Anxiolytic Effects of Cichorium intybus L. Oligo-Polysaccharides by Modulating Gut Microbiota, Neuronal Signaling Pathways, and Neuroinflammation in Chronic Sleep Deprivation-Stressed Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drugs and Reagents
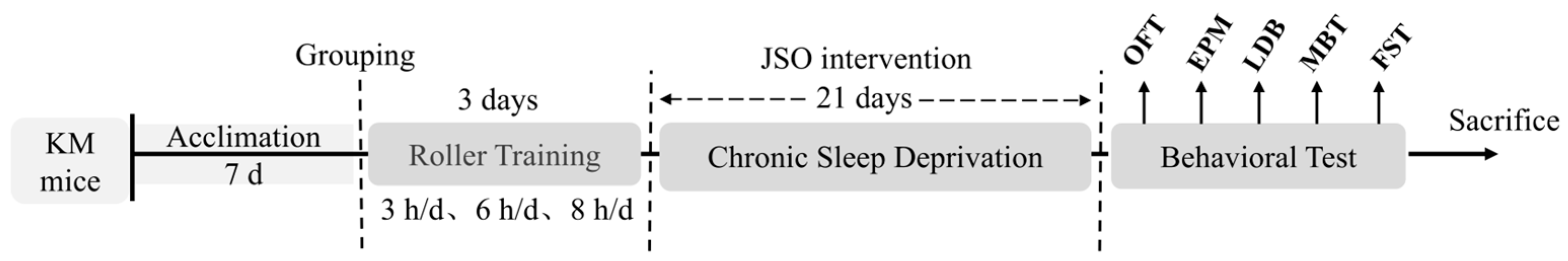
2.2. Experimental Design and Ethical Approval
2.3. Experimental Equipment
2.4. Establishment of CSD Model and Behavioral Testing
2.5. Behavioral Testing Methods
2.5.1. Open Field Test
2.5.2. Elevated Plus Maze Test
2.5.3. Light–Dark Test
2.5.4. Marble Burying Test
2.5.5. Forced Swimming Test
2.6. 16S rRNA Microbial Diversity Sequencing
2.7. Western Blot (WB) Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
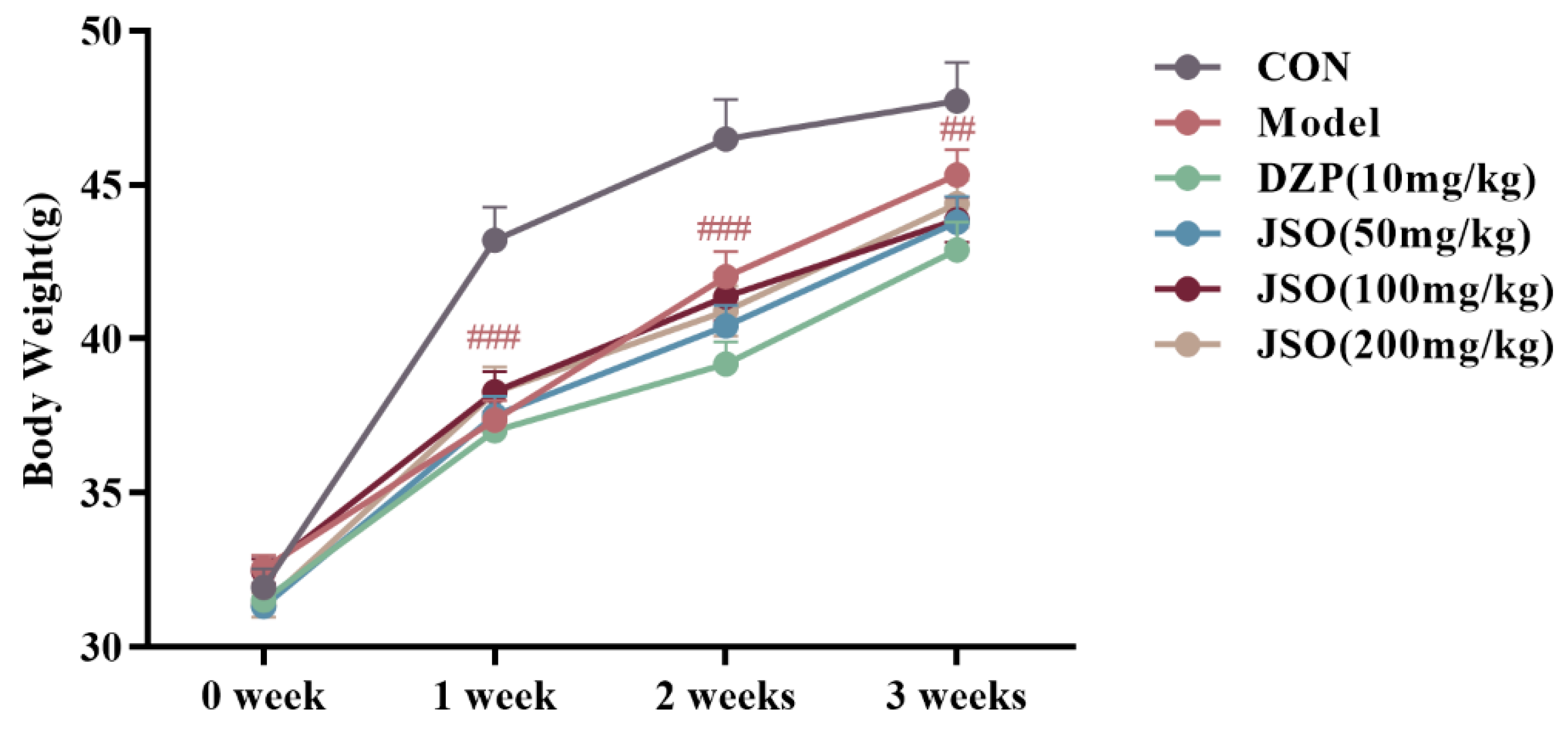
3.1. Effect of JSO on Body Weight in CSD-Stressed Mice
3.2. Behavior Assessment
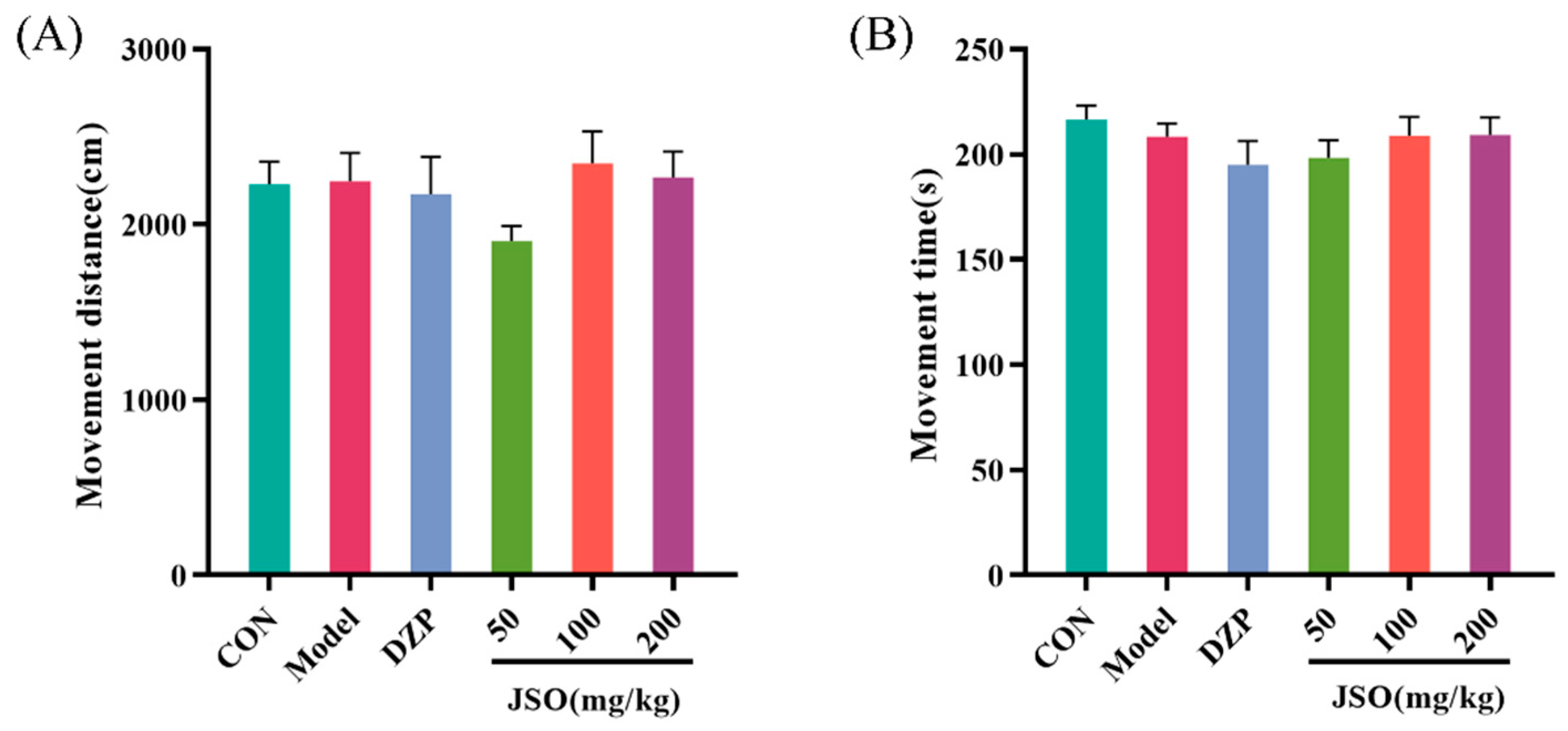
3.2.1. Effect of JSO on the OFT in CSD-Stressed Mice
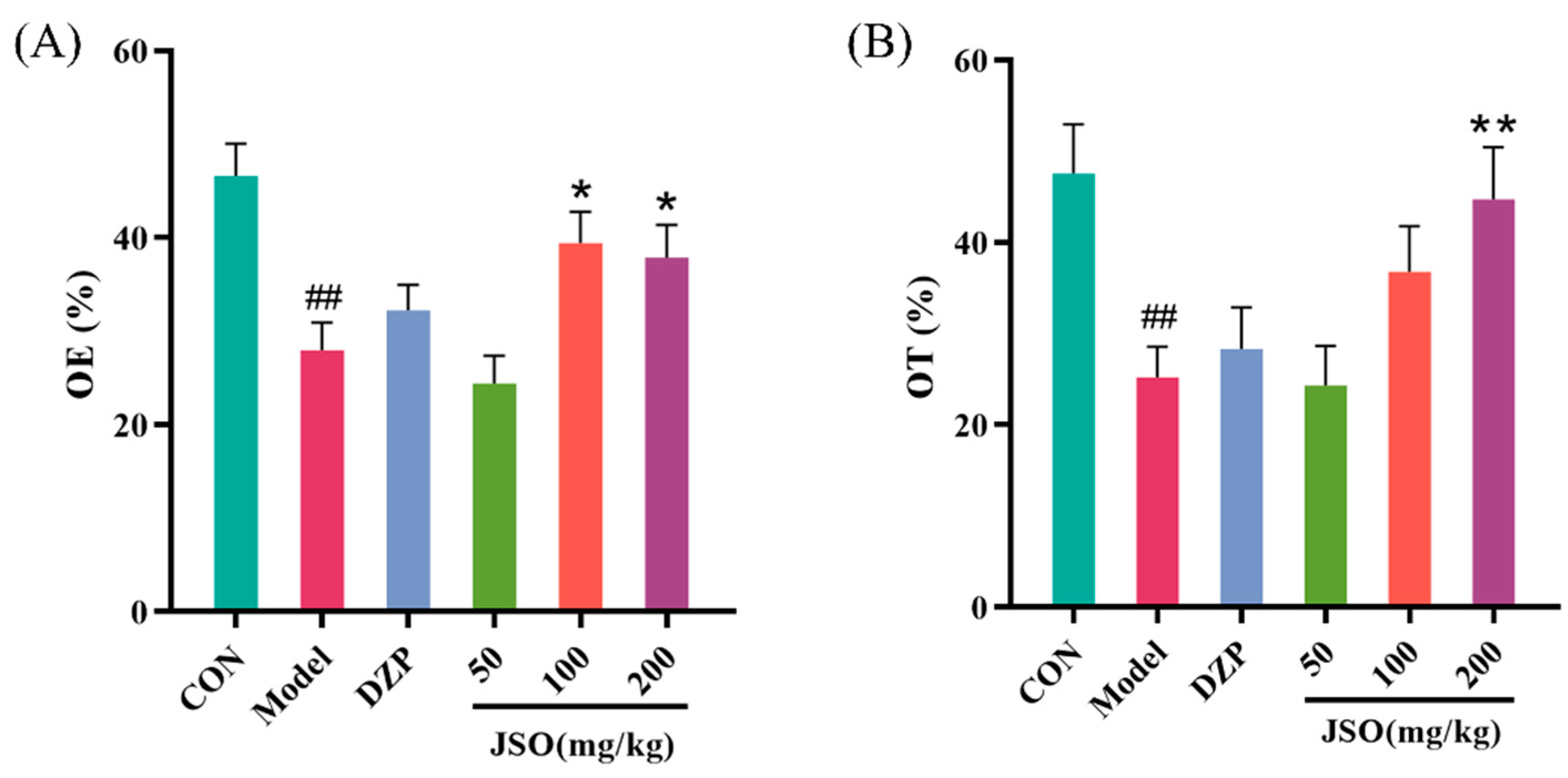
3.2.2. Effect of JSO on the EPM in CSD-Stressed Mice
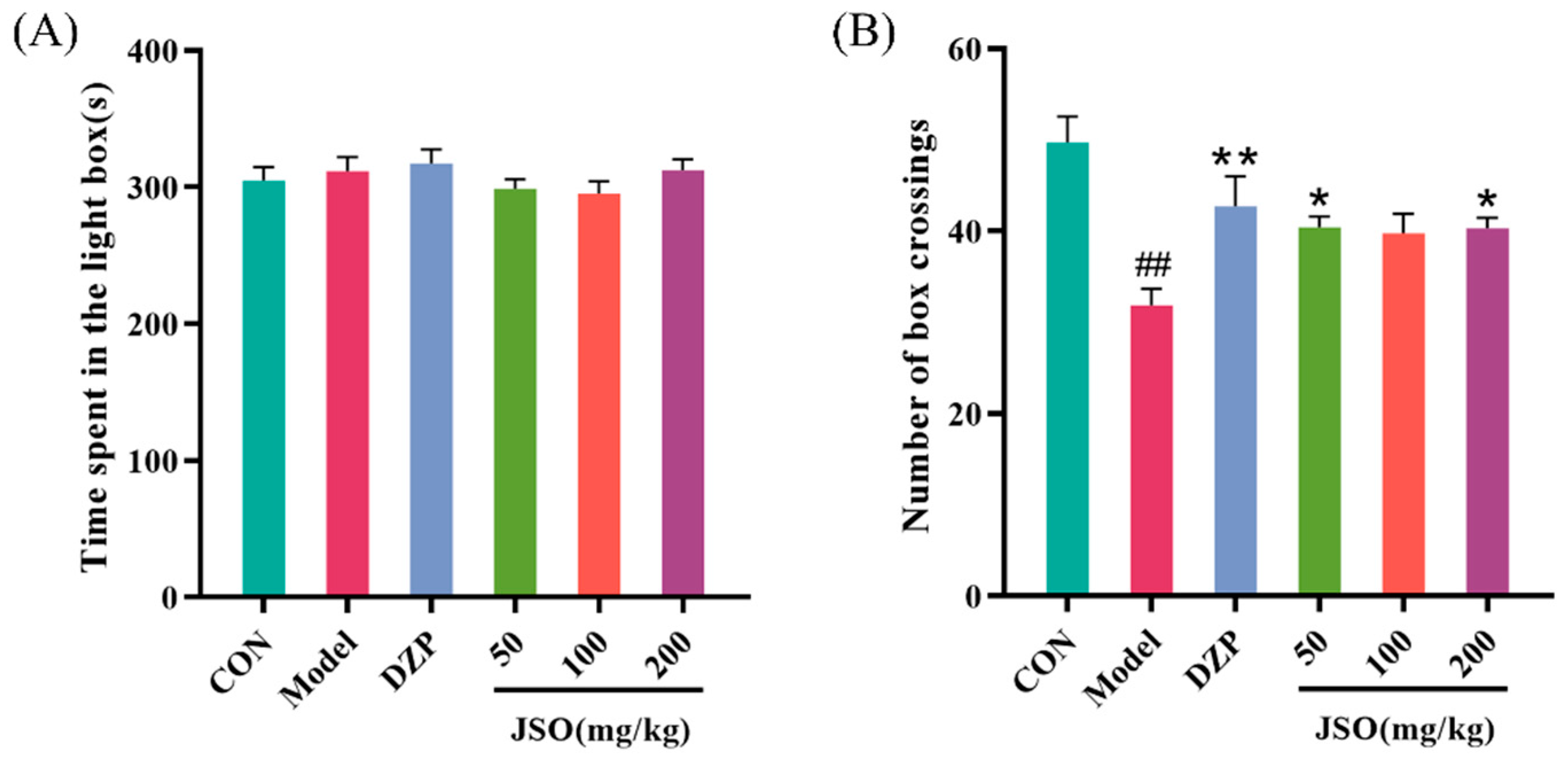
3.2.3. Effect of JSO on the LDT in CSD-Stressed Mice
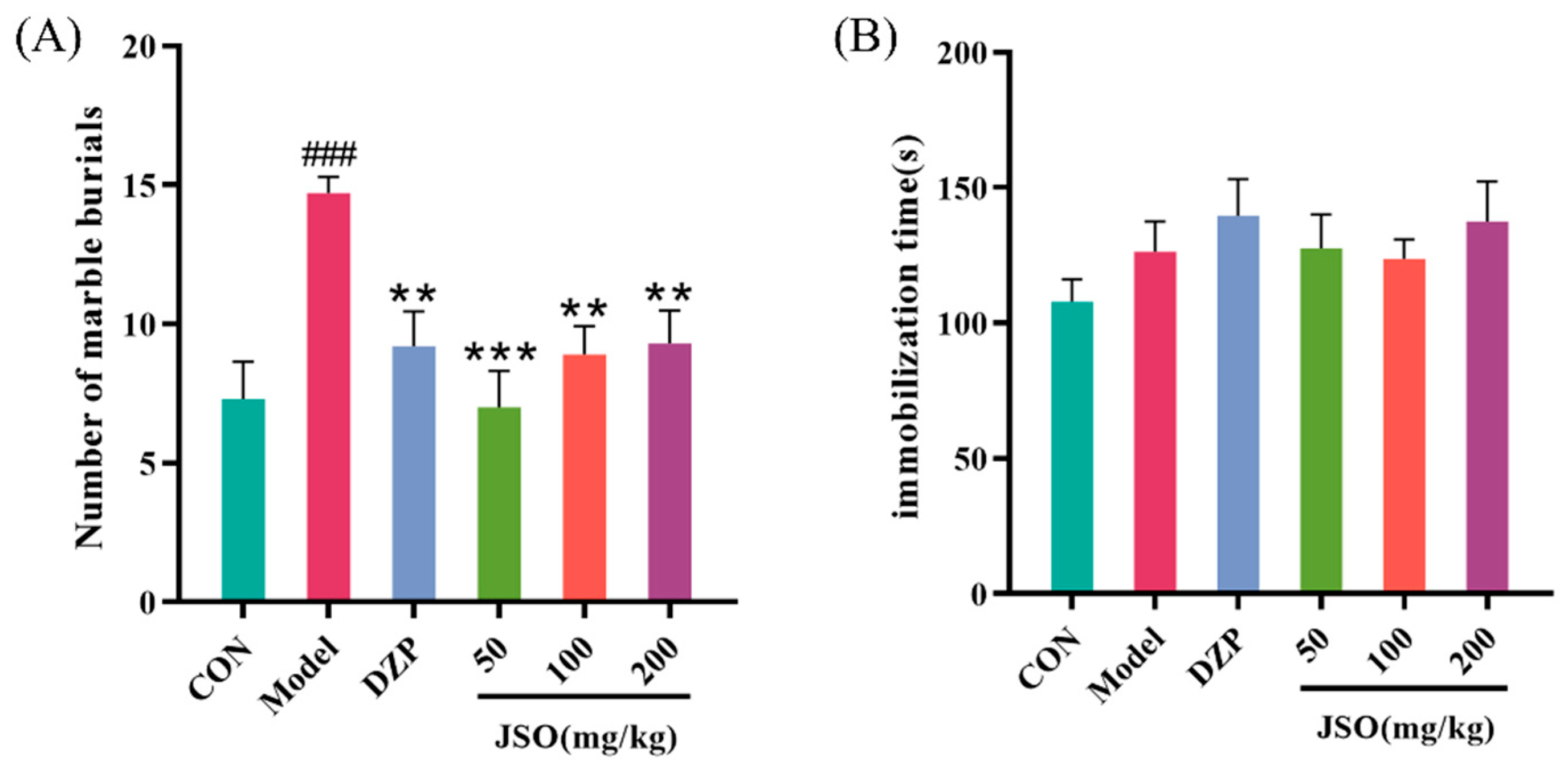
3.2.4. Effects of JSO on the MBT in CSD-Stressed Mice
3.2.5. Effect of JSO on the FST in CSD-Stressed Mice
3.3. Effect of JSO on the Gut Microbiota Diversity in CSD-Stressed Mice
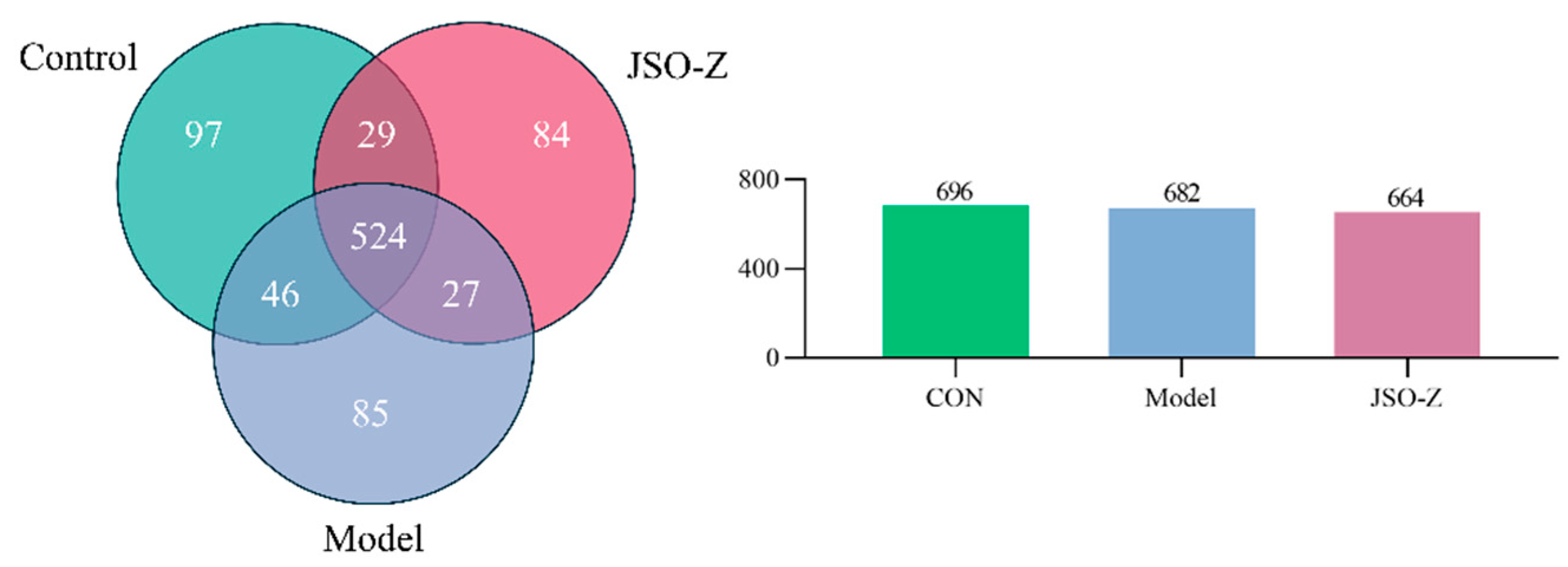
3.3.1. Operational Taxonomic Units (OTU) Analysis
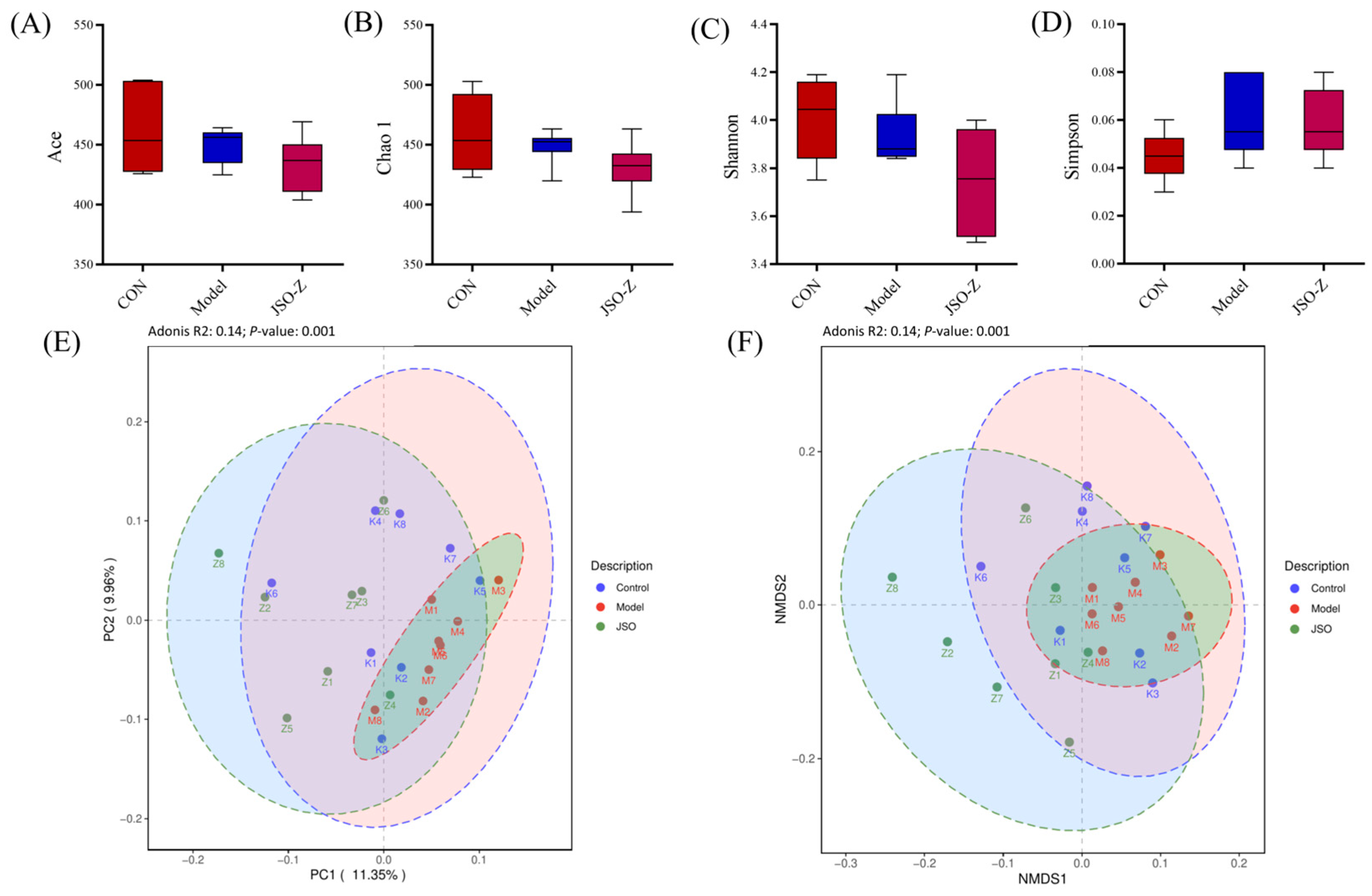
3.3.2. Biodiversity Analysis of Gut Microbiota
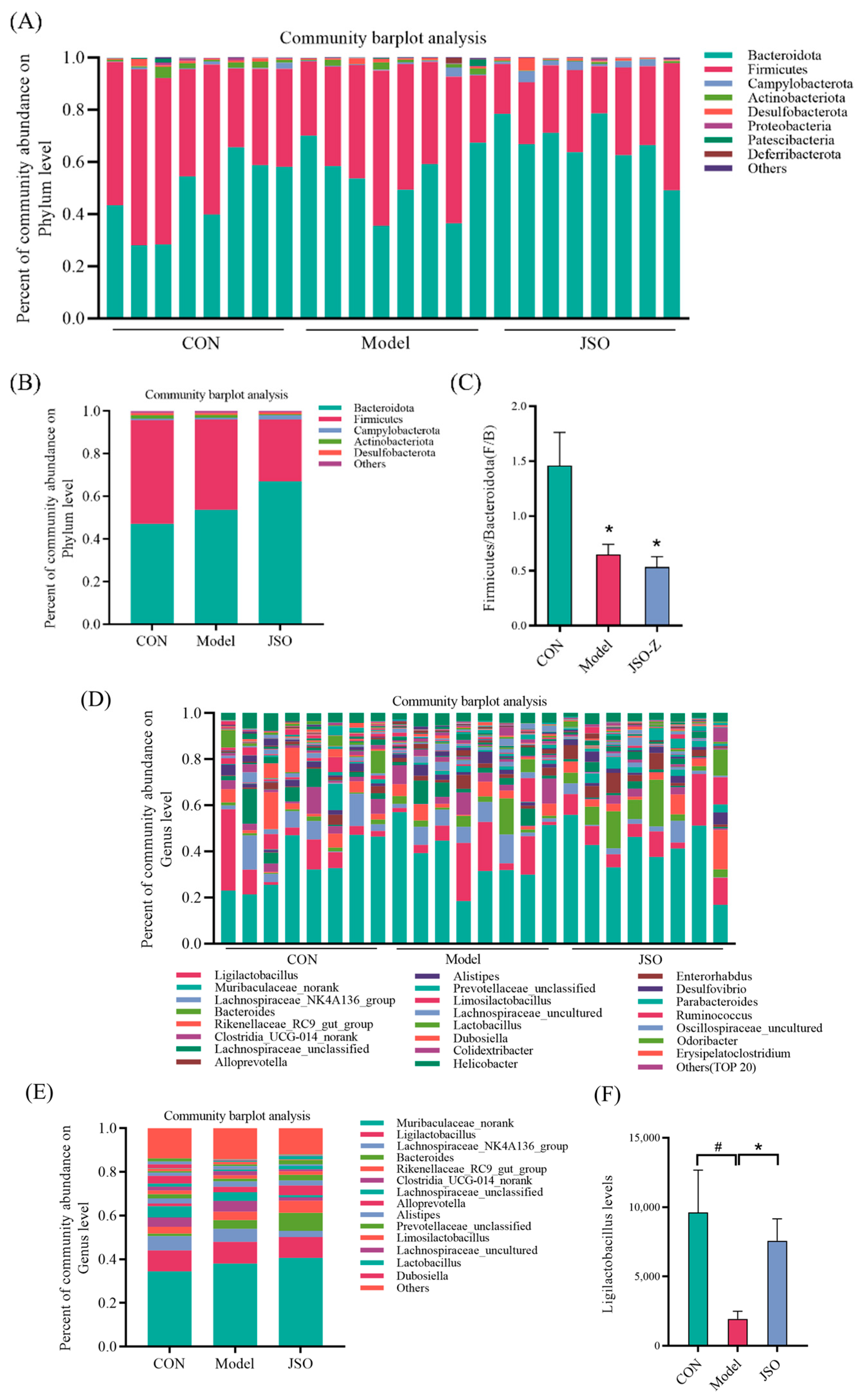
3.3.3. Analysis of Gut Microbiota Composition at the Phylum and Genus Levels
3.3.4. Differential Microbial Genera Analysis in JSO-Treated Gut
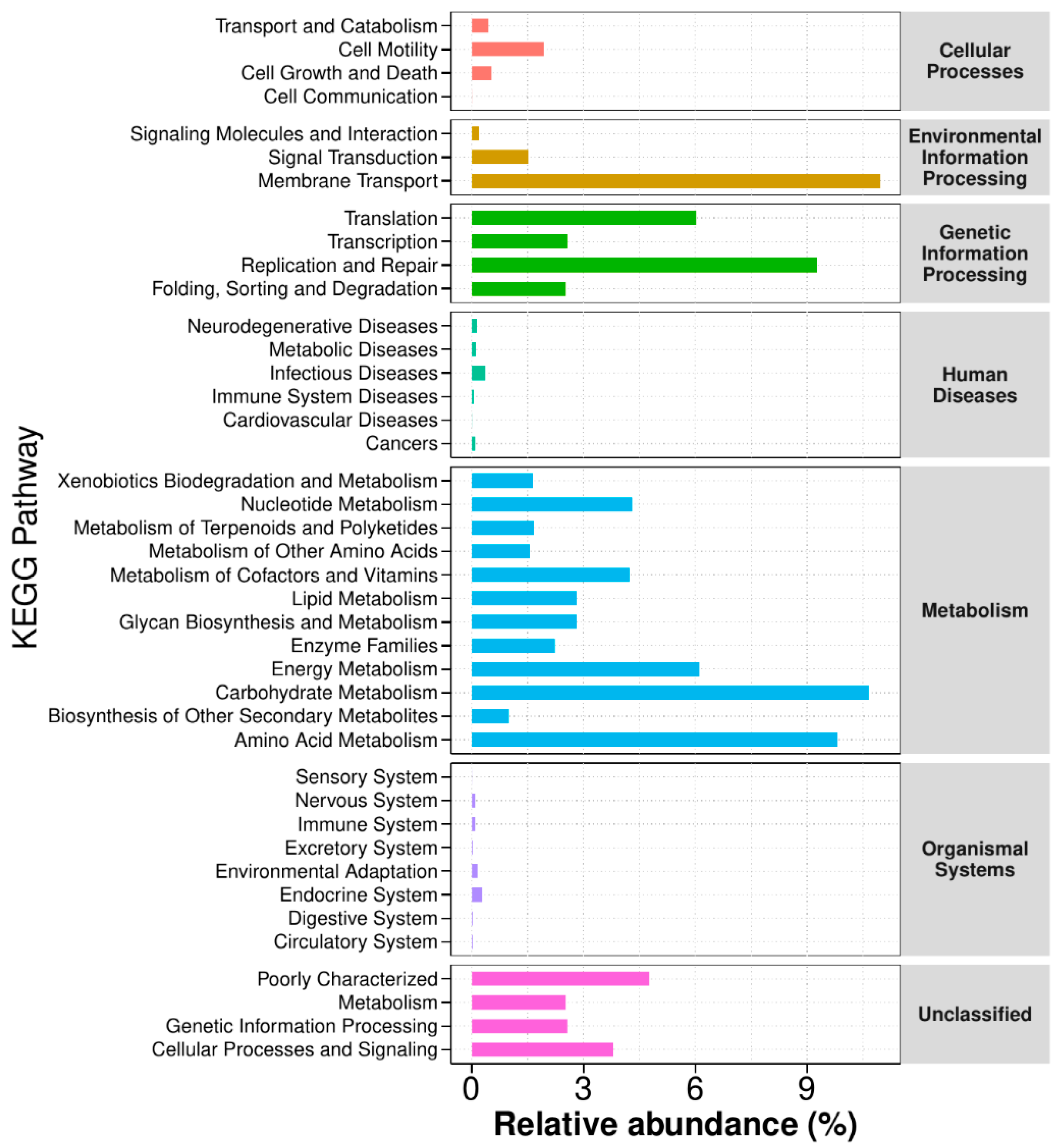
3.3.5. Functional Annotation Analysis of KEGG Metabolic Pathways
3.4. Effect of JSO on Cortical Pathway-Related Proteins in CSD-Stressed Mice
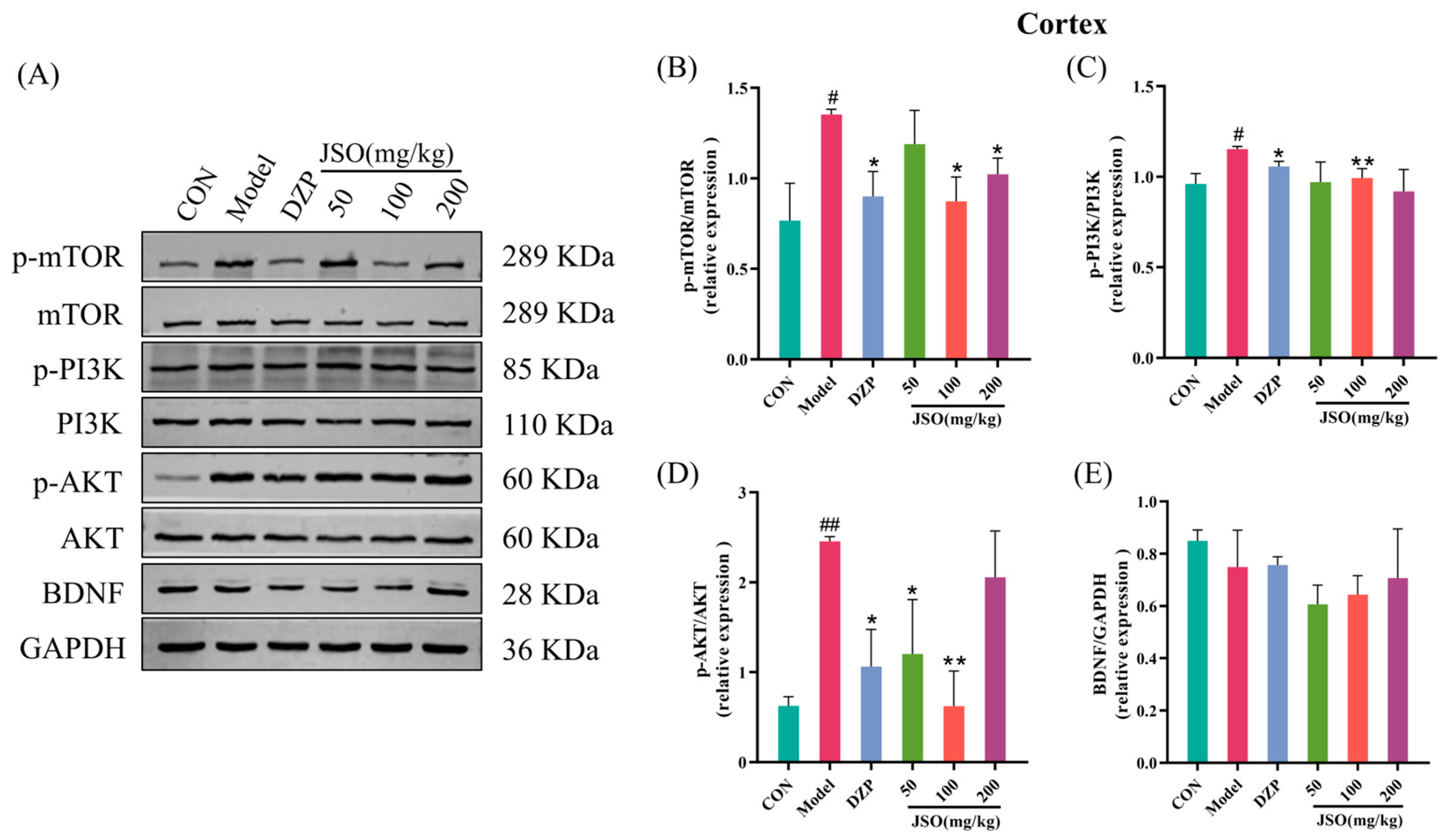
3.4.1. Effect of JSO on the Expression of PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway Proteins
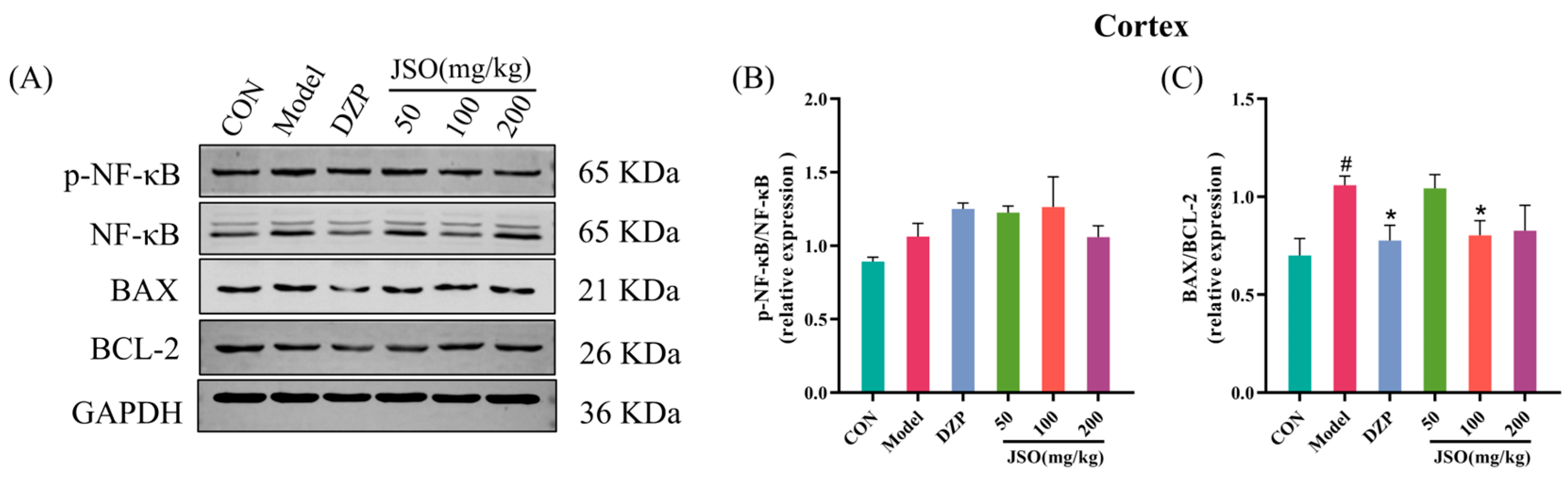
3.4.2. Effect of JSO on p-NF-κB/NF-κB and BAX/BCL-2 Proteins Expression in the Cortex
3.5. Effect of JSO on Hippocampal Pathway-Related Proteins in CSD-Stressed Mice
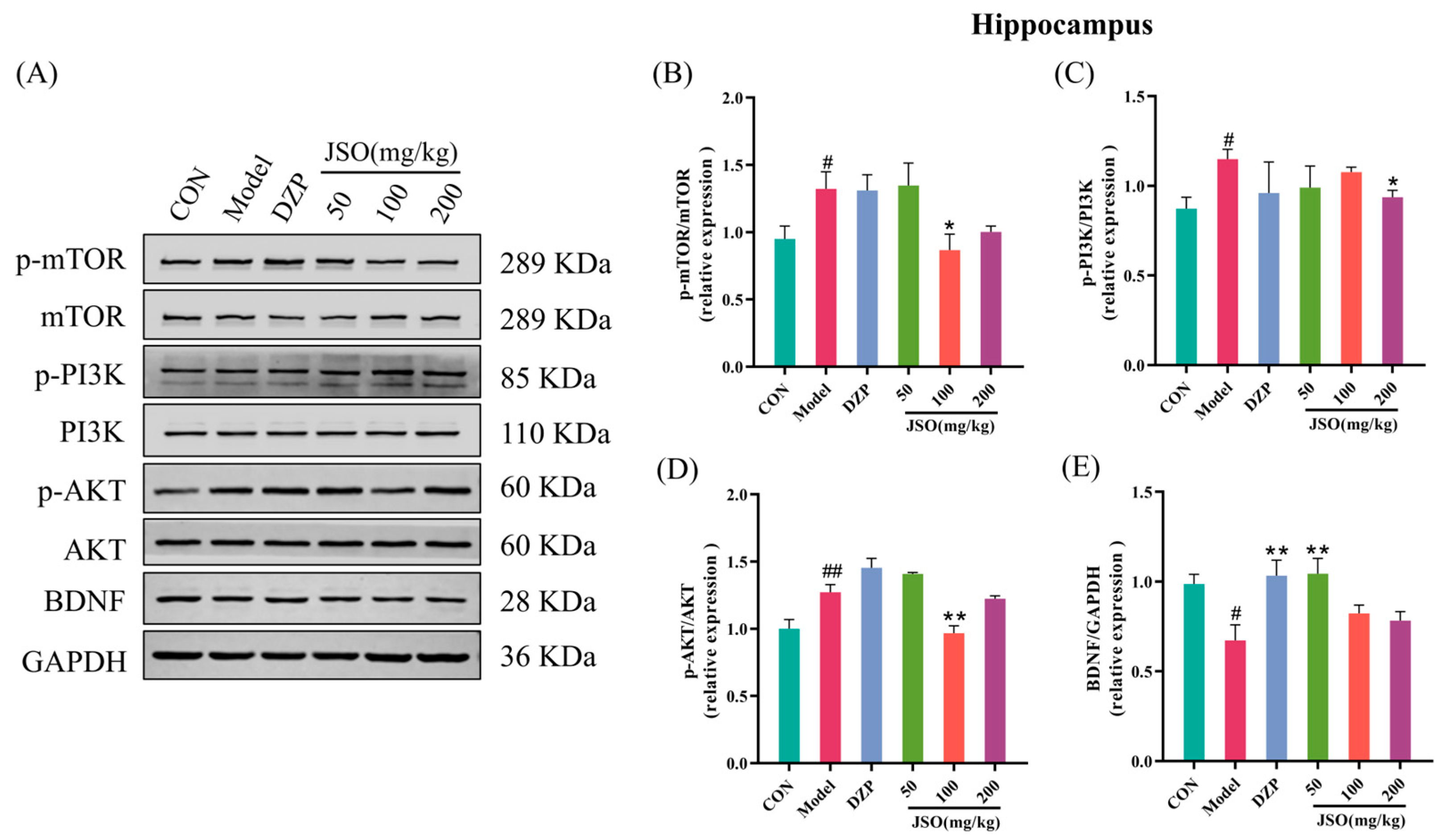
3.5.1. Effect of JSO on PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway and BDNF Expression in the Hippocampus
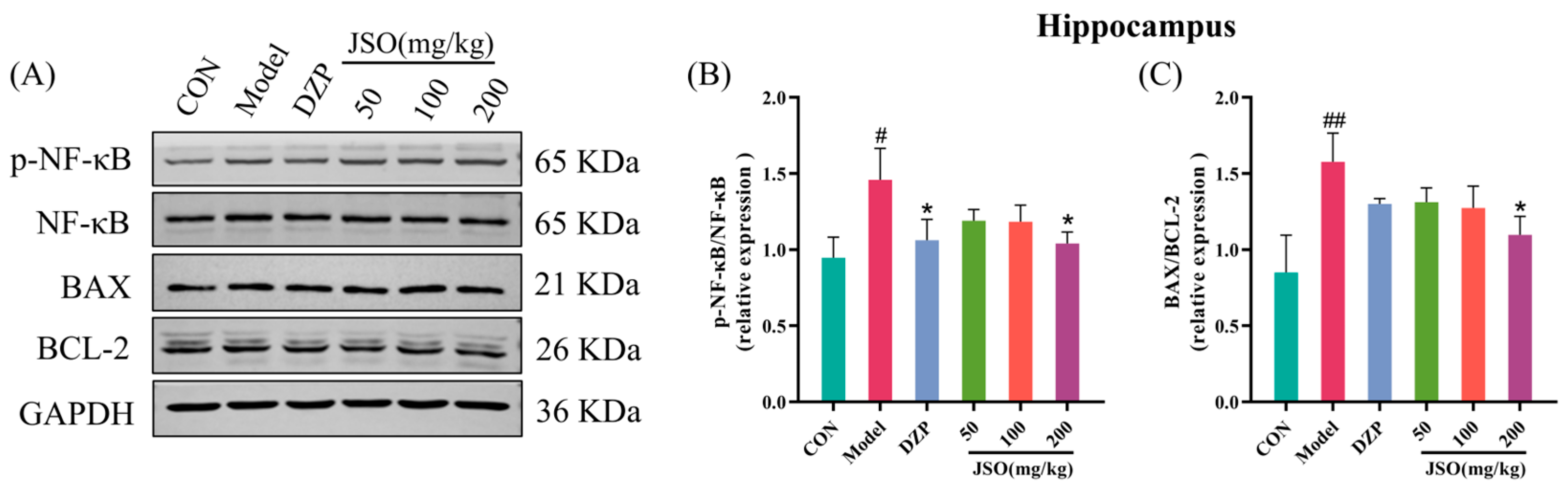
3.5.2. Effects of JSO on p-NF-κB/NF-κB and BAX/BCL-2 Proteins Expression in the Hippocampus
3.5.3. Effects of JSO on Hippocampal Neuroinflammation-Associated Proteins
