Investigation of Biogenic Amines and Quality in Jerky, Bacon, and Sausage: Chinese Traditional Meat Product
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Samples
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Determination of TVB-N, Nitrite Residue, Protein Content
2.4. Determination of Proteolysis Index (PI)
2.5. Free Amino Acid (FAA)
2.6. Biogenic Amines (BAs)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
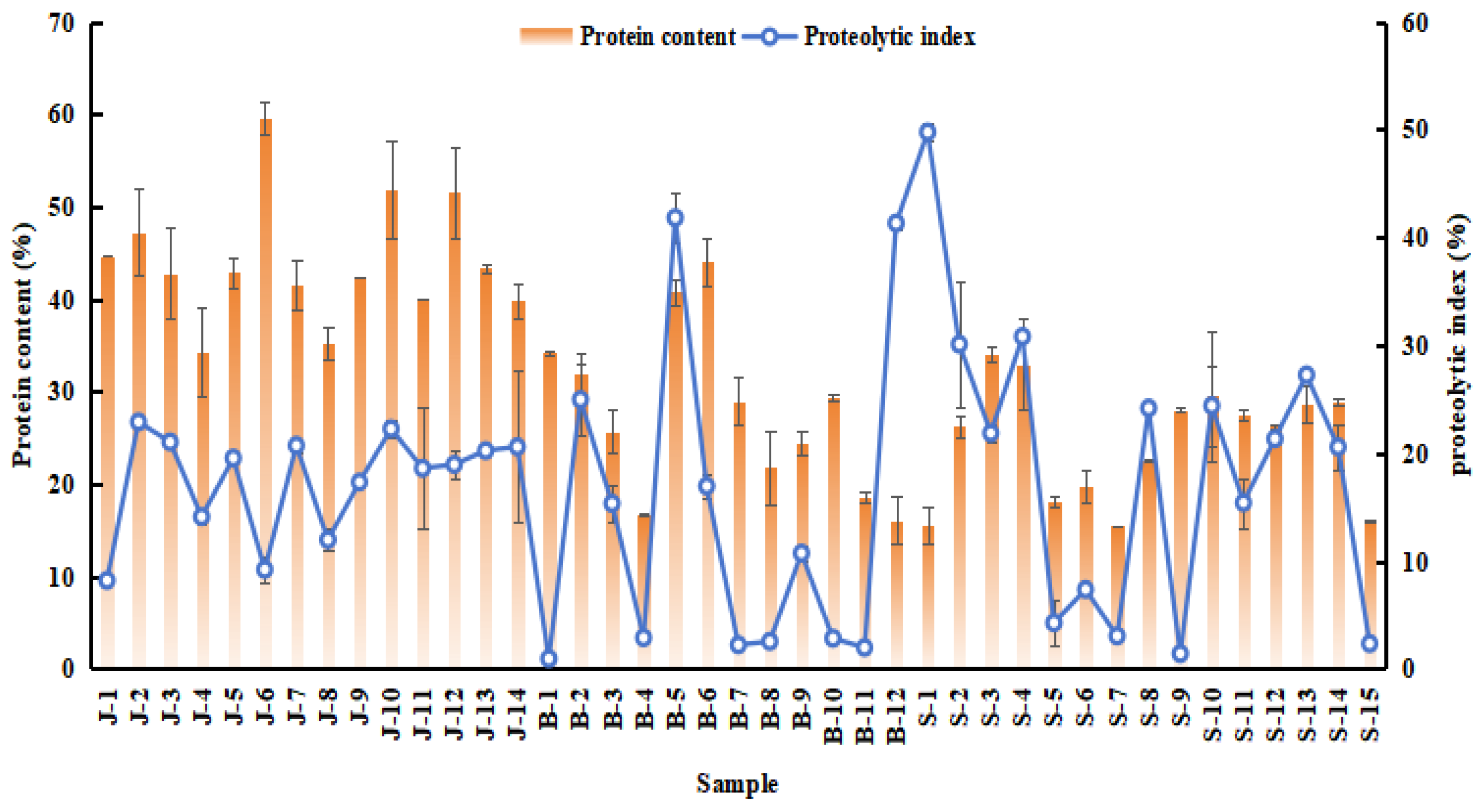
3.1. Protein Content and Proteolytic Index (PI) of Traditional Meat Products
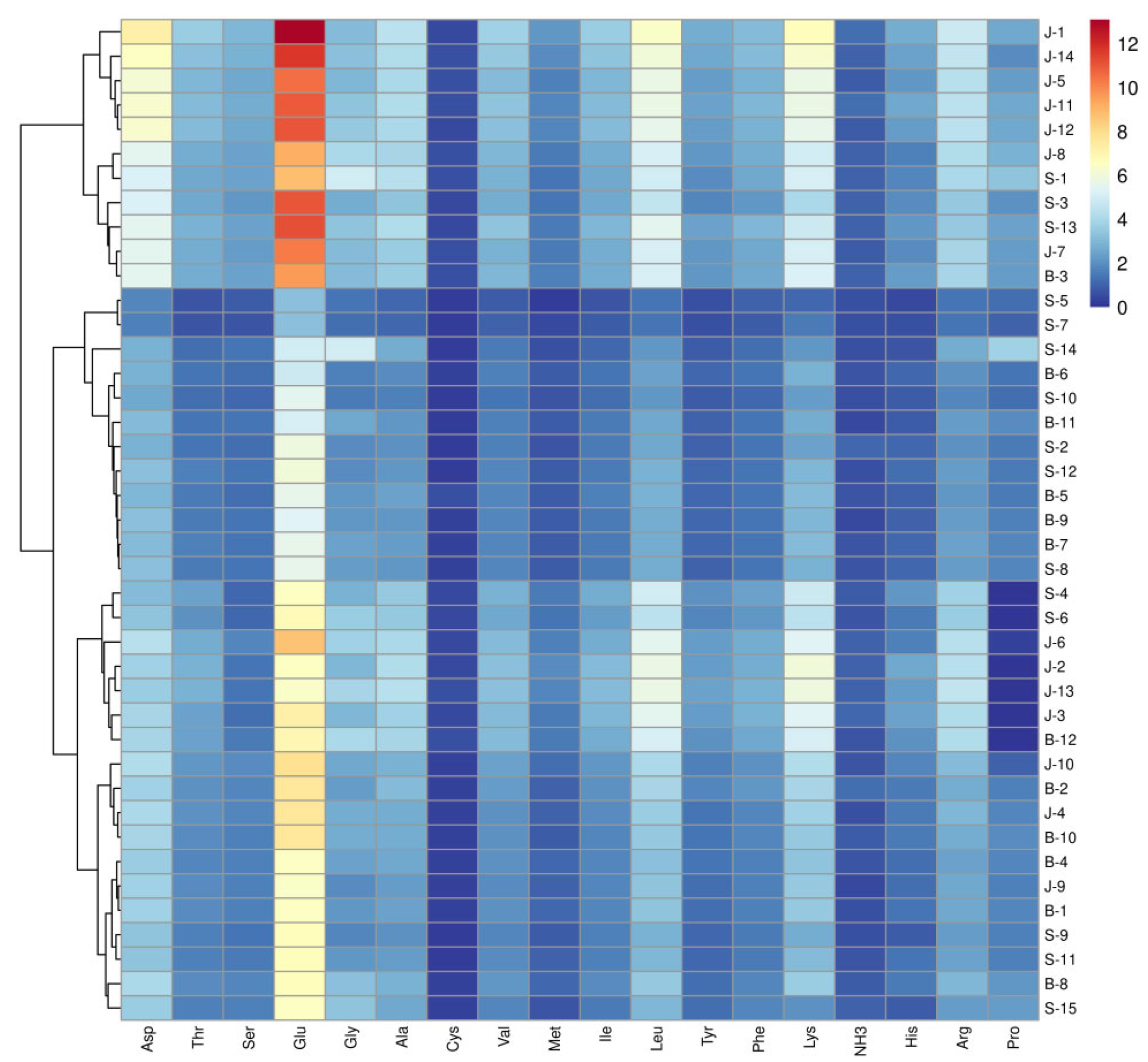
3.2. Analysis of Free Amino Acid Content in Traditional Meat Products from Different Regions
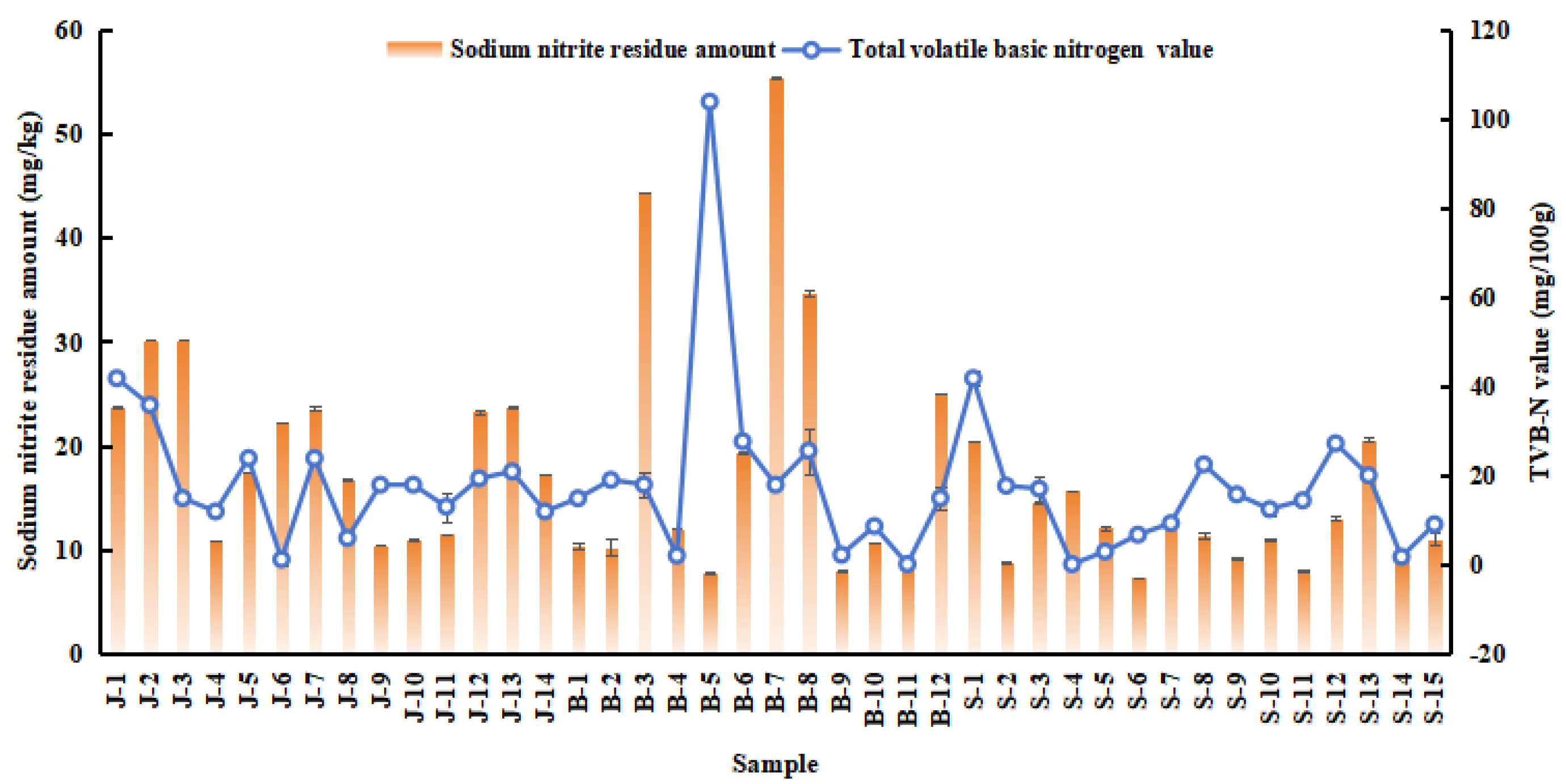
3.3. Analysis of Sodium Nitrite Residue Amount and TVB-N in Traditional Meat Products from Different Regions
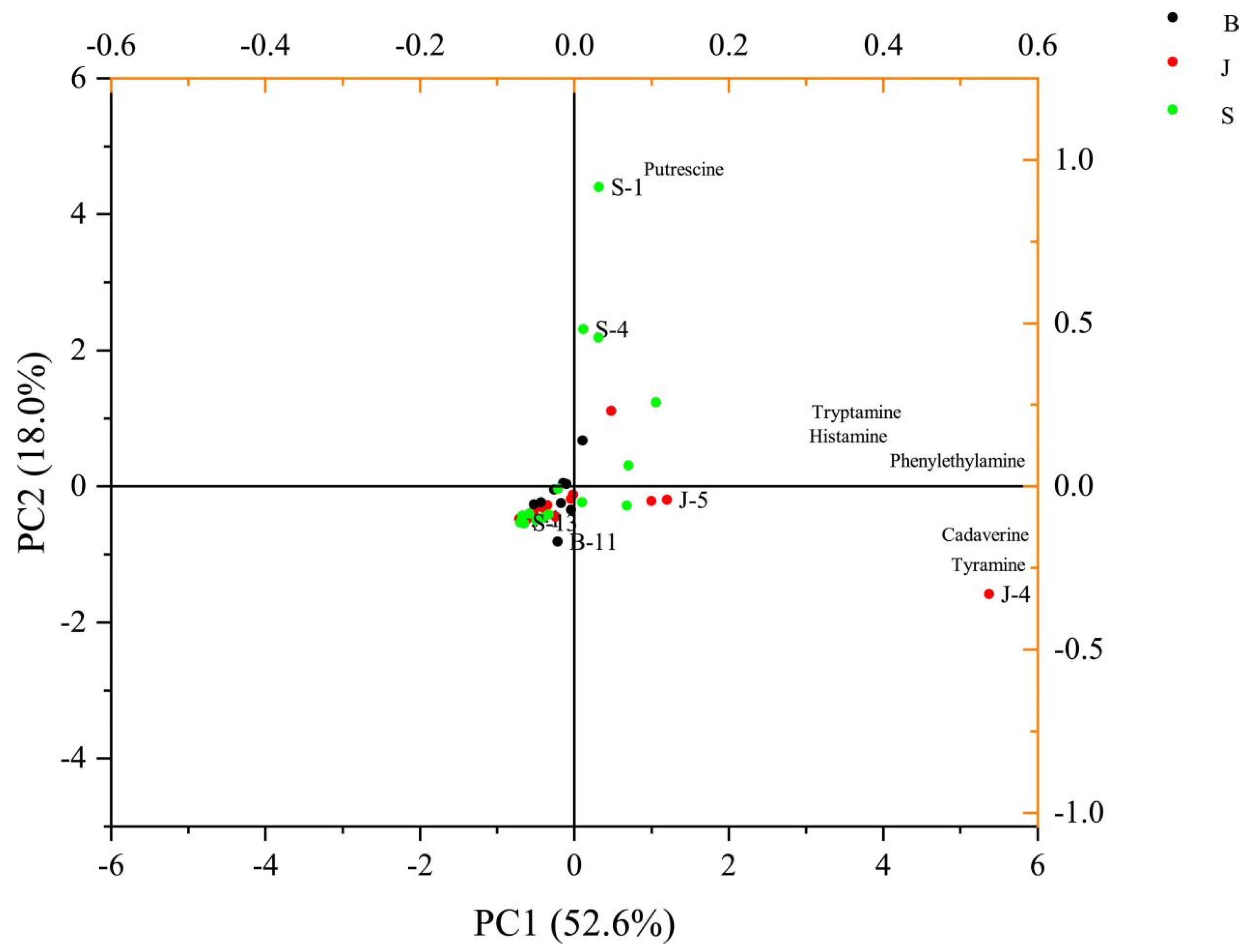
3.4. Analysis of BAs in Traditional Meat Products from Different Regions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MAO | Monoamine oxidase |
| BAs | Biogenic amines |
| FAA | Free amino acid |
| NPN | Non-protein nitrogen |
| PI | Proteolysis index |
| TVB-N | Total volatile basic nitrogen |
References
- Zhang, W.G.; Xiao, S.; Samaraweera, H.; Lee, E.J.; Ahn, D.U. Improving functional value of meat products. Meat Sci. 2010, 86, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.L.; Xu, X.L.; Shu, R.H.; Zhou, G.H.; Meng, Y.; Sun, Y.M.; Chen, Y.P.; Wang, P. Characterization of biogenic amines and factors influencing their formation in traditional Chinese sausages. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Wang, X.X.; Qi, N.L.; Li, J.H.; Lin, L.J.; Han, Z.P. Determination of biogenic amines in traditional Chinese fermented foods by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC). Food Addit. Contam. A 2014, 31, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abril, A.G.; Calomata, P.; Pazos, M. High-Resolution Comparative and Quantitative Proteomics of Biogenic-Amine-Producing Bacteria and Virulence Factors Present in Seafood. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 4448–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahangari, H.; Kurbanoglu, S.; Ehsani, A.; Uslu, B. Latest trends for biogenic amines detection in foods: Enzymatic biosensors and nanozymes applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, K. Health effects and occurrence of dietary polyamines: A review for the period 2005–mid 2013. Food Chem. 2014, 161, 27–39. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, S.; Xu, X.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Ren, H.; Xiong, T.; Xie, M. Integrated metatranscriptomics and metabolomics revealed the metabolic pathways of biogenic amines during Laotan Suancai fermentation. Food Biosci. 2014, 57, 103517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcik, W.; Damaziak, K.; Łukasiewicz-Mierzejewska, M.; Świder, O.; Niemiec, J.; Wójcicki, M.; Roszko, M.; Gozdowski, D.; Riedel, J.; Marzec, A. Correlation between Biogenic Amines and Their Precursors in Stored Chicken Meat. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świder, O.; Roszko, M.