Plant-Based Burgers Made with Green Banana Biomass (GBB) Associated with Teff and Chickpea Derivatives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
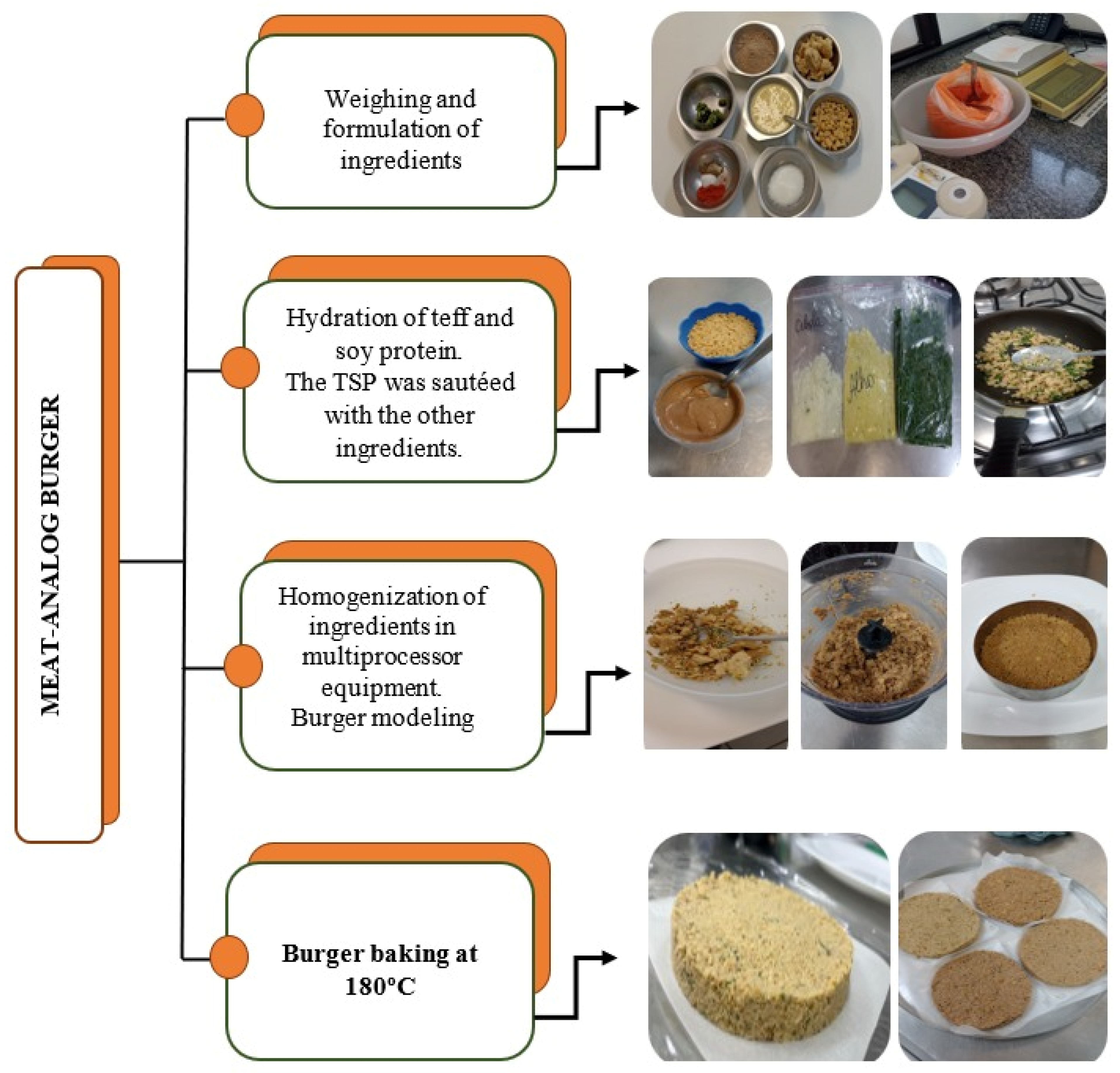
2.1. Acquisition of Ingredients and Preparation of Meat Analog Burgers
2.2. GBB Making
2.3. Making and Molding of the Plant-Based Burgers
2.4. Physical Analyses
2.4.1. Weight
2.4.2. Diameter
2.4.3. Height
2.4.4. Water Retention Capacity–WRC
2.4.5. Color
2.4.6. Texture
2.5. Chemical Analysis
2.5.1. Sample Preparation
2.5.2. Proximate Composition and Caloric Values
2.5.3. Soluble, Insoluble, and Total Fibers
2.5.4. Hydrogen Potential-pH
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
Chemical Analyses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zuin, V.G.; Araripe, E.; Zanotti, K.; Stahl, A.M.; Gomes, C.J.C. Alternative Products Selling Sustainability? A Brazilian Case Study on Materials and Processes to Produce Plant-Based Hamburger Patties. Sustain. Chem. 2022, 3, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, S.L.; McSweeney, M.B. Characterizing the properties of hybrid meat burgers made with pulses and chicken. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2022, 27, 100492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohrer, B.M. An investigation of the formulation and nutritional composition of modern meat analogue products. Food Sci. Human Wellness 2019, 8, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, I.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Joo, S.-T. Meat analog as future food: A review. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2020, 62, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhsh, A.; Lee, E.-Y.; Ncho, C.M.; Kim, C.-J.; Son, Y.-M.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Joo, S.-T. Quality Characteristics of Meat Analogs Through the Incorporation of Textured Vegetable Protein: A Systematic Review. Foods 2022, 11, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos Nessler, M.A.; Silva, A.C.S.A.E.; Cardoso, A.A.; Tremea, E.; Da Silva, G.G.; Maciel, J.C.T.; Da Silva, M.N. Production of Mixed Burger Without Chemical Additives. Symp. Health Food 2019, 3. Available online: https://portaleventos.uffs.edu.br/index.php/SSA/article/view/11100 (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Higuera, J.M.; Santos, H.M.; Oliveira, A.F.; Nogueira, A.R.A. Animal and Vegetable Protein Burgers: Bromatological Analysis, Mineral Composition, and Bioaccessibility Evaluation. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 1, 1821–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stragliotto, L.K.; Ferrari, G.T.; Campagnol, P.C.B.; Strasburg, V.J.; Zandonadi, R.P.; Oliveira, V.R.d. Green banana by-products on the chemical, technological and sensory quality of meat products. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2022, 30, 100614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teles, G.C.; Miyoshi, J.H.; Crozatti, T.T.d.S.; Oliveira, P.R.S.; Luckesi, D.; Barros, R.d.A. Green banana biomass: Functional food, a review. Res. Soc. Dev. 2022, 11, e355111435339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destro, T.M.; Souza Junior, H.; Lima, T.G.; Miranda, L.A.; Ferreira, M.P. Potential use of green banana biomass in the preparation of chocolate cake and salty pie. Agron. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auriema, B.E.; Braz Corrêa, F.J.; Guimarães, J.d.T.; Soares, P.T.d.S.; Rosenthal, A.; Zonta, E.; Rosa, R.C.C.; Luchese, R.H.; Esmerino, E.A.; Mathias, S.P. Green banana biomass: Physicochemical and functional properties and its potential as a fat replacer in a chicken mortadella. LWT 2021, 140, 110686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riquette, R.F.R.; Ginani, V.C.; Leandro Edos, S.; de Alencar, E.R.; Maldonade, I.R.; de Aguiar, L.A.; de Souza Acácio, G.M.; Mariano, D.R.H.; Zandonadi, R.P. Do production and storage affect the quality of green banana biomass? LWT 2019, 111, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F. Chemical composition and food uses of teff (Eragrostis tef). Food Chem. 2018, 239, 402–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemneh, S.T.; Emire, S.A.; Hitzmann, B.; Zettel, V. Comparative Study of Chemical Composition, Pasting, Thermal and Functional Properties of Teff (Eragrostis tef) Flours Grown in Ethiopia and South Africa. Int. J. Food Prop. 2022, 25, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homem, R.v.; Proserpio, C.; Cattaneo, C.; Rockett, F.C.; Schmidt, H.d.O.; Komeroski, M.R.; Rios, A.d.O.; Pagliarini, E.; Oliveira, V.R.d. New opportunities for gluten-free diet: Teff (Eragrostis tef) as fibre source in baking products. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 4697–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira do Nascimento, K.; do Nascimento Dias Paes, S.; Reis de Oliveira, I.; Pereira Reis, I.; Maria Augusta, I. Teff: Suitability for Different Food Applications and as a Raw Material of Gluten-Free, a Literature Review. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 6, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholakova, A.; Zhelyazkova, T.; Gerdzhikova, M. Significance of teff (Eragrostis tef (Zucc.) Trotter) as a new fodder crop for Bulgaria. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2023, 15, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barretto, R.; Buenavista, R.M.; Rivera, J.l.; Wang, S.; Prasad, P.V.V.; Siliveru, K. Teff (Eragrostis tef) processing, utilization and future opportunities: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 3125–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, T.C.R.; Camargos, L.F.d.; Camilo, P.A.; Jesus, F.G.d.; Siqueira, A.P.S. Technological characterization of chickpea flour BRS cristalino variety. Braz. J. Food Technol. 