Impact of Freezing and Freeze Drying on Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Survival: Mechanisms of Cell Damage and the Role of Pre-Freezing Conditions and Cryoprotectants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Bacterial Strains, Medium and Growth Conditions
2.2. Preparation of Cell Suspension and Feed Solutions
2.3. Freeze Thawing and Freeze Drying
2.4. Determination of Survival Rate
2.5. Measurement of Metabolic Activity of LGG
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Impact of Resuspension Solvent
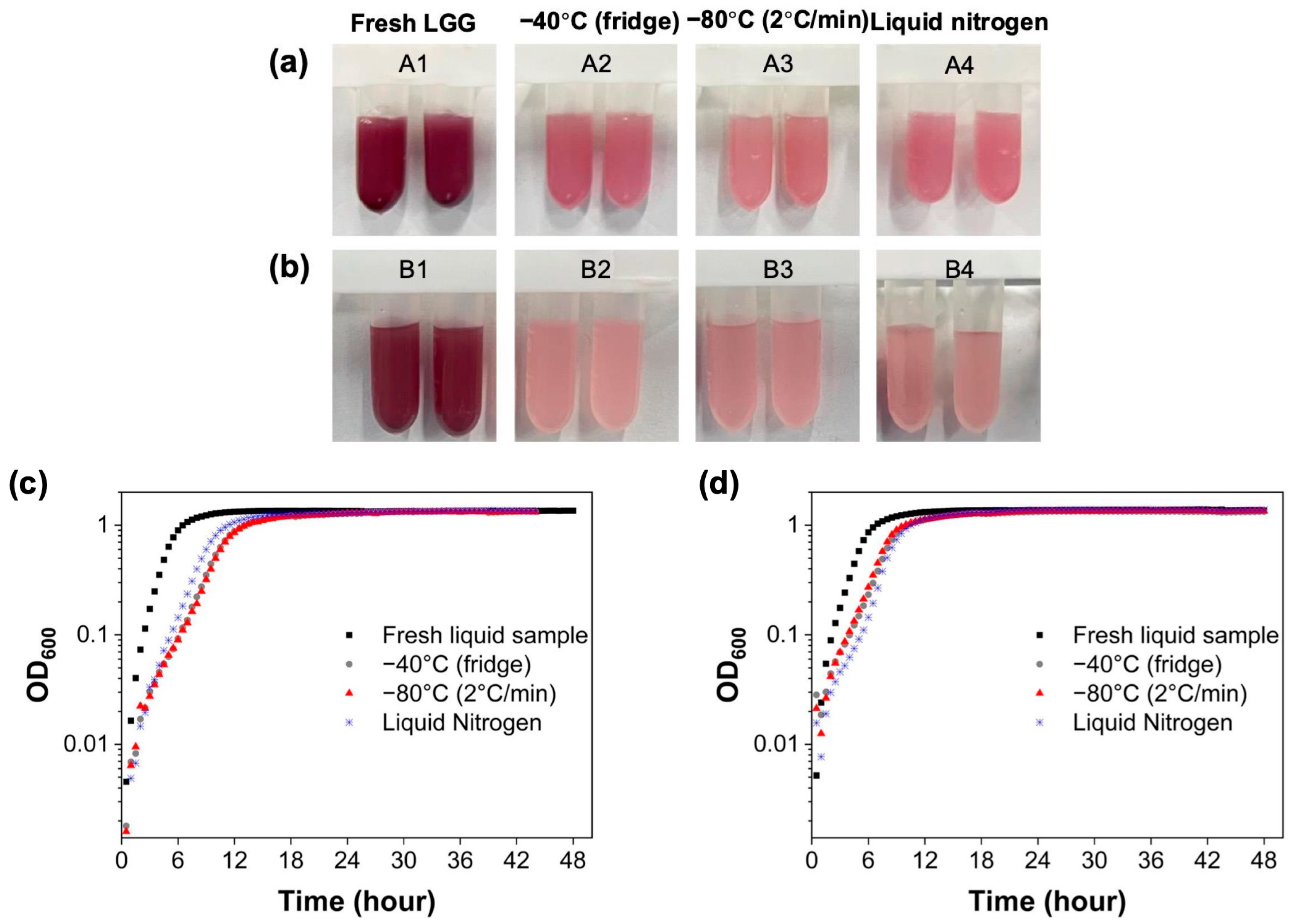
3.2. Impact of Freezing Temperature and Freezing Rate
3.3. Impact of Freezing Duration
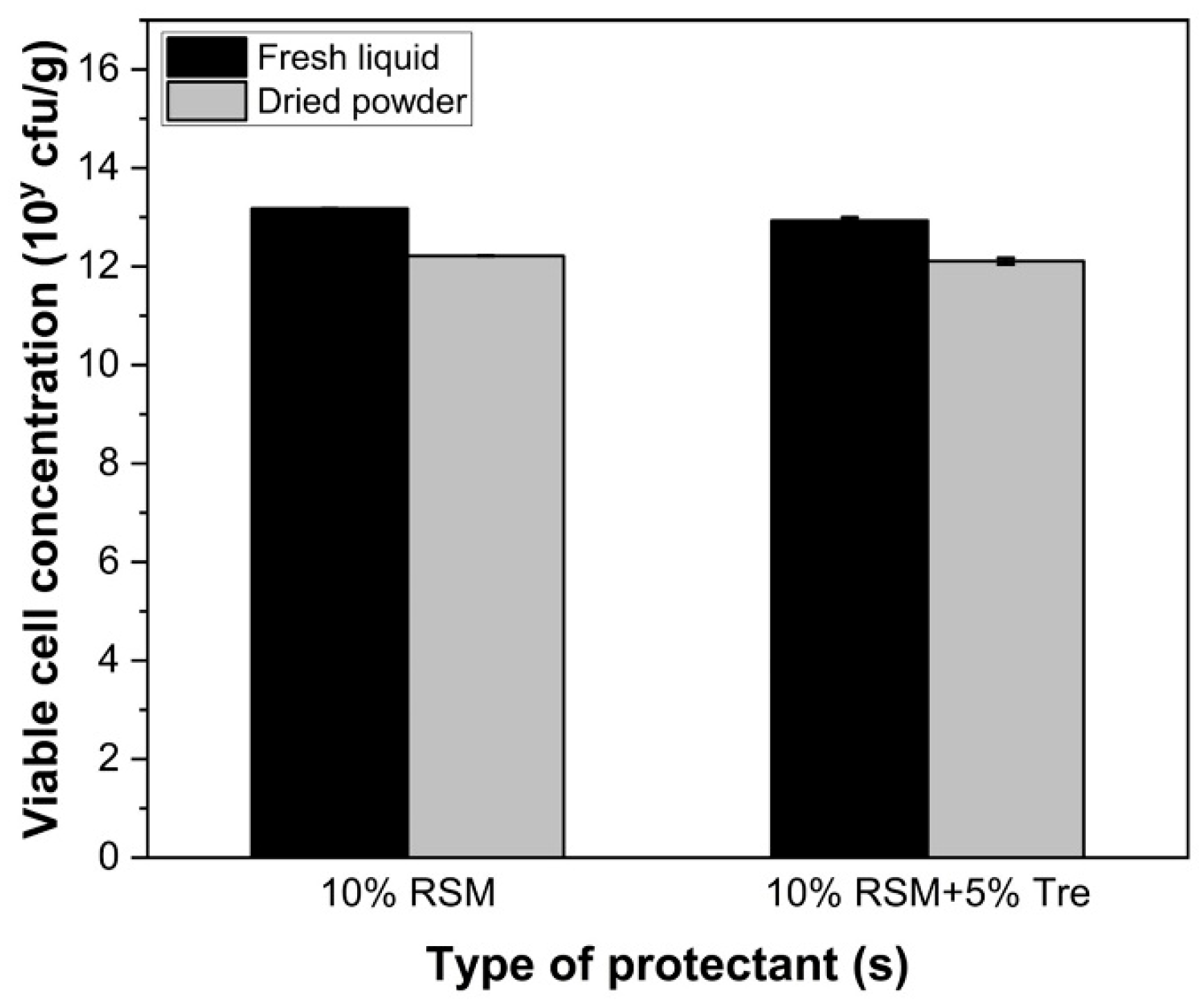
3.4. Impact of Dehydration
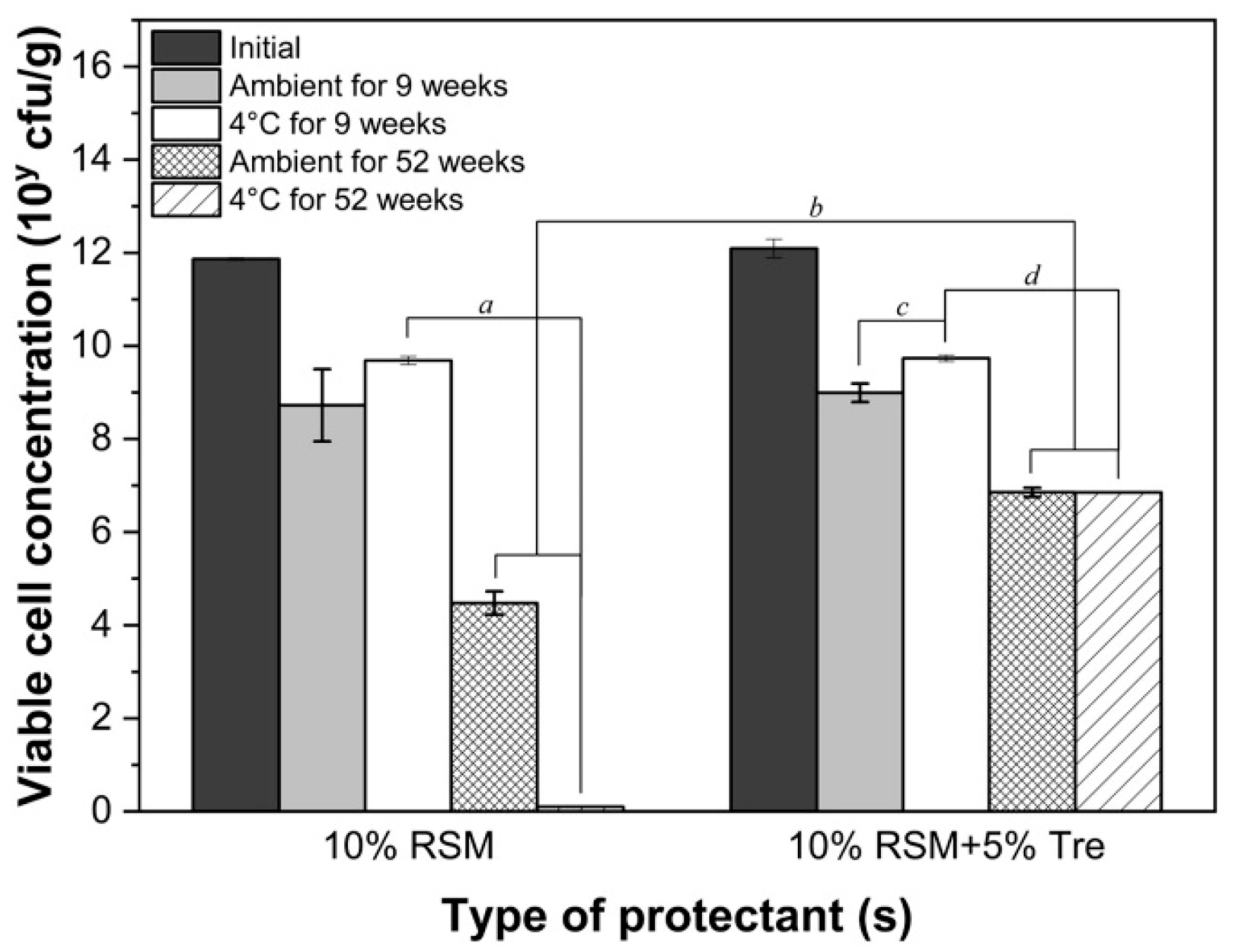
3.5. Impact of Cryoprotectants
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Division, N. Probiotics in Food. In Health and Nutritional Properties and Guidelines for Evaluation; FAO: Rome, Italy; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Fenster, K.; Freeburg, B.; Hollard, C.; Wong, C.; Rønhave Laursen, R.; Ouwehand, A.C. The Production and Delivery of Probiotics: A Review of a Practical Approach. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culligan, E.P.; Hill, C.; Sleator, R.D. Probiotics and gastrointestinal disease: Successes, problems and future prospects. Gut Pathog. 2009, 1, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, K.J. Probiotic bacteria in fermented foods: Product characteristics and starter organisms. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 73, 374s–379s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ershidat, O.T.M.; Mazahreh, A.S. Probiotics bacteria in fermented dairy products. Pak. J. Nutr. 2009, 8, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champagne, C.P.; Gardner, N.J.; Roy, D. Challenges in the addition of probiotic cultures to foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 45, 61–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez, S.; Malik, K.A.; Ah Kang, S.; Kim, H.Y. Probiotics and their fermented food products are beneficial for health. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 100, 1171–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, M.K.; Giri, S.K. Probiotic functional foods: Survival of probiotics during processing and storage. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 9, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez, B.E.; Ledeboer, A.M. Drying of Probiotics: Optimization of Formulation and Process to Enhance Storage Survival. Dry. Technol. 