Large Yellow Croaker Roe Protein Isolates/Gellan Gum Hydrogels Improve the Alleviating Effect of Curcumin on DSS-Induced Colitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Cur-Loaded PG Hydrogels
2.3. Cryo-Scanning Electron Microscopy (Cryo-SEM)
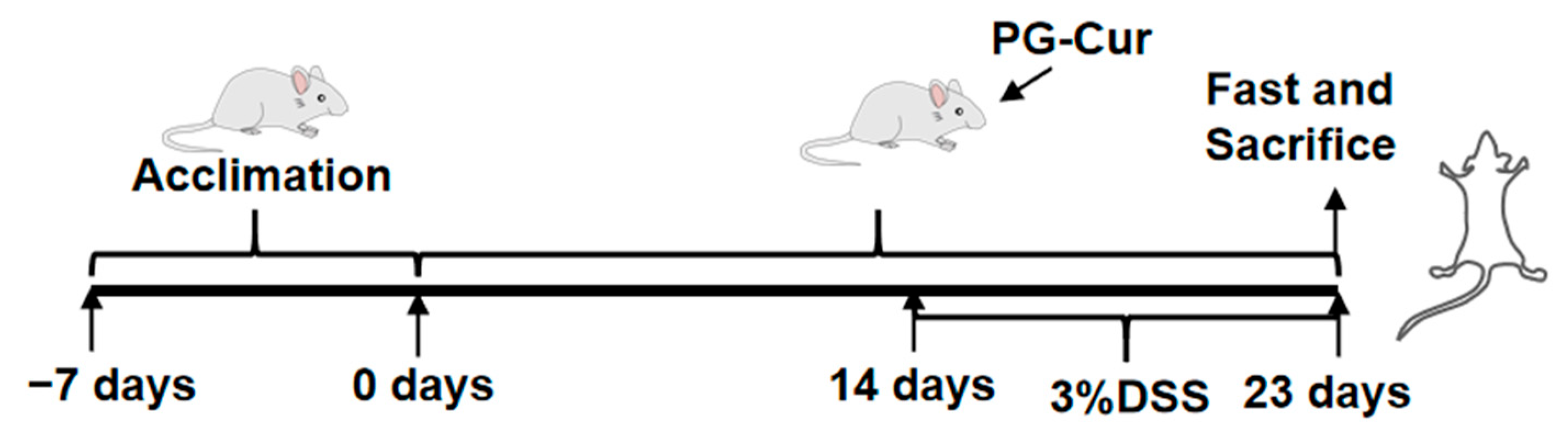
2.4. Animals
2.5. Dietary Intervention and DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Mice
2.6. Mouse DAI Assessment
2.7. Colonic Histopathological Analysis
2.8. Enzymatic Activities of Myeloperoxidase (MPO) and Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (iNOS)
2.9. TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-10 Levels
2.10. Analysis of Gut Microbiota Composition
2.10.1. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
2.10.2. Illumina MiSeq Sequencing
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
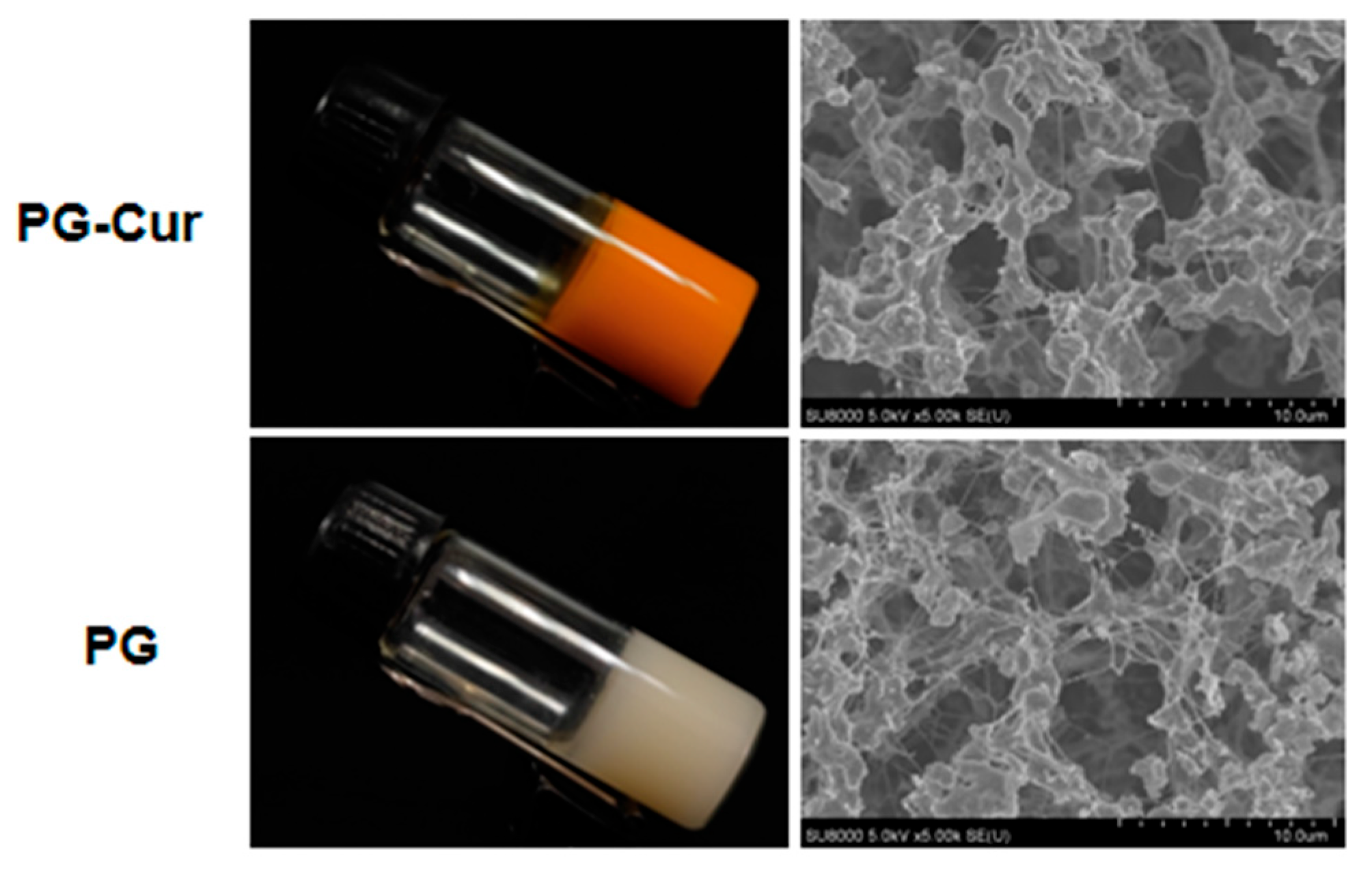
3.1. Visual Appearance and Microstructural Properties of PG and PG-Cur
3.2. Effect of PG-Cur on Body Weight, DAI, and Colon Length in a DSS-Induced UC Mouse Model
3.3. Effect of PG-Cur on Colon Variations in the DSS-Stimulated UC Mouse Model
3.4. Effect of PG-Cur on MPO and iNOS Activity in the DSS-Stimulated UC Mouse Model
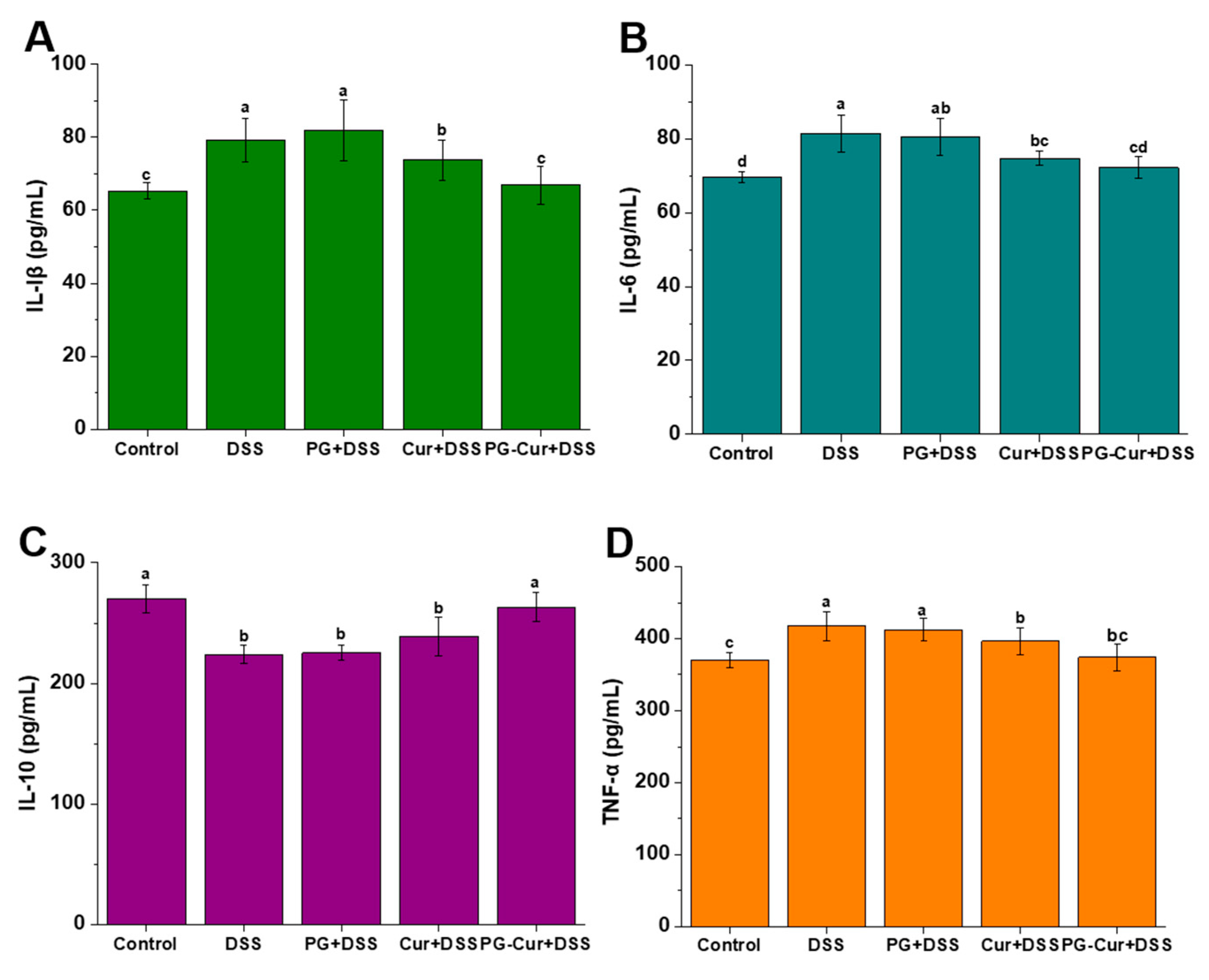
3.5. Effect of PG-Cur on Protein Levels of IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-10 in the DSS-Stimulated UC Mouse Model
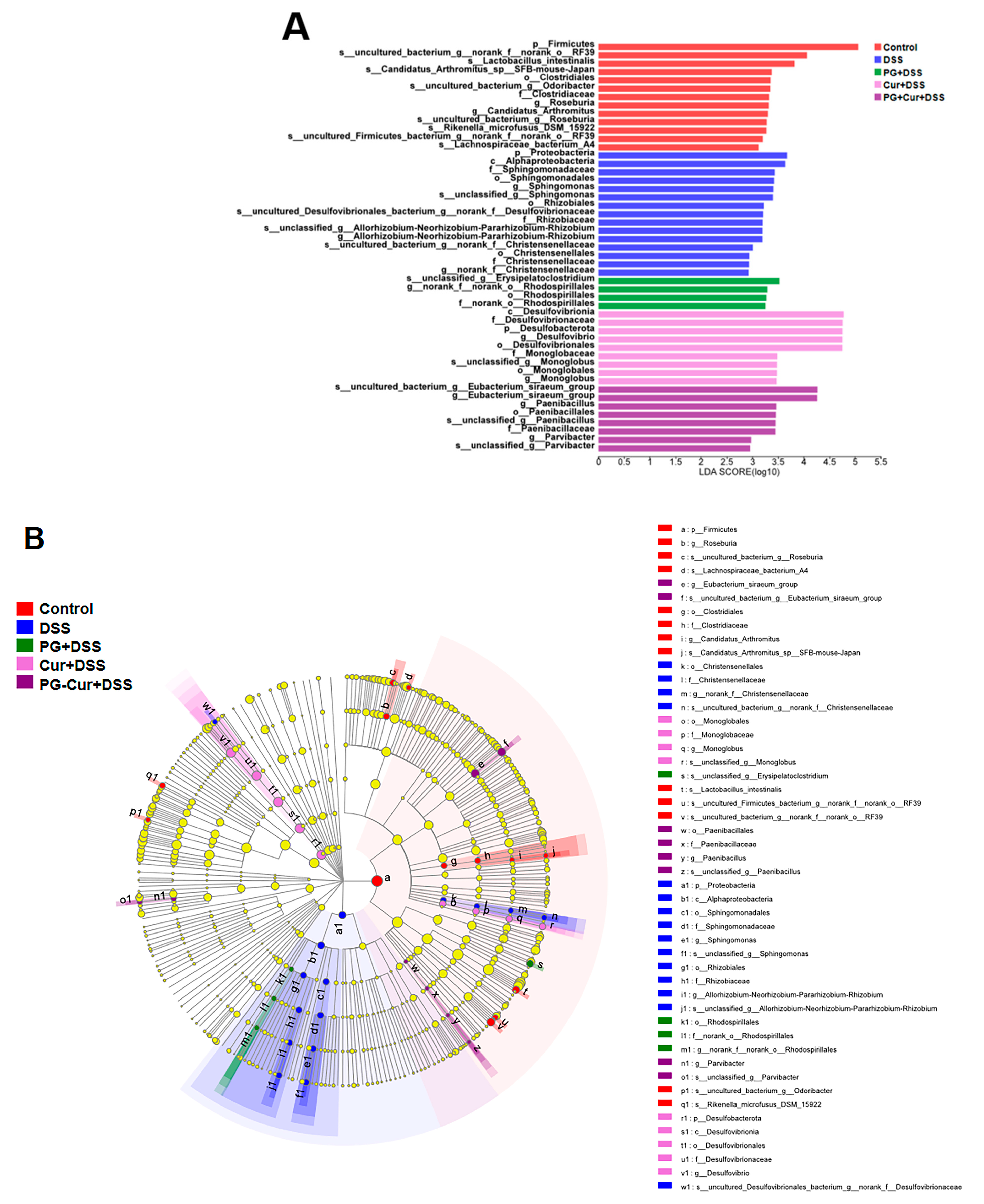
3.6. Effect of PG-Cur on Microbial Composition in the DSS-Stimulated UC Mouse Model
3.6.1. Microbial Composition Analysis
3.6.2. Heatmap Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| pcRPIs | Pseudosciaena crocea roe protein isolates |
| GG | gellan gum |
| Cur | curcumin |
| GDL | glucono-δ-lactone |
| PG | Pseudosciaena crocea roe protein isolates/gellan gum hydrogels |
| DSS | dextran sulfate sodium |
| UC | ulcerative colitis |
| DAI | disease activity index |
| LDA | linear discriminant analysis |
References
- Tian, M.; Li, D.; Ma, C.; Feng, Y.; Hu, X.; Chen, F. Barley leaf insoluble dietary fiber alleviated dextran sulfate sodium-induced mice colitis by modulating gut microbiota. Nutrients 2021, 13, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, R.; Lin, M.; Zhang, C.; Shi, J.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Q.