2022, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariod, A.A.; Abd Elagdir, M. Effect of partial replacement of meat with chickpea flour, soybean flour and skimmed milk powder on physicochemical and sensory evaluation properties of camel meat burger. Cogent Food Agric. 2024, 10, 2321673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Rosa, M.Y.; Lobato, F.H.S. Cashew burger: Elaboração e análise sensorial de hambúrguer à base de caju (Anacardium occidentale L.). Res. Soc. Dev. 2020, 9, e615985958. [Google Scholar]
- INMETRO. Portaria Inmetro nº 236—22 de dezembro 1994—Balanças. Available online: http://www.inmetro.gov.br/legislacao/detalhe.asp?seq_classe=1&seq_ato=180 (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Lovis, K.L.; Schneider, T.M.; Foralosso, F.B.; da Silveira, S.M.; Junior, Á.V.; Fronza, N. Desenvolvimento de creme de mesa tipo maionese a base de biomassa: Comparação com molho de maionese tradicional. In Anais da Mostra Nacional de Iniciação Científica e Tecnológica Interdisciplinar (MICTI); Instituto Federal Catarinense-Campus Concórdia: Videira, Brazil, 2019; p. 1. ISSN 2316-7165. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, A.N.A.; Pasquali, M.A.D.B.; Schnorr, C.E.; Martins, J.J.A.; Araújo, G.T.; Rocha, A.P.T. Development and characterization of blends formulated with banana peel and banana pulp for the production of blends powders rich in antioxidant properties. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 5289–5297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loesecke, V. Escala de Maturação de Von Loesecke. 1950. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/FIGURA-2-Escala-de-maturacao-de-VON-LOESECKE-1950_fig2_281715599 (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- Roque-Specht, V.F.; Simoni, V.; Parise, N.; Cardoso, P.G. Avaliação da capacidade de retenção de água em peitos de frango em função do pH final. Curr. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2009, 15, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Park, J.B.; Hwang, I.K. Quality attributes of various varieties of Korean red pepper powders (Capsicum annuum L.) and color stability during sunlight exposure. J. Food Sci. 2002, 67, 2957–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabuig, G.G. Texturometría Instrumental: Puesta a Punto y Aplicación a la Tecnología de Alimentos, 1st ed.; [Capítulo 1]; Universidad de Oviedo: Asturias, Spain, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC). Official Methods of Analysis, 19th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Mumbai, India, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Adolfo Lutz. Physicochemical Methods for Food Analysis; Instituto Adolfo Lutz: São Paulo, Brazil, 2008; p. 1020. [Google Scholar]
- IBM Corp. (n.d.). IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 29.0; [Computer Software]; IBM Corp: Armonk, NY, USA.
