Metals on the Menu—Analyzing the Presence, Importance, and Consequences
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Regulations and Standards Regarding the Presence of Heavy Metals in Food
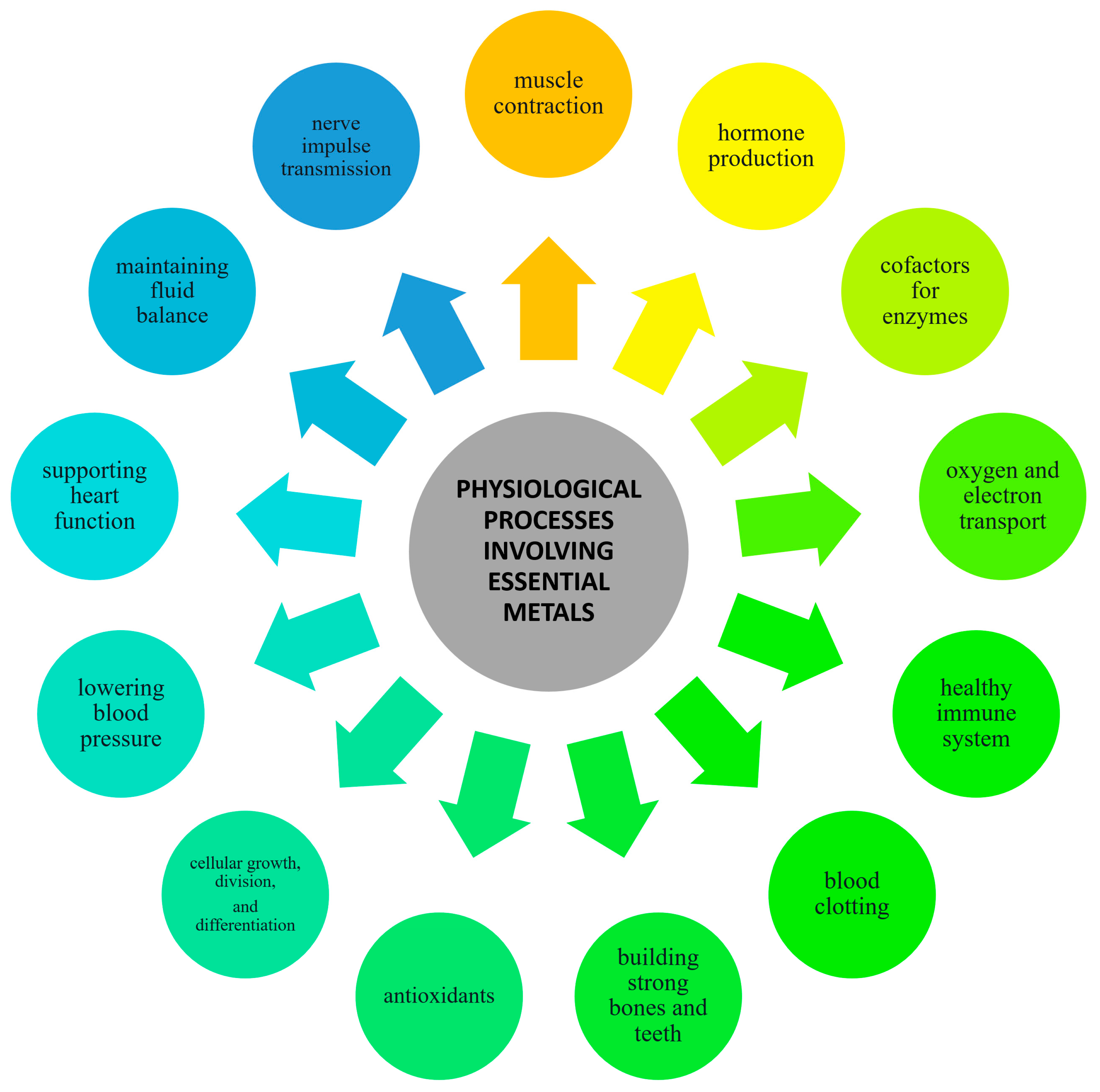
3. Essential Metals in Food
3.1. Sodium
3.2. Potassium
3.3. Magnesium
3.4. Calcium
3.5. Zinc
3.6. Iron
3.7. Copper
3.8. Cobalt
3.9. Chromium
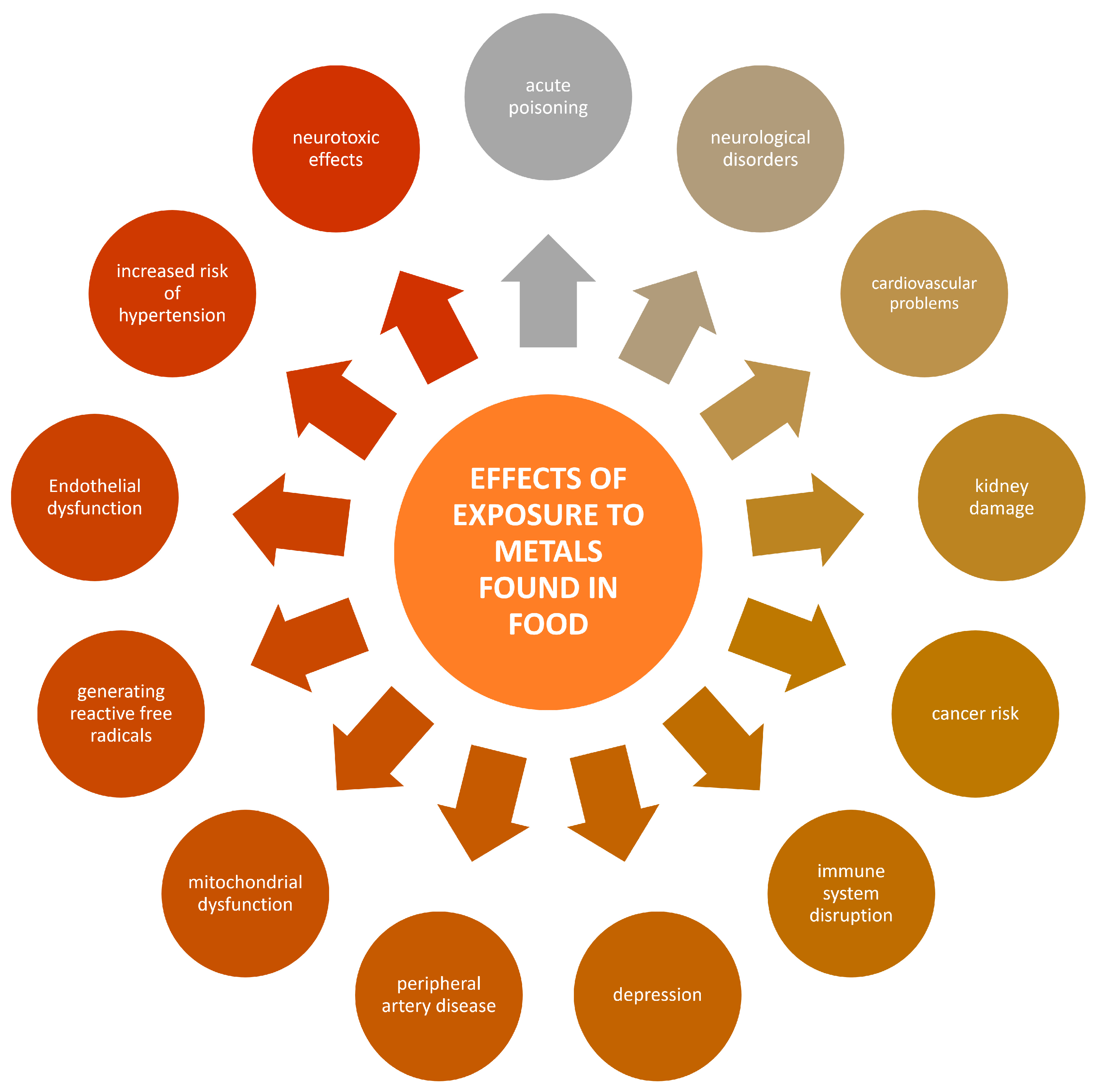
4. Toxic Metals in Food
4.1. Lead
4.2. Cadmium
4.3. Arsenic
4.4. Nickel
4.5. Mercury
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lazarević-Pašti, T.; Tasić, T.; Milanković, V.; Potkonjak, N. Molecularly Imprinted Plasmonic-Based Sensors for Environmental Contaminants—Current State and Future Perspectives. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, B.A.; Alexander, J.; Oskarsson, A. Chapter 6—Toxic Metals in Food. In Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals, 4th ed.; Nordberg, G.F., Fowler, B.A., Nordberg, M., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scutarașu, E.C.; Trincă, L.C. Heavy Metals in Foods and Beverages: Global Situation, Health Risks and Reduction Methods. Foods 2023, 12, 3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K.; Lee, S.S.; Zhang, M.; Tsang, Y.F.; Kim, K.-H. Heavy metals in food crops: Health risks, fate, mechanisms, and management. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffus, J.H. “Heavy metals” a meaningless term? (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2002, 74, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustakas, M. The Role of Metal Ions in Biology, Biochemistry and Medicine. Materials 2021, 14, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.B.; Beeregowda, K.N. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashanth, L.; Kattapagari, K.K.; Chitturi, R.T.; Baddam, V.R.R.; Prasad, L.K. A review on role of essential trace elements in health and disease. J. Dr. YSR Univ. Health Sci. 2015, 4, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, C.Y. Neuropsychiatric manifestations of alkali metal deficiency and excess. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1984, 21, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.W.; Baqar, S.; Jerums, G.; Ekinci, E.I. Sodium and its role in cardiovascular disease–the debate continues. Front. Endocrinol. 2016, 7, 232191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, S.; Provenzano, M.; Gagliardi, I.; Michael, A.; Liberti, M.E.; De Nicola, L.; Conte, G.; Garofalo, C.; Andreucci, M. Sodium Intake and Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustsson, A.; Qvarforth, A.; Engström, E.; Paulukat, C.; Rodushkin, I. Trace and major elements in food supplements of different origin: Implications for daily intake levels and health risks. Toxicol. Rep. 2021, 8, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy Metal Toxicity and the Environment. In Molecular, Clinical and Environmental Toxicology: Volume 3: Environmental Toxicology; Luch, A., Ed.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvi, A.; Rajasekar, A.; Theerthagiri, J.; Ananthaselvam, A.; Sathishkumar, K.; Madhavan, J.; Rahman, P.K.S.M. Integrated Remediation Processes Toward Heavy Metal Removal/Recovery From Various Environments-A Review. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenntech. Available online: https://www.lenntech.com/processes/heavy/heavy-metals/heavy-metals.htm (accessed on 19 April 2024).
