Hydroxyl Radical-Induced Oxidation on the Properties of Cathepsin H and Its Influence in Myofibrillar Proteins Degradation of Coregonus peled In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Preparation of Myofibrillar Proteins (MPs)
2.3. Oxidative Treatment of Cathepsin H and Myofibrillar Protein
2.4. Measurement of the Carbonyls in Cathepsin H
2.5. Determination of the Sulfhydryl Content in Cathepsin H
2.6. Structural Analysis of Cathepsin H
2.6.1. Endogenous Fluorescence Spectrum
2.6.2. UV Absorption Spectrum
2.6.3. Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectral
2.7. Assay of Calponin H Activity
2.8. Incubations
2.9. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Protein Oxidation of Cathepsin H
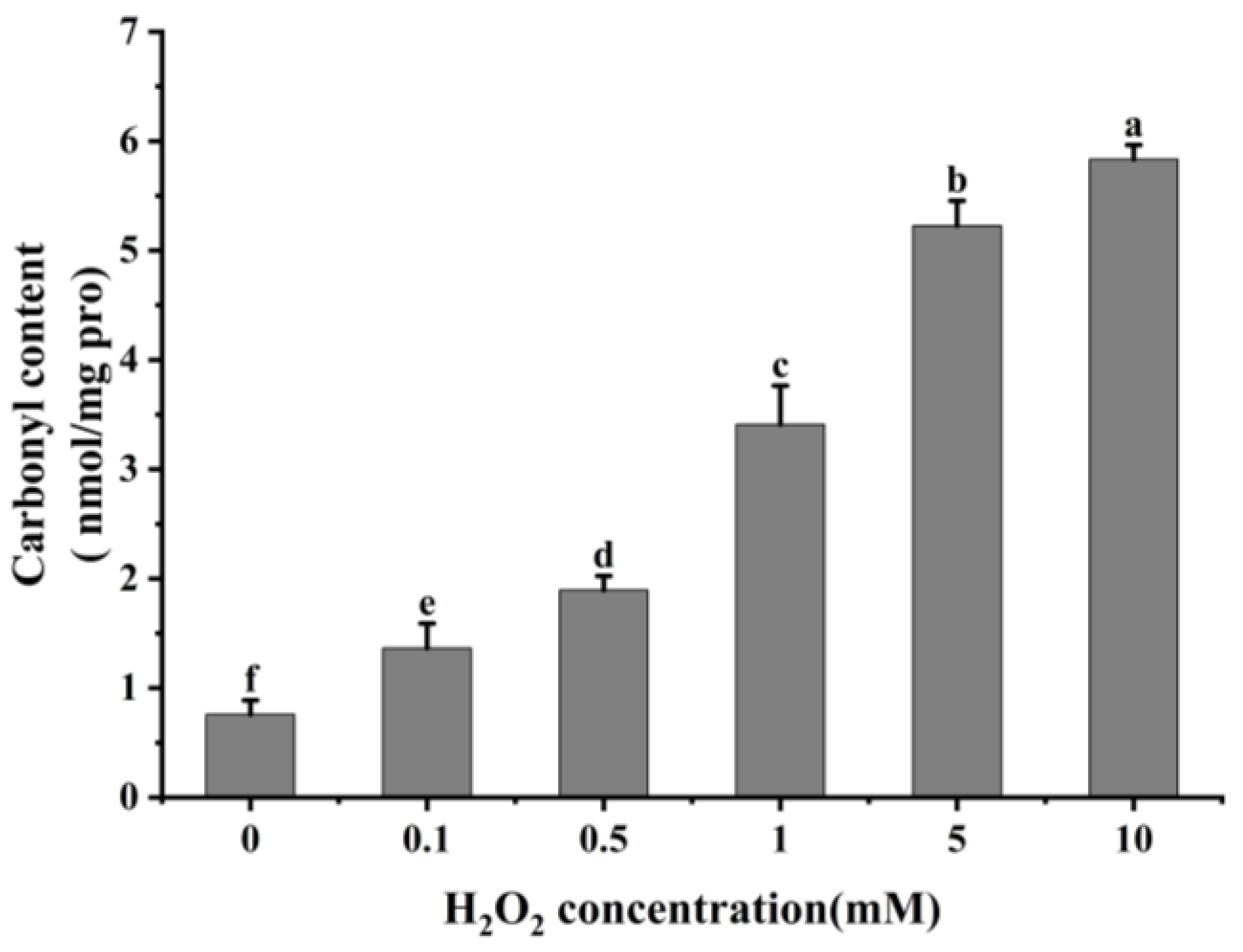
3.1.1. Carbonyl Content
3.1.2. Total Sulfhydryl
3.2. Impact of In Vitro Oxidation on Cathepsin H Structure
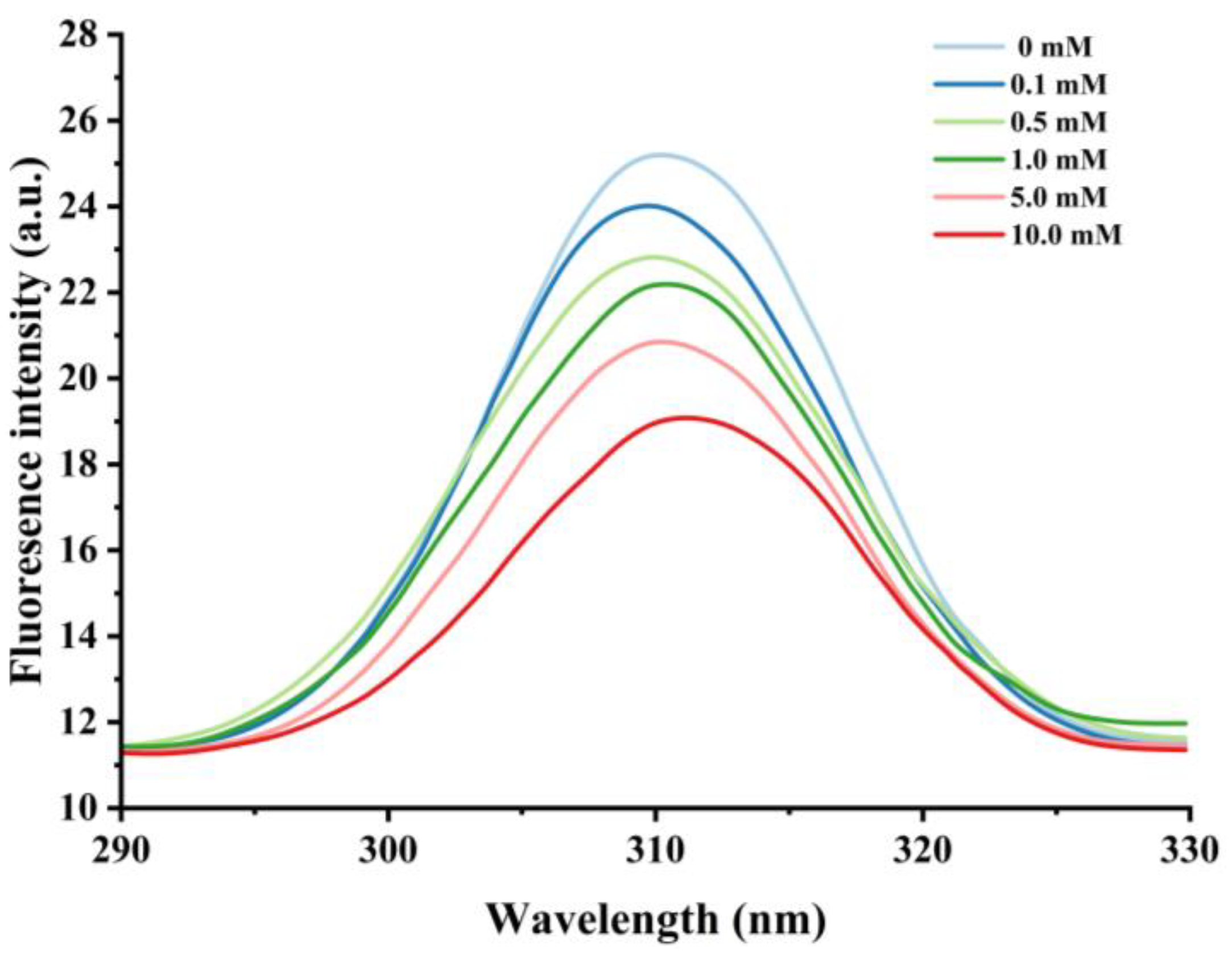
3.2.1. Changes in Intrinsic Fluorescence
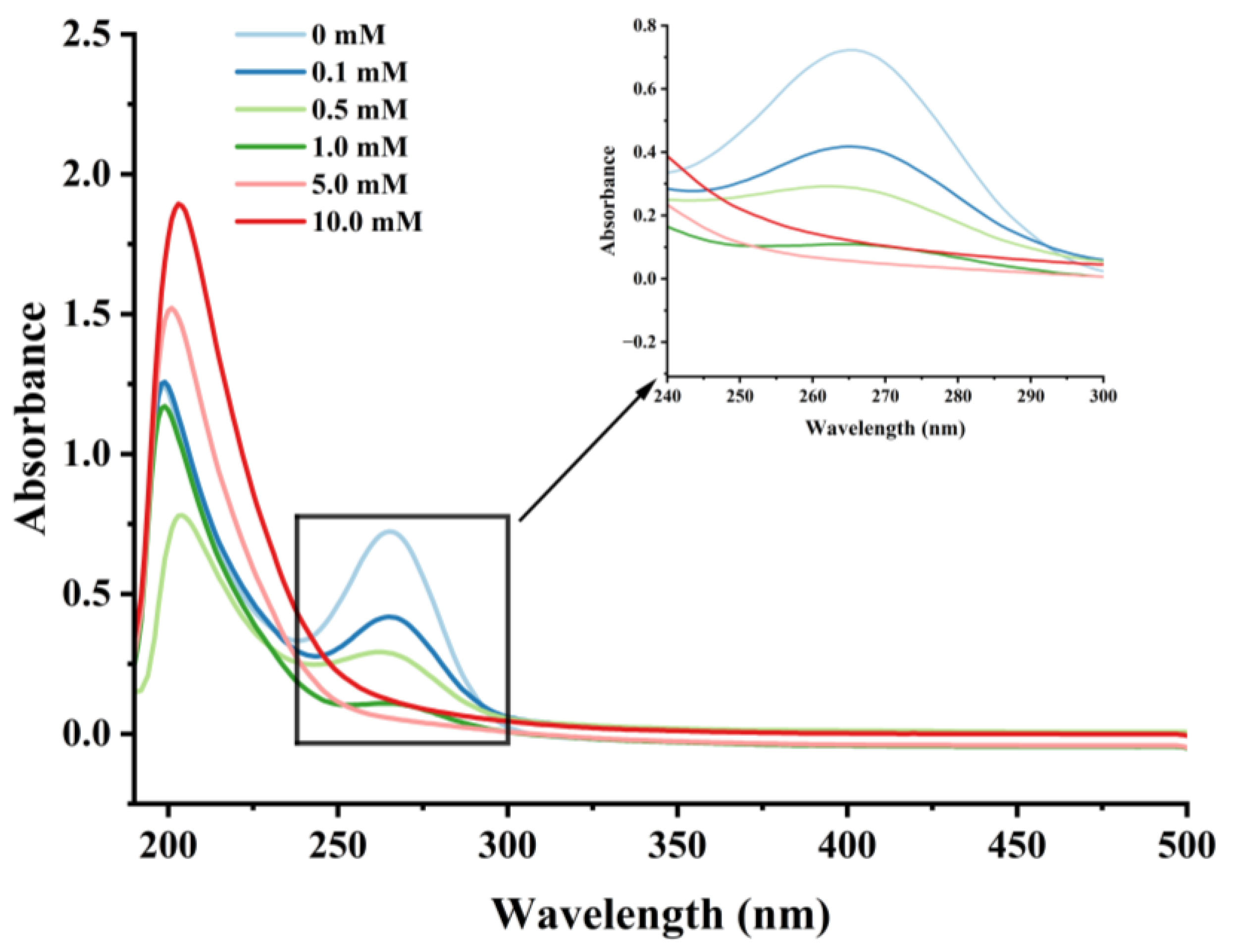
3.2.2. Changes in UV Absorption Spectral
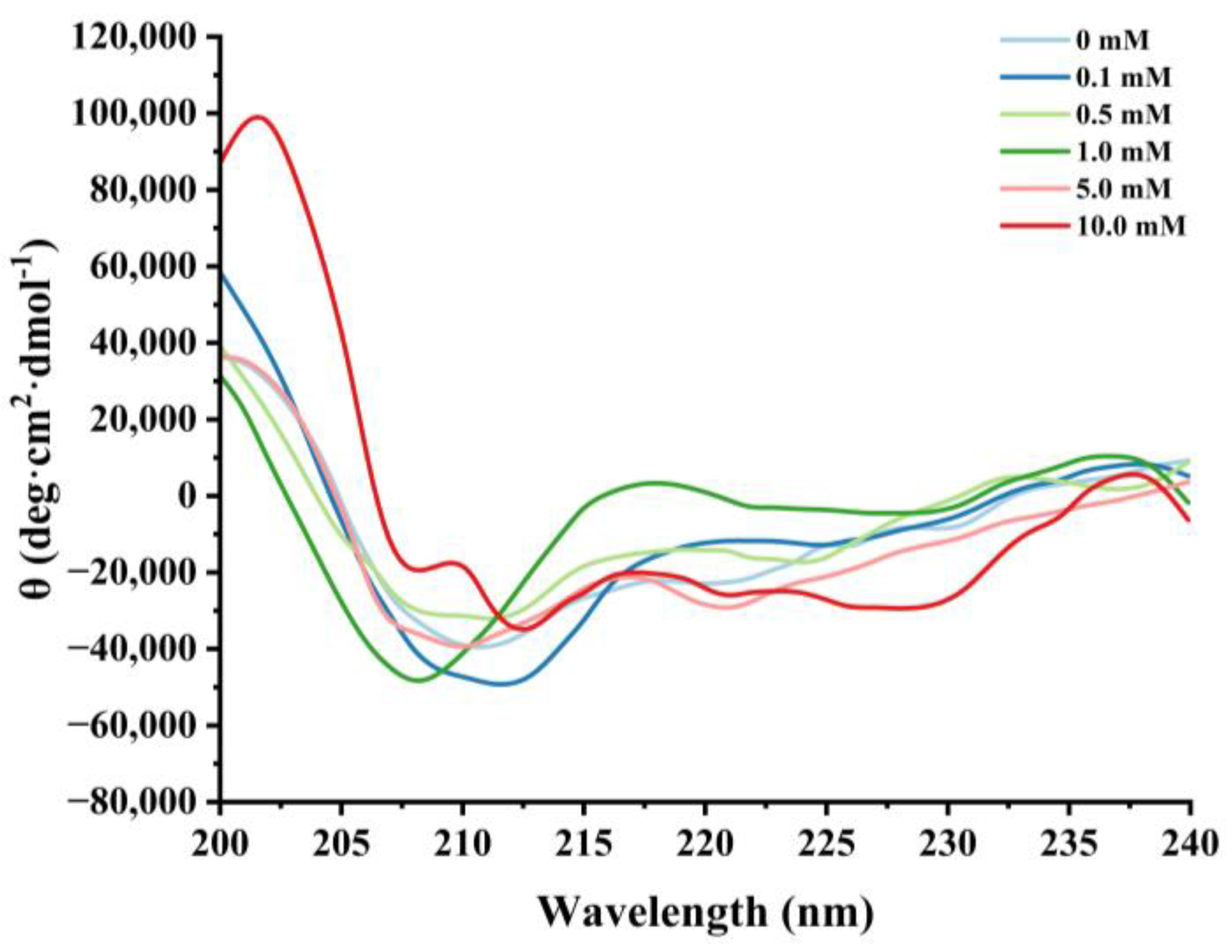
3.2.3. Changes in Circular Dichroism
3.3. Effects of In Vitro Oxidation on Cathepsin H Activity
3.4. In Vitro Degradation of Myofibrillar Proteins by Oxidized Cathepsin H
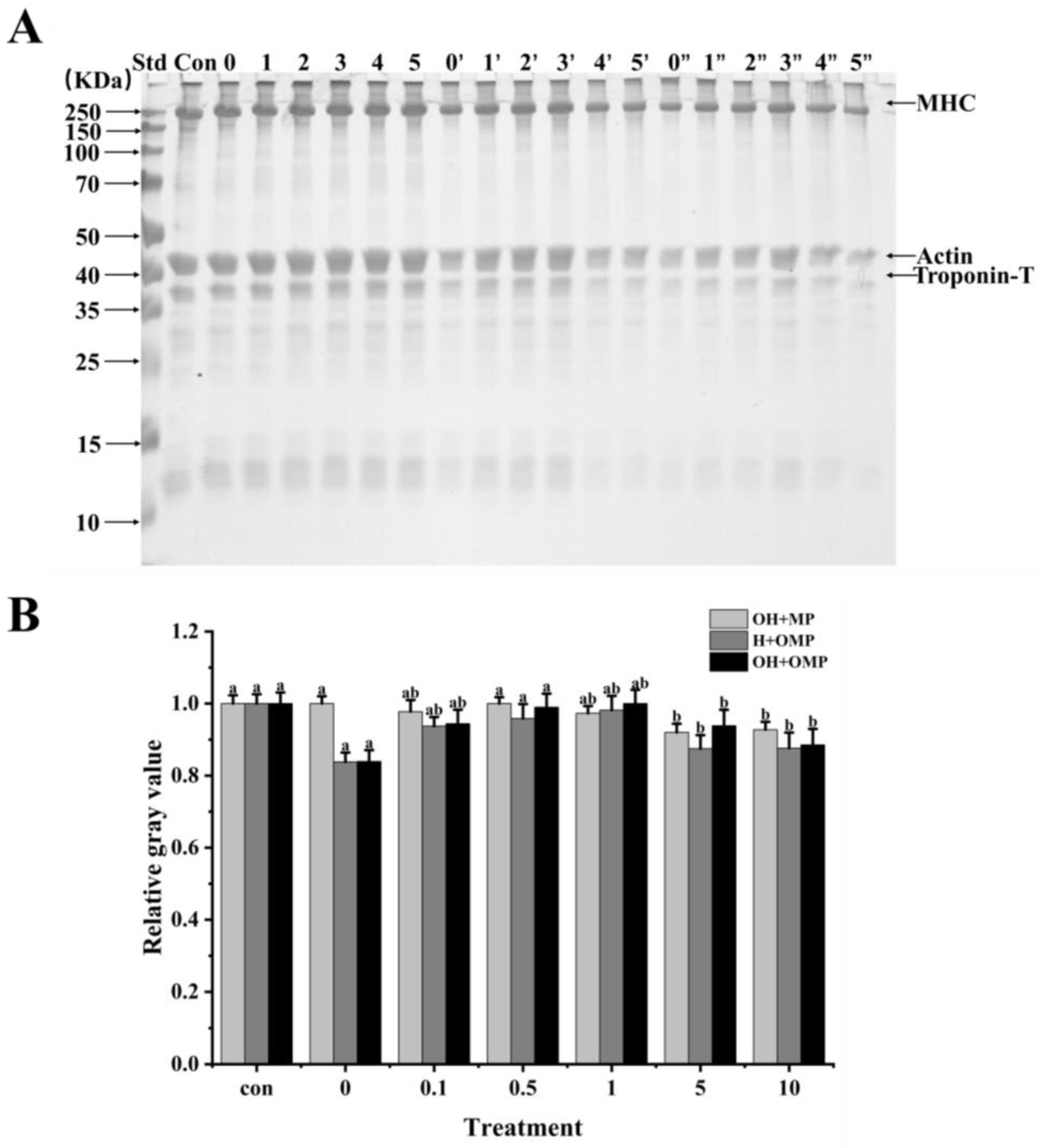
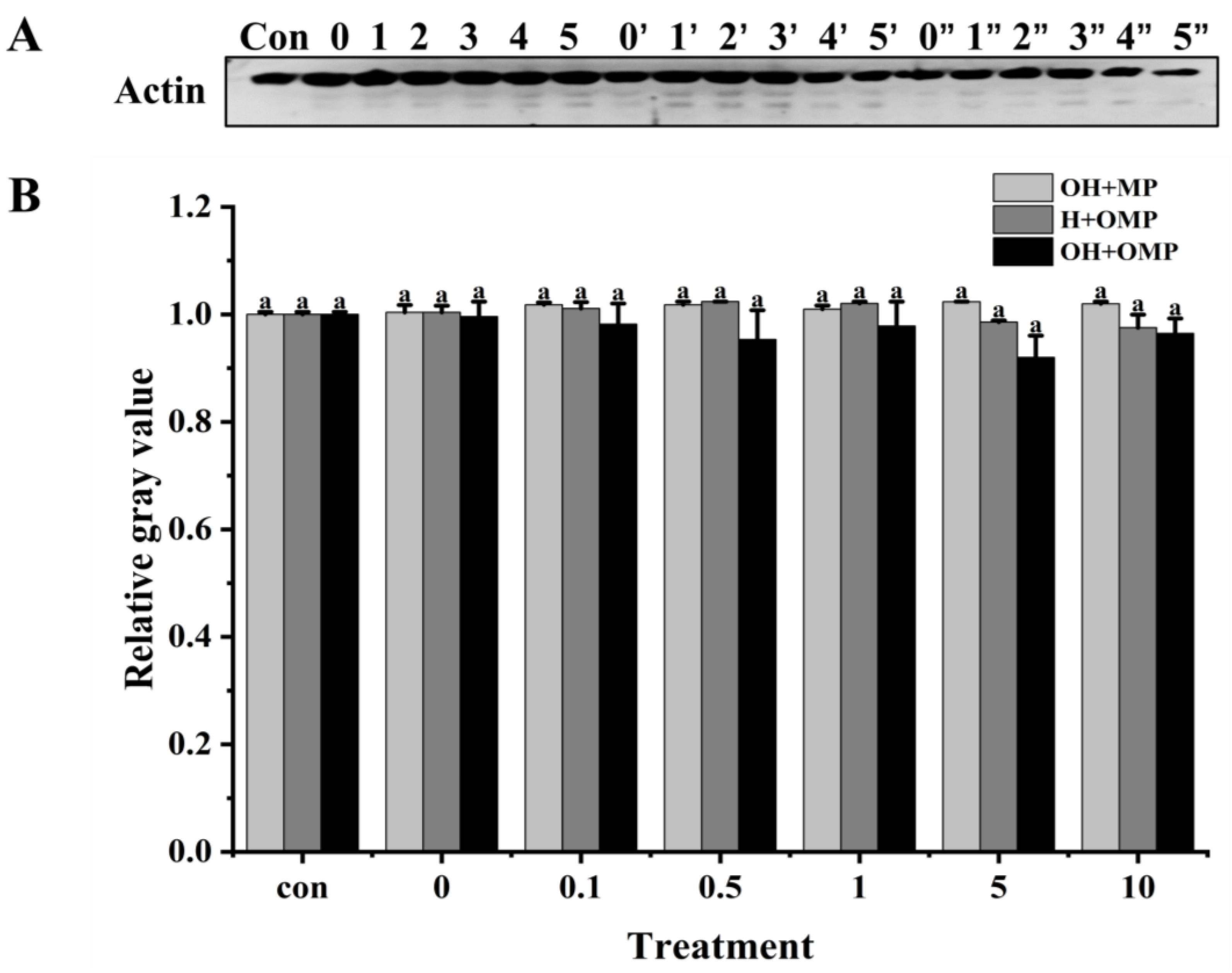
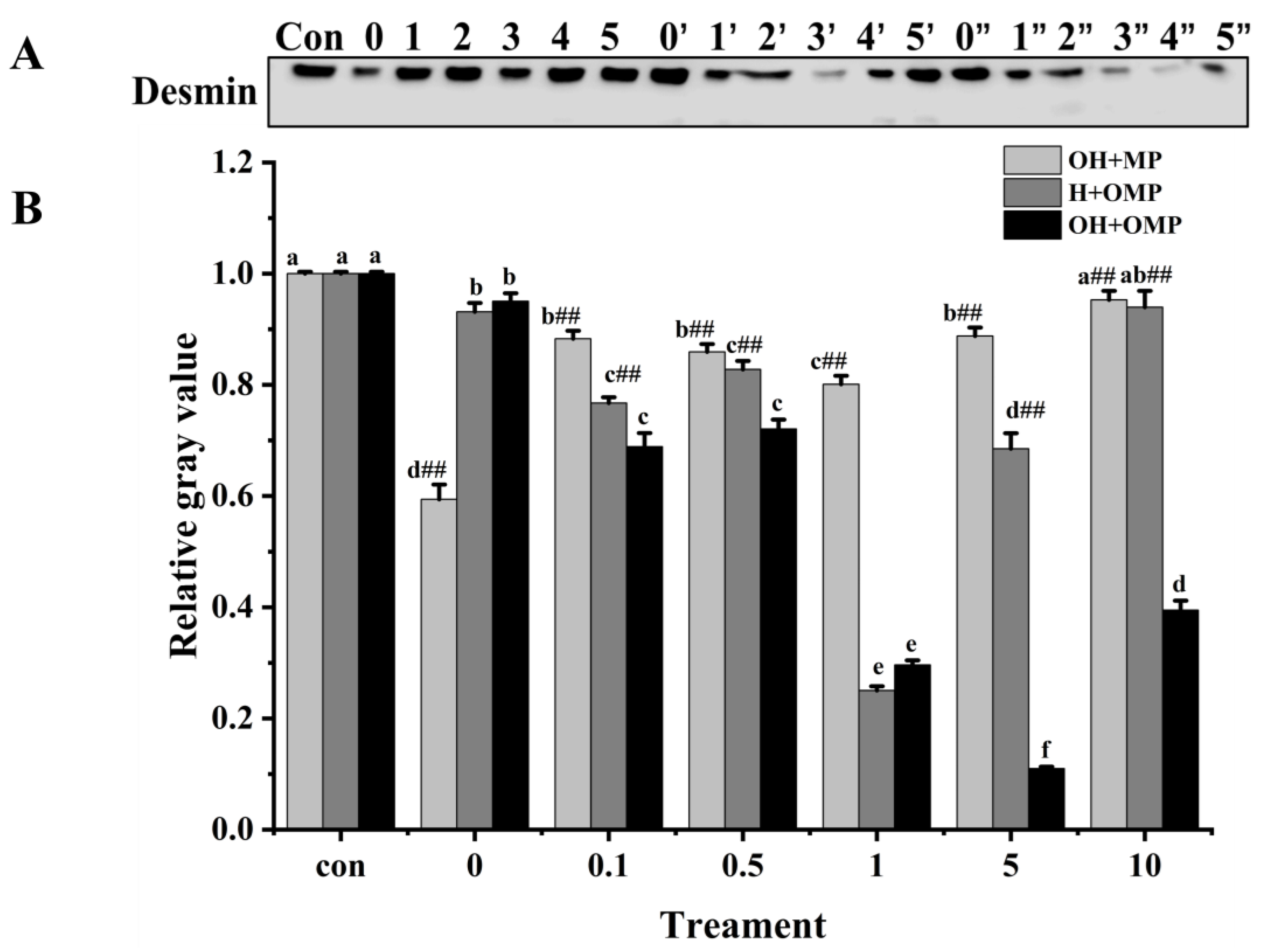
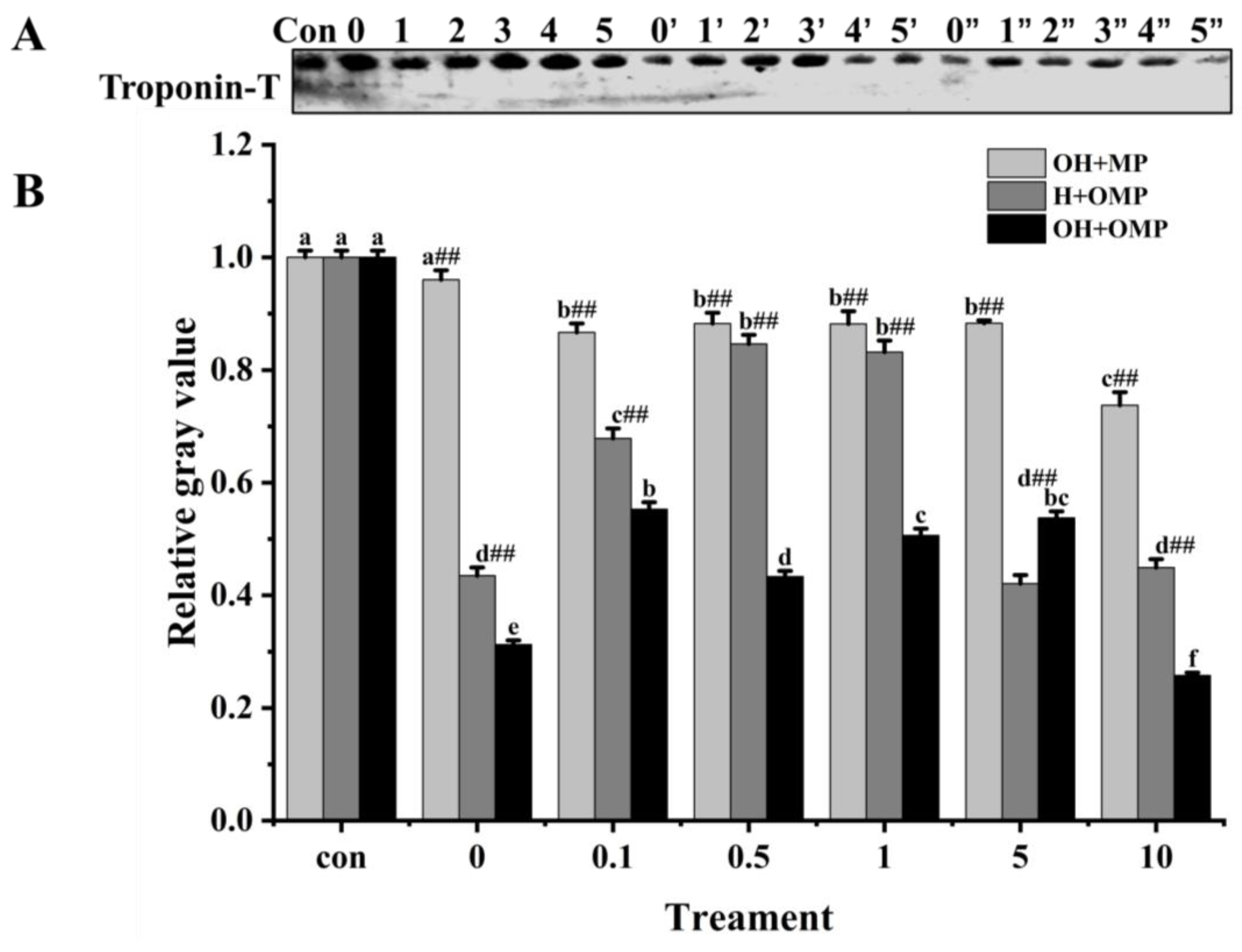
3.4.1. General
3.4.2. Myosin Heavy Chains
3.4.3. Actin
3.4.4. Desmin
3.4.5. Troponin-T
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Luo, Y. Effects of Chilling and Partial Freezing on Rigor Mortis Changes of Bighead Carp (Aristichthys nobilis) Fillets: Cathepsin Activity, Protein Degradation and Microstructure of Myofibrils. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, C2725–C2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Liu, P.; Wang, C.; Deng, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. Oxidation of Cathepsin D by Hydroxy Radical: Its Effect on Enzyme Structure and Activity against Myofibrillar Proteins Extracted from Coregonus peled. Molecules 2023, 28, 5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Deng, X.; Lei, Y.; Liu, P.; Lu, S.; Zhang, J. Effects of µ-calpain oxidation on Coregonus peled myofibrillar protein degradation in vitro. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, P.; Deng, X.; Guo, X.; Mao, X.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J. Effects of hydroxyl radical oxidation on myofibrillar protein and its susceptibility to μ-calpain proteolysis. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 137, 110453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimogianopoulos, D.; Grigorakis, K. Effective algorithmic operational framework for fish texture evaluation in industry: Achieving maturity. Aquac. Fish. 2023, 8, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Benjakul, S. Proteolysis and Its Control Using Protease Inhibitors in Fish and Fish Products: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, N.B.; Ranveer, R.C.; Bhagwat, P.K.; Ozogul, F.; Benjakul, S.; Pillai, S.; Annapure, U.S. Cold plasma for the preservation of aquatic food products: An overview. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 4407–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Regenstein, J.M.; Zang, J.; Xia, W.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, F. Inhibitory effects of chitosan-based coatings on endogenous enzyme activities, proteolytic degradation and texture softening of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) fillets stored at 4 °C. Food Chem. 2018, 262, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y.; Lametsch, R. Search for proteomic markers for stunning stress and stress-induced textural tenderization in silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) fillets using label-free strategy. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Jia, S.; Liu, J.; Gao, P.; Yu, D.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Yu, P.; Xia, W.; Zhan, X. The relationship between degradation of myofibrillar structural proteins and texture of superchilled grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) fillet. Food Chem. 2019, 301, 125278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, S.; Liu, Y.; Gao, S.; Tan, Y.