- De Marchi, M.; Costa, A.; Pozza, M.; Goi, A.; Manuelian, C.L. Detailed characterization of plant-based burgers. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samard, S.; Maung, T.T.; Gu, B.Y.; Kim, M.H.; Ryu, G.H. Influences of extrusion parameters on physicochemical properties of textured vegetable proteins and its meatless burger patty. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 30, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrasik, Z.; Sigvaldson, M.; Soladoye, O.P.; Gaudette, N.J. Utilization of pea starch and fibre fractions for replacement of wheat crumb in beef burgers. Meat Sci. 2020, 161, 107974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, K.L.; Alves, C.A.N.; Moisés de Sousa, F.; Souza Gusmão, T.A.; Alves Filho, E.G.; Barros de Vasconcelos, L. Chemometrics applied to physical, physicochemical and sensorial attributes of chicken hamburgers blended with green banana and passion fruit epicarp biomasses. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2021, 24, 100337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botella-Martínez, C.; Viuda-Martos, M.; Fernández-López, J.A.; Pérez-Alvarez, J.A.; Fernández-López, J. Development of plant-based burgers using gelled emulsions as fat source and beetroot juice as colorant: Effects on chemical, physicochemical, appearance and sensory characteristics. LWT 2022, 172, 114193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Miller, R.; Laird, H.; Riaz, M.N. Beef flavor vegetable hamburger patties with high moisture meat analogs (HMMA) with pulse proteins-peas, lentils, and faba beans. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 4048–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, J.R.; Araújo, Í.M.d.S.; Pinto, C.O.; Goiana, M.L.; Rodrigues, M.d.C.P.; Lima, L.V.d. Obtaining cashew kernel protein concentrate from nut processing by-product and its use to formulate vegetal burger. Braz. J. Food Technol. 2021, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latunde-Dada, G.O.; Kajarabille, N.; Rose, S.; Arafsha, S.M.; Kose, T.; Aslam, M.F.; Hall, W.L.; Sharp, P.A. Content and Availability of Minerals in Plant-Based Burgers Compared with a Meat Burger. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilón-Llico, R.; Siguas-Cruzado, L.; Apaza-Humerez, C.R.; Morales-García, W.C.; Silva-Paz, R.J. Protein Quality and Sensory Perception of Hamburgers Based on Quinoa, Lupin and Corn. Foods 2022, 11, 3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhsh, A.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, E.-Y.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Joo, S.-T. Evaluation of Rheological and Sensory Characteristics of Plant-Based Meat Analog with Comparison to Beef and Pork. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2021, 41, 983–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, N.; Ahlawat, S.S.; Sharma, D.P.; Dabur, R.S. Novel trends in development of dietary fiber rich meat products—A critical review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakopoulou, K.; Dekkers, B.; van der Goot, A.J. Plant-Based Meat Analogues. In Sustainable Meat Production and Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtain, F.; Grafenauer, S. Plant-based meat substitutes in the flexitarian age: An audit of products on supermarket shelves. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Evans, N.M.; Liu, H.; Shao, S. A review of research on plant-based meat alternatives: Driving forces, history, manufacturing, and consumer attitudes. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2639–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 October 2011 on the Provision of Food Information to Consumers. 2011. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2011/1169/2018-01-01 (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- National Health Surveillance Agency—Anvisa-Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária. Fluxograma para Uso da Informação Nutricional Complementar. 2012. Available online: https://www.gov.br/anvisa/pt-br/centraisdeconteudo/publicacoes/alimentos/manuais-guias-e-orientacoes/fluxograma-para-uso-de-alegacoes-nutricionais.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Brasil Ministério da Saúde; Secretaria de Vigilância Sanitária. Portaria nº 27, de 13 de Janeiro de 1998: Regulamento Técnico Referente à Informação Nutricional Complementar. Diário Oficial da União: Poder Executivo, de 16 de Janeiro de 1998. 1998. Available online: https://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/saudelegis/svs1/1998/prt0027_13_01_1998.html (accessed on 1 April 2024).