- Carmona, A.; Roudeau, S.; Ortega, R. Molecular Mechanisms of Environmental Metal Neurotoxicity: A Focus on the Interactions of Metals with Synapse Structure and Function. Toxics 2021, 9, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althomali, R.H.; Abbood, M.A.; Saleh, E.A.M.; Djuraeva, L.; Abdullaeva, B.S.; Habash, R.T.; Alhassan, M.S.; Alawady, A.H.R.; Alsaalamy, A.H.; Najafi, M.L. Exposure to heavy metals and neurocognitive function in adults: A systematic review. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2024, 36, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnet-Tschudi, F.; Zurich, M.G.; Boschat, C.; Corbaz, A.; Honegger, P. Involvement of Environmental Mercury and Lead in the Etiology of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Rev. Environ. Health 2006, 21, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modabbernia, A.; Velthorst, E.; Reichenberg, A. Environmental risk factors for autism: An evidence-based review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Mol. Autism 2017, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandravanshi, L.; Shiv, K.; Kumar, S. Developmental toxicity of cadmium in infants and children: A review. Environ. Anal. Health Toxicol. 2021, 36, e2021003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, S.E.; Bridges, C.C. Chronic Kidney Disease and Exposure to Nephrotoxic Metals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, B.; Pritchard, D.J. Etiology of Osteosarcoma. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2002, 397, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosevic, E.; Stanisavljevic, N.; Boskovic, S.; Stamenkovic, N.; Novkovic, M.; Bavelloni, A.; Cenni, V.; Kojic, S.; Jasnic, J. Antitumor activity of natural pigment violacein against osteosarcoma and rhabdomyosarcoma cell lines. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 10975–10987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anka, A.U.; Usman, A.B.; Kaoje, A.N.; Kabir, R.M.; Bala, A.; Kazem Arki, M.; Hossein-Khannazer, N.; Azizi, G. Potential mechanisms of some selected heavy metals in the induction of inflammation and autoimmunity. Eur. J. Inflamm. 2022, 20, 1721727X221122719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitropoulou, C.; Fragoulakis, V.; Rakicevic, L.B.; Novkovic, M.M.; Vozikis, A.; Matic, D.M.; Antonijevic, N.M.; Radojkovic, D.P.; Schaik, R.H.v.; Patrinos, G.P. Economic analysis of pharmacogenomic-guided clopidogrel treatment in Serbian patients with myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Pharmacogenomics 2016, 17, 1775–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novkovic, M.; Matic, D.; Kusic-Tisma, J.; Antonijevic, N.; Radojkovic, D.; Rakicevic, L. Analysis of the CYP2C19 genotype associated with bleeding in Serbian STEMI patients who have undergone primary PCI and treatment with clopidogrel. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 74, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, F.D.; Whelton, P.K. High Blood Pressure and Cardiovascular Disease. Hypertension 2020, 75, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Mo, L.; Huang, H.; Mo, L.; Zhu, W.; Li, W.; Yang, G.; Chen, L.; Wu, Y.; Song, J.; et al. Cadmium contributes to atherosclerosis by affecting macrophage polarization. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 173, 113603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Vladykovskaya, E.N.; Haberzettl, P.; Sithu, S.D.; D’Souza, S.E.; States, J.C. Arsenic exacerbates atherosclerotic lesion formation and inflammation in ApoE-/- mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 241, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metryka, E.; Kupnicka, P.; Kapczuk, P.; Aszakiewicz, B.; Piotrowska, K.; Tkacz, M.; Gutowska, I.; Chlubek, D.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I. Lead (Pb) Accumulation in Human THP-1 Monocytes/Macrophages In Vitro and the Influence on Cell Apoptosis. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 955–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, L.; Araujo, J.A.; Barchowsky, A.; Belcher, S.; Berridge, B.R.; Chiamvimonvat, N.; Chiu, W.A.; Cogliano, V.J.; Elmore, S.; Farraj, A.K.; et al. Key Characteristics of Cardiovascular Toxicants. Environ. Health Perspect. 2021, 129, 095001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Official Journal of the European Union. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32023R0915 (accessed on 2 April 2024).
- Codex Alimentarius International Food Standards. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/shproxy/es/?lnk=1&url=https%253A%252F%252Fworkspace.fao.org%252Fsites%252Fcodex%252FMeetings%252FCX-735-11%252FWD%252Fcf11_INF01x.pdf (accessed on 2 April 2024).
- Wong, C.; Roberts, S.M.; Saab, I.N. Review of regulatory reference values and background levels for heavy metals in the human diet. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 130, 105122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strazzullo, P.; Leclercq, C. Sodium. Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 188–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Principles of Nerve Cell Communication. Alcohol Health Res. World 1997, 21, 107–108.
- U.S. Department of Agriculture. Available online: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/746775/nutrients (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- U.S. Department of Agriculture. Available online: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/595507/nutrients (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- National Institutes of Health. Available online: https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/list-all/ (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Santos, J.A.; Sparks, E.; Thout, S.R.; McKenzie, B.; Trieu, K.; Hoek, A.; Johnson, C.; McLean, R.; Arcand, J.; Campbell, N.R.C.; et al. The Science of Salt: A global review on changes in sodium levels in foods. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2019, 21, 1043–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayedi, A.; Ghomashi, F.; Zargar, M.S.; Shab-Bidar, S. Dietary sodium, sodium-to-potassium ratio, and risk of stroke: A systematic review and nonlinear dose-response meta-analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, J.T.; Patterson, K.Y.; Bodner, J.E.; Douglas, L.W.; Veillon, C.; Kelsay, J.L.; Mertz, W.; Smith, J.C., Jr. Sodium and potassium intake and balance in adults consuming self-selected diets. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1984, 40, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, L.J.; Frohlich, E.D.; Hall, J.E.; Pearson, T.A.; Sacco, R.L.; Seals, D.R.; Sacks, F.M.; Smith, S.C.; Vafiadis, D.K.; Horn, L.V.V. The Importance of Population-Wide Sodium Reduction as a Means to Prevent Cardiovascular Disease and Stroke. Circulation 2011, 123, 1138–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guideline: Sodium Intake for Adults and Children; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, R.M.; Padfield, P.L.; Seckl, J.R. Disorders of sodium balance. BMJ 2006, 332, 702–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, S. Severe hyponatraemia: Complications and treatment. QJM Int. J. Med. 1995, 88, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, M.M.; Barstow, C.H.; Pyzocha, N.J. Diagnosis and management of sodium disorders: Hyponatremia and hypernatremia. Am. Fam. Physician 2015, 91, 299–307. [Google Scholar]
- Muhsin, S.A.; Mount, D.B. Diagnosis and treatment of hypernatremia. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 30, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mente, A.; O’Donnell, M.; Yusuf, S. Sodium Intake and Health: What Should We Recommend Based on the Current Evidence? Nutrients 2021, 13, 3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-J.; Yeh, T.-L.; Shih, M.-C.; Tu, Y.-K.; Chien, K.-L. Dietary Sodium Intake and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balafa, O.; Kalaitzidis, R.G. Salt sensitivity and hypertension. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2021, 35, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Trieu, K.; Yoshimura, S.; Neal, B.; Woodward, M.; Campbell, N.R.C.; Li, Q.; Lackland, D.T.; Leung, A.A.; Anderson, C.A.M.; et al. Effect of dose and duration of reduction in dietary sodium on blood pressure levels: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. BMJ 2020, 368, m315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.A.; Cavanaugh, K.L. Dietary Sodium in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Comprehensive Approach. Semin. Dial. 2010, 23, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.G.; Dangler, C.A.; Taylor, N.S.; King, A.; Koh, T.J.; Wang, T.C. High-salt diet induces gastric epithelial hyperplasia and parietal cell loss, and enhances Helicobacter pylori colonization in C57BL/6 mice. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 4823–4828. [Google Scholar]
- D’Elia, L.; Galletti, F.; Strazzullo, P. Dietary Salt Intake and Risk of Gastric Cancer. Cancer Treat. Res. 2014, 159, 83–95. [Google Scholar]
