Effects of Different Types of Starch on Physicochemical Properties and Microstructure of Beef during Cold Storage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Equipment
2.2. Preparation of Minced Beef
2.3. Preparation of Beef Gel
2.4. pH
2.5. Chroma
2.6. Water-Retaining Property
2.6.1. Water Content
2.6.2. Cooking Loss (CL)
2.6.3. Non-Expressible Water, NW, and Water-Holding Capacity, WHC
2.6.4. Thawing Loss
2.6.5. Emulsion Stability
2.7. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA)
2.8. Dynamic Rheological Measurement
2.9. Sensory Evaluation
2.10. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
2.11. Fat Oxidation Index
2.11.1. Peroxide Value (POV)
2.11.2. Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances (TBARSs)
2.12. Protein Oxidation Index
2.12.1. Surface Hydrophobic
2.12.2. Carbonyl Content
2.12.3. Protein Solubility
2.12.4. Sulfhydryl Content
2.12.5. Dityrosine
2.13. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy
2.14. Tertiary Structure
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
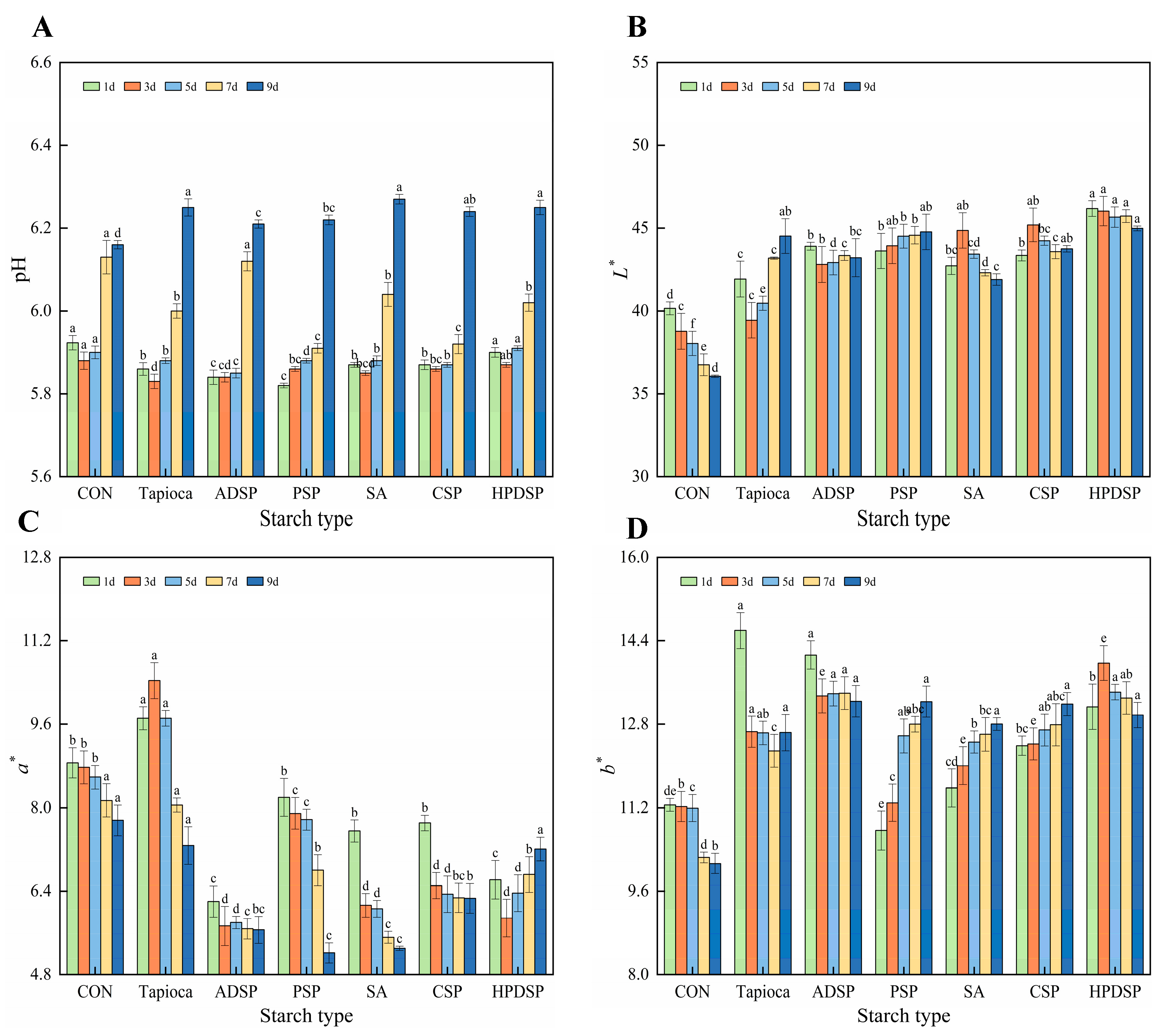
3.1. pH and Chroma
3.1.1. PH
3.1.2. Chroma
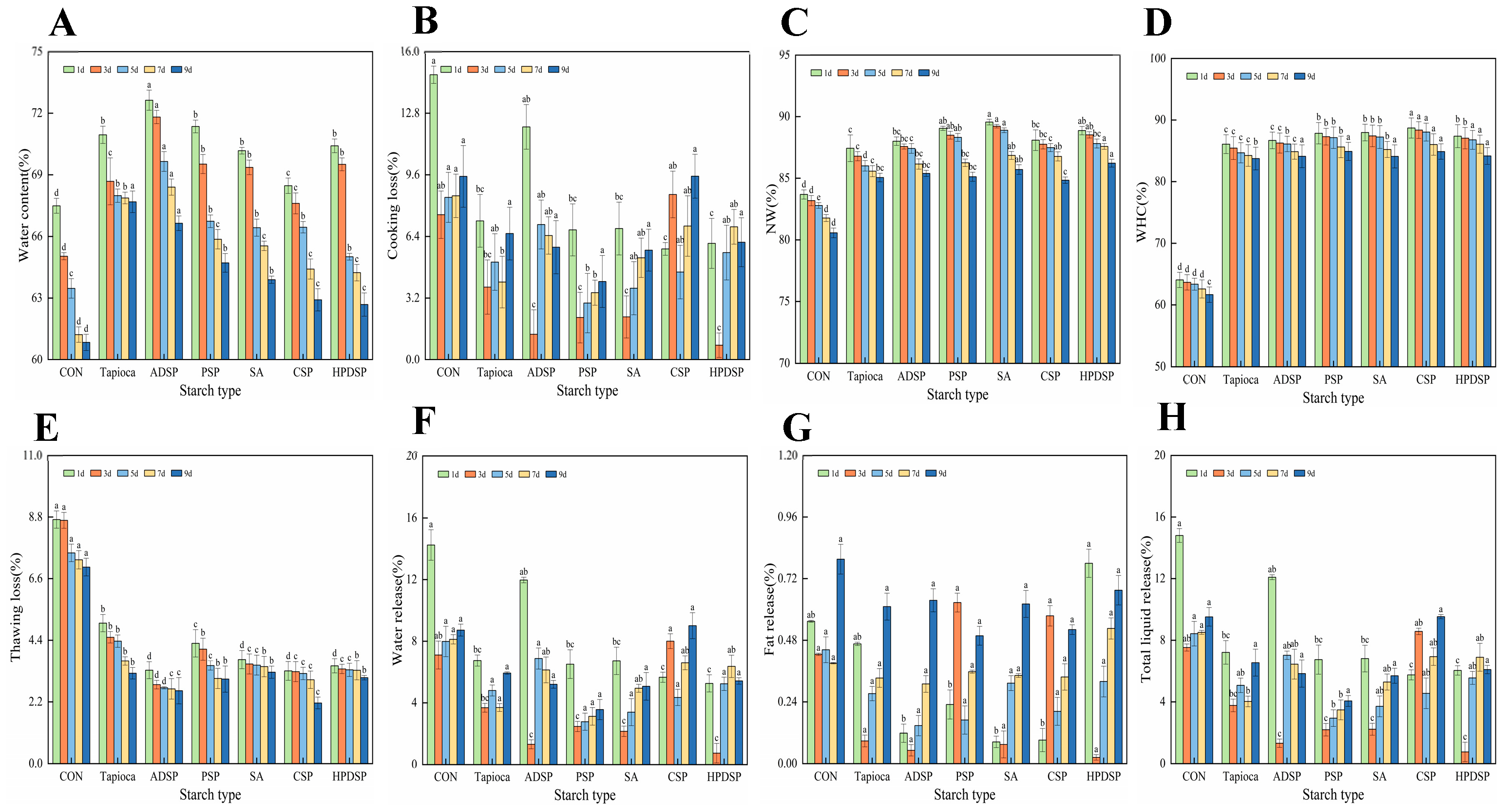
3.2. Water-Retaining Property
3.2.1. Water Content
3.2.2. Cooking Loss (CL)
3.2.3. Non-Expressible Water, NW
3.2.4. Water-Holding Capacity, WHC
3.2.5. Thawing Loss
3.2.6. Emulsion Stability
3.3. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA)
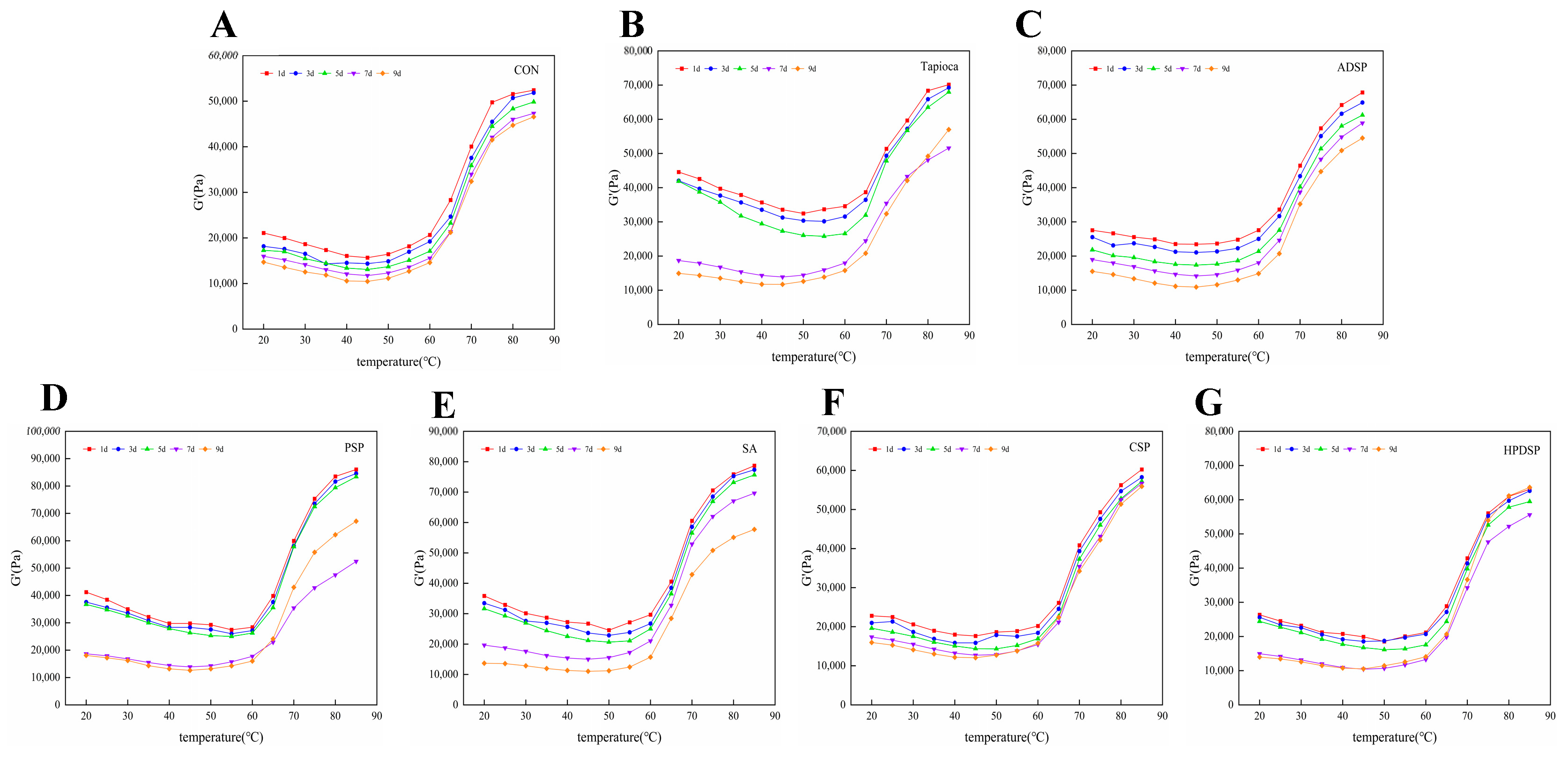
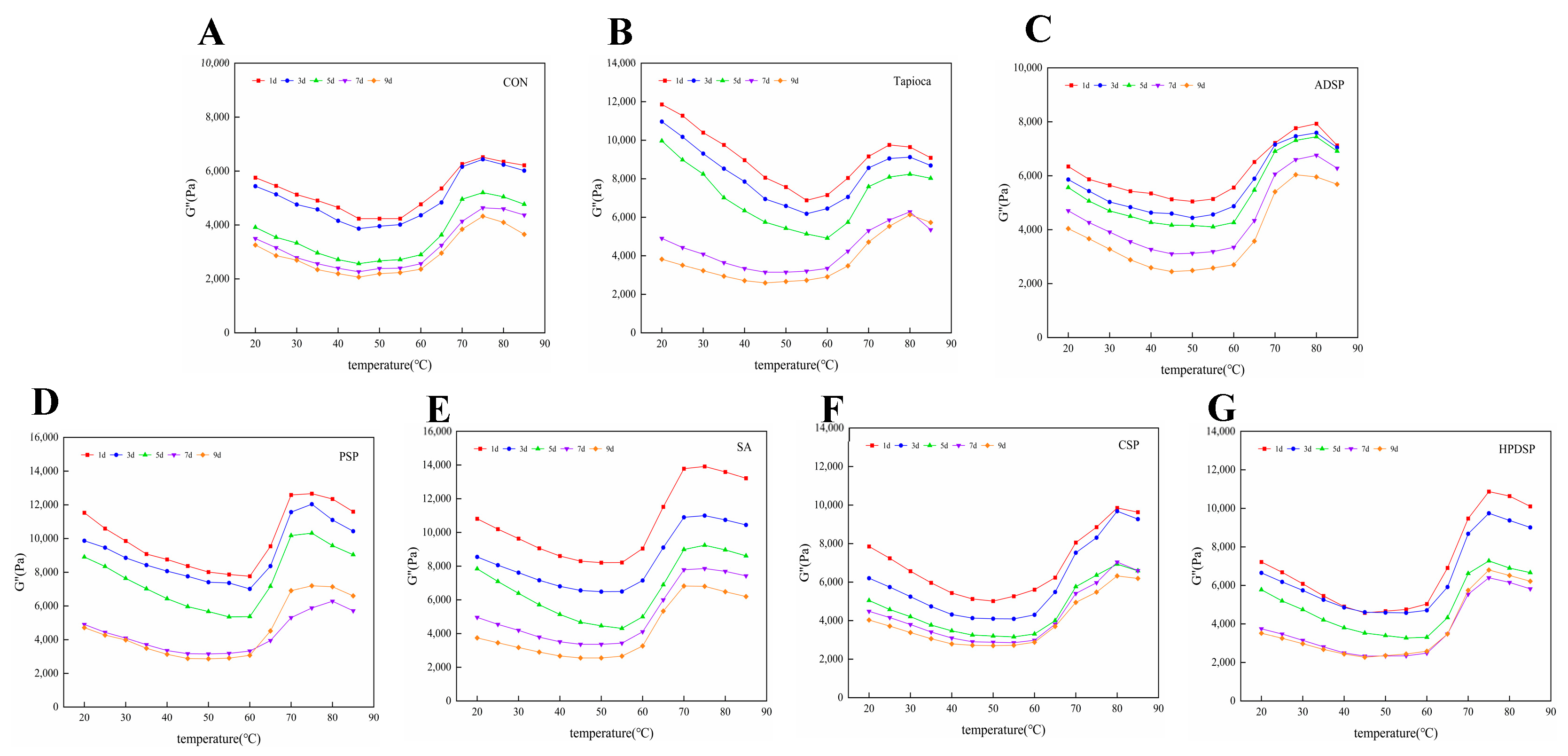
3.4. Dynamic Rheological Measurement
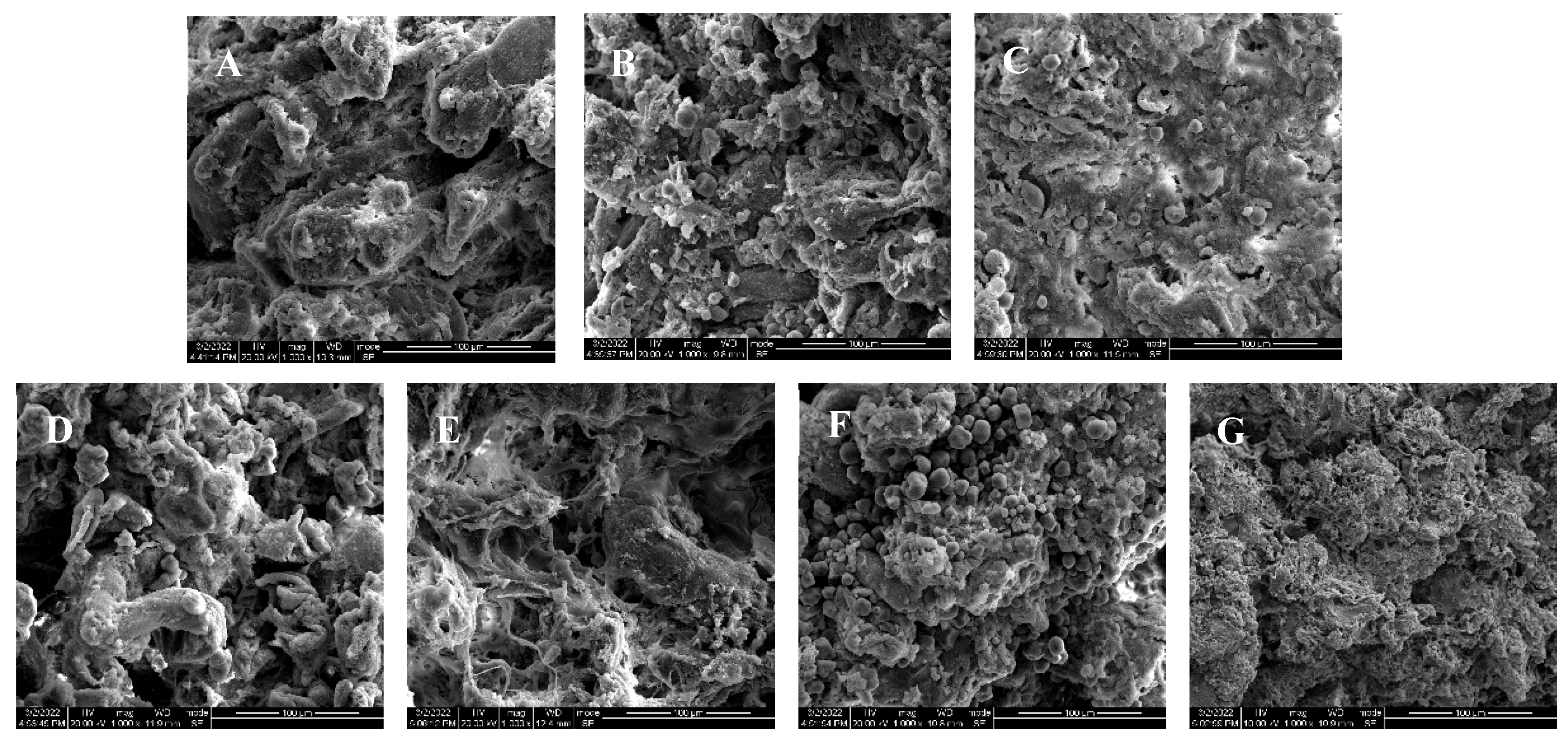
3.5. Sensory Evaluation and Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
3.5.1. Sensory Evaluation
3.5.2. SEM
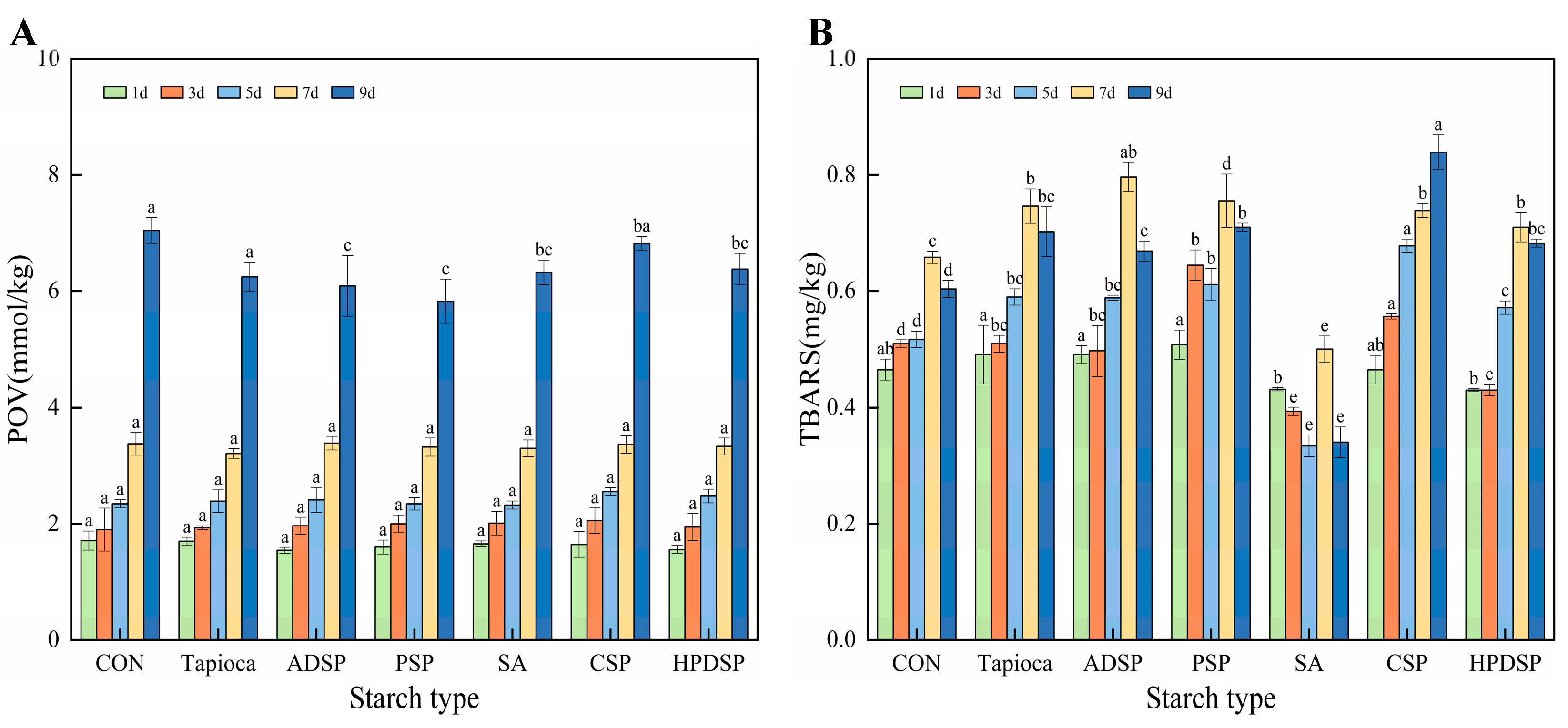
3.6. Lipid Oxidation Index
3.6.1. POV
3.6.2. Thiobarbiturate Number (TBARS)
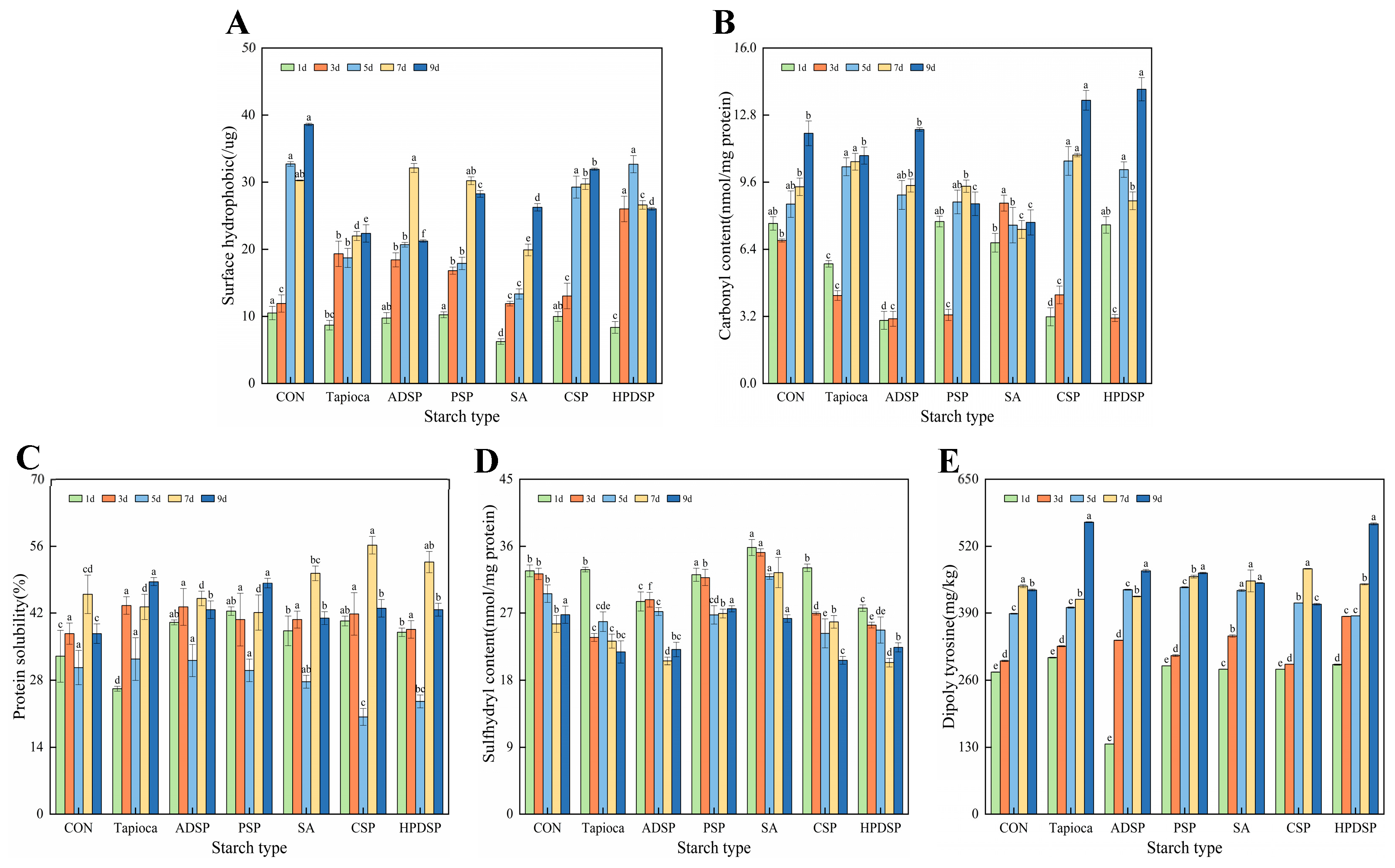
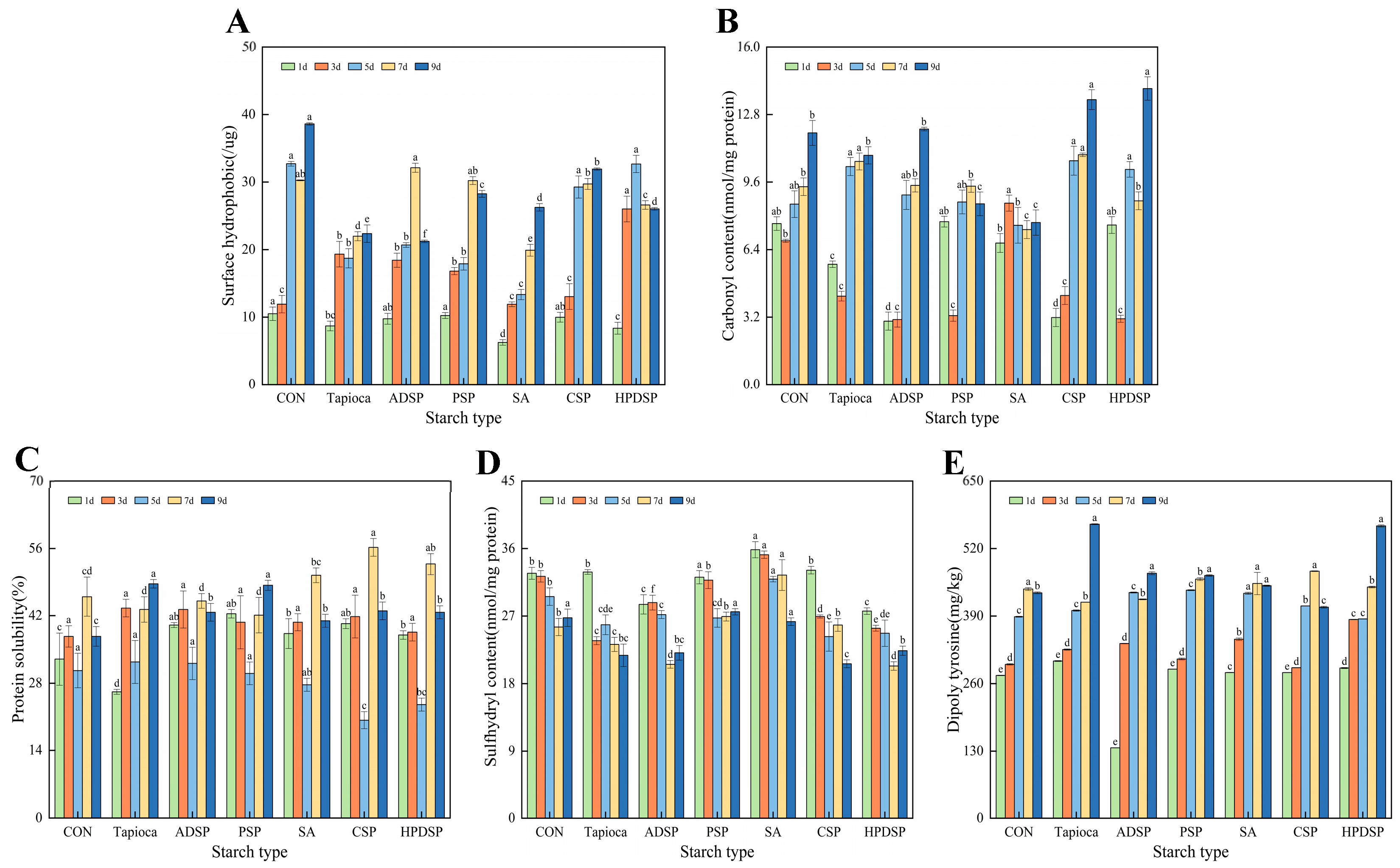
3.7. Protein Oxidation Index
3.7.1. Surface Hydrophobic
3.7.2. Carbonyl Content
3.7.3. Protein Solubility
3.7.4. Sulfhydryl Content
3.7.5. Dityrosine
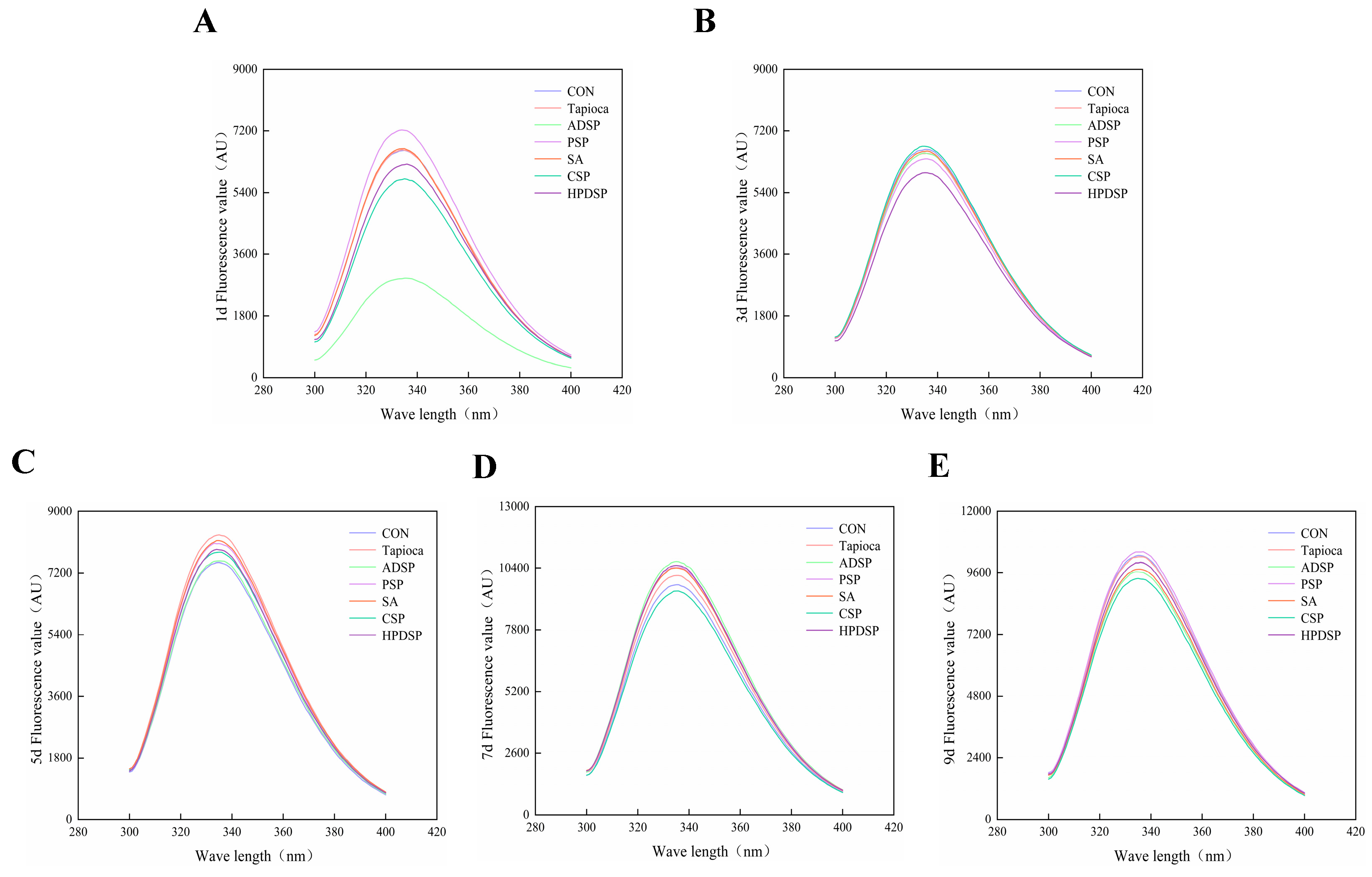
3.8. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy and Tertiary Structure
3.8.1. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy
3.8.2. Tertiary Structure
4. Discussion
4.1. pH and Chroma
4.2. Water-Retaining Property
4.3. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA) and Gel Strength
4.4. Dynamic Rheological Measurement
4.5. Sensory Evaluation and Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
