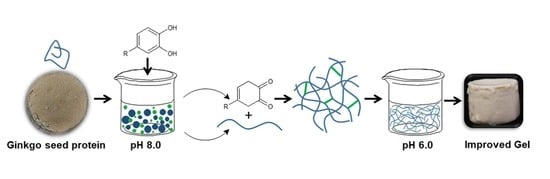
Alkali-Induced Phenolic Acid Oxidation Enhanced Gelation of Ginkgo Seed Protein
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Ginkgo Seed Protein Isolate (GSPI)
2.3. Preparation of GSPI-Phenolic Acid Sols
2.4. Solubility of GSPI-Phenolic Acid Sols
2.5. Surface Hydrophobicity of GSPI-Phenolic Acid Sols
2.6. Particle Size and ζ-Potential of GSPI-Phenolic Acid Sols
2.7. Intrinsic Fluorescence
2.8. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.9. Dynamic Rheological Analysis
2.10. Preparation of GSPI-Phenolic Acid Gels
2.11. Water Holding Capacity (WHC) of GSPI-Phenolic Acid Gels
2.12. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA) of GSPI-Phenolic acid Gels
2.13. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.14. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
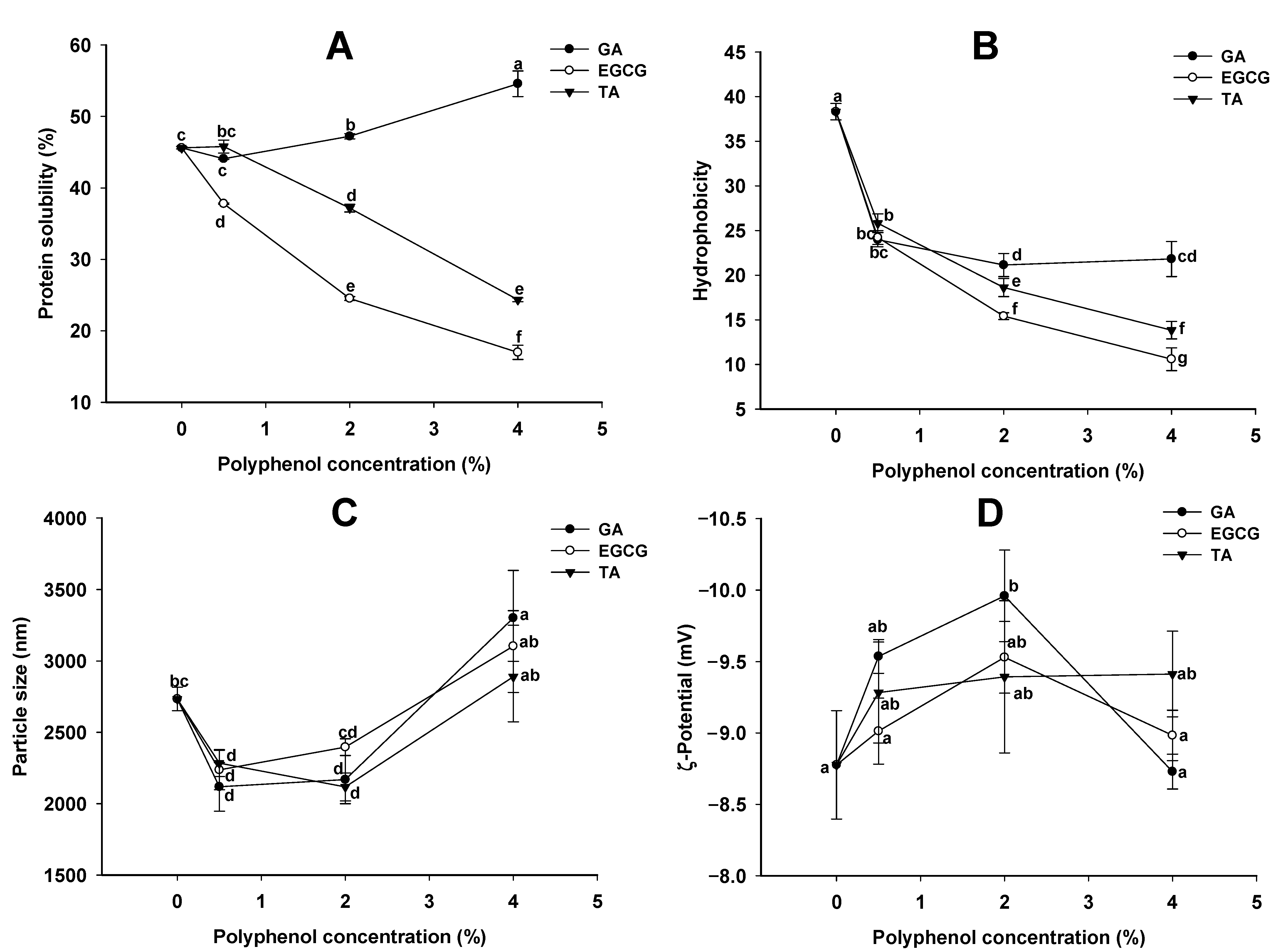
3.1. Effects of Oxidized Phenolic Acids on Properties of the GSPI Sols
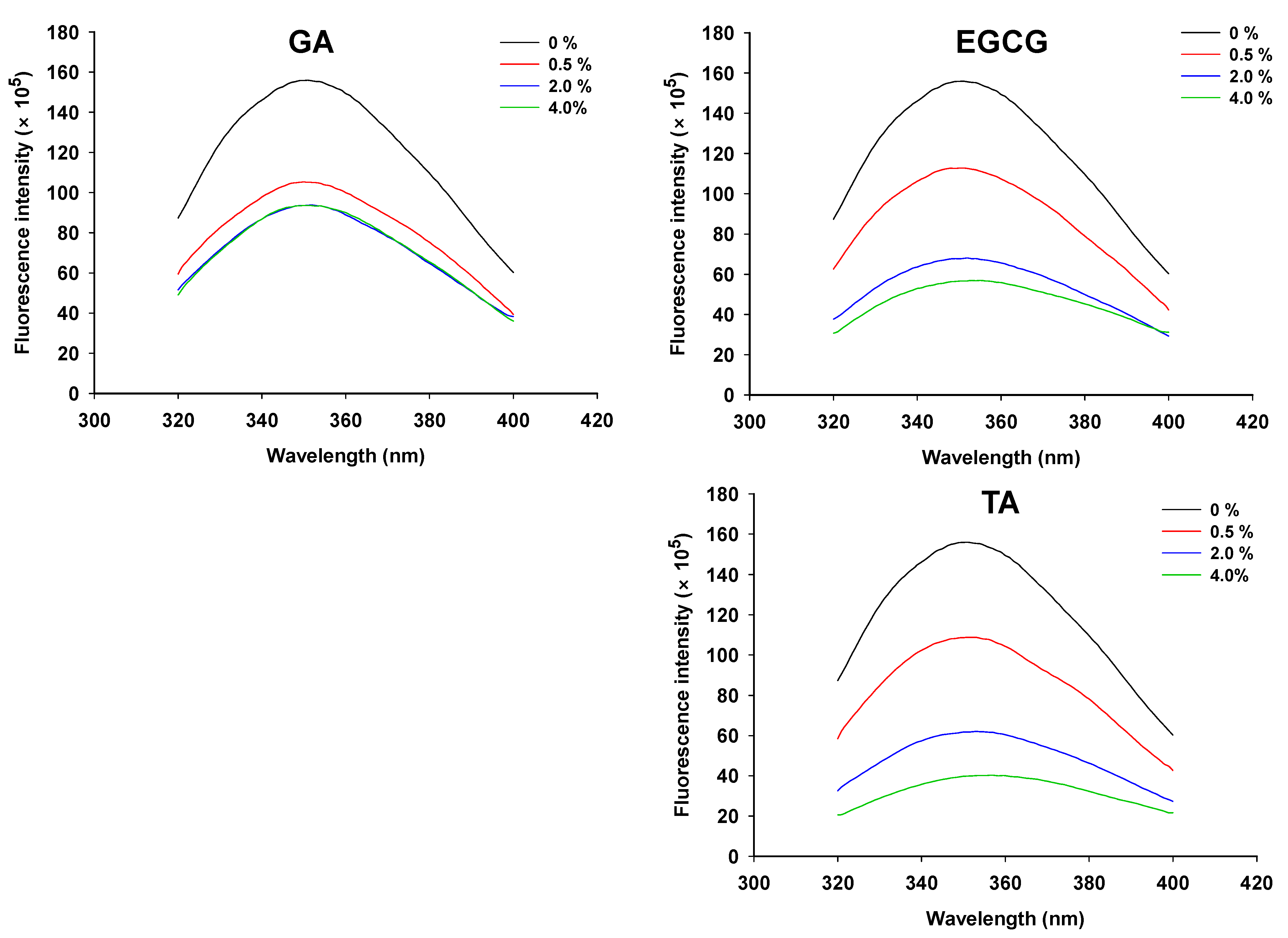
3.2. Intrinsic Fluorescence of the GSPI Sols
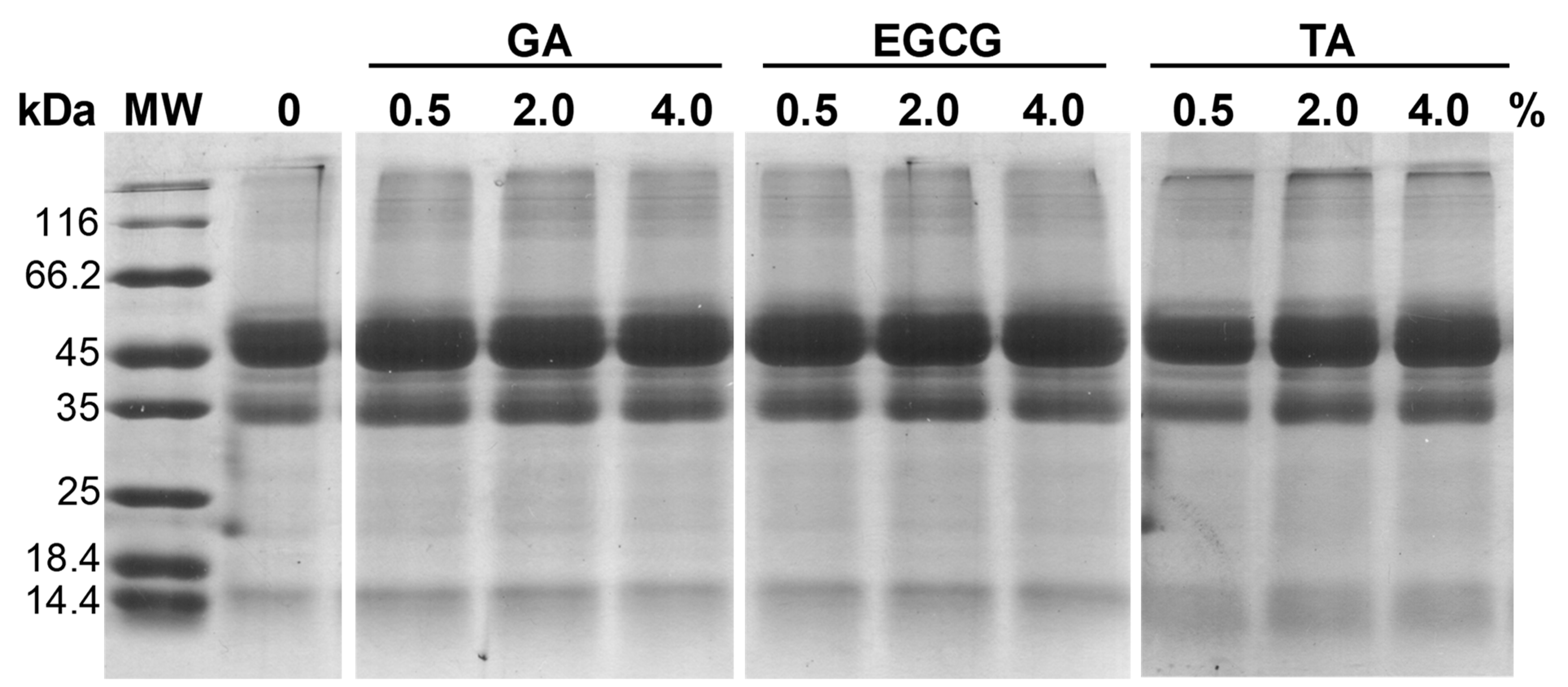
3.3. SDS-PAGE of Phenolic Acid-Treated GSPI
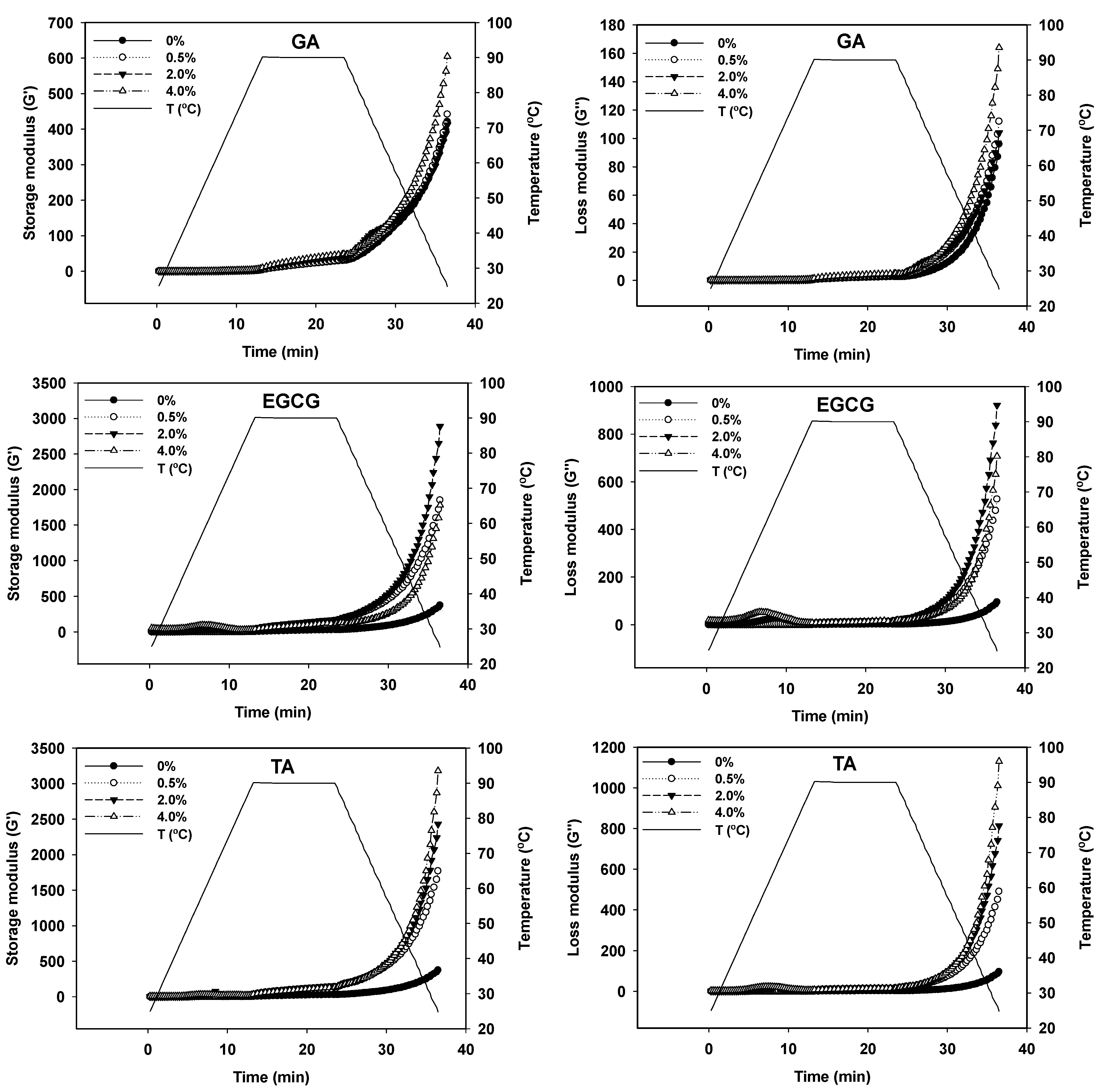
3.4. Rheological Characteristics of GSPI-Phenolic Acid Gels
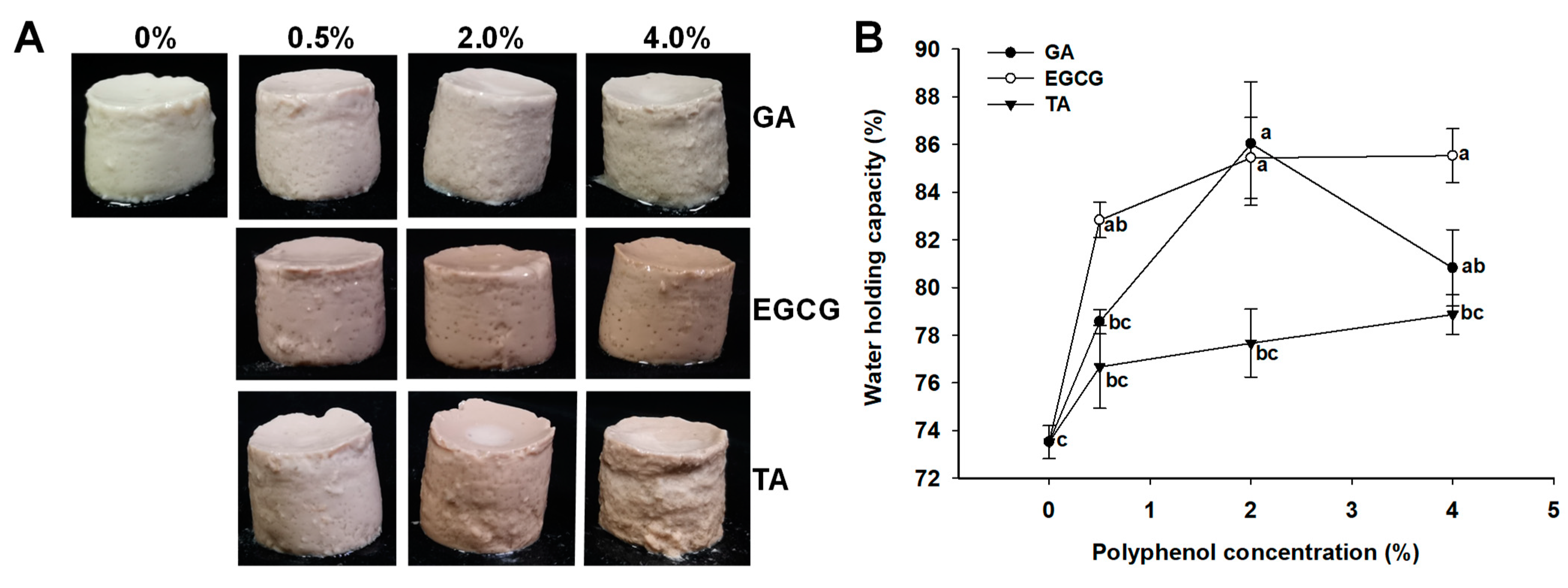
3.5. Appearance and WHC of GSPI-Phenolic Acid Gels
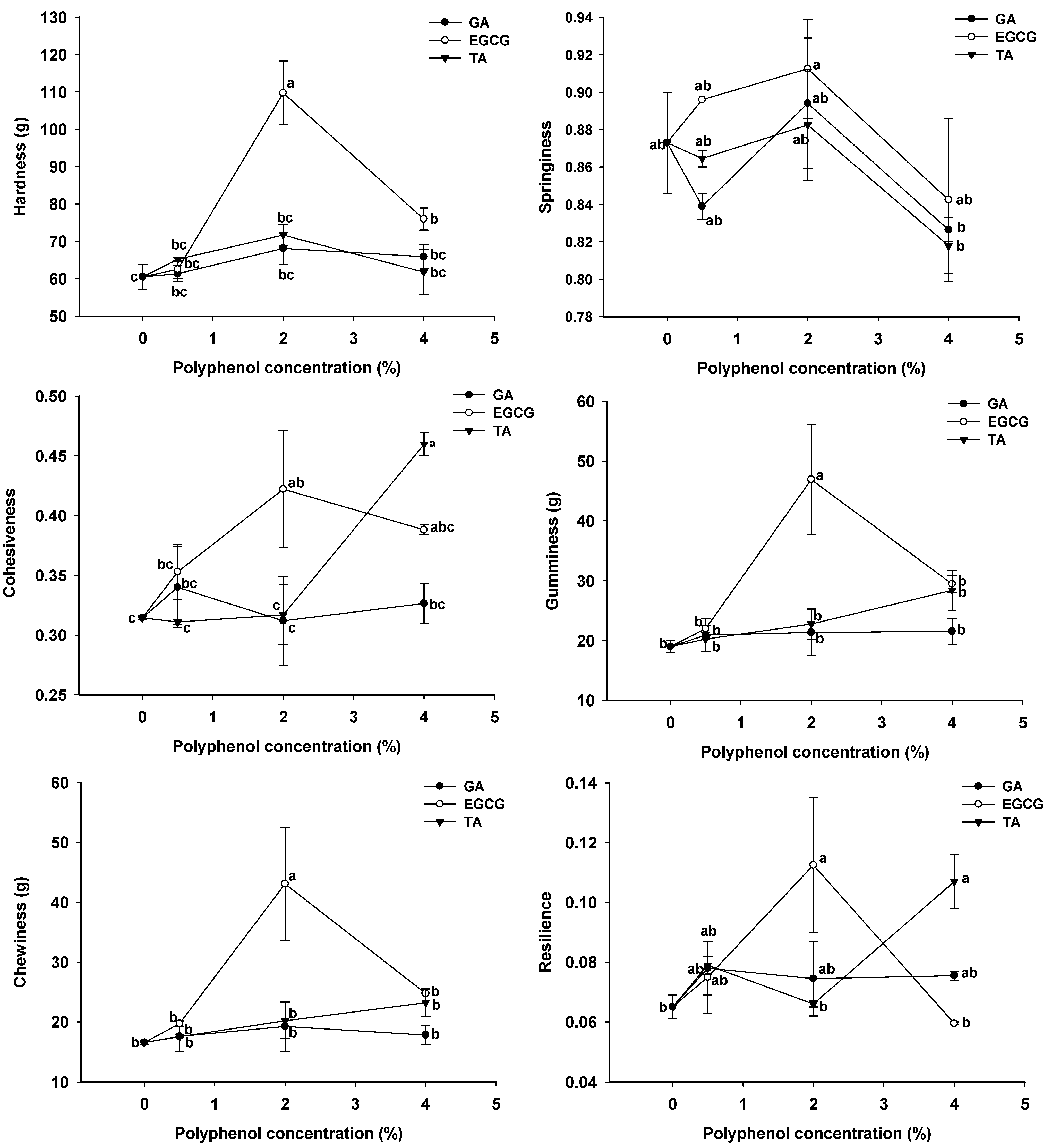
3.6. Texture Profile Analysis of GSPI-Phenolic Acid Gels
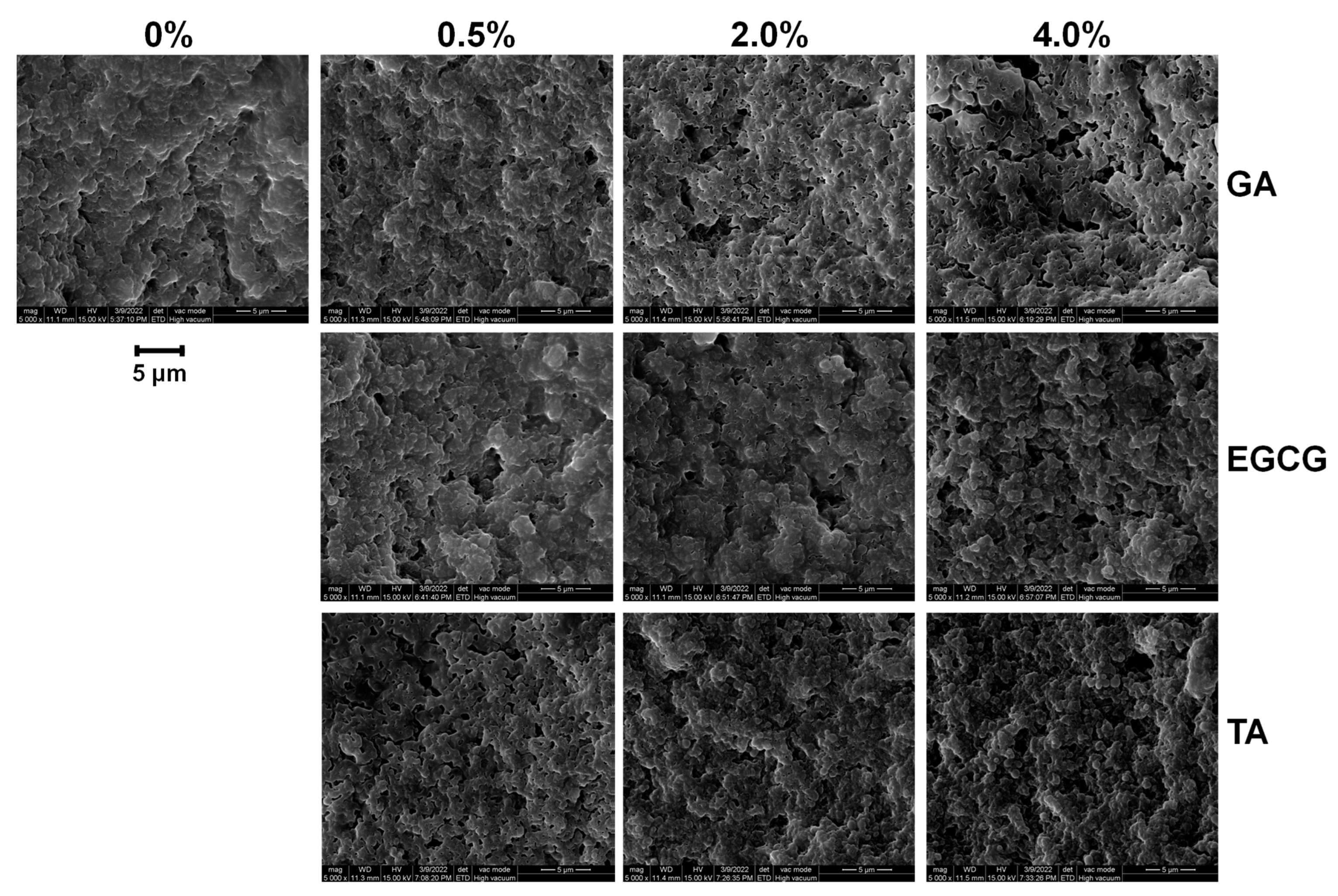
3.7. Microstructure of GSPI-Phenolic Acid Gels
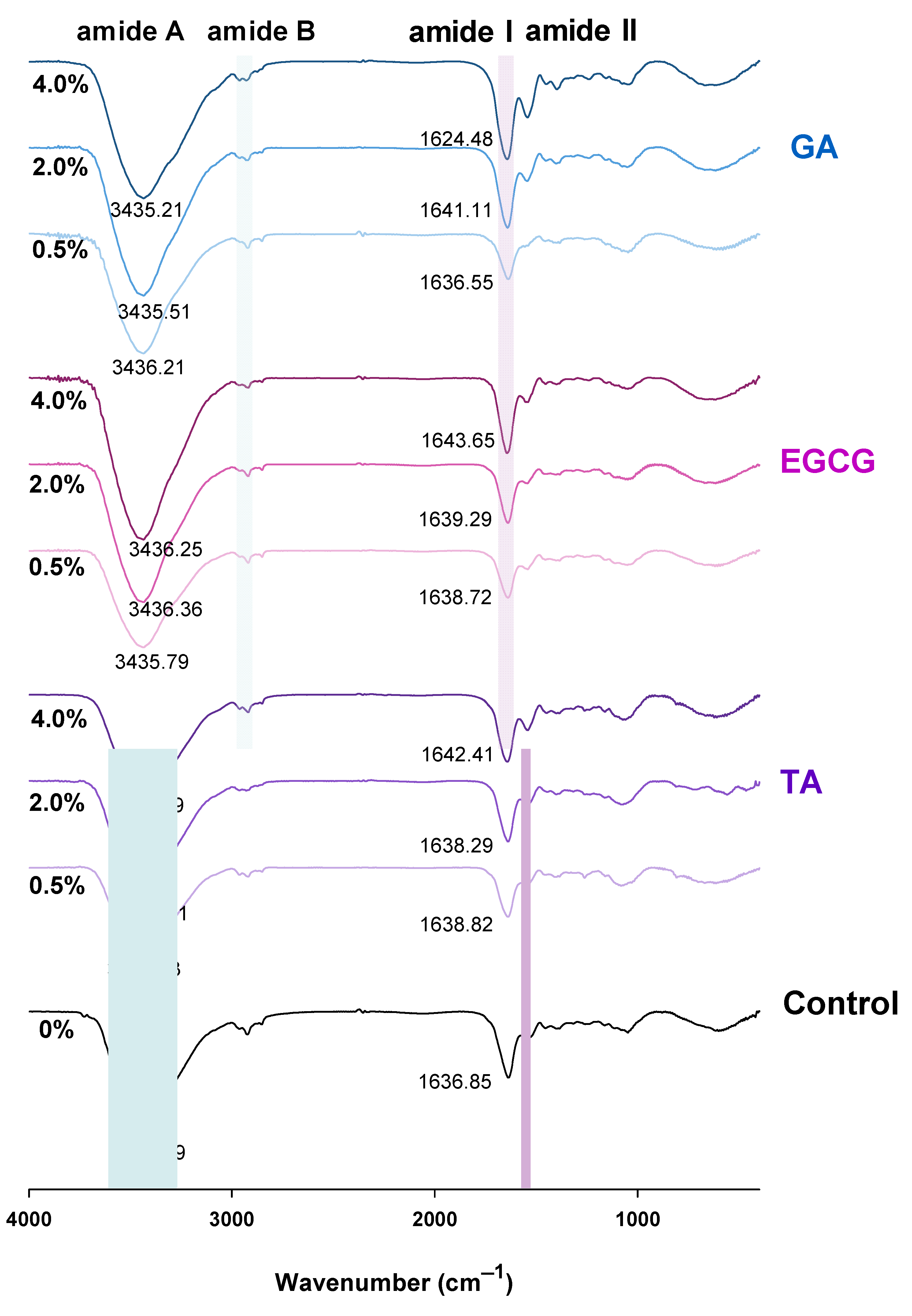
3.8. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectrum
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Floret, C.; Monnet, A.F.; Micard, V.; Walrand, S.; Michon, C. Replacement of animal proteins in food: How to take advantage of nutritional and gelling properties of alternative protein sources. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2021, 63, 920–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, C.; Zhang, J.; Yao, H.; Zhou, J.