Exploration of New Lipid Nutrients and Their Characterization in Herbal Teas Using Non-Targeted Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
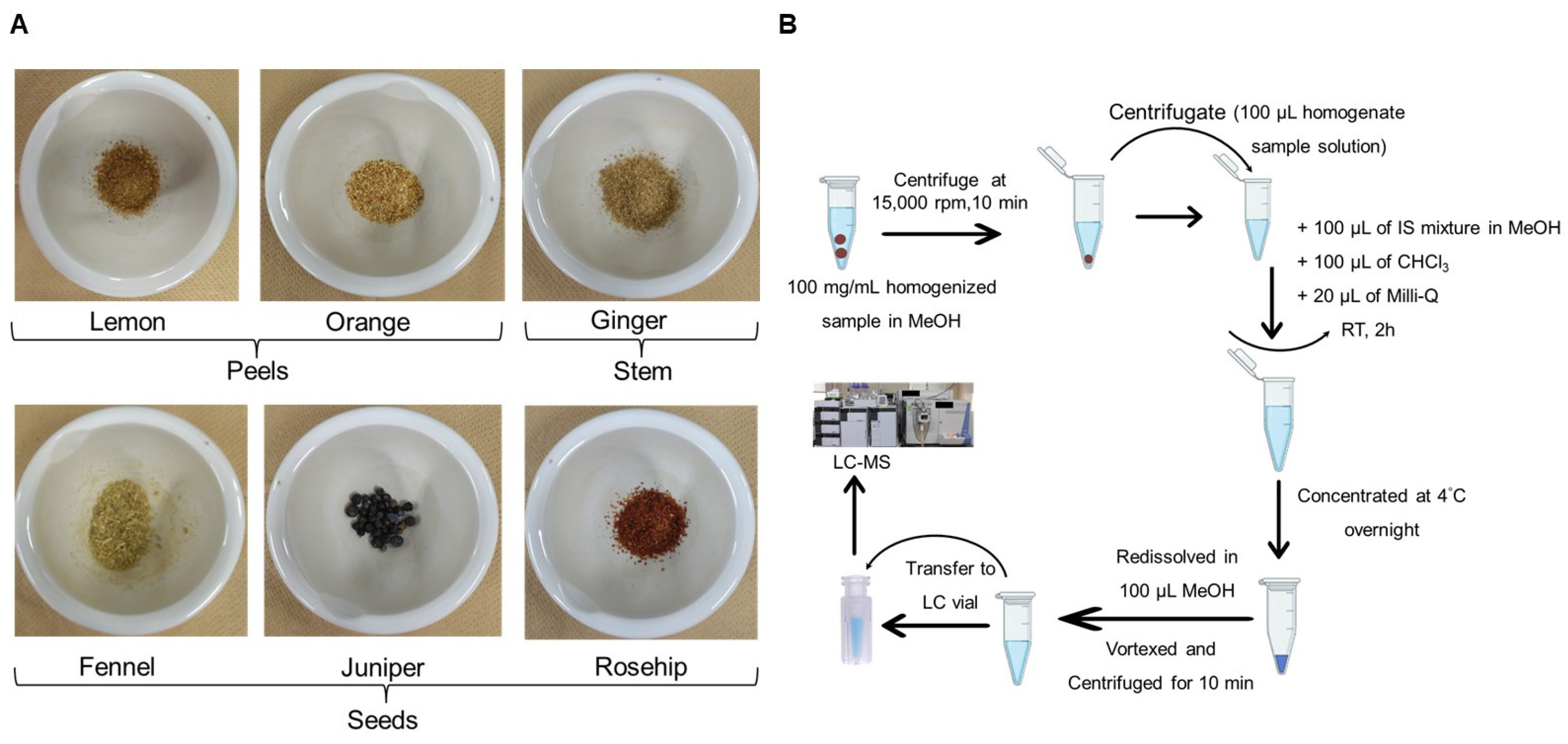
2.1. Sample Information
2.2. Materials
2.3. Extraction of Total Lipids from Herbal Teas
2.4. Non-Targeted Lipidomic Analysis Using an HPLC–LTQ Orbitrap MS
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
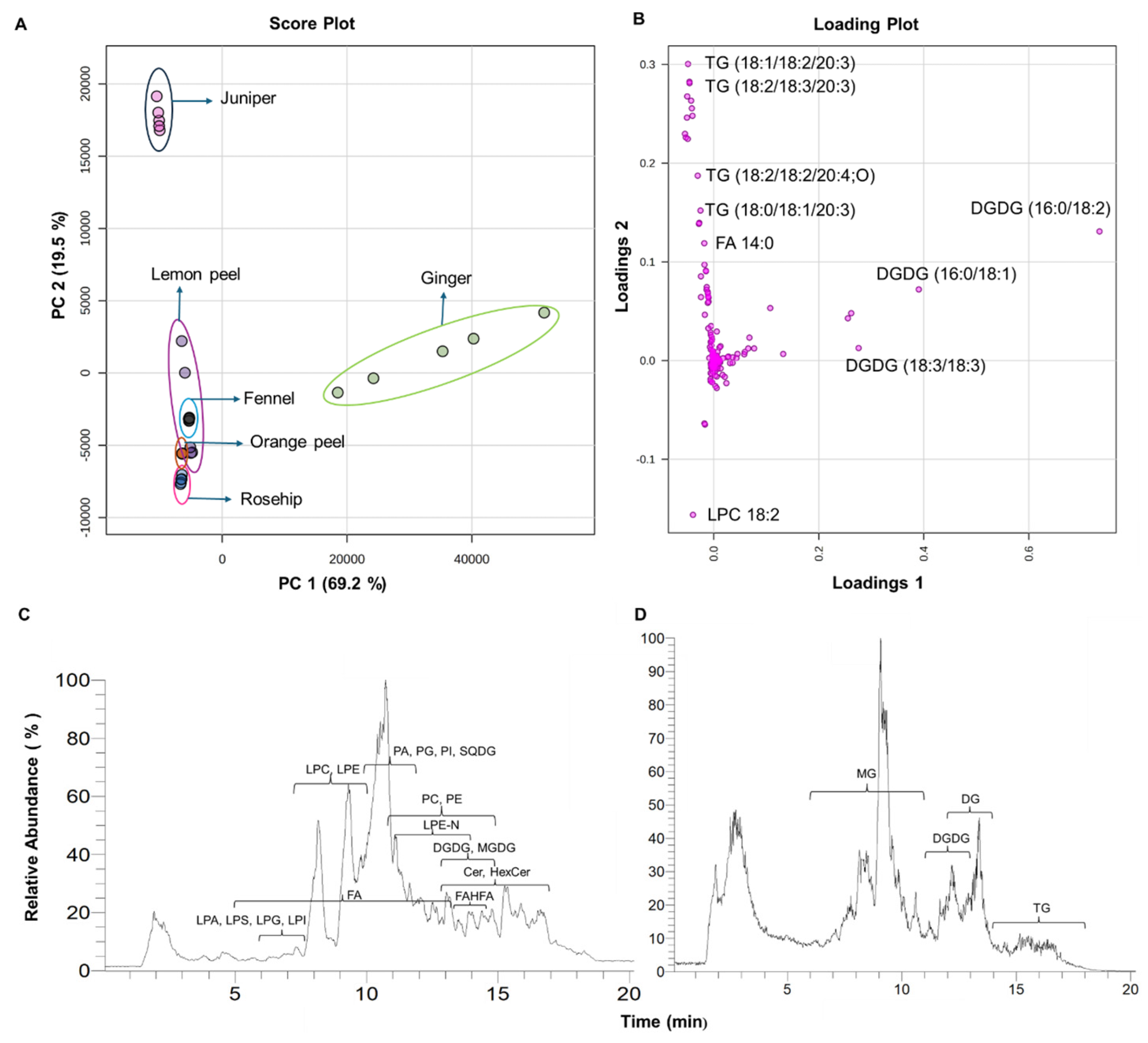
3.1. Total Lipid Extraction in Six Herbal Teas and Their Lipidomic Profiles
3.2. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) of Six Types of Herbal Teas
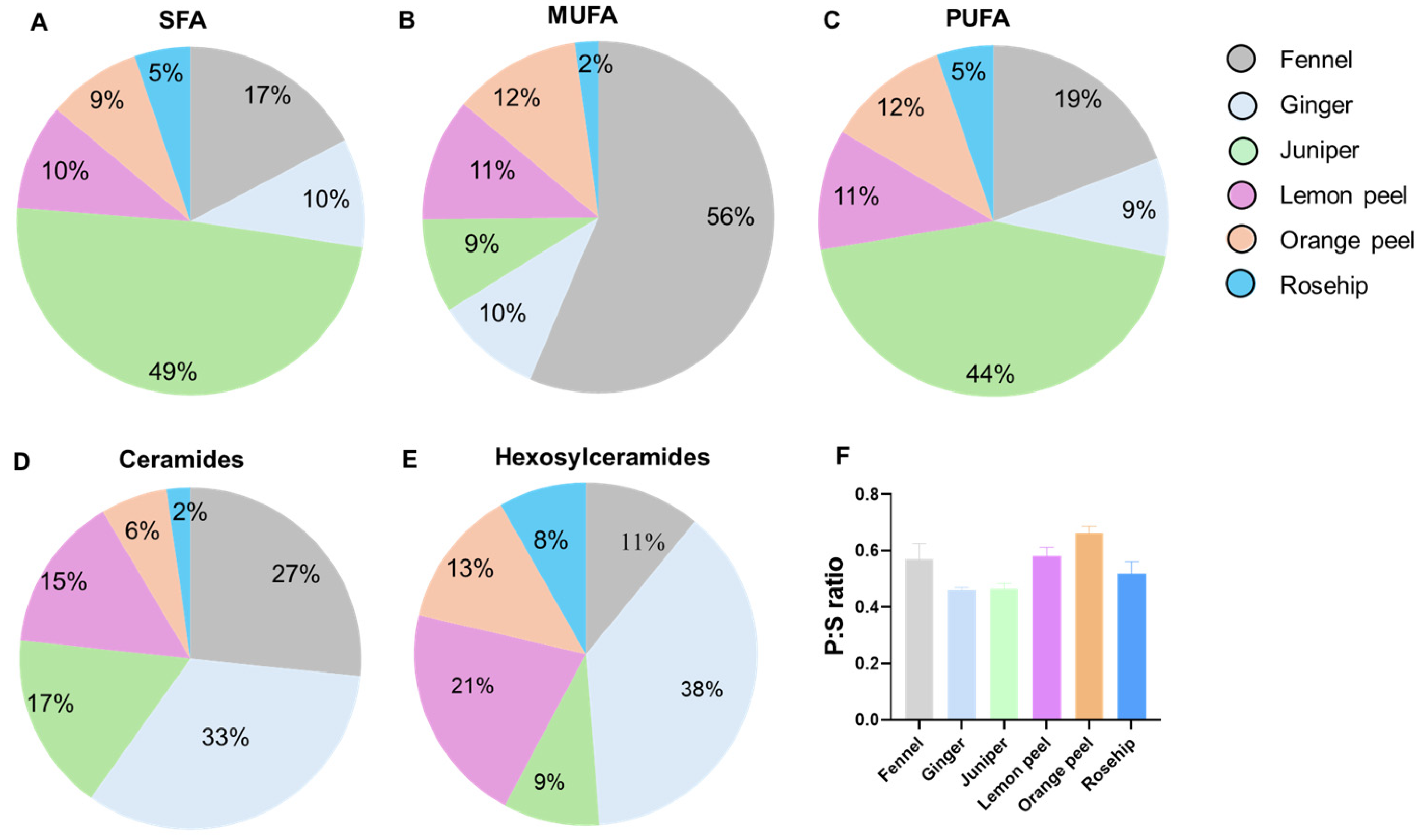
3.3. Distribution of Lipid Compositions in Six Types of Herbal Teas
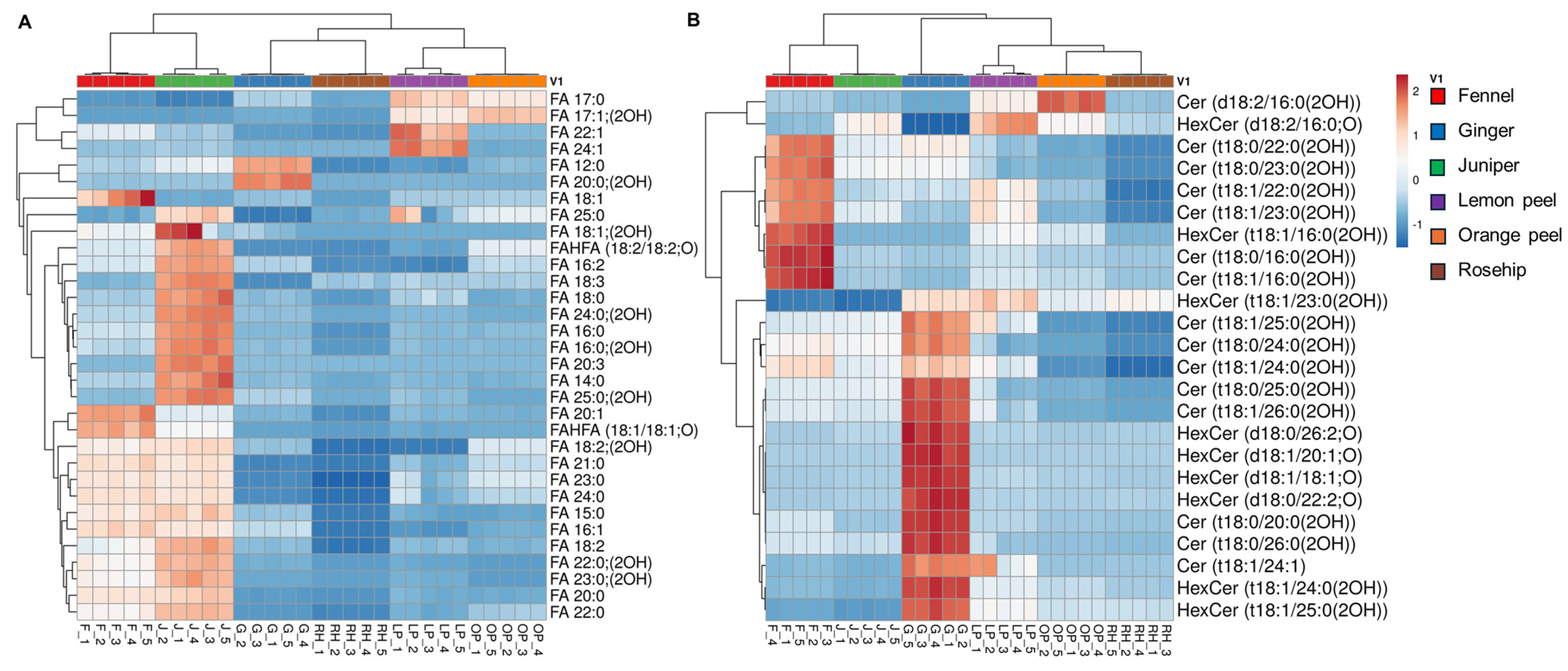
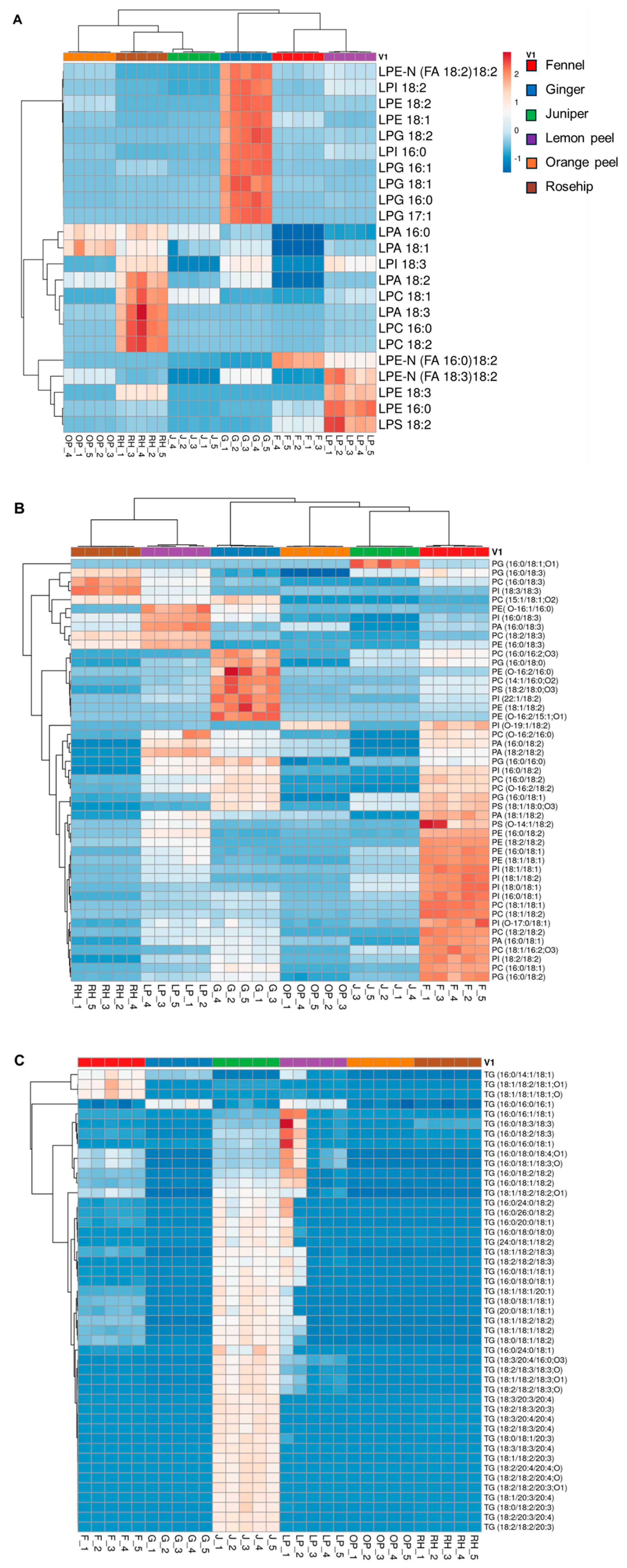
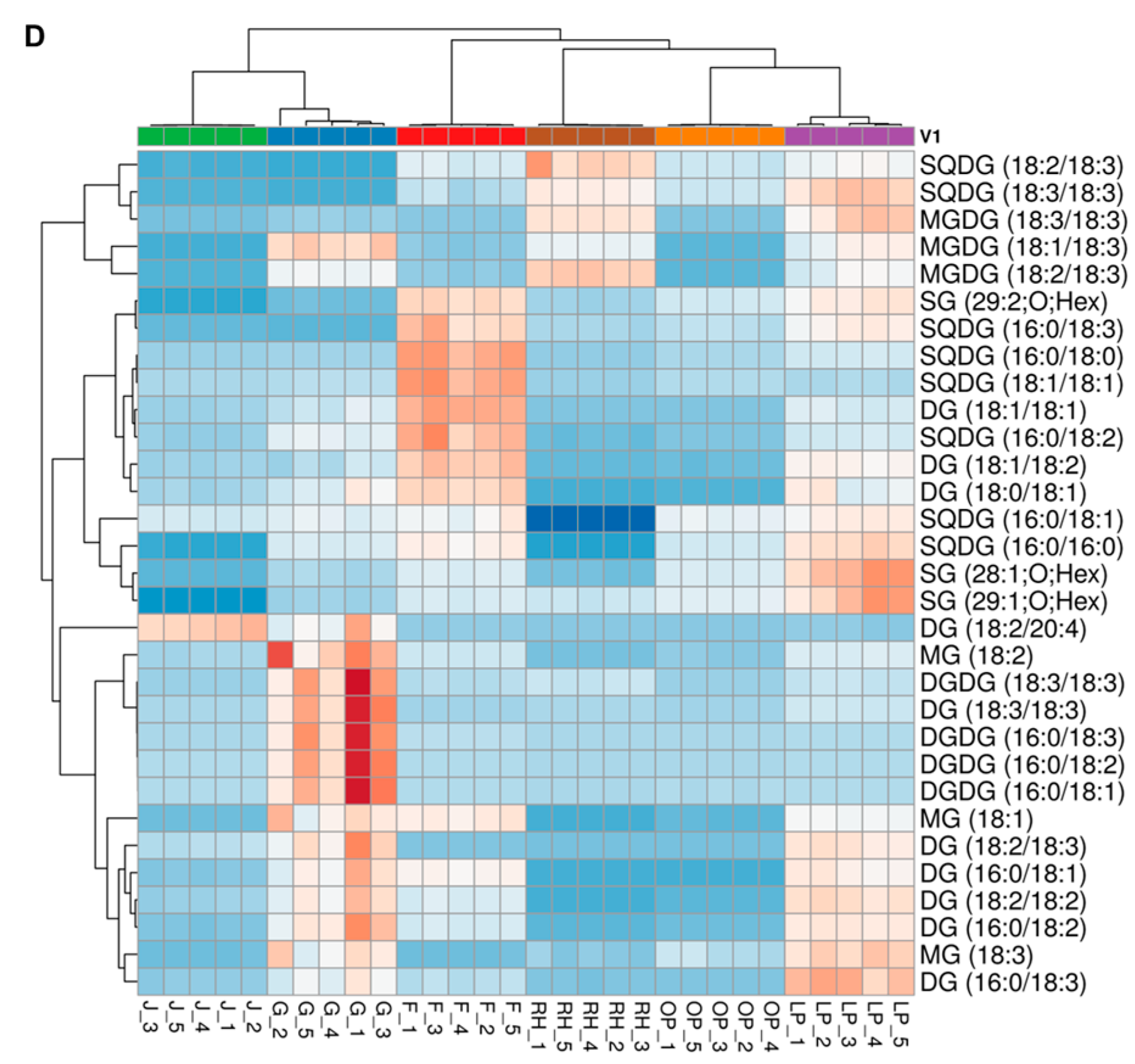
3.4. Hierarchical Cluster Correlation Analysis of Lipids Characterized in Six Herbal Teas
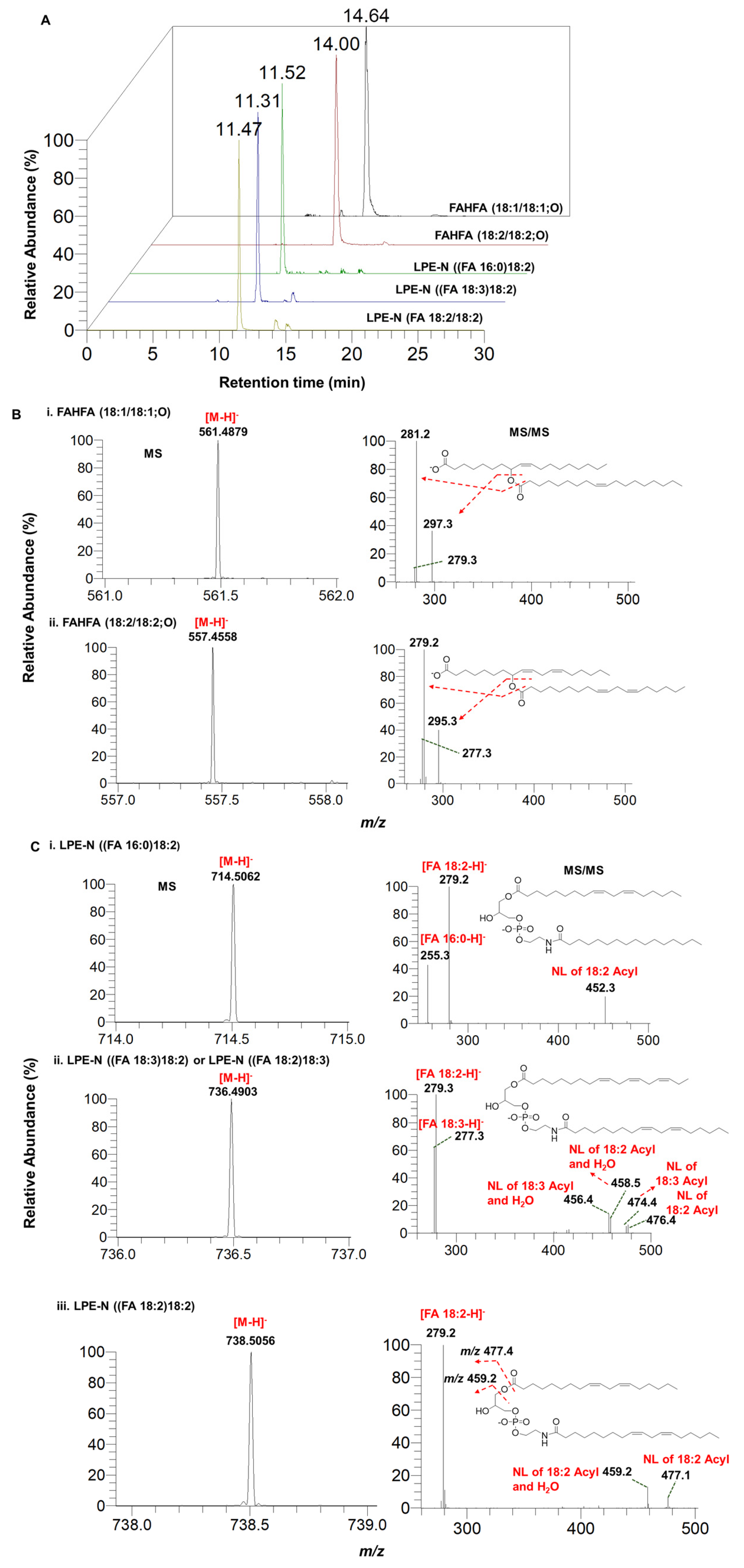
3.5. Identification and Characterization of Fatty Acid Esters of Hydroxy Fatty Acids (FAHFAs) and N-acyl-lysophosphatidylethanolamine (LPE-N) in Herbal Teas
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, G.; Kapoor, I.P.S.; Singh, P.; de Heluani, C.S.; de Lampasona, M.P.; Catalan, C.A.N. Chemistry, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Investigations on Essential Oil and Oleoresins of Zingiber Officinale. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 3295–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Assri, E.M.; Hajib, A.; Choukri, H.; Gharby, S.; Lahkimi, A.; Eloutassi, N.; Bouia, A. Nutritional Quality, Lipid, and Mineral Profiling of Seven Moroccan Apiaceae Family Seeds. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2023, 160, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consuelo, M.; Äaz-Maroto, D.I.; Di, I.J.; Hidalgo, Ä.