4.6. Lipid Oxidation Index
4.7. Protein Oxidation Index
4.8. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy and Tertiary Structure
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meng, X.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Wu, P.; Xu, Z.; Gao, Z.; Mintah, B.K.; Dabbour, M. An overview of factors affecting the quality of beef meatballs: Processing and preservation. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 1961–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Han, Z.; Arbab, A.A.I.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Z. Effect of Aging Time on Meat Quality of Longissimus Dorsi from Yunling Cattle: A New Hybrid Beef Cattle. Animals 2020, 10, 1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, B. Effects of different paprikas on the quality characteristics and volatile flavor components of spiced beef. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Li, J. Effect of sodium starch octenyl succinate-based Pickering emulsion on the physicochemical properties of hairtail myofibrillar protein gel subjected to multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshag Osman, M.F.; Mohamed, A.A.; Mohamed Ahmed, I.A.; Alamri, M.S.; Al Juhaimi, F.Y.; Hussain, S.; Ibraheem, M.A.; Qasem, A.A. Acetylated corn starch as a fat replacer: Effect on physiochemical, textural, and sensory attributes of beef patties during frozen storage. Food Chem. 2022, 388, 132988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Zhang, W.; Garcia-Oliveira, P.; Carpena, M.; Prieto, M.A.; Bohrer, B.; Lorenzo, J.M. Protein Oxidation in Muscle Foods: A Comprehensive Review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Liu, J.; Tan, B.; Guo, Z.; Li, B.; Li, H. The temporal evolution mechanism of structure and function of oxidized soy protein aggregates. Food Chem. X 2022, 15, 100382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Mhaske, P.; Farahnaky, A.; Kasapis, S.; Majzoobi, M. Cassava starch: Chemical modification and its impact on functional properties and digestibility, a review. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 129, 107542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zeng, L.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Wen, X. Structure and physicochemical properties of cross-linked and acetylated tapioca starches affected by oil modification. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pematilleke, N.; Kaur, M.; Adhikari, B.; Torley, P.J. Investigation of the effects of addition of carboxy methyl cellulose (CMC) and tapioca starch (TS) on the beef patties targeted to the needs of people with dysphagia: A mixture design approach. Meat Sci. 2022, 191, 108868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Liang, X.; Xu, Y.; Kong, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H. In-depth insight into the effects of tapioca or corn acetylated distarch phosphate on the gel properties and in vitro digestibility of kung-wan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Ji, L.; Zhang, T.; Xue, Y.; Xue, C. Effects of pre-emulsification by three food-grade emulsifiers on the properties of emulsified surimi sausage. J. Food Eng. 2019, 247, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Fang, L.; Wang, C.; Shi, L.; Chang, T.; Yang, H.; Cui, M. Effects of starches on the textural, rheological, and color properties of surimi–beef gels with microbial tranglutaminase. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, F.; Dong, D.; Yu, B.; Hou, Z.-H.; Cui, B. Rheology, thermal properties, and microstructure of heat-induced gel of whey protein–acetylated potato starch. Starch-Starke 2017, 69, 1600344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, X.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zou, X.; Shi, J. Preparation of edible antibacterial films based on corn starch /carbon nanodots for bioactive food packaging. Food Chem. 2024, 444, 138467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wang, J.; Hu, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Ge, Q.; Yu, H. Effect of typical starch on the rheological properties and NMR characterization of myofibrillar protein gel. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Lan, X.; He, G.; Jia, D. Effect of hydroxypropyl distarch phosphate on the retrogradation properties of sterilized pea starch jelly and its possible mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 247, 125629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, P.; Hong, J.; Jia, R.; Deng, S.; Yu, X.; Wei, H.; Yang, W. Effect of hydroxypropyl distarch phosphate on the physicochemical characteristics and structure of shrimp myofibrillar protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 125, 107417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Gu, L.; Su, Y.; Chang, C.; Dong, S.; Tang, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, J. Formation of egg yolk-modified