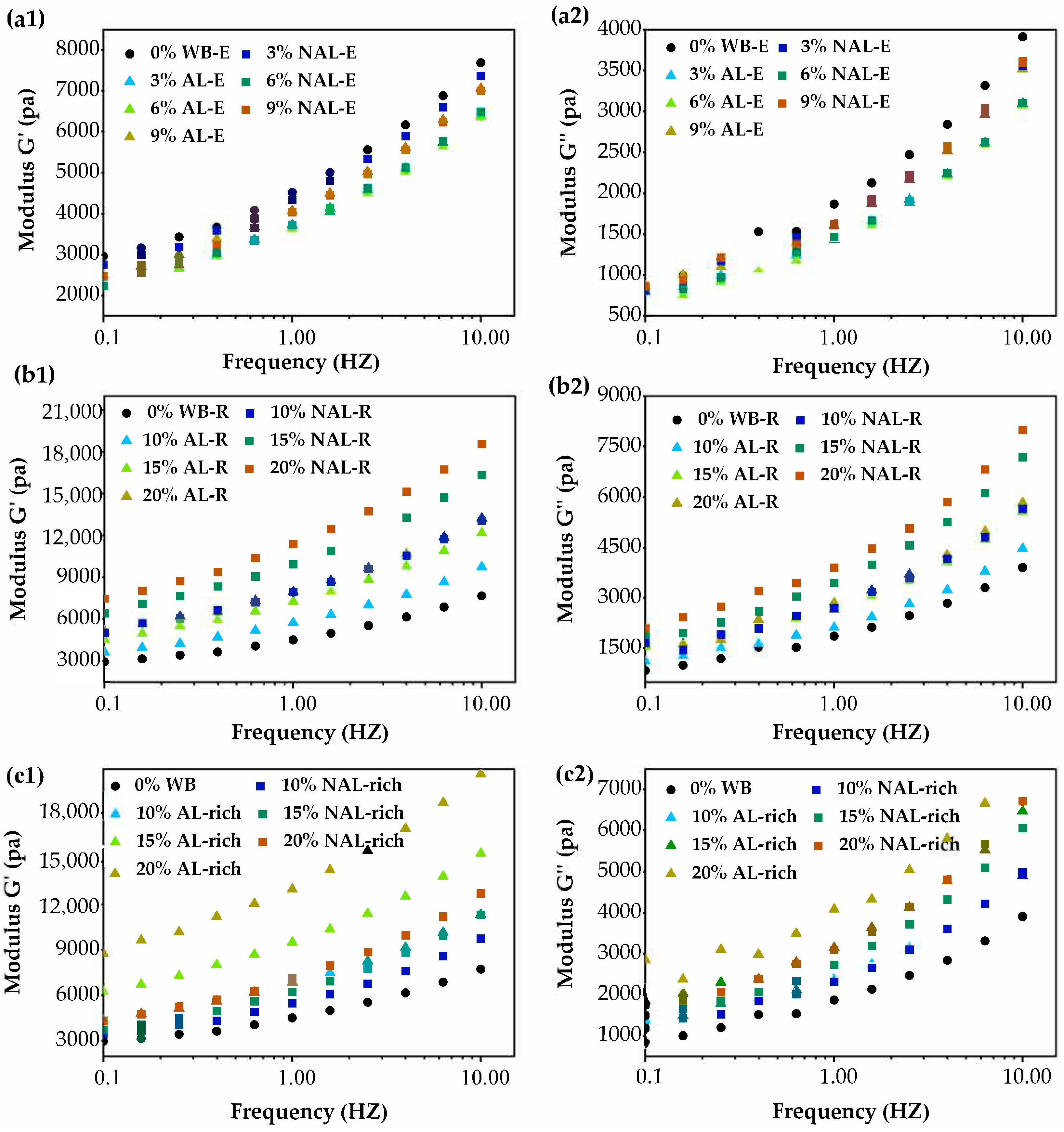
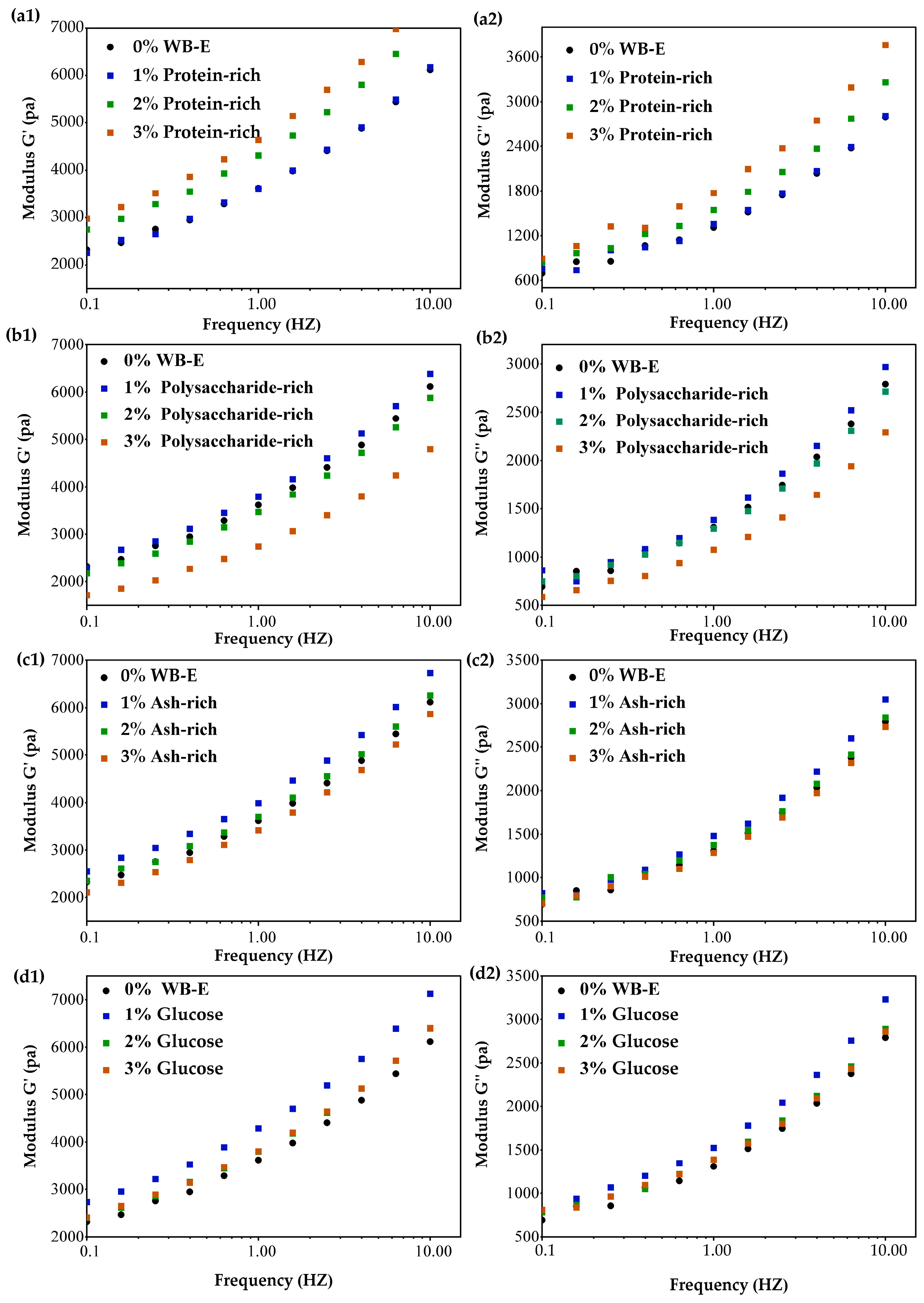
3.3. Influence of WB-E on Thermal and Rheological Properties of Wheat Gluten
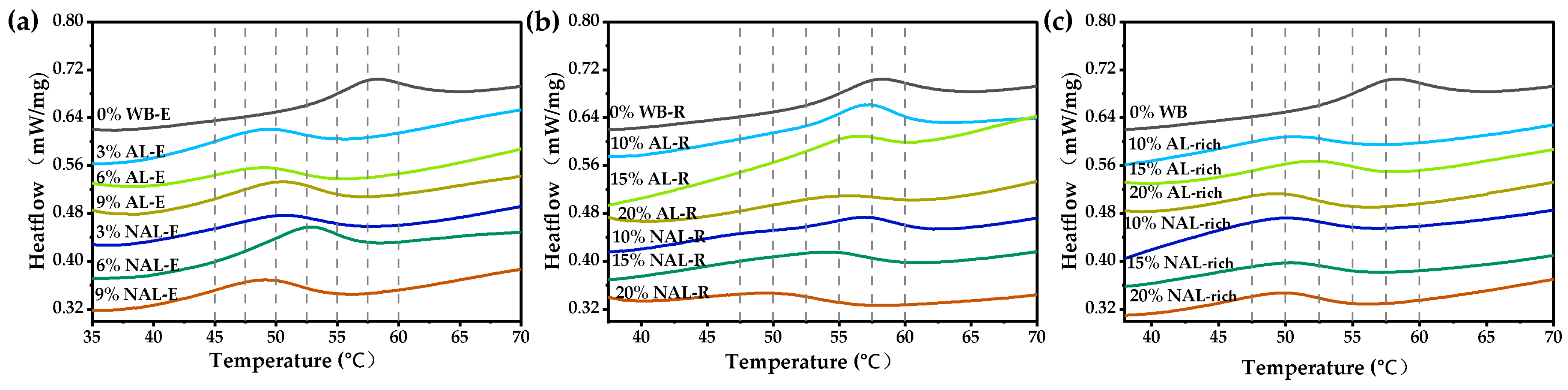
3.4. Influence of WB-E on Thermal Properties and Pasting Characteristics of Starch
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Z.; Mense, A.L.; Brewer, L.R.; Shi, Y. Wheat bran layers: Composition, structure, fractionation, and potential uses in foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 6636–6659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Liu, G.; Cao, X.; Zhu, S.; Li, Q.; Ji, G.; Han, Y.; Xiao, H. Hypoglycemic effects of wheat bran alkyresorcinols in high-fat/high-sucrose diet and low-dose streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic male mice and protection of pancreatic β cells. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 3282–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, M.; Rakha, A.; Xiaobo, Z.; Mahmood, M.A. Complimenting gluten free bakery products with dietary fiber: Opportunities and constraints. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 83, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, L.; Xiong, Y.; Tong, L.; Wang, F.; Fan, B.; Gong, J. Effect of different agricultural conditions, practices, and processing on levels of total arsenic and species in cereals and vegetables: A review. Food Control 2023, 152, 109876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirhadi, M.; Shariatifar, N.; Bahmani, M.; Manouchehri, A. Heavy metals in wheat grain and its impact on human health: A mini-review. J. Chem. Health Risks 2022, 12, 421–426. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, K.H.; Ohm, J.B.; Simsek, S. Whole wheat bread: Effect of bran fractions on dough and end-product quality. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 78, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Stump, M.; Wu, W.; Li, Y. Exploring the chemical composition, antioxidant potential, and bread quality effects of the nutritional powerhouse: Wheat bran—A mini-review. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 14, 100898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoine, C.; Peyron, S.; Mabille, F.; Lapierre, C.; Bouchet, B.; Abecassis, J.; Rouau, X. Individual contribution of grain outer layers and their cell wall structure to the mechanical properties of wheat bran. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 2026–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemery, Y.; Rouau, X.; Lullien-Pellerin, V.; Barron, C.; Abecassis, J. Dry processes to develop wheat fractions and products with enhanced nutritional quality. J. Cereal Sci. 2007, 46, 327–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, B.A. Cell Walls of Cereal Grains. Cereal Foods World 2006, 51, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Mense, A.L.; Brewer, L.R.; Shi, Y.C. Wheat bran arabinoxylans: Chemical structure, extraction, properties, health benefits, and uses in foods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, 13366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Yang, W.; Wu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Wei, Z.; Wang, T.; Ampofo, K.A.; Ma, H.; Cui, F.; Yang, X. ARTP mutagenesis to improve mycelial polysaccharide production of Grifola frondosa using a mixture of wheat bran and Rice bran as substrate. J. Food Qual. 2021, 2021, 6110743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prueckler, M.; Siebenhandl-Ehn, S.; Apprich, S.; Hoeltinger, S.; Haas, C.; Schmid, E.; Kneifel, W. Wheat bran-based biorefinery 1: Composition of wheat bran and strategies of functionalization. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 56, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Qiao, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Q.; Ou, X.; Wang, X. Isolation, structural, functional, and bioactive properties of cereal arabinoxylan—A critical review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 15437–15457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederix, S.A.; Van Hoeymissen, K.E.; Courtin, C.M.; Delcour, J.A. Water-extractable and water-unextractable arabinoxylans affect gluten agglomeration behavior during wheat flour gluten−starch separation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 7950–7956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Hou, C.; Zhao, X.; Tian, M.; Gu, Z.; Yang, R. Molecular characterization of water-extractable arabinoxylan from wheat bran and its effect on the heat-induced polymerization of gluten and steamed bread quality. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balandrán-Quintana, R.R.; Mercado-Ruiz, J.N.; Mendoza-Wilson, A.M. Wheat bran proteins: A review of their uses and potential. Food Rev. Int. 2015, 31, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzuwaid, N.T.; Pleming, D.; Fellows, C.M.; Sissons, M. Fortification of durum wheat spaghetti and common wheat bread with wheat bran protein concentrate-impacts on nutrition and technological properties. Food Chem. 2021, 334, 127497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzuwaid, N.T.; Sissons, M.; Laddomada, B.; Fellows, C.M. Nutritional and functional properties of durum wheat bran protein concentrate. Cereal Chem. 2019, 97, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bondt, Y.; Liberloo, I.; Roye, C.; Goos, P.; Courtin, C.M. The impact of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) bran on wheat starch gelatinization: A differential scanning calorimetry study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 241, 116262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Wu, L.; Cai, W.; Xiao, G.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, H. Subcritical water extraction-based methods affect the physicochemical and functional properties of soluble dietary fibers from wheat bran. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 124987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hassane Hamadou, A.; Shen, Q.; Xu, B. Tempering–preservation treatment inactivated lipase in wheat bran and retained phenolic compounds. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 57, 2104–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mense, A.L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Q.; Shi, Y. Hydrothermal treatment and enzymatic hydrolysis of wheat bran and their effects on physical structure. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 4, 642–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, G.; Tilley, M.; Chen, R.; Perez-Fajardo, M.; Wu, X.; Li, Y. Enhancing gluten network formation and bread-making performance of wheat flour using wheat bran aqueous extract. Foods 2024, 13, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wootton, M.; Shams-Ud-Din, M. The effects of aqueous extraction on the performance of wheat bran in bread. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1986, 37, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obadi, M.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Y.; Xu, B. Factors affecting frozen cooked noodle quality: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, C.; Li, E.; Gilbert, R.G.; Xu, B. A molecular explanation of wheat starch physicochemical properties related to noodle eating quality. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 106035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Li, H.; Li, D.; Zhang, D.; Huang, Y.; Obadi, M.; Xu, B. The relation between wheat starch properties and noodle springiness: From the view of microstructure quantitative analysis of gluten-based network. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Xia, Q.; Zha, B.; Sun, J.; Xu, B.; Chen, Z. Triboelectric separation of wheat bran tissues: Influence of tribo–material, water content, and particle size. J. Food Process Eng. 2020, 43, 13346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z. Triboelectric separation of aleurone cell-cluster from wheat bran fragments in nonuniform electric field. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teobaldi, A.G.; Barrera, G.N.; Ribotta, P.D. Effect of damaged starch and wheat-bran arabinoxylans on wheat starch and wheat starch–gluten systems. Foods 2024, 13, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Association of Cereal Chemists. Approved Methods of the AACC, 11th ed.; The Association: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2009; Volume 1, Method 44-15, 30-25, 46-10, 08-01, 76-21 and 66-50. [Google Scholar]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 19th ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2012; AOAC Official Method 006.011 and 965.017. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, S.S. Phenol-sulfuric acid method for total carbohydrates. In Food Analysis Laboratory Manual; Nielsen, S.S., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, A.; Jain, R.; Jain, S. Quantitative analysis of reducing sugars by 3, 5-dinitrosalicylic acid (DNSA method). In Basic Techniques in Biochemistry, Microbiology and Molecular Biology; Jain, A., Jain, R., Jain, S., Eds.; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 181–183. [Google Scholar]
