Effect of pH-Shifted Compound Heating Treatment on the Structure and Properties of Walnut Protein Isolate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. pH-Shifted Compound Heating Treatment of WPI
2.3. Determination of Solubility
2.4. Determination of Foaming Capacity (FA) and Foaming Stability (FS)
2.5. Determination of Particle Size and Potential
2.6. Determination of SDS-PAGE
2.7. Determination of Free Sulfhydryl Content (R-SH)
2.8. Determination of Ultraviolet Absorption Spectra (UV)
2.9. Determination of Endogenous Fluorescence Spectra
2.10. Determination of H0
2.11. Determination of SEM
2.12. Determination of FTIR
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
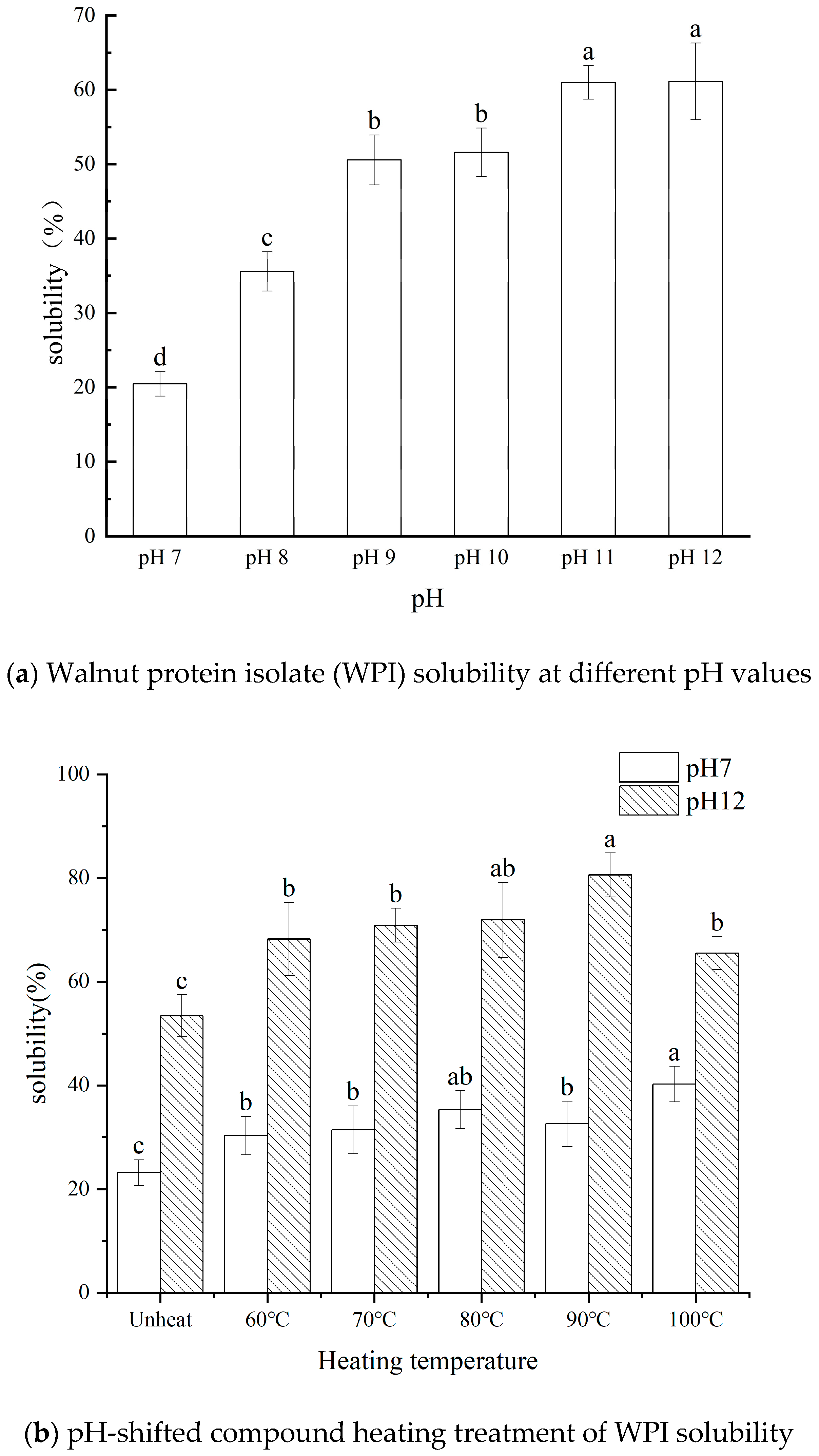
3.1. Influence of pH-Shifted Compound Heating Treatment of WPI on Solubility
3.2. Effect of pH-Shifted Compound Heating Treatment of WPI on FA and FS
3.3. Effect of pH-Shifted Compound Heating Treatment of WPI on Particle Size and Potential
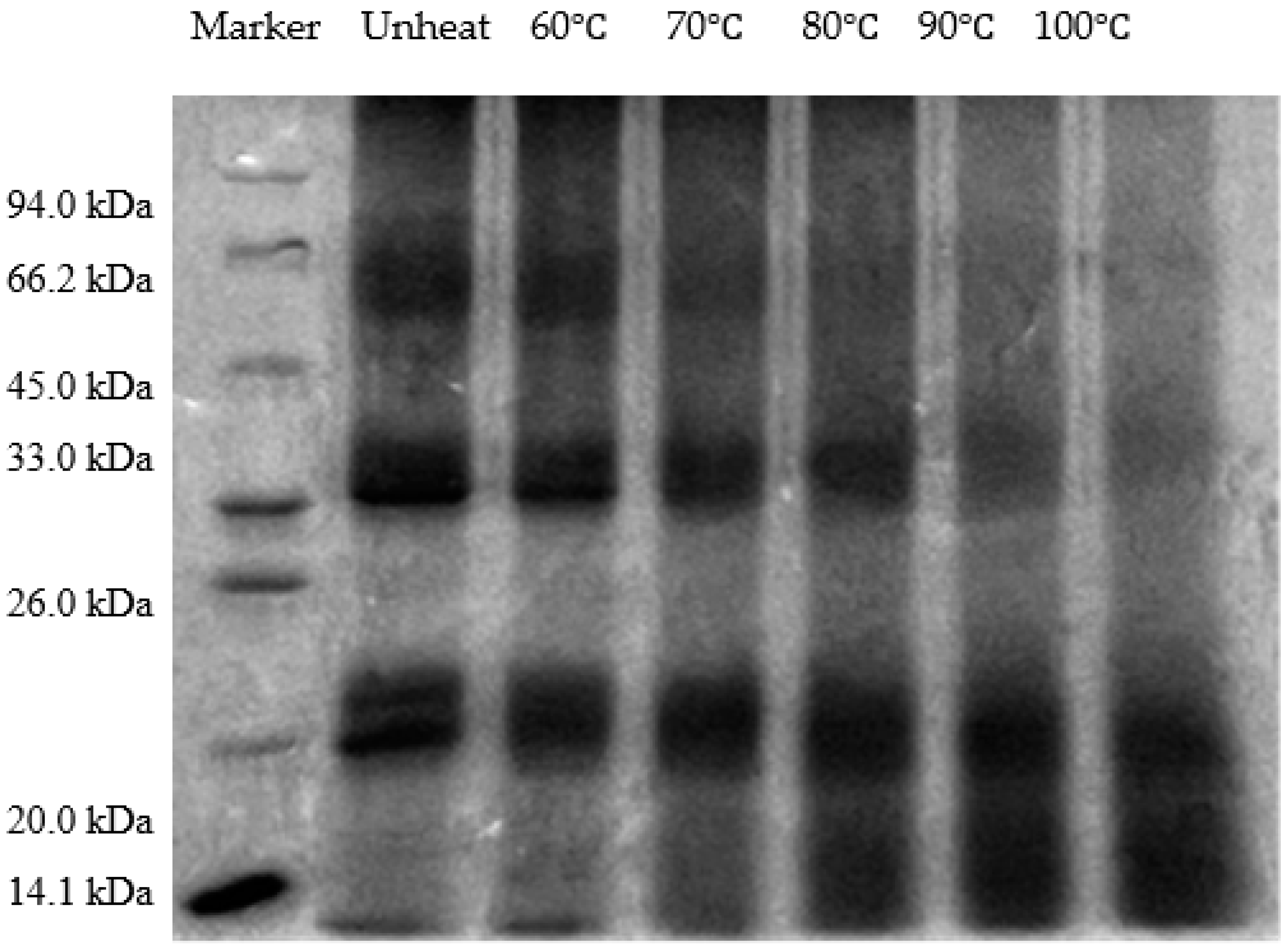
3.4. Effect of pH-Shifted Compound Heating Treatment of WPI on SDS-PAGE
3.5. Effect of pH-Shifted Compound Heating Treatment of WPI on R-SH Content
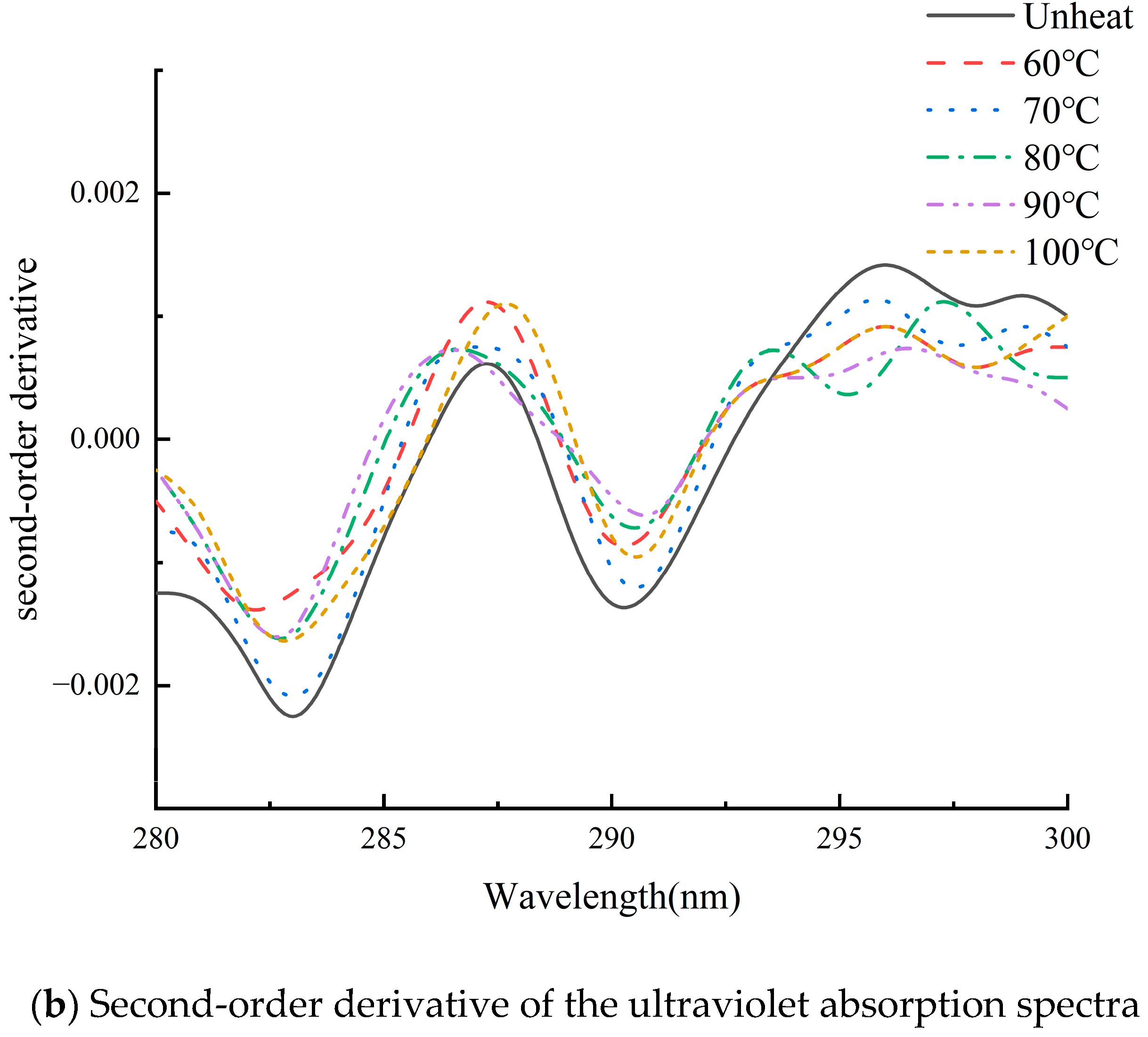
3.6. Effect of pH-Shifted Compound Heating Treatment of WPI on UV
3.7. Effect of pH-Shifted Compound Heating Treatment of WPI on Endogenous Fluorescence Spectra
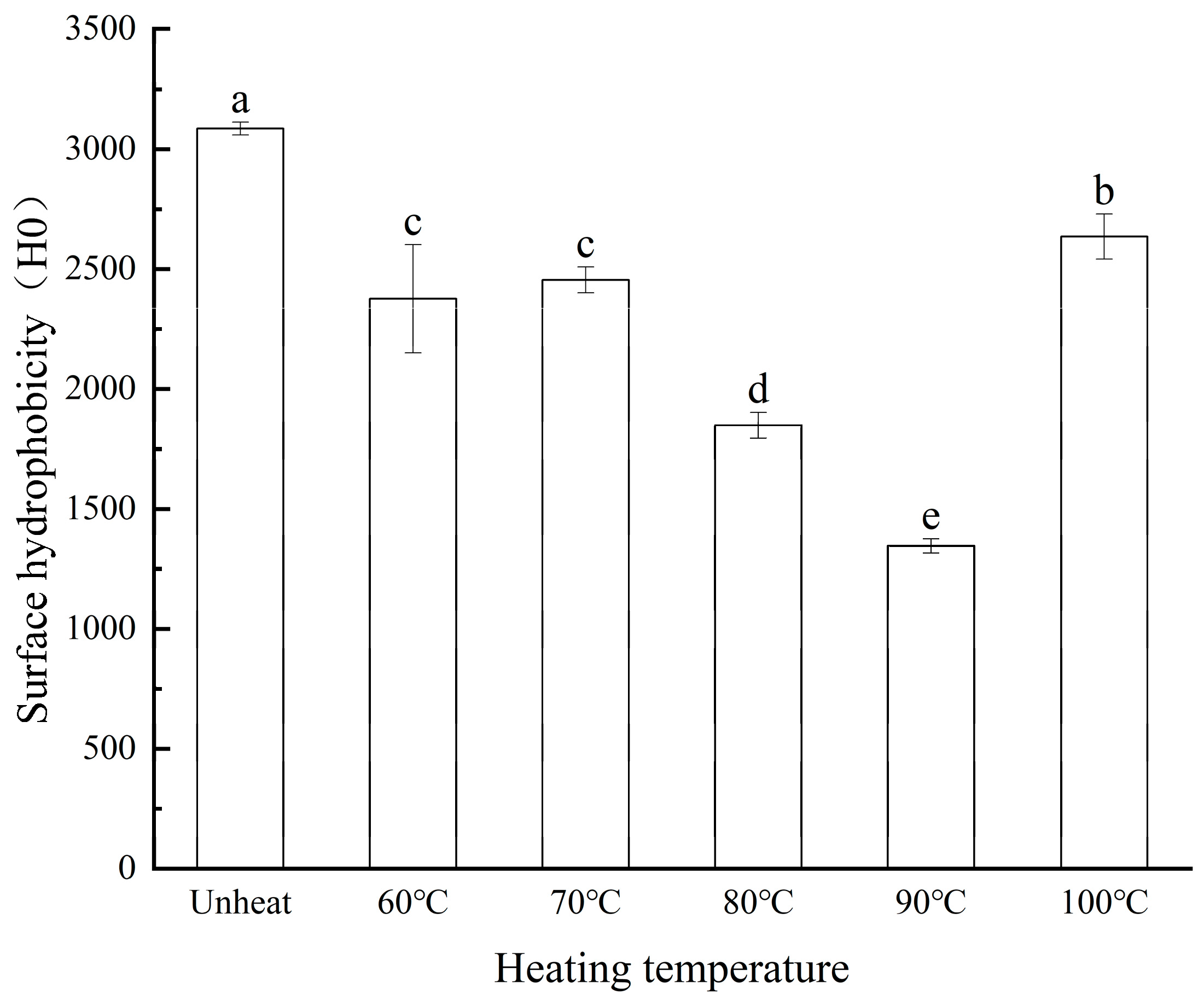
3.8. Effect of pH-Shifted Compound Heating Treatment of WPI on H0
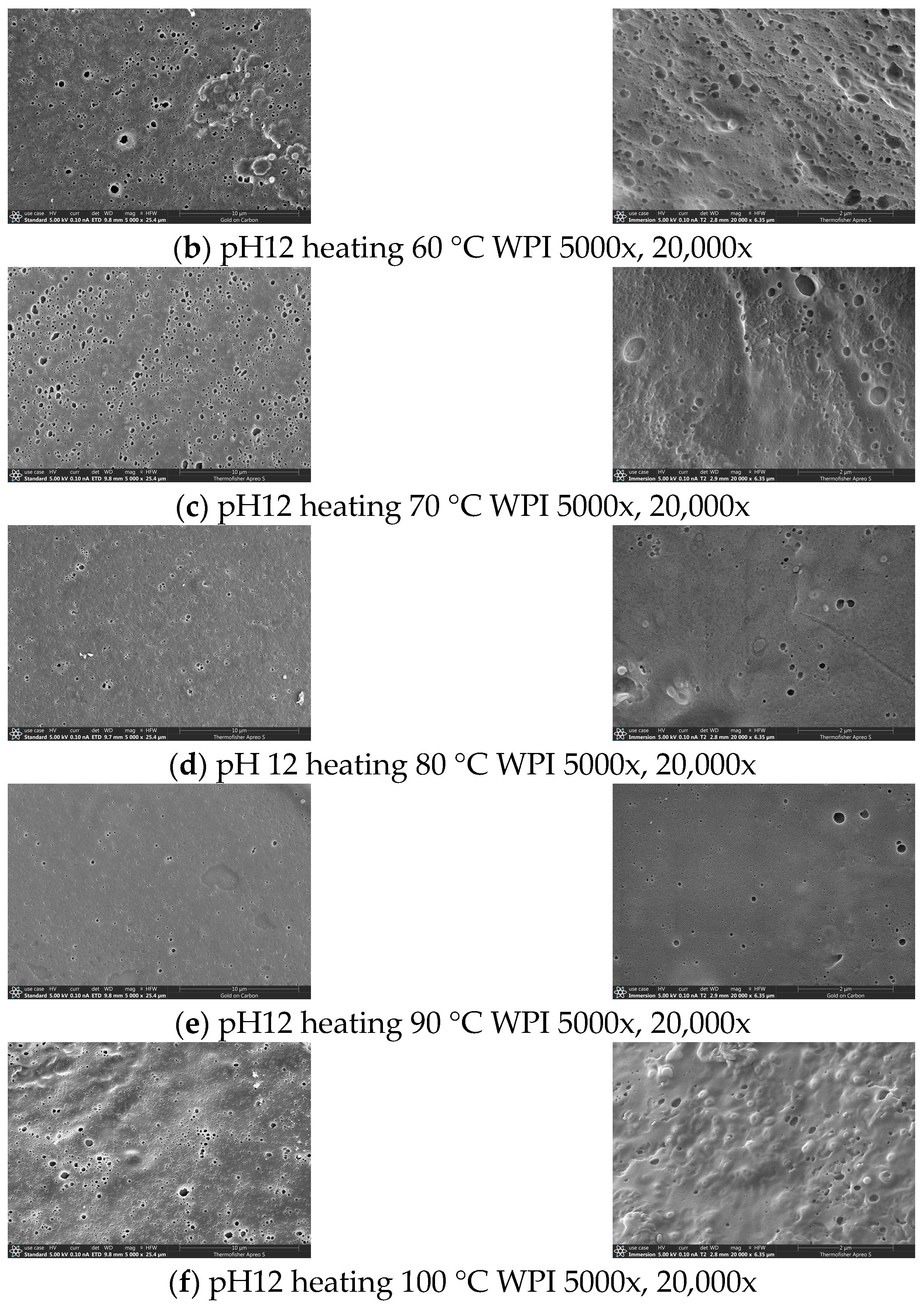
3.9. Scanning Electron Microscopy of pH-Shifted Compound Heating Treatment WPI
3.10. Effect of pH-Shifted Compound Heating Treatment of WPI on FTIR
