Comprehensive Analysis of the Yield and Leaf Quality of Fresh Tea (Camellia sinensis cv. Jin Xuan) under Different Nitrogen Fertilization Levels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Experimental Design and Collection of Tea Samples
2.3. Determination of Total Polyphenols
2.4. Determination of Free Amino Acids
2.5. Determination of Chlorophyll
2.6. Analysis of Caffeine, Theanine, and Catechins
2.7. Gene Expression Analysis by qPCR
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
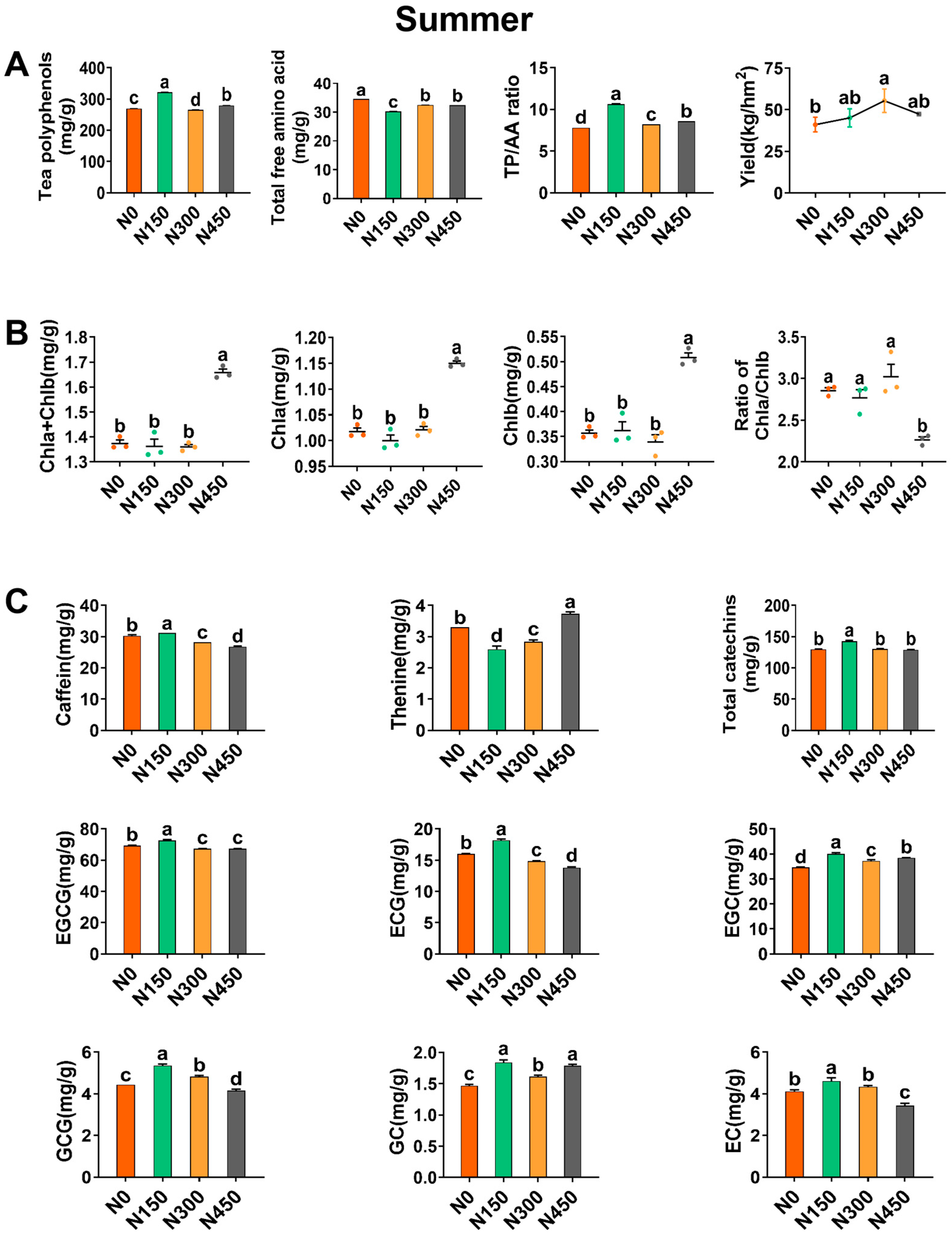
3.1. Effects of Summer Nitrogen Application on Yield and Biochemical Components
3.1.1. Effect of Summer Nitrogen Application on Yield
3.1.2. Effect of Summer Nitrogen Application on Chlorophyll
3.1.3. The Influence of Nitrogen Application in Summer on the Total Polyphenol Content and the Total Content of Free Amino Acids
3.1.4. Effect of Summer Nitrogen Application on Caffeine, Theanine, and Catechins
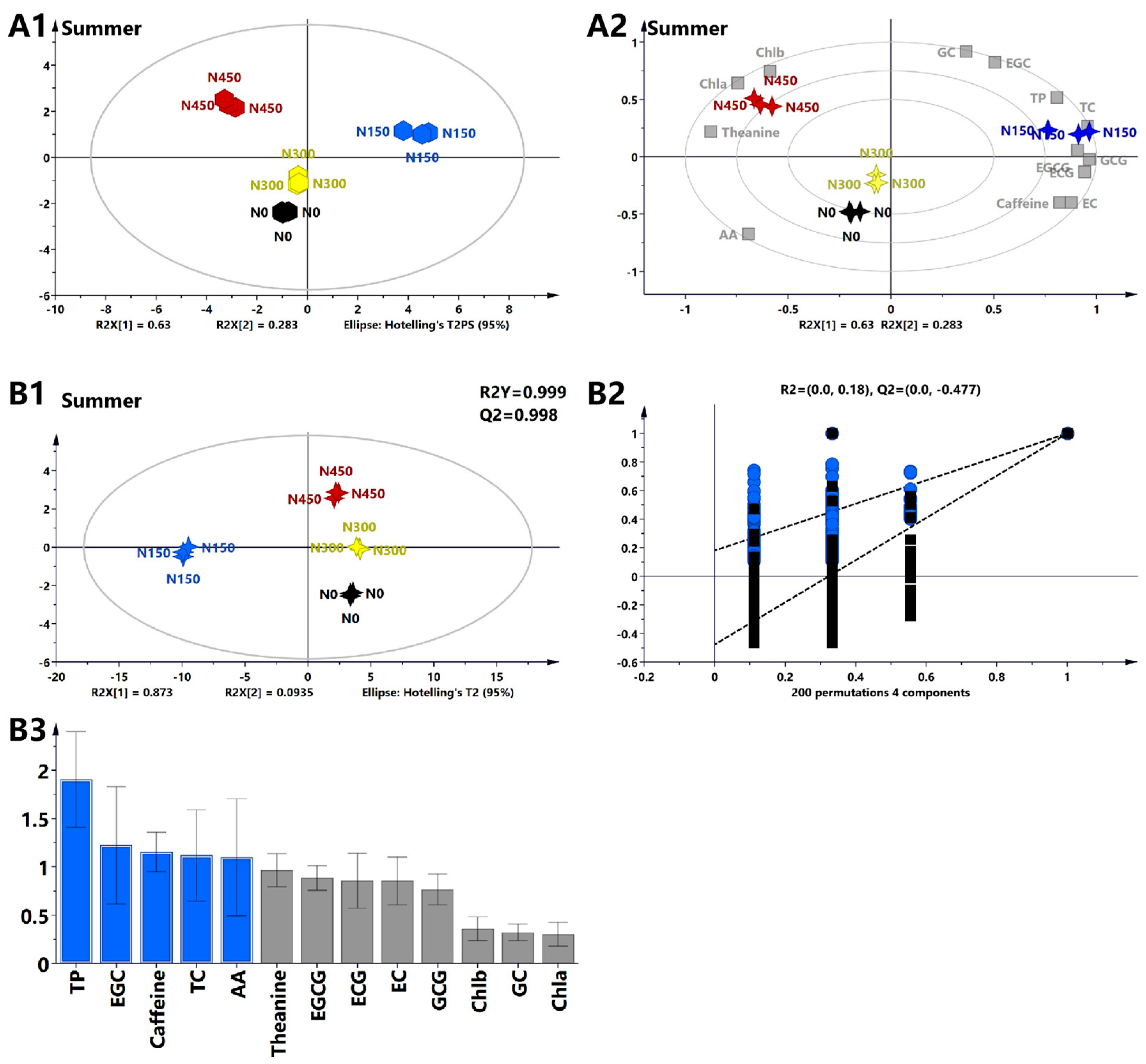
3.1.5. Multivariate Statistical Analysis of the Primary Biochemical Components of Tea Leaves in Summer
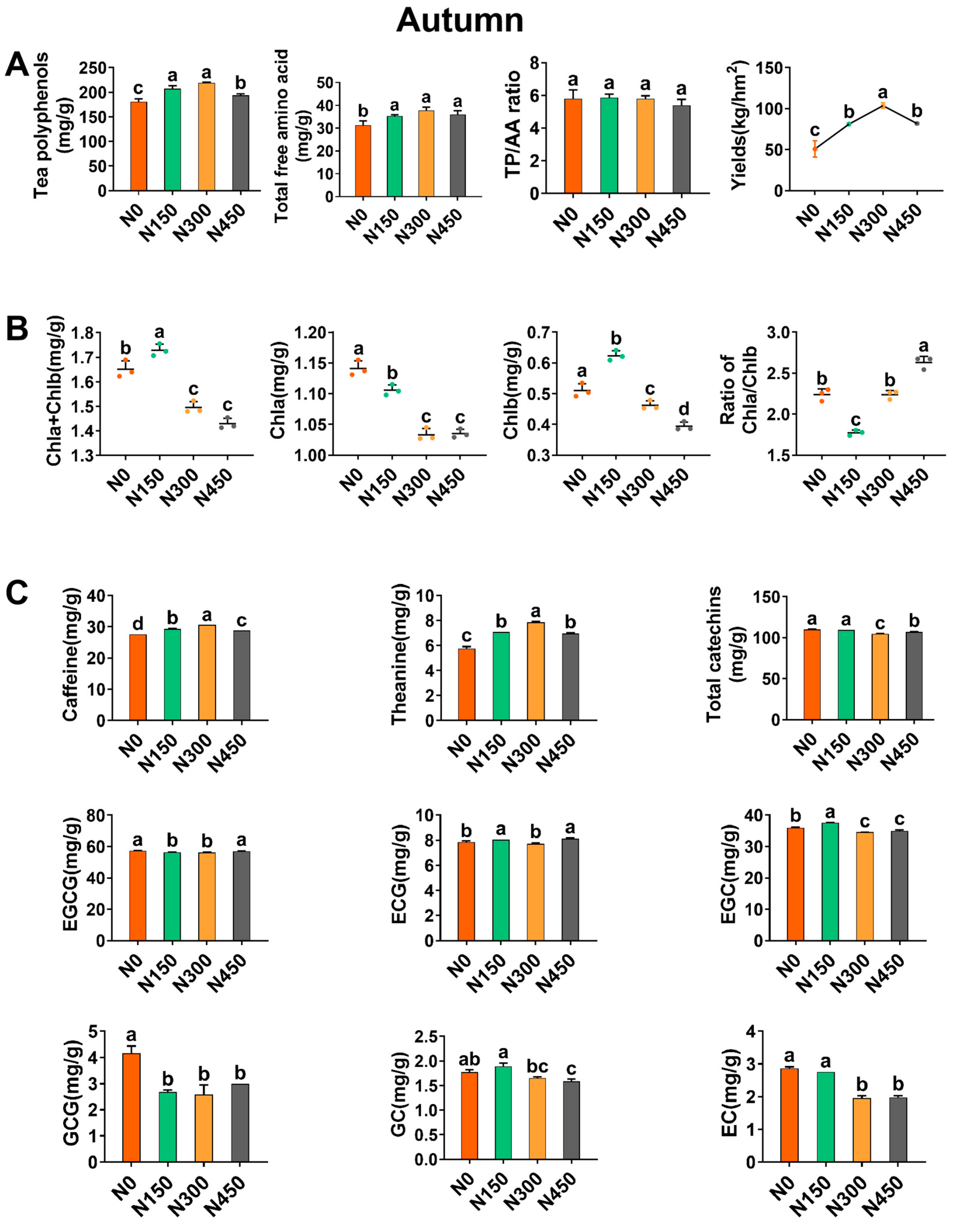
3.2. Effects of Summer Nitrogen Application on Yield and Biochemical Components
3.2.1. Effect of Autumn Nitrogen Application on Yield
3.2.2. Effect of Autumn Nitrogen Application on Chlorophyll
3.2.3. The Influence of Nitrogen Application in Autumn on the Total Polyphenol Content and the Total Content of Free Amino Acids
