LC-MS/MS-Based Metabolomics and Multivariate Statistical Analysis Reveal the Mechanism of Rhodotorula mucilaginosa Proteases on Myofibrillar Protein Degradation and the Evolution of Taste Compounds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Identification of Yeast Strains
2.2. Measurement of Protease Activities
2.3. Influence of pH and Temperature on Protease Activities
2.4. Impact of Inhibitors and Metal Ions on Protease Activities
2.5. Determination of Kinetic Parameters
2.6. Preparation of the Protease-Treated MP Samples
2.7. SDS-PAGE
2.8. Assessment of Protein Hydrolysis Index (PI)
2.9. Surface Hydrophobicity
2.10. FTIR and Secondary Structure Determination
2.11. Evaluation of Surface Morphology and Particle Size
2.12. Free Amino Acids (FAAs) Analysis
2.13. Metabolite Analysis by LC-MS/MS
2.14. Electronic Tongue Determination
2.15. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
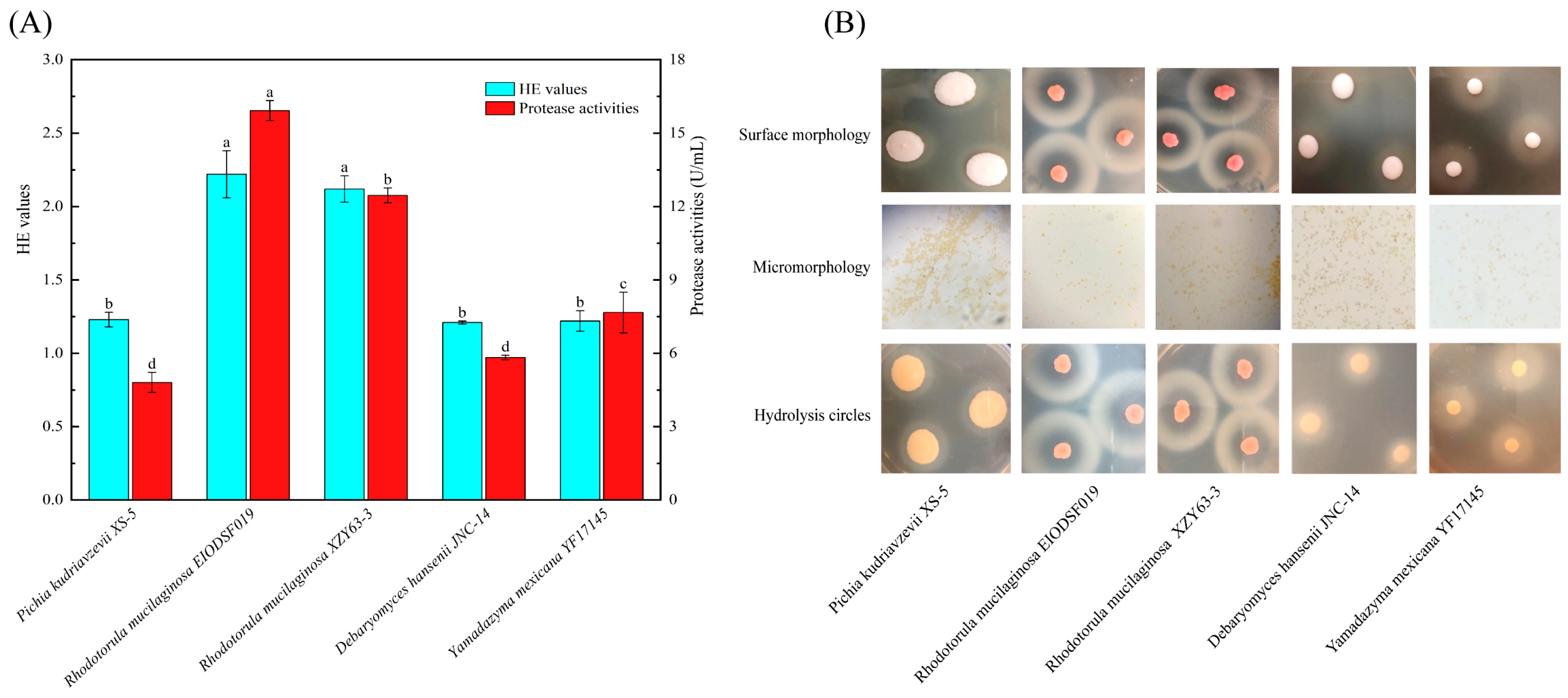
3.1. Biological Identification and Determination of Protease Activities in Yeasts
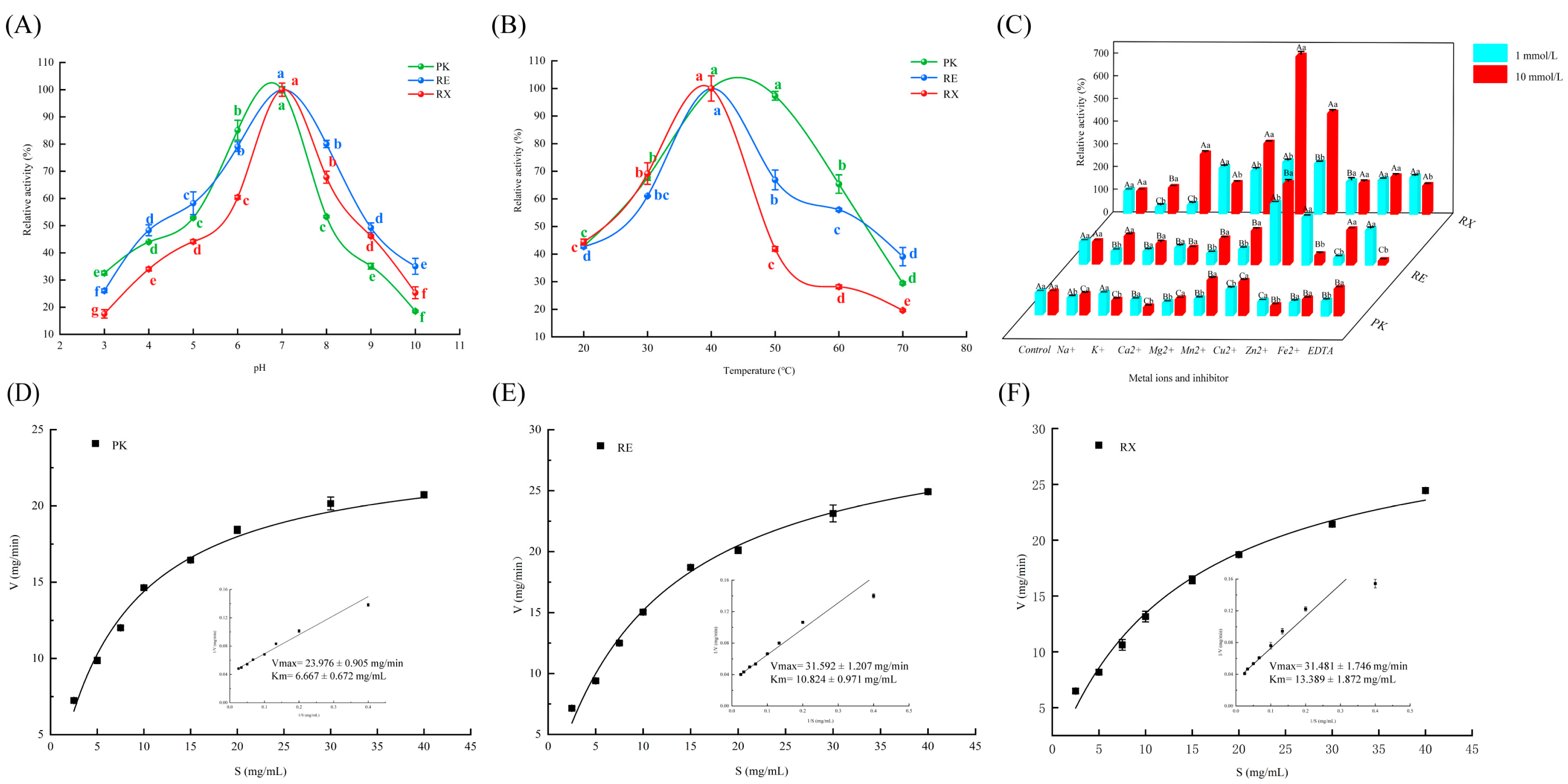
3.2. Effects of pH and Temperature on Yeast Protease Activities
3.3. Effects of Metal Ions and Inhibitors on Yeast Protease Activities
3.4. Analysis of Protease Kinetic Parameters
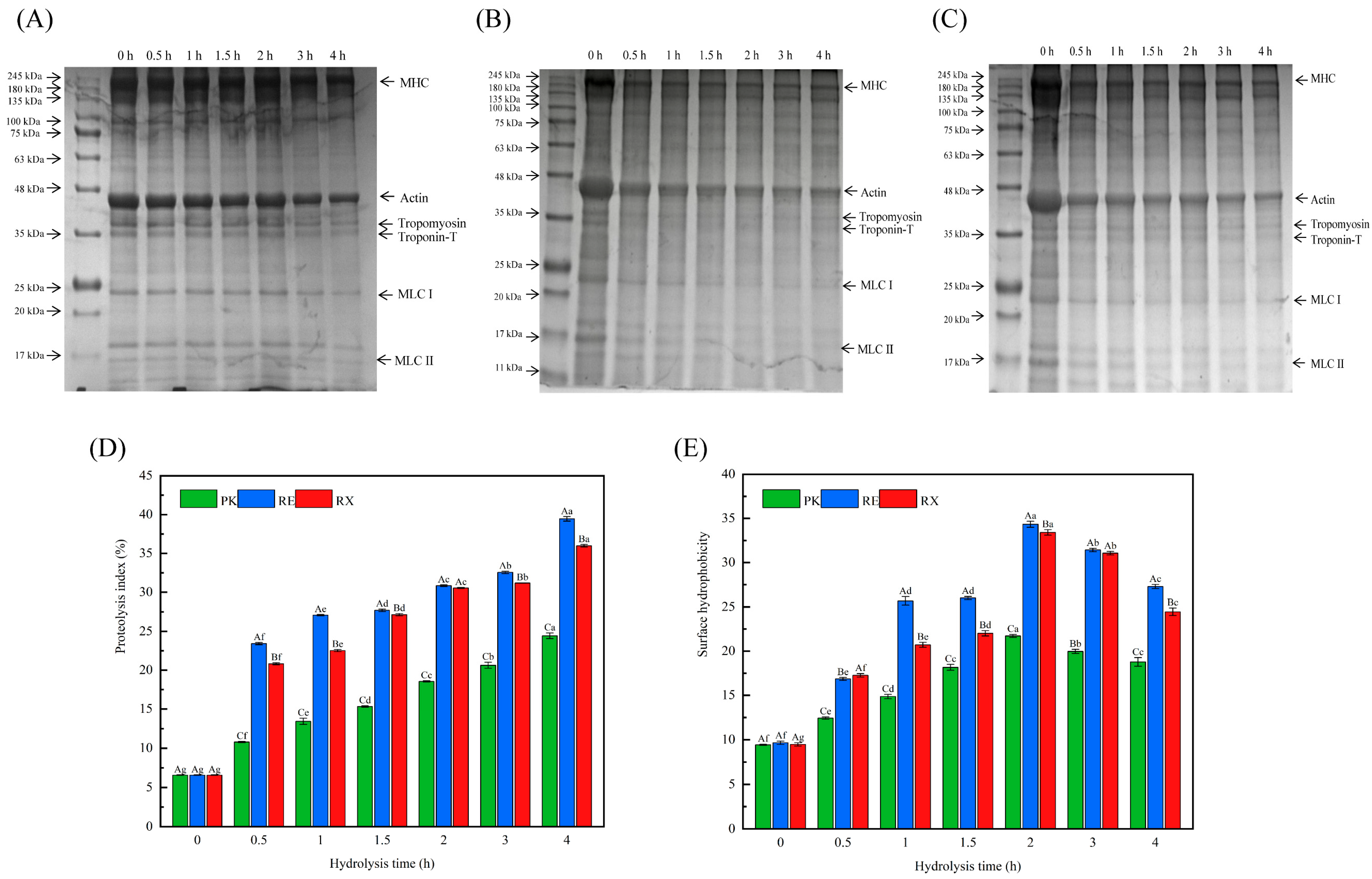
3.5. SDS-PAGE After Protease Treatment of MPs
3.6. Analysis of PI Values and Surface Hydrophobicity
3.7. Analysis of FTIR Peak Attribution and Secondary Structure
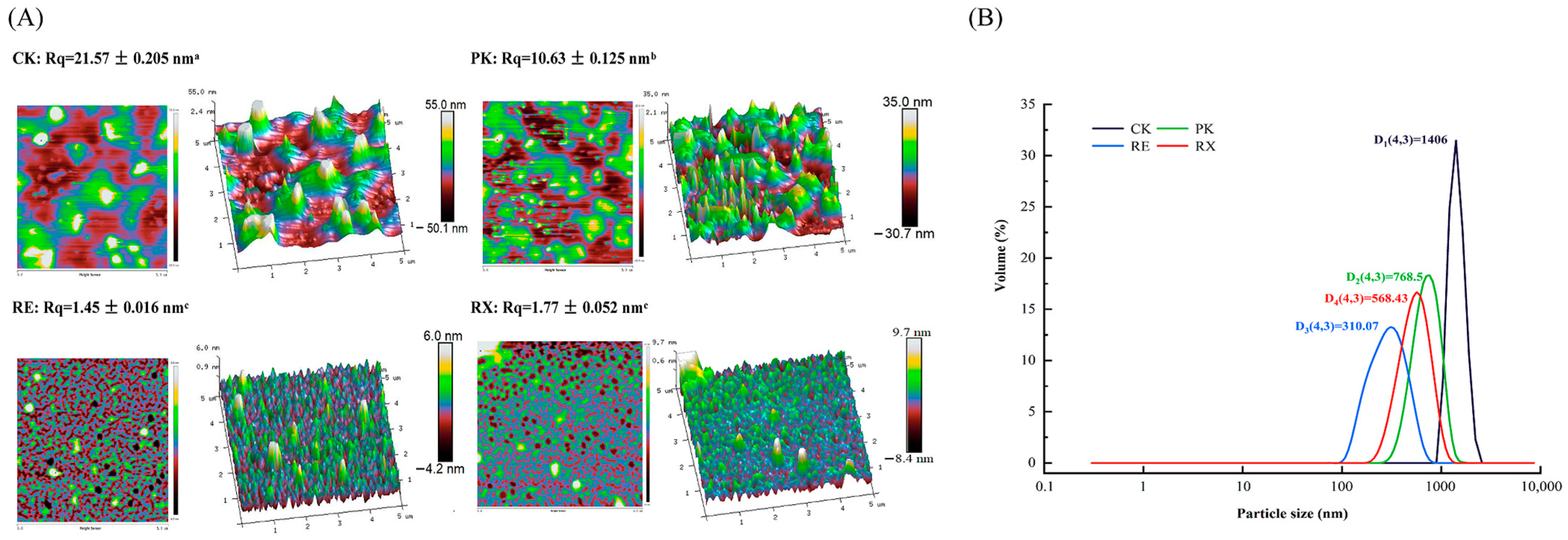
3.8. Analysis of Surface Morphology and Particle Size
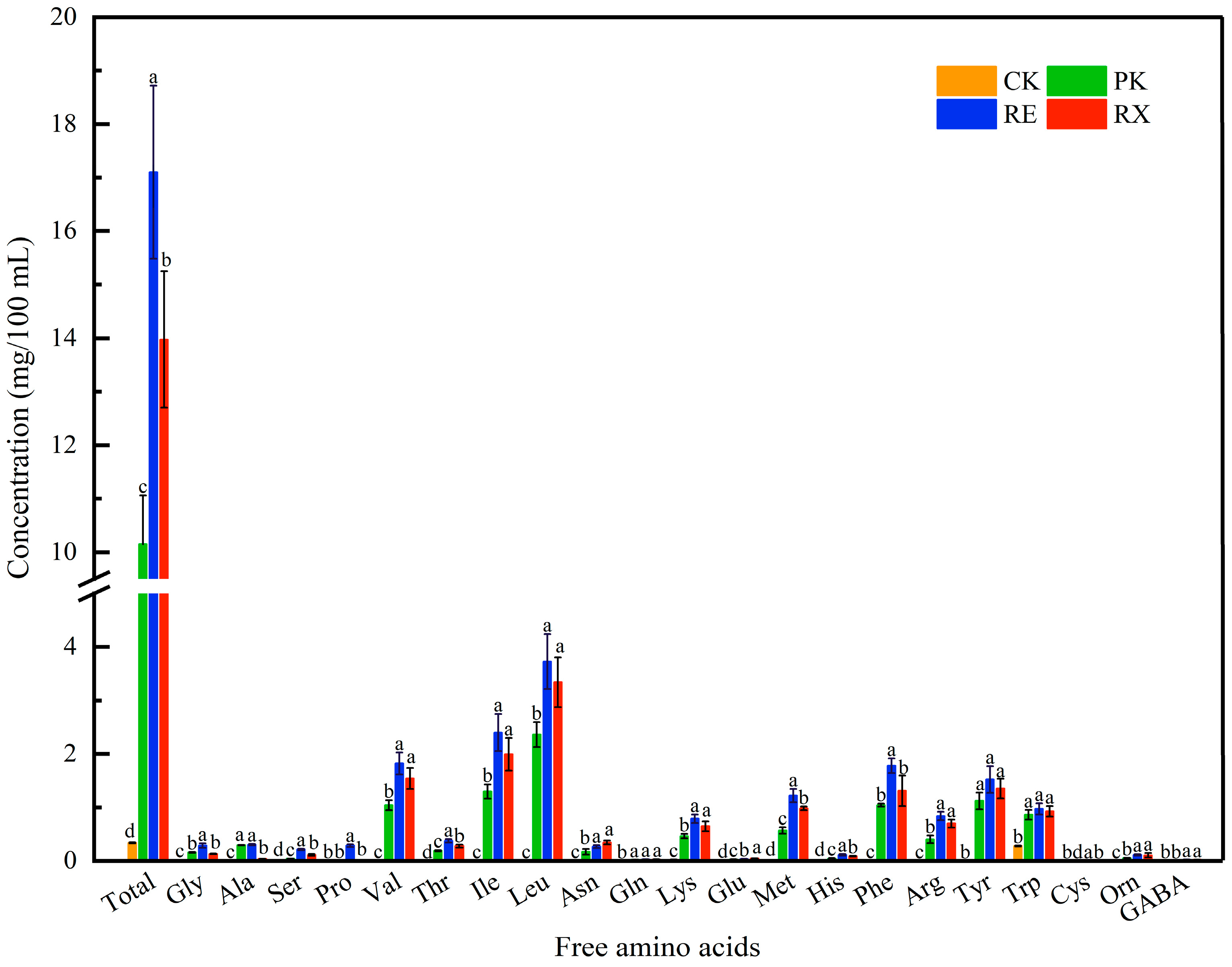
3.9. FAA Analysis
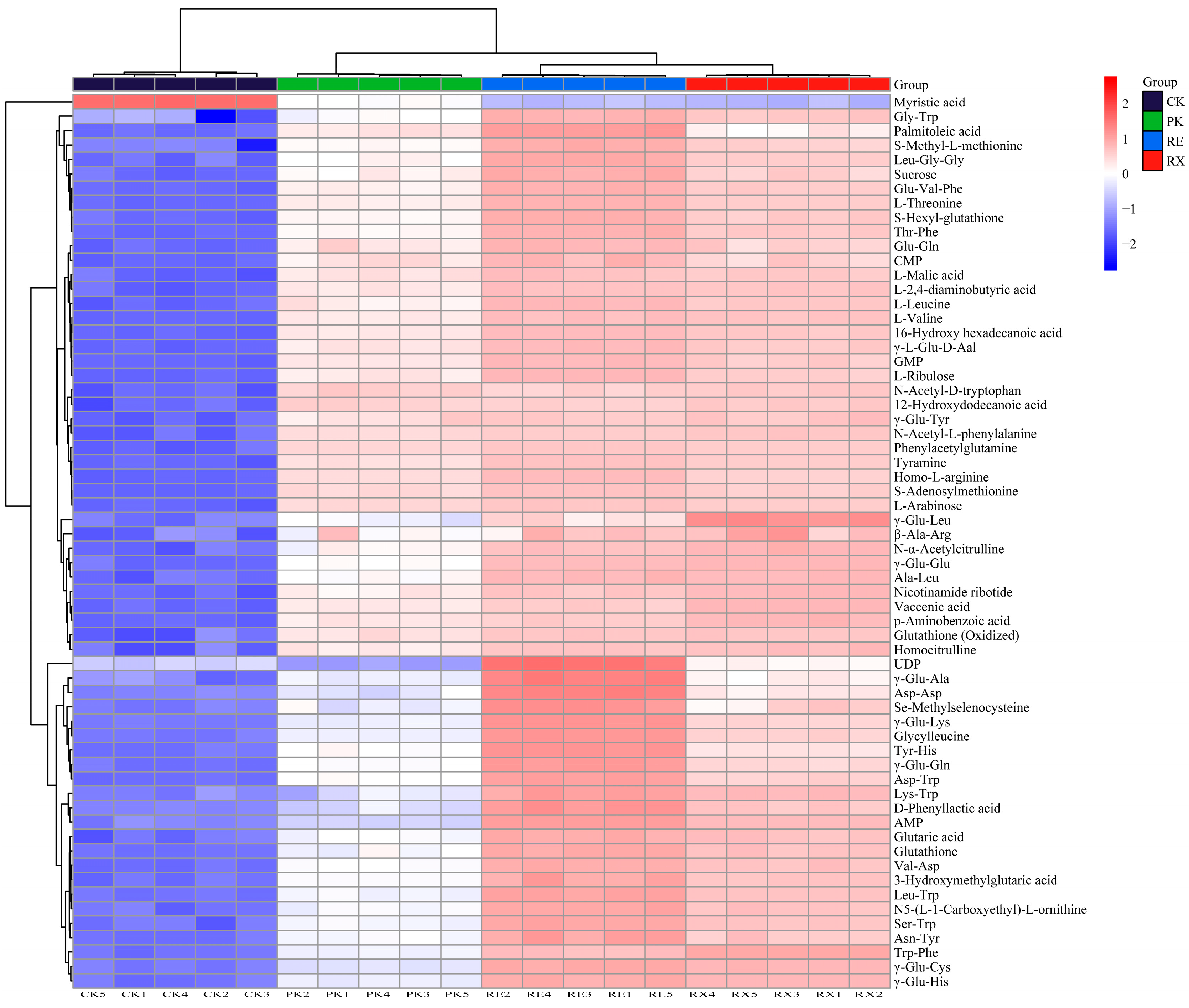
3.10. Metabolite Analysis
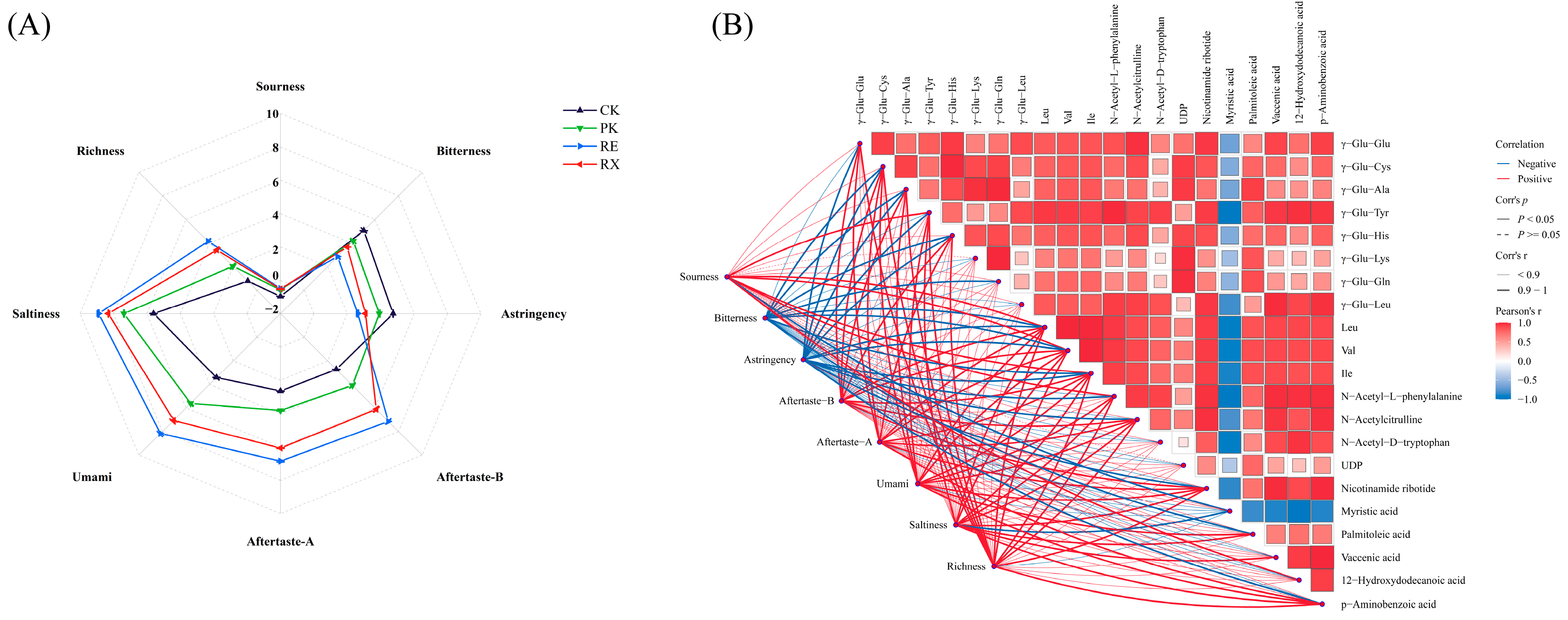