2007, 25, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Prashanth, N.; Kumari, B.C. Fundamentals and applications of lyophilization. J. Adv. Pharm. Res. 2011, 2, 157–169. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, F.; Cenard, S.; Passot, S. Freeze-Drying of Lactic Acid Bacteria. In Cryopreservation and Freeze-Drying Protocols; Wolkers, W.F., Oldenhof, H., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 477–488. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Cui, S.W.; Chen, M.; Li, Y.; Liang, R.; Xu, F.; Zhong, F. Protective approaches and mechanisms of microencapsulation to the survival of probiotic bacteria during processing, storage and gastrointestinal digestion: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2863–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-Q.; Pu, J.; Yu, X.-Q.; Xia, Y.-J.; Ai, L.-Z. Influence of freezing temperature before freeze-drying on the viability of various Lactobacillus plantarum strains. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 3066–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polo, L.; Manes-Lazaro, R.; Olmeda, I.; Cruz-Pio, L.E.; Medina, A.; Ferrer, S.; Pardo, I. Influence of freezing temperatures prior to freeze-drying on viability of yeasts and lactic acid bacteria isolated from wine. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 122, 1603–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, F.; Marechal, P.-A.; Gervais, P. Cell size and water permeability as determining factors for cell viability after freezing at different cooling rates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhang, G. Effect of protective agents, freezing temperature, rehydration media on viability of malolactic bacteria subjected to freeze-drying. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 99, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvankhah, A.; Emam-Djomeh, Z.; Askari, G. Encapsulation and delivery of bioactive compounds using spray and freeze-drying techniques: A review. Dry. Technol. 2020, 38, 235–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.W.; Kong, J.; Zhu, H.K.; Mao, B.Y.; Cui, S.M.; Zhao, J.X. Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium and Lactococcus response to environmental stress: Mechanisms and application of cross-protection to improve resistance against freeze-drying. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 802–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, K.; Alegria, A.; Bron, P.A.; de Angelis, M.; Gobbetti, M.; Kleerebezem, M.; Lemos, J.A.; Linares, D.M.; Ross, P.; Stanton, C.; et al. Stress Physiology of Lactic Acid Bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 837–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold, G.; Aguilera, J.M. Ice morphology: Fundamentals and technological applications in foods. Food Biophys. 2009, 4, 378–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murga, M.a.L.F.; Font de Valdez, G.; Disalvo, A.b.E. Changes in the Surface Potential of Lactobacillus acidophilus under Freeze–Thawing Stress. Cryobiology 2000, 41, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, X.; Huang, S.; Wang, J.; Fu, N.; Jeantet, R.; Chen, X.D. Effect of culturing lactic acid bacteria with varying skim milk concentration on bacteria survival during heat treatment. J. Food Eng. 2021, 294, 110396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzardo, M.d.C.; Amalfa, F.; Nunez, A.; Diaz, S.; De Lopez, A.B.; Disalvo, E. Effect of trehalose and sucrose on the hydration and dipole potential of lipid bilayers. Biophys. J. 2000, 78, 2452–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtake, S.; Wang, Y.J. Trehalose: Current use and future applications. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 2020–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulmer, H.M.; Gänzle, M.G.; Vogel, R.F. Effects of high pressure on survival and metabolic activity of Lactobacillus plantarum TMW1. 460. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 3966–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Fu, N.; Woo, M.W.; Chen, X.D. Exploring the interactions between Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and whey protein isolate for preservation of the viability of bacteria through spray drying. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 2995–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-M.; Che, L.-H.; Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Xu, B.-C. An effective strategy for improving the freeze-drying survival rate of Lactobacillus curvatus and its potential protective mechanism. Food Biosci. 2024, 58, 103794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiocco, D.; Capozzi, V.; Goffin, P.; Hols, P.; Spano, G. Improved adaptation to heat, cold, and solvent tolerance in Lactobacillus plantarum. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 77, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Zhang, M.; Liu, W.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Bai, B. Novel synergistic freezing methods and technologies for enhanced food product quality: A critical review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 1979–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Tian, F.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Effects of cryoprotectants on viability of Lactobacillus reuteri CICC6226. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 92, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martos, G.; Minahk, C.; Font de Valdez, G.; Morero, R. Effects of protective agents on membrane fluidity of freeze-dried Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yu, X.; Lu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Lai, P.F.-H.; Ai, L. Optimal combination of multiple cryoprotectants and freezing-thawing conditions for high lactobacilli survival rate during freezing and frozen storage. LWT 2019, 99, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschenbrenner, M.; Foerst, P.; Kulozik, U. Freeze-drying of Probiotics. In Advances in Probiotic Technology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 213–241. [Google Scholar]
- Pehkonen, K.S.; Roos, Y.H.; Miao, S.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C. State transitions and physicochemical aspects of cryoprotection and stabilization in freeze-drying of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 1732–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, S.; Kleinhans, F.; Mazur, P. Intracellular ice formation in yeast cells vs. cooling rate: Predictions from modeling vs. experimental observations by differential scanning calorimetry. Cryobiology 2009, 58, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, F.; Beal, C.; Corrieu, G. Operating conditions that affect the resistance of lactic acid bacteria to freezing and frozen storage. Cryobiology 2001, 43, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.S.; Khunajakr, N.; Dunn, N.W. Effect of cold shock on protein synthesis and on cryotolerance of cells frozen for long periods in Lactococcus lactis. Cryobiology 1998, 37, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foschino, R.; Fiori, E.; Galli, A. Survival and residual activity of Lactobacillus acidophilus frozen cultures under different conditions. J. Dairy Res. 1996, 63, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsvetkov, T.; Shishkova, I. Studies on the effects of low temperatures on lactic acid bacteria. Cryobiology 1982, 19, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozoǧlu, T.; Özilgen, M.; Bakir, U. Survival kinetics of lactic acid starter cultures during and after freeze drying. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1987, 9, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaenhammer, T.; Kleeman, E. Growth characteristics, bile sensitivity, and freeze damage in colonial variants of Lactobacillus acidophilus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1981, 41, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, E. The Effects of Freezing on Marine Bacteria.: I. Quantitative Studies. J. Biol. Board Can. 1934, 1, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broeckx, G.; Vandenheuvel, D.; Claes, I.J.J.; Lebeer, S.; Kiekens, F. Drying techniques of probiotic bacteria as an important step towards the development of novel pharmabiotics. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 505, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, J. Lateral stresses in membranes at low water potential. Funct. Plant Biol. 1987, 14, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Lin, J.; Zhong, Q. Probiotic powders prepared by mixing suspension of Lactobacillus salivarius NRRL B-30514 and spray-dried lactose: Physical and microbiological properties. Food Res. Int. 2020, 127, 108706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, N.; Hao, F.; Zhang, S.; Mao, H.; Lu, W.; Chen, X.D.; Wu, W.D. The survival and stability of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG as affected by particle formation during spray drying and spray-freeze drying. J. Food Eng. 2024, 383, 112252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubalek, Z. Protectants used in the cryopreservation of microorganisms. Cryobiology 2003, 46, 205–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneghel, J.; Passot, S.; Cenard, S.; Refregiers, M.; Jamme, F.; Fonseca, F. Subcellular membrane fluidity of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp bulgaricus under cold and osmotic stress. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 6907–6917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasmeijer, N.; Stankovic, M.; de Waard, H.; Frijlink, H.W.; Hinrichs, W.L. Unraveling protein stabilization mechanisms: Vitrification and water replacement in a glass transition temperature controlled system. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Proteins Proteom. 