-M.; Sa, Ä.; Nchez-Palomo, E.; Soledad, M. Volatile Components and Key Odorants of Fennel (Foeniculum vulgare Mill.) and Thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.) Oil Extracts Obtained by Simultaneous Distillation–Extraction and Supercritical Fluid Extraction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 5385–5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, L.; Carvalho, A.M.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. The Nutritional Composition of Fennel (Foeniculum vulgare): Shoots, Leaves, Stems and Inflorescences. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 814–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.T.; Raghu, R.; Lin, S.H.; Wang, S.Y.; Kuo, C.H.; Tseng, Y.J.; Sheen, L.Y. Metabolomics of Ginger Essential Oil against Alcoholic Fatty Liver in Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 11231–11240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vutyavanich, T.; Kraisarin, T.; Ruangsri, R. Ginger for Nausea and Vomiting in Pregnancy: Randomized, Double-Masked, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Obstet. Gynecol. 2001, 97, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikkhah Bodagh, M.; Maleki, I.; Hekmatdoost, A. Ginger in gastrointestinal disorders: A systematic review of clinical trials. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 7, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrman, B.; Rosenblat, M.; Hayek, T.; Coleman, R.; Aviram, M. Ginger Extract Consumption Reduces Plasma Cholesterol, Inhibits LDL Oxidation and Attenuates Development of Atherosclerosis in Atherosclerotic, Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, A.; Wang, Z.; Takahashi, S.; Tokuda, T.; Miura, N.; Hasegawa, J. Upregulation of MRNA of Retinoid Binding Protein and Fatty Acid Binding Protein by Cholesterol Enriched-Diet and Effect of Ginger on Lipid Metabolism. Life Sci. 2009, 84, 903–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, D.; Das, A.; Bhattacharya, A.; Chakrabarti, G. Aqueous Extract of Ginger Shows Antiproliferative Activity through Disruption of Microtubule Network of Cancer Cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 