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y. Mechanisms of fish protein degradation caused by grass carp spoilage bacteria: A bottom-up exploration from the molecular level, muscle microstructure level, to related quality changes. Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, Z.; Donkor, O.; Street, W.A.; Vasiljevic, T. Calpains- and cathepsins-induced myofibrillar changes in post-mortem fish: Impact on structural softening and release of bioactive peptides. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 23, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaarder, M.Ø.; Bahuaud, D.; Veiseth-Kent, E.; Mørkøre, T.; Thomassen, M.S. Relevance of calpain and calpastatin activity for texture in super-chilled and ice-stored Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) fillets. Food Chem. 2011, 132, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, O.; Solberg, C.; Johnston, I.A. Activity of aspargate (cathepsin D), cysteine proteases (cathepsins B, B + L, and H), and matrix metallopeptidase (collagenase) and their influence on protein and water-holding capacity of muscle in commercially farmed Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 5953–5959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chéret, R.; Delbarre-Ladrat, C.; de Lamballerie-Anton, M.; Verrez-Bagnis, V. Calpain and cathepsin activities in post mortem fish and meat muscles. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 1474–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Li, Y. A review of inhibition mechanisms of surimi protein hydrolysis by different exogenous additives and their application in improving surimi gel quality. Food Chem. 2024, 456, 140002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, J.W.; Roisen, F.J.; Yorke, G.; Lee, J.A.; McElligott, M.A.; Triemer, D.F.; St John, A. Lysosomes and proteolytic enzyme activities in cultured striated muscle cells. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1981, 29, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stauber, W.T.; Ong, S.H. Fluorescence demonstration of a cathepsin H-like protease in cardiac, skeletal and vascular smooth muscles. Histochem. J. 1982, 14, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, M.; Deng, S.; Xu, W.; Liu, Y.; Geng, Z.; Sun, C.; Bian, H.; Liu, F. Postmortem changes in actomyosin dissociation, myofibril fragmentation and endogenous enzyme activities of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) muscle. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Jia, S.; Huang, Z.; Luo, Y. Effect of different stunning methods on antioxidant status, in vivo myofibrillar protein oxidation, and the susceptibility to oxidation of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) fillets during 72 h postmortem. Food Chem. 2017, 45, 21963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estévez, M. Protein carbonyls in meat systems: A review. Meat Sci. 2011, 89, 259–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, M.N.; Heinonen, M.; Baron, C.P.; Estevez, M. Protein oxidation in muscle foods: A review. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Xiong, Y.L.; Kong, B.; Zhao, X.; Liu, N. Hydroxyl radical-stressed whey protein isolate: Chemical and structural properties. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2012, 5, 2454–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Huang, J.; Huang, F.; Huang, M.; Zhou, G. Influence of oxidation on the susceptibility of purified desmin to degradation by μ-calpain, caspase-3 and -6. Food Chem. 2014, 150, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Zhou, K.; Yi, S.; Zhu, W.; Xu, Y.; Lin, H.; Li, J. Effect of hydroxyl radicals on biochemical and functional characteristics of myofibrillar protein from large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlin, K.M.; Huff-Lonergan, E.; Rowe, L.; Lonergan, S.M. Effect of oxidation, pH, and ionic strength on calpastatin inhibition of μ-and m-calpain. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 84, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, X.; Zhu, X.; Mao, X.; Guo, X.; Deng, X.; Zhang, J. μ-Calpain oxidation and proteolytic changes on myofibrillar proteins from Coregonus peled in vitro. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, L.J.; Maddock, K.; Lonergan, S.M.; Huff-Lonergan, E. Oxidative environments decrease tenderization of beef steaks through inactivation of μ-calpain. J. Anim. Sci. 2004, 82, 3254–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wen, G. Effects of cathepsins on gel strength and water-holding capacity of myofibrillar protein gels from bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis) under a hydroxyl radical-generation oxidizing system. Foods 2022, 11, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Xiong, Y.L.; Alderton, A.L. Concentration effects of hydroxyl radical oxidizing systems on biochemical properties of porcine muscle myofibrillar protein. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smuder, A.J.; Kavazis, A.N.; Hudson, M.B.; Nelson, W.B.; Powers, S.K. Oxidative stress enhances myofibrillar protein degradation via calpain and caspase-3. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 1046.14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; He, Y.; Xiong, S.; Liu, Y.; Yin, T.; Hu, Y.; You, J. Effect of Mild Ozone Oxidation on Structural Changes of Silver Carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) Myosin. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 10, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Xia, W.; Jiang, Q. Pressure-induced changes of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) myofibrillar protein structure. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2014, 238, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Lin, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Ahmed, I.; Chen, H. Changes of structure and IgE binding capacity of shrimp (Metapenaeus ensis) tropomyosin followed by acrolein treatment. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 1028–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, T.A.; Morrissey, M.T.; Peters, M.Y.; An, H. Purification and characterization of Pacific whiting proteases. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 2421–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Huang, F.; Huang, M.; Zhou, G. Influence of oxidation on myofibrillar proteins degradation from bovine via μ-calpain. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Huang, H.; Li, L.; Yang, X.; Hao, S.; Chen, S.; Deng, J. The effects of modified atmosphere packaging and enzyme inhibitors on protein oxidation of tilapia muscle during iced storage. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 17, 6468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Boeren, S.; Ertbjerg, P. Myofibrillar protein oxidation affects filament charges, aggregation and water-holding. Meat Sci. 2018, 135, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xiong, Y.L.; Chen, J. Oxidation-induced unfolding facilitates myosin cross-linking in myofibrillar protein by microbial transglutaminase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 8020–8027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Ertbjerg, P. Effects of protein oxidation on the texture and water-holding of meat: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 3564–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Li, H.; Emara, A.M.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, M.; He, Z. Effect of in vitro oxidation on the water retention mechanism of myofibrillar proteins gel from pork muscles. Food Chem. 2020, 315, 126226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Liu, R.; Wang, H.; Hua, C.; Song, S.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, W. Effects of oxidation in vitro on structures and functions of myofibrillar protein from beef muscles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 5866–5873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chizoba Ekezie, F.-G.; Cheng, J.-H.; Sun, D.-W. Effects of Mild Oxidative and Structural Modifications Induced by Argon Plasma on Physicochemical Properties of Actomyosin from King Prawn (Litopenaeus Vannamei). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 13285–13294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skjervold, P.; Taylor, R.; Wold, J.; Berge, P.; Abouelkaram, S.; Culioli, J.; Dufour, E. Development of intrinsic fluorescent multispectral imagery specific for fat, connective tissue, and myofibers in meat. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefevre, F.; Fauconneau, B.; Thompson, J.W.; Gill, T.A. Thermal denaturation and aggregation properties of Atlantic salmon myofibrils and myosin from white and red muscles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 4761–4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.-Q.; Luo, S.-Z.; Zhong, X.-Y.; Cai, J.; Jiang, S.