SNP Array for Small-Shrimp (Genus Acetes) Origin Determination Using Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Sequence Analyzing
2.3. SNP Discovery
2.4. Designing SNP Genotyping Array
2.5. Machine Learning Analysis
3. Results
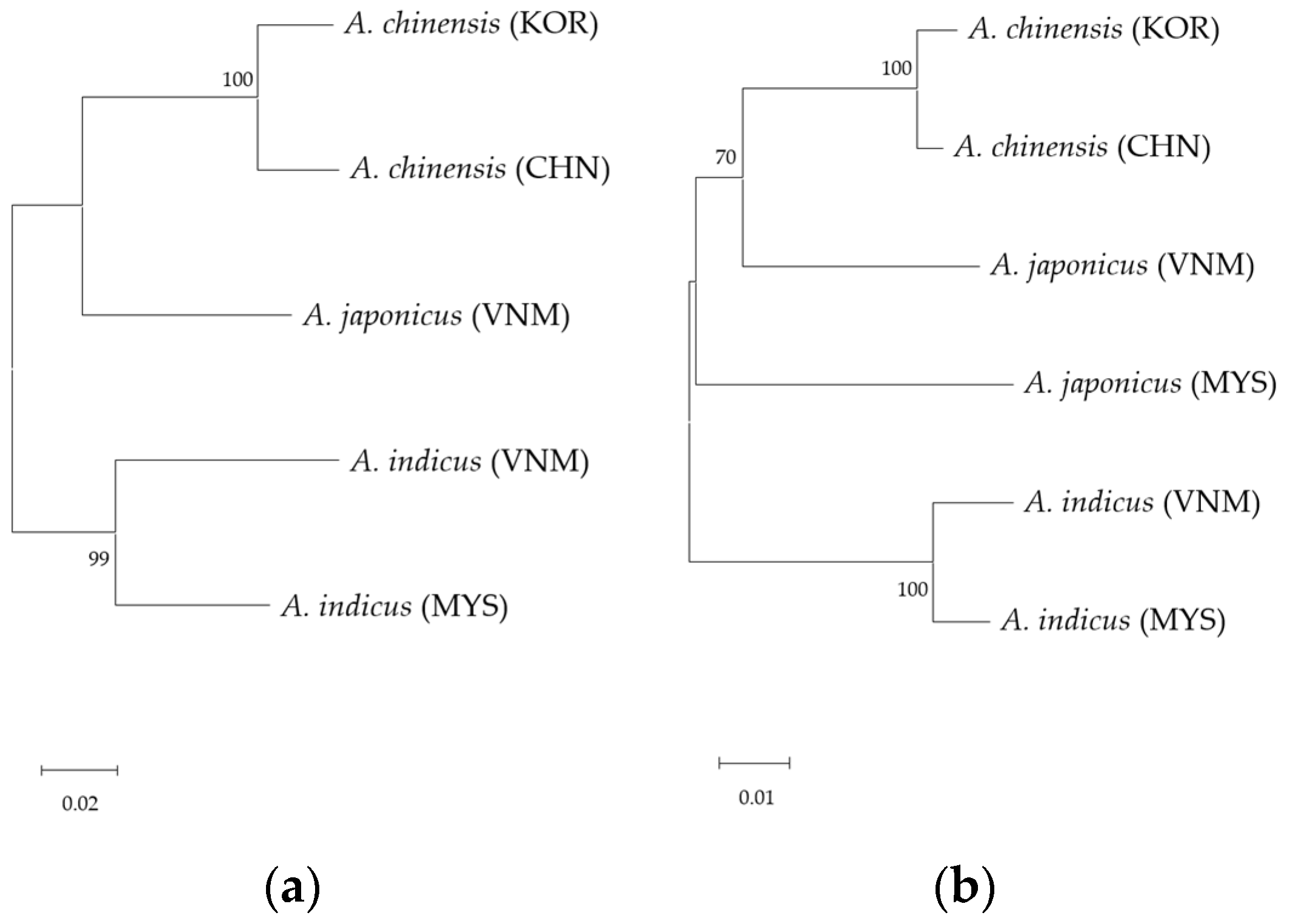
3.1. Sequencing Analysis
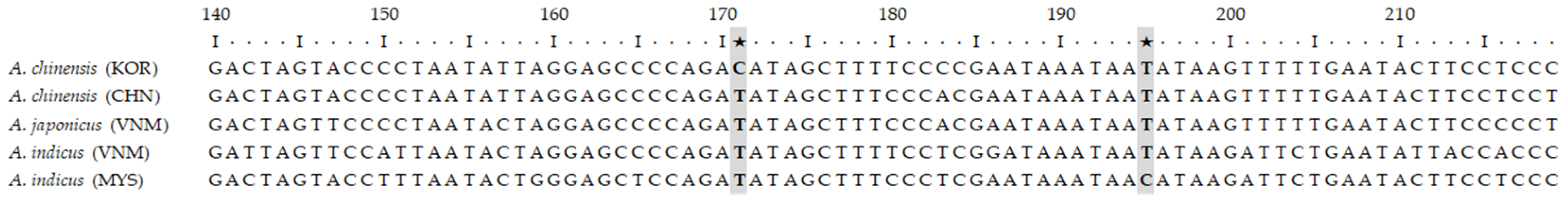
3.2. SNP Discovery
3.3. Designing SNP Genotyping Array
3.4. Analyzing Genotyping Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hicks, D. Seafood safety and quality: The consumer’s role. Foods 2016, 5, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lulijwa, R.; Rupia, E.J.; Alfaro, A.C. Antibiotic use in aquaculture, policies and regulation, health and environmental risks: A review of the top 15 major producers. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 640–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sheikha, A.F.; Xu, J. Traceability as a key of seafood safety: Reassessment and possible applications. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2017, 25, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onozaka, Y.; Honkanen, P.; Altintzoglou, T. Sustainability, perceived quality and country of origin of farmed salmon: Impact on consumer choices in the USA, France and Japan. Food Policy 2023, 117, 102452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizik, T. Agri-food trade competitiveness: A review of the literature. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claret, A.; Guerrero, L.; Aguirre, E.; Rincón, L.; Hernández, M.D.; Martínez, I.; Peleteiro, J.B.; Grau, A.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, C. Consumer preferences for sea fish using conjoint analysis: Exploratory study of the importance of country of origin, obtaining method, storage conditions and purchasing price. Food Qual. Prefer. 2012, 26, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, E.S.; Park, Y.J.; Kim, E.M.; An, C.M.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Song, J.H.; Kang, J.H. Development of primer set for the identification of fish species in surimi products using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Food Control 2017, 79, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.-H.; Kang, H.-S.; Noh, E.-S.; Park, J.-Y.; An, C.-M. Isolation and characterization of novel microsatellite markers for the northern mauxia shrimp, Acetes chinensis, using pyrosequencing. Mar. Genom. 2014, 18, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.-H.; Noh, E.-S.; Park, J.-Y.; An, C.-M.; Choi, J.-H.; Kim, J.-K. Rapid origin determination of the northern mauxia shrimp (Acetes chinensis) based on allele specific polymerase chain reaction of partial mitochondrial 16S rRNA gene. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 28, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.M.; Byun, S.G.; An, C.M.; Kang, J.H.; An, H.S.; Dong, C.M.; Kim, M.J.; Hong, Y.K.; Park, J.Y. Development of single nucleotide polymorphism markers from ESTs for discrimination between domestic and imported manila clams, Ruditapes philippinarum. Food Control 2014, 40, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, E.S.; Kang, H.S.; An, C.M.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, E.M.; Kang, J.H. Rapid and specific identification of genus Cynoglossus by multiplex PCR assays using species-specific derived from the COI region. J. Life Sci. 2016, 26, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, E.S.; Lee, M.N.; Kim, E.M.; Park, J.Y.; Noh, J.K.; An, C.M.; Kang, J.H. Development of a multiplex PCR assay for rapid identification of Larimichthys polyactis, L. crocea, Atrobucca nibe, and Pseudotolithus elongates. J. Life Sci. 2017, 27, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-M.; Dong, C.M.; Lee, M.N.; Noh, J.K.; Noh, E.S.; Nam, B.H.; Kim, Y.