Optimization of Ultraviolet-B Treatment for Enrichment of Total Flavonoids in Buckwheat Sprouts Using Response Surface Methodology and Study on Its Metabolic Mechanism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Treatment and Experimental Design
2.2. RSM Methods for Determining Optimal Germination Conditions
2.3. Total Flavonoids and Phenols Content
2.4. H2O2, MDA, and —Content
2.5. Antioxidant Capacity
2.6. Antioxidant Enzyme Activity
2.7. Metabolic Enzyme Activity Assay
2.8. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
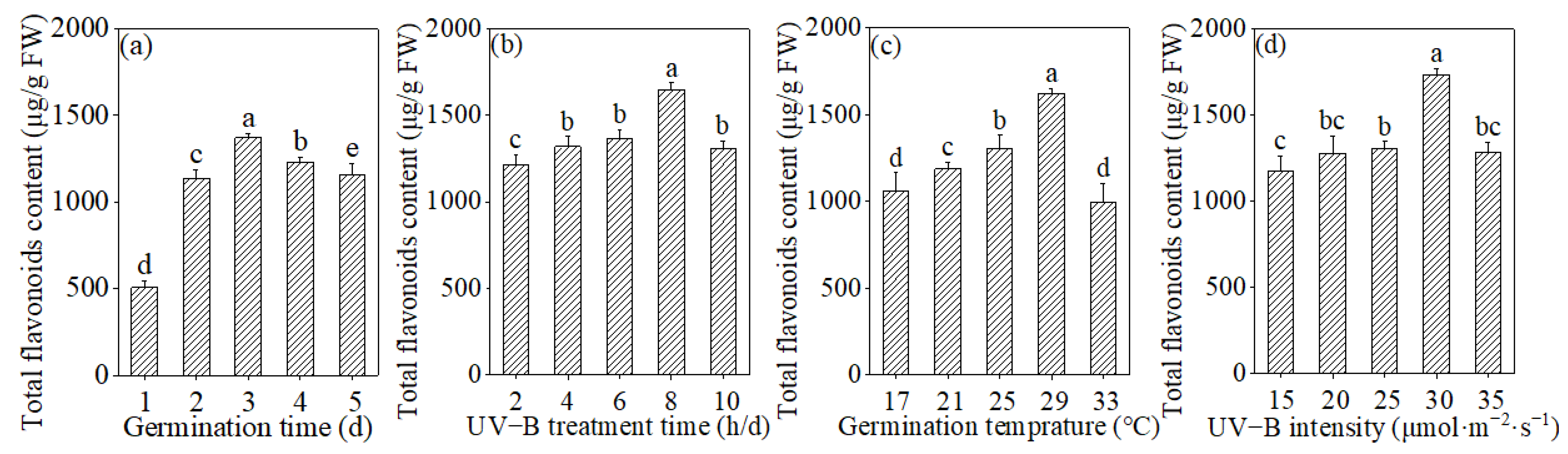
3.1. Effects of Germination Time, UV-B Treatment Time, Germination Temperature, and UV-B Intensity on the Total Flavonoids Content
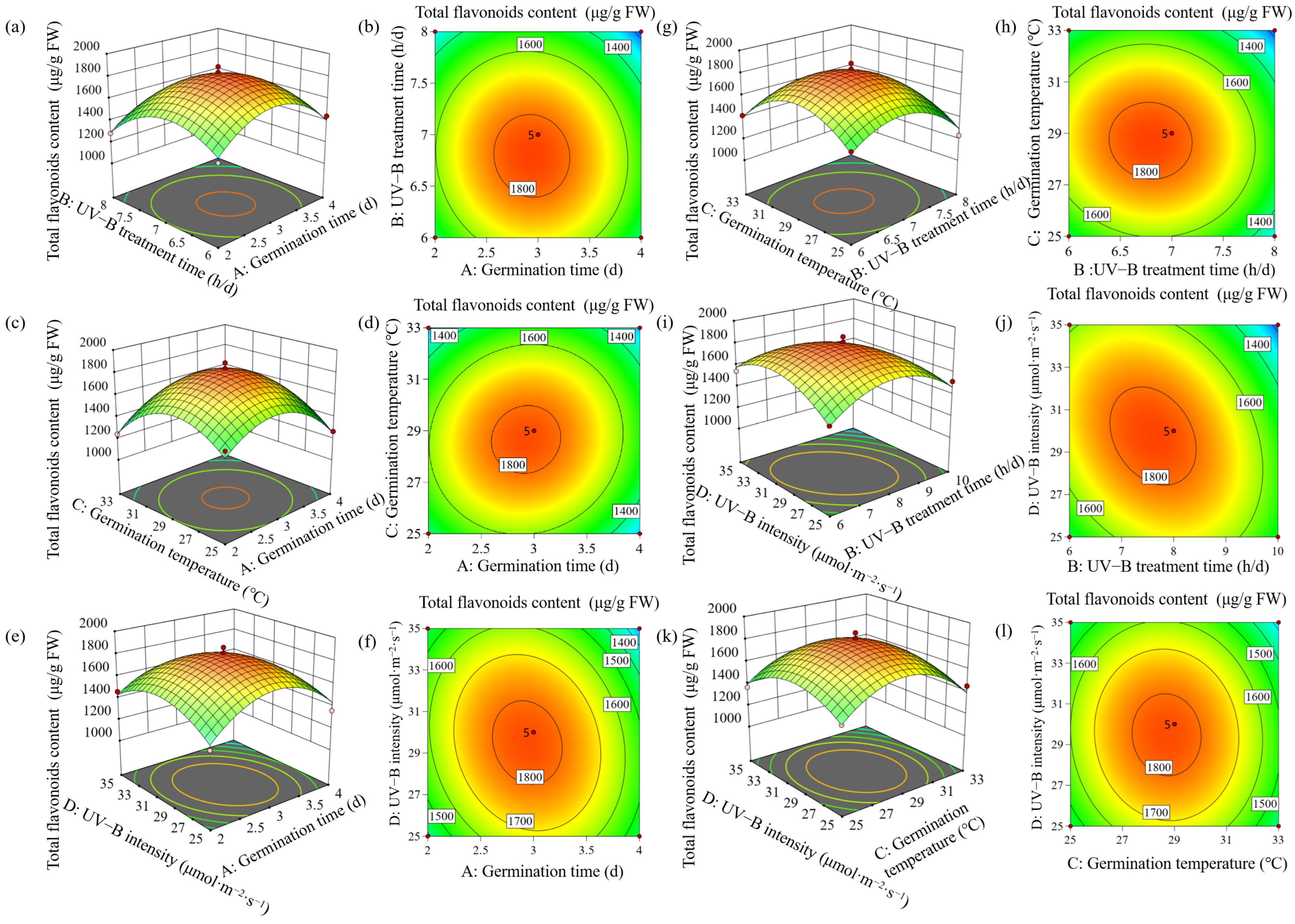
3.2. Statistical Analysis of RSM
23.07BC − 111.14BD − 20.97CD − 273.44A2 − 230.45B2 − 270.29C2 − 183.27D2
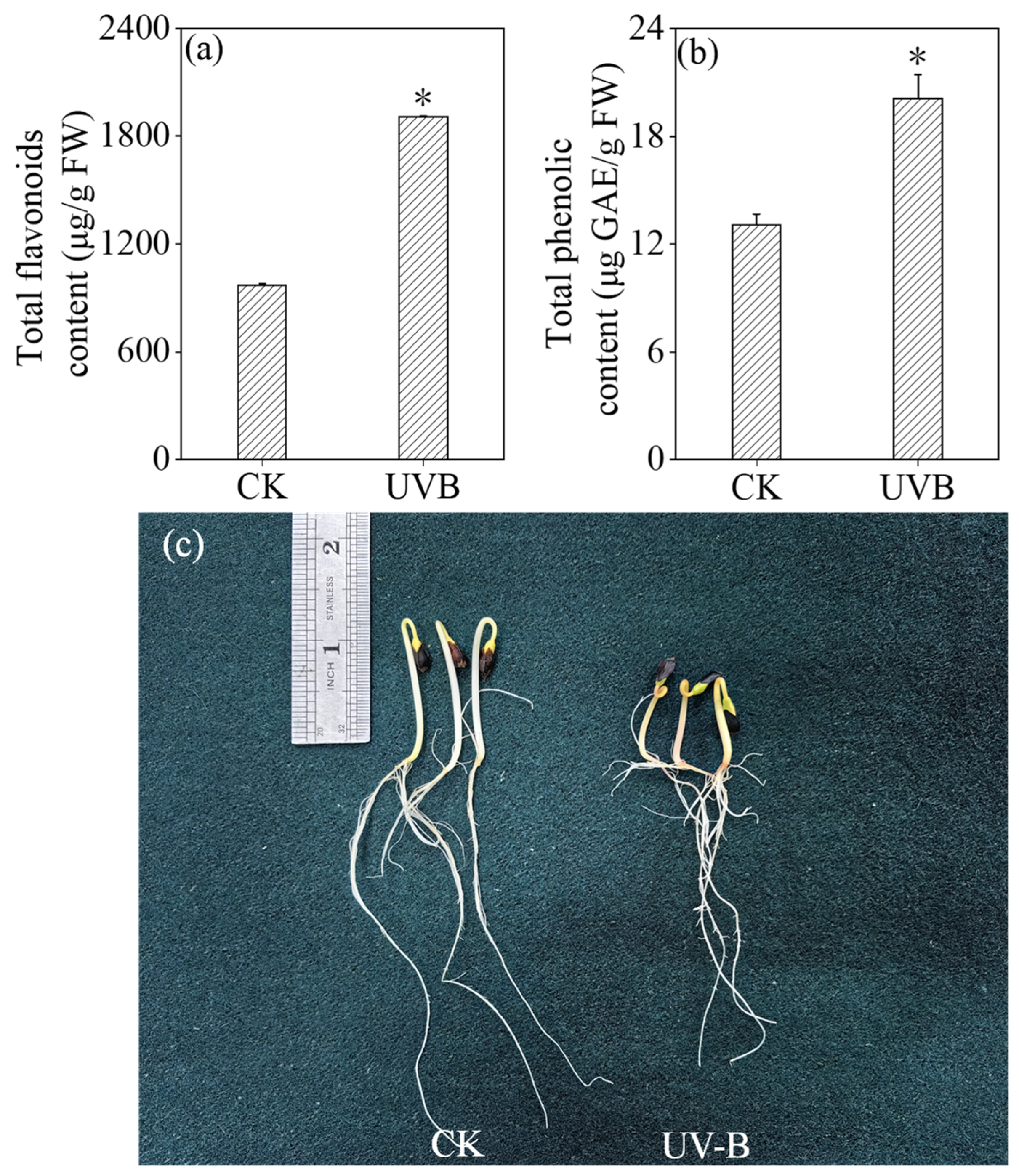
3.3. Effects of UV-B Treatment on the Contents of Total Flavonoids and Total Phenols
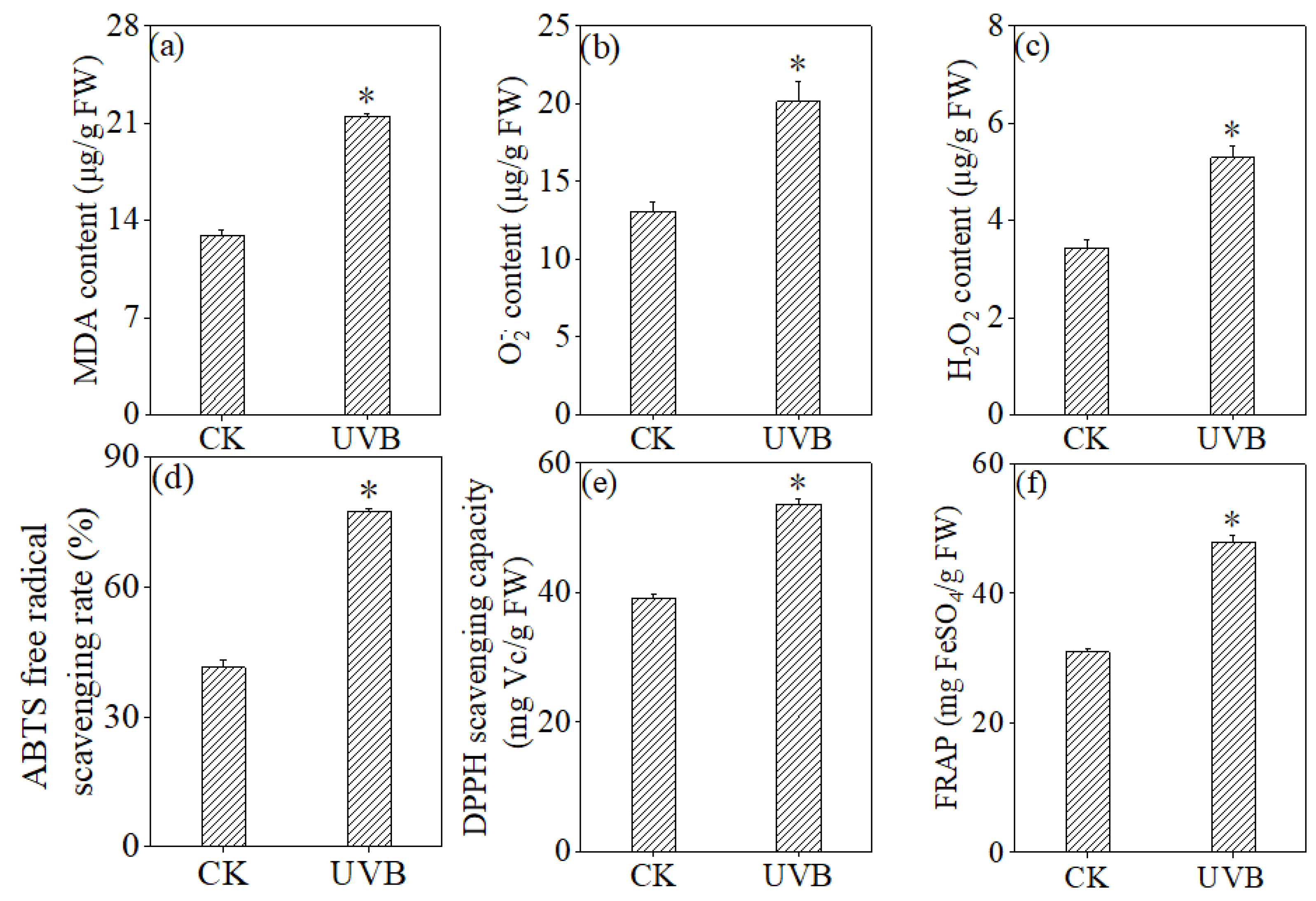
3.4. Effects of UV-B Treatment on Antioxidant System
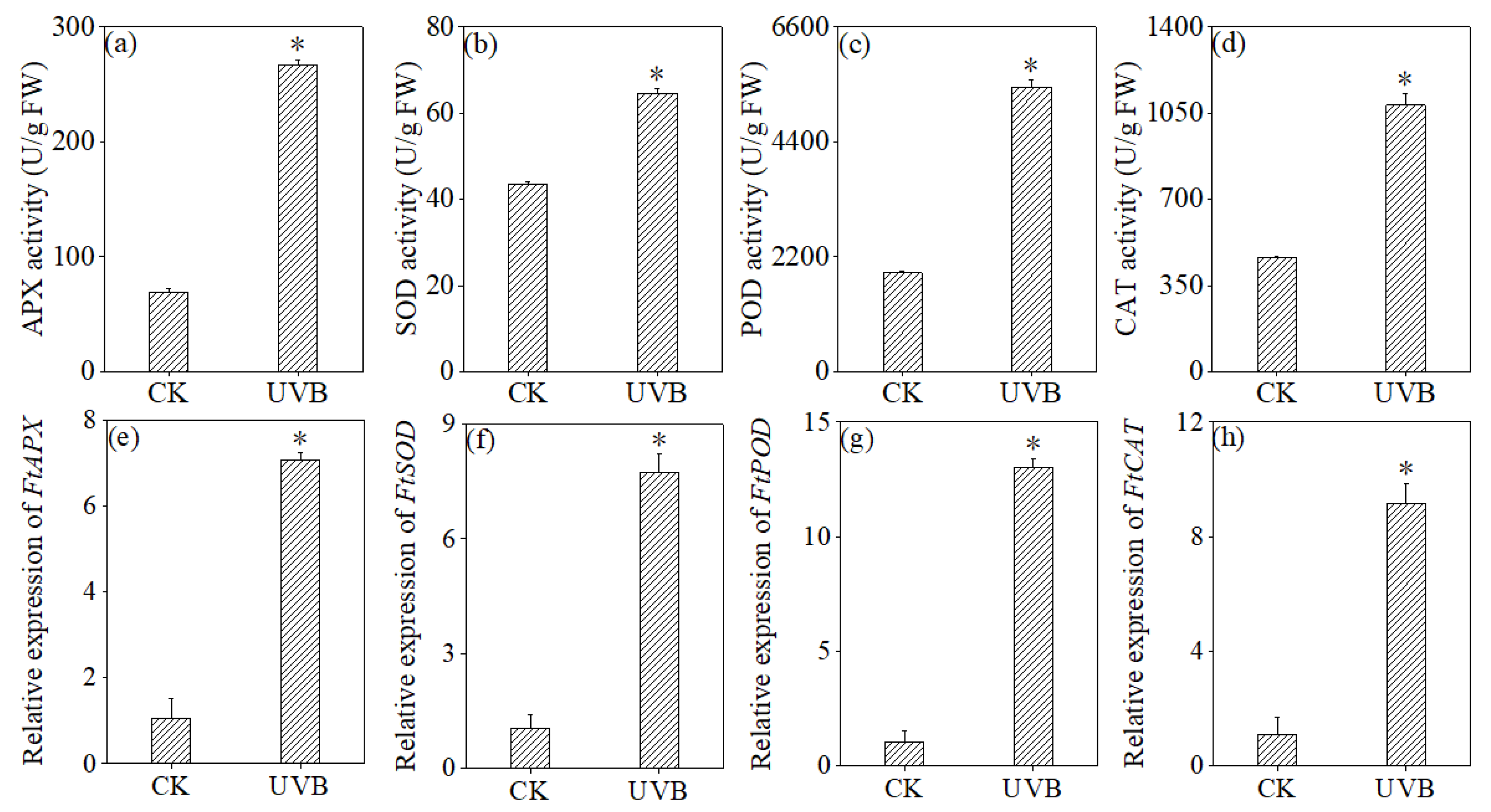
3.5. Effects of UV-B Treatment on Antioxidant Enzyme Activities and Expression Levels of Related Genes in Buckwheat Sprouts
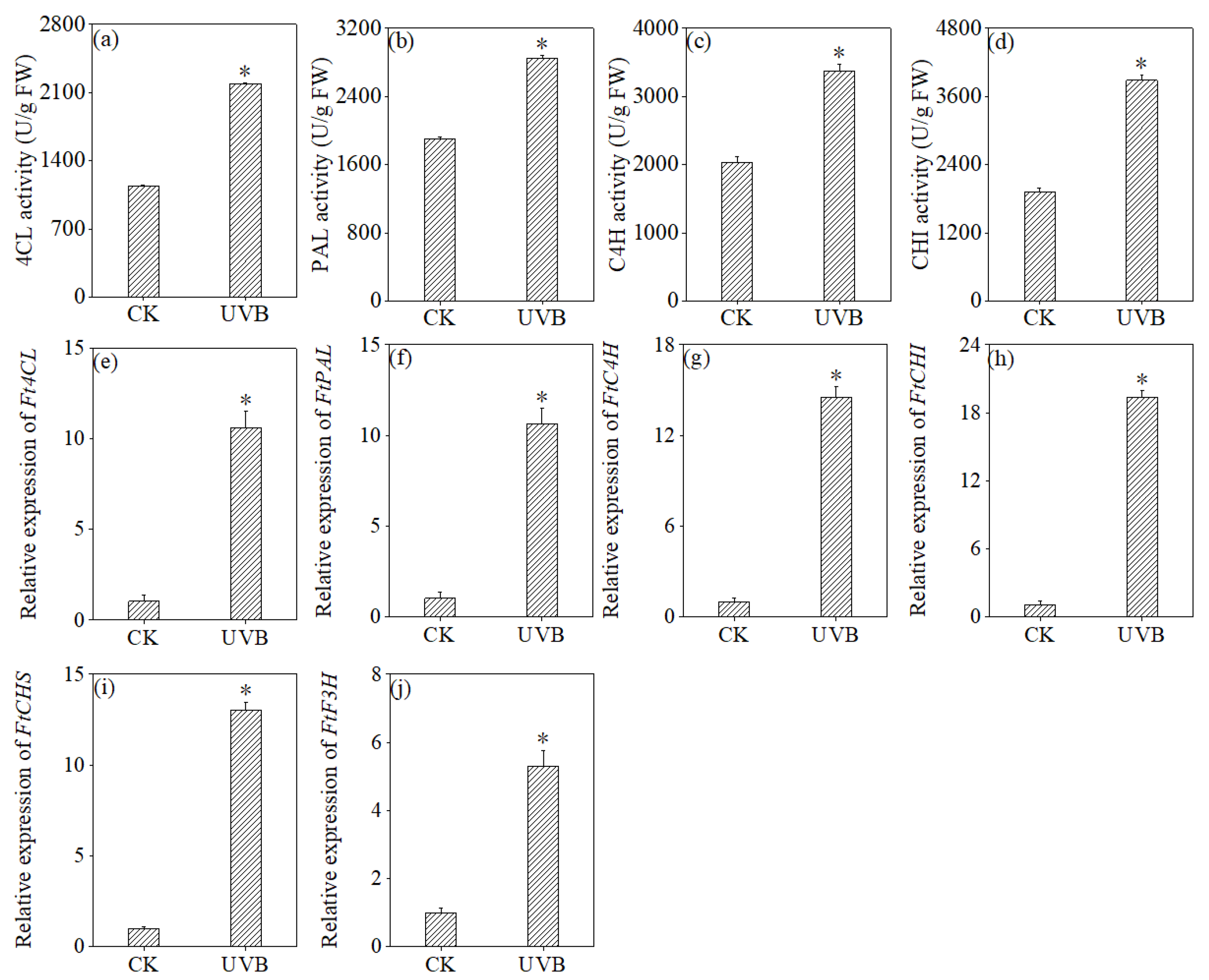
3.6. Effects of UV-B Treatment on the Expression Levels of Metabolic Enzymes and Related Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chinma, C.E.; Adedeji, O.E.; Jolayemi, O.S.; Ezeocha, V.C.; Ilowefah, M.A.; Rosell, C.M.; Adebo, J.A.; Wilkin, J.D.; Adebo, O.A. Impact of germination on the techno-functional properties, nutritional composition, and health-promoting compounds of brown rice and its products: A. review. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 8–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benincasa, P.; Falcinelli, B.; Lutts, S.; Stagnari, F.; Galieni, A. Sprouted Grains: A Comprehensive Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmens, E.; Moroni, A.V.; Pagand, J.; Heirbaut, P.; Ritala, A.; Karlen, Y.; Lê, K.; Broeck, H.C.V.D.; Brouns, F.J.; De Brier, N.; et al. Impact of Cereal Seed Sprouting on Its Nutritional and Technological Properties: A Critical Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 305–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.-N.; Li, R.; Li, Z.-J.; Tan, B. Effect of germination in the form of paddy rice and brown rice on their phytic acid, GABA, γ-oryzanol, phenolics, flavonoids and antioxidant capacity. Food Res. Int. 2022, 159, 111603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.R.; Kwon, S.