starch complex and its stabilization effect on high internal phase emulsions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 116726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, F.A.d.; Neto, O.C.; Santos, L.M.R.d.; Ferreira, E.H.R.; Rosenthal, A. Effect of high pressure on fish meat quality—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 66, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.-J.; Liu, S.-Z.; Li, H.-H.; He, J.; Feng, J.-T.; Zhang, X.; Yan, H. Effects of Portulaca oleracea L. extract on lipid oxidation and color of pork meat during refrigerated storage. Meat Sci. 2019, 147, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, J.; Lee, J.; Jo, K.; Jo, C.; Song, M.; Jung, S. Application of winter mushroom powder as an alternative to phosphates in emulsion-type sausages. Meat Sci. 2018, 143, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Pourramezan, H.; Ramezan, Y.; Roy, S.; Zhang, W.; Assadpour, E.; Zou, J.; Jafari, S.M. Application of gums as techno-functional hydrocolloids in meat processing and preservation: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 268, 131614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewthong, P.; Wattanachant, S. Effect of sugar and starch levels on electrical conductivity of marinade solutions in improving water-holding capacity of marinated broiler breast meat. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2019, 28, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lu, H.; Lou, H.; Acharya, D.R.; Shi, Y.; Chen, Q. Synthesis and characterization of Neurospora intermedia-based composite mycoprotein gel meat: Insight into the effect of pH and soluble starch on water-holding capacity and texture properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 155, 110190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zang, M.; Zhao, B.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, N.; Liu, M.; Li, S.; Lv, G.; Liu, B.; et al. Effect of citrus fiber on the phosphate-mediated gel properties of myofibrillar protein and partial replacement of phosphate. LWT 2023, 173, 114274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhao, H.; Cao, C.; Kong, B.; Xia, X.; Liu, Q. Application of temperature-controlled ultrasound treatment and its potential to reduce phosphate content in frankfurter-type sausages by 50%. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2021, 71, 105379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Luo, Y. Comparison of gel properties and biochemical characteristics of myofibrillar protein from bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis) affected by frozen storage and a hydroxyl radical-generation oxidizing system. Food Chem. 2017, 223, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Liang, X.; Kong, B.; Cao, C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H. Investigation of the effects and mechanism of incorporation of cross-linked/acetylated tapioca starches on the gel properties and in vitro digestibility of kung-wan. Meat Sci. 2023, 204, 109265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, K.; Yousuf, O.; Qadri, O.S.; Jahan, K.; Osama, K.; Islam, R.U. Incorporation of soluble dietary fiber in comminuted meat products: Special emphasis on changes in textural properties. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2022, 27, 100288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fan, M.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, S.; Xiong, S.; Yin, T.; Zhang, B. Effect of micro- and nano-starch on the gel properties, microstructure and water mobility of myofibrillar protein from grass carp. Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Huang, Q.; Zhong, S.; Li, X.; Xiong, S.; Xie, J.; Yin, T.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, S. Gel properties of myofibrillar protein as affected by gelatinization and retrogradation behaviors of modified starches with different crosslinking and acetylation degrees. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 96, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Huang, Q.; Hu, T.; Xiong, S.; Zhao, S. Effects and mechanism of modified starches on the gel properties of myofibrillar protein from grass carp. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 64, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Q.; Chen, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, X.; Ren, F. Effects of konjac glucomannan and acetylated distarch phosphate on the gel properties of pork meat myofibrillar proteins. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 2899–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, H.; Yang, L.; He, Z. Effects of hydroxyl radical oxidation on the stability and biochemical functions of rex rabbit meat. LWT 2024, 203, 116295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.-W.; Chen, Y.-W.; Cai, W.-Q.; Dong, X.-P.; Wang, Y.-R.; Zheng, L.