- Antoine, C.; Peyron, S.; Lullien-Pellerin, V.; Abecassis, J.; Rouau, X. Wheat bran tissue fractionation using biochemical markers. J. Cereal Sci. 2004, 39, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobberstein, D.; Bunzel, M. Separation and detection of cell wall-bound ferulic acid dehydrodimers and dehydrotrimers in cereals and other plant materials by reversed phase high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 8927–8935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Shen, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, B. Intact aleurone cells limit the hydrolysis of endogenous lipids in wheat bran during storage. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna-Valdez, J.; Balandrán-Quintana, R.; Azamar-Barrios, J.; Clamont-Montfort, G.R.; Mendoza-Wilson, A.; Mercado-Ruiz, J.; Madera-Santana, T.; Rascon-Chu, A.; Chaquilla-Quilca, G. Structural and physicochemical characterization of nanoparticles synthesized from an aqueous extract of wheat bran by a cold-set gelation/desolvation approach. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 62, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hamer, R.J.; Vliet, T.V.; Gruppen, H.; Marseille, H.; Weegels, P.L. Effect of water unextractable solids on gluten formation and properties: Mechanistic considerations. J. Cereal Sci. 2002, 37, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noort, M.W.J.; Haaster, D.V.; Hemery, Y.; Schols, H.A.; Hamer, R.J. The effect of particle size of wheat bran fractions on bread quality—Evidence for fibre–protein interactions. J. Cereal Sci. 2010, 52, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-T.; Kerr, E.D.; Schulz, B.L.; Gidley, M.J.; Dhital, S. Pasting properties of high-amylose wheat in conventional and high-temperature Rapid Visco Analyzer: Molecular contribution of starch and gluten proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.A.; Soh, C.H.; Ganguli, N.K.; Sissons, M. A survey of water–extractable arabinopolymers in bread and durum wheat and the effect of water-extractable arabinoxylan on durum dough rheology and spaghetti cooking quality. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2008, 88, 2551–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labat, E.; Rouau, X.; Morel, M.-H. Effect of flour water-extractable pentosans on molecular associations in gluten during mixing. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2002, 35, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Obadi, M.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, S.; Xu, B. Effect of steaming and defatting treatments of oats on the processing and eating quality of noodles with a high oat flour content. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 89, 102794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chao, H.; Xu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, N. Bran characteristics impact the whole wheat noodle quality. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, 29322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.; Hoseney, R. Role of salt in baking. Cereal Foods World 2008, 53, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, R.; Sommerville, M. The effects of non-starch polysaccharides on the extent of gelatinisation, swelling and α-amylase hydrolysis of maize and wheat starches. Food Hydrocoll. 2003, 17, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhong, F.; Douglas Goff, H.; Li, Y. Study on starch-protein interactions and their effects on physicochemical and digestible properties of the blends. Food Chem. 2019, 280, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, G.; Blanchard, C.; Zhao, J. Effects of glutelin and globulin on the physicochemical properties of rice starch and flour. J. Cereal Sci. 2014, 60, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, S.; Obadi, M.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Jiang, S.; Xu, B. The impact of starch degradation induced by pre-gelatinization treatment on the quality of noodles. Food Chem. 2020, 302, 125267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miaomiao, S.; Xuena, D.; Yanqiu, C.; Xiaolong, J.; Yanqi, L.; Yizhe, Y. Preparation and characterization of extruded yam starch–soy protein isolate complexes and their effects on the quality of dough. Foods 2023, 12, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jane, J.L. Mechanism of Starch Gelatinization in Neutral Salt Solutions. Starch-Stärke 2006, 45, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samutsri, W.; Suphantharika, M. Effect of salts on pasting, thermal, and rheological properties of rice starch in the presence of non-ionic and ionic hydrocolloids. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 1559–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Liu, Q.; Lin, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Qiu, C.; Jiao, A.; Jin, Z. The influence of water-soluble arabinoxylan on the rheological properties of model dough and the interfacial properties of imitation dough liquor. Food Chem. 2025, 483, 144307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Huang-Fu, Z.-Y.; Tian, X.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Hu, X.; Zou, L. Arabinoxylan of varied structural features distinctively affects the functional and in vitro digestibility of wheat starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 140, 108615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, X.; Zhu, L.; Xiang, M.; Zhao, S.; Cheng, Z.; Qiao, D.; Zhang, B. Insight of soy protein isolate to decrease the gel properties corn starch based binary system: Rheological and structural investigation. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 160, 110750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




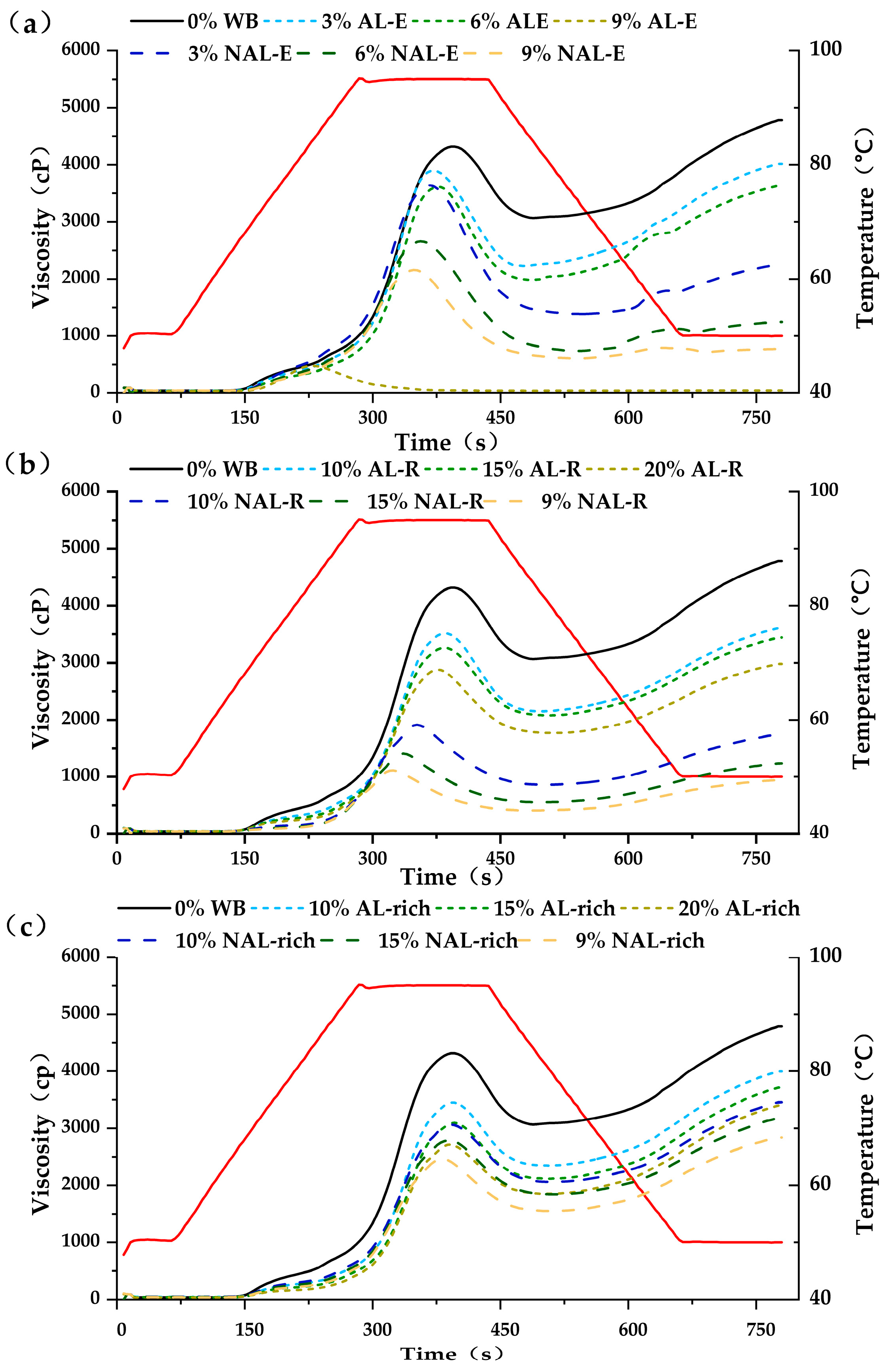
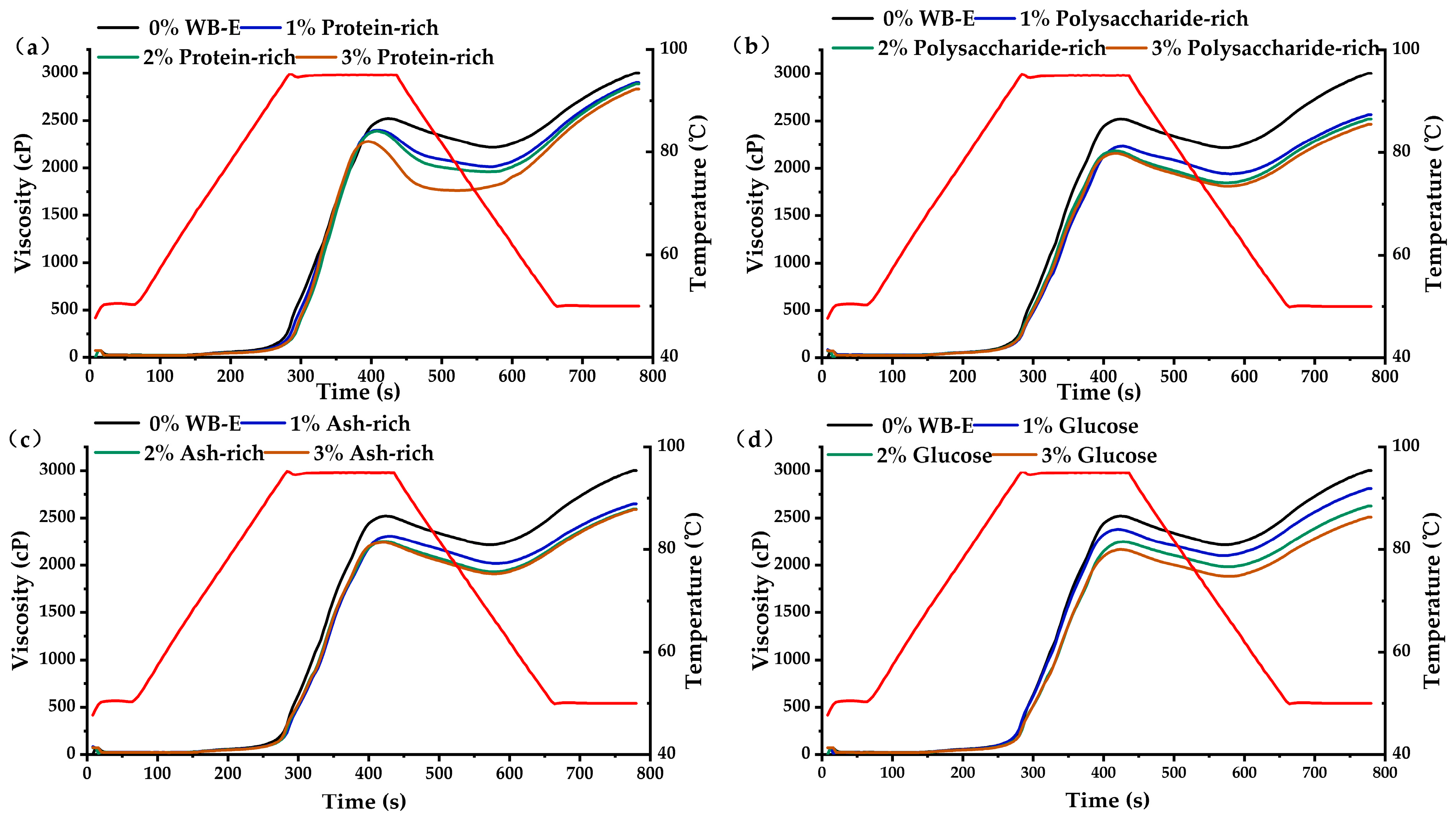
| Samples | Wheat Bran | AL-Rich Fraction | NAL-Rich Fraction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water (%) | 10.13 ± 0.05 a | 9.19 ± 0.05 b | 8.01 ± 0.23 c |
| Starch (%) | 13.08 ± 0.16 a | 3.58 ± 0.01 b | 2.13 ± 0.04 c |
| Lipids (%) | 3.22 ± 0.06 b | 5.41 ± 0.03 a | 2.98 ± 0.14 b |
| Ash (%) | 6.22 ± 0.02 b | 9.85 ± 0.04 a | 5.15 ± 0.04 c |
| Phosphorus (%) | 1.29 ± 0.00 b | 2.18 ± 0.04 a | 0.93 ± 0.01 c |
| Protein (%) | 16.56 ± 0.02 b | 20.13 ± 0.00 a | 11.86 ± 0.01 c |
| Ferulic acid (mg/g) | 4.150 ± 0.630 a | 5.077 ± 0.628 a | 3.924 ± 0.332 a |
| p-coumaric acid (mg/g) | 0.498 ± 0.056 a | 0.608 ± 0.017 a | 0.534 ± 0.033 a |
| Proportion of AL (%) | 44.9% | 75.9% | 32.4% |
| WB Layer Fractions | AL-Rich Fraction | NAL-Rich Fraction | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AL-E | AL-R | NAL-E | NAL-R | |