| Ingredients | Formulations (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 (100%) | F2 (75%) | F3 (60%) | F4 (50%) | |
| Green banana biomass (GBB) | 100 | 75 | 60 | 50 |
| Brown teff flour | - | 12.5 | 20 | 25 |
| Canned chickpeas | - | 12.5 | 20 | 25 |
| Chickpeas flour | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Chickpeas aquafaba | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Dried textured soy protein | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Ground black pepper | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Garlic in natura | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Onion in natura | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Chives and parsley in natura | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Refined sea salt | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 |
| Soybean oil | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Smoked paprika | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
| Dried seasoning (garlic, onion, rosemary, cilantro, parsley) | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 |
| Crushed ice | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Physical Analyses | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Weight (g) | FinalWeight (g) | Initial Diameter (cm) | Final Diameter (cm) | Initial Height (cm) | Final Height (cm) | |
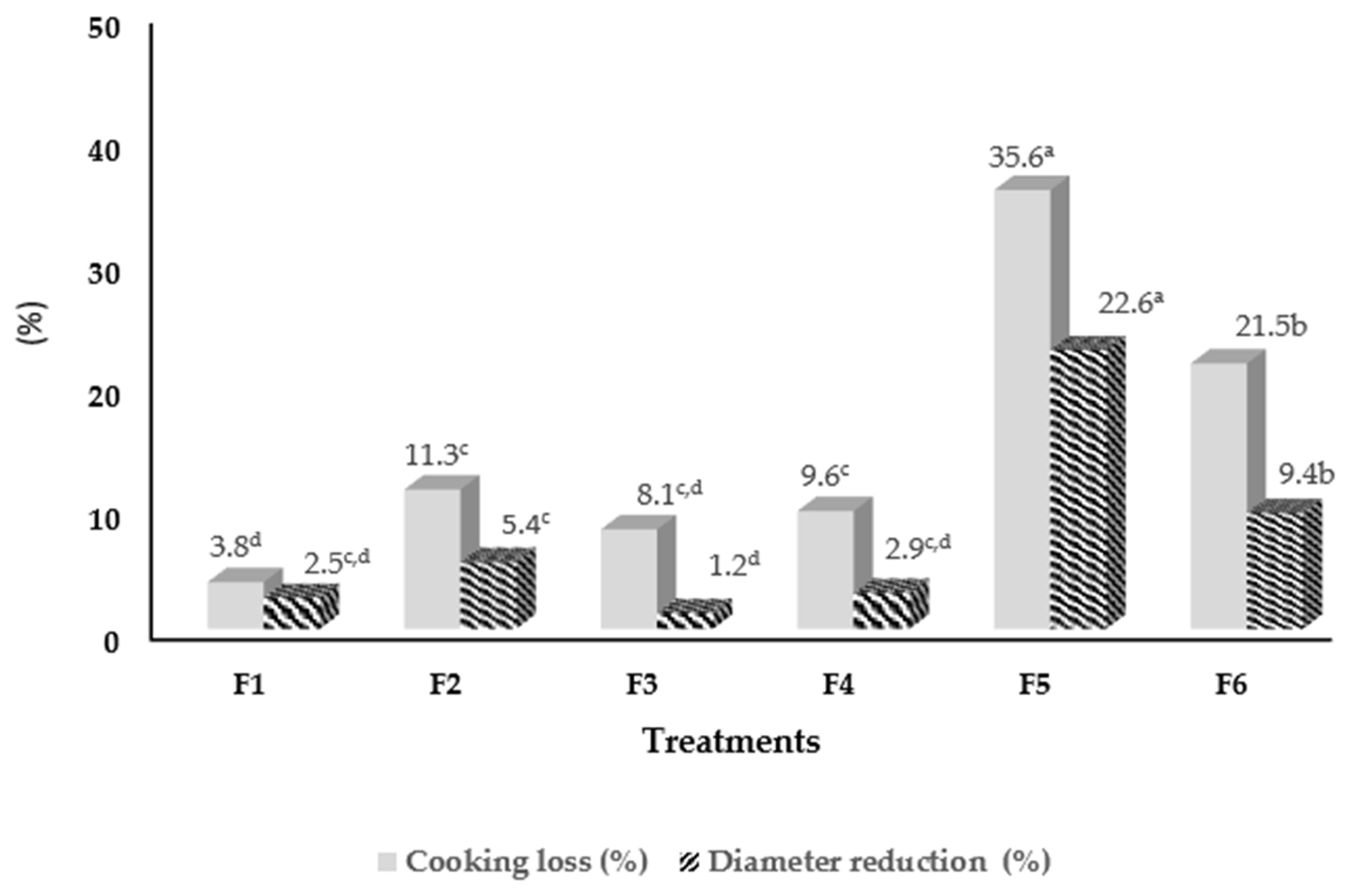
| F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 | 184.33 ± 2.51 c 206.66 ±5.85 b 214.66 ± 1.52 ab 223.00 ± 11.35 a 169.25 ± 3.23 c 116.22 ± 0.94 d | 177.33 ± 2.08 c 183.33 ± 8.08 bc 197.33 ± 2.51 ab 201.66 ± 11.01 a 108.91 ± 7.15 d 91.18 ±2.48 d | 10.91 ± 0.27 c 11.78 ± 0.37 b 11.42 ± 0.26 bc 12.33 ± 0.56 a 11.06 ± 0.33 c 8.57 ± 0.27 d | 10.65 ± 0.16 c 11.17 ± 0.30 b 11.27 ± 0.23 b 11.96 ± 0.58 a 8.55 ±0.22 d 7.76 ±0.15 e | 1.72 ±0.08 d 1.96 ± 0.12 bc 1.80 ± 0.14 cd 2.04 ± 0.11 b 2.11 ± 0.15 b 2.42 ± 0.09 a | 1.48 ± 0.13 c 1.46 ± 0.07 c 1.44 ± 0.07 c 1.57 ± 0.12 bc 1.68 ± 0.09 b 2.10 ± 0.15 a |