-J.; Kim, J.H.; Duan, S.; Eom, S.H. Light-Induced Antioxidant Phenolic Changes among the Sprouts of Lentil Cultivar. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puntel, R.T.; Stefanello, R.; Garcia, W.J.d.S.; Dorneles, L.S. Aluminum and UV-C light on seed germination and initial growth of white oats. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2024, 87, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Bian, Z.; Yuan, X.; Chen, X.; Lu, C. A review on the effects of light-emitting diode (LED) light on the nutrients of sprouts and microgreens. Elsevier 2020, 99, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, S.; Dong, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wu, N. Effects of microwave treatment on the microstructure, germination characteristics, morphological characteristics and nutrient composition of maize. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2024, 165, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, N.; Agrawal, A.; Pati, A.K. A Mini Review on effects of Microwave on Seed Germination. Res. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2023, 15, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyakane, N.E.; Markus, E.D.; Sedib, M.M. The Effects of Magnetic Fields on Plants Growth: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Food Eng. 2018, 5, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Chen, H.; Xia, M.; Liao, Q.; Zhao, J.; Peng, L.; Zou, L.; Zhao, G. The Impacts of Plant Hormones on the Growth and Quality of Sprouts. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2024, 17, 2913–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, L.S.P.; Zivcak, M.; Brestic, M.; Sytar, O. The Contribution of Buckwheat Genetic Resources to Health and Dietary Diversity. Curr. Genom. 2016, 17, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, D.A.; Khalid, N.; Ahmad, A.; Randhawa, M. Phytochemicals and biofunctional properties of buckwheat: A review. J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 152, 349–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Huang, X.; Zou, Y.; Yang, T. Effects of Germination on the Nutritional Properties, Phenolic Profiles, and Antioxidant Activities of Buckwheat. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, H1111–H1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Bian, Z.; Wang, S. Effects of Different Treatments on the Germination, Enzyme Activity, and Nutrient Content of Buckwheat. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2020, 26, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Peng, W.T. A review: The nutrition components, active substances and flavonoid accumulation of Tartary buckwheat sprouts and innovative physical technology for seeds germinating. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1168361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Wang, T.; Gan, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Jin, B. Plant flavonoids: Classification, distribution, biosynthesis, and antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2022, 30, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Gao, H.; Chen, X. A Review of Classification, Biosynthesis, Biological Activities and Potential Applications of Flavonoids. Molecules 2023, 28, 4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiczkowski, W.; Szawara-Nowak, D.; Dbski, H.; Mitrus, J.; Horbowicz, M. Comparison of flavonoids profile in sprouts of common buckwheat cultivars and wild tartary buckwheat. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1977–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Hu, M.; Yang, J.; Yin, Y.; Fang, W. Ultraviolet-B Radiation Stimulates Flavonoid Biosynthesis and Antioxidant Systems in Buckwheat Sprouts. Foods 2024, 13, 3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Tang, W.; Zhou, X.; Wu, Y. Combined Effects of Blue and Ultraviolet Lights on the Accumulation of Flavonoids in Tartary Buckwheat Sprouts. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2016, 66, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, T.G.; Kim, D.O.; Eom, S.H. Effects of light sources on major flavonoids and antioxidant activity in common buckwheat sprouts. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.C.; Sun, J.T. Changes in phenolic content, phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) activity, and antioxidant capacity of two buckwheat sprouts in relation to germination. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 7, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, X.; Niu, M.; Wang, R.; Chen, Z. Effect of additives on flavonoids, D-chiro-Inositol and trypsin inhibitor during the germination of tartary buckwheat seeds. J. Cereal Sci. 2013, 58, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Xuan, Z.; He, Y.; Lutts, S.; Korpelainen, H.; Li, C. Principal component analysis of intraspecific responses of tartary buckwheat to UV-B radiation under field conditions. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2007, 61, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębski, H.; Szwed, M.; Wiczkowski, W.; Szawara-Nowak, D.; Bączek, N.; Horbowicz, M. UV-B radiation increases anthocyanin levels in cotyledons and inhibits the growth of common buckwheat seedlings. Acta Biol. Hung. 2016, 67, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loan, L.; Thuy, N. Optimization of germination process of “Cam” brown rice by response surface methodology and evaluation of germinated rice quality. Food Res. 2019, 4, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y. Germination Promotes Flavonoid Accumulation of Finger Millet (Eleusine coracana L.): Response Surface Optimization and Investigation of Accumulation Mechanism. Plants 2024, 13, 2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Shi, A.; Liu, L.; Hui, H.; Wang, Q. Optimisation for resveratrol accumulation during peanut germination with phenylalanine feeding & ultrasound-treatment using response surface methodology. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijngaard, H.H.; Ulmer, H.M.; Arendt, E.K. The effect of germination temperature on malt quality of buckwheat. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2005, 63, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, J.; Liu, Y.; Hui, Y.Y.; Wan, B.; Liu, J.; Qian, C.L.; Jin, C.H. 2-aminoindan-2-phosphonic acid alleviates oxidative browning in fresh-cut lily bulbs. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e16449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Tian, X.; Yang, J.; Yang, Z.; Tao, J.; Fang, W. Melatonin mediates isoflavone accumulation in germinated soybeans (Glycine max L.) under ultraviolet-B stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 175, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Zhao, C.; Yang, M.; Yin, D. ZnCl2 treatment improves nutrient quality and Zn accumulation in peanut seeds and sprouts. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, G.R.; Li, M.J.; Ma, F.W.; Liang, D. Antioxidant capacity and the relationship with polyphenol and Vitamin C in Actinidia fruits. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Xu, S.; Zou, X.; Zheng, Y.; Qiu, F. Changes of Antioxidative Enzymes and Lipid Peroxidation in Leaves and Roots of Waterlogging-Tolerant and Waterlogging-Sensitive Maize Genotypes at Seedling Stage. Agric. Sci. China 2010, 9, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, P.; Chen, Z.; Gu, Z.; Yang, R. NaCl stress on physio-biochemical metabolism and antioxidant capacity in germinated hulless barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 1755–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Fang, W.; Yin, Y. Crosstalk between ethylene and melatonin activates isoflavone biosynthesis and antioxidant systems to produce high-quality soybean sprouts. Plant Sci. 2024, 347, 