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Gao, F. Genipin-crosslinked human serum albumin coating using a tannic acid layer for enhanced oral administration of curcumin in the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Food Chem. 2020, 330, 127241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulart, R.D.A.; Barbalho, S.M.; Lima, V.M.; Souza, G.A.D.; Matias, J.N.; Araújo, A.C.; Rubira, C.J.; Buchaim, R.L.; Buchaim, D.V.; de Carvalho, A.C.A.; et al. Effects of the use of curcumin on ulcerative colitis and crohn’s disease: A systematic review. J. Med. Food 2021, 24, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; He, L.; Mao, B.; Chen, S.; Martinez, V.; Guo, X.; Shen, X.; Liu, B.; Li, C. Commensal flora triggered target anti-inflammation of alginate-curcumin micelle for ulcerative colitis treatment. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 203, 111756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Wang, D.; Chen, W.; Li, Y.; Si, G.; Yang, T. Quality of evidence supporting the role of supplement curcumin for the treatment of ulcerative colitis: An overview of systematic reviews. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2022, 2022, 3967935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Gan, Y.; Li, Y.; Qi, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Fang, X.; Jiao, J.; Han, X.; Gao, W.; Zhao, J. Protein-polysaccharide-based delivery systems for enhancing the bioavailability of curcumin: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 250, 126153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Ma, L.; Zu, M.; Song, H.; Xiao, B. Oral administration of chondroitin sulfate-functionalized nanoparticles for colonic macrophage-targeted drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 223, 115126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, N.; Zhao, P.; Ayue, S.; Qi, S.; Ye, Y.; He, H.; Dai, L.; Luo, R.; Chang, D.; Gao, F. Folic acid-modified lactoferrin nanoparticles coated with a laminarin layer loaded curcumin with dual-targeting for ulcerative colitis treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 232, 123229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Ping, H.; Wang, K.; Ding, H.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Z.; Du, Q. Oral delivery of pectin-chitosan hydrogels entrapping macrophage-targeted curcumin-loaded liposomes for the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 647, 123510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-L.; Yang, B.-Q.; Liu, W.-J.; Tao, H.; Zhang, B. Curcumin loaded high internal phase emulsions: Formulation and potential to alleviate DSS-induced ulcerative colitis. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yan, S.; Qi, B.; Jiang, L. New insights into the cross-linking mechanism of soybean protein-based double dynamic cross-linking hydrogels for the controlled delivery of curcumin. Food Res. Int. 2025, 211, 116456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Kong, H.; Guo, L.; Wei, G. Recent advances in protein hydrogels: From design, structural and functional regulations to healthcare applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milenkova, S.; Zahariev, N.; Ambrus, R.; Pilicheva, B.; Marudova, M. A study on the stoichiometry of casein/chitosan gel complexes as a delivery system for quercetin. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Chen, S.; Luo, M.; Ning, F.; Zhu, X.; Xiong, H. Preparation and self-assembly mechanism of bovine serum albumin–citrus peel pectin conjugated hydrogel: A potential delivery system for vitamin C. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 7377–7384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, C.; Sun, X.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, D.; Xu, Y. Fabrication and characterization of cold-gelation whey protein-chitosan complex hydrogels for the controlled release of curcumin. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, R.; Mao, L.; Gao, Y. Ethanol-induced composite hydrogel based on propylene glycol alginate and zein: Formation, characterization and application. Food Chem. 2018, 255, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.-N.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Gao, L.-Y.; Lai, B.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.-C.; Wu, H.-T. Scallop hydrolysates/κ-carrageenan hydrogels improve the alleviating effect of curcumin on DSS-induced colitis. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 112, 106000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.N.; Xue, S.; Han, J.R.; Yan, J.N.; Shang, W.H.; Hong, J.N.; Wu, H.T. Simultaneous extraction by acidic and saline solutions and characteristics of the lipids and proteins from large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) roes. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.-N.; Han, J.-R.; Yin, Z.-K.; Yan, J.-N.; Jiang, X.-Y.; Wu, H.-T. Conjugation of (–)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and protein isolate from large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) roe: Improvement of antioxidant activity and structural characteristics. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 5948–5955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.-N.; Jia, J.; Yan, J.-N.; Xu, S.-Q.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Wu, H.-T. Non-covalent interactions between large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) roe protein isolates and curcumin: Implications for enhanced curcumin delivery. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.-N.; Yan, J.-N.; Xu, S.