2013, 1834, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.S.; Silva, J.; Ho, P.; Teixeira, P.; Malcata, F.X.; Gibbs, P. Survival of freeze-dried Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus rhamnosus during storage in the presence of protectants. Biotechnol. Lett. 2002, 24, 1587–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, P.; Kylli, P.; Heinonen, M.; Jouppila, K. Storage stability of microencapsulated cloudberry (Rubus chamaemorus) phenolics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 11251–11261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santivarangkna, C.; Higl, B.; Foerst, P. Protection mechanisms of sugars during different stages of preparation process of dried lactic acid starter cultures. Food Microbiol. 2008, 25, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaprakash, P.; Gaiani, C.; Edorh, J.M.; Borges, F.; Beaupeux, E.; Maudhuit, A.; Desobry, S. Comparison of Electrostatic Spray Drying, Spray Drying, and Freeze Drying for Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG Dehydration. Foods 2023, 12, 3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Wu, P.; Dhital, S.; Yu, A.; Chen, X.D. Impact of Freezing and Freeze Drying on Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Survival: Mechanisms of Cell Damage and the Role of Pre-Freezing Conditions and Cryoprotectants. Foods 2025, 14, 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101817
Wang J, Wu P, Dhital S, Yu A, Chen XD. Impact of Freezing and Freeze Drying on Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Survival: Mechanisms of Cell Damage and the Role of Pre-Freezing Conditions and Cryoprotectants. Foods. 2025; 14(10):1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101817
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Junyan, Peng Wu, Sushil Dhital, Aibing Yu, and Xiao Dong Chen. 2025. "Impact of Freezing and Freeze Drying on Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Survival: Mechanisms of Cell Damage and the Role of Pre-Freezing Conditions and Cryoprotectants" Foods 14, no. 10: 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101817
APA StyleWang, J., Wu, P., Dhital, S., Yu, A., & Chen, X. D. (2025). Impact of Freezing and Freeze Drying on Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Survival: Mechanisms of Cell Damage and the Role of Pre-Freezing Conditions and Cryoprotectants. Foods, 14(10), 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101817