Ł.; Wójcicki, M.; Szymczyk, K. Biogenic Amines and Free Amino Acids in Traditional Fermented Vegetables-Dietary Risk Evaluation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 856–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regubalan, B.; Ananthanarayan, L. Investigation of biogenic amines content in fermented idli batter during storage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 1775–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ana, M.M.; Clemencia, C.; Sendra, E.; Sayas, E.; Juana, F.; José, N.P. Lipolysis, proteolysis and sensory characteristics of a Spanish fermented dry-cured meat product (salchichón) with oregano essential oil used as surface mold inhibitor. Meat Sci. 2011, 89, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Orte, P.; Lapeña, A.; Peña-Gallego, A.; Astrain, J.; Baron, C.; Pardo, I.; Polo, L.; Ferrer, S.; Cacho, J.; Ferreira, V. Biogenic amine determination in wine fermented in oak barrels: Factors affecting formation. Food Res. Int. 2008, 41, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simunovic, S.; Orevi, V.; Lakievi, B.; Djekic, I.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Barba, F.J. Digital evaluation of nitrite-reduced “kulen” fermented sausage quality. J. Food Qual. 2022, 2022, 2480746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmen, B.; Natalia, C.; Ociel, M.; Andrea, B.; Mariela, H. Biogenic amine content in C hilean G auda cheese: Physico-chemical and microbiological factors that may influence this content. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2014, 67, 554–561. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA—European Food Safety Authority; Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ). Scientific opinion on risk base control of biogenic amine formation in fermented foods. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2393–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Y.; Sun, L.N.; Su, L.; Wang, H.T.; Wang, D.; Liu, J.L.; Sun, E.K.; Hu, G.H.; Liu, C.; Gao, A.; et al. Effects of Microbial Communities on Volatile Profiles and Biogenic Amines in Beef Jerky from Inner Mongolian Districts. Foods 2022, 11, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.W.; Zhang, W.G. Biogenic amines and volatile N-nitrosamines in Chinese smoked-cured bacon (Larou) from industrial and artisanal origins. Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2023, 16, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashi, A.; Sarkadi, S.L.; Kenesei, G. Effect of high hydrostatic pressure on the free amino acid and biogenic amine content of different sausages during storage. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2025. prepublish. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komprda, T.; Smělá, D.; Pechová, P.; Kalhotka, L.; Štencl, J.; Klejdus, B. Effect of starter culture, spice mix and storage time and temperature on biogenic amine content of dry fermented sausages. Meat Sci. 2004, 67, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB-5009.228-2016; Determination of Volatile Basic Nitrogen in Food. State Food and Drug Administration of the State Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.33-2010; Determination of Nitrites and Nitrates in Food. State Food and Drug Administration of the State Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2010.