3.11. The Changes of Taste Attributes of Enzyme-Treated MPs
3.12. Correlation Between Key Metabolites and Taste Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MP | Myofibrillar protein |
| RE | Rhodotorula mucilaginosa EIODSF019 |
| RX | Rhodotorula mucilaginosa XZY63-3 |
| PK | Pichia kudriavzevii XS-5 |
| TCA | Trichloroacetic acid |
| PI | Protein hydrolysis index |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy |
| FAA | Free amino acids |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis |
References
- Zhang, T.M.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Chen, C.; Jiang, T.; Fang, S.Y.; Liu, H.; Tong, H.H.; Xia, Q.; Sun, Y.Y.; et al. TMT-labelled quantitative proteomics reveals the mechanism of Rhodotorula mucilaginosa on proteolysis of dry-cured ham: Structural protein degradation, amino acid release and taste improvement. Food Chem. 2025, 472, 142991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Colmenero, F.; Ventanas, J.; Toldrá, F. Nutritional composition of dry-cured ham and its role in a healthy diet. Meat Sci. 2010, 84, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.N.; Liang, Y.Q.; Xia, Q.; Pan, D.D.; Du, L.H.; He, J.; Sun, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Cao, J.X.; et al. LC-MS/MS-based metabolomics and multivariate statistical analysis reveal the mechanism of yeast extracellular proteases on myofibrillar protein degradation, metabolite development and sensory characteristics improvement. Food Microbiol. 