3.2.4. Effect of Autumn Nitrogen Application on Caffeine, Theanine, and Catechins
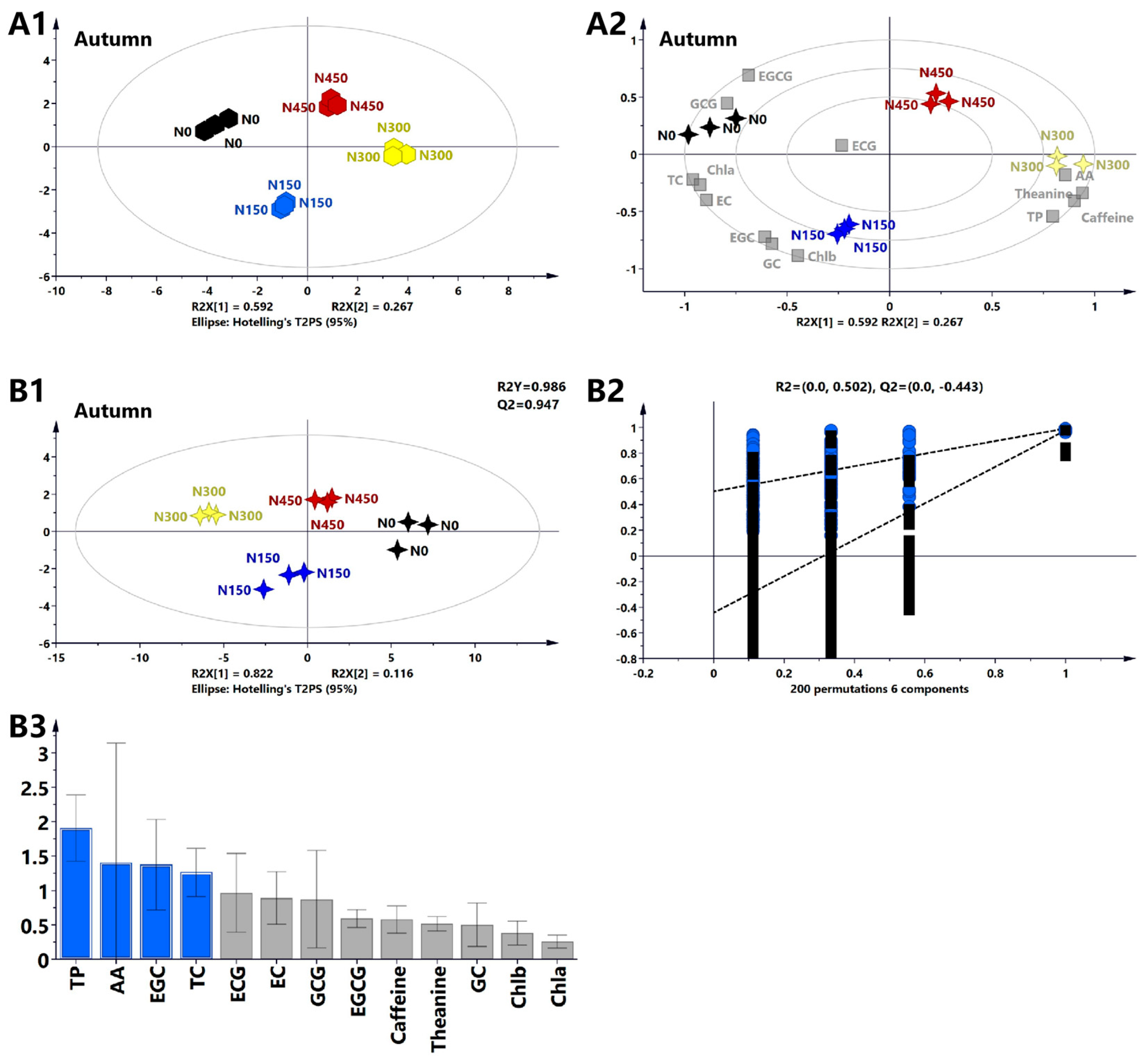
3.2.5. Multivariate Statistical Analysis of the Primary Biochemical Components of Tea Leaves in Autumn
3.3. The Effect of Nitrogen Application on Gene Expression Levels in Summer and Autumn
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, T.; Lin, S.; Chen, Z.; Yang, T.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Xu, G.; Wan, X.; Zhang, Z. Theanine, a tea-plant-specific non-proteinogenic amino acid, is involved in the regulation of lateral root development in response to nitrogen status. Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, uhac267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benti, T.; Debela, A.; Bekele, Y.; Suleman, S. Influence of clone and nitrogen application level on quality of green tea in some selected tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) in Southwest Ethiopia. Heliyon 2022, 8, E10179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Liu, M.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, L.; Shi, Y.; Ruan, J. Preferential assimilation of NH4+ over NO3− in tea plant associated with genes involved in nitrogen transportation, utilization and catechins biosynthesis. Plant Sci. 2020, 291, 110369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Li, H.; Tai, Y.; Dong, C.; Cheng, X.; Xia, E.; Chen, Z.; Li, F.; Wan, X.; Zhang, Z. Transcriptional regulation of amino acid metabolism in response to nitrogen deficiency and nitrogen forms in tea plant root (Camellia sinensis L.). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebello, R.; Burgess, P.J.; Girkin, N.T. Identifying Sustainable Nitrogen Management Practices for Tea Plantations. Nitrogen 2022, 3, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.Y.; Burgos, A.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, D.; Ruan, J. Lipidomics analysis unravels the effect of nitrogen fertilization on lipid metabolism in tea plant (Camellia sinensis L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Ni, K.; Long, L.; Ruan, J. Nitrogen transport and assimilation in tea plant (Camellia sinensis): A review. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1249202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njira, K.O.; Nabwami, J. A review of effects of nutrient elements on crop quality. Afr. J. Food Agric. Nutr. Dev. 2015, 15, 9777–9793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Yi, X.; Li, Y.; Ma, L.; Ruan, J.; Tang, Q. The effect of nitrogen fertilization on biomass and nutrient storage in the fibrous roots of tea plants (Camellia sinensis) during summer and autumn. Acta Ecol. Sinica 2016, 36, 411–419. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yan, P.; Shen, C.; Fan, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Han, W. Tea planting affects soil acidification and nitrogen and phosphorus distribution in soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 254, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Hao, S.; Zhou, J.; Feng, W.; Zhu, M.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y. Profiling volatile compounds in fresh leaves of 22 major oolong tea germplasm cultivated in Fujian of China. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 327, 112849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Li, D.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, T.; Ling, T.; Chen, Q. Research Advance on Tea Biochemistry. J. Tea Sci. 2015, 35, 1–10. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Jin, J.; Sun, C.; Ye, D.; Liu, Y. Simultaneous determination of six main types of lipid-soluble pigments in green tea by visible and near-infrared spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2019, 270, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Lu, Y.T.; Qiu, Q.L.; Fan, D.M.; Wang, X.C.; Zheng, X.Q. Influence of different nitrogen sources on carbon and nitrogen metabolism and gene expression in tea plants (Camellia sinensis L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 167, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Ye, J.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Zheng, X.; He, H. Characteristic amino acids in tea leaves as quality indicator for the evaluation of Wuyi Rock Tea in different culturing regions. J. Appl. Bot. Food Qual. 2018, 91, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Duan, J.; Jiang, Y.M.; Shi, J.; Peng, L.; Xue, S.; Kakuda, Y. Production, Quality, and Biological Effects of Oolong Tea (Camellia sinensis). Food Rev. Int. 2011, 27, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zhou, J.; Pan, W.; Tang, R.; Ma, Q.; Xu, M.; Qi, T.; Ma, Z.; Fu, H.; Wu, L. Impact of N application rate on tea (Camellia sinensis) growth and soil bacterial and fungi communities. Plant Soil 2022, 475, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.; Haerdter, R.; Gerendas, J. Impact of nitrogen supply on carbon/nitrogen allocation: A case study on amino acids and catechins in green tea Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze plants. Plant Biol. 2010, 12, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Yao, Q.; Xia, E.; Gao, L. Metabolomics and Transcriptomics Analyses Reveal Nitrogen Influences on the Accumulation of Flavonoids and Amino Acids in Young Shoots of Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis L.) Associated with Tea Flavor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9828–9838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, R.A.J.S. Systems biology for enhanced plant nitrogen nutrition. Science 2012, 336, 1673–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T 2440-2017; Urea. Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- GB/T 8313-2018; Determination of Total Polyphenols and Catechins Content in Tea. State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2018.