-O.; Jung, H.S. Development of multiplex species-specific PCR for the simultaneous identification of three closely related species in the genera Misgurnus and Paramisgurnus. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 24, 101144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaad, I.; Lundquist, C.J.; Erdmann, M.V.; Costello, M.J. Ecological criteria to identify areas for biodiversity conservation. Biol. Conserv. 2017, 213, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.K.; Luikart, G.; Waples, R.S. Genetic monitoring as a promising tool for conservation and management. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breed, M.F.; Harrison, P.A.; Blyth, C.; Byrne, M.; Gaget, V.; Gellie, N.J.C.; Hodgson, R.; Mills, J.G.; Prowse, T.A.A.; Steane, D.A.; et al. The potential of genomics for restoring ecosystems and biodiversity. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čandek, K.; Kuntner, M. DNA barcoding gap: Reliable species identification over morphological and geographical scales. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leaché, A.D.; Oaks, J.R. The utility of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) data in phylogenetics. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2017, 48, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canturk, K.M.; Emre, R.; Kınoglu, K.; Başpınar, B.; Sahin, F.; Ozen, M. Current status of the use of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in forensic practices. Genet. Test Mol. Biomark. 2014, 18, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, M.I.; Mitchell, T.M. Machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospects. Science 2015, 349, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, J.C.; Mirzal, A.; Haron, H.; Hamed, H.N.A. Supervised, unsupervised, and semi-supervised feature selection: A review on gene selection. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf. 2016, 13, 971–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swan, A.L.; Mobasheri, A.; Allaway, D.; Liddell, S.; Bacardit, J. Application of machine learning to proteomics data: Classification and biomarker identification in postgenomics biology. OMICS 2013, 17, 595–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Liang, Y.; Li, Y.; Du, W. Long noncoding RNA identification: Comparing machine learning based tools for long noncoding transcripts discrimination. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 8496165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Palumbi, S.R.; Martin, A.; Romano, S.; McMillan, W.O.; Stice, L.; Grabowski, G.; University of Hawaii at Manoa; Kewalo Marine Laboratory (Eds.) The Simple Fool’s Guide to PCR, Version 2.0; Department of Zoology and Kewalo Marine Laboratory, University of Hawaii: Honolulu, HI, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformationcs 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, M.; Frank, E.; Holmes, G.; Pfahringer, B.; Reutemann, P.; Witten, I.H. The WEKA data mining software: An update. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newsl. 2009, 11, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, L.; Soon, J.M. Food safety, food fraud, and food defense: A fast evolving literature. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, R823–R834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurica, K.; Brčić Karačonji, I.; Lasić, D.; Bursać Kovačević, D.; Putnik, P. Unauthorized food manipulation as a criminal offense: Food authenticity, legal frameworks, analytical tools and cases. Foods 2021, 10, 2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sample No. | Indicated Origin | Collection Date | Population Size | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Korea | Sinan-gun | 7 March 2023 | 48 |
