Effects of Low Field Temperature on the Physicochemical Properties and Fine Structure Stability of High-Quality Rice Starch during the Grain Filling Stage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
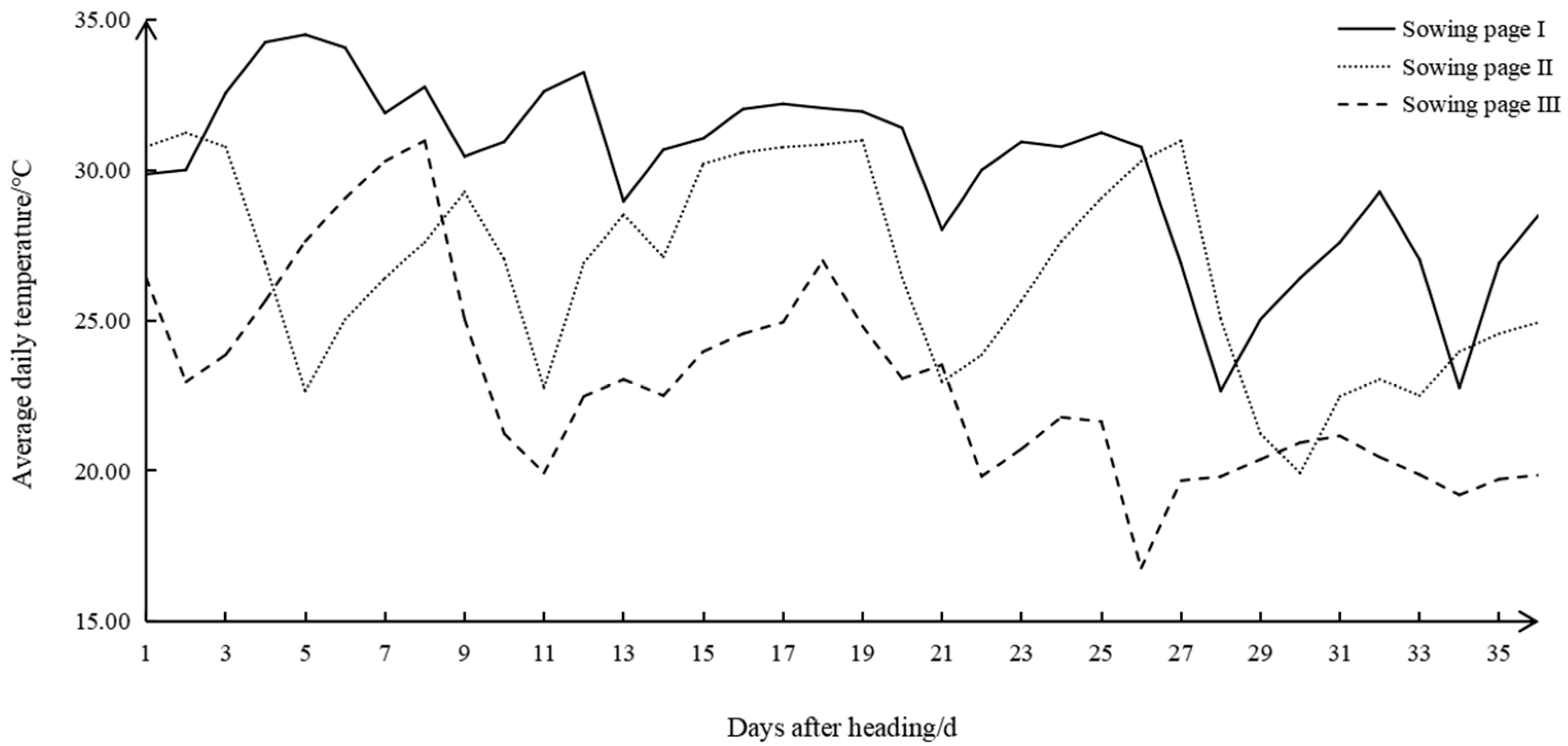
2.2. Temperature Treatments and Samplings
2.3. Starch Components
2.4. Starch Isolation
2.5. Pasting Property
2.6. Thermodynamic Property
2.7. Starch Granule Morphology and Size Analysis
2.8. Analysis of X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.9. Analysis of Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.10. High-Performance Anion-Exchange Chromatography (HPAEC)
2.11. Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC)
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Determination of Sowing Date
3.2. Amylose, Amylopectin and Total Starch Content
3.3. Pasting Properties
3.4. Thermal Properties
3.5. Starch Granule Morphology and Particle Size Distribution
3.6. Crystal Structure
3.7. Chain Length Distribution of Amylopectin
3.8. Relative Molecular Weight Distribution of Starch
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, M.; Shen, J.; Yuan, L.; Jiang, R.; Chen, X.; Davies, W.J.; Zhang, F. Improving crop productivity and resource use efficiency to ensure food security and environmental quality in China. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Wen, J.; Ji, L.; Chen, Z.; Fang, F. Current situations, problems and prospects of rice seed industry in China. China Rice 2022, 28, 74–78. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Hu, W.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, T.; Liu, Y. Process, problems and prospect of high-quality rice breeding in hunan provinc. China Rice 2022, 28, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Z.; Chen, B.; Tian, Y. Highly branched corn starch: Preparation, encapsulation, and release of ascorbic acid. Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.F.; Wang, D.Y.; Li, H.; Tao, L.X.; Zhang, X.F. Influence of temperature and sunlight conditions on rice grain filling and quality in different growth stages. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2009, 30, 375–382+387. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.J.; Li, L.; Tian, J.Y.; Zhang, C.X.; Wang, J.; Yu, E.W.; Xing, Z.P.; Guo, B.W.; Wei, H.Y.; Huo, Z.Y.; et al. Effects of dynamic low temperature during the grain filling stage on starch morphological structure, physicochemical properties, and eating quality of soft japonica rice. Cereal Chem. 2020, 97, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.; Xiong, R.; Tan, X.; Wang, H.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, S.; Shang, Q.; Pan, X.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, J.; et al. Low temperature and light combined stress after heading on starch fine structure and physicochemical properties of late-season indica rice with different grain quality in southern China. Food Res. Int. 2023, 164, 112320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Tetlow, I.J.; Nawaz, S.; Iqbal, A.; Mubin, M.; Nawaz ul Rehman, M.S.; Butt, A.; Lightfoot, D.A.; Maekawa, M. Effect of high temperature on grain filling period, yield, amylose content and activity of starch biosynthesis enzymes in endosperm of basmati rice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 2237–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Wei, H.; Guo, B.; Dai, Q.; Wei, C.; Gao, H.; Hu, Y.; Cui, P.; Li, M.; Huo, Z.; et al. The effects of chilling stress after anthesis on the physicochemical properties of rice (Oryza sativa L.) starch. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Wu, J.; Luo, Q.; Li, J.; Zhuang, W.; Xiao, G.; Deng, Q.; Lei, D.; Bai, B. Influence of high natural field temperature during grain filling stage on the morphological structure and physicochemical properties of rice (Oryza sativa L.) starch. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5009.9-2023; GB 5009.9-2023; The National Standard for Determination of Starch in Foods. Standards Institution of China. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2023.
- Blazek, J.; Copeland, L. Pasting and swelling properties of wheat flour and starch in relation to amylose content. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 71, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Qian, Z.; Wei, H.; Guo, B.; Xu, K.; Dai, Q.; Zhang, H.; Huo, Z. The effects of field pre-harvest sprouting on the morphological structure and physicochemical properties of rice (Oryza sativa L.) starch. Food Chem. 2019, 278, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandhu, K.S.; Siroha, A.K.; Punia, S.; Sangwan, L.; Nehra, M.; Purewal, S.S. Effect of degree of cross linking on physicochemical, rheological and morphological properties of Sorghum starch. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2021, 2, 100073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Tan, X.; Huang, S.; Pan, X.; Shi, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, Y. Effects of experimental warming on physicochemical properties of indica rice starch in a double rice cropping system. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.S.; Guo, D.W.; Zhao, L.X.; Zhang, X.D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.M.; Wei, C.X. Comparative structure of starches from high-amylose maize inbred lines and their hybrids. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, C.Y.; Wang, J.D.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, G.Y. Effect of low temperature treatment in booting and filling stage on yield components and quality of main rice cultivars in sanjiang plain. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2018, 39, 751–761. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.Y.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, H.W.; Qu, Z.J.; Wang, X.P.; Duan, Y.Y.; Yang, R. Effects of low temperature stress during grain filling on starch formation and accumulation of superior and inferior grains in rice. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2022, 36, 487–504. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.D.; Wang, L.; Xiao, Y.H.; Wang, F.; Zhang, G.L.; Tang, W.B.; Deng, H.B. Grain quality characterization of hybrid rice restorer lines with resilience to suboptimal temperatures during filling stage. Foods 2022, 11, 3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, K.; Suzuki, K.; Iijima, K.; Ebana, K. Variation in cooking and eating qualitytraits in Japanese rice germplasm accessions. Breed. Sci. 2016, 66, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Qu, J.; Li, Z.