2872–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Miyamoto, M.; Murakami, A.; Ohigashi, H.; Osawa, T.; Uchida, K. A Phase II Detoxification Enzyme Inducer from Lemongrass: Identification of Citral and Involvement of Electrophilic Reaction in the Enzyme Induction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 302, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Inouye, S.; Abe, S. Anti-Candida and Radical Scavenging Activities of Essential Oils and Oleoresins of Zingiber Officinale Roscoe and Essential Oils of Other Plants Belonging to the Family Zingiberaceae. Drug Discov. Ther. 2011, 5, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzanna, R.; Lindmark, L.; Frondoza, C.G. Review Ginger-An Herbal Medicinal Product with Broad Anti-Inflammatory Actions. J. Med. Food. 2005, 8, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Su, R.; Yuan, H.; Zhou, H.; Jiangfang, Y.; Liu, X.; Luo, J. Widely Targeted Volatilomics and Metabolomics Analysis Reveal the Metabolic Composition and Diversity of Zingiberaceae Plants. Metabolites 2023, 13, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belov, T.; Terenzhev, D.; Bushmeleva, K.N.; Davydova, L.; Burkin, K.; Fitsev, I.; Gatiyatullina, A.; Egorova, A.; Nikitin, E. Comparative Analysis of Chemical Profile and Biological Activity of Juniperus communis L. Berry Extracts. Plants 2023, 12, 3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumitrescu, E.; Muselin, F.; Dumitrescu, C.S.; Orasan-Alic, S.A.; Moruzi, R.F.; Doma, A.O.; Mohamed, E.A.; Cristina, R.T. Juniper communis L. Essential Oils from Western Romanian Carpathians: Bio-Structure and Effective Antibacterial Activity. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofikoya, O.O.; Eronen, E.; Mäkinen, M.; Jänis, J. Production and Characterization of Hydrothermal Extracts of the Needles from Four Conifer Tree Species: Scots Pine, Norway Spruce, Common Juniper, and European Larch. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 1540–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, M.; Ashraf, M.S.; Mushtaq, N.; Nawaz, H.; Mustafa, M.I.; Ahmad, F.; Younas, M.; Javaid, A. Influence of Varying Levels of Dried Citrus Pulp on Nutrient Intake, Growth Performance and Economic Efficiency in Lambs. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2018, 46, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhidary, I.A.; Abdelrahman, M.M. Effects of Naringin Supplementation on Productive Performance, Antioxidant Status and Immune Response in Heat-Stressed Lambs. Small Rumin. Res. 2016, 138, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simitzis, P.E.; Charismiadou, M.A.; Goliomytis, M.; Charalambous, A.; Ntetska, I.; Giamouri, E.; Deligeorgis, S.G. Antioxidant Status, Meat Oxidative Stability and Quality Characteristics of Lambs Fed with Hesperidin, Naringin or α-Tocopheryl Acetate Supplemented Diets. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purba, R.A.P.; Yuangklang, C.; Paengkoum, S.; Paengkoum, P. Milk Fatty Acid Composition, Rumen Microbial Population and Animal Performance in Response to Diets Rich in Linoleic Acid Supplemented with. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2020, 62, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, S.C.; Cottica, S.M.; Boeing, J.S.; Samensari, R.B.; Santos, G.T.; Visentainer, J.V.; Zeoula, L.M. Effect of Feeding Phenolic Compounds from Propolis Extracts to Dairy Cows on Milk Production, Milk Fatty Acid Composition, and the Antioxidant Capacity of Milk. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2014, 193, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrill Alfred, H., Jr.; Schmelz, E.-M.; Wang, E.; Schroeder, J.; Dillehay, J.; Dirck, L.; Riley Ronald, T. Role of Dietary Sphingolipids and Inhibitors of Sphingolipid Metabolism in Cancer and Other Diseases. J. Nutr. 1995, 125, 1677S–1682S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, S.; Zhao, H.