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wagner, J.R.; Sorgentini, D.A.; Anon, M.C. Thermal and electrophoretic behavior, hydrophobicity, and some functional properties of acid-treated soy isolates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 1881–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Hua, Y.; Chen, G. Amino Acid Composition, Molecular Weight Distribution and Gel Electrophoresis of Walnut (Juglans regia L.) Proteins and Protein Fractionations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 2003–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.X.; Cai, S.B.; Wang, O.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, L. A comprehensive review on walnut protein: Extraction, modification, functional properties and its potential applications. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 16, 101141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Kong, X.Z.; Zhang, C.M.; Hua, Y.F. Effect of heat treatment on the properties of soy protein-stabilised emulsions. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 1554–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.Z.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.J.; Liang, J.; Wang, R.; Chen, Y.; Ma, W.J.; Qi, B.K.; Zhang, M. Effects of ultrasound on the structure and physical properties of black bean protein isolates. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Chen, J.; Xiong, Y.L. Structural and Emulsifying Properties of Soy Protein Isolate Subjected to Acid and Alkaline pH-Shifting Processes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 7576–7583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.W.; Mu, T.H.; Zhang, M.; Goffin, D. Effect of heat treatments on the structure and emulsifying properties of protein isolates from cumin seeds (Cuminum cyminum). Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2018, 24, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadesky, L.; Walkling-Ribeiro, M.; Kriner, K.T.; Karwe, M.V.; Moraru, C.I. Structural changes induced by high-pressure processing in micellar casein and milk protein concentrates. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 7055–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.J.; Zhou, Z. Solubility and emulsifying properties of phosphorylated walnut protein isolate extracted by sodium trimetaphosphate. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 143, 111117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5009.5-2016; Determination of Protein in Food. Standard Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Zhao, M.; Xiong, W.F.; Chen, B.X.; Zhu, J.; Wang, L.F. Enhancing the solubility and foam ability of rice glutelin by heat treatment at pH12: Insight into protein structure. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, H.T.; Xia, X.F.; Sun, F.D.; Kong, B.H. Effect of ultrasound-assisted immersion thawing on emulsifying and gelling properties of chicken myofibrillar protein. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 142, 111016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ding, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.X.; Li, Y.G.; Wang, R.; Luo, X.H.; Li, Y.A.; Li, J.; Chen, Z. Effect of electron beam on the functional properties and structure of defatted wheat germ proteins. J. Food Eng. 2017, 202, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.Y.; Zhang, M.J.; Ma, M.H. Emulsifying properties of ovalbumin: Improvement and mechanism by phosphorylation in the presence of sodium tripolyphosphate. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 60, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardine, P.J.; Coombs, D.H. Capsid expansion follows the initiation of DNA packaging in bacteriophage T4. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 284, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Xiong, H.; Selomulya, C.; Chen, X.D.; Huang, S.F.; Ruan, X.