Characterization of Degraded Konjac Glucomannan from an Isolated Bacillus licheniformis Strain with Multi-Enzyme Synergetic Action
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Isolation and Identification of KGM-Degrading Bacteria
2.3. TLC Analysis of KGM Hydrolysis Products
2.4. Growth and Enzyme Production
2.5. Determination of KGM Degradation Ability of Z7-1
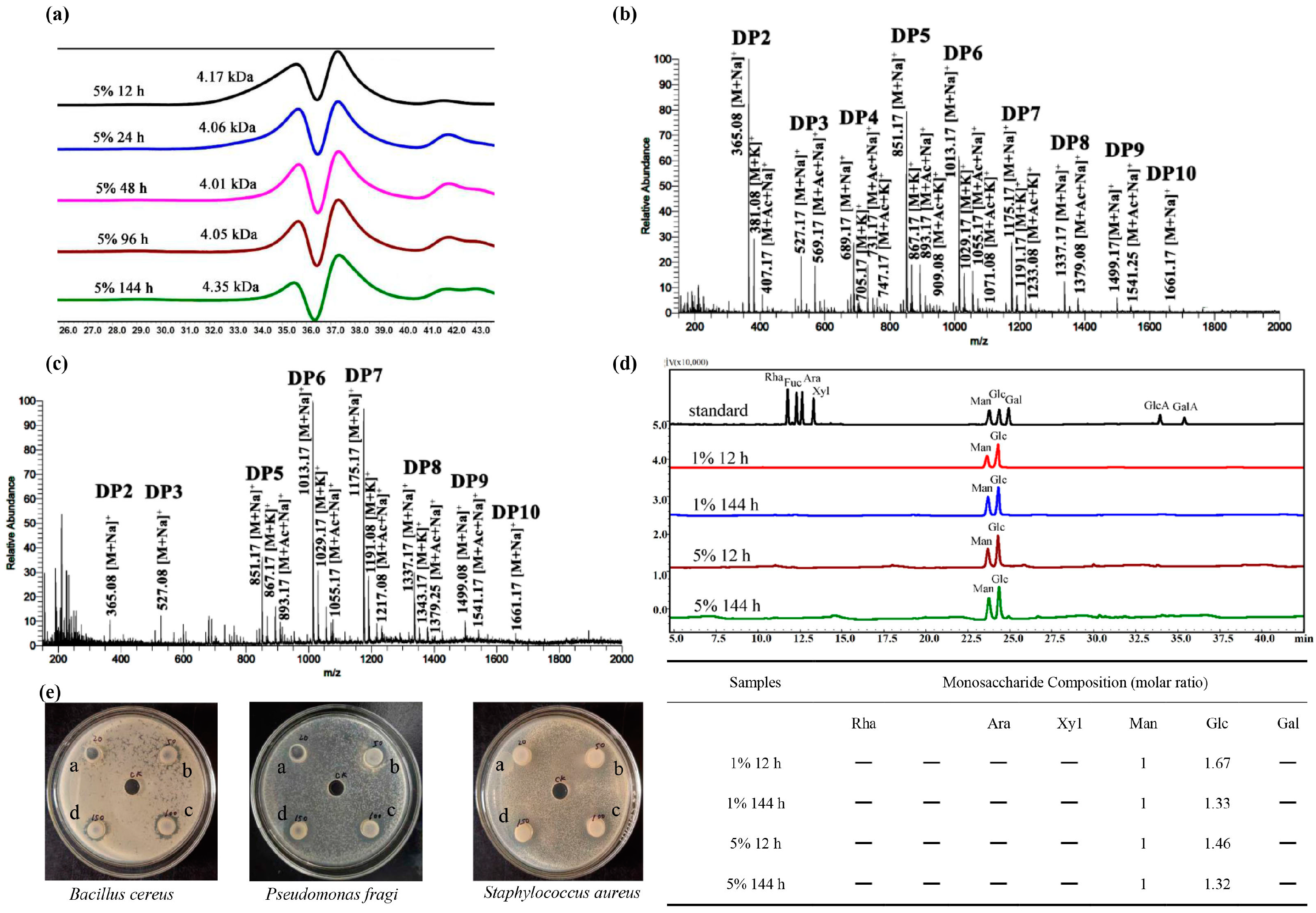
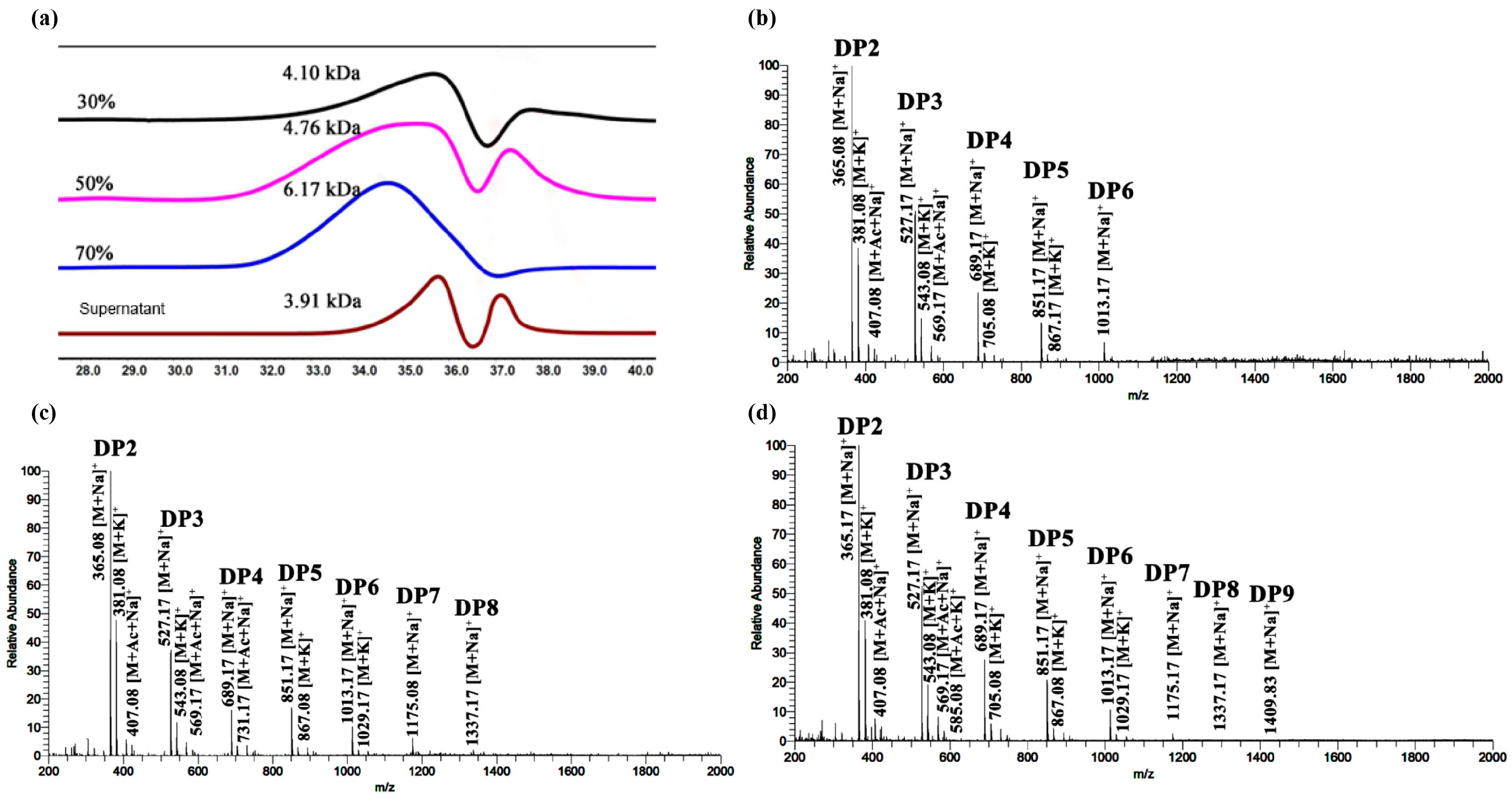
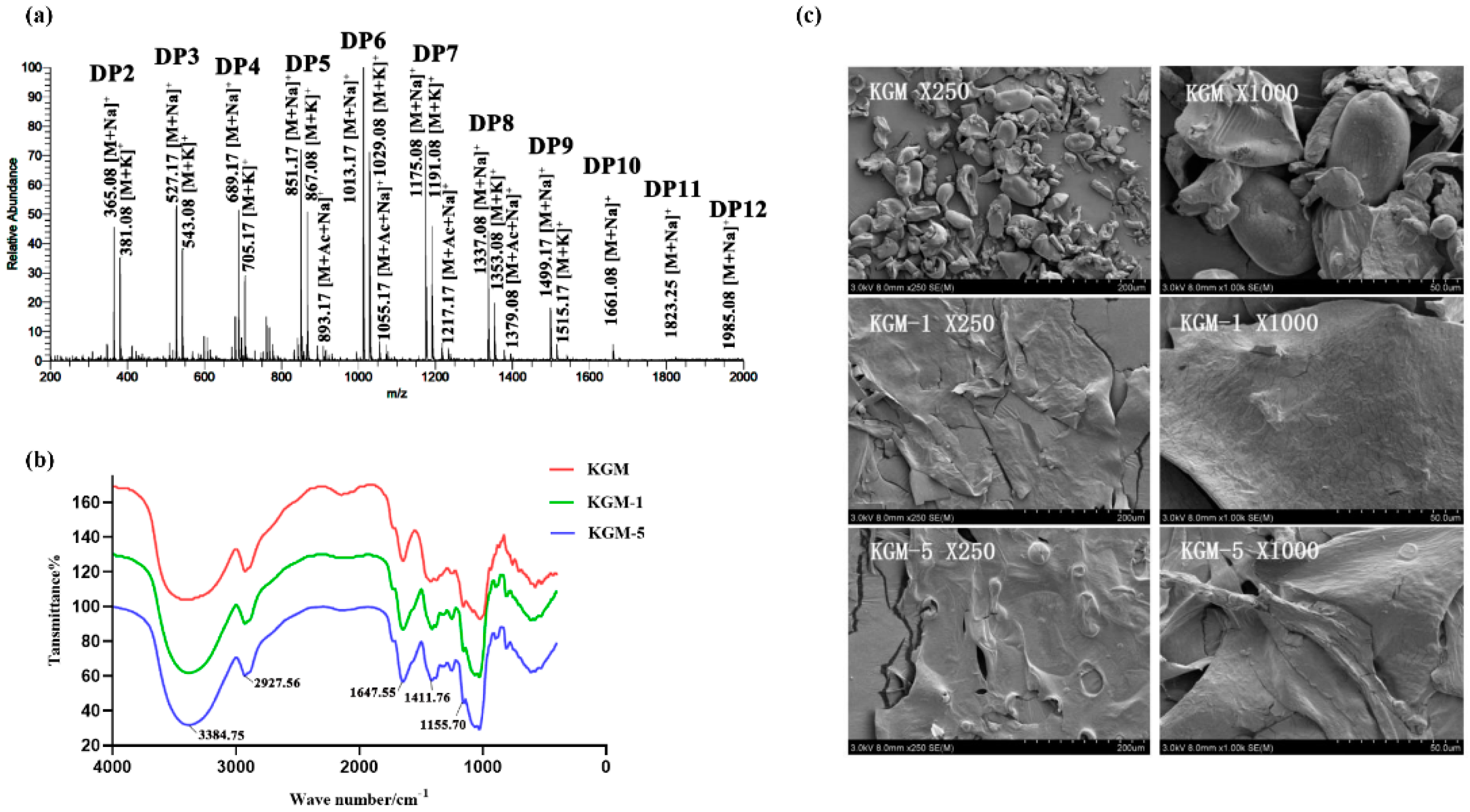
2.6. Physicochemical Characterization of the KGM Degradation Components
2.6.1. Determination of Molecular Weight and Monosaccharide Composition
2.6.2. ESI-MS Analysis
2.6.3. FT-IR and SEM
2.6.4. Antibacterial Activities
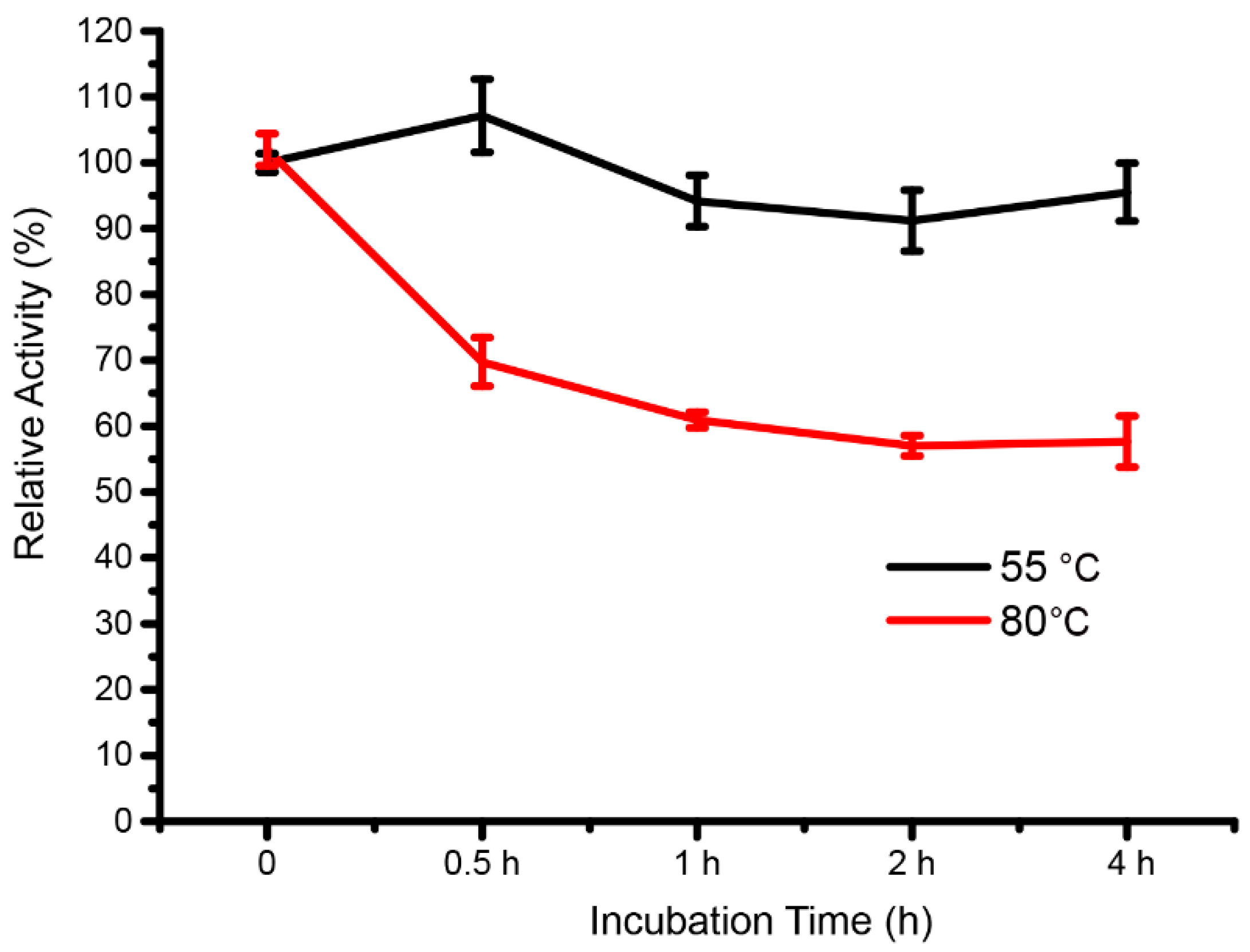
2.7. Thermal Stability of Extracellular Enzymes and Zymogram Analysis
2.8. Carbohydrate-Active Enzymes of Strain Z7-1 for KGM Hydrolysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Identification of the KGM-Degrading Strain
3.2. Degrading Ability of Strain Z7-1 for Substrates with Different KGM Concentrations
3.3. Characterization and Purification of KGM Degradation Products
3.4. Carbohydrate-Active Enzymes of Strain Z7-1 for Hydrolysis of KGM
3.5. Thermal Stability of the Extracellular Enzymes for KGM Hydrolysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alonso-Sande, M.; Teijeiro-Osorio, D.; Remuñán-López, C.; Alonso, M.J. Glucomannan, a promising polysaccharide for biopharmaceutical purposes. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 72, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Rhim, J.W. Recent progress in konjac glucomannan-based active food packaging films and property enhancement strategies. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 128, 107572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.H.; Song, A.X.; Yao, Z.P.; Wu, J.Y. Protective effects of natural and partially degraded konjac glucomannan on Bifidobacteria against antibiotic damage. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Sun, X.; Yu, W.; Shi, C.; Zhang, X.; Yu, H.; Ma, F. Enhanced konjac glucomannan hydrolysis by lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases and generating prebiotic oligosaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 253, 117241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Peng, S.; Xu, Z.; Xiong, B.; Wen, C.; Yao, M.; Pang, J. Synergetic degradation of konjac glucomannan by gamma-ray irradiation and hydrogen peroxide. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 93, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lan, G.; Ran, L.; Xiao, Y.; Yu, K.; Lu, B.; Dai, F.; Wu, D.; Lu, F. A novel wound dressing based on a konjac glucomannan/silver nanoparticle composite sponge effectively kills bacteria and accelerates wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 183, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Lin, D.; Zhao, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, X. Enhanced anti-obesity effects of bacterial cellulose combined with konjac glucomannan in high-fat diet-fed C57BL/6J mice. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 5260–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, W.; Song, G.; Zhong, P.; Ren, Y.; Zhong, G. Structural complexity of Konjac glucomannan and its derivatives governs the diversity and outputs of gut microbiota. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 292, 119639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Fang, J.; Huang, W.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Gong, G.; Huang, L.; Lin, X.; Wang, Z. The intervention effects of konjac glucomannan with different molecular weights on high-fat and high-fructose diet-fed obese mice based on the regulation of gut microbiota. Food Res. Int. 2023, 165, 112498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Ni, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, D.; Wu, C.; Pang, J. Physicochemical properties of degraded