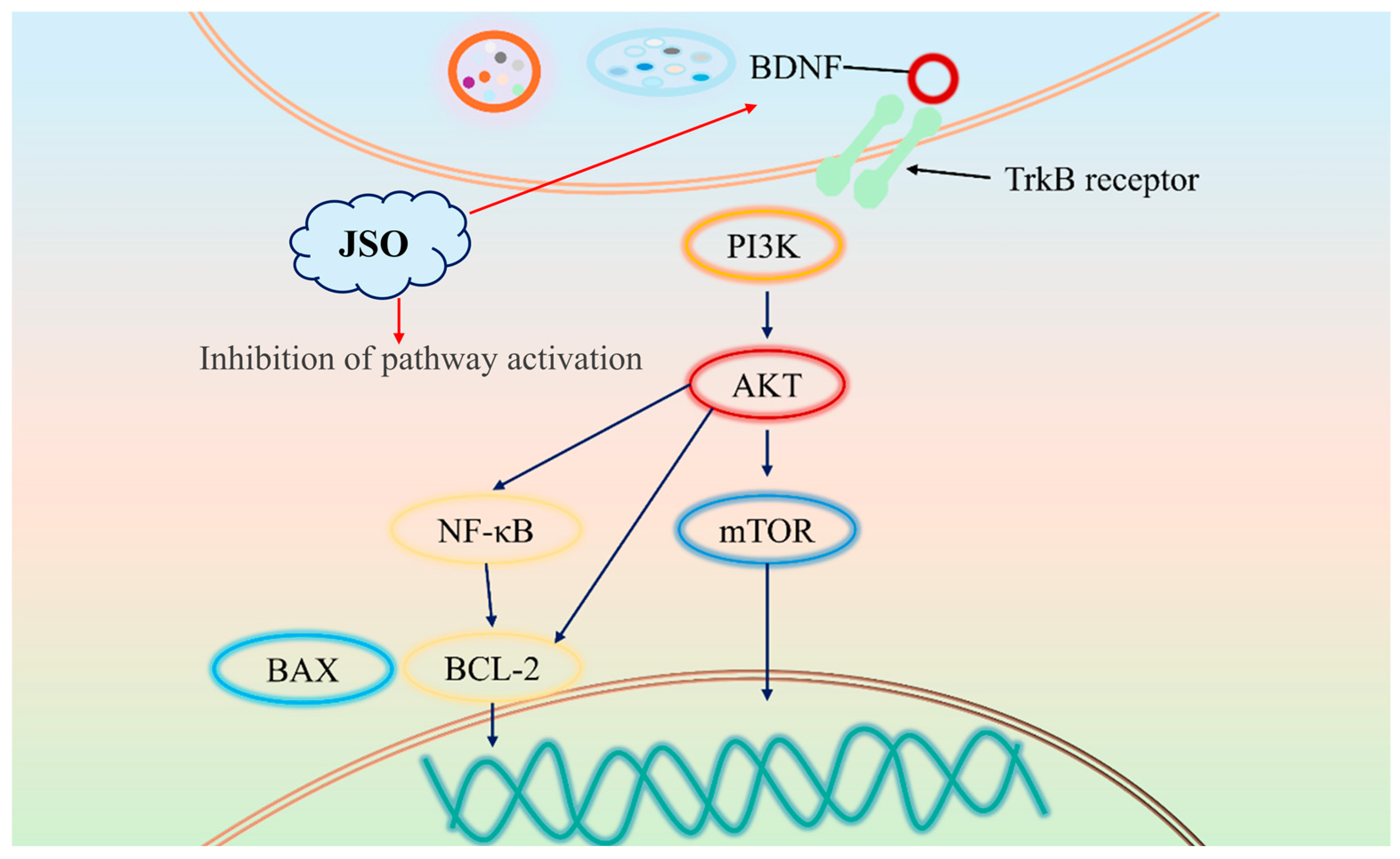
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Craske, M.; Stein, M.; Eley, T.; Milad, M.; Holmes, A.; Rapee, R.; Wittchen, H. Anxiety disorders. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittchen, H.U. Generalised anxiety disorder: An insight into the burden on the individual and society. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2000, 10, 350–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, R.C.; Chiu, W.T.; Demler, O.; Walters, E.E. Prevalence, Severity, and Comorbidity of 12-Month DSM-IV Disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2005, 62, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fergus, T.A.; Kelley, L.P.; Griggs, J.O. The combination of health anxiety and somatic symptoms: Specificity to anxiety sensitivity cognitive concerns among patients in primary care. Psychiatry Res. 2016, 239, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lader, M.; Kyriacou, A. Withdrawing Benzodiazepines in Patients with Anxiety Disorders. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2016, 18, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, J.; Bressi, J.; Lê, M.-L.; Neal, D.; Cadogan, C.; Witt-Doerring, J.; Witt-Doerring, M.; Wright, S. Prescribing and deprescribing guidance for benzodiazepine and benzodiazepine receptor agonist use in adults with depression, anxiety, and insomnia: An international scoping review. eClinicalMedicine 2024, 70, 102507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, K.; Hunsberger, H.C. Benzodiazepine-induced anterograde amnesia: Detrimental side effect to novel study tool. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1257030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowitz, M.; Eaton, C.; Haney, N.; Kohn, T.; Li, O.; Pil, E.; Herati, A. (018) Negative Perceptions Among Young Adult Males Towards Antidepressants and Their Sexual Side Effects: A Case for Atypical Agents? J. Sex. Med. 2023, 20, qdad060-018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, J.C.F.; Van Den Berg, P.B.; Tobi, H.; De Jong, L.T.W.; Berg, V.D. Combined use of SSRIs and NSAIDs increases the risk of gastrointestinal adverse effects. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2003, 55, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freret, T.; Largilliere, S.; Nee, G.; Coolzaet, M.; Corvaisier, S.; Boulouard, M. Fast Anxiolytic-Like Effect Observed in the Rat Conditioned Defensive Burying Test, after a Single Oral Dose of Natural Protein Extract Products. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarma, M.K.; Saha, D.; Das, B.K.; Das, T.; Azizov, S.; Kumar, D. A delve into the pharmacological targets and biological mechanisms of Paederia foetida Linn.: A rather invaluable traditional medicinal plant. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2023, 396, 2217–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maimaiti, A.; Yahapu, W.; Chen, L.; Ma, X.; Yao, G. Research progress on active components of Cichorium intybus L. Chin. J. Ethnomed. Ethnopharm. 2023, 32, 65–69. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xie, M.; Jiang, B.; Song, L.; Lu, M. Research progress on health functions and product development of Cichorium intybus L. polysaccharides. Liaoning Agric. Sci. 2020, 5, 59–61. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Yao, Y.; Li, X.; Dong, J.; Zhang, A. Alteration of GABAergic signaling is associated with anxiety-like behavior in temporal lobe epilepsy mice. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 93, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Maton, N.; Delzenne, N.M. Oligofructose Promotes Satiety in Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet: Involvement of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1. Obes. Res. 2005, 13, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taper, H.S.; Roberfroid, M. Influence of Inulin and Oligofructose on Breast Cancer and Tumor Growth1. J. Nutr. 1999, 129, 1488S–1491S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafabadi, M.E.; Nasiraie, L.R.; Pirblouti, A.G.; Noori, H.R. Biological and prebiotic activities of polysaccharides from Taraxacum officinale F. H. Wigg., Cichorium intybus L., and Gundelia tournefortii L. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Jiang, N.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, R.; He, Q.; Chang, Q.; Liu, X. Effects of inulin-type oligosaccharides (JSO) from Cichorium intybus L. on behavioral deficits induced by chronic restraint stress in mice and associated molecular alterations. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1484337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Bei, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, F.; Pan, R.; Chang, Q.; He, Q.; Liu, X.; et al. Cichorium intybus L. Oligo-Polysaccharides (CIO) Exerts Antianxiety and Antidepressant Effects on Mice Experiencing Behavioral Despair and Chronic Unpredicted Mild Stress. Foods 2025, 14, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundelin, T.; Holding, B.C. Trait Anxiety Does Not Predict the Anxiogenic Response to Sleep Deprivation. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 880641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, R.G. The use of a plus-maze to measure anxiety in the mouse. Psychopharmacology 1987, 92, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellow, S.; File, S.E. Anxiolytic and anxiogenic drug effects on exploratory activity in an elevated plus-maze: A novel test of anxiety in the rat. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1986, 24, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porsolt, R.D.; Bertin, A.; Jalfre, M. Behavioral despair in mice: A primary screening test for antidepressants. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Therapie 1977, 229, 327–336. [Google Scholar]
- Porsolt, R.D.; Bertin, A.; Jalfre, M. “Behavioural despair” in rats and mice: Strain differences and the effects of imipramine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1978, 51, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Wu, X. Brain Neurotransmitter Modulation by Gut Microbiota in Anxiety and Depression. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 649103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Jin, H.; Kwok, L.-Y.; Sun, Z.; Liong, M.-T.; Zhang, H. Probiotic consumption relieved human stress and anxiety symptoms possibly via modulating the neuroactive potential of the gut microbiota. Neurobiol. Stress 2021, 14, 100294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-T.; Sun, C.-L.; Lai, T.-T.; Liou, C.-W.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Xue, J.-Y.; Wang, H.-W.; Chai, L.M.X.; Lee, Y.-J.; Chen, S.-L.; et al. Oral short-chain fatty acids administration regulates innate anxiety in adult microbiome-depleted mice. Neuropharmacology 2022, 214, 109140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chen, L.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Hsu, C.; Zeng, J.; et al. Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids ameliorate methamphetamine-induced depression- and anxiety-like behaviors in a Sigmar-1 receptor-dependent manner. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 4801–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, C.A.; Diaz-Arteche, C.; Eliby, D.; Schwartz, O.S.; Simmons, J.G.; Cowan, C.S.M. The gut microbiota in anxiety and depression—A systematic review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2021, 83, 101943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado-Franco, J.J.; Ellison, A.; Moore, C.; Weerts, E.; Williams, D. You are what you vape: Implications of THC chronic self-administration in changes in the gut microbiome of rats. J. Immunol. 