-L. Effects of sodium erythorbate and sodium tripolyphosphate on the lipid oxidation of Russian sturgeon with sous-vide cooking. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 106, 104345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezrian, A.; Shahbazi, Y. Application of nanocompostie chitosan and carboxymethyl cellulose films containing natural preservative compounds in minced camel’s meat. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 1146–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. Solubilization and stable dispersion of myofibrillar proteins in water through the destruction and inhibition of the assembly of filaments using high-intensity ultrasound. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2020, 67, 105160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Q.; Xia, X.; Chen, Q.; Liu, H.; Kong, B. High-intensity ultrasound combined with glycation enhances the thermal stability and in vitro digestion behaviors of myofibrillar protein aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 251, 126301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estévez, M. Protein carbonyls in meat systems: A review. In Proceedings of the 57th International Congress of Meat Science and Technology (ICoMST), Ghent, Belgium, 7–12 August 2011; pp. 259–279. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Du, X.; Wang, B.; Pan, N.; Xia, X.; Bao, Y. Inhibiting effect of ice structuring protein on the decreased gelling properties of protein from quick-frozen pork patty subjected to frozen storage. Food Chem. 2021, 353, 129104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; Li, Z.; Feng, X. Dose-dependent effects of rosmarinic acid on formation of oxidatively stressed myofibrillar protein emulsion gel at different NaCl concentrations. Food Chem. 2018, 243, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Wang, M.; Yang, H.; Shan, A.; Feng, X. Dietary supplementation of resveratrol improved the oxidative stability and spatial conformation of myofibrillar protein in frozen-thawed duck breast meat. Food Biosci. 2021, 43, 101261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Tang, X.; Chen, Y.; You, Y. Chemical forces and water holding capacity study of heat-induced myofibrillar protein gel as affected by high pressure. Food Chem. 2015, 188, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Shi, H.; Xu, P.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Wang, D. Combined effect of ultrasound and sodium bicarbonate marination on chicken breast tenderness and its molecular mechanism. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2019, 59, 104735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
