A Rapid and Sensitive Gold Nanoparticle-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Chlorantraniliprole in Agricultural and Environmental Samples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
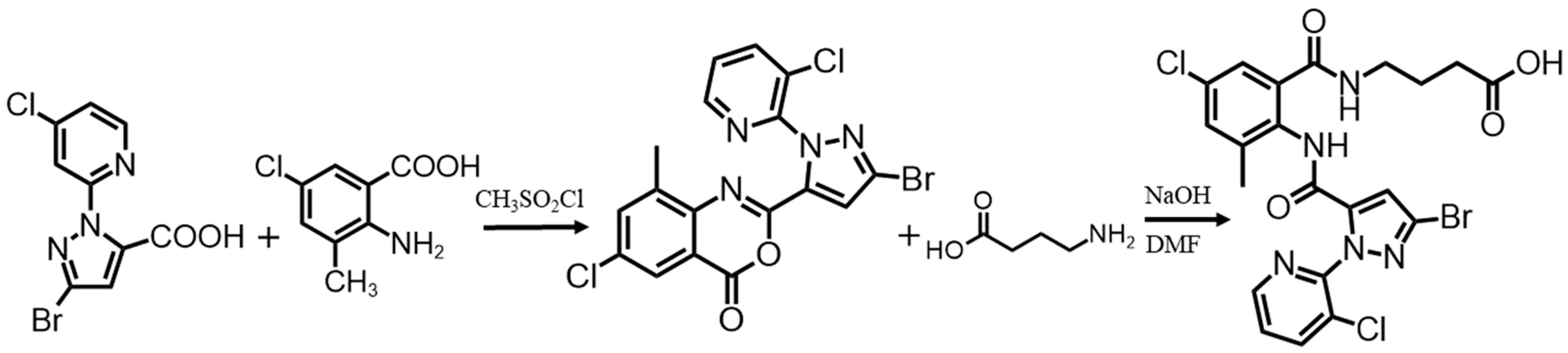
2.2. Preparation of Hapten and Antigens
2.3. Preparation of anti-CAP mAb
2.4. Evaluation of Anti-CAP mAb
2.5. Preparation of the AuNP-Labeled mAb Probe
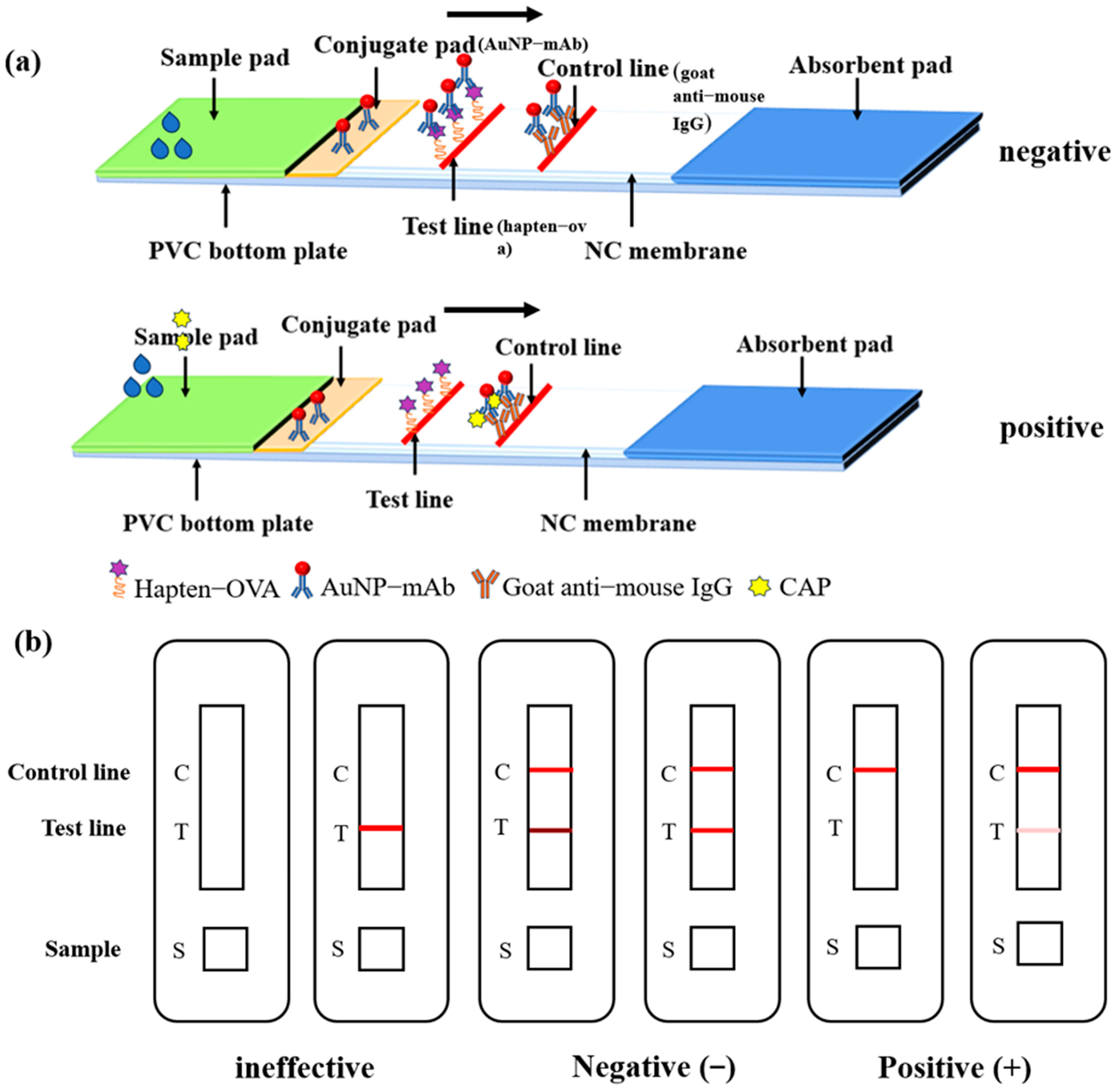
2.6. Preparation of AuNP-LFIA Strips
2.7. Procedure of the AuNP-LFIA
2.8. Detection of Spiked Samples
2.9. Verification by UPLC−MS/MS
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Hapten and Antigens
3.2. Characterization of anti-CAP mAb
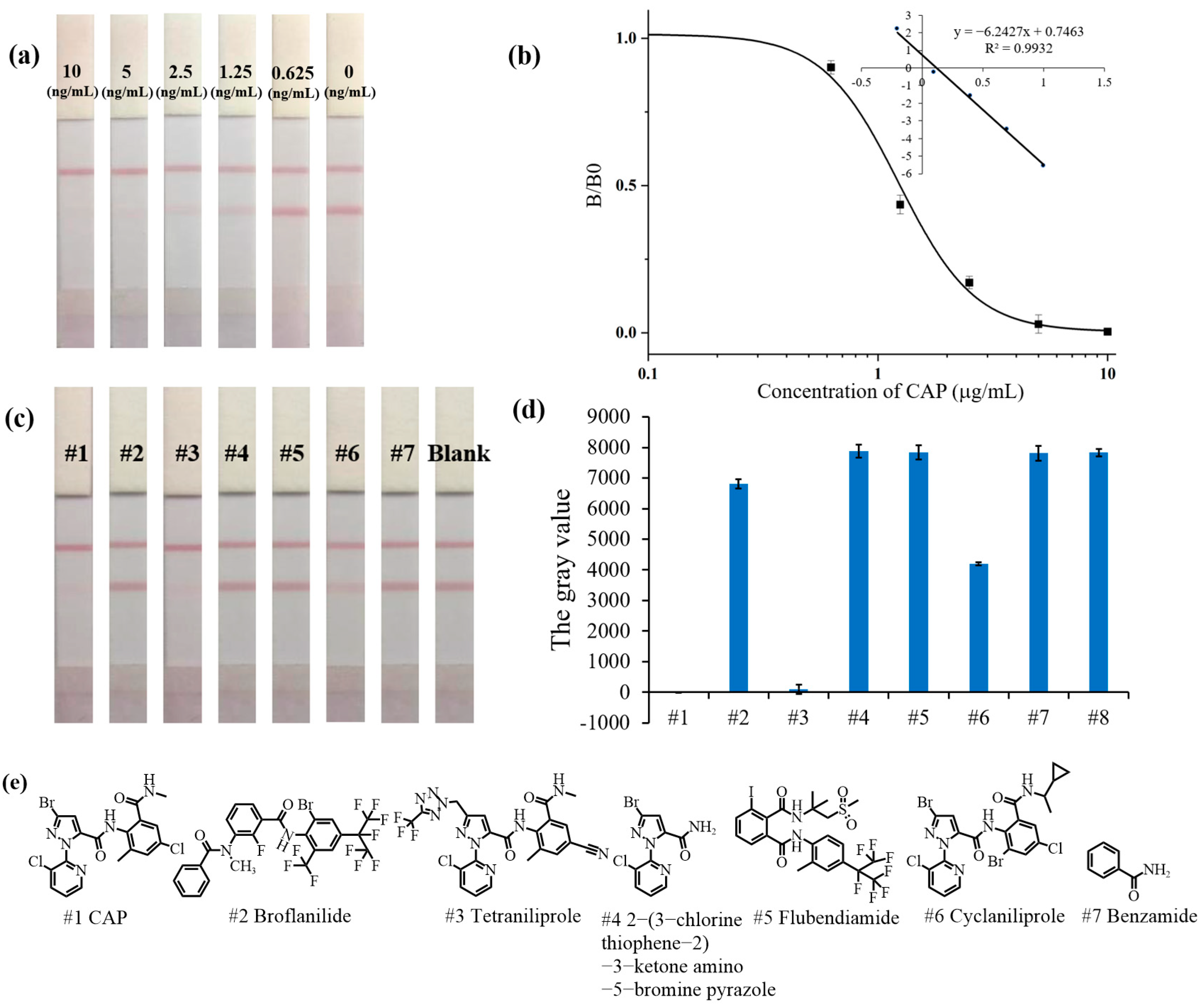
3.3. Sensitivity of the AuNP-LFIA
3.4. Specificity of the AuNP-LFIA
3.5. Robustness of the AuNP-LFIA
3.6. Analysis of Spiked Samples
3.7. Validation by UPLC−MS/MS
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Casida, J.E.; Bryant, R.J. The ABCs of pesticide toxicology: Amounts, biology, and chemistry. Toxicol. Res. 2017, 6, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.R.; Swale, D.R.; Anderson, T.D. Comparative effects of technical-grade and formulated chlorantraniliprole to the survivorship and locomotor activity of the honey bee, Apis mellifera (L.). Pest. Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 2582–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Wang, G.; Xu, W.; Xiao, Y.; Peng, Y. Transcriptome analysis of fat accumulation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes induced by chlorantraniliprole. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1091477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 2763–2021; National Food Safety Standard—Maximum Residue Limits for Pesticides in Food. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing China, 2021.
- (EU) 2022/1343; Pesticide Residue (s) and Maximum Residue Levels (mg/kg). European Union (EU): Maastricht, The Netherlands, 2022.
- Liu, T.; Dong, M.; Zhou, F.; Yang, D.; Zhang, X. Development and validation of an analytical method for detecting chlorantraniliprole residues in fresh tea leaves. Food Sci. Human. Wellness 2019, 8, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramasivam, M. Dissipation kinetics, dietary and ecological risk assessment of chlorantraniliprole residue in/on tomato and soil using GC-MS. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariappan, P.; Kaithamalai, B. Dissipation kinetics, decontamination and risk assessment of chlorantraniliprole in okra and soil under open field condition using GC-MS. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 102, 3694–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Song, X.; Tian, K.; Chen, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Min, S. Quantitative determination of additive Chlorantraniliprole in Abamectin preparation: Investigation of bootstrapping soft shrinkage approach by mid-infrared spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 191, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Chang, H.; Gu, Y.; Haibin, S.; Siwei, W. Residue dynamics of spirotetramat and its metabolites & chlorantraniliprole in longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.). Chin. J. Pestic. Sci. 2021, 23, 1235–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Mandal, K.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, B.; Singh, B. Persistence of chlorantraniliprole granule formulation in sugarcane field soil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 2289–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.M.; Chai, W.G.; Wu, Y.L. Residues of chlorantraniliprole in rice field ecosystem. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Qiao, C.; Luo, J.; Guo, L.; Pang, T.; Pang, R.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, R.; Xie, H. Development and validation of a method for the analysis of five diamide insecticides in edible mushrooms using modified QuEChERS and HPLC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2020, 333, 127468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Chang, H.; Liu, Y.; Sun, H. Determination of chlorantraniliprole, cyantraniliprole and its metabolites residues in litchi using QuEChERS and high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Chin. J. Pestic. Sci. 2022, 24, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Huang, Y.; Sun, W.; Li, F.; Zhang, S.; Fang, S.; Wang, M.; Hua, X. Carboxyl retained hapten of quinclorac produces highly sensitive antibody and immunochromatographic assay. Microchem. J. 2022, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, P.; Hu, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, H.; Xie, Y.; Yao, W.; Guo, Y.; Qian, H. Nucleic Acid Amplification Techniques in Immunoassay: An Integrated Approach with Hybrid Performance. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 5783–5797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, F.; Li, F.; Jia, Y.; Wang, M.; Hua, X.; Wang, L. Development of Ic-ELISA and Colloidal Gold Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Determination of Cypermethrin in Agricultural Samples. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Liu, K.; Xu, C.; Liu, F.; Li, Q.X.; Liu, S.; Wang, B. Development of a sensitive monoclonal antibody-based indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for analysing chlorantraniliprole residues. Food Chem. 2014, 143, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Wang, K.; Vasylieva, N.; Zhou, H.; Xue, X.; Wang, B.; Li, Q.X.; Hammock, B.D.; Xu, T. Development of a nanobody-based ELISA for the detection of the insecticides cyantraniliprole and chlorantraniliprole in soil and the vegetable bok choy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 2503–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, Q.; Xia, P.; Kong, F.; Qiu, J.; Fang, S.; Hua, X. Rapid and sensitive detection of quizalofop-p-ethyl by gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow immunoassay in agriproducts and environmental samples. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, D.; Li, P.; Tang, X.; Zhang, W. Determination of deoxynivalenol by ELISA and immunochromatographic strip assay based on monoclonal antibodies. Toxin Rev. 2019, 40, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, K.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, W.; He, L.; Guo, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q.X.; Liu, S.; Wang, B. Development of a monoclonal antibody-based ELISA for the detection of the novel insecticide cyantraniliprole. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 35874–35881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.K.; Keum, Y.S.; Hwang, E.C.; Park, B.S.; Chang, H.R.; Li, Q.X.; Kim, J.H. Hapten syntheses and antibody generation for a new herbicide, metamifop. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 5416–5422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Ahn, K.C.; Sun, Q.; Hu, B.; Wang, J.; Liu, F. Hapten heterology for a specific and sensitive indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for organophosphorus insecticide fenthion. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 596, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, T.; Zhu, X.; Xu, L.; Liu, F.; Hu, B.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, B. Determination of N-Methylcarbamate Insecticide Metolcarb by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2006, 34, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yi, G.X.; He, S.P.; Wang, B.M.; Yu, C.X.; Li, G.; Zhai, Z.X.; Li, Z.H.; Li, Q.X. Development of a monoclonal antibody-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the herbicide chlorimuron-ethyl. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 4948–4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronopoulou, E.; Uribe-Benninghoff, A.; Corbett, C.R.; Berry, J.D. Hybridoma technology for the generation of rodent mAbs via classical fusion. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1131, 47–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepehr, K.S.; Baradaran, B.; Majidi, J.; Abdolalizadeh, J.; Aghebati, L.; Shahneh, F.Z. Development and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against human CD20 in Balb/c mice. Hum. Antibodies 2012, 21, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobrovnik, S.A. Determination of antibody affinity by ELISA. Theory. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2003, 57, 213–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillen, I.; Gabaldon, J.A.; Nunez-Delicado, E.; Puchades, R.; Maquieira, A.; Morais, S. Detection of sulphathiazole in honey samples using a lateral flow immunoassay. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Atwater, M.; Wang, J.; Huo, Q. Extinction coefficient of gold nanoparticles with different sizes and different capping ligands. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2007, 58, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Guo, L.; Kuang, H.; Xu, L.; Xu, C.; Liu, L. Preparation of a broad-specific monoclonal antibody and development of an immunochromatographic assay for monitoring of anthranilic diamides in vegetables and fruits. Analyst 2022, 147, 5149–5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, K. Determination of the dissipation dynamics and residue behaviors of chlorantraniliprole in sugarcane and soil by LC-MS/MS. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krotzky, A.; Zeeh, B. Pesticides report 33. Immunoassays for residue analysis of agrochemicals: Proposed guidelines for precision, standardization and quality control (Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 1995, 67, 2065–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshfetrat, S.M.; Fasihi, K.; Moradnia, F.; Kamil Zaidan, H.; Sanchooli, E. A label-free multicolor colorimetric and fluorescence dual mode biosensing of HIV-1 DNA based on the bifunctional NiFe2O4@UiO-66 nanozyme. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1252, 341073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EPA/600/8-80/038 (NTIS PB82208752); Analysis of Pesticide Residues in Human and Environmental Samples. US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Washington, DC, USA, 1980.