- GB 5009.5-2016; Determination of Protein in Food. State Food and Drug Administration of the State Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Hughes, M.C.; Kerry, J.P.; Arendt, E.K. Characterization of proteolysis during the ripening of semi-dry fermented sausages. Meat Sci. 2002, 62, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5009.124-2016; Determination of Amino Acids in Food. State Food and Drug Administration of the State Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Sun, X.Y.; Du, B.; Zhao, L.H.; Jin, Y.; Su, L.; Tian, J.J.; Wu, J. The effect of different starter cultures on biogenic amines and quality of fermented mutton sausages stored at 4 and 20 °C temperatures. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 4472–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, A.O.; Eva, M.H.; Jose, M.B.; Lorenzo, D.L.H. Changes in the Components of Dry-Fermented Sausages during Ripening. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2010, 39, 329–367. [Google Scholar]
- Kai, X.T.; Tiange, S.; Michael, G. Effect of starter cultures on taste-active amino acids and survival of pathogenic Escherichia coli in dry fermented beef sausages. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 244, 2203–2212. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Mo, M.; Wang, A.L.; Tang, B.B.; He, Q. Changes in N-nitrosamines, Residual Nitrites, Lipid Oxidation, Biogenic Amines, and Microbiota in Chinese Sausages Following Treatment with Tea Polyphenols and Their Palmitic Acid-modified Derivatives. J. Food Prot. 2023, 86, 100072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.B.; Hu, G.H.; Wang, H.T.; Wang, L.M.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zou, Y.F.; Zhao, L.H.; Zhou, F.; Jin, Y. Effect of Mixed Starters on Proteolysis and Formation of Biogenic Amines in Dry Fermented Mutton Sausages. Foods 2021, 10, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekhit, A.E.D.A.; Holman, B.W.B.; Giteru, S.G.; Hopkins, D.L. Total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N) and its role in meat spoilage: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 280–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naila, A.; Flint, S.; Fletcher, G.; Bremer, P.; Meerdink, G. Control of biogenic amines in food—Existing and emerging approaches. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraqueza, M.J.; Alfaia, C.M.; Barreto, A.S. Biogenic amine formation in turkey meat under modified atmosphere packaging with extended shelf life: Index of freshness. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simion, A.M.C.; Vizireanu, C.; Alexe, P.; Franco, I.; Carballo, J. Effect of the use of selected starter cultures on some quality, safety and sensorial properties of dacia sausage, a traditional romanian dry-sausage variety. Food Control 2014, 35, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilović, B.; Joković, N.; Petrović, L.; Veljović, K.; Tolinački, M.; Savić, D. The characterisation of lactic acid bacteria during the fermentation of an artisan Serbian sausage (PetrovskáKlobása). Meat Sci. 2011, 88, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercolini, D.; Casaburi, A.; Nasi, A.; Ferrocino, I.; Di Monaco, R.; Ferranti, P.; Mauriello, G.; Villani, F. Different molecular types of Pseudomonas fragi have the same overall be haviour as meat spoilers. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 142, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansur, A.R.; Song, E.J.; Cho, Y.S.; Nam, Y.D.; Choi, Y.S.; Kim, D.O.; Seo, D.H.; Nam, T.G. Comparative evaluation of spoilage-related bacterial diversity and metabolite profiles in chilled beef stored under air and vacuum packaging. Food Microbiol. 2019, 77, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, J.; Huang, M. Monitoring and identification of spoilage-related microorganisms in braised chicken with modified atmosphere packaging during refrigerated storage. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargossi, E.; Gardini, F.; Gatto, V.; Chiara, M.; Sandra, T.; Giulia, T. The capability of tyramine production and correlation between phenotypic and genetic characteristics of Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis strains. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nnodim, C.L.; Odu, N.N.; Ogbonna, N.D.; Kiin-Kabari, D.B. Screening of Yeasts Other than Saccharomyces for Amino acid Decarboxylation. Biotechnol. J. Int. 2021, 25, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urs, V.; Ramlal, S.; Batra, H.V. An In-vitro Screening for Biogenic Amines Producing Microorganisms from Fermented Foods and its Degradation by Bacteria from Canine Saliva. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 13, 271–280. [Google Scholar]
- Ramalingam, S.; Bahuguna, A.; Lim, S.M.; Joe, A.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, M. Quantification of Biogenic Amines in 35 Korean Cottage Industry Traditional Gochujang (Fermented Red Pepper Paste) Products. Foods 2021, 10, 2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aykut, B.; Esmeray, K.; Yilmaz, U.; Fatih, Ö. Suppression effects of aqueous and ethanolic extracts of propolis on biogenic amine production by Morganella psychrotolerans. LWT 2020, 131, 109771. [Google Scholar]
- Toro-Funes, N.; Bosch-Fuste, J.; Latorre-Moratalla, M.L.; Veciana-Nogués, M.T.; Vidal-Carou, M.C. Biologically active amines in fermented and non-fermented commercial soybean products from the spanish market. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekici, K.; Omer, A.K. Biogenic amines formation and theirimportance in fermented foods. BIO Web Conf. 2020, 17, 00232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabagias, I.; Badeka, A.; Kontominas, M.G. Shelf life extension of lamb meat using thyme or oregano essential oils and modified atmosphere packaging. Meat Sci. 2011, 88, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakke, M.; Sato, T.; Ichikawa, K.; Nishimura, I. Histamine dehydrogenase from Rhizobium sp.: Gene cloning, expression in Escherichia coli, characterization and application to histamine determination. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 119, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.C.; Li, B.B.; Zhao, L.L.; Wang, Q.L.; Li, B.K.; Lu, S.L. The effects of amine oxidase-producing starter culture on biogenic amine accumulation in traditional Chinese smoked horsemeat sausages. J. Food Saf. 2019, 39, 12638. [Google Scholar]
| Product | Sample | Location of the Company (China) | Latitude and Longitude | Ingredients |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jerky | J-1 | Alxa Left Banner | E105.67, N38.83 | vegetable oil, edible salt, spices |
| J-2 | Alxa Right Banner | E101.67, N39.22 | vegetable oil, edible salt, spices | |
| J-3 | Ejin Banner | E101.06, N41.95 | vegetable oil, edible salt, spices | |
| J-4 | Ordos | E116.41, N39.91 | vegetable oil, edible salt | |
| J-5 | Dongsheng District | E109.96, N39.82 | vegetable oil, edible salt | |
| J-6 | Dalad Banner | E110.03, N40.41 | vegetable oil, edible salt | |
| J-7 | Tsining District | E113.17, N41 | vegetable oil, edible salt, spices | |
| J-8 | Urad Front Banner | E113.21, N40.78 | vegetable oil, edible salt, spices | |
| J-9 | Xilingol League | E116.05, N43.93 | vegetable oil, edible salt, spices | |
| J-10 | Zhenglan Banner | E115.99, N42.24 | vegetable oil, edible salt, spices | |
| J-11 | Bordered Yellow Banner | E113.85, N42.23 | vegetable oil, edible salt, spices | |
| J-12 | Ulan Hot | E122.09, N46.07 | edible salt, aginomoto, spices | |
| J-13 | Hinggan League | E122.04, N46.08 | vegetable oil, edible salt, spices | |
| J-14 | Ili | E81.32, N43.92 | salt, vegetable oil, monosodium glutamate, soy sauce, additives | |
| Bacon | B-1 | Hubei | E109.48, N30.3 | Chinese prickly ash, edible salt, cypress twig, cinnamon, orange peel |