- D’Elia, L.; Rossi, G.; Ippolito, R.; Cappuccio, F.P.; Strazzullo, P. Habitual salt intake and risk of gastric cancer: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, R.M.; Wang, N.X. Chapter Three—Potassium. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Eskin, N.A.M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 89–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekri, R.; Noël, L.; Millour, S.; Vastel, C.; Kadar, A.; Sirot, V.; Leblanc, J.-C.; Guérin, T. Calcium, magnesium, sodium and potassium levels in foodstuffs from the second French Total Diet Study. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2012, 25, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, D.H.; Terker, A.S. Why your mother was right: How potassium intake reduces blood pressure. Trans. Am. Clin. Climatol. Assoc. 2015, 126, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Strohfeldt, K.A. Alkali Metals. In Essentials of Inorganic Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 19–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healthline. Available online: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/foods-loaded-with-potassium (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Weaver, C.M. Potassium and Health. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 368S–377S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.J.; MacGregor, G.A. Beneficial effects of potassium on human health. Physiol. Plant. 2008, 133, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, L. Guideline: Potassium Intake for Adults and Children; World Health Organisation (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Greer, R.C.; Marklund, M.; Anderson, C.A.M.; Cobb, L.K.; Dalcin, A.T.; Henry, M.; Appel, L.J. Potassium-Enriched Salt Substitutes as a Means to Lower Blood Pressure. Hypertension 2020, 75, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddy, F.J.; Vanhoutte, P.M.; Feletou, M. Role of potassium in regulating blood flow and blood pressure. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2006, 290, R546–R552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aburto, N.J.; Hanson, S.; Gutierrez, H.; Hooper, L.; Elliott, P.; Cappuccio, F.P. Effect of increased potassium intake on cardiovascular risk factors and disease: Systematic review and meta-analyses. BMJ Br. Med. J. 2013, 346, f1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekmekcioglu, C.; Elmadfa, I.; Meyer, A.L.; Moeslinger, T. The role of dietary potassium in hypertension and diabetes. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 72, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casado, F.; Mudunuru, S.A.; Nasr, R. A Case of Hypokalemia Possibly Induced by Nafcillin. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, L.V.; Hashmi, M.F.; Farrell, M.W. Hyperkalemia; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Weglicki, W.; Quamme, G.; Tucker, K.; Haigney, M.; Resnick, L. Potassium, Magnesium, and Electrolyte Imbalance and Complications in Disease Management. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2005, 27, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, A.A.; Panonnummal, R. ‘Magnesium’-the master cation-as a drug—Possibilities and evidences. BioMetals 2021, 34, 955–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.-J.; Na, H.-S.; Do, S.-H. Magnesium and Pain. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, S.L. Magnesium in Disease Prevention and Overall Health. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 378S–383S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serefko, A.; Szopa, A.; Wlaź, P.; Nowak, G.; Radziwoń-Zaleska, M.; Skalski, M.; Poleszak, E. Magnesium in depression. Pharmacol. Rep. 2013, 65, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, C.G. Magnesium metabolism in health and disease. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2009, 41, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.-S.; Chao, Y.-Y.; Huang, W.-D.; Hong, C.-Y.; Kao, C.H. Effect of magnesium deficiency on antioxidant status and cadmium toxicity in rice seedlings. J. Plant Physiol. 2011, 168, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaknejad, N.; Moshtaghie, A.A.; Shahanipour, K.; Bahrami, S. The Protective Roles of Zinc and Magnesium in Cadmium-Induced Renal Toxicity in Male Wistar Rats. IJT 2015, 8, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentini, D.; Cappadone, C.; Farruggia, G.; Prata, C. Magnesium: Biochemistry, Nutrition, Detection, and Social Impact of Diseases Linked to Its Deficiency. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food, F. Drug Administration, Revision of the Nutrition and Supplement Facts Label. Fed. Regist 2016, 81, 33741–33999. [Google Scholar]
- Aal-Hamad, A.H.; Al-Alawi, A.M.; Kashoub, M.S.; Falhammar, H. Hypermagnesemia in Clinical Practice. Medicina 2023, 59, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, S.; Rapoport, J.; Zlotnik, M.; Brami, J.L.; Heimer, D.; Chaimovitz, C. Extreme Hypermagnesemia Due to Ingestion of Dead Sea Water. Nephron 2008, 47, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Laecke, S. Hypomagnesemia and hypermagnesemia. Acta Clin. Belg. 2019, 74, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jürgen, V. Magnesium: Nutrition and Homoeostasis. AIMS Public Health 2016, 3, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.A.M. Low magnesium and atherosclerosis: An evidence-based link. Mol. Asp. Med. 2003, 24, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, P.-C.T.; Pham, P.-A.T.; Pham, S.V.; Pham, P.-T.T.; Pham, P.-M.T.; Pham, P.-T.T. Hypomagnesemia: A clinical perspective. Int. J. Nephrol. Renov. Dis. 2014, 7, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchowski, M.S. Calcium in the Context of Dietary Sources and Metabolism. In Calcium: Chemistry, Analysis, Function and Effects; Preedy, V.R., Ed.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beto, J.A. The Role of Calcium in Human Aging. Clin. Nutr. Res. 2015, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyad, M.A. The potential benefits of dietary and/or supplemental calcium and vitamin D. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2003, 21, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, I.R.; Bristow, S.M.; Bolland, M.J. Calcium supplements: Benefits and risks. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 278, 354–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Chandel, K.S.A.; Bhalani, V.D.; Shrivastava, R. Importance of Dietary Supplements to the Health. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2021, 17, 583–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Valle, H.B.; Yaktine, A.L.; Taylor, C.L.; Ross, A.C. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- IOF—International Osteoporosis Foundation. Available online: https://www.osteoporosis.foundation/patients/prevention/calcium-content-of-common-foods (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Spiegel, D.M.; Brady, K. Calcium balance in normal individuals and in patients with chronic kidney disease on low- and high-calcium diets. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, C.; James, T. Perforated gastric ulcer as the initial manifestation of hyperparathyroidism. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e240570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herishanu, Y.; Abramsky, O.; Lavy, S. Focal Neurological Manifestations in Hypercalcemia. Eur. Neurol. 2008, 4, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, T.; Arnaud Sampaio, V.F.; Lameu, C.; Ulrich, H. Calcium signalling: A common target in neurological disorders and neurogenesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 95, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Lu, Q.; Wan, Z.; Geng, T.; Li, R.; Zhu, K.; Li, L.; Chen, X.; Pan, A.; Manson, J.E.; et al. Associations of Habitual Calcium Supplementation With Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality in Individuals With and Without Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2023, 47, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, M.D.; Silverberg, S.J. Primary hyperparathyroidism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, J.; Arora, S. Oncologic Metabolic Emergencies. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 31, 941–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunyecz, J.A. The use of calcium and vitamin D in the management of osteoporosis. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2008, 4, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khandare, A.L.; Harikumar, R.; Sivakumar, B. Severe Bone Deformities in Young Children From Vitamin D Deficiency and Fluorosis in Bihar-India. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2005, 76, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katiyar, V. Analysis of cases of tetany-a clinical study. J. Adv. Med. Dent. Sci. Res. 2015, 3, 133–136. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, B.L.; Brown, E.M.; Collins, M.T.; Jüppner, H.; Lakatos, P.; Levine, M.A.; Mannstadt, M.M.; Bilezikian, J.P.; Romanischen, A.F.; Thakker, R.V. Epidemiology and Diagnosis of Hypoparathyroidism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 2284–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, G.; Williams, M.R.; Riach, R.A. Calcium, cell signalling and cataract. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 1994, 13, 623–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosol, T.J.; Capen, C.C. Chapter 23—Calcium-Regulating Hormones and Diseases of Abnormal Mineral (Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium) Metabolism. In Clinical Biochemistry of Domestic Animals, 5th ed.; Kaneko, J.J., Harvey, J.W., Bruss, M.L., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1997; pp. 619–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, R.S. The Role of Zinc in Growth and Cell Proliferation. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1500S–1508S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, H.; Rink, L. The immune system and the impact of zinc during aging. Immun. Ageing 2009, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.S.; King, J.C.; Lowe, N. A Review of Dietary Zinc Recommendations. Food Nutr. Bull. 2016, 37, 443–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maret, W.; Sandstead, H.H. Zinc requirements and the risks and benefits of zinc supplementation. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2006, 20, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huth, P.J.; Fulgoni, V.L.; Keast, D.R.; Park, K.; Auestad, N. Major food sources of calories, added sugars, and saturated fat and their contribution to essential nutrient intakes in the U.S. diet: Data from the national health and nutrition examination survey (2003–2006). Nutr. J. 2013, 12, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healthdirect. Available online: https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/foods-high-in-zinc (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Mayo Clinic Web Site. Available online: https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements-zinc/art-20366112 (accessed on 2 April 2024).
