Comparison of Nutritional Quality and Functional Active Substances in Different Parts of Eight Lotus Seed Cultivars
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Measurement of Total Phenol and Flavonoid Content
2.3. Measurement of Soluble Sugar Content
2.4. Measurement of Total Starch and Amylose Content
2.5. Protein Content and Vitamin C (VC) Content
2.6. Measurement of Crude Fat Content
2.7. Measurement of DPPH Radical Scavenging Capacity
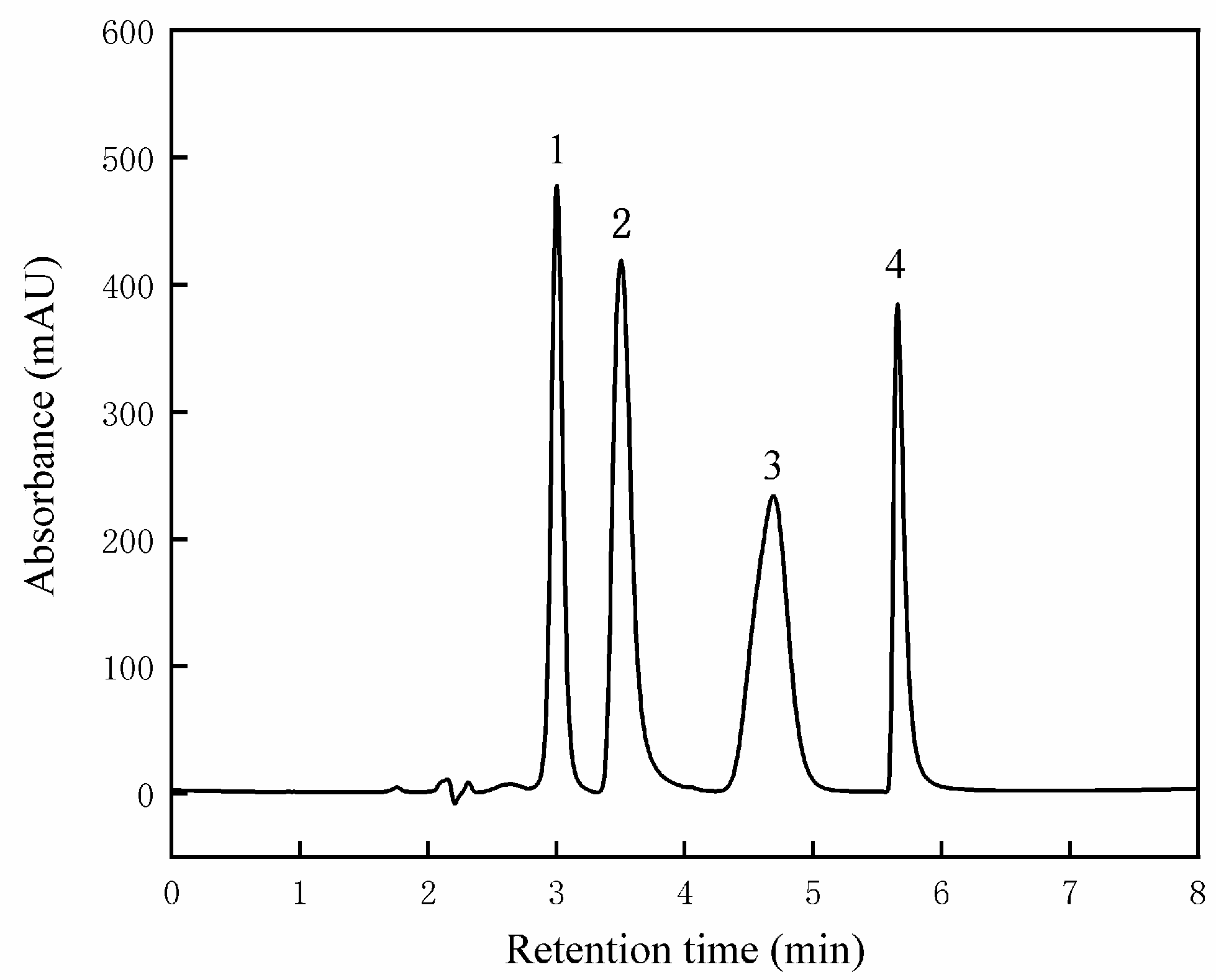
2.8. Measurement of Alkaloids in Lotus Plumule
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Protein and Soluble Sugar Content
3.2. Analysis of Crude Fat Content
3.3. Analysis of VC Content
3.4. Differences in Total Starch and Amylose Content
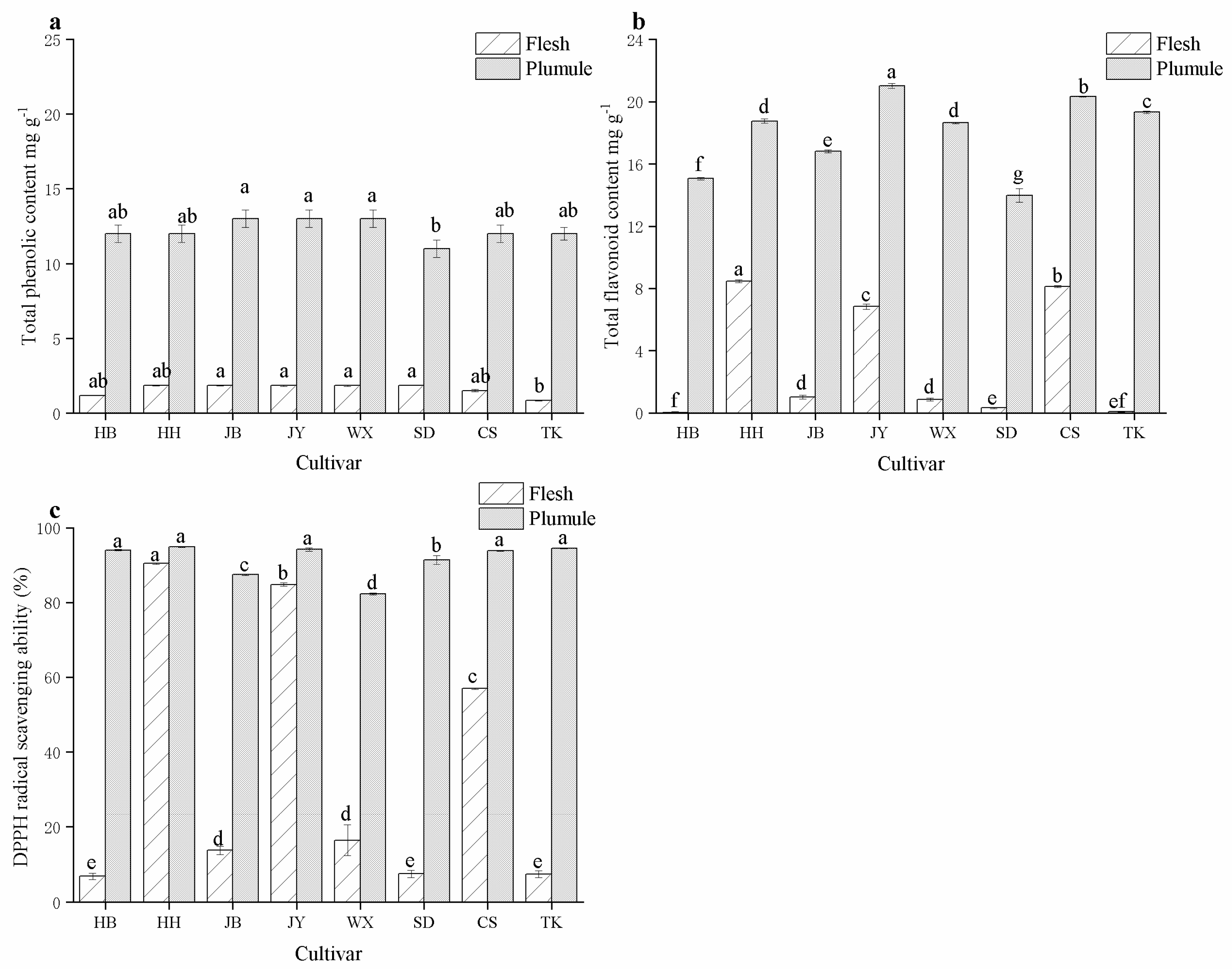
3.5. Total Phenolic Content, Flavonoid Content, and DPPH Antioxidant Capacity of Different Varieties of Lotus Seeds
3.6. Differences in Alkaloid Content
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Zhu, F. Structures, properties, and applications of lotus starches. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 332–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangar, S.P.; Dunno, K.; Kumar, M.; Mostafa, H.; Maqsood, S. A comprehensive review on lotus seeds (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.): Nutritional composition, health-related bioactive properties, and industrial applications. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 89, 104937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, C.; Guo, M.; Contreras, M.d.M. Quantitative Analysis and Comparison of Flavonoids in Lotus Plumules of Four Representative Lotus Cultivars. J. Spectrosc. 2017, 2017, 7124354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, S.-S.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Li, E.-H.; Yang, H.; Huang, W. Identification and antioxidant properties of polyphenols in lotus seed epicarp at different ripening stages. Food Chem. 2015, 185, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirkol, G. Antibacterial activity of the seeds, roots and shoots of Lotus populations. Legume Res. 2018, 41, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arooj, M.; Imran, S.; Inam-ur-Raheem, M.; Rajoka, M.S.R.; Sameen, A.; Siddique, R.; Sahar, A.; Tariq, S.; Riaz, A.; Hussain, A.; et al. Lotus seeds (Nelumbinis semen) as an emerging therapeutic seed: A comprehensive review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 3971–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poornima, P.; Quency, R.S.; Padma, V.V. Neferine induces reactive oxygen species mediated intrinsic pathway of apoptosis in HepG2 cells. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.B. Cultivation of lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn. ssp. nucifera) and its utilization in China. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2009, 56, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Yan, S.; Li, J. Impact of harvesting time on the chemical composition and quality of fresh lotus seeds. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2020, 61, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, R.; Han, Y.; Wu, W.; Fang, X.; Mu, H.; Gao, H.; Chen, H. Perspectives. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 205, 112522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.-B.; Xu, L.-B.; Chi, W.-W.; Jia, X.-Z.; Zeng, S. Nutrient composition and in vitro glycemic index of lotus seeds harvested at different stages of maturation. Curr. Top. Nutraceutical Res. 2015, 13, 249–258. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhong, B.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Shi, L.; Aziz, A.; Rauf, A.; Aljohani, A.S.M.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Suleria, H.A.R. LC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS Characterization and Estimation of the Antioxidant Potential of Phenolic Compounds from Different Parts of the Lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) Seed and Rhizome. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 14630–14642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Zeng, S.; Huang, X.; Guo, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zheng, B. Nutritional composition, physiological functions and processing of lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.) seeds: A review. Phytochem. Rev. 2015, 14, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.-L.; Liu, X.-X.; Huang, X.-Y.; Dai, X.-M.; Zhang, M.; Fang, F.-F.; Luo, L.-P. Chemical Deterioration of Lotus Seeds during Storage. J. Food Qual. 2016, 39, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhull, S.B.; Chandak, A.; Collins, M.N.; Bangar, S.P.; Chawla, P.; Singh, A. Lotus Seed Starch: A Novel Functional Ingredient with Promising Properties and Applications in Food—A Review. Starch-Starke 2022, 74, 2200064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Orthofer, R.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of folin-ciocalteu reagent. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 299, 152–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zheng, H.; Sheng, K.; Liu, W.; Zheng, L. Effects of melatonin treatment on the postharvest quality of strawberry fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2018, 139, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Lin, W.; Tong, L.; Liu, X.; Zhong, K.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Zhou, S. Hypolipidaemic effects of oat flakes and β-glucans derived from four Chinese naked oat (Avena nuda) cultivars in Wistar–Lewis rats. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Zhi, H.; Yang, C.; Wang, L.; Long, J.; Xiao, L.; Liang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, S.; et al. Chemical composition of alkaloids of Plumula nelumbinis and their antioxidant activity from different habitats in China. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 125, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, F.; Ouyang, L.; Deng, N.; Yin, F.; He, J.; Lei, D.; Gao, J.; Zeng, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; et al. Determination of 7 Kinds of Alkaloids in Semen Nelumbinis and Its Products by HPLC. Processes 2022, 10, 2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Ren, J.; Liu, C.; Jiang, J.; Yang, H.; Li, J. Genetic characteristics and QTL analysis of the soluble sugar content in ripe tomato fruits. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 276, 109785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puspa, H.Y.D.A.; Ni’matullah, A.B.A.; Mohamad, L.A.; Mulyana, H.; Wisnu, B. Protein Content in Snake Fruit Cultivar Pondoh (Salacca edulis Reinw.) with Aseptic Condition in Room Storage. J. Appl. Food Technol. 2019, 6, 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Siaw, M.O.; Wang, Y.-J.; McClung, A.M.; Mauromoustakos, A. Effect of protein denaturation and lipid removal on rice physicochemical properties. LWT 2021, 150, 112015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemour, K.; Adda, A.; Chouhim, K.M.A.; Labdelli, A.; Merah, O. Amylase Activity and Soluble Sugars Content of Durum Wheat Seeds During Germination Under Water Stress. Agric. Res. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; Ao, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Wu, B.; Li, X.; Wang, G.; Xiao, J.; et al. qFC6, a major gene for crude fat content and quality in rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 2675–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Mu, X.; Cui, H.; Sun, Y.; Xue, J.; Jia, X.; Li, R. Comprehensive mining of storage oil related genes in developing seed of Abelmoschus esculentus. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 291, 110612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Kahramanoglu, I.; Chen, J.; Gan, Z.; Chen, C. Effects of Hot Air Treatments on Postharvest Storage of Newhall Navel Orange. Plants 2020, 9, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Centeno, M.R.; Rosselló, C.; Simal, S.; Garau, M.C.; López, F.; Femenia, A. Physico-chemical properties of cell wall materials obtained from ten grape varieties and their byproducts: Grape pomaces and stems. LWT 2010, 43, 1580–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agasimani, S.; Selvakumar, G.; Joel, A.J.; Ram, S.G. A Simple and Rapid Single Kernel Screening Method to Estimate Amylose Content in Rice Grains. Phytochem. Anal. 2013, 24, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Kim, H.-R.; Lim, M.-H.; Ko, H.-M.; Chin, J.-E.; Lee, H.B.; Kim, I.-C.; Bai, S. Construction of a direct starch-fermenting industrial strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae producing glucoamylase, α-amylase and debranching enzyme. Biotechnol. Lett. 2010, 32, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Huang, B.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Rivenbark, J.; Lappe, R.L.; James, M.G.; Myers, A.M.; Hennen-Bierwagen, T.A. Functional Interactions between Starch Synthase III and Isoamylase-Type Starch-Debranching Enzyme in Maize Endosperm. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanlayavattanakul, M.; Chaikul, P.; Kongkow, M.; Iempridee, T.; Lourith, N. Anti-aging of phenolic-rich Acanthus ebracteatus Vahl. extracts. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2023, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Yifei, Y.; Zhiqin, Z. Phenolic and flavonoid contents of mandarin(Citrus reticulata Blanco) fruit tissues and their antioxidant capacity as evaluated by DPPH and ABTS methods. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cao, Y.; Chen, S.; Lin, J.; Bian, J.; Huang, D. Anti-Inflammation Activity of Flavones and Their Structure-Activity Relationship. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 7285–7302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Gao, Y.; Huang, J. Extraction and purification of antioxidative flavonoids from Chionanthus retusa leaf. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1085562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouéour, G.L.; Thépenier, P.; Richard, B.; Petermann, C.; Ghédira, K.; Zèches-Hanrot, M. Lotusine G: A new cyclopeptide alkaloid from Zizyphus lotus. Fitoterapia 2002, 73, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Liu, T.; Guo, M. Current Advances in the Metabolomics Study on Lotus Seeds. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.-Y.; Cai, L.-H.; Cai, X.-L.; Wang, Y.-J.; Li, Y.-Q. Structure characterization of protein fractions from lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) seed. J. Mol. Struct. 2011, 1001, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emilio, A.P.; Rafael, U.L.; de la Rosa, L.A. Bioactive components and health effects of pecan nuts and their byproducts: A review. J. Food Bioact. 2018, 1, 56–92. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, R.; Sridhar, K.R. Nutritional quality evaluation of electron beam-irradiated lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) seeds. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Chen, B.; Zeng, H.; Guo, Z.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, B. Effect of Microwave Irradiation on the Physicochemical and Digestive Properties of Lotus Seed Starch. In Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Phytochemicals in Medicine and Food (ISPMF), Shanghai, China, 26–29 June 2015; pp. 2442–2449. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.-J.; Shin, H.-S. Antioxidative effect of lotus seed and seedpod extracts. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 21, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.M.; Guo, X.; Fu, X.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yan, H.; Liu, R.H. Comparative Assessment of Phenolic Content and in Vitro Antioxidant Capacity in the Pulp and Peel of Mango Cultivars. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 13507–13527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manthey, J.A.; Perkins-Veazie, P. Influences of Harvest Date and Location on the Levels of beta-Carotene, Ascorbic Acid, Total Phenols, the in Vitro Antioxidant Capacity, and Phenolic Profiles of Five Commercial Varieties of Mango (Mangifera indica L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 10825–10830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Shen, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Jiang, H.; Bi, H.; Huang, M.; Zhou, H.; Zeng, S. In vitro characterization of ABC transporters involved in the absorption and distribution of liensinine and its analogs. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 150, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Chen, W.; Han, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ye, J.; Wang, H.; Gao, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y. The Taste-Masking Mechanism of Chitosan at the Molecular Level on Bitter Drugs of Alkaloids and Flavonoid Glycosides from Traditional Chinese Medicine. Molecules 2022, 27, 7455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Tian, Y.; Ke, X.-M.; Tan, Q.-C.; Han, X.; Ma, H.-Y.; Pei, J.; Lin, J.-Z.; Xu, R.-C.; Han, L.; et al. Amphiphilic Block Copolymers: A Novel Substance for Bitter-Masking in Aqueous Solutions. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 1586–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Cultivar | HB | HH | JB | JY | WX | SD | CS | TK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liensinine | 0.93 ± 0.02 a | 0.49 ± 0.01 c | 0.48 ± 0.01 c | 0.15 ± 0.01 g | 0.30 ± 0.01 f | 0.42 ± 0.01 d | 0.37 ± 0.00 e | 0.6 ± 0.02 b |
| Isoliensinine | 2.69 ± 0.03 d | 2.89 ± 0.01 c | 3.06 ± 0.00 b | 2.96 ± 0.01 c | 2.65 ± 0.01 d | 2.67 ± 0.01 d | 3.08 ± 0.01 b | 3.22 ± 0.08 a |
| Neferine | 7.87 ± 0.00 e | 8.89 ± 0.01 b | 6.96 ± 0.00 h | 8.63 ± 0.01 d | 7.02 ± 0.04 g | 8.73 ± 0.00 c | 9.47 ± 0.01 a | 7.42 ± 0.04 f |
| Lotusine | 6.95 ± 0.01 c | 7.02 ± 0.01 b | 6.35 ± 0.01 d | 6.94 ± 0.01 c | 5.88 ± 0.03 f | 5.91 ± 0.00 f | 7.09 ± 0.01 a | 6.08 ± 0.03 e |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Dong, W.; Yi, Y.; Wang, L.; Hou, W.; Ai, Y.; Wang, H.; Min, T. Comparison of Nutritional Quality and Functional Active Substances in Different Parts of Eight Lotus Seed Cultivars. Foods 2024, 13, 2335. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13152335
Liu X, Dong W, Yi Y, Wang L, Hou W, Ai Y, Wang H, Min T. Comparison of Nutritional Quality and Functional Active Substances in Different Parts of Eight Lotus Seed Cultivars. Foods. 2024; 13(15):2335. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13152335
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xueting, Wanyu Dong, Yang Yi, Limei Wang, Wenfu Hou, Youwei Ai, Hongxun Wang, and Ting Min. 2024. "Comparison of Nutritional Quality and Functional Active Substances in Different Parts of Eight Lotus Seed Cultivars" Foods 13, no. 15: 2335. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13152335
APA StyleLiu, X., Dong, W., Yi, Y., Wang, L., Hou, W., Ai, Y., Wang, H., & Min, T. (2024). Comparison of Nutritional Quality and Functional Active Substances in Different Parts of Eight Lotus Seed Cultivars. Foods, 13(15), 2335. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13152335