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ma, H. Advances in renewable plant-derived protein source: The structure, physicochemical properties affected by ultrasonication. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 53, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isah, T. Rethinking Ginkgo biloba L.: Medicinal uses and conservation. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2015, 9, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, F.; Wang, Y.J.; Sandhu, H.S.; Gielis, J.; Shi, P.J. Comparison of seed morphology of two ginkgo cultivars. J. For. Res. 2020, 31, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q. The main active constituents and detoxification process of Ginkgo biloba seeds and their potential use in functional health foods. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2019, 83, 103247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zou, M.; Wang, Y.; Cao, F.; Su, E. Ginkgo seed proteins: Characteristics, functional properties and bioactivities. Plant Food Hum. Nutr. 2021, 76, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Xu, S.Y. Optimization of processing parameters for cloudy ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba Linn.) juice. J. Food Eng. 2007, 80, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Cao, J.; Zhang, W.; Tang, C.; Cao, F.; Su, E. Improvement of quality of Ginkgo biloba seeds powder by solid-state fermentation with Eurotium cristatum for developing high-value ginkgo seeds products. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2022, 7, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shi, M.; Cao, F.; Su, E. Ginkgo biloba seed exocarp: A waste resource with abundant active substances and other components for potential applications. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, C.H.; Chen, X.J.; Jia, L.Q.; Guo, X.N.; Chen, R.S.; Wang, H.D. Carbon peak and carbon neutrality in China: Goals, implementation path and prospects. Chin. Geol. 2021, 4, 720–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, C.Z.; Ye, J.Z.; Chen, H.X.; Tao, R.; Cao, F.L. Effects of high hydrostatic pressure treatment on structural, allergenicity, and functional properties of proteins from ginkgo seeds. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 2016, 34, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Deng, Y.; Xie, P.; Liu, L.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, J. Novel bioactive peptides from Ginkgo biloba seed protein and evaluation of their α-glucosidase inhibition activity. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xie, P.; Huang, L. Inhibitory effect of Ginkgo biloba seeds peptides on methylglyoxal-induced glycations. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 172, 113587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Bassey, A.P.; Cao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Huang, M.; Yang, H. Food protein aggregation and its application. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhao, J.; Guo, F.; Wang, Y. Enhanced gelling properties and hydration capacity of ginkgo seed proteins by genipin cross-linking. Food Chem. 2023, 399, 133924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, C.; Zhao, J.; Ma, T.; He, Z.; Huang, M.; Wang, Y. Modification of structure and functionalities of ginkgo seed proteins by pH-shifting treatment. Food Chem. 2021, 358, 129862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akharume, F.U.; Aluko, R.E.; Adedeji, A.A. Modification of plant proteins for improved functionality: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 198–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppler, J.K.; Schwarz, K.; van der Goot, A.J. Covalent modification of food proteins by plant-based ingredients (polyphenols and organosulphur compounds): A commonplace reaction with novel utilization potential. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 101, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, T.C.; Caleja, C.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C. Vaccinium myrtillus L. fruits as a novel source of phenolic compounds with health benefits and industrial applications-a review. Curr. Pharm. Design. 2020, 26, 1917–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Ambigaipalan, P. Phenolics and polyphenolics in foods, beverages and spices: Antioxidant activity and health effects—A review. J. Funct. Foods. 2015, 18, 820–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, R.; Oliveira, H.; Fernandes, I.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Perez-Gregorio, R. Recent advances in extracting phenolic compounds from food and their use in disease prevention and as cosmetics. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2021, 61, 1130–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozdal, T.; Capanoglu, E.; Altay, F. A review on protein–phenolic interactions and associated changes. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 954–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vékey, K.; Malorni, A.; Pòcsfalvi, G.; Piperno, A.; Romeo, G.; Uccella, N. Biophenol−protein supramolecular models by fast atom bombardment-mass spectrometric experiments. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 2447–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourvellec, C.L.; Renard, C.M.G.C. Interactions between polyphenols and macromolecules: Quantification methods and mechanisms. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2012, 52, 213–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.R.; Lin, Y.S.; Tang, D.B.; Yang, H.G.; Liu, X.M. Structural and gelation properties of five polyphenols-modified pork myofibrillar protein exposed to hydroxyl radicals. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 156, 113073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.; Jiang, J.; True, A.D.; Xiong, Y.L. Myofibrillar protein cross-linking and gelling behavior modified by structurally relevant phenolic compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 1308–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Ma, W.; Huang, J.; Xiong, Y.L. Effects of sodium pyrophosphate coupled with catechin on the oxidative stability and gelling properties of myofibrillar protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 104, 105722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Nakai, S. Hydrophobicity determined by a fluorescence probe method and its correlation with surface properties of proteins. BBA 1980, 624, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, L.A.; Fadel, O.M.; Tavares, G.M. How does the thermal-aggregation behavior of black cricket protein isolate affect its foaming and gelling properties? Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 110, 106169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriprablom, J.; Luangpituksa, P.; Wongkongkatep, J.; Pongtharangkul, T.; Suphantharika, M. Influence of pH and ionic strength on the physical and rheological properties and stability of whey protein stabilized O/W emulsions containing xanthan gum. J. Food Eng. 2019, 242, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.G.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, T.; Chi, S.Y.; Gao, F.; Li, J.; Tian, B.; Shi, W.T.; et al. Effect of heat treatment on the nonlinear rheological properties of acid-induced soy protein isolate gels modified by high-pressure homogenization. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 157, 113094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Li, W. Influence of γ-aminobutyric acid on gelling properties of heat-induced whey protein gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.D.; Liu, C.Q.; Zhao, J.; Li, W.W.; Wang, Y.S. Physicochemical properties of a