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, F.; Blennow, A.; Liu, X. Rice starch multi-level structure and functional relationships. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 275, 118777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Wu, J.; Xu, H.; Xiao, Y.; Xie, H.; Shi, W. The deterioration of starch physiochemical and minerals in high-quality indica rice under low-temperature stress during grain filling. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 14, 1295003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, K.; Gu, X.; Lu, W.; Lu, D. Effects of weak-light stress during grain filling on the physicochemical properties of normal maize starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 202, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Hao, W.; Lu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, Q.; Fan, X.; Luo, J.; Liu, Q. A comparative evaluation of the effect of SSI and Wx allelic variation on rice grain quality and starch physicochemical properties. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.; Xie, J.; Chen, L.; Yang, T.; Tan, X.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, X.; Zeng, Y.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, J.; et al. Water irrigation management affects starch structure and physicochemical properties of indica rice with different grain quality. Food Chem. 2021, 347, 129045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.M.; Chang, E.H.; Xu, W.; Wang, Z.Q.; Yang, J.C. Effects of low temperature during grain filling on the structure of endosperm in hybrid rice. Acta Agron. Sin. 2006, 1, 96–102+164–166. [Google Scholar]
- Dhital, S.; Butardo, V.M.; Jobling, S.A., Jr.; Gidley, M.J. Rice starch granule amylolysis—Differentiating effects of particle size, morphology, thermal properties and crystalline polymorph. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevenou, O.; Hill, S.E.; Farhat, I.A.; Mitchell, J.R. Organisation of the external region of the starch granule as determined by infrared spectroscopy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2002, 31, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.P.; Wang, J.K.; Wang, Y.L.; Chen, Y.H.; Zhu, D.F.; Chen, H.Z.; Xiang, J.; Zhang, Y.K.; Liu, X.J.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Response of rice starch synthesis to night temperature changes. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2020, 34, 525–538. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.X.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Z.W.; Zhang, Z.J.; Yang, J.C.; Zhu, Q.S. The physiochemical characteristics of amylopectin and their relationships to pasting properties of rice flour in different varieties. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2006, 6, 1122–1129. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, B.; Yang, X.; Zou, L.; Liu, J.; Liang, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, N.; Ren, G.; Zhang, L.; et al. Starch chain-length distributions determine cooked foxtail millet texture and starch physicochemical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 320, 121240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Mao, B.; Zhang, C.; Shao, Y.; Wu, T.; Hu, L.; Hu, Y.; Tang, L.; Li, Y.; Tang, W.; et al. Influence of physicochemical properties and starch fine structure on the eating quality of hybrid rice with similar apparent amylose content. Food Chem. 2021, 353, 12946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Cultivar | Treatment | Amylose Content (%) | Amylopectin Content (%) | Total Starch Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YZX | CT | 12.90 ± 0.26 b | 62.82 ± 0.65 a | 75.72 ± 0.40 a |
| LT | 13.87 ± 0.29 a | 57.99 ± 1.90 b | 71.86 ± 1.84 a | |
| YXYLS | CT | 11.90 ± 0.26 b | 65.77 ± 1.97 a | 77.67 ± 2.07 a |
| LT | 13.67 ± 0.29 a | 58.41 ± 1.05 b | 72.08 ± 1.31 a | |
| NX 42 | CT | 15.33 ± 0.15 b | 61.89 ± 1.30 a | 77.22 ± 1.27 a |
| LT | 17.13 ± 0.15 a | 53.78 ± 0.80 b | 70.91 ± 0.93 b | |
| YLY 2646 | CT | 14.53 ± 0.12 b | 56.58 ± 0.57 a | 71.11 ± 0.62 a |
| LT | 15.90 ± 0.00 a | 52.94 ± 0.76 b | 68.84 ± 0.76 a |
| Cultivar | Treatment | PV (cP) | TV (cP) | BD (cP) | FV (cP) | SB (cP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YZX | CT | 2152 ± 57 a | 1377 ± 39 a | 774 ± 95 a | 2064 ± 33 b | 687 ± 6 b |
| LT | 2274 ± 16 a | 1364 ± 13 a | 910 ± 30 a | 2313 ± 12 a | 949 ± 1 a | |
| YXYLS | CT | 901 ± 33 b | 617 ± 27 b | 284 ± 6 b | 1080 ± 37 b | 463 ± 10 b |
| LT | 2237 ± 14 a | 1440 ± 31 a | 797 ± 46 a | 2396 ± 19 a | 955 ± 16 a | |
| NX42 | CT | 2472 ± 18 a | 1735 ± 49 a | 738 ± 32 a | 2567 ± 44 b | 832 ± 6 b |
| LT | 2498 ± 31 a | 1743 ± 8 a | 755 ± 32 a | 2763 ± 11 a | 1020 ± 8 a | |
| YLY2646 | CT | 2712 ± 21 a | 1712 ± 35 a | 1001 ± 41 a | 2613 ± 31 b | 902 ± 7 b |
| LT | 2363 ± 25 b | 1631 ± 35 a | 733 ± 18 b | 2776 ± 34 a | 1146 ± 6 a |
| Cultivar | Treatment | To (°C) | TP (°C) | Tc (°C) | ΔH (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YZX | CT | 71.86 ± 0.22 a | 77.13 ± 0.34 a | 81.68 ± 0.55 a | 6.16 ± 0.16 a |
| LT | 69.84 ± 0.56 b | 75.48 ± 0.44 a | 79.79 ± 0.42 a | 5.35 ± 0.22 b | |
| YXYLS | CT | 71.54 ± 0.65 a | 77.61 ± 0.53 a | 82.20 ± 0.59 a | 5.43 ± 0.32 a |
| LT | 69.31 ± 0.08 b | 75.39 ± 0.16 b | 80.15 ± 0.20 b | 5.43 ± 0.32 a | |
| NX42 | CT | 71.04 ± 0.13 a | 76.41 ± 0.12 a | 81.20 ± 0.15 a | 5.92 ± 0.03 a |
| LT | 67.57 ± 0.14 b | 73.07 ± 0.16 b | 77.87 ± 0.21 b | 5.81 ± 0.20 a | |
| YLY2646 | CT | 71.41 ± 0.26 a | 77.19 ± 0.19 a | 81.23 ± 0.95 a | 5.23 ± 0.74 a |
| LT | 65.44 ± 0.14 b | 72.54 ± 0.12 b | 77.41 ± 0.10 b | 4.50 ± 0.27 a |
| Cultivar | Treatment | Volume Percentage/% | Surface Area Percentage/% | Number Percentage/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d < 10 μm | d ≥ 10 μm | d < 10 μm | d ≥ 10 μm | d < 10 μm | d ≥ 10 μm | ||
| YZX | CT | 29.71 ± 0.76 a | 70.29 ± 0.76 b | 58.17 ± 0.04 a | 41.83 ± 0.04 b | 93.24 ± 0.04 a | 6.76 ± 0.04 b |
| LT | 24.34 ± 0.21 b | 75.66 ± 0.21 a | 48.13 ± 0.02 b | 51.87 ± 0.02 a | 89.88 ± 0.15 b | 10.12 ± 0.15 a | |
| YXYLS | CT | 26.25 ± 0.12 b | 73.75 ± 0.12 a | 55.92 ± 0.42 b | 44.08 ± 0.42 a | 94.04 ± 0.01 b | 5.96 ± 0.01 a |
| LT | 33.62 ± 0.31 a | 66.38 ± 0.31 b | 65.48 ± 0.03 a | 34.52 ± 0.03 b | 96.58 ± 0.05 a | 3.42 ± 0.05 b | |