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Tu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, G. Lipidomic Profiling Using GC and LC-MS/MS Revealed the Improved Milk Quality and Lipid Composition in Dairy Cows Supplemented with Citrus Peel Extract. Food Res. Intl. 2022, 161, 111767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Calle, M.; Priego-Capote, F.; Luque De Castro, M.D. Ultrasound-Assisted Emulsification–Extraction of Orange Peel Metabolites Prior to Tentative Identification by LC–QTOF MS/MS. Talanta 2015, 141, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benavente-García, O.; Castillo, J. Update on Uses and Properties of Citrus Flavonoids: New Findings in Anticancer, Cardiovascular, and Anti-Inflammatory Activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 6185–6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addi, M.; Elbouzidi, A.; Abid, M.; Tungmunnithum, D.; Elamrani, A.; Hano, C. An Overview of Bioactive Flavonoids from Citrus Fruits. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manthey, J.; Guthrie, N.; Grohmann, K. Biological Properties of Citrus Flavonoids Pertaining to Cancer and Inflammation. Curr. Med. Chem. 2001, 8, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, K.; Phillips, C. Potential Antimicrobial Uses of Essential Oils in Food: Is Citrus the Answer? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, A.A.; Balanč, B.; Volić, M.; Pećinar, I.; Živković, J.; Šavikin, K.P. Rosehip Extract-Loaded Liposomes for Potential Skin Application: Physicochemical Properties of Non- and UV-Irradiated Liposomes. Plants 2023, 12, 3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarirad, S.; Mehrabi, M.; Divband, B.; Kosari-Nasab, M. Biofabrication of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Fruit Extract of Rosa Canina and Their Toxic Potential against Bacteria: A Mechanistic Approach. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 59, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grajzer, M.; Prescha, A.; Korzonek, K.; Wojakowska, A.; Dziadas, M.; Kulma, A.; Grajeta, H. Characteristics of Rose Hip (Rosa canina L.) Cold-Pressed Oil and Its Oxidative Stability Studied by the Differential Scanning Calorimetry Method. Food Chem. 2015, 188, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilyasoǧlu, H. Characterization of Rosehip (Rosa canina L.) Seed and Seed Oil. Int. J. Food Prop. 2014, 17, 1591–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowda, S.G.B.; Yifan, C.; Gowda, D.; Tsuboi, Y.; Chiba, H.; Hui, S.P. Analysis of Antioxidant Lipids in Five Species of Dietary Seaweeds by Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddabasave, S.G.; Minami, Y.; Gowda, D.; Furuko, D.; Chiba, H.; Hui, S.P. Lipidomic Analysis of Non-Esterified Furan Fatty Acids and Fatty Acid Compositions in Dietary Shellfish and Salmon by UHPLC/LTQ-Orbitrap-MS. Food Res. Intl. 2021, 144, 110325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malek, M.A.; Gowda, S.G.B.; Gowda, D.; Hui, S.-P. Analysis of Lipid Composition and Characterization of Acyl Steryl Glycosides in Rose Petals by Using Nontargeted LC/MS. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 2385–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddabasave, S.G.; Minami, Y.; Gowda, D.; Chiba, H.; Hui, S.P. Detection and Characterization of Lipids in Eleven Species of Fish by Non-Targeted Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, R.L.; Deluc, L.G.; Marpeau, A.M. Conifer Seeds: Oil Content and Fatty Acid Composition. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1996, 73, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, N.H.; Kholif, A.E.; Azzaz, H.H. Fennel and Ginger Improved Nutrient Digestibility and Milk Yield and Quality in Early Lactating Egyptian Buffaloes. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2022, 22, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Z.; Xue, L.Y.; Gao, L.; Qin, X.M.; Du, G.H. Ginger Extract Extends the Lifespan of Drosophila Melanogaster through Antioxidation and Ameliorating Metabolic Dysfunction. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 49, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessema, E.N.; Gebre-Mariam, T.; Neubert, R.H.H.; Wohlrab, J. Potential Applications of Phyto-Derived Ceramides in Improving Epidermal Barrier Function. Skin. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2017, 30, 115–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanston-Flatt, S.K.; Day, C.; Bailey, C.J.; Flatt, P.R. Traditional Plant Treatments for Diabetes. Studies in Normal and Streptozotocin Diabetic Mice. Diabetologia 1990, 33, 462–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.B.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, C.W.; Lee, H.K.; Oh, T.-K.; Kim, S.C. Comparison between Ethanolic and Aqueous Extracts from Chinese Juniper Berries for Hypoglycaemic and Hypolipidemic Effects in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 115, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Xie, Q.; Liang, L.; Luo, J.; Jiang, S.; Peng, C.; Wang, W. An Efficient Workflow for Quality Control Marker Screening and Metabolite Discovery in Dietary Herbs by LC-Orbitrap-MS/MS and Chemometric Methods: A Case Study of Chrysanthemum Flowers. Foods 2024, 13, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumus, Z.P. Assessment of Toxic Pyrrolizidine and Tropane Alkaloids in Herbal Teas and Culinary Herbs Using LC-Q-ToF/MS. Foods 2023, 12, 3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malongane, F.; McGaw, L.J.; Debusho, L.K.; Mudau, F.N. Sensory Characteristics and Volatile Compounds of Herbal Teas and Mixtures of Bush Tea with Other Selected Herbal Teas of South Africa. Foods 2020, 9, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabry, P.; Weber, S.; Teipel, J.; Richling, E.; Walch, S.G.