| Water Retention Capacity—WRC (%) | Color | Firmness (g) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | a* | b* | |||
| F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 | 35.94 ± 13.10 a 30.18 ± 0.26 a 39.95 ± 13.87 a 32.57 ± 0.97 a 28.85 ± 0.53 a 27.19 ± 2.37 a | 53.11 ± 1.85 a 45.77 ± 1.28 b 44.87 ± 1.23 b 44.50 ± 0.87 b 44.10 ± 4.60 b 34.40 ± 1.14 c | 2.33 ± 0.50 d 6.09 ± 0.58 c 5.99 ± 0.54 c 6.07 ± 0.29 c 8.92 ± 1.11 b 14.00 ± 1.54 a | 22.55 ± 1.68 a 22.30 ± 1.39 a 19.92 ± 0.97 b 20.01 ± 0.55 b 12.98 ± 1.62 d 15.16 ± 0.92 c | 1133.52 ± 192.22 b 1978.42 ± 501.38 b 2096.81 ± 718.17 b 2512.98 ± 329.19 b 9112.68 ± 1936.30 a 1485.49 ± 452.95 b |
| Elasticity (g) | Cohesiveness (g) | Resilience (g) | Chewiness (kgf) | Gumminess (kgf) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 | 1.38 ± 0.011 a 1.36 ± 0.008 a 1.37 ± 0.178 a 1.36 ± 0.004 a 1.08 ± 0.011 c 1.19 ± 0.020 b | 1.14 ± 0.127 a 1.04 ± 0.075 a 1.11 ± 0.060 a 1.16 ± 0.080 a 0.77 ± 0.054 b 1.08 ± 0.125 a | 3644.80 ± 577.25 b 6296.80 ± 1762.60 b 5908.40 ± 1449.98 b 6299.00 ± 1056.75 b 21263.40 ± 5046.16 a 2811.40 ± 961.81 b | 1797.20 ± 212.56 d 2815.00 ± 219.09 c 3206.00 ± 182.22 c 3994.00 ± 290.63 b 7649.80 ± 619.48 a 1931.80 ± 236.93 d | 129,655.13 ± 14552.96 a 118,174.31 ± 8589.67 a 126,451.95 ± 6790.30 a 132,141.63 ± 9215.50 a 87704.28 ± 6158.32 b 123,267.28 ± 14526.62 a |
| Chemical Parameters | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture (%) | Ash (%) | Proteins (%) | Lipids (%) | CHO (%) | Kcal | pH (%) | |
| F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 | 61.91 ± 0.55 a 58.53 ± 0.29 b 60.09 ± 0.73 ab 61.42 ± 0.63 a 45.09 ± 0.28 d 55.40 ± 1.70 c | 2.10 ± 0.13 a 2.45 ± 0.06 a 2.18 ± 0.08 a 2.25 ± 0.02 a 3.62 ± 4.71 a 3.07 ± 0.16 a | 8.75 ± 1.20 c 8.13 ± 1.02 c 10.29 ± 4.97 bc 10.25 ± 0.21 bc 31.53 ± 10.42 a 23.10 ± 4.05 ab | 3.58 ± 0.24 b 2.32 ± 0.63 b 3.07 ± 0.55 b 3.19 ± 2.10 b 16.04 ± 5.64 a 2.60 ± 1.24 b | 23.63 ± 1.27 a 28.55 ± 1.36 a 24.36 ± 4.63 a 22.87 ± 2.06 a 3.70 ± 11.93 b 12.59 ± 6.33 ab | 161.80 ± 2.89 b 167.73 ± 4.06 b 166.23 ± 5.88 b 254.63 ± 82.36 ab 285.30 ± 15.72 a 174.30 ± 1.73 b | 7.62 ± 0.03 b 7.51 ± 0.02 c 7.58 ± 0.03 bc 7.61 ± 0.02 b 7.57 ± 0.03 b 7.93 ± 0.02 a |