112197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgonovi, S.M.; Chiarello, E.; Pasini, F.; Picone, G.; Marzocchi, S.; Capozzi, F.; Bordoni, A.; Barbiroli, A.; Marti, A.; Iametti, S.; et al. Effect of Sprouting on Biomolecular and Antioxidant Features of Common Buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum). Foods 2023, 12, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altkarde, E.; Güzel, N. Impact of germination pre-treatments on buckwheat and Quinoa: Mitigation of anti-nutrient content and enhancement of antioxidant properties. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Sasaki, T.; Tetsuka, T.; Ikoma, H.; Kohyama, K. Effects of Sprouting on Texture of Cooked Buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) Noodles. Plant Prod. Sci. 2015, 12, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Wang, P.; Yang, R.; Gu, Z. Effects of UV-B radiation on the isoflavone accumulation and physiological-biochemical changes of soybean during germination. Food Chem. 2018, 250, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavarín-Martínez, C.D.; Reyes-Moreno, C.; Milán-Carrillo, J.; Perales-Sánchez, J.X.K.; Canizalez-Román, V.A.; Cuevas-Rodriguez, E.-O.; López-Valenzuela, J.A.; Gutiérrez-Dorado, R. Effect of germination and UV-B elicitation on chemical compositions, antioxidant activities, and phytochemical contents of underutilised Mexican blue maize seeds. Int. Food Res. J. 2022, 29, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tevini, M.; Thoma, U.; Iwanzik, W. Effects of Enhanced UV-B Radiation on Germination, Seedling Growth, Leaf Anatomy and Pigments of Some Crop Plants. Z. Für Pflanzenphysiol. 1983, 109, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Sun, W.; Ma, Z.; Guo, C.; Chen, J.; Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, H. Integrated network analyses identify MYB4R1 neofunctionalization in the UV-B adaptation of Tartary buckwheat. Plant Commun. 2022, 3, 100414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.Y.; Peng, C.C.; Yang, Y.L.; Peng, R.Y. Optimization of bioactive compounds in buckwheat sprouts and their effect on blood cholesterol in hamsters. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, A.; Li, X.; Hu, X.; Ma, Z.; Wu, K.; Zhang, H.; Hao, M.; Wei, S. Dynamic Changes in Polyphenol Compounds, Antioxidant Activity, and PAL Gene Expression in Different Tissues of Buckwheat during Germination. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 5723–5730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Hao, T.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, W.; Xiao, Y.; Meng, X.; Fang, X. Relationships between antioxidant compounds and antioxidant activities of tartary buckwheat during germination. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 2458–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Zaidul, I.; Suzuki, T.; Mukasa, Y.; Hashimoto, N.; Takigawa, S.; Noda, T.; Matsuura-Endo, C.; Yamauchi, H. Comparison of phenolic compositions between common and tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum) sprouts. Food Chem. 2008, 110, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, K.; Sato, T. Differences in the Ratios of Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside and Cyanidin-3-O-rutinocide to Total Anthocyanin under UV and Non-UV Conditions in Tartary Buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum Garten). Plant Prod. Sci. 2009, 12, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krahl, M.; Back, W.; Zarnkow, M.; Kreisz, S. Determination of Optimised Malting Conditions for the Enrichment of Rutin, Vitexin and Orientin in Common Buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench). J. Inst. Brew. 2008, 114, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, H. Dual effects of slightly acidic electrolyzed water (SAEW) treatment on the accumulation of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and rutin in germinated buckwheat. Food Chem. 2016, 201, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Xu, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Peng, W. Effects of microwave irradiation on the expression of key flavonoid biosynthetic enzyme genes and the accumulation of flavonoid products in Fagopyrum tataricum sprouts. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 101, 103275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Wang, N.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Bian, Z. Effect of co-treatment of microwave and exogenous l-phenylalanine on the enrichment of flavonoids in Tartary buckwheat sprouts. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 2014–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.M.; Arasu, M.V.; Kim, Y.B.; Park, S.U.; Kim, S.J. Phenylalanine and LED lights enhance phenolic compound production in Tartary buckwheat sprouts. Food Chem. 2015, 177, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Logacheva, M.D.; Meng, Y.; Hu, J.; Wan, D.; Li, L.; Dagmar, J.; Wang, Z.; Georgiev, M.I.; Yu, Z. Jasmonate-Responsive MYB Factors Spatially Repress Rutin Biosynthesis in Fagopyrum tataricum. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 8, 1955–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Duarte, C.M.; Susana, A. Contrasting Responses of Marine and Freshwater Photosynthetic Organisms to UVB Radiation: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpelainen, H.; He, Y.; Xuan, Z.; Yao, Y.; Li, C.; Li, Y. Effects of ultraviolet-B radiation on crop growth, development, yield and leaf pigment concentration of tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum) under field conditions. Eur. J. Agron. 2006, 25, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yang, R.; Zhou, T.; Gu, Z. UV-B mediates isoflavone accumulation and oxidative-antioxidant system responses in germinating soybean. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Guo, Y. Microwave Irradiation Enhances the Germination Rate of Tartary Buckwheat and Content of Some Compounds in Its Sprouts. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2018, 68, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.; Wang, C.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Fang, W.; Yin, Y. The Impact of Lighting Treatments on the Biosynthesis of Phenolic Acids in Black Wheat Seedlings. Foods 2024, 13, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, T.; Han, R. Magnesium and nitrogen co-doped carbon dots alleviate UV-B radiation damage in wheat seedlings. Pak. J. Bot. 2024, 56, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Karagi, U.; Liu, X.; Cui, J.; Gui, J.; Gu, M.; Gao, W. Effects of ultrasonication on increased germination and improved seedling growth of aged grass seeds of tall fescue and Russian wildrye. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; Wang, N.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Bian, Z. Effects of microwave and exogenous l-phenylalanine treatment on phenolic constituents, antioxidant capacity and enzyme inhibitory activity of Tartary buckwheat sprouts. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 32, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, Z.X.; Wang, J.F.; Ma, H.; Wang, S.M.; Wang, S.M. Effect of microwave radiation on antioxidant capacities of Tartary buckwheat sprouts. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 3913–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almuhayawi, M.S.; Hassan, A.H.A.; Abdel-Mawgoud, M.; Khamis, G.; Selim, S.; Jaouni, S.K.A.; Abdelgawad, H. Laser light as a promising approach to improve the nutritional value, antioxidant capacity and anti-inflammatory activity of flavonoid-rich buckwheat sprouts. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.K.; Chiang, B.H.; Chen, Y.S.; Yang, J.H.; Liu, C.L. Improving the antioxidant activity of buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricm Gaertn) sprout with trace element water. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Sum of Squares | df | Means Square | F Value | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 1.239 × 106 | 14 | 88,484.46 | 26.70 | <0.0001 |