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Quantitative NMR Spectrometry of Phenylpropanoids, including Isoeugenol in Herbs, Spices, and Essential Oils. Foods 2024, 13, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.F.; Yan, J.W.; Zhang, T.Y.; Xiao, H.M.; Feng, Y.Q. Comprehensive Screening and Identification of Fatty Acid Esters of Hydroxy Fatty Acids in Plant Tissues by Chemical Isotope Labeling-Assisted Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 10056–10063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takumi, H.; Kato, K.; Ohto, N.T.; Nakanishi, H.; Kamasaka, H.; Kuriki, T. Analysis of Fatty Acid Esters of Hydroxyl Fatty Acid in Nut Oils and Other Plant Oils. J. Oleo Sci. 2021, 70, ess21123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colborne, A.J.; Laidman, D.L. The Extraction and Analysis of Wheat Phospholipids. Phytochemistry 1975, 14, 2639–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malek, M.A.; B. Gowda, S.G.; M. Gangadhara, R.; Gowda, D.; Hui, S.-P. Exploration of New Lipid Nutrients and Their Characterization in Herbal Teas Using Non-Targeted Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Foods 2024, 13, 1877. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13121877
Malek MA, B. Gowda SG, M. Gangadhara R, Gowda D, Hui S-P. Exploration of New Lipid Nutrients and Their Characterization in Herbal Teas Using Non-Targeted Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Foods. 2024; 13(12):1877. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13121877
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalek, Md Abdul, Siddabasave Gowda B. Gowda, Rachana M. Gangadhara, Divyavani Gowda, and Shu-Ping Hui. 2024. "Exploration of New Lipid Nutrients and Their Characterization in Herbal Teas Using Non-Targeted Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry" Foods 13, no. 12: 1877. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13121877
APA StyleMalek, M. A., B. Gowda, S. G., M. Gangadhara, R., Gowda, D., & Hui, S.-P. (2024). Exploration of New Lipid Nutrients and Their Characterization in Herbal Teas Using Non-Targeted Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Foods, 13(12), 1877. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13121877








