Effect of Multi-Mode Divergent Ultrasound Pretreatment on Hardness, Microstructure and Digestion of Acid-Induced Whey Protein Gels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Ultrasound Pretreatment on Whey Protein
2.3. Whey Protein Gels (WPG) Preparation
2.4. Rheological Properties Analysis
2.5. Turbidity Determination
2.6. Gel Solubility
2.7. Gel Hardness
2.8. Scan Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.9. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.10. Simulated Digestion of WPG
2.11. Particle Size Distribution of the Solid Digesta
2.12. Free Amino Group Determination
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
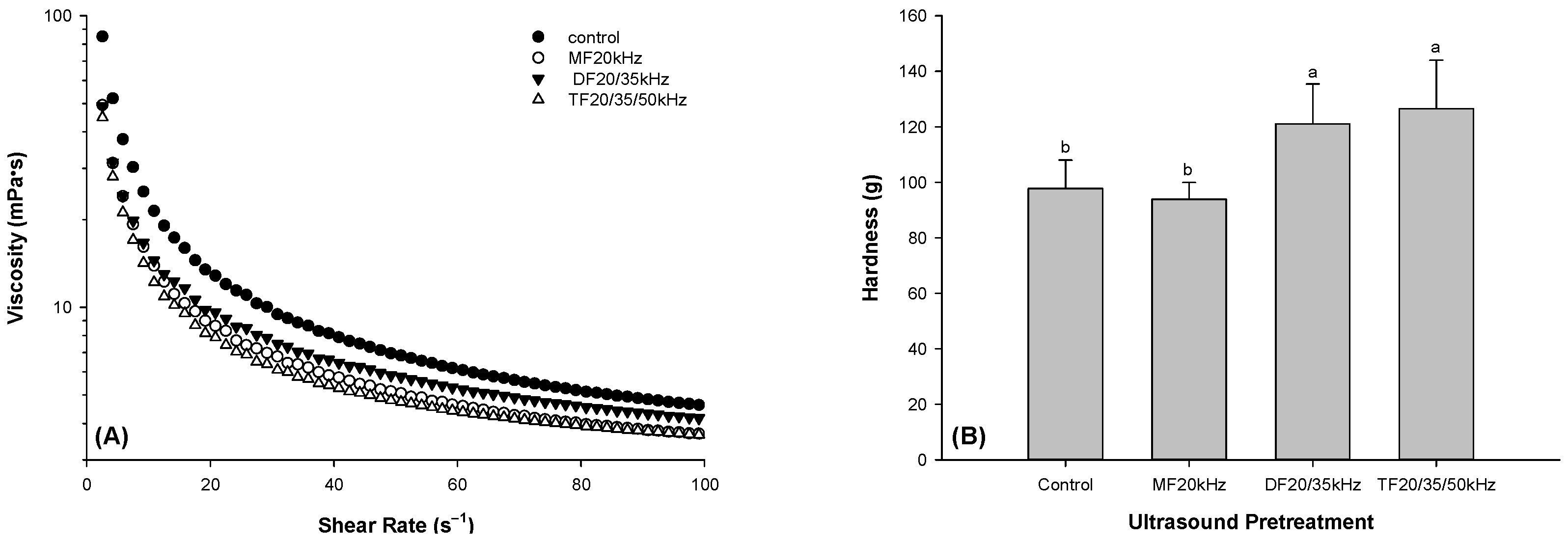
3.1. Effect of Ultrasonic Frequency Mode on the Viscosity of Whey Protein Solution
3.2. Hardness of WPG
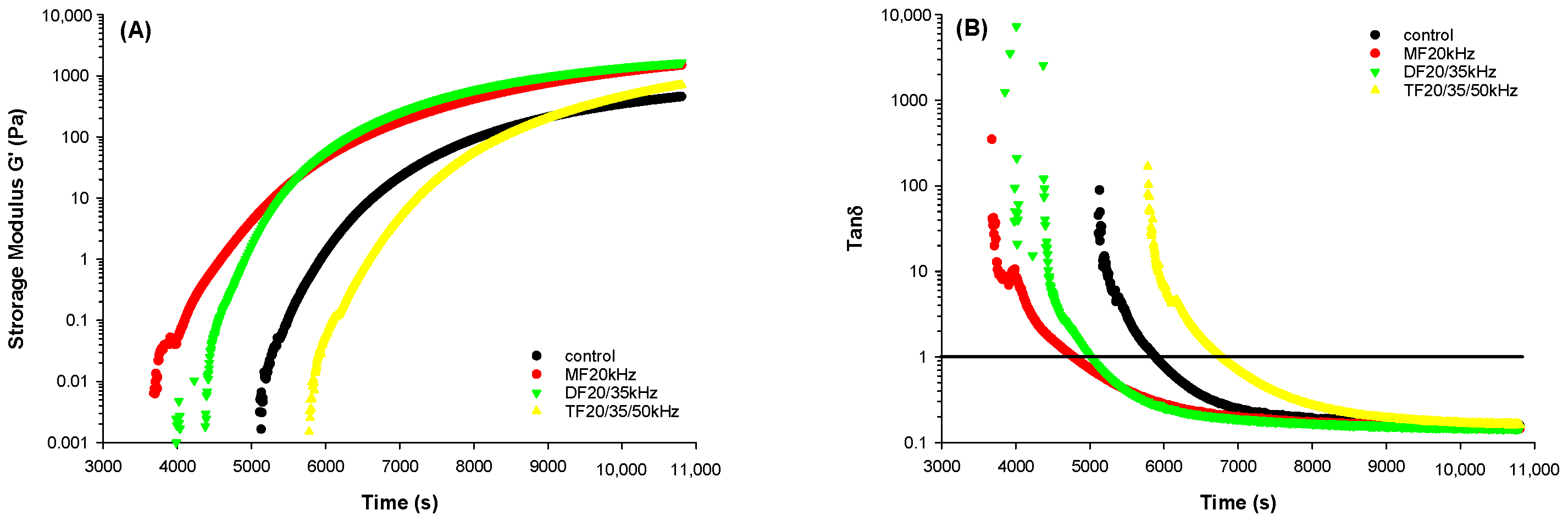
3.3. Rheological Properties of WPG
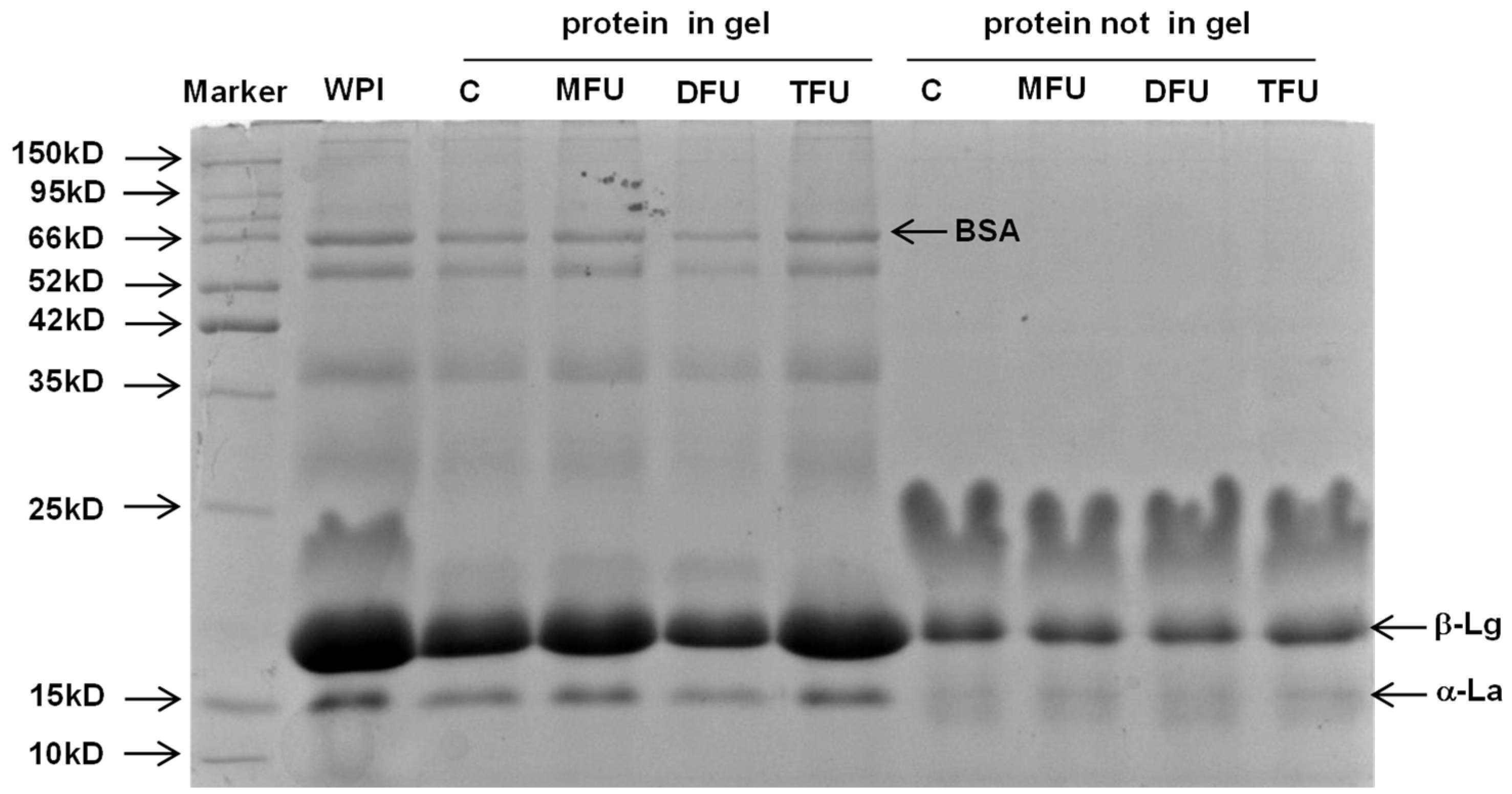
3.4. Protein Distribution in Whey Protein Gel
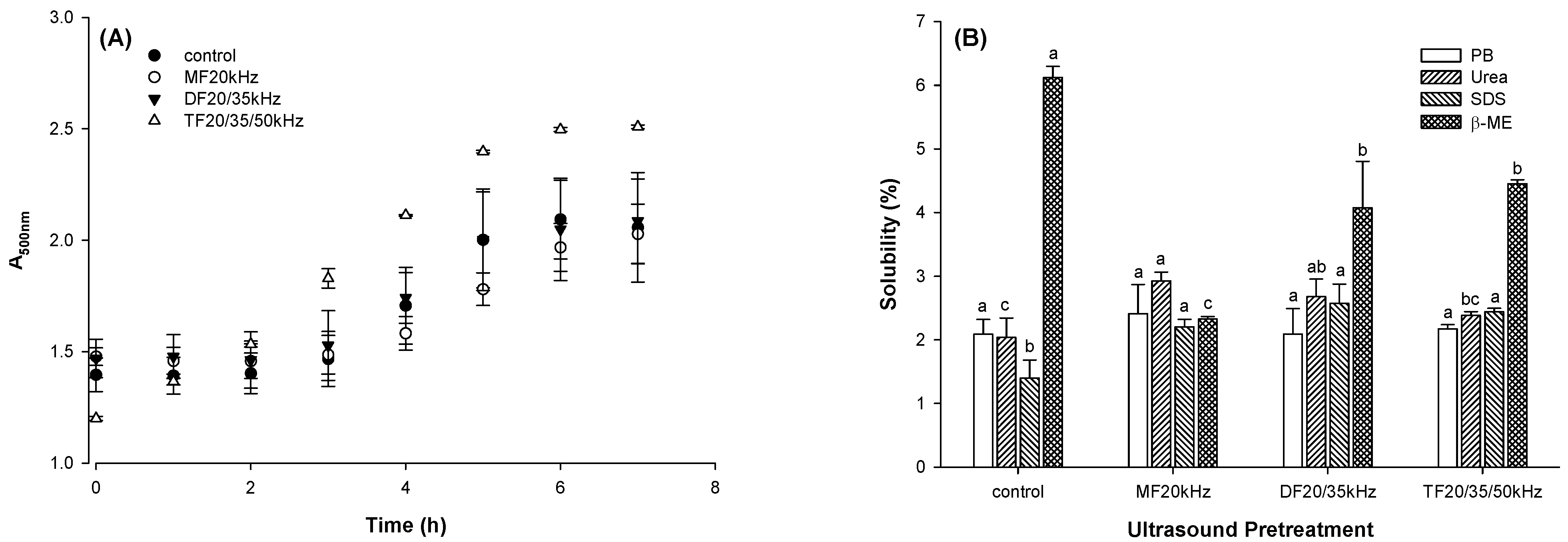
3.5. Turbidity and Chemical Forces
3.5.1. Turbidity
3.5.2. Chemical Forces
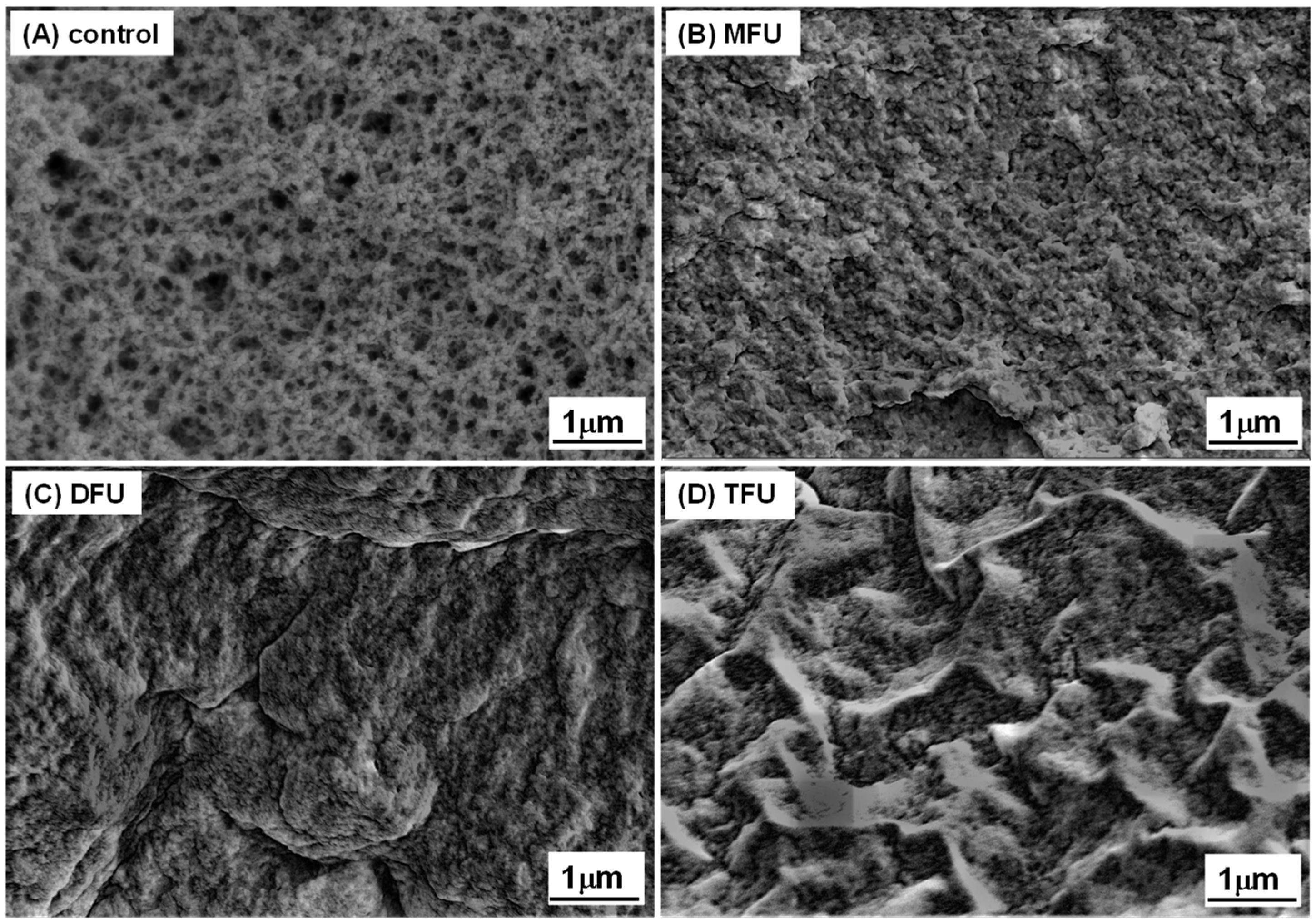
3.6. Microstructure of GDL-Induced Whey Protein Gel
3.7. Digestion of GDL-Induced Whey Protein Gel
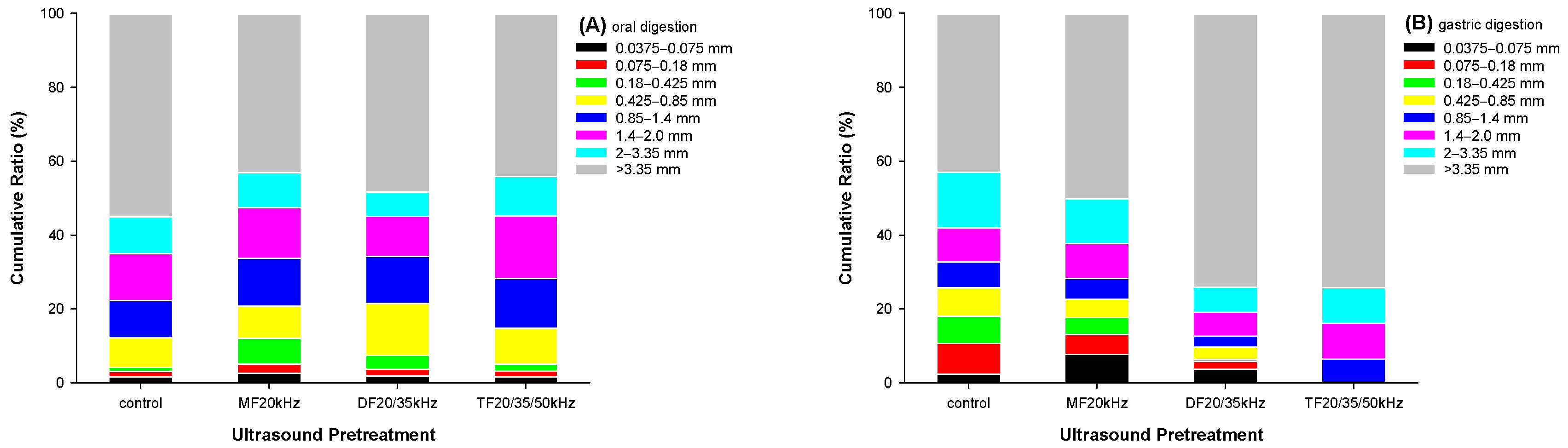
3.7.1. Physical Digestion of WPG
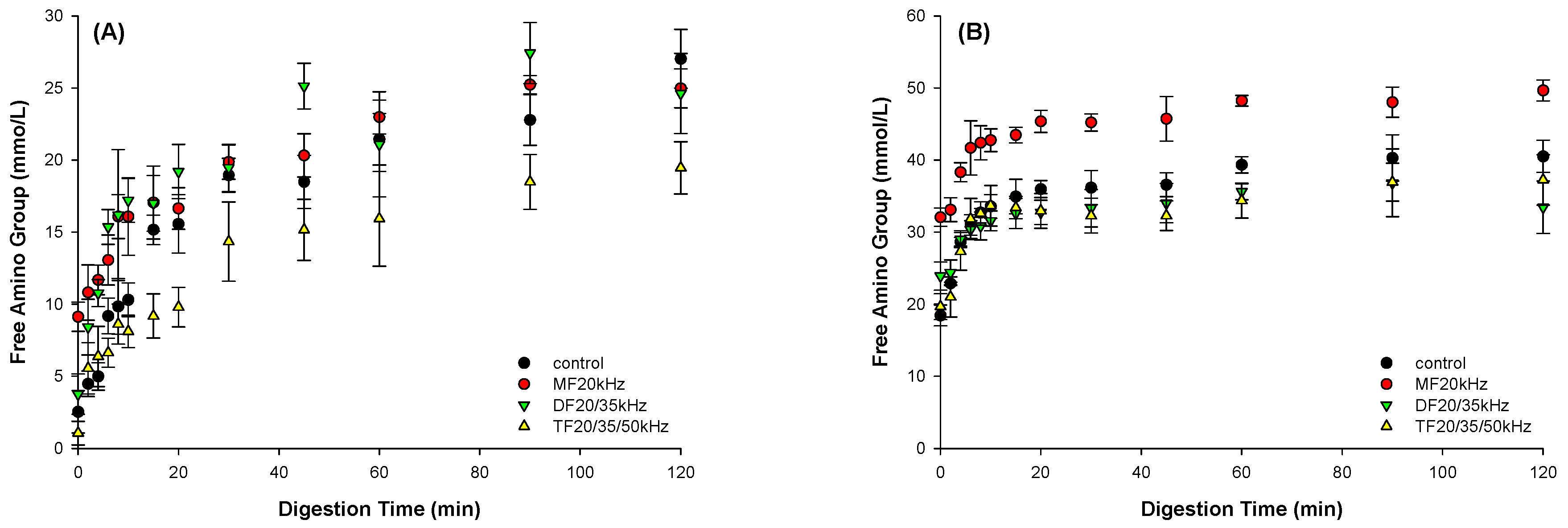
3.7.2. Chemical Digestion of WPG
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, Y.P.; Mezzenga, R. Design principles of food gels. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebishy, E.; Du, H.; Brito-Oliveira, T.C.; Pinho, S.C.; Miao, S. Saltiness perception in gel-based food systems (gels and emulsion-filled gels). Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, L.G.L.; Odelli, D.; de Carvalho, A.F.; Martins, E.; Delaplace, G.; Peixoto, P.P.D.; Silva, N.F.N.; Casanova, F. Combination of Milk and Plant Proteins to Develop Novel Food Systems: What Are the Limits? Foods 2023, 12, 2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teimouri, S.; Kasapis, S.; Dokouhaki, M. Diffusional characteristics of food protein-based