| Fibers | Treatments | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 (%) | F2 (%) | F3 (%) | F4 (%) | F5 (%) | F6 (%) | |
| Total fibers Insoluble fibers Soluble fibers | 3.62 ± 0.08 b 3.03 ± 0.04 a 0.59 ± 0.03 b | 3.74 ± 0.08 b 3.03 ± 0.16 a 0.71 ± 0.08 ab | 3.97 ± 0.01 b 3.19 ± 0.05 a 0.78 ± 0.07 ab | 4.15 ± 0.61 b 3.55 ± 0.51 a 0.59 ± 0.10 b | -- -- -- | 5.69 ± 0.14 a 3.25 ± 0.35 a 1.14 ± 0.21 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mercês, Z.d.C.d.; Salvadori, N.M.; Evangelista, S.M.; Cochlar, T.B.; Medeiros, C.d.S.; Lima, R.G.H.; Bandeira, A.S.; Souza, A.K.F.d.; Rios, A.d.O.; Oliveira, V.R.d. Plant-Based Burgers Made with Green Banana Biomass (GBB) Associated with Teff and Chickpea Derivatives. Foods 2025, 14, 1782. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101782
Mercês ZdCd, Salvadori NM, Evangelista SM, Cochlar TB, Medeiros CdS, Lima RGH, Bandeira AS, Souza AKFd, Rios AdO, Oliveira VRd. Plant-Based Burgers Made with Green Banana Biomass (GBB) Associated with Teff and Chickpea Derivatives. Foods. 2025; 14(10):1782. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101782
Chicago/Turabian StyleMercês, Ziane da Conceição das, Natalia Maldaner Salvadori, Sabrina Melo Evangelista, Tatiana Barbieri Cochlar, Cristine da Silva Medeiros, Rafaela Giuliana Hermelino Lima, Amanda Soares Bandeira, Ana Karolina Fortunato de Souza, Alessandro de Oliveira Rios, and Viviani Ruffo de Oliveira. 2025. "Plant-Based Burgers Made with Green Banana Biomass (GBB) Associated with Teff and Chickpea Derivatives" Foods 14, no. 10: 1782. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101782
APA StyleMercês, Z. d. C. d., Salvadori, N. M., Evangelista, S. M., Cochlar, T. B., Medeiros, C. d. S., Lima, R. G. H., Bandeira, A. S., Souza, A. K. F. d., Rios, A. d. O., & Oliveira, V. R. d. (2025). Plant-Based Burgers Made with Green Banana Biomass (GBB) Associated with Teff and Chickpea Derivatives. Foods, 14(10), 1782. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101782