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, W.J. Effects of Spray Drying and Freeze Drying on the Properties of Protein Isolate from Rice Dreg Protein. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 1759–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.G.; Chu, S.; Lu, J.K.; Wang, P.; Ma, M.H. Molecular and structural properties of three major protein components from almond kernel. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Yan, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Qi, B.; Li, Y. Different interactions driving the binding of soy proteins (7S/11S) and flavonoids (quercetin/rutin): Alterations in the conformational and functional properties of soy proteins. Food Chem. 2022, 396, 133685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Liu, T.X.; Tang, C.H. Use of oligomeric globulins to efficiently fabricate nanoemulsions: Importance of enhanced structural stability by introducing trehalose. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 141, 108695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.Y.; McClements, D.J.; Dai, L.; He, X.Y.; Li, Y.; Ji, N.; Qin, Y.; Xiong, L.; Sun, Q.J. Improvement of pasting and gelling properties of potato starch using a direct vapor-heat moisture treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 219, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.T.; Guan, C.; Ma, C.H.; Xu, H.H. Nuclei-induced formation of amyloid fibrils in whey protein: Effects of enzyme hydrolysis on the ability of nuclei to induce fibril formation. Food Chem. 2023, 410, 135433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.X.; Xu, Y.; Shi, C.H.; Liu, Y.; Bi, S. Formation mechanism and functional properties of walnut protein isolate and soy protein isolate nanoparticles using the pH-cycle technology. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1135048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.F.; Fan, T.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhang, X.W.; Sun, Y.L.; Liu, H.K. Influence of pH and salt concentration on functional properties of walnut protein from different extraction methods. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 2833–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roussel, H.; Cheftel, J.C. Mechanisms of gelation of sardine proteins—Influence of thermal-processing and of various additives on the texture and protein solubility of kamaboko gels. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1990, 25, 260–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muneer, F.; Johansson, E.; Hedenqvist, M.S.; Plivelic, T.S.; Kuktaite, R. Impact of pH Modification on Protein Polymerization and Structure-Function Relationships in Potato Protein and Wheat Gluten Composites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Xu, Z.; Chen, M.; Cheng, Y. Effects of pH and heat treatments on structure and functional properties of rice proteins. Food Mach. 2018, 34, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Othmeni, I.; Blecker, C.; Karoui, R. pH-dependent emulsifying properties of pea protein isolate: Investigation of the structure Function relationship. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 290, 139105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.F.; Wang, B.; Zhao, B.T.; Meng, Y.C.; Chen, J.; Yang, F.M. Effect of Hydrothermal Treatment on the Structure and Functional Properties of Quinoa Protein Isolate. Foods 2022, 11, 2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.Y.; Khanzada, G.; Harwalkar, V.R. Thermal gelation of oat globulin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1988, 36, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C. Study on Thermal Aggregation