-T.; Zheng, Z. Changes in chemical interactions and protein conformation during heat-induced wheat gluten gel formation. Food Chem. 2017, 214, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; He, Z.; Gan, X.; Li, H. Effect of peroxyl radicals on the structure and gel properties of isolated rabbit meat myofibrillar proteins. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 2687–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, F.; Diao, X.; Kong, B.; Xia, X. Moisture migration, microstructure damage and protein structure changes in porcine longissimus muscle as influenced by multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Meat Sci. 2017, 133, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Xia, W.; Rustad, T.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, Q. Changes in myofibrillar structure of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) as affected by endogenous proteolysis under acidic condition. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 2171–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yang, R. The effect of pulsed electric fields on the inactivation and structure of lysozyme. Food Chem. 2008, 110, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, Y.; Nakaya, M.; Ochiai, Y.; Watabe, S. Characterization of fast skeletal myosin from white croaker in comparison with that from walleye pollack. Fish. Sci. 2006, 72, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, T.; Ohno, T.; Otsuka-Fuchino, H.; Matsumoto, J.J.; Tsuchiya, T. Carp Natural Actomyosin: Thermal Denaturation Mechanism. J. Food Sci. 1994, 59, 1002–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, M.B.; Stamenkovic, I.; Winterbourn, C.C. Interaction with substrate sensitises caspase-3 to inactivation by hydrogen peroxide. FEBS Lett. 2002, 517, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lametsch, R.; Roepstorff, P.; Moller, H.; Bendixen, E. Identification of myofibrillar substrates for μ-calpain. Meat Sci. 2004, 68, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.A.; Vang, B.; Pedersen, A.M.; Martinez, I.; Olsen, R.L. Post-mortem degradation of myosin heavy chain in intact fish muscle: Effects of pH and enzyme inhibitors. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 1090–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.-Q.; Liu, R.; Zhang, W.; Ben, A.; Wang, R. In vitro susceptibility of oxidized myosin by μ-calpain or caspase-3 and the determination of the oxidation sites of myosin heavy chains. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 8629–8636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morzel, M.; Gatellier, P.; Sayd, T.; Renerre, M.; Laville, E. Chemical oxidation decreases proteolytic susceptibility of skeletal muscle myofibrillar proteins. Meat Sci. 2006, 73, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, Z.; Morton, J.D.; Mason, S.L.; Bekhit, A.E.-D.A. Role of calpain system in meat tenderness: A review. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2018, 7, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonergan, E.H.; Zhang, W.; Lonergan, S.M. Biochemistry of postmortem muscle—Lessons on mechanisms of meat tenderization. Meat Sci. 2010, 86, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, X.; Ma, M.; Liu, P.; Deng, X.; Zhang, J. Hydroxyl Radical-Induced Oxidation on the Properties of Cathepsin H and Its Influence in Myofibrillar Proteins Degradation of Coregonus peled In Vitro. Foods 2024, 13, 2531. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13162531
Fan X, Ma M, Liu P, Deng X, Zhang J. Hydroxyl Radical-Induced Oxidation on the Properties of Cathepsin H and Its Influence in Myofibrillar Proteins Degradation of Coregonus peled In Vitro. Foods. 2024; 13(16):2531. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13162531
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Xuemei, Mengjie Ma, Pingping Liu, Xiaorong Deng, and Jian Zhang. 2024. "Hydroxyl Radical-Induced Oxidation on the Properties of Cathepsin H and Its Influence in Myofibrillar Proteins Degradation of Coregonus peled In Vitro" Foods 13, no. 16: 2531. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13162531
APA StyleFan, X., Ma, M., Liu, P., Deng, X., & Zhang, J. (2024). Hydroxyl Radical-Induced Oxidation on the Properties of Cathepsin H and Its Influence in Myofibrillar Proteins Degradation of Coregonus peled In Vitro. Foods, 13(16), 2531. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13162531