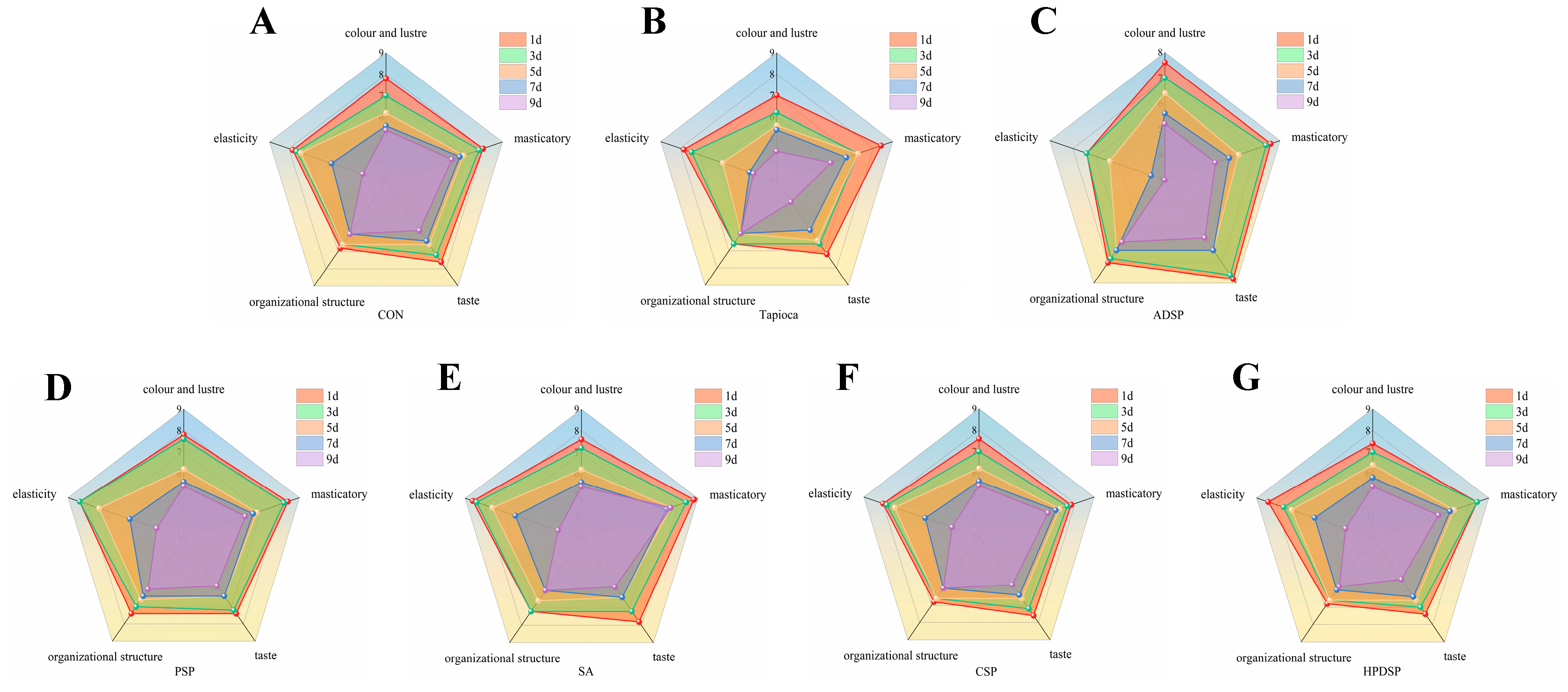
| Item | Standard | Mark |
|---|---|---|
| Color and luster | White, dull, yellow | 1 10 |
| Taste | Coarse taste, strong powdery feeling | 1 10 |
| Masticatory | Chew 1–5 times, and the product will become meat residue Chew more than 10 times, the product will become meat residue | 1 10 |
| Organizational structure | The surface of the section is uneven, there are pores, and the tissue is loose The surface of the section is flat, without porosity, and the tissue is compact | 1 10 |
| Elasticity | It does not recover after finger pressure Recover immediately after pressing with your fingers | 1 10 |
| Starch Type | Number of Days | Hardness/g | Springiness | Cohesiveness | Adhesiveness/g.s | Chewiness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 1 | 2493 ± 91 a | 0.83 ± 0.01 a | 0.69 ± 0.01 a | 1716 ± 61 a | 1424 ± 51 a |
| 3 | 2789 ± 26 a | 0.81 ± 0.01 a | 0.70 ± 0.01 a | 1957 ± 26 a | 1591 ± 18 a | |
| 5 | 2871 ± 49 a | 0.81 ± 0.01 a | 0.71 ± 0.01 a | 2042 ± 18 a | 1658 ± 44 a | |
| 7 | 2899 ± 15 a | 0.77 ± 0.01 b | 0.72 ± 0.01 a | 2251 ± 114 a | 1746 ± 20 a | |
| 9 | 2954 ± 45 a | 0.73 ± 0.01 b | 0.73 ± 0.01 a | 2357 ± 81 a | 1816 ± 20 a | |
| Tapioca | 1 | 2191 ± 43 a | 0.82 ± 0.03 a | 0.58 ± 0.05 b | 1274 ± 128 b | 1048 ± 138 b |
| 3 | 2218 ± 90 a | 0.72 ± 0.01 b | 0.58 ± 0.01 b | 1290 ± 75 b | 931 ± 61 b | |
| 5 | 1908 ± 54 c | 0.77 ± 0.07 b | 0.51 ± 0.06 b | 963 ± 102 c | 746 ± 154 b | |
| 7 | 2555 ± 125 a | 0.82 ± 0.01 a | 0.69 ± 0.04 a | 1749 ± 12 b | 1440 ± 22 a | |
| 9 | 1998 ± 197 b | 0.76 ± 0.05 b | 0.52 ± 0.03 c | 1040 ± 81 b | 792 ± 32 c | |
| ADSP | 1 | 872 ± 39 d | 0.65 ± 0.02 c | 0.46 ± 0.05 c | 401 ± 9 c | 260 ± 12 d |
| 3 | 1072 ± 49 b | 0.74 ± 0.05 b | 0.49 ± 0.01 c | 525 ± 48 c | 390 ± 60 c | |
| 5 | 1576 ± 19 c | 0.74 ± 0.04 b | 0.48 ± 0.06 c | 763 ± 61 c | 565 ± 64 c | |
| 7 | 1534 ± 116 c | 0.72 ± 0.14 b | 0.62 ± 0.04 b | 940 ± 59 c | 672 ± 111 c | |
| 9 | 1568 ± 49 c | 0.79 ± 0.03 b | 0.56 ± 0.03 c | 883 ± 29 c | 696 ± 21 c | |
| PSP | 1 | 1825 ± 39 b | 0.80 ± 0.02 a | 0.58 ± 0.03 b | 1057 ± 53 b | 842 ± 61 b |
| 3 | 2538 ± 78 a | 0.77 ± 0.04 b | 0.58 ± 0.03 b | 1474 ± 28 b | 1138 ± 72 b | |
| 5 | 1877 ± 54 c | 0.74 ± 0.02 b | 0.52 ± 0.01 b | 984 ± 39 c | 726 ± 16 b | |