Behavior and Mechanism of Rice Glutelin. Master’s Thesis, Hubei University of Technology, Wuhan, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.G.; Cao, Y.; Lei, S.M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.H.; Hu, J.; Li, Z.K.; Liu, R.; Ge, Q.F.; Yu, H. Protein structure and sulfhydryl group changes affected by protein gel properties: Process of thermal-induced gel formation of myofibrillar protein. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 1834–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Gao, S.; Xiang, X.; Li, X.; Yu, X.; Li, S. Physicochemical, structural and adhesion properties of walnut protein isolate-xanthan gum composite adhesives using walnut protein modified by ethanol. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 192, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, R.; Balny, C. UV-visible derivative spectroscopy under high pressure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 2002, 1595, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.P.; Deng, L.P.; Wang, Y.R.; McClements, D.J.; Luo, S.J.; Liu, C.M. Impact of rutin on the foaming properties of soybean protein: Formation and characterization of flavonoid-protein complexes. Food Chem. 2021, 362, 130238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.X.; Tan, B.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.D.; Sun, X.J. The phenolic profile of walnut meal protein isolate and interaction of phenolics with walnut protein. Food Res. Int. 2023, 170, 113042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.Y. Effects of pH-Shifting and Ultrasound on Molecular Structure of Peanut Protein. Master’s Thesis, Henan University of Technology, Zhengzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, G.; Qian, L.; Yan, L.; Baohua, K.; Jianchun, H. The Effect of pH-Shifting Combined with Heating Treatment on Structural Properties of Soybean Protein Isolate. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 15, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Zhang, F.X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L.T.; Lin, S.W.; Liu, D.Y. The beneficial effects of rutin on myofibrillar protein gel properties and related changes in protein conformation. Food Chem. 2019, 301, 125206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, F.H.D.; Delgado, G.G.; Costa, T.S.D.; Tasic, L. Applications of fluorescence spectroscopy in protein conformational changes and intermolecular contacts. BBA Adv. 2023, 3, 100091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Li, J.S.; Huang, G.X.; Yan, L.J. Predicting Protein Surface Property with its Surface Hydrophobicity. Protein Pept. Lett. 2021, 28, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yan, C.J.; Lin, M.; He, C.W.; Xu, Y.F.; Huang, Y.K.; Zhou, Z. The effects of conjugation of walnut protein isolate with polyphenols on protein solubility, antioxidant activity, and emulsifying properties. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.Z.; Li, X.H.; Wang, H.J.; Hua, Y.F.; Huang, Y.R. Effect of lipoxygenase activity on the gelling properties of in defatted soybean flour soybean protein isolate. Food Chem. 2008, 106, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Müller, E.; Meffert, M.; Gerthsen, D. On the Progress of Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy (STEM) Imaging in a Scanning Electron Microscope. Microsc. Microanal. 2018, 24, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.S.; Ma, Z.; Jing, P. Interaction of soy protein isolate fibrils with betalain from red beetroots: Morphology, spectroscopic characteristics and thermal stability. Food Res. Int. 2020, 135, 109289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Zhao, Y.J.; Xiao, C.Q.