2023, 210, 228.07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, M.G.; Passot, S.; Campoy, S.; Olivares, M.; Fonseca, F. Ligilactobacillus salivarius functionalities, applications, and manufacturing challenges. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 57–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Peng, Q.; Tian, Y.; Chen, X.; Tian, D.; Ma, L.; Gong, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Shi, B. Transcriptional and functional analysis of epilactose transport and catabolism in the probiotic Ligilactobacillus salivarius ZL6. Food Biosci. 2025, 63, 105750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhalim, K.A. Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) from gastrointestinal disorders, metabolism, epigenetics, central nervous system to cancer—A mini-review. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2024, 388, 110851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, C.; Li, W.; Zhao, B.; He, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, T.; Li, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, Z. Short-chain fatty acids mediate gut microbiota–brain communication and protect the blood–brain barrier integrity. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2025, 1545, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Shi, L.; Bao, M.-Y.; Yu, F.-L.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.-X.; Lin, J.-C.; Jia, W.; et al. Dietary ellagic acid therapy for CNS autoimmunity: Targeting on Alloprevotella rava and propionate metabolism. Microbiome 2024, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.C.; Gourley, S.L.; Ressler, K.J. Prelimbic BDNF and TrkB signaling regulates consolidation of both appetitive and aversive emotional learning. Transl. Psychiatry 2012, 2, e205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillot, C.R.; Kelly, M.E.; Phillips, N.B.; Su, M.-Y.; Douglas, M.E.; Poe, D.J.; Berman, M.E.; Liang, T. BDNF and stress/mood-related interactions on emotional disorder symptoms, executive functioning, and deliberate self-harm. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2023, 163, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Zou, R.; Song, L.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, B.; Wang, G.; Lee, Y.-k.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Ingestion of Bifidobacterium longum subspecies infantis strain CCFM687 regulated emotional behavior and the central BDNF pathway in chronic stress-induced depressive mice through reshaping the gut microbiota. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 7588–7598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwan, A.R.; Hing, B.; Erickson, J.C.; Hutchings, G.; Urama, C.; Norton-Hughes, E.; D’Ippolito, M.; Berry, S.; Delibegovic, M.; Grassmann, F.; et al. An ancient polymorphic regulatory region within the BDNF gene associated with obesity modulates anxiety-like behaviour in mice and humans. Mol. Psychiatry 2024, 29, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Xu, J.; Shen, J.; Tang, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Sun, J. Esketamine Prevents Postoperative Emotional and Cognitive Dysfunction by Suppressing Microglial M1 Polarization and Regulating the BDNF-TrkB Pathway in Ageing Rats with Preoperative Sleep Disturbance. Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 61, 5680–5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Wei, S.; Wei, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, M.; Wu, J. Anger Emotional Stress Influences VEGF/VEGFR2 and Its Induced PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Neural Plast. 2016, 2016, 4129015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maidana, L.M.; Guerra, J.M.d.S.; Souza-Pereira, A.; Lins, M.P.; Moreira-Silva, M.J.; Paiva, E.G.; Godinho, D.B.; Royes, L.F.F.; Rambo, L.M. Previous strength training attenuates ouabain-induced bipolar disorder-related behaviors and memory deficits in rats: Involvement of hippocampal ERK/CREB and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways. Neurochem. Int. 2025, 183, 105919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Ni, H.; Sun, J.; Yang, X.; Chen, W.; Zhao, W.; Zhong, X.; He, C.; et al. Sinisan Protects Primary Hippocampal Neurons Against Corticosterone by Inhibiting Autophagy via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 627056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Gui, Q.; Wu, G.; Zhu, W.; Dong, X.; Shen, M.; Fu, X.; Shi, G.; Luo, H.; Yang, X.; et al. Long noncoding RNA Nespas inhibits apoptosis of epileptiform hippocampal neurons by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2021, 398, 112384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Mahapatra, K.K.; Praharaj, P.P.; Patra, S.; Mishra, S.R.; Patil, S.; Bhutia, S.K. Prolonged glutamine starvation reactivates mTOR to inhibit autophagy and initiate autophagic lysosome reformation to maintain cell viability. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2024, 177, 106694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unteroberdörster, M.; Herring, A.; Bendix, I.; Lückemann, L.; Petschulat, J.; Sure, U.; Keyvani, K.; Hetze, S.; Schedlowski, M.; Hadamitzky, M. Neurobehavioral effects in rats with experimentally induced glioblastoma after treatment with the mTOR-inhibitor rapamycin. Neuropharmacology 2021, 184, 108424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehl, M.; Ladevèze, E.; Catania, C.; Cota, D.; Abrous, D.N. Inhibition of mTOR signaling by genetic removal of p70 S6 kinase 1 increases anxiety-like behavior in mice. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, E.J.; Reichardt, L.F. Neurotrophins: Roles in Neuronal Development and Function1. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 677–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Nagappan, G.; Lu, Y. BDNF and Synaptic Plasticity, Cognitive Function, and Dysfunction. In Neurotrophic Factors; Lewin, G.R., Carter, B.D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 223–250. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.; Poo, M.-m. Neurotrophin regulation of neural circuit development and function. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, P.; Schoeniger, A.; Edlich, F. Pro-apoptotic complexes of BAX and BAK on the outer mitochondrial membrane. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Cell Res. 2022, 1869, 119317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, D.L.; Tjandra, N. Inducible fold-switching as a mechanism to fibrillate pro-apoptotic BCL-2 proteins. Biopolymers 2021, 112, e23424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Han, F.; Shi, Y. Increased Neuronal Apoptosis in Medial Prefrontal Cortex is Accompanied with Changes of Bcl-2 and Bax in a Rat Model of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2013, 51, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.-Y.; Yan, H.-X.; Zhao, Y.-X.; Xu, H.; Hong, Y.-F.; Ma, Q.-Y.; Xu, Y.; Fu, Q.-Q. Effects of electroacupuncture on the behaviors and expressions of hippocampal neurotransmitters and Bax/Bcl-2 proteins in rat models of anxiety disorder. J. Acupunct. Tuina Sci. 2020, 18, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Zhang, M.; Hao, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, C. Neuroinflammation mechanisms of neuromodulation therapies for anxiety and depression. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wei, D.; Yan, M.; Su, S.; Pan, H.; Wang, Q. Effects of sleep deprivation on anxiety-depressive-like behavior and neuroinflammation. Brain Res. 2024, 1836, 148916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, E.; Kim, Y.