| B-2 | Chengdu | E104.07, N30.57 | salt, wine, spices, food additives | |
| B-3 | Guizhou | E106.63, N26.65 | edible salt, spices | |
| B-4 | Hunan | E112.94, N28.23 | edible salt, spices | |
| B-5 | Inner Mongolia | E111.77, N40.82 | edible salt | |
| B-6 | Jinhua | E119.65, N29.08 | edible salt, additives | |
| B-7 | Xuanwei | E101.76, N25.19 | sugar, salt, wine, spices, additives | |
| B-8 | Longxi | E104.63, N35 | clove, amomum villosum, salt, zanthoxylum bungeanum, ginger peel, daxiang, caoshao, fennel, wine, spices | |
| B-9 | Zhejiang | E120.58, N30.05 | sugar, salt, wine, monosodium glutamate, additives | |
| B-10 | Guangdong | E110.36, N21.27 | sugar, salt, wine, soy sauce, food additives | |
| B-11 | Anhui | E117.23, N31.82 | edible salt | |
| B-12 | Yunnan | E102.83, N24.88 | edible salt, spices | |
| Sausage | S-1 | Xinjiang | E87.63, N43.79 | edible salt |
| S-2 | Hubei | E109.48, N30.3 | salt, wine, sugar, monosodium glutamate, chili, pepper | |
| S-3 | Chengdu | E104.07, N30.57 | salt, sugar, chili, pepper, spices | |
| S-4 | Guizhou | E106.63, N26.65 | sugar, salt, pepper, monosodium glutamate | |
| S-5 | Guangdong | E110.36, N21.27 | soybean protein powder, sugar, salt, wine, gluten powder | |
| S-6 | Anhui | E117.33, N31.73 | sugar, salt, Baijiu, additives | |
| S-7 | Harbin | E126.54, N45.8 | salt, sugar, monosodium glutamate, garlic, spices | |
| S-8 | Jiangxi | E114.97, N27.09 | salt, sesame oil, spices | |
| S-9 | Laiwu | E117.68, N36.21 | soy sauce, soy protein powder, salt, spices | |
| S-10 | Harbin | E126.54, N45.8 | sugar, wine, salt, star anise, pepper | |
| S-11 | YI Li | E118.36, N35.1 | salt, sugar, soy sauce, monosodium glutamate, spices, chicken essence | |
| S-12 | Ulan River | E121.95, N46.08 | vegetable oil, edible salt, spices | |
| S-13 | Xingan league | E122.09, N46.07 | vegetable oil, edible salt, spices | |
| S-14 | Zhejiang | E120.58, N30.05 | edible salt, additives | |
| S-15 | YiYang | E112.36, N28.55 | edible salt |
| Product | Sample | Tryptamine | Phenylethylamine | Putrescine | Cadaverine | Histamine | Tyramine | Total Biogenic Amine |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jerky | J1 | 9.77 ± 0.01 | 0.47 ± 0.01 | 1.08 ± 0.00 | <LOD | ND | 0.44 ± 0.00 | 11.76 ± 0.01 |
| J2 | 41.38 ± 1.80 | 78.45 ± 3.51 | 8.48 ± 0.42 | 31.70 ± 1.42 | 10.19 ± 1.72 | 10.40 ± 0.42 | 180.62 ± 9.27 | |
| J3 | 10.68 ± 0.00 | 0.21 ± 0.00 | ND | 11.31 ± 0.43 | 8.04 ± 0.34 | 0.49 ± 0.00 | 30.73 ± 0.77 | |
| J4 | 111.65 ± 9.35 | 397.09 ± 3.30 | 12.54 ± 0.55 | 446.79 ± 6.90 | 87.7 ± 15.71 | 576.47 ± 3.26 | 1632.24 ± 27.00 | |
| J5 | 71.55 ± 2.04 | 137.23 ± 2.95 | 22.77 ± 0.56 | 141.62 ± 2.58 | 30.61 ± 13.25 | 113.51 ± 3.66 | 517.29 ± 11.75 | |
| J6 | 59.01 ± 3.15 | 118.06 ± 1.74 | 19.53 ± 0.38 | 127.86 ± 4.06 | 38.7 ± 0.84 | 95.78 ± 1.78 | 458.94 ± 5.90 | |
| J7 | 22.31 ± 0.60 | ND | 7.29 ± 0.18 | 8.55 ± 0.21 | 4.93 ± 0.14 | 20.47 ± 0.52 | 63.56 ± 1.23 | |
| J8 | 19.23 ± 0.01 | 14.75 ± 0.10 | 1.92 ± 0.01 | 5.62 ± 0.04 | 37.33 ± 0.10 | 12.60 ± 0.07 | 91.45 ± 0.22 | |
| J9 | 12.72 ± 0.02 | 4.60 ± 0.02 | 1.64 ± 0.01 | 3.14 ± 0.03 | 3.36 ± 0.010 | 6.53 ± 0.01 | 31.98 ± 0.04 | |
| J10 | 34.00 ± 0.73 | 7.87 ± 0.15 | 4.72 ± 0.02 | 11.26 ± 0.13 | 11.07 ± 0.06 | 15.82 ± 0.01 | 84.74 ± 0.78 | |
| J11 | 2.60 ± 0.02 | 13.93 ± 0.30 | 3.49 ± 0.01 | 3.14 ± 0.03 | ND | 1.17 ± 0.00 | 24.33 ± 0.28 | |
| J12 | 28.06 ± 2.44 | 22.06 ± 1.86 | 3.28 ± 0.27 | 19.25 ± 1.69 | 11.75 ± 0.95 | 48.77 ± 4.50 | 133.17 ± 11.68 | |
| J13 | 39.99 ± 1.52 | 29.40 ± 1.38 | 55.03 ± 2.89 | 19.59 ± 0.94 | 135.64 ± 6.50 | 26.45 ± 1.97 | 306.10 ± 15.07 | |
| J14 | 45.9 ± 0.21 | 118.2 ± 0.55 | 6.57 ± 0.05 | 7.75 ± 0.03 | 1.39 ± 0.00 | 7.30 ± 0.01 | 187.11 ± 0.79 | |
| Bacon | B1 | 9.61 ± 0.39 | 12.49 ± 0.58 | 18.53 ± 0.89 | 18.7 ± 0.99 | 70.99 ± 3.61 | 28.95 ± 1.38 | 159.26 ± 7.75 |
| B2 | 17.37 ± 0.03 | 2.46 ± 0.01 | <LOD | 1.39 ± 0.02 | 1.90 ± 0.02 | 1.43 ± 0.01 | 24.55 ± 0.04 | |
| B3 | 19.62 ± 1.77 | 117.59 ± 10.74 | 22.26 ± 2.06 | 1.43 ± 0.24 | 1.49 ± 0.16 | 5.74 ± 0.58 | 168.12 ± 15.52 | |