| Sample | Spiked (mg/kg) | Visualization Results | Quantitative Results (mg/kg) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | 0 | − − − a | − − − | − − − | <LOD | / c | / |
| 0.025 | − − − | − − − | − − − | 0.016 ± 0.001 | 65.9 | 6.7 | |
| 0.05 | + + + b | + + + | + + + | 0.034 ± 0.002 | 68.0 | 5.9 | |
| 0.1 | + + + | + + + | + + + | 0.071 ± 0.002 | 71.2 | 2.3 | |
| 0.2 | + + + | + + + | + + + | 0.132 ± 0.003 | 65.8 | 1.9 | |
| Brown rice | 0 | − − − | − − − | − − − | <LOD | / | / |
| 0.025 | − − − | − − − | − − − | 0.015 ± 0.001 | 61.2 | 6.5 | |
| 0.05 | + + + | + + + | + + + | 0.033 ± 0.002 | 65.5 | 4.9 | |
| 0.1 | + + + | + + + | + + + | 0.065 ± 0.002 | 65.3 | 2.5 | |
| 0.2 | + + + | + + + | + + + | 0.141 ± 0.006 | 70.7 | 4.0 | |
| Apple | 0 | − − − | − − − | − − − | <LOD | / | / |
| 0.025 | − − − | − − − | − − − | 0.016 ± 0.001 | 64.0 | 3.2 | |
| 0.05 | + + + | + + + | + + + | 0.035 ± 0.001 | 70.0 | 4.6 | |
| 0.1 | + + + | + + + | + + + | 0.071 ± 0.002 | 71.1 | 2.9 | |
| 0.2 | + + + | + + + | + + + | 0.133 ± 0.004 | 66.3 | 3.1 | |
| Chinese cabbage | 0 | − − − | − − − | − − − | <LOD | / | / |
| 0.05 | − − − | − − − | − − − | 0.031 ± 0.002 | 61.5 | 6.1 | |
| 0.1 | + + + | + + + | + + + | 0.065 ± 0.002 | 65.6 | 3.2 | |
| 0.2 | + + + | + + + | + + + | 0.131 ± 0.005 | 65.8 | 3.9 | |
| 0.4 | + + + | + + + | + + + | 0.238 ± 0.016 | 59.7 | 6.8 | |
| Sample No. | UPLC–MS/MS (mg/kg) | AuNP-LFIA a | Sample No. | UPLC–MS/MS (mg/kg) | AuNP-LFIA a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | <LOQ |  | 6 | 0.062 |  |
| 2 | 0.005 | 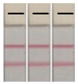 | 7 | 0.071 |  |
| 3 | 0.009 |  | 8 | 0.14 |  |
| 4 | 0.018 |  | 9 | 0.28 | 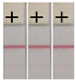 |
| 5 | 0.053 |  | 10 | 0.48 |  |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, M.; Hua, X. A Rapid and Sensitive Gold Nanoparticle-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Chlorantraniliprole in Agricultural and Environmental Samples. Foods 2024, 13, 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13020205
Wu Y, Li J, Zhu J, Zhang Z, Zhang S, Wang M, Hua X. A Rapid and Sensitive Gold Nanoparticle-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Chlorantraniliprole in Agricultural and Environmental Samples. Foods. 2024; 13(2):205. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13020205
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yanling, Jiao Li, Jie Zhu, Zhaoxian Zhang, Shuguang Zhang, Minghua Wang, and Xiude Hua. 2024. "A Rapid and Sensitive Gold Nanoparticle-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Chlorantraniliprole in Agricultural and Environmental Samples" Foods 13, no. 2: 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13020205
APA StyleWu, Y., Li, J., Zhu, J., Zhang, Z., Zhang, S., Wang, M., & Hua, X. (2024). A Rapid and Sensitive Gold Nanoparticle-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Chlorantraniliprole in Agricultural and Environmental Samples. Foods, 13(2), 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13020205






