Preparation and Regulation of Natural Amphiphilic Zein Nanoparticles by Microfluidic Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Analysis of Amino Acid Composition
2.3. Solubility of Zein in Ethanol
2.3.1. Fluorescence Analysis
2.3.2. Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Analysis
2.4. Preparation of Zein Nanoparticles via Microfluidics Technology
2.5. Controlling the Particle Size of ZNPs by Microfluidics Technology
2.6. Characterization of ZNPs
2.6.1. Microscopic Analysis
2.6.2. Particle Size and ζ Potential
2.6.3. Light Transmittance
2.6.4. Fluorescence Spectrum
2.6.5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.6.6. Solubility
2.6.7. Surface Hydrophobicity
2.6.8. Total/Free Sulfhydryl Group and Disulfide Bond Contents
2.6.9. Emulsifying Properties
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Zein’s Amino Acid Composition
3.2. Solubility of Zein in Ethanol
3.2.1. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
3.2.2. Light Transmittance
3.3. Physicochemical Properties of ZNPs
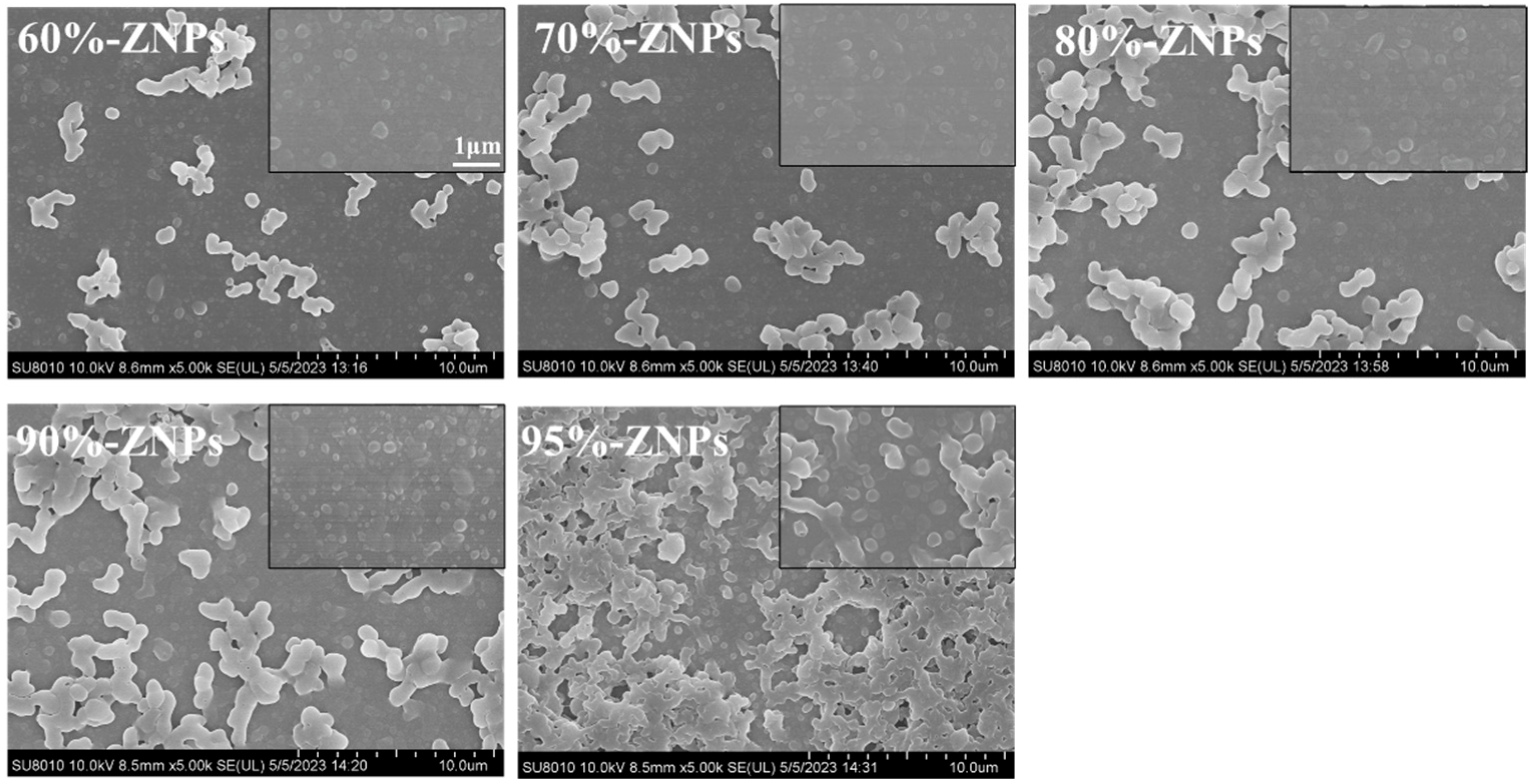
3.3.1. Microstructure and Microscopic Morphology
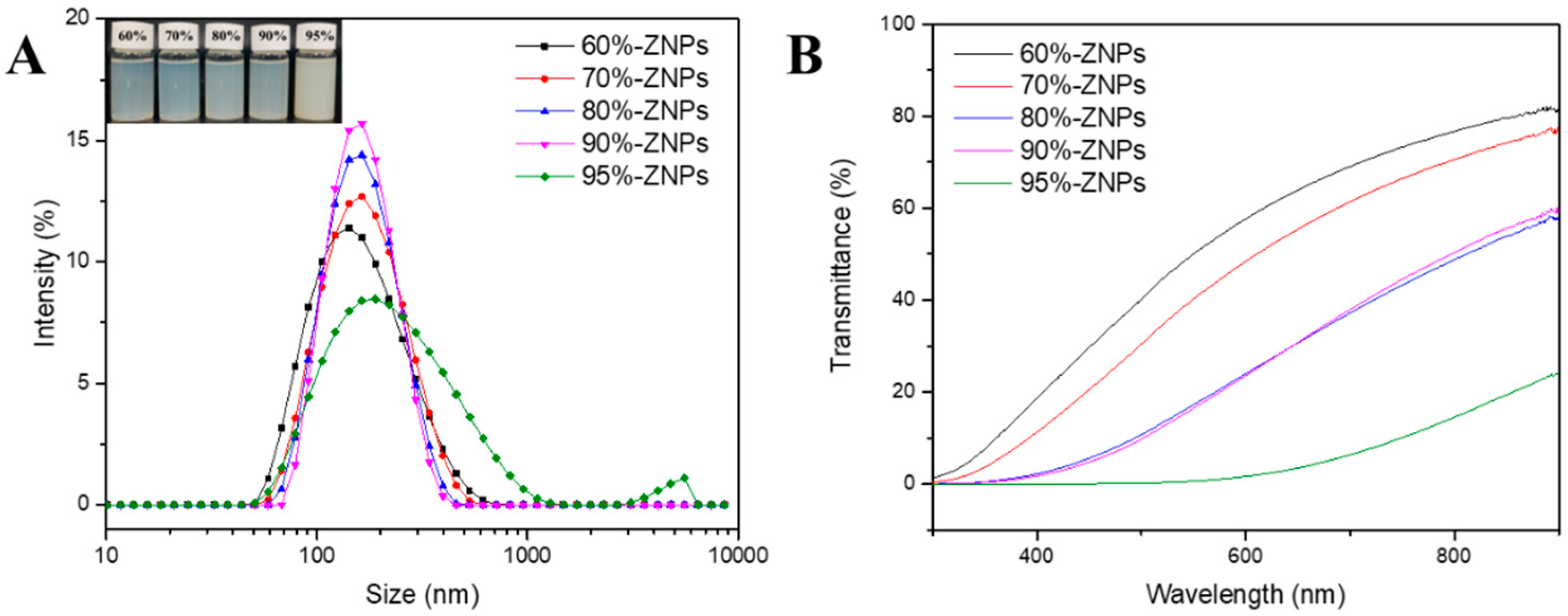
3.3.2. Particle Size and ζ Potential
3.3.3. Light Transmittance
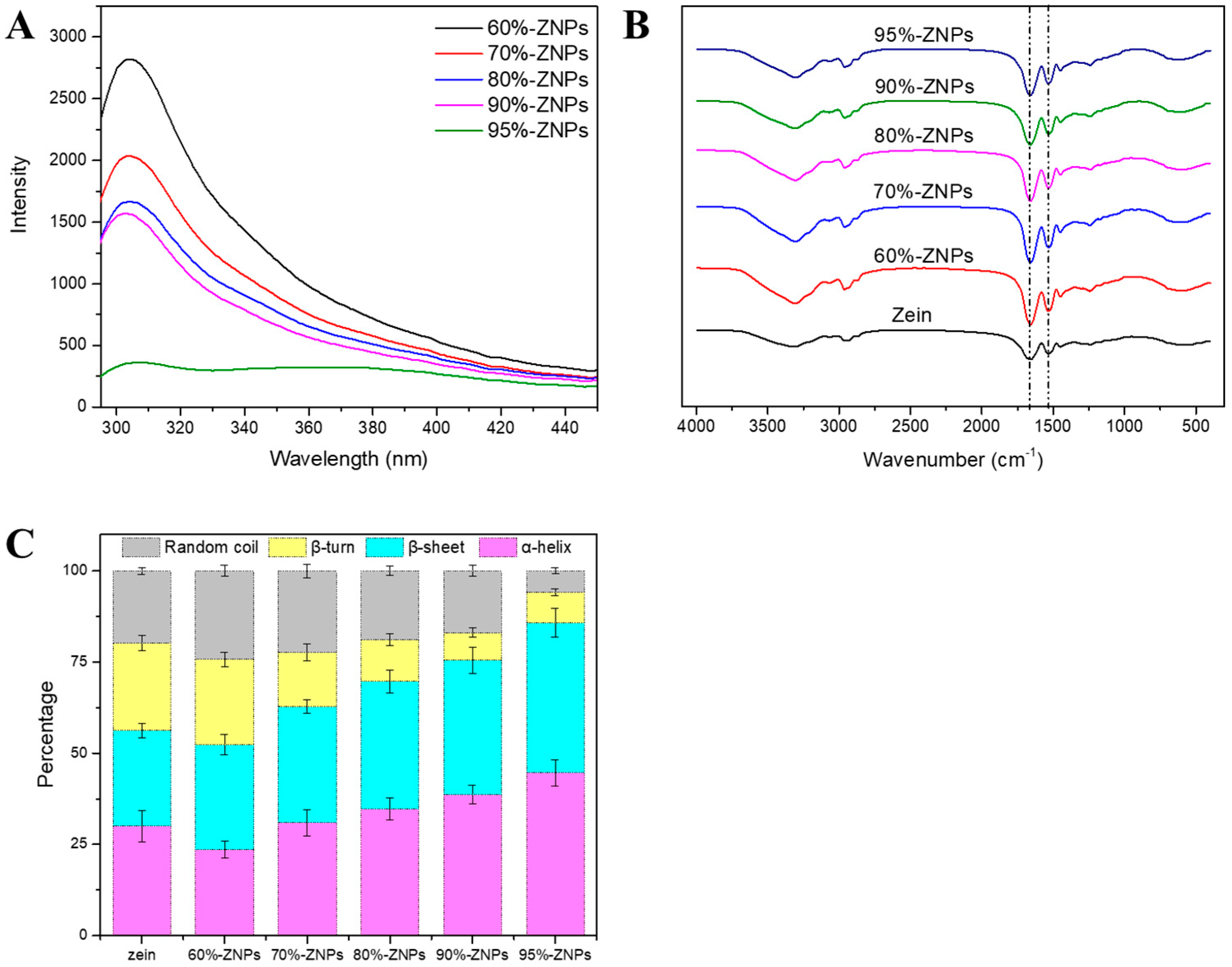
3.3.4. Fluorescence Spectrum
3.3.5. FTIR
3.4. Functional Characteristics of ZNPs
3.4.1. Solubility
3.4.2. Hydrophobicity
3.4.3. Total Sulfhydryl/Free Sulfhydryl/Disulfide Groups
3.4.4. Emulsifying Properties
3.5. Effect of Microfluidic Flow Rate on Particle Size
3.6. Mechanism of ZNPs Regulation by Microfluidic Technology
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Whitesides, G.M. The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 2006, 442, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, F.; Monica, P.A.; Hirvonen, J.; Fontana, F.; Santos, H.A.; Correia, A. Microfluidics as a cutting-edge technique for drug delivery applications. J. Drug Delivery Sci. Technol. 2016, 34, 76–87. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.A.; Zhuang, Y.; Guo, S.T.; Sohan, A.; Yin, B.F. Advances in Microfluidics Techniques for Rapid Detection of Pesticide Residues in Food. Foods 2023, 12, 2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olenskyj, A.G.; Feng, Y.; Lee, Y. Continuous microfluidic production of zein nanoparticles and correlation of particle size with physical parameters determined using CFD simulation. J. Food Eng. 2017, 211, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, T.M.; Quake, S.R. Microfluidics: Fluid physics at the nanoliter scale. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2005, 77, 977–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Chen, R.; Wang, X.; Zhao, C.X.; Chen, Q.; Hai, M.; Chen, D.; Yang, Z.; Weitz, D.A. Controlled co-precipitation of biocompatible colorant-loaded nanoparticles by microfluidics for natural color drinks. Lab. Chip 2019, 19, 2089–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ibarra-Sánchez, L.A.; Miller, M.J.; Lee, Y. Fabrication of zein-modified starch nanoparticle complexes via microfluidic chip and encapsulation of nisin. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, J.R.D.; de la Torre, L.G.; Costa, A.L.R. Droplet-Based Microfluidics as a Platform to Design Food-Grade Delivery Systems Based on the Entrapped Compound Type. Foods 2023, 12, 3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Kilker, S.; Lee, Y. A nozzle simulation chip toward high-throughput formation of curcumin-loaded zein nanoparticles with tunable properties. J. Food Sci. 2023, 88, 3524–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.C.; Wang, Q. Zein-Based Micro- and Nano-Particles for Drug and Nutrient Delivery: A Review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mônica, P.; Renata, D.L.; Fraceto, L.F. Zein Nanoparticles and Strategies to Improve Colloidal Stability: A Mini-Review. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; McClements, D.J.; Shi, A.M.; Zhi, L.Y.; Tian, Y.J.; Jiao, B.; Liu, H.Z.; Wang, Q. Janus particles: A review of their applications in food and medicine. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 63, 10093–10104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.J.; Zhang, L.M.; Yu, C.X.; Chen, J.L.; Ye, X.Q.; Zhang, F.M.; Linhardt, R.J.; Chen, S.G.; Pan, H.B. One-Pot Self-Assembly of Core-Shell Nanoparticles within Fibers by Coaxial Electrospinning for Intestine-Targeted Delivery of Curcumin. Foods 2023, 12, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.S.; Liu, Z.; Hei, X.; Wu, C.; Ma, X.J.; Hu, H.; Jiao, B.; Zhu, J.J.; Adhikari, B.; Wang, Q.; et al. Effect of Physical Modifications on Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Walnut Protein. Foods 2023, 12, 3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beveridge, T.; Toma, S.J.; Nakai, S. Determination of SH-and SS-Groups in Some Food Proteins Using Ellman’s Reagent. J. Food Sci. 1974, 39, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, K.N.; Kinsella, J.E. Emulsifying properties of proteins: Evaluation of a turbidimetric technique. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1978, 26, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, Y.C.; Liu, Y.; Qian, L.H.; Zhang, Y.H.; Li, H.J. Single/co-encapsulation capacity and physicochemical stability of zein and foxtail millet prolamin nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B. 2022, 217, 112685–112694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Xu, J. Aggregate formation of zein and its structural inversion in aqueous ethanol. J. Cereal Sci. 2008, 47, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Wang, J.M.; Cheng, L.M.; Lu, Y.L.; Li, S.H.; Chen, Y. Behavior of Zein in Aqueous Ethanol under Atmospheric Pressure Cold Plasma Treatment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 7352–7360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorina, B.; Alberto, B.; Diego, R.; Perinelli, G.; Bonacucina, L. Aggregation of zein in aqueous ethanol dispersions: Effect on cast film properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 360–368. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Ye, R.; Liu, J. Understanding of dispersion and aggregation of suspensions of zein nanoparticles in aqueous alcohol solutions after thermal treatment. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 50, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Jin, M. Zein nanoparticles produced by liquid-liquid dispersion. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 2380–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alargova, R.G.; Paunov, V.N.; Velev, O.D. Formation of polymer microrods in shear flow by emulsification--solvent attrition mechanism. Langmuir 2006, 22, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alargova, R.G.; Bhatt, K.H.; Paunov, V.N.; Velev, O.D. Scalable Synthesis of a New Class of Polymer Microrods by a Liquid–Liquid Dispersion Technique. Adv. Mater. 2010, 16, 1653–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Heat-induced self-assembly of zein nanoparticles: Fabrication, stabilization and potential application as oral drug delivery. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 90, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yin, L.L.; Padua, G.W. Effect of hydrophilic and lipophilic compounds on zein microstructures. Food Biophys. 2008, 3, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Q. Nanoparticles synthesized from soy protein: Preparation, characterization, and application for nutraceutical encapsulation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 2712–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giroux, H.J.; Houde, J.; Britten, M. Preparation of nanoparticles from denatured whey protein by pH-cycling treatment. Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.; Cheryan, M. Zein: The industrial protein from corn. Ind. Crops Prod. 2001, 13, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Lu, Y.; Han, J.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. Structure-modification by moderate oxidation in hydroxyl radical-generating systems promote the emulsifying properties of soy protein isolate. Food Struct. 2015, 6, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shen, R.; Yang, X.; Lin, D. Characterization of a novel konjac glucomannan film incorporated with Pickering emulsions: Effect of the emulsion particle sizes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 112, 106279.1–106279.11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, D.; Shen, R.; Yang, X. Bacterial cellulose nanofibers improved the emulsifying capacity of soy protein isolate as a stabilizer for pickering high internal-phase emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106279.1–106279.11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, D.H.; Shen, R.; Yang, X.B. Characterizations of novel konjac glucomannan emulsion films incorporated with high internal phase Pickering emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 109, 106088.1–106088.10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Fang, Z.; Shaoyun, W. Thermally-induced whey protein isolate-daidzein co-assemblies: Protein-based nanocomplexes as an inhibitor of precipitation/crystallization for hydrophobic drug. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 273–281. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Li, C.; Ullah, N.; Cao, J.; Lan, Y.; Ge, W.; Hackman, R.M.; Li, Z.; Chen, L. Susceptibility of whey protein isolate to oxidation and changes in physicochemical, structural, and digestibility characteristics. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 7602–7613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hei, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, S.S.; Wu, C.; Jiao, B.; Hu, H.; Ma, X.J.; Zhu, J.J.; Adhikari, B.; Wang, Q.; et al. Freeze-thaw stability of Pickering emulsion stabilized by modified soy protein particles and its application in plant-based ice cream. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 257, 128183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Jin, H.; Gao, Y.; Yan, S.; Xu, J. Effects of freeze-thaw cycles on the structure and emulsifying properties of peanut protein isolates. Food Chem. 2020, 330, 127215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ge, Y.Z.; Li, S.S.; Wu, C.; Hei, X.; Ren, G.Y.; Adhikari, B.; Wang, Q.; Shi, A.M. The properties of plant-based protein particles with co-spray drying agents. J. Food Eng. 2024, 371, 111961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Meng, X.; Sui, X.; Qi, B.; Zhou, L. Relationship Between Surface Hydrophobicity and Structure of Soy Protein Isolate Subjected to Different Ionic Strength. Int. J. Food Prop. 2015, 18, 1059–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.H.; Butt, M.S.; Sharif, M.K.; Sameen, A.; Mumtaz, S.; Sultan, M.T. Functional properties of protein isolates extracted from stabilized rice bran by microwave, dry heat, and parboiling. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2416–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamdar, S.N.; Rajalakshmi, V.; Pednekar, M.D.; Juan, F.; Yardi, V.; Sharma, A. Influence of degree of hydrolysis on functional properties, antioxidant activity and ACE inhibitory activity of peanut protein hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnik, R.; Gu, F.; Basto, P.; Cannizzaro, C.; Dean, L.; Kyei-Manu, W.; Langer, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Microfluidic platform for controlled synthesis of polymeric nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2906–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Amino Acids | Content | Amino Acid | Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aspartic acid | 4.51 ± 0.03 | Methionine | 1.32 ± 0.01 |
| Threonine | 2.39 ± 0.01 | Isoleucine | 3.43 ± 0.02 |
| Serine | 4.53 ± 0.02 | Leucine | 17.00 ± 0.10 |
| Glutamic acid | 21.60 ± 0.12 | Tyrosine | 4.35 ± 0.03 |
| Proline | 8.52 ± 0.01 | Phenylalanine | 5.82 ± 0.04 |
| Glycine | 1.26 ± 0.01 | Lysine | 0.18 ± 0.01 |
| Alanine | 8.34 ± 0.05 | Histidine | 1.25 ± 0.01 |
| Valine | 3.31 ± 0.02 | Arginine | 1.20 ± 0.02 |
| Samples | Size (nm) | PDI | ζ Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 60%-ZNPs | 131.01 ± 2.79 d | 0.15 ± 0.01 b | 39.43 ± 0.95 a |
| 70%-ZNPs | 143.07 ± 1.37 c | 0.16 ± 0.01 b | 38.26 ± 2.64 a |
| 80%-ZNPs | 150.32 ± 1.85 b | 0.14 ± 0.01 c | 39.46 ± 1.82 a |
| 90%-ZNPs | 155.77 ± 1.28 b | 0.13 ± 0.01 d | 39.91 ± 0.78 a |
| 95%-ZNPs | 224.93 ± 1.10 a | 0.28 ± 0.02 a | 34.33 ± 0.42 b |
| Samples | Solubility (%) | H0 |
|---|---|---|
| 60%-ZNPs | 16.73 ± 0.89 d | 187.47 ± 13.2 b |
| 70%-ZNPs | 19.19 ± 1.41 c | 157.75 ± 12.8 b |
| 80%-ZNPs | 23.77 ± 0.55 b | 109.64 ± 9.72 c |
| 90%-ZNPs | 32.83 ± 1.03 a | 90.43 ± 6.91 d |