2025, 128, 104715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.Y.; Xia, Q.; He, J.; Sun, Y.Y.; Dang, Y.L.; Zhou, G.H.; Geng, F.; Pan, D.D.; Cao, J.X. Insights into ultrasonic treatment on the mechanism of proteolysis and taste improvement of defective dry-cured ham. Food Chem. 2022, 388, 133059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.M.; Li, D.N.; Pan, D.D.; Xia, Q.; Sun, Y.Y.; Du, L.H.; He, J.; Zhou, C.Y.; Geng, F.; Cao, J.X. Insights into the mechanism of extracellular proteases from Penicillium on myofibrillar protein hydrolysis and volatile compound evolutions. Food Res. Int. 2024, 175, 113774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toldrá, F. The role of muscle enzymes in dry-cured meat products with different drying conditions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.Y.; Bai, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, C.B.; Xu, X.L.; Pan, D.D.; Cao, J.X.; Zhou, G.H. 1H NMR-based metabolomics and sensory evaluation characterize taste substances of Jinhua ham with traditional and modern processing procedures. Food Control 2021, 126, 107873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juraj, Č.; Cviková, P.; Peter, H.; Miroslava, K.Ã.; Simona, K.; Lukáš, H.; Marek, B.; Lenka, T.; Bučko, O.; Jana, T. The proteins degradation in dry cured meat and methods of analysis: A review. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food 2017, 7, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, J.H.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Sun, F.D.; Kong, B.H. Interaction between protease from Staphylococcus epidermidis and pork myofibrillar protein: Flavor and molecular simulation. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.Y.; Xia, Q.; Du, L.H.; He, J.; Sun, Y.Y.; Dang, Y.L.; Geng, F.; Pan, D.D.; Cao, J.X.; Zhou, G.H. Recent developments in off-odor formation mechanism and the potential regulation by starter cultures in dry-cured ham. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2023, 63, 8781–8795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purriños, L.; Fontán, M.C.G.; Carballo, J.; Lorenzo, J.M. Study of the counts, species and characteristics of the yeast population during the manufacture of dry-cured “lacón”. Effect of salt level. Food Microbiol. 2013, 34, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.X.; Mi, R.; Chen, X.; Zhu, Q.J.; Xiong, S.Y.; Qi, B.; Wang, S.W. Evaluation and selection of yeasts as potential aroma enhancers for the production of dry-cured ham. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-García, L.; Rivera-Jiménez, S.; Belloch, C.; Flores, M. Generation of aroma compounds in a fermented sausage meat model system by Debaryomyces hansenii strains. Food Chem. 2014, 151, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral, S.; Salvador, A.; Belloch, C.; Flores, M. Improvement the aroma of reduced fat and salt fermented sausages by Debaromyces hansenii inoculation. Food Control 2015, 47, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, R.; Chen, X.; Xiong, S.; Qi, B.; Li, J.P.; Qiao, X.L.; Chen, W.H.; Qu, C.; Wang, S.W. Predominant yeasts in Chinese Dong fermented pork (Nanx Wudl) and their aroma-producing properties in fermented sausage condition. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2021, 10, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purriños, L.; Carballo, J.; Lorenzo, J.M. The Influence of Debaryomyces hansenii, Candida deformans and Candida zeylanoides on the aroma formation of dry-cured “lacón”. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Almanza, A.; Montanez, J.C.; Aguilar-González, M.A.; Martínez-Ávila, C.; Rodríguez-Herrera, R.; Aguilar, C.N. Rhodotorula glutinis as source of pigments and metabolites for food industry. Food Biosci. 