-Q.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Wang, X.-C.; Wu, H.-T. Formation and characteristics of curcumin-loaded binary gels formed from large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) roe protein isolate and gellan gum. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.-N.; Du, Y.-N.; Jiang, X.-Y.; Xu, S.-Q.; Wu, H.-T. Curcumin-loaded composite hydrogel based on scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis) male gonad hydrolysates and κ-carrageenan: Characterization and in vitro digestibility. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 125, 107398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, L.; Qin, N.; Zhu, B.; Xia, X. Jellyfish skin polysaccharides enhance intestinal barrier function and modulate the gut microbiota in mice with DSS-induced colitis. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 10121–10135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Han, Z.; Wu, Y.; Lu, X.; Tang, X.; Xiao, J.; Li, N. Enhancing stability and anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin in ulcerative colitis therapy using liposomes mediated colon-specific drug delivery system. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 151, 112123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Cai, W.; Yang, D.; Wang, W.; Che, H.; Li, H. Effect of the arabinogalactan from Ixeris chinensis (Thunb.) Nakai. attenuates DSS-induced colitis and accompanying depression-like behavior. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 286, 138525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, F.; Wang, H.; Chen, B.; Hua, Y.; An, Z. Study on the ameliorative effects of hydroxypropyl betadex and betadex sulfobutyl ether sodium on acute ulcerative colitis induced by DSS in mice. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2025, 10, 100825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Peng, K.; Ruan, R.; Liu, Y.; Cui, X. Impact of anaerobic fermentation liquid on bok choy and mechanism of combined vitamin C from bok choy and allicin in treatment of DSS colitis. Foods 2025, 14, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.B.; Elzallat, M.; Mostafa Mohammed, D.; Hammam, O.A.; Tamim, A.; Abdel-Wareth, M.; Hassan, M. Helix pomatia mucin alleviates DSS-induced colitis in mice: Unraveling the cross talk between microbiota and intestinal chemokine. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Xu, M.; Cheng, X.; Li, N.; Xu, H.; Feng, Y.; Guan, T.; Xiao, L. Patrinia scabiosaefolia L. modulates the intestinal microecology to treat DSS-induced ulcerative colitis: UHPLC-OE-MS/MS, network pharmacology, and experimental validation. Foods 2025, 14, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, C. A curcumin-loaded biopolymeric nanocomposite alleviates dextran sulfate sodium induced ulcerative colitis via suppression of inflammation and oxidative stress. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 275, 133665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Xiao, M.; Ma, J.; Qu, Y.; Zou, L.; Zhang, J. Nano-in-micro alginate/chitosan hydrogel via electrospray technology for orally curcumin delivery to effectively alleviate ulcerative colitis. Mater. Des. 2022, 221, 110894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, M.; Silva, S.; Costa, E. Chapter 15—Uses of gellan gum for nutrient delivery. In Application of Gellan Gum as a Biomedical Polymer; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 309–321. [Google Scholar]
- Mundlia, J.; Munish, A.; Kumar, P. Enhanced biological activity of polyphenols on conjugation with gellan gum. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2021, 70, 712–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.-Q.; Liu, H.-X.; Yan, J.-N.; Wang, C.; Lai, B.; Wu, H.-T. Interaction mechanism and binding mode between different polyphenols and gellan gum. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 153, 110014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Si, X.; Chen, Q.; Ma, L.; Hou, M.; Xu, Z.; Kang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiao, B. Oral drug delivery systems for ulcerative colitis therapy: A comparative study with microparticles and nanoparticles. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2019, 19, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, E.; Romano, B.; Iannotti, F.A.; Parisi, O.A.; D’Armiento, M.; Pignatiello, S.; Coretti, L.; Lucafò, M.; Venneri, T.; Stocco, G.; et al. The non-euphoric phytocannabinoid cannabidivarin counteracts intestinal inflammation in mice and cytokine expression in biopsies from UC pediatric patients. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 149, 104464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.-L.; Qian, Y.; Li, G.-J.; Zhao, X. Anti-inflammatory effects of kudingcha methanol extract (Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng) in dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 8, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, Y.; Yue, X.; Peng, Y. Almond polysaccharides inhibit DSS-induced inflammatory response in ulcerative colitis mice through NF-κB pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 281, 136206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Barquero, L.; Villegas, I.; Sánchez-Calvo, J.M.; Talero, E.; Sánchez-Fidalgo, S.; Motilva, V.; de