| 7 | 2618 ± 70 a | 0.77 ± 0.04 b | 0.68 ± 0.02 b | 1786 ± 40 b | 1378 ± 61 b | |
| 9 | 2672 ± 94 a | 0.80 ± 0.03 a | 0.67 ± 0.02 b | 1780 ± 98 c | 1433 ± 131 b | |
| SA | 1 | 1880 ± 36 b | 0.86 ± 0.02 a | 0.65 ± 0.05 a | 1231 ± 96 b | 1054 ± 107 b |
| 3 | 2229 ± 63 a | 0.85 ± 0.04 a | 0.61 ± 0.05 a | 1369 ± 145 b | 1049 ± 28 a | |
| 5 | 2362 ± 33 b | 0.83 ± 0.03 a | 0.58 ± 0.06 b | 1361 ± 134 b | 1138 ± 151 b | |
| 7 | 2210 ± 25 a | 0.84 ± 0.04 a | 0.68 ± 0.02 b | 1500 ± 66 b | 1260 ± 110 b | |
| 9 | 2553 ± 44 a | 0.80 ± 0.02 a | 0.56 ± 0.03 c | 1440 ± 93 b | 1159 ± 106 b | |
| CSP | 1 | 1570 ± 61 c | 0.77 ± 0.02 b | 0.60 ± 0.01 a | 949 ± 32 c | 731 ± 46 c |
| 3 | 1889 ± 70 b | 0.79 ± 0.03 a | 0.60 ± 0.02 a | 1131 ± 27 b | 890 ± 14 b | |
| 5 | 2059 ± 25 b | 0.80 ± 0.05 ab | 0.61 ± 0.02 a | 1258 ± 31 b | 1008 ± 35 b | |
| 7 | 2553 ± 84 a | 0.81 ± 0.01 a | 0.67 ± 0.03 b | 1714 ± 119 b | 1391 ± 116 b | |
| 9 | 2167 ± 100 b | 0.82 ± 0.04 a | 0.71 ± 0.03 a | 1531 ± 92 b | 1257 ± 130 b | |
| HPDSP | 1 | 1242 ± 76 c | 0.73 ± 0.05 b | 0.53 ± 0.03 b | 660 ± 66 c | 486 ± 72 d |
| 3 | 1579 ± 78 c | 0.80 ± 0.06 a | 0.64 ± 0.06 a | 1017 ± 87 b | 818 ± 121 b | |
| 5 | 2335 ± 18 b | 0.83 ± 0.03 a | 0.68 ± 0.01 a | 1579 ± 19 b | 1305 ± 59 c | |
| 7 | 1850 ± 14 b | 0.73 ± 0.03 b | 0.55 ± 0.05 c | 1021 ± 90 c | 746 ± 99 c | |
| 9 | 1710 ± 94 c | 0.76 ± 0.06 b | 0.56 ± 0.04 c | 951 ± 97 c | 726 ± 121 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Du, R. Effects of Different Types of Starch on Physicochemical Properties and Microstructure of Beef during Cold Storage. Foods 2024, 13, 2767. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172767
Zhang S, Wang L, Wang Q, Wang Y, Wang L, Du R. Effects of Different Types of Starch on Physicochemical Properties and Microstructure of Beef during Cold Storage. Foods. 2024; 13(17):2767. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172767
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shulin, Lina Wang, Qiuyu Wang, Yuqi Wang, Linlin Wang, and Rongsheng Du. 2024. "Effects of Different Types of Starch on Physicochemical Properties and Microstructure of Beef during Cold Storage" Foods 13, no. 17: 2767. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172767
APA StyleZhang, S., Wang, L., Wang, Q., Wang, Y., Wang, L., & Du, R. (2024). Effects of Different Types of Starch on Physicochemical Properties and Microstructure of Beef during Cold Storage. Foods, 13(17), 2767. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172767