2014, 5, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H.; Li, C.J.; Cheng, P.; Yu, G.H. Rhodotorula mucilaginosa—Alternative sources of natural carotenoids, lipids, and enzymes for industrial use. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.Y.; Wang, C.; Tang, C.B.; Dai, C.; Bai, Y.; Yu, X.B.; Li, C.B.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H.; Cao, J.X. Label-free proteomics reveals the mechanism of bitterness and adhesiveness in Jinhua ham. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 125012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.H.; Huang, J.Q.; Xiong, S.J.; Zhang, L.L.; Xu, X.Y.; Xu, Y.Z.; Peng, F.; Huang, T.; Xiao, M.Y.; Xiong, T. Effects of enzyme treatment on the antihypertensive activity and protein structure of black sesame seed (Sesamum indicum L.) after fermentation pretreatment. Food Chem. 2023, 428, 136781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.Y.; Wu, X.Y.; Pan, D.D.; Xia, Q.; Sun, Y.Y.; Geng, F.; Cao, J.X. TMT-labeled quantitative proteomic reveals the mechanism of proteolysis and taste improvement of dry-cured bacon with Staphylococcus co-inoculation. Food Chem. 2024, 436, 137711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, R.Y.; Xia, Q.; Zhou, C.Y.; Geng, F.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.Y.; He, J.; Pan, D.D.; Cao, J.X. LC-MS/MS-based metabolomics and sensory evaluation characterize metabolites and texture of normal and spoiled dry-cured hams. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.Y.; Pan, D.D.; Xia, Q.; Sun, Y.Y.; Geng, F.; Cao, J.X.; Zhou, C.Y. The combination of high-throughput sequencing and LC-MS/MS reveals the mechanism of Staphylococcus inoculation on bacterial community succession and taste development during the processing of dry-cured bacon. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 7187–7198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, J.M.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B.H.; Sun, F.D. Biochemical properties of extracellular protease from Staphylococcus epidermidis isolated from Harbin dry sausages and its hydrolysis of meat protein. Food Biosci. 2021, 42, 101130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.A.; Chen, H.; Du, H.; Chen, C.; Lu, K.X.; Xue, Q.L.; Hu, Y.J. Dynamic changes in physicochemical property, biogenic amines content and microbial diversity during the fermentation of Sanchuan ham. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.J.; Hsu, T.H.; Jiang, S.T. Characterization of acidic protease from Aspergillus niger BCRC 32720. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.D.; Sun, Q.X.; Zhang, H.; Kong, B.H.; Xia, X.F. Purification and biochemical characteristics of the microbial extracellular protease from Lactobacillus curvatus isolated from Harbin dry sausages. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 987–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.Y.; Wu, J.Q.; Tang, C.B.; Li, G.; Dai, C.; Bai, Y.; Li, C.B.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H.; Cao, J.X. Comparing the proteomic profile of proteins and the sensory characteristics in Jinhua ham with different processing procedures. Food Control 2019, 106, 106694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves-López, C.; Paparella, A.; Tofalo, R.; Suzzi, G. Proteolytic activity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains associated with Italian dry-fermented sausages in a model system. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 150, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.J.; Schieber, A.; Gänzle, M.G. Formation of taste-active amino acids, amino acid derivatives and peptides in food fermentations—A review. Food Res. Int. 2016, 89, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heres, A.; Li, Q.; Toldrá, F.; Lametsch, R.; Mora, L. Purification and biochemical characteristics of the microbial extracellular protease from Lactobacillus curvatus isolated from Harbin dry sausagey-cured ham during its processing. Meat Sci. 2023, 206, 109323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.R.; Suo, R.; Liu, X.B.; Wang, Y.Y.; Sun, J.F.; Liu, Y.Q.; Wang, W.X.; Wang, J. Kokumi γ-glutamyl peptides: Some insight into their evaluation and detection, biosynthetic pathways, contribution and changes in food processing. Food Chem. Adv. 2022, 1, 100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, J.; De Gobba, C.; Zhang, L.; Bredie, W.L.P.; Lametsch, R. Production of Taste Enhancers from Protein Hydrolysates of Porcine Hemoglobin and Meat Using Bacillus amyloliquefaciens γ-Glutamyltranspeptidase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 11782–11789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.Z.; Fu, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhu, H.K.; Yu, Y.; Dai, H.J.; Han, J.D.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.F.; Zhang, Y.H. Protein Hydrolysates from Pleurotus geesteranus Modified by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens gamma-Glutamyl Transpeptidase Exhibit a Remarkable Taste-Enhancing Effect. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 12143–12155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, T.; Xia, Q.; Pan, D.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cao, J.; Gan, R.-Y.; Zhou, C. LC-MS/MS-Based Metabolomics and Multivariate Statistical Analysis Reveal the Mechanism of Rhodotorula mucilaginosa Proteases on Myofibrillar Protein Degradation and the Evolution of Taste Compounds. Foods 2025, 14, 1867. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111867
Zhang T, Xia Q, Pan D, Sun Y, Wang Y, Cao J, Gan R-Y, Zhou C. LC-MS/MS-Based Metabolomics and Multivariate Statistical Analysis Reveal the Mechanism of Rhodotorula mucilaginosa Proteases on Myofibrillar Protein Degradation and the Evolution of Taste Compounds. Foods. 2025; 14(11):1867. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111867
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Tianmeng, Qiang Xia, Daodong Pan, Yangying Sun, Ying Wang, Jinxuan Cao, Ren-You Gan, and Changyu Zhou. 2025. "LC-MS/MS-Based Metabolomics and Multivariate Statistical Analysis Reveal the Mechanism of Rhodotorula mucilaginosa Proteases on Myofibrillar Protein Degradation and the Evolution of Taste Compounds" Foods 14, no. 11: 1867. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111867
APA StyleZhang, T., Xia, Q., Pan, D., Sun, Y., Wang, Y., Cao, J., Gan, R.-Y., & Zhou, C. (2025). LC-MS/MS-Based Metabolomics and Multivariate Statistical Analysis Reveal the Mechanism of Rhodotorula mucilaginosa Proteases on Myofibrillar Protein Degradation and the Evolution of Taste Compounds. Foods, 14(11), 1867. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111867