| A-germination time (d) | 17,734.94 | 1 | 17,734.94 | 5.35 | 0.0364 |
| B-UV-B treatment time (h·d−1) | 1.12 × 105 | 1 | 1.12 × 105 | 33.69 | <0.0001 |
| C-germination temperature (°C) | 22,536.56 | 1 | 22,536.56 | 6.80 | 0.0207 |
| D-UV-B intensity (μmol·m−2·s−1) | 19,048.20 | 1 | 19,048.20 | 5.75 | 0.0310 |
| AB | 2532.73 | 1 | 2532.73 | 0.76 | 0.3967 |
| AC | 5083.04 | 1 | 5083.04 | 1.53 | 0.2359 |
| AD | 15,829.53 | 1 | 15,829.53 | 4.78 | 0.0463 |
| BC | 2128.19 | 1 | 2128.19 | 0.64 | 0.4363 |
| BD | 49,405.73 | 1 | 49,405.73 | 14.91 | 0.0017 |
| CD | 1758.84 | 1 | 1758.84 | 0.53 | 0.4783 |
| A2 | 4.85 × 105 | 1 | 4.85 × 105 | 146.36 | <0.0001 |
| B2 | 3.45 × 105 | 1 | 3.45 × 105 | 103.96 | <0.0001 |
| C2 | 4.74 × 105 | 1 | 4.74 × 105 | 143.01 | <0.0001 |
| D2 | 2.18 × 105 | 1 | 2.18 × 105 | 65.75 | <0.0001 |
| Residual | 46,391.15 | 14 | 3313.65 | ||
| Lack of fit | 40,318.41 | 10 | 4031.84 | 2.66 | 0.1796 |
| Pure Error | 6072.74 | 4 | 1518.19 | ||
| Cor total | 1.29 × 106 | 28 | |||
| R2 = 0.9639 | R2adj = 0.9278 | CV = 4.03% | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, J.; Hu, M.; Yang, J.; Fang, W.; Yin, Y. Optimization of Ultraviolet-B Treatment for Enrichment of Total Flavonoids in Buckwheat Sprouts Using Response Surface Methodology and Study on Its Metabolic Mechanism. Foods 2024, 13, 3928. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13233928
Xue J, Hu M, Yang J, Fang W, Yin Y. Optimization of Ultraviolet-B Treatment for Enrichment of Total Flavonoids in Buckwheat Sprouts Using Response Surface Methodology and Study on Its Metabolic Mechanism. Foods. 2024; 13(23):3928. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13233928
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Jiyuan, Meixia Hu, Jia Yang, Weiming Fang, and Yongqi Yin. 2024. "Optimization of Ultraviolet-B Treatment for Enrichment of Total Flavonoids in Buckwheat Sprouts Using Response Surface Methodology and Study on Its Metabolic Mechanism" Foods 13, no. 23: 3928. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13233928
APA StyleXue, J., Hu, M., Yang, J., Fang, W., & Yin, Y. (2024). Optimization of Ultraviolet-B Treatment for Enrichment of Total Flavonoids in Buckwheat Sprouts Using Response Surface Methodology and Study on Its Metabolic Mechanism. Foods, 13(23), 3928. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13233928