konjac glucomannan prepared by laser-assisted with hydrogen peroxide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, W.; Tu, L.; Wu, L.; Xiong, H.; Pang, J.; Sun, Y.M. Physicochemical properties and cellular protection against oxidation of degraded konjac glucomannan prepared by gamma-irradiation. Food Chem. 2017, 231, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelson, A.; Maaheimo, H.; Hakala, T.K. Hydrolysis of konjac glucomannan by Trichoderma reesei mannanase and endoglucanases Cel7B and Cel5A for the production of glucomannan-oligosaccharides. Carbohydr. Res. 2013, 372, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Huang, Y.C.; Yang, T.Y.; Jian, J.Y.; Chen, W.L.; Yang, C.H. Degradation of konjac glucomannan by Thermobifida fusca thermostable beta-mannanase from yeast transformant. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Wei, L.; Zhang, W.; Lei, Y.; Kong, Q.; Zhang, B. Production, characterization, and prebiotic activity of oligosaccharides from konjac glucomannan by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens WX-1. J. Funct. Foods. 2022, 88, 104872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Kao, M.R.; Li, J.; Sun, P.; Meng, Q.; Vyas, A.; Liang, P.H.; Wang, Y.S.; Hsieh, Y.S.Y. Novel two-step process in cellulose depolymerization: Hematite-mediated photocatalysis by lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase and Fenton reaction. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2022, 70, 9941–9947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Qin, D.; Cao, H.; Bai, Y. Enzymatic hydrolysis of polysaccharide from Auricularia auricula and characterization of the degradation product. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Zhan, Y.; Li, N.; Yu, D.; Gao, W.; Gu, Z.; Zhu, L.; Li, R.; Zhu, C. Enzymatic preparation of low-molecular-weight Laminaria japonica polysaccharides and evaluation of its effect on modulating intestinal microbiota in high-fat-diet-fed mice. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 14, 820892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blibech, M.; Mouelhi, S.; Farhat-Khemakhem, A.; Boukhris, I.; Ayeb, A.E.; Chouayekh, H. Selection of Bacillus subtilis US191 as a mannanase-producing probiotic candidate. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2019, 66, 858–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zeng, Q.; Qiao, W.; Wang, X.; Fan, J. Investigation production of mannan-oligosaccharides using konjac power by β-mannan manno-hydrolase from Aspergillus niger. Acta Agric. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2005, 14, 115–118. [Google Scholar]
- Rueckel, M.; Janson, S.; Solbak, A.; Fickler, A. Spatial activity mapping of ß-mannanase on soybean seeds. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnakomala, S.; Kahar, P.; Kashiwagi, N.; Lee, J.; Kudou, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Apriliana, P.; Yopi, Y.; Prasetya, B.; Ogino, C.; et al. Manno-oligosaccharide production from biomass hydrolysis by using endo-1,4-β-mannanase (manNj6-379) from Nonomuraea jabiensis ID06-379. Processes 2022, 10, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Huang, C.; Lin, W.; Bian, B.; Lai, C.; Ling, Z.; Yong, Q. A structure-activity understanding of the interaction between lignin and various cellulase domains. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 351, 127042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.D.; Shi, H.L.; Tang, Q.H.; Zhou, J.S.; Yao, L.G.; Jiao, Z.J.; Kan, Y.C. Genome mining and motif truncation of glycoside hydrolase family 5 endo -β-1,4-mannanase encoded by Aspergillus oryzae RIB40 for potential konjac flour hydrolysis or feed additive. Enzyme Microb. Tech. 2016, 93, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Liao, M.; Zhong, P.; Ding, J.; Wang, X.; Gong, G.; Huang, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q. Diversely regio-oxidative degradation of konjac glucomannan by lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase AA10 and generating antibacterial hydrolysate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266, 131094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, Q.; Kang, Z.; Wu, M.; Yin, H.; Duan, J. A homogeneous polysaccharide from Lycium barbarum: Structural characterizations, anti-obesity effects and impacts on gut microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 2074–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaturiwala, R.; Bagban, M.; Singh, T.A.; Modi, H.A. Partial purification and application of β-mannanase for the preparation of low molecular weight galacto and glucomannan. Biocatal. Agric. Biotech. 2021, 36, 102155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, X.; Liu, F.; Zhao, P.; Ding, Y. Preparation, composition analysis and antioxidant activities of konjac oligo-glucomannan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 130, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.Y.; Ma, L.Y.; Xie, M.Y.; Nie, S.P.; Wu, J.Y. Molecular properties and gut health benefits of enzyme-hydrolyzed konjac glucomannans. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 237, 116117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Men, Y.; Zhang, B.; Sun, Y. Prebiotic, immunomodulating, and antifatigue effects of konjac oligosaccharide. J. Food. Sci. 2018, 83, 3110–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.K.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.Q.; Song, X.X.; Yin, J.Y.; Nie, S.P. Exploring the partial degradation of polysaccharides: Structure, mechanism, bioactivities, and perspectives. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. 2023, 22, 4831–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzaiene, T.; Ziadi, M.; Enneifer, M.; Sellami, A.; Aydi, A.; Cherif, A.; Hamdi, M. Cellulolytic Bacillus strain: Production optimization using wheat bran under solid-state fermentation and investigation of its probiotic potential. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.H.; Xu, Y.X.; Li, Y.H.; Cao, J.; Song, F.L.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.M.; Yang, Y. Effects of konjac glucomannan with different molecular weights on gut microflora with antibiotic perturbance in vitro fecal fermentation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 273, 118546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Xie, Y.; Shabani, K.I.; Liu, X. Preparation, characterization and physicochemical properties of konjac glucomannan depolymerized by ozone assisted with microwave treatment. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 119, 106878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.M.; Wang, C.T.; Shen, C.H.; Wang, S.T.; Mao, J.Q.; Li, Z.; Gänzle, M.; Mao, J. Microbiota stratification and succession of amylase-producing Bacillus in traditional Chinese Jiuqu (fermentation starters). J. Sci. Food. Agric. 2020, 100, 3544–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Xue, Y.; Tang, F.; Cai, W.; Hao, G.; Shan, C. Quality improvement of jujube wine through mixed fermentation with Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Bacillus licheniformis. LWT 2022, 164, 133444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, D.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Wei, X.; Li, S.; Chen, S. High-level production of α-amylase by manipulating the expression of alanine racemase in Bacillus licheniformis. Biotechnol. Lett. 2017, 39, 1389–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Guo, Y.; Yolandani Ma, H. Production of value-added peptides from agro-industrial residues by solid-state fermentation with a new thermophilic protease-producing strain. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Niu, D.; McHunu, N.P.; Zhang, M.; Singh, S.; Wang, Z. Secretory expression of amylosucrase in Bacillus licheniformis through twin-arginine translocation pathway. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biot. 2024, 51, kuae004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuribayashi, L.M.; do Rio Ribeiro, V.P.; de Santana, R.C.; Ribeiro, E.J.; dos Santos, M.G.; Falleiros, L.N.S.S.; Guidini, C.Z. Immobilization of β-galactosidase from Bacillus licheniformis for application in the dairy industry. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2021, 105, 3601–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, M.; Lee, J.P.; Park, G.W.; Lee, J.S.; Park, H.J.; Min, K. Lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase (LPMO)-derived saccharification of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 359, 127501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Ding, J.; Liao, M.; Meng, X.; Fu, Y.; Huang, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q. Characterization of Degraded Konjac Glucomannan from an Isolated Bacillus licheniformis Strain with Multi-Enzyme Synergetic Action. Foods 2024, 13, 2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132041
Zhang X, Ding J, Liao M, Meng X, Fu Y, Huang L, Wang Z, Wang Q. Characterization of Degraded Konjac Glucomannan from an Isolated Bacillus licheniformis Strain with Multi-Enzyme Synergetic Action. Foods. 2024; 13(13):2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132041
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xueting, Jieqiong Ding, Minghong Liao, Xin Meng, Yubiao Fu, Linjuan Huang, Zhongfu Wang, and Qingling Wang. 2024. "Characterization of Degraded Konjac Glucomannan from an Isolated Bacillus licheniformis Strain with Multi-Enzyme Synergetic Action" Foods 13, no. 13: 2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132041
APA StyleZhang, X., Ding, J., Liao, M., Meng, X., Fu, Y., Huang, L., Wang, Z., & Wang, Q. (2024). Characterization of Degraded Konjac Glucomannan from an Isolated Bacillus licheniformis Strain with Multi-Enzyme Synergetic Action. Foods, 13(13), 2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132041