- GB/T 8314-2013; Tea-Determination of Free Amino Acids Conten. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- Liu, L.; Lin, N.; Liu, X.; Yang, S.; Wang, W.; Wan, X. From Chloroplast Biogenesis to Chlorophyll Accumulation: The Interplay of Light and Hormones on Gene Expression in Camellia sinensis cv. Shuchazao Leaves. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Cai, J.; Zheng, P.; Yuan, Y.; Tsewang, W.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, X.; Liao, J.; Sun, B.; Liu, S. Quantitatively Unravelling the Impact of High Altitude on Oolong Tea Flavor from Camellia sinensis Grown on the Plateaus of Tibet. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, F.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, F.; Yu, W.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Jian, G.; You, Z.; Zeng, L.J.M. Effects of long-term nitrogen fertilization on the formation of metabolites related to tea quality in subtropical China. Metabolites 2021, 11, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Z.; Liao, J.; Chen, J.; Li, A.; Lin, M.; Liu, H.; Huang, W.; Sun, B.; Liu, J.; Liu, S.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of fresh tea (Camellia sinensis cv. Lingtou Dancong) leaf quality under different nitrogen fertilization regimes. Food Chem. 2024, 439, 138127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, C.; Xu, B.; Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Liu, W.; Wan, S.; Tan, H.; Liu, Y.; et al. Synthetic nitrogen fertilizers alter the soil chemistry, production and quality of tea. A meta-analysis. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 38, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Wang, Y.; Kang, J.; Chen, Y.; Hong, L.; Li, M.; Jia, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jia, X.; Wu, Z.; et al. Effects of Long-Term Use of Organic Fertilizer with Different Dosages on Soil Improvement, Nitrogen Transformation, Tea Yield and Quality in Acidified Tea Plantations. Plants 2023, 12, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, J.; Ma, L.; Yi, X.; Shi, Y.; Ni, K.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Q. Integrated Nutrient Management in Tea Plantation to Reduce Chemical Fertilizer and Increase Nutrient Use Efficiency. J. Tea Sci. 2020, 40, 85–95. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Begum, Y.; Mondal, S.K. Comprehensive study of the genes involved in chlorophyll synthesis and degradation pathways in some monocot and dicot plant species. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 2387–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piyasena, K.N.P.; Hettiarachchi, L.J.F.C.A. Comparison of tea quality parameters of conventionally and organically grown tea, and effects of fertilizer on tea quality: A mini-review. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 3, 100399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Yang, X.; Shi, Y.; Yi, X.; Ji, L.; Cheng, Y.; Ni, K.; Ruan, J. Response of tea yield, quality and soil bacterial characteristics to long-term nitrogen fertilization in an eleven-year field experiment. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 166, 103976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuah, Y.Q.; Chang, S.K.; Ng, W.J.; Lam, M.Q.; Ee, K.Y. A review on matcha: Chemical composition, health benefits, with insights on its quality control by applying chemometrics and multi-omics. Food Res. Int. 2023, 170, 113007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, F.; Li, B.; Pang, Y.; Du, Z. Appropriate Nitrogen Form and Application Rate Can Improve Yield and Quality of Autumn Tea with Drip Irrigation. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Bai, Y.; Jin, Z.; Long, L.; Diao, W.; Chen, W.; Tan, L.; Tang, Q.; Tang, D. Effects of the Combined Application of Nitrogen and Selenium on Tea Quality and the Expression of Genes Involved in Nitrogen Uptake and Utilization in Tea Cultivar ‘Chuancha No.2’. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Han, Z.; Zhai, X.; Qin, C.; Wen, M.; Lai, G.; Ho, C.T.; Zhang, L.; Wan, X. Study on In Vitro Preparation and Taste Properties of N-Ethyl-2-Pyrrolidinone-Substituted Flavan-3-Ols. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 3832–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Liu, F.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.; Xu, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Gong, Y.; Yang, X. Analysis of chemical components in oolong tea in relation to perceived quality. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hua, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yuan, H. Influence of fixation methods on the chestnut-like aroma of green tea and dynamics of key aroma substances. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokharel, S.S.; Zhong, Y.; Changning, L.; Shen, F.; Li, L.; Parajulee, M.N.; Fang, W.; Chen, F. Influence of reduced N-fertilizer application on foliar chemicals and functional qualities of tea plants under Toxoptera aurantii infestation. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, W.; Li, Q.; Hu, X.; Zhang, D.; Yu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, M.; Ni, D. Comprehensive analysis of environmental factors on the quality of tea (Camellia sinensis var. sinensis) fresh leaves. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 319, 112177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.Q.; Nie, Y.; Gao, Y.; Huang, B.; Ye, J.H.; Lu, J.L.; Liang, Y.-R. Screening the cultivar and processing factors based on the flavonoid profiles of dry teas using principal component analysis. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2018, 67, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Hu, J.H.; Shi, Y.Z.; Liu, M.Y.; Zhang, Q.F.; Ruan, J.Y. Effects of nitrogen supply on flavonol glycoside biosynthesis and accumulation in tea leaves (Camellia sinensis). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 138, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.; Qian, Y.; Qiu, J. Identification of markers for tea authenticity assessment: Non-targeted metabolomics of highly similar oolong tea cultivars (Camellia sinensis var. sinensis). Food Control 2022, 142, 109223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, B.; Gardeström, P.; Keech, O. In response to partial plant shading, the lack of phytochrome A does not directly induce leaf senescence but alters the fine-tuning of chlorophyll biosynthesis. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 4037–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petroutsos, D.; Tokutsu, R.; Maruyama, S.; Flori, S.; Greiner, A.; Magneschi, L.; Cusant, L.; Kottke, T.; Mittag, M.; Hegemann, P.; et al. A blue-light photoreceptor mediates the feedback regulation of photosynthesis. Nature 2016, 537, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, J.; Qiu, Z.; Liao, J.; Li, A.; Chen, J.; Wu, Z.; Khan, W.; Sun, B.; Liu, S.; Zheng, P. Comprehensive Analysis of the Yield and Leaf Quality of Fresh Tea (Camellia sinensis cv. Jin Xuan) under Different Nitrogen Fertilization Levels. Foods 2024, 13, 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132091
Cai J, Qiu Z, Liao J, Li A, Chen J, Wu Z, Khan W, Sun B, Liu S, Zheng P. Comprehensive Analysis of the Yield and Leaf Quality of Fresh Tea (Camellia sinensis cv. Jin Xuan) under Different Nitrogen Fertilization Levels. Foods. 2024; 13(13):2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132091
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Jiajun, Zihao Qiu, Jinmei Liao, Ansheng Li, Jiahao Chen, Zehui Wu, Waqar Khan, Binmei Sun, Shaoqun Liu, and Peng Zheng. 2024. "Comprehensive Analysis of the Yield and Leaf Quality of Fresh Tea (Camellia sinensis cv. Jin Xuan) under Different Nitrogen Fertilization Levels" Foods 13, no. 13: 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132091
APA StyleCai, J., Qiu, Z., Liao, J., Li, A., Chen, J., Wu, Z., Khan, W., Sun, B., Liu, S., & Zheng, P. (2024). Comprehensive Analysis of the Yield and Leaf Quality of Fresh Tea (Camellia sinensis cv. Jin Xuan) under Different Nitrogen Fertilization Levels. Foods, 13(13), 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132091