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Zhao, M.M.; Su, G.W. Mechanism of the discrepancy in the enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency between defatted peanut flour and peanut protein isolate by Flavorzyme. Food Chem. 2015, 168, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.Y.; Qian, F.; Jiang, S.J.; Tuo, Y.F.; Mu, G.Q. Effect of Heat Treatments on the Secondary Structure of Milk Proteins Analyzed by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. Food Sci. 2017, 38, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.P.; Zhou, R.; Shi, Y.R.; Chen, H.C.; Du, Y. Effects of heating on the secondary structure of proteins in milk powders using mid-infrared spectroscopy. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chai, L.; Shi, W.; Tan, Y.; Che, X.; Lu, J.; Bai, B.; Zhang, C. Effect of pH-Shifted Compound Heating Treatment on the Structure and Properties of Walnut Protein Isolate. Foods 2025, 14, 1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101754
Chai L, Shi W, Tan Y, Che X, Lu J, Bai B, Zhang C. Effect of pH-Shifted Compound Heating Treatment on the Structure and Properties of Walnut Protein Isolate. Foods. 2025; 14(10):1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101754
Chicago/Turabian StyleChai, Liwen, Wei Shi, Yunxia Tan, Xudong Che, Jiankang Lu, Bingyao Bai, and Chunlan Zhang. 2025. "Effect of pH-Shifted Compound Heating Treatment on the Structure and Properties of Walnut Protein Isolate" Foods 14, no. 10: 1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101754
APA StyleChai, L., Shi, W., Tan, Y., Che, X., Lu, J., Bai, B., & Zhang, C. (2025). Effect of pH-Shifted Compound Heating Treatment on the Structure and Properties of Walnut Protein Isolate. Foods, 14(10), 1754. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101754