| NX42 | CT | 27.84 ± 0.05 b | 72.16 ± 0.05 a | 57.30 ± 0.22 b | 42.70 ± 0.22 a | 93.67 ± 0.06 a | 6.33 ± 0.06 a |
| LT | 30.61 ± 0.28 a | 69.39 ± 0.28 b | 58.89 ± 0.10 a | 41.11 ± 0.10 b | 93.83 ± 0.03 a | 6.17 ± 0.03 a | |
| YLY2646 | CT | 28.49 ± 0.44 b | 71.51 ± 0.44 a | 56.03 ± 0.24 b | 43.97 ± 0.24 a | 92.63 ± 0.24 b | 7.37 ± 0.24 a |
| LT | 37.41 ± 0.51 a | 63.59 ± 0.51 b | 66.04 ± 0.23 a | 33.96 ± 0.23 b | 95.51 ± 0.05 a | 4.49 ± 0.05 a | |
| Cultivar | Treatment | Degree of Crystallinity/% | Crystal Pattern | 1045/1022 cm−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YZX | CT | 19.14 ± 0.15 a | A | 0.69 ± 0.003 a |
| LT | 19.40 ± 0.12 a | A | 0.65 ± 0.003 b | |
| YXYLS | CT | 17.11 ± 0.17 a | A | 0.67 ± 0.013 a |
| LT | 17.43 ± 0.14 a | A | 0.63 ± 0.003 b | |
| NX42 | CT | 20.55 ± 0.08 a | A | 0.71 ± 0.007 a |
| LT | 21.83 ± 0.12 a | A | 0.68 ± 0.008 b | |
| YLY2646 | CT | 16.64 ± 0.13 a | A | 0.72 ± 0.004 a |
| LT | 16.57 ± 0.11 a | A | 0.67 ± 0.004 b |
| Cultivar | Treatment | Ap1 (%) | Ap2 (%) | AM (%) | Ap1/Ap2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YZX | CT | 67.46 ± 0.34 a | 21.74 ± 0.22 a | 10.79 ± 0.24 b | 3.10 ± 0.03 b |
| LT | 67.08 ± 0.28 a | 19.60 ± 0.17 b | 13.32 ± 0.11 a | 3.42 ± 0.16 a | |
| YXYLS | CT | 67.62 ± 0.22 a | 22.16 ± 0.39 a | 10.22 ± 0.52 b | 3.05 ± 0.13 b |
| LT | 65.57 ± 0.35 a | 19.13 ± 0.16 b | 15.31 ± 0.22 a | 3.43 ± 0.14 a | |
| NX42 | CT | 66.58 ± 0.21 a | 22.69 ± 0.41 a | 10.74 ± 0.29 b | 2.93 ± 0.11 b |
| LT | 64.86 ± 0.19 a | 18.67 ± 0.35 b | 16.47 ± 0.27 a | 3.47 ± 0.06 a | |
| YLY2646 | CT | 66.57 ± 0.15 a | 21.57 ± 0.27 a | 11.86 ± 0.17 b | 3.09 ± 0.08 b |
| LT | 66.53 ± 0.24 a | 19.65 ± 0.32 b | 13.83 ± 0.17 a | 3.39 ± 0.02 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pang, X.; Zhang, D.; Xue, H.; Yao, D.; Shen, H.; Mou, B.; Gu, P.; Zhou, R.; Meng, F.; Wu, J.; et al. Effects of Low Field Temperature on the Physicochemical Properties and Fine Structure Stability of High-Quality Rice Starch during the Grain Filling Stage. Foods 2024, 13, 3094. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13193094
Pang X, Zhang D, Xue H, Yao D, Shen H, Mou B, Gu P, Zhou R, Meng F, Wu J, et al. Effects of Low Field Temperature on the Physicochemical Properties and Fine Structure Stability of High-Quality Rice Starch during the Grain Filling Stage. Foods. 2024; 13(19):3094. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13193094
Chicago/Turabian StylePang, Xutong, Dongmeng Zhang, Haobo Xue, Dongping Yao, Hong Shen, Baohui Mou, Panqi Gu, Ruijuan Zhou, Fudie Meng, Jun Wu, and et al. 2024. "Effects of Low Field Temperature on the Physicochemical Properties and Fine Structure Stability of High-Quality Rice Starch during the Grain Filling Stage" Foods 13, no. 19: 3094. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13193094
APA StylePang, X., Zhang, D., Xue, H., Yao, D., Shen, H., Mou, B., Gu, P., Zhou, R., Meng, F., Wu, J., Lei, D., & Bai, B. (2024). Effects of Low Field Temperature on the Physicochemical Properties and Fine Structure Stability of High-Quality Rice Starch during the Grain Filling Stage. Foods, 13(19), 3094. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13193094