| B4 | 29.29 ± 0.03 | 7.80 ± 0.07 | 14.48 ± 0.00 | 61.55 ± 0.01 | 48.54 ± 0.03 | 56.79 ± 0.03 | 218.45 ± 0.17 | |
| B5 | 66.09 ± 0.45 | 49.39 ± 0.58 | 55.25 ± 2.40 | 14.47 ± 0.23 | 16.27 ± 0.63 | 54.45 ± 10.02 | 255.92 ± 12.32 | |
| B6 | 12.04 ± 0.08 | 3.49 ± 0.09 | 0.65 ± 0.01 | 1.47 ± 0.02 | 0.88 ± 0.02 | 2.98 ± 0.04 | 21.51 ± 0.16 | |
| B7 | 63.89 ± 0.59 | 3.14 ± 0.06 | 0.61 ± 0.03 | 3.40 ± 0.03 | 1.85 ± 0.51 | 2.07 ± 0.32 | 74.96 ± 0.54 | |
| B8 | 80.49 ± 0.77 | 8.62 ± 0.16 | 0.48 ± 0.01 | 74.81 ± 0.66 | 4.94 ± 0.12 | 2.77 ± 0.05 | 172.11 ± 1.70 | |
| B9 | 5.76 ± 0.05 | 18.00 ± 0.01 | 15.81 ± 0.02 | 33.54 ± 0.05 | 37.78 ± 0.11 | 43.25 ± 0.16 | 154.14 ± 0.27 | |
| B10 | 18.59 ± 0.19 | 19.87 ± 0.54 | 13.18 ± 0.47 | 6.14 ± 0.21 | 46.67 ± 2.44 | 15.21 ± 0.31 | 119.65 ± 3.72 | |
| B11 | 8.15 ± 0.03 | 5.39 ± 0.71 | 2.07 ± 0.01 | 121.09 ± 0.81 | 0.15 ± 0.00 | 3.84 ± 0.00 | 140.69 ± 0.14 | |
| B12 | 15.75 ± 0.61 | 27.61 ± 0.56 | 10.28 ± 0.05 | 2.26 ± 0.61 | 2.65 ± 0.09 | 5.24 ± 0.87 | 63.79 ± 1.69 | |
| Sausage | S1 | 63.68 ± 1.04 | 80.84 ± 1.42 | 258.96 ± 4.18 | 3.91 ± 0.06 | 35.51 ± 0.65 | 7.18 ± 0.24 | 450.08 ± 7.50 |
| S2 | 5.25 ± 0.59 | 6.50 ± 0.12 | <LOD | 10.50 ± 0.02 | 0.57 ± 0.02 | 3.89 ± 0.04 | 26.71 ± 0.75 | |
| S3 | 3.55 ± 0.46 | 64.11 ± 0.39 | 1.04 ± 0.02 | 12.27 ± 0.07 | 4.65 ± 0.14 | 2.09 ± 0.09 | 88.05 ± 0.53 | |
| S4 | 18.90 ± 0.05 | 127.79 ± 0.63 | 153.61 ± 0.21 | 17.88 ± 0.31 | 11.45 ± 0.47 | 1.46 ± 0.05 | 331.09 ± 1.70 | |
| S5 | 29.29 ± 0.03 | 7.80 ± 0.07 | 14.48 ± 0.00 | 61.55 ± 0.01 | 48.54 ± 0.03 | 56.79 ± 0.03 | 218.45 ± 0.17 | |
| S6 | 203.87 ± 0.69 | 134.68 ± 17.81 | 51.79 ± 0.26 | ND | 3.63 ± 0.06 | 96.08 ± 0.02 | 490.05 ± 16.77 | |
| S7 | 1.51 ± 0.00 | 10.84 ± 0.02 | 4.64 ± 0.01 | <LOD | 3.50 ± 0.01 | 3.70 ± 0.01 | 24.42 ± 0.03 | |
| S8 | 127.62 ± 3.99 | 25.80 ± 0.13 | 1.58 ± 0.07 | 69.80 ± 0.09 | 92.73 ± 0.28 | 9.09 ± 0.24 | 326.62 ± 3.73 | |
| S9 | 7.94 ± 0.92 | 36.82 ± 3.48 | 1.66 ± 0.43 | 20.08 ± 0.73 | ND | 1.86 ± 0.25 | 68.36 ± 5.57 | |
| S10 | 11.95 ± 0.04 | 73.71 ± 0.30 | 2.63 ± 0.02 | 11.53 ± 0.07 | ND | 9.27 ± 0.32 | 109.09 ± 0.71 | |
| S11 | 105.74 ± 0.05 | 9.78 ± 0.12 | 1.69 ± 0.02 | 9.80 ± 0.12 | ND | ND | 127.01 ± 0.20 | |
| S12 | 10.37 ± 0.07 | 88.21 ± 19.67 | 157.81 ± 35.16 | 84.51 ± 18.74 | 32.34 ± 7.55 | 8.36 ± 2.02 | 381.60 ± 83.22 | |
| S13 | 1.94 ± 0.02 | 4.31 ± 0.11 | 0.58 ± 0.02 | 3.90 ± 0.22 | 0.48 ± 0.00 | 3.67 ± 0.01 | 14.88 ± 0.30 | |
| S14 | 43.94 ± 1.15 | 45.08 ± 4.65 | ND | 62.70 ± 0.08 | 92.64 ± 0.35 | 101.72 ± 7.75 | 346.08 ± 13.13 | |
| S15 | 14.60 ± 2.68 | 15.40 ± 5.03 | 3.20 ± 0.11 | 3.33 ± 1.7 | 3.70 ± 1.37 | 2.78 ± 0.4 | 43.00 ± 11.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, X.; He, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, M.; Hu, G.; Sun, E.; Sun, L.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, L. Investigation of Biogenic Amines and Quality in Jerky, Bacon, and Sausage: Chinese Traditional Meat Product. Foods 2025, 14, 1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111842
Sun X, He X, Wang D, Zhang M, Hu G, Sun E, Sun L, Jin Y, Zhao L. Investigation of Biogenic Amines and Quality in Jerky, Bacon, and Sausage: Chinese Traditional Meat Product. Foods. 2025; 14(11):1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111842
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Xueying, Xige He, Dan Wang, Min Zhang, Guanhua Hu, Erke Sun, Lina Sun, Ye Jin, and Lihua Zhao. 2025. "Investigation of Biogenic Amines and Quality in Jerky, Bacon, and Sausage: Chinese Traditional Meat Product" Foods 14, no. 11: 1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111842
APA StyleSun, X., He, X., Wang, D., Zhang, M., Hu, G., Sun, E., Sun, L., Jin, Y., & Zhao, L. (2025). Investigation of Biogenic Amines and Quality in Jerky, Bacon, and Sausage: Chinese Traditional Meat Product. Foods, 14(11), 1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111842