| 2 | Korea | - | 7 March 2023 | 48 |
| 3 | Korea | Ganghwa-gun | 7 March 2023 | 47 |
| 4 | Korea | - | 8 March 2023 | 48 |
| 5 | Korea | Incheon-si | 24 March 2023 | 48 |
| 6 | Korea | Yeonpyeong Island | 24 March 2023 | 43 |
| 7 | Korea | Boryeong-si | 24 March 2023 | 48 |
| 8 | Korea | Taean-gun | 24 March 2023 | 47 |
| 9 | Korea | - | 24 March 2023 | 48 |
| 10 | Korea | Mokpo-si | 24 March 2023 | 48 |
| 11 | China | - | 24 March 2023 | 46 |
| 12 | Vietnam | - | 7 March 2023 | 46 |
| 13 | Vietnam | - | 7 March 2023 | 48 |
| 14 | Malysia | - | 26 June 2023 | 23 |
| Species (Origin) | COI Region | 16S rRNA Region | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 171 | 195 | 135 | 206 | 291 | 322 | 411 | 458 | |
| A. chinensis (KOR) | C | T | A | C | A | A | A | T |
| A. chinensis (CHN) | T | T | A | C | A | A | A | T |
| A. japonicus (VNM) | T | T | A | C | T | A | A | C |
| A. japonicus (MYS) | - | - | A | T | A | A | T | T |
| A. indicus (VNM) | T | T | A | C | A | G | A | C |
| A. indicus (MYS) | T | C | G | C | A | A | A | C |
| SNP ID | Target Gene | Position | SNP | Fluidigm Assay ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| COI-171 | COI | 171 | ..CCAGA[C/T]ATAGC.. | GTA0343170 |
| COI-195 | COI | 195 | ..AATAA[C/T]ATAAG.. | GTA0343171 |
| 16S-135 | 16S rRNA | 135 | ..TTTAA[G/A]AATTA.. | GTA0343174 |
| 16S-206 | 16S rRNA | 206 | ..CTTTA[T/C]TGTTT.. | GTA0343420 |
| 16S-417 | 16S rRNA | 411 | ..GTCCA[T/A]ATCGA.. | GTA0343172 |
| 16S-464 | 16S rRNA | 458 | …CCTTT[T/C]TAATG.. | GTA0343173 |
| Species (Origin) | Sample 1 (Korea) | Sample 2 (China) | Sample 3 (Vietnam 1) | Sample 4 (Vietnam 2) | Sample 5 (Malaysia) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. chinensis (KOR) | 16 | - | - | - | - |
| A. chinensis (CHN) | - | 16 | - | - | - |
| A. japonicus (VNM) | - | - | 16 | 16 | - |
| A. japonicus (MYS) | - | - | - | - | 7 |
| A. indicus (VNM) | - | - | - | - | - |
| A. indicus (MYS) | - | - | - | - | 25 |
| Species accuracy | 100% | 100% | 100% | 0% | 100% |
| Origin accuracy | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noh, E.S.; Lee, M.N.; Dong, C.-M.; Park, J.; Jung, H.S.; Kim, W.-J.; Kim, Y.-O. SNP Array for Small-Shrimp (Genus Acetes) Origin Determination Using Machine Learning. Foods 2024, 13, 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132087
Noh ES, Lee MN, Dong C-M, Park J, Jung HS, Kim W-J, Kim Y-O. SNP Array for Small-Shrimp (Genus Acetes) Origin Determination Using Machine Learning. Foods. 2024; 13(13):2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132087
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoh, Eun Soo, Mi Nan Lee, Chun-Mae Dong, Jungwook Park, Hyo Sun Jung, Woo-Jin Kim, and Young-Ok Kim. 2024. "SNP Array for Small-Shrimp (Genus Acetes) Origin Determination Using Machine Learning" Foods 13, no. 13: 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132087
APA StyleNoh, E. S., Lee, M. N., Dong, C.-M., Park, J., Jung, H. S., Kim, W.-J., & Kim, Y.-O. (2024). SNP Array for Small-Shrimp (Genus Acetes) Origin Determination Using Machine Learning. Foods, 13(13), 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132087