-K. Neuroinflammation-Associated Alterations of the Brain as Potential Neural Biomarkers in Anxiety Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brydges, S.D.; Broderick, L.; McGeough, M.D.; Pena, C.A.; Mueller, J.L.; Hoffman, H.M. Divergence of IL-1, IL-18, and cell death in NLRP3 inflammasomopathies. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 4695–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Sheng, H.; Bao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Ni, X. NLRP3 inflammasome activation mediates estrogen deficiency-induced depression- and anxiety-like behavior and hippocampal inflammation in mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 56, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munshi, S.; Albrechet-Souza, L.; dos-Santos, R.C.; Stelly, C.E.; Secci, M.E.; Gilpin, N.W.; Tasker, J.G. Acute Ethanol Modulates Synaptic Inhibition in the Basolateral Amygdala via Rapid NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Regulates Anxiety-Like Behavior in Rats. J. Neurosci. 2023, 43, 7902–7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Chen, F.; Qiang, M.; Liu, M.; Pan, R.; Chang, Q.; Wang, N.; Usmani, M.W.; et al. Anxiolytic Effects of Cichorium intybus L. Oligo-Polysaccharides by Modulating Gut Microbiota, Neuronal Signaling Pathways, and Neuroinflammation in Chronic Sleep Deprivation-Stressed Mice. Foods 2025, 14, 1859. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111859
Zhao Y, Zhang Y, Luo Y, Chen F, Qiang M, Liu M, Pan R, Chang Q, Wang N, Usmani MW, et al. Anxiolytic Effects of Cichorium intybus L. Oligo-Polysaccharides by Modulating Gut Microbiota, Neuronal Signaling Pathways, and Neuroinflammation in Chronic Sleep Deprivation-Stressed Mice. Foods. 2025; 14(11):1859. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111859
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yongzhi, Yiwen Zhang, Yanqin Luo, Fang Chen, Meng Qiang, Mengchao Liu, Ruile Pan, Qi Chang, Ning Wang, Muhammad Wasim Usmani, and et al. 2025. "Anxiolytic Effects of Cichorium intybus L. Oligo-Polysaccharides by Modulating Gut Microbiota, Neuronal Signaling Pathways, and Neuroinflammation in Chronic Sleep Deprivation-Stressed Mice" Foods 14, no. 11: 1859. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111859
APA StyleZhao, Y., Zhang, Y., Luo, Y., Chen, F., Qiang, M., Liu, M., Pan, R., Chang, Q., Wang, N., Usmani, M. W., Jiang, N., & Liu, X. (2025). Anxiolytic Effects of Cichorium intybus L. Oligo-Polysaccharides by Modulating Gut Microbiota, Neuronal Signaling Pathways, and Neuroinflammation in Chronic Sleep Deprivation-Stressed Mice. Foods, 14(11), 1859. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111859