- Sandstead, H.H.; Smith, J.C. Deliberations and Evaluations of Approaches, Endpoints and Paradigms for Determining Zinc Dietary Recommendations. J. Nutr. 1996, 126, 2410S–2418S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxfield, L.; Shukla, S.; Crane, J.S. Zinc Deficiency. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, R.K. Excessive Intake of Zinc Impairs Immune Responses. JAMA 1984, 252, 1443–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Navarrete, N.; Camacho, M.M.; Martínez-Lahuerta, J.; Martínez-Monzó, J.; Fito, P. Iron deficiency and iron fortified foods—A review. Food Res. Int. 2002, 35, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R. Nonhematological Benefits of Iron. Am. J. Nephrol. 2007, 27, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, C.E.; Mahoney, A.W. Contributions of heme and nonheme iron to human nutrition. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1992, 31, 333–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HealthLinkBC. Available online: https://www.healthlinkbc.ca/healthy-eating-physical-activity/food-and-nutrition/nutrients/iron-foods (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Wieringa, F.T.; Dijkhuizen, M.A.; Berger, J. Sources of Iron: Diet, Supplemental, and Environmental. In Nutritional Anemia; Karakochuk, C.D., Zimmermann, M.B., Moretti, D., Kraemer, K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trumbo, P.; Yates, A.A.; Schlicker, S.; Poos, M. Dietary Reference Intakes—Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium, and Zinc. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2001, 101, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percy, L.; Mansour, D.; Fraser, I. Iron deficiency and iron deficiency anaemia in women. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2017, 40, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, G.; Gordeuk, V.R. Benefits and risks of iron therapy for chronic anaemias. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 35, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/topics/anaemia_in_women_and_children (accessed on 22 April 2024).
- Man, Y.; Xu, T.; Adhikari, B.; Zhou, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B. Iron supplementation and iron-fortified foods: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 4504–4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, D.L.; Collinson, A. Red Meat, Dietary Heme Iron, and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: The Involvement of Advanced Lipoxidation Endproducts. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasricha, S.-R.; Tye-Din, J.; Muckenthaler, M.U.; Swinkels, D.W. Iron deficiency. Lancet 2021, 397, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbaspour, N.; Hurrell, R.F.; Kelishadi, R. Review on iron and its importance for human health. J. Res. Med. Sci. Off. J. Isfahan Univ. Med. Sci. 2014, 19, 164–174. [Google Scholar]
- Kabat, G.C.; Rohan, T.E. Does excess iron play a role in breast carcinogenesis? An unresolved hypothesis. Cancer Causes Control 2007, 18, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torti, S.V.; Torti, F.M. Cellular Iron Metabolism in Prognosis and Therapy of Breast Cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2013, 18, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X. Does iron have a role in breast cancer? Lancet Oncol. 2008, 9, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, S.; Hoque, N.; Nasrin, N.; Hossain, M.; Rizwan, F.; Biswas, K.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Rahman, S.; Hoskin, D.W.; Sultana, S.; et al. Iron Overload and Breast Cancer: Iron Chelation as a Potential Therapeutic Approach. Life 2022, 12, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajbouj, K.; Shafarin, J.; Hamad, M. Estrogen-dependent disruption of intracellular iron metabolism augments the cytotoxic effects of doxorubicin in select breast and ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 4655–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyllie, S.; Liehr, J.G. Enhancement of estrogen-induced renal tumorigenesis in hamsters by dietary iron. Carcinogenesis 1998, 19, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- de Romaña, D.L.; Olivares, M.; Uauy, R.; Araya, M. Risks and benefits of copper in light of new insights of copper homeostasis. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2011, 25, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Fartusie, F.S.; Mohssan, S.N. Essential trace elements and their vital roles in human body. Indian J. Adv. Chem. Sci. 2017, 5, 127–136. [Google Scholar]
- El Sabry, M.I.; Stino, F.K.R.; El-Ghany, W.A.A. Copper: Benefits and risks for poultry, livestock, and fish production. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fewtrell, L.; Kay, D.; Jones, F.; Baker, A.; Mowat, A. Copper in drinking water—An investigation into possible health effects. Public Health 1996, 110, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tümer, Z.; Møller, L.B. Menkes disease. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 18, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klevay, L.M. Cardiovascular Disease from Copper Deficiency—A History1. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 489S–492S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.C.; Caballero, B.; Cousins, R.J.; Tucker, K.L.; Ziegler, T.R. Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease, 11th ed.; Jones & Bartlett Learning: Burlington, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 1–1616. [Google Scholar]
- Bagheri, S.; Squitti, R.; Haertlé, T.; Siotto, M.; Saboury, A.A. Role of Copper in the Onset of Alzheimer’s Disease Compared to Other Metals. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 9, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, S.; Higashi, A.; Nakamura, T.; Matsuda, I. Nutritional Copper Deficiency in Severely Handicapped Patients on a Low Copper Enteral Diet for a Prolonged Period. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1988, 7, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairweather-Tait, S.J.; Harvey, L.J.; Collings, R. Risk–benefit analysis of mineral intakes: Case studies on copper and iron. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2010, 70, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Cheng, Z.-W.; Huang, C.-G.; Ye, Z.-Q.; Sun, L.-J.; Chen, H.; Fu, B.-B.; Zhou, K.; Fang, Z.-R.; Wang, Z.-J.; et al. Long-term exposure to copper induces mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in mouse hearts. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 234, 113329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, D.J. Safety guidelines for copper in water. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 67, 1098S–1102S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, D.; Cooke, A.; Young, T.R.; Deery, E.; Robinson, N.J.; Warren, M.J. The requirement for cobalt in vitamin B12: A paradigm for protein metalation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Res. 2021, 1868, 118896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolovskaya, O.M.; Plessl, T.; Bailey, H.; Mackinnon, S.; Baumgartner, M.R.; Yue, W.W.; Froese, D.S.; Taga, M.E. Naturally occurring cobalamin (B12) analogs can function as cofactors for human methylmalonyl-CoA mutase. Biochimie 2021, 183, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, R.; Allen, L.H.; Bjørke-Monsen, A.-L.; Brito, A.; Guéant, J.-L.; Miller, J.W.; Molloy, A.M.; Nexo, E.; Stabler, S.; Toh, B.-H.; et al. Vitamin B12 deficiency. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltrusch, S. The Role of Neurotropic B Vitamins in Nerve Regeneration. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 9968228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.; Lauria, G.; Catalano, A.; Carocci, A.; Sinicropi, M.S. Prevalence of Cobalt in the Environment and Its Role in Biological Processes. Biology 2023, 12, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niklewicz, A.; Smith, A.D.; Smith, A.; Holzer, A.; Klein, A.; McCaddon, A.; Molloy, A.M.; Wolffenbuttel, B.H.R.; Nexo, E.; McNulty, H.; et al. The importance of vitamin B12 for individuals choosing plant-based diets. Eur. J. Nutr. 2023, 62, 1551–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, A.; Harrington, D.; Robinson, S. Vitamin B<sub>12</sub> deficiency. BMJ Br. Med. J. 2014, 349, g5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cámara-Martos, F.; Moreno-Rojas, R. Cobalt: Toxicology. In Encyclopedia of Food and Health; Caballero, B., Finglas, P.M., Toldrá, F., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippini, T.; Tancredi, S.; Malagoli, C.; Malavolti, M.; Bargellini, A.; Vescovi, L.; Nicolini, F.; Vinceti, M. Dietary Estimated Intake of Trace Elements: Risk Assessment in an Italian Population. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahey, S.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, M.; Kumar, V.; Bhardwaj, R. A critical review on toxicity of cobalt and its bioremediation strategies. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.H.L.; Wang, A.Y.-M. Chapter Twelve—Vitamin B12 and chronic kidney disease. In Vitamins and Hormones; Litwack, G., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 325–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koplay, M.; Gulcan, E.; Ozkan, F. Association between Serum Vitamin B12 Levels and the Degree of Steatosis in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Investig. Med. 2011, 59, 1137–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.X.; Wahlin, Å.; Basun, H.; Fastbom, J.; Winblad, B.; Fratiglioni, L. Vitamin B12 and folate in relation to the development of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 2001, 56, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahn, G.B.; Abato, J.E.; Jadavji, N.M. Role of vitamin B12 deficiency in ischemic stroke risk and outcome. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbert, V. Staging vitamin B−12 (cobalamin) status in vegetarians. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1994, 59, 1213S–1222S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atila, N.E.; Atila, A.; Kaya, Z.; Bulut, Y.E.; Oner, F.; Topal, K.; Bayraktutan, Z.; Bakan, E. The Role of Manganese, Cadmium, Chromium and Selenium on Subjective Tinnitus. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 2844–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelclova, D.; Sklensky, M.; Janicek, P.; Lach, K. Severe cobalt intoxication following hip replacement revision: Clinical features and outcome. Clin. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seghizzi, P.; D’Adda, F.; Borleri, D.; Barbic, F.; Mosconi, G. Cobalt myocardiopathy. A critical review of literature. Sci. Total Environ. 1994, 150, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gál, J.; Hursthouse, A.; Tatner, P.; Stewart, F.; Welton, R. Cobalt and secondary poisoning in the terrestrial food chain: Data review and research gaps to support risk assessment. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 821–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickens, K.P.; Patierno, S.R.; Ceryak, S. Chromium genotoxicity: A double-edged sword. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 188, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balali-Mood, M.; Naseri, K.; Tahergorabi, Z.; Khazdair, M.R.; Sadeghi, M. Toxic Mechanisms of Five Heavy Metals: Mercury, Lead, Chromium, Cadmium, and Arsenic. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 643972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wani, S.; Weskamp, C.; Marple, J.; Spry, L. Acute Tubular Necrosis Associated with Chromium Picolinate–Containing Dietary Supplement. Ann. Pharmacother. 2006, 40, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Su, H.; Gu, Y.; Song, X.; Zhao, J. Carcinogenicity of chromium and chemoprevention: A brief update. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 4065–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, T.-L.; Kuo, C.-C.; Pan, W.-H.; Chung, Y.-T.; Chen, C.-Y.; Wu, T.-N.; Wang, S.-L. The decline in kidney function with chromium exposure is exacerbated with co-exposure to lead and cadmium. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Food Additives and Nutrient Sources added to Food (ANS). Scientific Opinion on the safety of trivalent chromium as a nutrient added for nutritional purposes to foodstuffs for particular nutritional uses and foods intended for the general population (including food supplements). EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastmond, D.A.; MacGregor, J.T.; Slesinski, R.S. Trivalent Chromium: Assessing the Genotoxic Risk of an Essential Trace Element and Widely Used Human and Animal Nutritional Supplement. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2008, 38, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EUFIC. Available online: https://www.eufic.org/en/whats-in-food/article/chromium-in-the-diet (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Bhattacharya, S.; Fontaine, A.; MacCallum, P.E.; Drover, J.; Blundell, J. Stress across generations: DNA methylation as a potential mechanism underlying intergenerational effects of stress in both post-traumatic stress disorder and pre-clinical predator stress rodent models. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, C.M.; Proctor, D.M.; Suh, M.; Haws, L.C.; Kirman, C.R.; Harris, M.A. Assessment of the mode of action underlying development of rodent small intestinal tumors following oral exposure to hexavalent chromium and relevance to humans. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2013, 43, 244–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dana, L.; Neela, G.; Amy, L.H.; Kurt, S. Identifying occupational carcinogens: An update from the IARC Monographs. Occup. Environ. Med. 2018, 75, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, R.; Upreti, R.K.; Seth, P.K.; Chaturvedi, U.C. Effects of chromium on the immune system. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2002, 34, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, F.; Maleki, V.; Saleh-Ghadimi, S.; Kooshki, F.; Pourghassem Gargari, B. Potential roles of chromium on inflammatory biomarkers in diabetes: A Systematic. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2019, 46, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dworzański, W.; Sembratowicz, I.; Cholewińska, E.; Tutaj, K.; Fotschki, B.; Juśkiewicz, J.; Ognik, K. Effects of Different Chromium Compounds on Hematology and Inflammatory Cytokines in Rats Fed High-Fat Diet. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 614000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikhhossein, F.; Amini, M.R.; Shahinfar, H.; Djafari, F.; Safabakhsh, M.; Shab-Bidar, S. Effects of chromium supplementation on inflammatory biomarkers: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2020, 37, 101147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, T.; Liu, Y.; Buchner, V.; Tchounwou, P.B. Neurotoxic Effects and Biomarkers of Lead Exposure: A Review. Rev. Environ. Health 2009, 24, 15–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellinger, D.; Leviton, A.; Waternaux, C.; Needleman, H.; Rabinowitz, M. Longitudinal Analyses of Prenatal and Postnatal Lead Exposure and Early Cognitive Development. N. Engl. J. Med. 1987, 316, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanphear, B.P.; Hornung, R.; Khoury, J.; Yolton, K.; Baghurst, P.; Bellinger, D.C.; Canfield, R.L.; Dietrich, K.N.; Bornschein, R.; Greene, T.; et al. Low-Level Environmental Lead Exposure and Children’s Intellectual Function: An International Pooled Analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnaas, L.; Rothenberg, S.J.; Flores, M.-F.; Martinez, S.; Hernandez, C.; Osorio, E.; Velasco, S.R.; Perroni, E. Reduced Intellectual Development in Children with Prenatal Lead Exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brubaker, C.J.; Dietrich, K.N.; Lanphear, B.P.; Cecil, K.M. The influence of age of lead exposure on adult gray matter volume. NeuroToxicology 2010, 31, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slikker, W.; Paule, M.G.; Wang, C. Handbook of Developmental Neurotoxicology; Slikker, W., Jr., Paule, M.G., Wang, C., Eds.; an imprint of Elsevier; Academic Press: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sadiq, S.; Ghazala, Z.; Chowdhury, A.; Büsselberg, D. Metal Toxicity at the Synapse: Presynaptic, Postsynaptic, and Long-Term Effects. J. Toxicol. 2012, 2012, 132671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordemann, J.M.; Austin, R.N. Lead neurotoxicity: Exploring the potential impact of lead substitution in zinc-finger proteins on mental health. Metallomics 2016, 8, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Guan, R.-L.; Liu, M.-C.; Shen, X.-F.; Chen, J.Y.; Zhao, M.-G.; Luo, W.-J. Lead Exposure Impairs Hippocampus Related Learning and Memory by Altering Synaptic Plasticity and Morphology During Juvenile Period. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 3740–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lidsky, T.I.; Schneider, J.S. Lead neurotoxicity in children: Basic mechanisms and clinical correlates. Brain 2003, 126, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, A.; Trujillo, K.A. Neurotoxicity of low-level lead exposure: History, mechanisms of action, and behavioral effects in humans and preclinical models. NeuroToxicology 2019, 73, 58–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidemann, D.K.; Weaver, V.M.; Fadrowski, J.J. Toxic environmental exposures and kidney health in children. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2016, 31, 2043–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadrowski, J.J.; Abraham, A.G.; Navas-Acien, A.; Guallar, E.; Weaver, V.M.; Furth, S.L. Blood Lead Level and Measured Glomerular Filtration Rate in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collin, M.S.; Venkatraman, S.K.; Vijayakumar, N.; Kanimozhi, V.; Arbaaz, S.M.; Stacey, R.G.S.; Anusha, J.; Choudhary, R.; Lvov, V.; Tovar, G.I.; et al. Bioaccumulation of lead (Pb) and its effects on human: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2022, 7, 100094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Al-Awadi, A.A.; Khan, K.M. Lead Affects Vitamin D Metabolism in Rats. Nutrients 2018, 10, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flora, G.; Gupta, D.; Tiwari, A. Toxicity of lead: A review with recent updates. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2012, 5, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenland, K.; Boffetta, P. Lead and cancer in humans: Where are we now? Am. J. Ind. Med. 2000, 38, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao Linda, M.; Friesen Melissa, C.; Xiang, Y.-B.; Cai, H.; Koh, D.-H.; Ji, B.-T.; Yang, G.; Li, H.-L.; Locke Sarah, J.; Rothman, N.; et al. Occupational Lead Exposure and Associations with Selected Cancers: The Shanghai Men’s and Women’s Health Study Cohorts. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Lestón, J.; Roma-Torres, J.; Mayan, O.; Schroecksnadel, S.; Fuchs, D.; Moreira, A.O.; Pásaro, E.; Méndez, J.; Teixeira, J.P.; Laffon, B. Assessment of Immunotoxicity Parameters in Individuals Occupationally Exposed to Lead. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2012, 75, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, A.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.S.; Chaturvedi, A.K.; Shabnam, A.A.; Subrahmanyam, G.; Mondal, R.; Gupta, D.K.; Malyan, S.K.; Kumar, S.S.; et al. Lead Toxicity: Health Hazards, Influence on Food Chain, and Sustainable Remediation Approaches. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chwalba, A.; Maksym, B.; Dobrakowski, M.; Kasperczyk, S.; Pawlas, N.; Birkner, E.; Kasperczyk, A. The effect of occupational chronic lead exposure on the complete blood count and the levels of selected hematopoietic cytokines. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 355, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambelunghe, A.; Sallsten, G.; Borné, Y.; Forsgard, N.; Hedblad, B.; Nilsson, P.; Fagerberg, B.; Engström, G.; Barregard, L. Low-level exposure to lead, blood pressure, and hypertension in a population-based cohort. Environ. Res. 2016, 149, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoi, M.F.; Lo, C.W.H.; Cheung, T.T.; Cheung, B.M.Y. Blood lead level and risk of hypertension in the United States National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2016. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guldbrand, C.; Barregard, L.; Sallsten, G.; Forsgard, N.; Lundh, T.; Borné, Y.; Fagerberg, B.; Engström, G.; Bergström, G.; Harari, F. Low-level exposure to lead and atherosclerosis in the carotid arteries: Results from the Swedish population-based cohort SCAPIS. Environ. Res. 2024, 244, 117900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.; Kim, S.; Cho, S.; Kim, H.; Jung, I.; Moon, J.-D.; Park, W.-J. The Association Between Blood Lead Levels and Coronary Artery Calcium Score Determined by Using Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2023, 38, e203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Huang, P.-C.; Wu, C.; Sung, F.-C.; Su, T.-C. Association between urine lead levels and cardiovascular disease risk factors, carotid intima-media thickness and metabolic syndrome in adolescents and young adults. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 223, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, R.; Ramond, A.; O’Keeffe, L.M.; Shahzad, S.; Kunutsor, S.K.; Muka, T.; Gregson, J.; Willeit, P.; Warnakula, S.; Khan, H.; et al. Environmental toxic metal contaminants and risk of cardiovascular disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2018, 362, k3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, C.; Cabrera, C.; Lorenzo, M.L.; López, M.C. Cadmium levels in wine, beer and other alcoholic beverages: Possible sources of contamination. Sci. Total Environ. 1996, 181, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwazono, Y.; Kido, T.; Nakagawa, H.; Nishijo, M.; Honda, R.; Kobayashi, E.; Dochi, M.; Nogawa, K. Biological half-life of cadmium in the urine of inhabitants after cessation of cadmium exposure. Biomarkers 2009, 14, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridges, C.C.; Zalups, R.K. Molecular and ionic mimicry and the transport of toxic metals. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 204, 274–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branca, J.J.V.; Morucci, G.; Pacini, A. Cadmium-induced neurotoxicity: Still much ado. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 1879. [Google Scholar]