| Yield (%) | 30.61 ± 0.79 c | 68.44 ± 1.16 b | 15.08 ± 0.45 d | 83.73 ± 0.74 a |
| Water (%) | 8.94 ± 0.22 b | 10.94 ± 0.03 a | 9.40 ± 0.17 b | 11.07 ± 0.09 a |
| Ash (%) | 19.51 ± 0.00 a | 5.85 ± 0.08 c | 16.09 ± 0.02 b | 2.77 ± 0.01 d |
| Protein (%) | 29.41 ± 0.43 a | 16.15 ± 0.32 c | 22.61 ± 0.85 b | 9.96 ± 0.28 d |
| Lipids (%) | 4.38 ± 0.02 b | 5.85 ± 0.14 a | 2.14 ± 0.03 d | 3.54 ± 0.09 c |
| Non-Starch polysaccharide (%) | 29.89 ± 0.21 d | 58.52 ± 0.11 b | 39.04 ± 0.18 c | 70.65 ± 0.15 a |
| Phosphorus (%) | 3.83 ± 0.01 a | 1.08 ± 0.05 c | 2.81 ± 0.01 b | 0.62 ± 0.01 d |
| Composition | WB-E | Protein-Rich Fraction | Polysaccharide-Rich Fraction | Ash-Rich Fraction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water (%) | 23.69 ± 0.40 b | 6.34 ± 0.12 d | 10.16 ± 0.28 c | 29.89 ± 0.83 a |
| Protein (%) | 23.32 ± 0.0.26 c | 78.34 ± 0.54 a | 9.89 ± 0.48 d | 17.12 ± 0.29 b |
| Ash (%) | 19.25 ± 0.00 b | 1.84 ± 0.17 d | 18.06 ± 0.05 c | 32.35 ± 0.40 a |
| Total carbohydrates (%) | 31.70 ± 1.03 c | 13.10 ± 1.03 d | 53.44 ± 1.66 a | 20.51 ± 0.24 b |
| Reducing sugar (%) | 8.19 ± 0.22 b | 2.05 ± 0.07 c | 3.19 ± 0.09 c | 19.20 ± 0.64 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, B.; Yu, C.; Chen, Z.; Xu, B. Effects of Aqueous Extracts from Wheat Bran Layers on the Functional Properties of Wheat Starch and Gluten. Foods 2025, 14, 1988. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111988
Wu B, Yu C, Chen Z, Xu B. Effects of Aqueous Extracts from Wheat Bran Layers on the Functional Properties of Wheat Starch and Gluten. Foods. 2025; 14(11):1988. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111988
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Bingbing, Chunlei Yu, Zhongwei Chen, and Bin Xu. 2025. "Effects of Aqueous Extracts from Wheat Bran Layers on the Functional Properties of Wheat Starch and Gluten" Foods 14, no. 11: 1988. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111988
APA StyleWu, B., Yu, C., Chen, Z., & Xu, B. (2025). Effects of Aqueous Extracts from Wheat Bran Layers on the Functional Properties of Wheat Starch and Gluten. Foods, 14(11), 1988. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111988