materials as nutraceutical delivery systems: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 122, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Alvi, T.; Biswas, A.; Shityakov, S.; Gusinskaia, T.; Lavrentev, F.; Dutta, K.; Khan, M.K.I.; Stephen, J.; Radhakrishnan, M. Food gels: Principles, interaction mechanisms and its microstructure. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 12530–12551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaee, A.; Mohammadian, M.; Jafari, S.M. Whey and soy protein-based hydrogels and nano-hydrogels as bioactive delivery systems. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 70, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhao, J.; Guo, F.; Qin, J.; Wang, Y. Hyaluronic acid modulates techno-functional and digestion properties of heat-induced ginkgo seed protein isolate gel. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Ye, A.Q.; Singh, H. Characterizations of emulsion gel formed with the mixture of whey and soy protein and its protein digestion under in vitro gastric conditions. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2024, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasberger, K.; Hammershoj, M.; Corredig, M. Lupin protein-stabilized oil droplets contribute to structuring whey protein emulsion-filled gels. Food Res. Int. 2024, 178, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Ge, H.F.; Zhao, J.; Liu, C.Q.; Wang, Y.S. L-Theanine Improves the Gelation of Ginkgo Seed Proteins at Different pH Levels. Gels 2024, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Q.; Ding, Y.H.; Zhao, Y.M.; Ma, H.L. Strategies to improve the emulsification properties of rice proteins as a promising source of plant-based emulsifiers: An updated mini-review. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.C.; Zhang, W.A.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Chen, X. Structural and functional modification of food proteins by high power ultrasound and its application in meat processing. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 1914–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinton, M.B.; dos Santos, B.A.; Lorenzo, J.P.M.; Cichoski, A.J.P.; Boeira, C.P.; Campagnol, P.C.B. Green technologies as a strategy to reduce NaCl and phosphate in meat products: An overview. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 40, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, A.; Mehany, T.; Pandiselvam, R.; Siddiqui, S.A.; Mir, N.A.; Malik, M.A.; Sujayasree, O.J.; Alamuru, K.C.; Khanashyam, A.C.; Casanova, F.; et al. Sonoprocessing: Mechanisms and recent applications of power ultrasound in food. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.G.; Tiliwa, E.S.; Yan, W.Q.; Azam, S.M.R.; Wei, B.X.; Zhou, C.S.; Ma, H.L.; Bhandari, B. Recent development in high quality drying of fruits and vegetables assisted by ultrasound: A review. Food Res. Int. 2022, 152, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhangu, S.K.; Ashokkumar, M. Theory of Sonochemistry. Top. Curr. Chem. 2016, 374, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrapala, J.; Oliyer, C.; Kentish, S.; Ashokkumar, M. Ultrasonics in food processing. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2012, 19, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, N.S.M.; Anandan, S.; Sivashanmugam, P.; Flores, E.M.M.; Ashokkumar, M. A correlation between cavitation bubble temperature, sonoluminescence and interfacial chemistry—A minireview. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 85, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L.; Xu, B.G.; Zhou, C.S.; Yagoub, A.A.; Cai, Z.; Yu, X.J. Multi-frequency ultrasound-assisted dialysis modulates the self-assembly of alcohol-free zein-sodium caseinate to encapsulate curcumin and fabricate composite nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 122, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbour, M.; Jiang, H.; Mintah, B.K.; Wahia, H.; He, R.H. Ultrasonic-assisted protein extraction from sunflower meal: Kinetic modeling, functional, and structural traits. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 74, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayum, A.; Rashid, A.; Liang, Q.F.