- Marchetti, C. Interaction of metal ions with neurotransmitter receptors and potential role in neurodiseases. BioMetals 2014, 27, 1097–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlowe, M.; Cossairt, A.; Moon, C.; Errera, J.; MacNeel, A.; Peak, R.; Ray, J.; Schroeder, C. Main and interaction effects of metallic toxins on classroom behavior. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 1985, 13, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruebarrena, M.A.; Hawe, C.T.; Lee, Y.M.; Branco, R.C. Mechanisms of Cadmium Neurotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, P.; Zhao, X. Circulatory Levels of Toxic Metals (Aluminum, Cadmium, Mercury, Lead) in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease: A Quantitative Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 62, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, K.; Kaur, P.; Gupta, G.D.; Singh, S. Metals associated neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease: Insight to physiological, pathological mechanisms and management. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 753, 135873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, O.; Ecochard, V.; Mahéo, S.; Gross, G.; Bodin, P.; Teissié, J.; Escudier, J.-M.; Paquereau, L. α,β-D-Constrained Nucleic Acids Are Strong Terminators of Thermostable DNA Polymerases in Polymerase Chain Reaction. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, Q.; Song, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Bian, J.; Liu, X.; Gu, J.; et al. Cadmium induced inhibition of autophagy is associated with microtubule disruption and mitochondrial dysfunction in primary rat cerebral cortical neurons. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2016, 53, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Du, Y. Cadmium and Its Neurotoxic Effects. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 898034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharrazian, D. Exposure to Environmental Toxins & Autoimmune Conditions. Integr. Med. Clin. J. 2024, 23, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, K.-L.; Klaassen, C.D. Neurotoxic effects of cadmium in young rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1982, 63, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usai, C.; Barberis, A.; Moccagatta, L.; Marchetti, C. Pathways of Cadmium Influx in Mammalian Neurons. J. Neurochem. 1999, 72, 2154–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, P. Mechanisms of cadmium carcinogenesis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satarug, S. Dietary Cadmium Intake and Its Effects on Kidneys. Toxics 2018, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satarug, S.; Vesey, D.A.; Gobe, G.C.; Phelps, K.R. Estimation of health risks associated with dietary cadmium exposure. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 329–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Cruz, E.Y.; Amador-Martínez, I.; Aranda-Rivera, A.K.; Cruz-Gregorio, A.; Pedraza Chaverri, J. Renal damage induced by cadmium and its possible therapy by mitochondrial transplantation. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 361, 109961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prozialeck, W.C.; Edwards, J.R. Mechanisms of Cadmium-Induced Proximal Tubule Injury: New Insights with Implications for Biomonitoring and Therapeutic Interventions. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 343, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippini, T.; Malagoli, C.; Wise, L.A.; Malavolti, M.; Pellacani, G.; Vinceti, M. Dietary cadmium intake and risk of cutaneous melanoma: An Italian population-based case-control study. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2019, 56, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julin, B.; Wolk, A.; Johansson, J.E.; Andersson, S.O.; Andrén, O.; Åkesson, A. Dietary cadmium exposure and prostate cancer incidence: A population-based prospective cohort study. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Lee, J.; Woo, H.D.; Kim, D.W.; Choi, I.J.; Kim, Y.-I.; Kim, J. Association between dietary cadmium intake and early gastric cancer risk in a Korean population: A case–control study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 3255–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kresovich, J.K.; Erdal, S.; Chen, H.Y.; Gann, P.H.; Argos, M.; Rauscher, G.H. Metallic air pollutants and breast cancer heterogeneity. Environ. Res. 2019, 177, 108639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florez-Garcia, V.A.; Guevara-Romero, E.C.; Hawkins, M.M.; Bautista, L.E.; Jenson, T.E.; Yu, J.; Kalkbrenner, A.E. Cadmium exposure and risk of breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Environ. Res. 2023, 219, 115109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Järup, L. Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 68, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genchi, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Lauria, G.; Carocci, A.; Catalano, A. The Effects of Cadmium Toxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Yao, W.; Ba, Q.; Wang, H. Effects of Cadmium Exposure on the Immune System and Immunoregulation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 695484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olszowski, T.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I.; Gutowska, I.; Chlubek, D. Pro-inflammatory properties of cadmium. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2012, 59, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.C.; Almeida Lopes, A.C.B.; Urbano, M.R.; Carvalho, M.d.F.H.; Silva, A.M.R.; Tinkov, A.A.; Aschner, M.; Mesas, A.E.; Silbergeld, E.K.; Paoliello, M.M.B. An updated systematic review on the association between Cd exposure, blood pressure and hypertension. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramjoo, H.; Arab-Zozani, M.; Feyzi, A.; Naghizadeh, A.; Aschner, M.; Naimabadi, A.; Farkhondeh, T.; Samarghandian, S. The association between environmental cadmium exposure, blood pressure, and hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 35682–35706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerberg, B.; Barregard, L.; Sallsten, G.; Forsgard, N.; Östling, G.; Persson, M.; Borné, Y.; Engström, G.; Hedblad, B. Cadmium exposure and atherosclerotic carotid plaques—Results from the Malmö diet and Cancer study. Environ. Res. 2015, 136, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barregard, L.; Sallsten, G.; Harari, F.; Andersson Eva, M.; Forsgard, N.; Hjelmgren, O.; Angerås, O.; Fagman, E.; Persson, M.; Lundh, T.; et al. Cadmium Exposure and Coronary Artery Atherosclerosis: A Cross-Sectional Population-Based Study of Swedish Middle-Aged Adults. Environ. Health Perspect. 2021, 129, 067007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, G.; Berglund, G.; Blomberg, A.; Brandberg, J.; Engström, G.; Engvall, J.; Eriksson, M.; de Faire, U.; Flinck, A.; Hansson, M.G.; et al. The Swedish CArdioPulmonary BioImage Study: Objectives and design. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 278, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinkov, A.A.; Filippini, T.; Ajsuvakova, O.P.; Skalnaya, M.G.; Aaseth, J.; Bjørklund, G.; Gatiatulina, E.R.; Popova, E.V.; Nemereshina, O.N.; Huang, P.-T.; et al. Cadmium and atherosclerosis: A review of toxicological mechanisms and a meta-analysis of epidemiologic studies. Environ. Res. 2018, 162, 240–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellez-Plaza, M.; Guallar, E.; Fabsitz, R.; Howard, B.; Umans, J.; Francesconi, K.; Goessler, W.; Devereux, R.; Navas-Acien, A. Cadmium Exposure and Incident Peripheral Arterial Disease. Circulation. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2013, 6, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ujueta, F.; Arenas, I.A.; Diaz, D.; Yates, T.; Beasley, R.; Navas-Acien, A.; Lamas, G.A. Cadmium level and severity of peripheral artery disease in patients with coronary artery disease. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2019, 26, 1456–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, M.; Rachamalla, M.; Niyogi, S.; Datusalia, A.K.; Flora, S.J.S. Molecular Mechanism of Arsenic-Induced Neurotoxicity including Neuronal Dysfunctions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llobet, J.M.; Falcó, G.; Casas, C.; Teixidó, A.; Domingo, J.L. Concentrations of Arsenic, Cadmium, Mercury, and Lead in Common Foods and Estimated Daily Intake by Children, Adolescents, Adults, and Seniors of Catalonia, Spain. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 838–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.I.; Ahmad, M.F.; Ahmad, I.; Ashfaq, F.; Wahab, S.; Alsayegh, A.A.; Kumar, S.; Hakeem, K.R. Arsenic Exposure through Dietary Intake and Associated Health Hazards in the Middle East. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uttara, B.; Singh, V.A.; Zamboni, P.; Mahajan, T.R. Oxidative Stress and Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Review of Upstream and Downstream Antioxidant Therapeutic Options. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2009, 7, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolins, M.; Ruchirawat, M.; Landrigan, P. The Developmental Neurotoxicity of Arsenic: Cognitive and Behavioral Consequences of Early Life Exposure. Ann. Glob. Health 2014, 80, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahaman, M.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Mise, N.; Sikder, M.T.; Ichihara, G.; Uddin, M.K.; Kurasaki, M.; Ichihara, S. Environmental arsenic exposure and its contribution to human diseases, toxicity mechanism and management. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 289, 117940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heng, Y.Y.; Asad, I.; Coleman, B.; Menard, L.; Benki-Nugent, S.; Hussein Were, F.; Karr, C.J.; McHenry, M.S. Heavy metals and neurodevelopment of children in low and middle-income countries: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0265536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Miah, M.; Aschner, M. Metals and Neurodegeneration [version 1; peer review: 3 approved]. F1000Research 2016, 5, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, C.; Soni, M.; Kumar, V. Mitochondrial oxidative stress and dysfunction in arsenic neurotoxicity: A review. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2016, 36, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flora, S.J.S.; Bhadauria, S.; Pant, S.C.; Dhaked, R.K. Arsenic induced blood and brain oxidative stress and its response to some thiol chelators in rats. Life Sci. 2005, 77, 2324–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, K.; Fatima, F.; Akash, M.S.H. Biochemical investigation of association of arsenic exposure with risk factors of diabetes mellitus in Pakistani population and its validation in animal model. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Lou, B.; Wu, R.; Wang, G.; Lu, C.; Wang, H.; Pi, J.; Xu, Y. The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Arsenic Toxicity. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, C.; Chhikara, S.; Kumar, V. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Arsenic-Induced Hepatotoxicity: Pathogenic and Therapeutic Implications. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, K.H.; Tsukahara, S.; Maekawa, F.; Nohara, K.; Nakamura, K.; Tanoue, A. Role of Environmental Chemical Insult in Neuronal Cell Death and Cytoskeleton Damage. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 38, 1109–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.F.; Shaw, P.J.; De Vos, K.J. The role of mitochondria in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 710, 132933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarazúa, S.; Bürger, S.; Delgado, J.M.; Jiménez-Capdeville, M.E.; Schliebs, R. Arsenic affects expression and processing of amyloid precursor protein (APP) in primary neuronal cells overexpressing the Swedish mutation of human APP. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2011, 29, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin-Chan, M.; Navarro-Yepes, J.; Quintanilla-Vega, B. Environmental pollutants as risk factors for neurodegenerative disorders: Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strumylaite, L.; Kregzdyte, R.; Kucikiene, O.; Baranauskiene, D.; Simakauskiene, V.; Naginiene, R.; Damuleviciene, G.; Lesauskaite, V.; Zemaitiene, R. Alzheimer’s Disease Association with Metals and Metalloids Concentration in Blood and Urine. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre-Omar, C.; Liu, E.; Dalle, C.; d’Incamps, B.L.; Bigou, S.; Daube, C.; Karpf, L.; Davenne, M.; Robil, N.; Jost Mousseau, C.; et al. Neurofilament accumulations in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients’ motor neurons impair axonal initial segment integrity. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2023, 80, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFuria, J.; Shea, T.B. Arsenic inhibits neurofilament transport and induces perikaryal accumulation of phosphorylated neurofilaments: Roles of JNK and GSK-3β. Brain Res. 2007, 1181, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henchcliffe, C. Blood and cerebrospinal fluid markers in Parkinson’s disease: Current biomarker findings. Curr. Biomark. Find. 2014, 2015, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson-Mora, J.; Escobar, M.L.; Rodríguez-Durán, L.; Massieu, L.; Montiel, T.; Rodríguez, V.M.; Hernández-Mercado, K.; Gonsebatt, M.E. Gestational exposure to inorganic arsenic (iAs3+) alters glutamate disposition in the mouse hippocampus and ionotropic glutamate receptor expression leading to memory impairment. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, K.F.W.; Barnett, D.; Cory-Slechta, D.A.; Xia, H. Early Low-Level Arsenic Exposure Impacts Post-Synaptic Hippocampal Function in Juvenile Mice. Toxics 2021, 9, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mónaco, N.M.; Bartos, M.; Dominguez, S.; Gallegos, C.; Bras, C.; Esandi, M.d.C.; Bouzat, C.; Giannuzzi, L.; Minetti, A.; Gumilar, F. Low arsenic concentrations impair memory in rat offpring exposed during pregnancy and lactation: Role of α7 nicotinic receptor, glutamate and oxidative stress. NeuroToxicology 2018, 67, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, C.; Kazemi, M.; Cheng, H.; Mohammadi, H.; Babaei, A.; Taheri, E.; Moradi, S. Associations between exposure to heavy metals and the risk of chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2021, 51, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Niu, Q.; Xu, M.; Rui, D.; Xu, S.; Feng, G.; Ding, Y.; Li, S.; Jing, M. Factors Affecting Arsenic Methylation in Arsenic-Exposed Humans: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yan, X.; Tang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cao, X.; Ran, X.; Ma, G.; Hu, T.; Qureshi, A.; et al. Study on the mechanism of arsenic-induced renal injury based on SWATH proteomics technology. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2024, 83, 127390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangleben, N.L.; Skibola, C.F.; Smith, M.T. Arsenic immunotoxicity: A review. Environ. Health 2013, 12, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaw, J.; Marshall, G.; Yuan, Y.; Ferreccio, C.; Steinmaus, C.; Smith, A.H. Increased Childhood Liver Cancer Mortality and Arsenic in Drinking Water in Northern Chile. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2008, 17, 1982–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hu, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Z. Arsenic trioxide inhibits lung metastasis of mouse colon cancer via reducing the infiltration of regulatory T cells. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 15165–15173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, L.N. 21—An update on the immunotoxic effects of arsenic exposure. In Handbook of Arsenic Toxicology, 2nd ed.; Flora, S.J.S., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2023; pp. 551–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, B.H.; Mann, K.K. Arsenic as an immunotoxicant. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2022, 454, 116248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germolec, D.R.; Yoshida, T.; Gaido, K.; Wilmer, J.L.; Simeonova, P.P.; Kayama, F.; Burleson, F.; Dong, W.; Lange, R.W.; Luster, M.I. Arsenic induces overexpression of growth factors in human keratinocytes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1996, 141, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Li, A.; Mei, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, K.; Xu, Q. The association of arsenic exposure with hypertension and blood pressure: A systematic review and dose–response meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 289, 117914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhyankar Lalita, N.; Jones Miranda, R.; Guallar, E.; Navas-Acien, A. Arsenic Exposure and Hypertension: A Systematic Review. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, J.A.; Mattison, C.; Fretts, A.M.; Umans, J.G.; Cole, S.A.; Voruganti, V.S.; Goessler, W.; Best, L.G.; Zhang, Y.; Tellez-Plaza, M.; et al. Arsenic, blood pressure, and hypertension in the Strong Heart Family Study. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, F.; Graziano, J.H.; Parvez, F.; Liu, M.; Paul, R.R.; Shaheen, I.; Sarwar, G.; Ahmed, A.; Islam, T.; et al. Arsenic Exposure From Drinking Water, Arsenic Methylation Capacity, and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Bangladesh. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 178, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nong, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Guallar, E.; Zhong, Q. Arsenic Exposure and Predicted 10-Year Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Risk Using the Pooled Cohort Equations in U.S. Hypertensive Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flyvholm, M.A.; Nielsen, G.D.; Andersen, A. Nickel content of food and estimation of dietary intake. Z. Leb. Unters. Forsch 1984, 179, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, G.N.; Packirisamy, S. Systemic nickel: The contribution made by stainless-steel cooking utensils. Contact Dermat. 1995, 32, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahiya, S.; Karpe, R.; Hegde, A.G.; Sharma, R.M. Lead, cadmium and nickel in chocolates and candies from suburban areas of Mumbai, India. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2005, 18, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramtahal, G.; Chang-Yen, I.; Bekele, I.; Bekele, F.; Wilson, L.; Sukha, B.; Maharaj, K. Cost-effective Method of Analysis for the Determination of Cadmium, Copper, Nickel and Zinc in Cocoa Beans and Chocolates. J. Food Res. 2014, 4, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, D.A.; Garland, T.R.; Wildung, R.E.; Drucker, H. Nickel in Plants: II. Distribution and Chemical Form in Soybean Plants 1. Plant Physiol. 1978, 62, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, A.; Meyer, D.; Mayer, F. Heavy metal toxicities: Levels of nickel, cobalt and chromium in the soil and plants associated with visual symptoms and variation in growth of an oat crop. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1973, 24, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM); Schrenk, D.; Bignami, M.; Bodin, L.; Chipman, J.K.; Del Mazo, J.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; Hogstrand, C.; Hoogenboom, L.; Leblanc, J.-C.; et al. Update of the risk assessment of nickel in food and drinking water. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e06268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Y.; Yang, J.; Ma, L.; Jin, L.; Bai, Y. Associations of nickel exposure and kidney function in U.S. adults, NHANES 2017–2018. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2022, 74, 127065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Lee, S.-J. Association of Blood Heavy Metal Levels and Renal Function in Korean Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Xi, S. The effects of heavy metals on human metabolism. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2020, 30, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, R.S.B.; Unrine, J.M.; Vangala, C.; Sanderson, W.T.; Mandayam, S.; Murray, K.O. Evidence of nickel and other trace elements and their relationship to clinical findings in acute Mesoamerican Nephropathy: A case-control analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.-C.; Wu, C.-L.; Kor, C.-T.; Lian, I.-B.; Chang, C.-H.; Chang, T.-H.; Chang, C.-C.; Chiu, P.-F. Prospective associations between environmental heavy metal exposure and renal outcomes in adults with chronic kidney disease. Nephrology 2018, 23, 830–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieter, M.P.; Jameson, C.W.; Tucker, A.N.; Luster, M.I.; French, J.E.; Hong, H.L.; Boorman, G.A. Evaluation of tissue disposition, myelopoietic, and immunologic responses in mice after long-term exposure to nickel sulfate in the drinking water. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 1988, 24, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Bucchianico, S.; Gliga, A.R.; Åkerlund, E.; Skoglund, S.; Wallinder, I.O.; Fadeel, B.; Karlsson, H.L. Calcium-dependent cyto- and genotoxicity of nickel metal and nickel oxide nanoparticles in human lung cells. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2018, 15, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belliardo, C.; Di Giorgio, C.; Chaspoul, F.; Gallice, P.; Bergé-Lefranc, D. Direct DNA interaction and genotoxic impact of three metals: Cadmium, nickel and aluminum. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2018, 125, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM). Scientific Opinion on the risks to public health related to the presence of nickel in food and drinking water. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.T.-T.; Lua, W.-H.; Poh, J.-J.; Ling, W.-L.; Yeo, J.Y.; Gan, S.K.-E. Molecular Insights of Nickel Binding to Therapeutic Antibodies as a Possible New Antibody Superantigen. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 676048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechara, R.; Nabhan, M.; Antonios, D.; Azouri, H.; Pallardy, M. IL-27 Production and Regulation in Human Dendritic Cells Treated with the Chemical Sensitizer NiSO4. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2018, 31, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakob, A.; Mussotter, F.; Ohnesorge, S.; Dietz, L.; Pardo, J.; Haidl, I.D.; Thierse, H.-J. Immunoproteomic identification and characterization of Ni2+-regulated proteins implicates Ni2+ in the induction of monocyte cell death. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriarity, R.J.; Liberda, E.N.; Tsuji, L.J.S. Subsistence fishing in the Eeyou Istchee (James Bay, Quebec, Canada): A regional investigation of fish consumption as a route of exposure to methylmercury. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perelló, G.; Martí-Cid, R.; Llobet, J.M.; Domingo, J.L. Effects of Various Cooking Processes on the Concentrations of Arsenic, Cadmium, Mercury, and Lead in Foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 11262–11269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/environmental-contaminants-food/mercury-levels-commercial-fish-and-shellfish-1990-2012 (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Gao, Z.; Wu, N.; Du, X.; Li, H.; Mei, X.; Song, Y. Toxic Nephropathy Secondary to Chronic Mercury Poisoning: Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes. Kidney Int. Rep. 2022, 7, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, K.M.; Cauvi, D.M.; Toomey, C.B.; Hultman, P.; Kono, D.H. Mercury-induced inflammation and autoimmunity. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2019, 1863, 129299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajsuvakova, O.P.; Tinkov, A.A.; Aschner, M.; Rocha, J.B.T.; Michalke, B.; Skalnaya, M.G.; Skalny, A.V.; Butnariu, M.; Dadar, M.; Sarac, I.; et al. Sulfhydryl groups as targets of mercury toxicity. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 417, 213343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, M. Minamata Disease: Methylmercury Poisoning in Japan Caused by Environmental Pollution. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1995, 25, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakir, F.; Damluji, S.F.; Amin-Zaki, L.; Murtadha, M.; Khalidi, A.; Al-Rawi, N.Y.; Tikriti, S.; Dhahir, H.I.; Clarkson, T.W.; Smith, J.C.; et al. Methylmercury Poisoning in Iraq. Science 1973, 181, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carocci, A.; Rovito, N.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Genchi, G. Mercury Toxicity and Neurodegenerative Effects. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Whitacre, D.M., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weihe, P.; Debes Joensen, H. Dietary recommendations regarding pilot whale meat and blubber in the Faroe Islands. Int. J. Circumpolar Health 2012, 71, 18594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, M.; Rocha, J.B.T.; Aschner, M. Mechanisms of methylmercury-induced neurotoxicity: Evidence from experimental studies. Life Sci. 2011, 89, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aschner, M.; Syversen, T. Methylmercury: Recent advances in the understanding of its neurotoxicity. Ther. Drug Monit. 2005, 27, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, A.; Julshamn, K.; Ringdal, O.; Mørkøre, J. Trace elements intake in the Faroe Islands II. Intake of mercury and other elements by consumption of pilot whales (Globicephalus meleanus). Sci. Total Environ. 1987, 65, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, T.; Rostampour, N.; Fallah, A.A.; Hesami, A. The association between mercury levels and autism spectrum disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2017, 44, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dack, K.; Fell, M.; Taylor, C.M.; Havdahl, A.; Lewis, S.J. Prenatal Mercury Exposure and Neurodevelopment up to the Age of 5 Years: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mychasiuk, R.; Gibb, R.; Kolb, B. Prenatal stress alters dendritic morphology and synaptic connectivity in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus of developing offspring. Synapse 2012, 66, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, H.; Sasaki, G.; Nishikawa, M.; Hara, M. Effects of subcytotoxic cadmium on morphology of glial fibrillary acidic protein network in astrocytes derived from murine neural stem/progenitor cells. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 40, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juárez, B.I.; Portillo-Salazar, H.; González-Amaro, R.; Mandeville, P.; Aguirre, J.R.; Jiménez, M.E. Participation of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors on methylmercury-induced DNA damage in rat frontal cortex. Toxicology 2005, 207, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, K.-i.; Nakanishi, H.; Moriguchi, S.; Fukuyama, N.; Eto, K.; Wakamiya, J.; Murao, K.; Arimura, K.; Osame, M. Involvement of enhanced sensitivity of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors in vulnerability of developing cortical neurons to methylmercury neurotoxicity. Brain Res. 2001, 901, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson Thomas, W.; Magos, L.; Myers Gary, J. The Toxicology of Mercury—Current Exposures and Clinical Manifestations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1731–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, K.M.; Christy, J.M.; Cauvi, D.M.; Kono, D.H. Environmental xenobiotic exposure and autoimmunity. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2018, 10, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salonen, J.T.; Seppänen, K.; Lakka, T.A.; Salonen, R.; Kaplan, G.A. Mercury accumulation and accelerated progression of carotid atherosclerosis: A population-based prospective 4-year follow-up study in men in eastern Finland. Atherosclerosis 2000, 148, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi Anna, L.; Weihe, P.; Budtz-Jørgensen, E.; Jørgensen Poul, J.; Salonen Jukka, T.; Tuomainen, T.-P.; Murata, K.; Nielsen Hans, P.; Petersen Maria, S.; Askham, J.; et al. Methylmercury Exposure and Adverse Cardiovascular Effects in Faroese Whaling Men. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.F.; Singh, K.; Chan, H.M. Mercury Exposure, Blood Pressure, and Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Dose–response Meta-analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, 076002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type of Culinary Salt | Sodium Content (mg per Teaspoon) |
|---|---|
| Iodized salt | 2360 |
| Kosher salt | 1240 |
| Low-sodium salt | 1770 |
| Pink Himalayan salt | 1680 |
| Sea salt | 2000 |
| Type of Milk | Calcium Content (mg per 200 mL) |
|---|---|
| Semi-skimmed cow milk | 240 |
| Skimmed cow milk | 244 |
| Whole cow milk | 236 |
| Sheep milk | 380 |
| Coconut milk | 54 |
| Oat milk | 16 |
| Almond milk | 90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Milanković, V.; Tasić, T.; Leskovac, A.; Petrović, S.; Mitić, M.; Lazarević-Pašti, T.; Novković, M.; Potkonjak, N. Metals on the Menu—Analyzing the Presence, Importance, and Consequences. Foods 2024, 13, 1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13121890
Milanković V, Tasić T, Leskovac A, Petrović S, Mitić M, Lazarević-Pašti T, Novković M, Potkonjak N. Metals on the Menu—Analyzing the Presence, Importance, and Consequences. Foods. 2024; 13(12):1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13121890
Chicago/Turabian StyleMilanković, Vedran, Tamara Tasić, Andreja Leskovac, Sandra Petrović, Miloš Mitić, Tamara Lazarević-Pašti, Mirjana Novković, and Nebojša Potkonjak. 2024. "Metals on the Menu—Analyzing the Presence, Importance, and Consequences" Foods 13, no. 12: 1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13121890
APA StyleMilanković, V., Tasić, T., Leskovac, A., Petrović, S., Mitić, M., Lazarević-Pašti, T., Novković, M., & Potkonjak, N. (2024). Metals on the Menu—Analyzing the Presence, Importance, and Consequences. Foods, 13(12), 1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13121890