la Alarcón Lastra, C. Curcumin, a Curcuma longa constituent, acts on MAPK p38 pathway modulating COX-2 and iNOS expression in chronic experimental colitis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2007, 7, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wen, Z.; Fu, H.; Hu, J.; Ye, X.; Kang, L.; Li, X.; Yang, X. Oral delivery of curcumin via multi-bioresponsive polyvinyl alcohol and guar gum based double-membrane microgels for ulcerative colitis therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 221, 806–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudter, J.; Neurath, M.F. II-6 signaling in inflammatory bowel disease: Pathophysiological role and clinical relevance. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2007, 13, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, P.L.; Wallace, J.L. Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Mediat. Inflamm. 1997, 6, 508147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosmann, T.R.; Sad, S. The expanding universe of T-cell subsets: Th1, Th2 and more. Immunol. Today 1996, 17, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, A.W.; Sanderson, J.D.; Churcher, C.; Parkes, G.C.; Hudspith, B.N.; Rayment, N.; Brostoff, J.; Parkhill, J.; Dougan, G.; Petrovska, L. High-throughput clone library analysis of the mucosa-associated microbiota reveals dysbiosis and differences between inflamed and non-inflamed regions of the intestine in inflammatory bowel disease. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, S.; Wang, C.; Lou, Y.; Xia, X.; Xu, H. Whole and polysaccharide powdered Sporisorium reilianum improves DSS-induced colitis in BALB/c mice by modulating gut microbiota. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 79, 104409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pan, H.; Liu, J.-X.; Li, T.; Liu, S.; Shi, W.; Sun, C.; Fan, M.; Xue, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. I-Arabinose inhibits colitis by modulating gut microbiota in mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13299–13306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wu, T.; Du, D.; Mei, J.; Luo, H.; Liu, Z.; Saleemi, M.K.; Zhang, R.; Chang, C.; Mehmood, M.A.; et al. Transcriptome and gut microbiota profiling revealed the protective effect of tibetan tea on ulcerative colitis in mice. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 748594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Li, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, K.; Lin, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L. Construction of a “Bacteria-Metabolites” co-expression network to clarify the anti–ulcerative colitis effect of flavonoids of sophora flavescens aiton by regulating the “Host–Microbe” interaction. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 710052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhya, I.; Hansen, R.; El-Omar, E.M.; Hold, G.L. IBD—What role do Proteobacteria play? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, E.J.C.; Citron, D.M.; Peraino, V.A.; Cross, S.A. Desulfovibrio desulfuricans bacteremia and review of human Desulfovibrio infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 2752–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latham, E.A.; Pinchak, W.E.; Trachsel, J.; Allen, H.K.; Callaway, T.R.; Nisbet, D.J.; Anderson, R.C. Paenibacillus 79R4, a potential rumen probiotic to enhance nitrite detoxification and methane mitigation in nitrate-treated ruminants. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latham, E.A.; Pinchak, W.E.; Trachsel, J.; Allen, H.K.; Callaway, T.R.; Nisbet, D.J.; Anderson, R.C. Isolation, characterization and strain selection of a Paenibacillus species for use as a probiotic to aid in ruminal methane mitigation, nitrate/nitrite detoxification and food safety. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 263, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, Y.-N.; Wang, Y.-X.; Yan, J.-N.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Jia, J.; Wu, H.-T. Large Yellow Croaker Roe Protein Isolates/Gellan Gum Hydrogels Improve the Alleviating Effect of Curcumin on DSS-Induced Colitis. Foods 2025, 14, 1921. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111921
Du Y-N, Wang Y-X, Yan J-N, Zhang Q, Wang Y-Q, Jia J, Wu H-T. Large Yellow Croaker Roe Protein Isolates/Gellan Gum Hydrogels Improve the Alleviating Effect of Curcumin on DSS-Induced Colitis. Foods. 2025; 14(11):1921. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111921
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Yi-Nan, Yi-Xu Wang, Jia-Nan Yan, Qian Zhang, Yu-Qiao Wang, Jiao Jia, and Hai-Tao Wu. 2025. "Large Yellow Croaker Roe Protein Isolates/Gellan Gum Hydrogels Improve the Alleviating Effect of Curcumin on DSS-Induced Colitis" Foods 14, no. 11: 1921. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111921
APA StyleDu, Y.-N., Wang, Y.-X., Yan, J.-N., Zhang, Q., Wang, Y.-Q., Jia, J., & Wu, H.-T. (2025). Large Yellow Croaker Roe Protein Isolates/Gellan Gum Hydrogels Improve the Alleviating Effect of Curcumin on DSS-Induced Colitis. Foods, 14(11), 1921. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111921