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Kang, L.X.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhou, C.W.; Hussain, M.; Ren, X.F.; et al. Ultrasonic and homogenization: An overview of the preparation of an edible protein-polysaccharide complex emulsion. Compr. Rev. Food. Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 4242–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Q.; Ma, H.L.; Wang, Y.Y. Recent advances in modified food proteins by high intensity ultrasound for enhancing functionality: Potential mechanisms, combination with other methods, equipment innovations and future directions. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 85, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, Z.J.; Gregersen, S.B.; Wiking, L.; Hammershoj, M.; Simonsen, A.C. Microstructural changes in acid milk gels due to temperature-controlled high-intensity ultrasound treatment: Quantification by analysis of super-resolution microscopy images. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2022, 75, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangar, S.P.; Esua, O.J.; Sharma, N.; Thirumdas, R. Ultrasound-assisted modification of gelation properties of proteins: A review. J. Texture Stud. 2022, 53, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Gu, C.; Wei, R.; Luan, Y.; Liu, R.; Ge, Q.; Yu, H.; Wu, M. Enhanced gelling properties of myofibrillar protein by ultrasound-assisted thermal-induced gelation process: Give an insight into the mechanism. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 94, 106349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.H.; Ma, H.L.; Wang, K.; Azam, S.M.R.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhou, J.; Qu, W.J. Ultrasound frequency effect on soybean protein: Acoustic field simulation, extraction rate and structure. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 145, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.G.; Azam, S.M.R.; Feng, M.; Wu, B.G.; Yan, W.Q.; Zhou, C.S.; Ma, H.L. Application of multi-frequency power ultrasound in selected food processing using large-scale reactors: A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 81, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Zhao, C.H.; Guo, M.R. Effects of high intensity ultrasound on acid-induced gelation properties of whey protein gel. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 39, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregersen, S.B.; Wiking, L.; Hammershoj, M. Acceleration of acid gel formation by high intensity ultrasound is linked to whey protein denaturation and formation of functional milk fat globule-protein complexes. J. Food Eng. 2019, 254, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.J.; Li, T.; Wang, K.L.; He, Y.T.; Fu, R.X.; Yu, R.; Zhao, P.P.; Oh, K.C.; Jiang, Z.M.; Hou, J.C. Investigation of the consequences of ultrasound on the physicochemical, emulsification, and gelatinization characteristics of citric acid-treated whey protein isolate. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 10628–10639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdeniz, V.; Akalin, A.S. New approach for yoghurt and ice cream production: High-intensity ultrasound. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczynska-Mleko, M.; Nishinari, K.; Mleko, S.; Terpilowski, K.; Pérez-Huertas, S. Cold gelation of whey protein isolate with sugars in an ultrasound environment. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 139, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.L.; Yan, M.; Xue, S.Q.; Zhang, T.H.; Shen, X. Influence of ultrasound and enzymatic cross-linking on freeze-thaw stability and release properties of whey protein isolate hydrogel. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 7253–7265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, D.; Le Feunteun, S.; Marze, S.; Souchon, I. Structuring food to control its disintegration in the gastrointestinal tract and optimize nutrient bioavailability. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 46, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Yeboah, G.B.; Guo, X.Y.; Donkor, P.O.; Wu, J. Gelling Characteristics of Emulsions Prepared with Modified Whey Protein by Multiple-Frequency Divergent Ultrasound at Different Ultrasonic Power and Frequency Mode. Polymers 2022, 14, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Donkor, P.O.; Yeboah, G.B.; Ayim, I.; Wu, J.; Ma, H.L. Modulating the in vitro digestion of heat-set whey protein emulsion gels via gelling properties modification with sequential ultrasound pretreatment. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 149, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frydenberg, R.P.; Hammershoj, M.; Andersen, U.; Greve, M.T.; Wiking, L. Protein denaturation of whey protein isolates (WPIs) induced by high intensity ultrasound during heat gelation. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; Ma, F.; Cheng, Y. Improving the solubility and digestibility ofpotato protein with an online ultrasound-assisted pH shifting treatment at medium temperature. Foods 2020, 9, 1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Cheng, Y. Mechanical properties, picrostructure, andin vitro digestion of transglutaminase-crosslinked whey protein and potato protein hydrolysate composite gels. Foods 2023, 12, 2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gornall, A.G.; Bardawill, C.J.; David, M.M. Determination of serum proteins by means of the biuret reaction. J. Biol. Chem. 1949, 177, 751–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Xiong, Y.L. Extreme pH treatments enhance the structure-reinforcement role of soy protein isolate and its emulsions in pork myofibrillar protein gels in the presence of microbial transglutaminase. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Liu, C.; Zhao, J.; Guo, F.; Wang, Y. pH dominates the formation of ginkgo seed protein and whey protein composite gels. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minekus, M.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu, C.; Carrière, F.; Boutrou, R.; Corredig, M.; Dupont, D.; et al. A standardised static in vitro digestion method suitable for food—An international consensus. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spellman, D.; McEvoy, E.; O’Cuinn, G.; FitzGerald, R.J. Proteinase and exopeptidase hydrolysis of whey protein: Comparison of the TNBS, OPA and pH stat methods for quantification of degree of hydrolysis. Int. Dairy J. 2003, 13, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.Y.; Liang, Z.Q.; Zhang, C.Y.; Hao, S.Q.; Han, H.Y.; Du, P.; Li, A.L.; Shao, H.; Li, C.; Liu, L.B. Ultrasonic modification of whey protein isolate: Implications for the structural and functional properties. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 152, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Suárez, J.C.; Xiong, Y.L. Effect of transglutaminase-induced cross-linking on gelation of myofibrillar/soy protein mixtures. Meat Sci. 2003, 65, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Donkor, P.O.; Ren, X.F.; Wu, J.; Agyemang, K.; Ayim, I.; Ma, H.L. Effect of ultrasound pretreatment with mono-frequency and simultaneous dual frequency on the mechanical properties and microstructure of whey protein emulsion gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiey, L.; Britten, M. Effect of protein composition on the rheological properties of acid-induced whey protein gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Faria, J.T.; Minim, V.P.R.; Minim, L.A. Evaluating the effect of protein composition on gelation and viscoelastic characteristics of acid-induced whey protein gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 32, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Qin, L.; Wu, C.; Du, M. Ultrasound treatment improved the physicochemical characteristics of cod protein and enhanced the stability of oil-in-water emulsion. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, Z.; Razavi, S.M.A.; Varidi, M. Sequential ultrasound and transglutaminase treatments improve functional, rheological, and textural properties of whey protein concentrate. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 43, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharlamova, A.; Nicolai, T.; Chassenieux, C. Heat-induced gelation of mixtures of casein micelles with whey protein aggregates. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 92, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Ye, A.; Lad, M.; Dalgleish, D.; Singh, H. Effect of gel structure on the gastric digestion of whey protein emulsion gels. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 1214–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, N.; Ye, A.; Wolber, F.M.; Singh, H. In-mouth breakdown behaviour and sensory perception of emulsion gels containing active or inactive filler particles loaded with capsaicinoids. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 106076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Bellissimo, N.; Rousseau, D. Role of gel structure in controlling in vitro intestinal lipid digestion in whey protein emulsion gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 69, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, Y.; Shi, X.; Yeboah, G.B.; Chen, L.; Wu, J. Effect of Multi-Mode Divergent Ultrasound Pretreatment on Hardness, Microstructure and Digestion of Acid-Induced Whey Protein Gels. Foods 2024, 13, 1926. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13121926
Cheng Y, Shi X, Yeboah GB, Chen L, Wu J. Effect of Multi-Mode Divergent Ultrasound Pretreatment on Hardness, Microstructure and Digestion of Acid-Induced Whey Protein Gels. Foods. 2024; 13(12):1926. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13121926
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Yu, Xiaolong Shi, Georgina Benewaa Yeboah, Lihong Chen, and Juan Wu. 2024. "Effect of Multi-Mode Divergent Ultrasound Pretreatment on Hardness, Microstructure and Digestion of Acid-Induced Whey Protein Gels" Foods 13, no. 12: 1926. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13121926
APA StyleCheng, Y., Shi, X., Yeboah, G. B., Chen, L., & Wu, J. (2024). Effect of Multi-Mode Divergent Ultrasound Pretreatment on Hardness, Microstructure and Digestion of Acid-Induced Whey Protein Gels. Foods, 13(12), 1926. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13121926