ginkgo seed protein-pectin composite gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 118, 106781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.S.; Ding, J.Z.; Andrade, J.; Rababah, T.M.; Almajwal, A.; Abulmeaty, M.M.; Feng, H. Modifying the physicochemical properties of pea protein by pH-shifting and ultrasound combined treatments. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 38, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.D.; Yu, Z.L.; Zeng, W.C. Structural and functional modifications of myofibrillar protein by natural phenolic compounds and their application in pork meatball. Food Res. Int. 2021, 148, 110593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L.; Lin, S.; Liu, D. The beneficial effects of rutin on myofibrillar protein gel properties and related changes in protein conformation. Food Chem. 2019, 301, 125206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Pan, Y.; Yang, Z.; Rao, J.; Chen, B. Modification of β-lactoglobulin by phenolic conjugations: Protein structural changes and physicochemical stabilities of stripped hemp oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by the conjugates. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 128, 107578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aewsiri, T.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Eun, J.B.; Wierenga, P.A.; Gruppen, H. Antioxidative activity and emulsifying properties of cuttlefish skin gelatin modified by oxidised phenolic compounds. Food Chem. 2009, 117, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Wang, L.; Shao, J.; Liu, D.; Kong, B. Changes in the structural and gel properties of pork myofibrillar protein induced by catechin modification. Meat Sci. 2017, 127, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Shao, H.; Fang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, C.Y.; Li, Q. Mechanism and effects of polyphenol derivatives for modifying collagen. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 4272–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Wang, Z.; Feng, X.; Kan, J. Promotion of fishy odor release by phenolic compounds through interactions with myofibrillar protein. Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, T.; Lu, Y.; Lin, X.; Hu, X.; Liu, L.; He, Z.; Wu, X. Effect of chlorogenic acid covalent conjugation on the allergenicity, digestibility and functional properties of whey protein. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 125024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.; Xiong, Y.L. Glucose oxidase promotes gallic acid-myofibrillar protein interaction and thermal gelation. Food Chem. 2019, 293, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balange, A.K.; Benjakul, S. Effect of oxidised phenolic compounds on the gel property of mackerel (Rastrelliger kanagurta) surimi. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 42, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Tang, D.; Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, M.; Liu, X. The dose-dependent effects of polyphenols and malondialdehyde on the emulsifying and gel properties of myofibrillar protein-mulberry polyphenol complex. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 130005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, A.; Soltanahmadi, S.; Chen, J.S.; Stokes, J.R. Oral tribology: Providing insight into oral processing of food colloids. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 117, 106635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Munir, S.; Yu, X.; Yin, T.; You, J.; Liu, R.; Xiong, S.; Hu, Y. Double-crosslinked effect of TGase and EGCG on myofibrillar proteins gel based on physicochemical properties and molecular docking. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balange, A.; Benjakul, S. Enhancement of gel strength of bigeye snapper (Priacanthus tayenus) surimi using oxidised phenolic compounds. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, C.; Ma, W.; Kuang, J.; Huang, J.; Xiong, Y.L. Textural properties, microstructure and digestibility of mungbean starch–flaxseed protein composite gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 126, 107482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.; Arken, A.; Wali, A.; Gao, Y.; Aisa, H.A.; Yili, A. Effect of phenolic compound-protein covalent conjugation on the physicochemical, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant activities of silk sericin. Process Biochem. 2022, 117, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Watowita, P.; Chen, R.; Shi, Y.; Geng, J.T.; Takahashi, K.; Li, L.; Osako, K. Multilayer gelatin/myofibrillar films containing clove essential oil: Properties, protein-phenolic interactions, and migration of active compounds. Food Packag. Shelf. 2022, 32, 100842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Liu, C.; Zhao, J.; Guo, F.; You, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y. Alkali-Induced Phenolic Acid Oxidation Enhanced Gelation of Ginkgo Seed Protein. Foods 2023, 12, 1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12071506
Zhang W, Liu C, Zhao J, Guo F, You J, Zhang L, Wang Y. Alkali-Induced Phenolic Acid Oxidation Enhanced Gelation of Ginkgo Seed Protein. Foods. 2023; 12(7):1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12071506
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wei, Changqi Liu, Jing Zhao, Fengxian Guo, Jieyu You, Luyan Zhang, and Yaosong Wang. 2023. "Alkali-Induced Phenolic Acid Oxidation Enhanced Gelation of Ginkgo Seed Protein" Foods 12, no. 7: 1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12071506
APA StyleZhang, W., Liu, C., Zhao, J., Guo, F., You, J., Zhang, L., & Wang, Y. (2023). Alkali-Induced Phenolic Acid Oxidation Enhanced Gelation of Ginkgo Seed Protein. Foods, 12(7), 1506. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12071506