| 95%-ZNPs | 20.65 ± 1.67 c | 217.74 ± 9.93 a |
| Samples | Total-SH Group (μmol/g) | Free-SH Group (μmol/g) | Disulfide Bond (μmol/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 60%-ZNPs | 16.65 ± 0.13 a | 2.55 ± 0.14 a | 7.05 ± 0.15 d |
| 70%-ZNPs | 16.46 ± 0.14 ab | 1.29 ± 0.13 c | 7.58 ± 0.14 b |
| 80%-ZNPs | 16.44 ± 0.23 ab | 0.90 ± 0.08 d | 7.77 ± 0.11 a |
| 90%-ZNPs | 16.23 ± 0.10 b | 1.75 ± 0.07 b | 7.23 ± 0.09 c |
| 95%-ZNPs | 16.92 ± 0.31 a | 2.59 ± 0.16 a | 7.15 ± 0.27 c |
| Samples | EAI (m2/g) | ESI (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 60%-ZNPs | 4.42 ± 0.64 b | 49.06 ± 0.65 d |
| 70%-ZNPs | 4.47 ± 0.78 b | 53.08 ± 0.84 c |
| 80%-ZNPs | 5.03 ± 0.37 a | 61.01 ± 1.12 a |
| 90%-ZNPs | 4.65 ± 0.27 ab | 55.50 ± 0.97 b |
| 95%-ZNPs | 4.66 ± 0.42 ab | 50.46 ± 0.64 d |
| Inner Phase Flow Rate (mL/h) | Outer Phase Flow Rate (mL/h) | Particle Size (nm) | PDI |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | 10 | 182.81 ± 0.92 a | 0.25 ± 0.01 a |
| 1.5 | 20 | 169.65 ± 1.61 b | 0.25 ± 0.01 a |
| 1.5 | 30 | 148.72 ± 2.16 e | 0.10 ± 0.01 d |
| 1.5 | 40 | 140.71 ± 2.54 f | 0.26 ± 0.01 a |
| 1.5 | 50 | 133.13 ± 1.48 g | 0.15 ± 0.02 b |
| 0.5 | 30 | 132.79 ± 0.41 g | 0.13 ± 0.02 c |
| 1 | 30 | 144.92 ± 1.86 ef | 0.26 ± 0.02 a |
| 2 | 30 | 152.34 ± 0.61 d | 0.13 ± 0.01 c |
| 2.5 | 30 | 157.91 ± 2.42 c | 0.14 ± 0.03 bc |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Ma, X.; Ge, Y.; Hei, X.; Zhang, X.; Hu, H.; Zhu, J.; Adhari, B.; Wang, Q.; Shi, A. Preparation and Regulation of Natural Amphiphilic Zein Nanoparticles by Microfluidic Technology. Foods 2024, 13, 1730. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13111730
Liu Z, Ma X, Ge Y, Hei X, Zhang X, Hu H, Zhu J, Adhari B, Wang Q, Shi A. Preparation and Regulation of Natural Amphiphilic Zein Nanoparticles by Microfluidic Technology. Foods. 2024; 13(11):1730. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13111730
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhe, Xiaojie Ma, Yanzheng Ge, Xue Hei, Xinyu Zhang, Hui Hu, Jinjin Zhu, Benu Adhari, Qiang Wang, and Aimin Shi. 2024. "Preparation and Regulation of Natural Amphiphilic Zein Nanoparticles by Microfluidic Technology" Foods 13, no. 11: 1730. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13111730
APA StyleLiu, Z., Ma, X., Ge, Y., Hei, X., Zhang, X., Hu, H., Zhu, J., Adhari, B., Wang, Q., & Shi, A. (2024). Preparation and Regulation of Natural Amphiphilic Zein Nanoparticles by Microfluidic Technology. Foods, 13(11), 1730. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13111730










