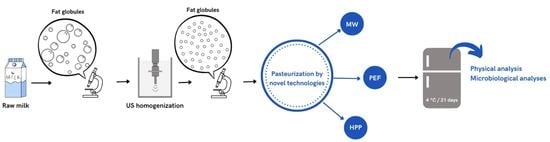
Effect of the Application of Ultrasound to Homogenize Milk and the Subsequent Pasteurization by Pulsed Electric Field, High Hydrostatic Pressure, and Microwaves
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials and Experimental Design
2.2. Homogenization by Continuous US System
2.3. Pasteurization Treatments
2.3.1. HPP System
2.3.2. PEF System
2.3.3. MW System
2.4. Droplet Size Distribution
2.5. Zeta (ζ)-Potential Measurements
2.6. Color
2.7. Rheological Behavior
2.8. Microbial Growth during Storage
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
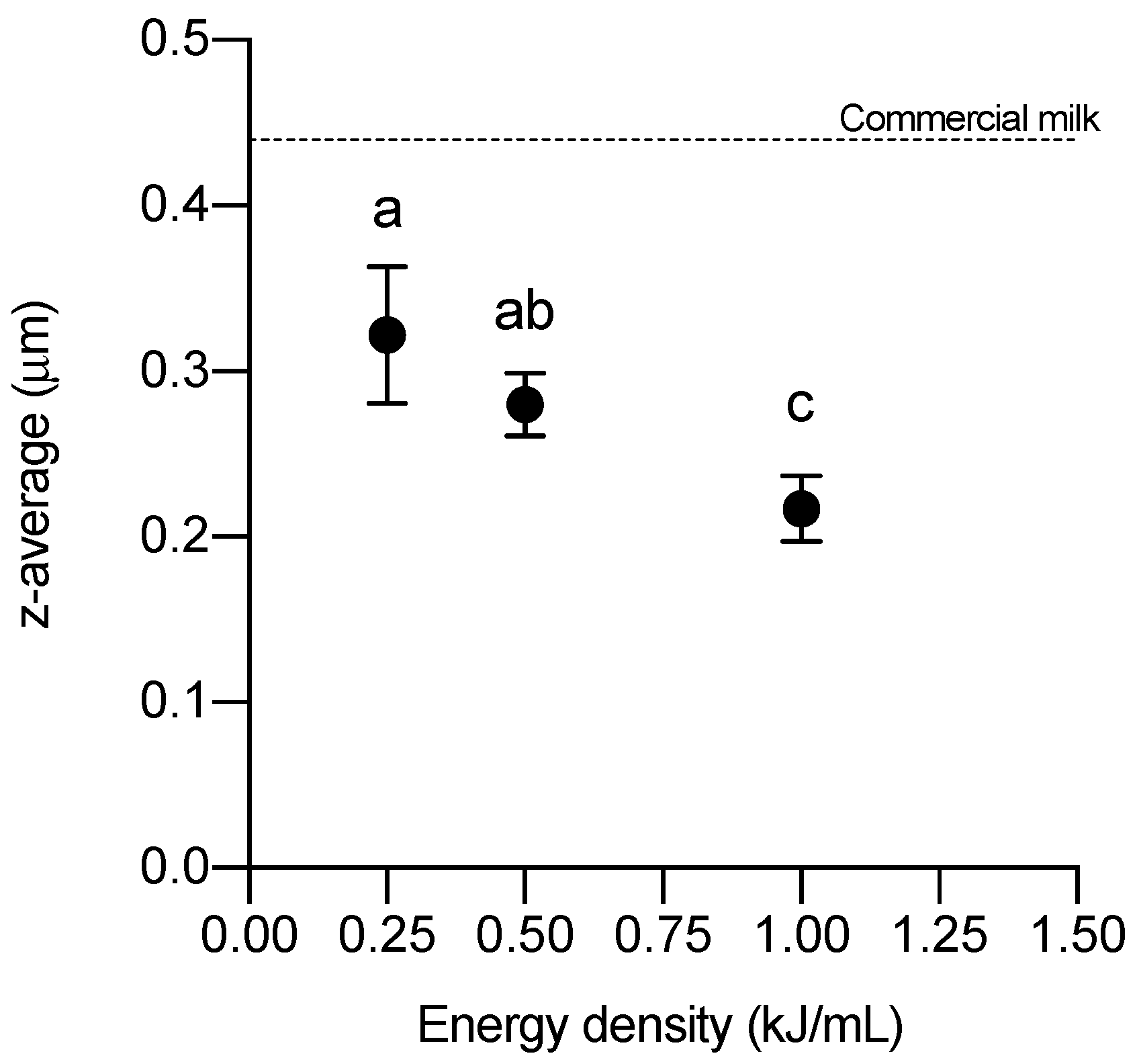
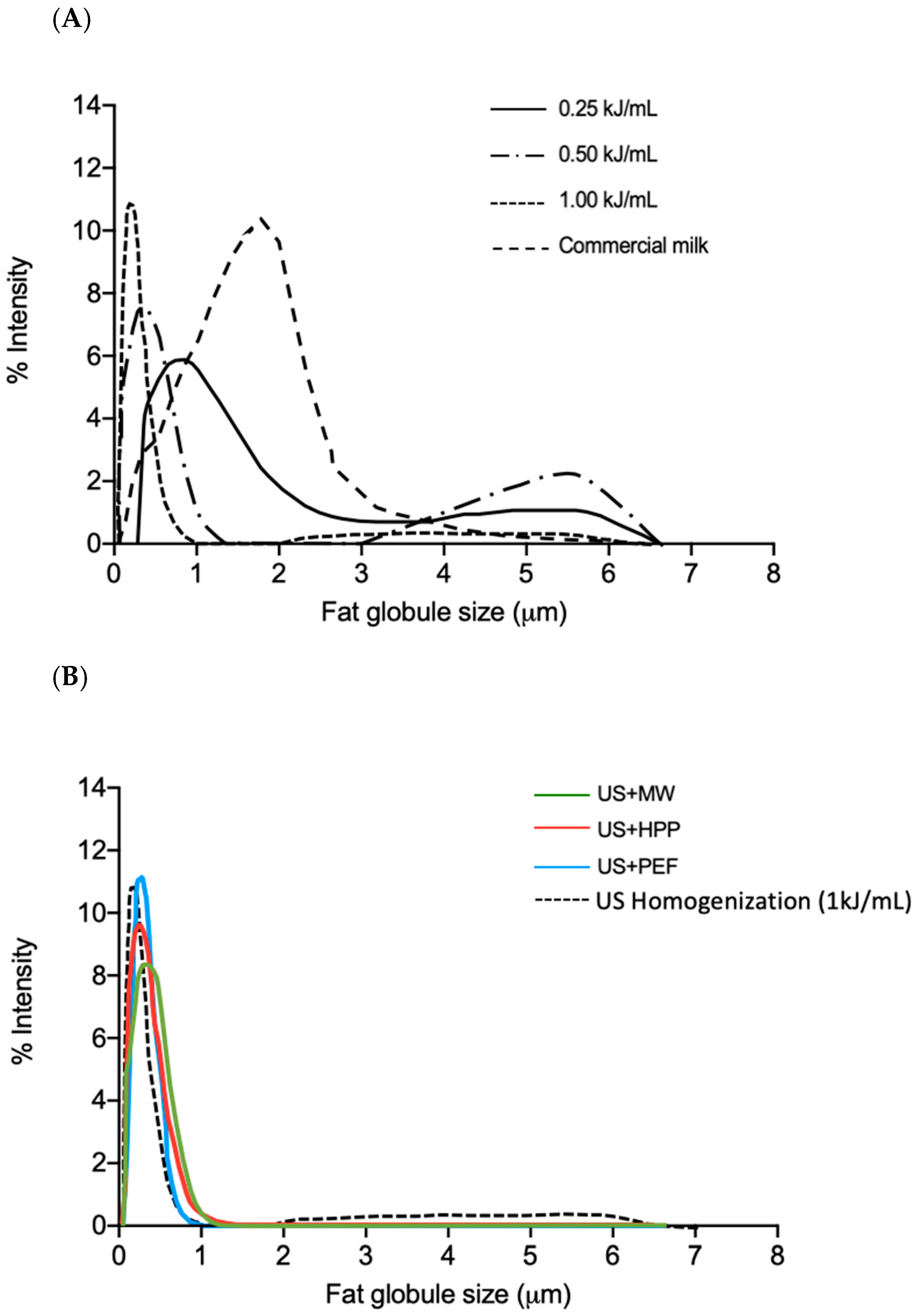
3.1. Fat Globule Size Distribution
3.2. Stability of Fat Globules
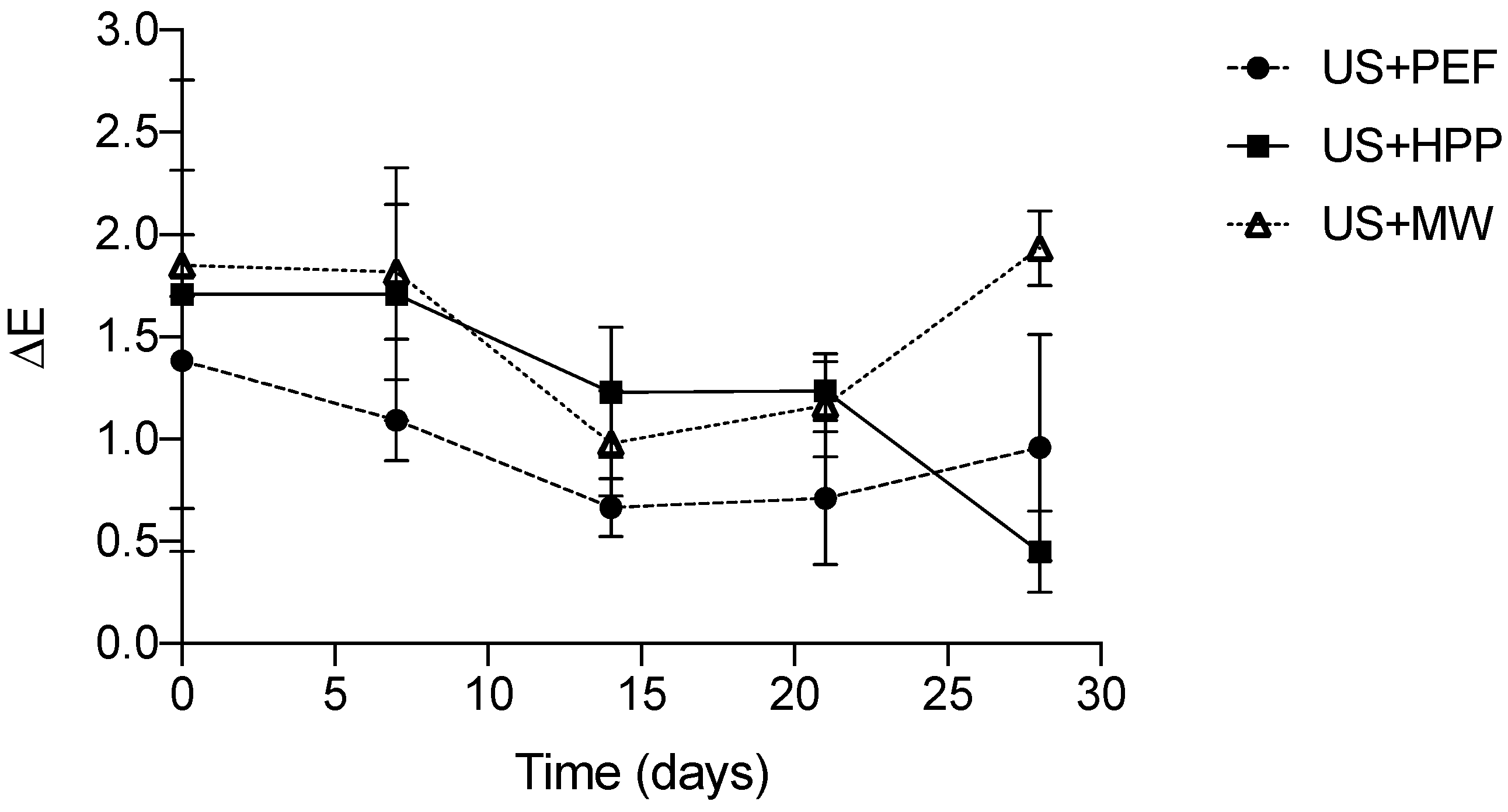
3.3. Color Analysis
3.4. Rheological Behavior
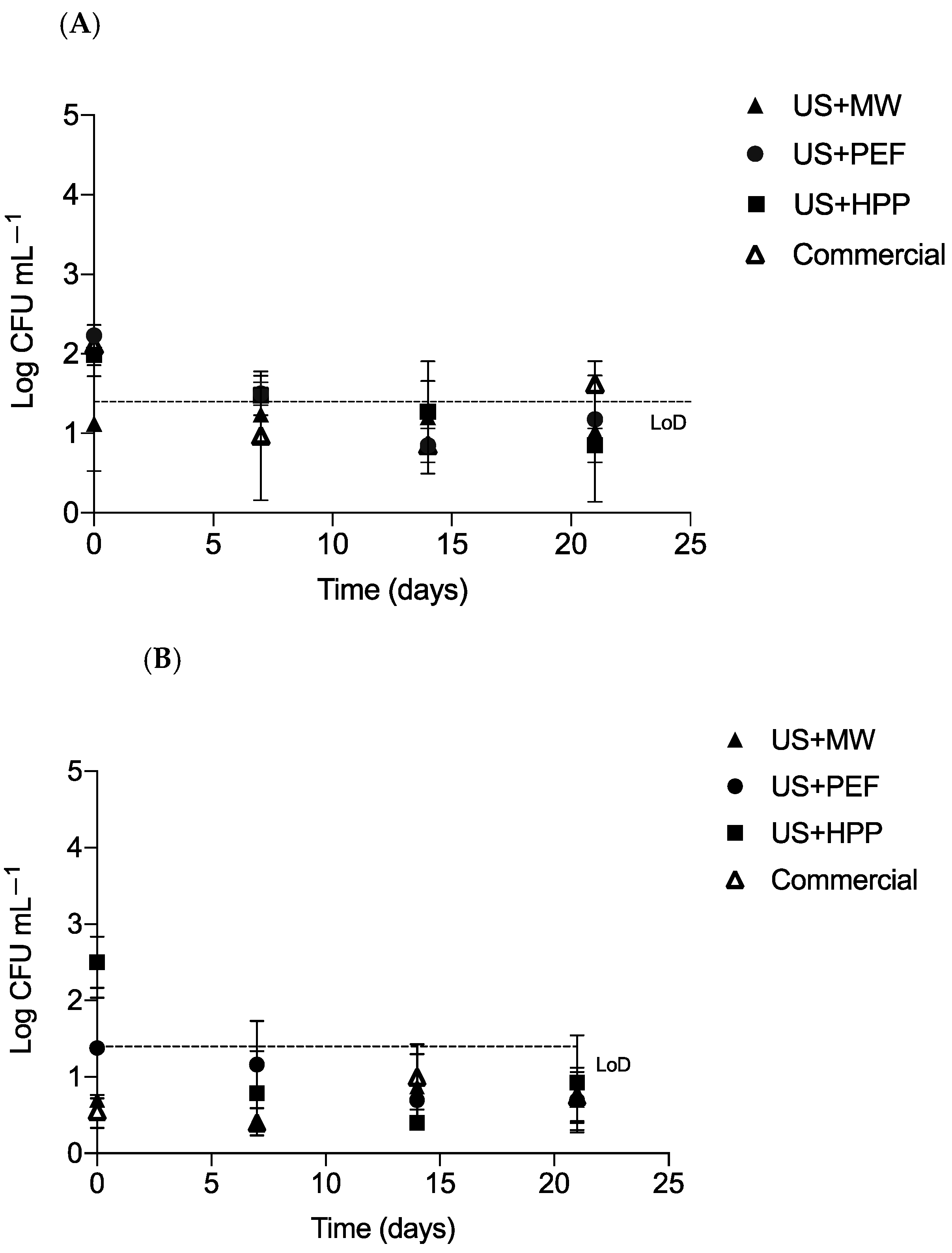
3.5. Microbiological Shelf Life
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raso, J.; Heinz, V.; Álvarez, I.; Toepfl, S. (Eds.) Part III. Applications of Pulsed Electric Fields in the Food Industry. In Pulsed Electric Fields Technology for the Food Industry; Food Engineering Series; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 299–468. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekaran, S.; Ramanathan, S.; Basak, T. Microwave Food Processing—A Review. Food Res. Int. 2013, 52, 243–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendueles, E.; Omer, M.K.; Alvseike, O.; Alonso-Calleja, C.; Capita, R.; Prieto, M. Microbiological Food Safety Assessment of High Hydrostatic Pressure Processing: A Review. LWT–Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astráin-Redín, L.; Ciudad-Hidalgo, S.; Raso, J.; Condón, S.; Cebrián, G.; Álvarez, I. Application of High-Power Ultrasound in the Food Industry. In Sonochemical Reactions; Karakuş, S., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 103–126. [Google Scholar]
- Demirok, N.T.; Yıkmış, S. Combined Effect of Ultrasound and Microwave Power in Tangerine Juice Processing: Bioactive Compounds, Amino Acids, Minerals, and Pathogens. Processes 2022, 10, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roobab, U.; Abida, A.; Chacha, J.S.; Athar, A.; Madni, G.M.; Ranjha, M.M.A.N.; Rusu, A.V.; Zeng, X.-A.; Aadil, R.M.; Trif, M. Applications of Innovative Non-Thermal Pulsed Electric Field Technology in Developing Safer and Healthier Fruit Juices. Molecules 2022, 27, 4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yikmis, S. Investigation of the Effects of Non-Thermal, Combined and Thermal Treatments on the Physicochemical Parameters of Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) Juice. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2019, 25, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, A.; Abdul Karim Shah, N.N.; Sulaiman, A.; Mohd Adzahan, N.; Aadil, R.M. Pulsed Electric Field of Goat Milk: Impact on Escherichia coli ATCC 8739 and Vitamin Constituents. J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 44, e13779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, A.; Samuelsson, L.M.; Loveday, S.M.; Gupta, T.B. Applications of Novel Processing Technologies to Enhance the Safety and Bioactivity of Milk. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 4652–4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miano, A.C.; Ibarz, A.; Augusto, P.E.D. Mechanisms for Improving Mass Transfer in Food with Ultrasound Technology: Describing the Phenomena in Two Model Cases. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 29, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astráin-Redín, L.; Alejandre, M.; Raso, J.; Cebrián, G.; Álvarez, I. Direct Contact Ultrasound in Food Processing: Impact on Food Quality. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 633070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Lopez, L.M.; Garcia-Galicia, I.A.; Tirado-Gallegos, J.M.; Sanchez-Vega, R.; Huerta-Jimenez, M.; Ashokkumar, M.; Alarcon-Rojo, A.D. Recent Advances in the Application of Ultrasound in Dairy Products: Effect on Functional, Physical, Chemical, Microbiological and Sensory Properties. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 73, 105467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaire, R.A.; Gogate, P.R. Intensified Recovery of Lactose from Whey Using Thermal, Ultrasonic and Thermosonication Pretreatments. J. Food Eng. 2018, 237, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.R.; Murthy, Z.V.P. Ultrasound Assisted Crystallization for the Recovery of Lactose in an Anti-Solvent Acetone. Cryst. Res. Technol. 2009, 44, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammoh, S.; Alu’datt, M.H.; Tranchant, C.C.; Al-U’datt, D.G.; Alhamad, M.N.; Rababah, T.; Kubow, S.; Haddadin, M.S.Y.; Ammari, Z.; Maghaydah, S.; et al. Modification of the Functional and Bioactive Properties of Camel Milk Casein and Whey Proteins by Ultrasonication and Fermentation with Lactobacillus Delbrueckii subsp. Lactis. LWT 2020, 129, 109501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Jia, J.; Kuang, C.; Yang, H. Effect of Ultrasonic Pretreatment on Whey Protein Hydrolysis by Alcalase: Thermodynamic Parameters, Physicochemical Properties and Bioactivities. Process Biochem. 2018, 67, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.H.M.C.; Silva, E.K.; Alvarenga, V.O.; Moraes, J.; Freitas, M.Q.; Silva, M.C.; Raices, R.S.L.; Sant’Ana, A.S.; Meireles, M.A.A.; Cruz, A.G. Effects of Ultrasound Energy Density on the Non-Thermal Pasteurization of Chocolate Milk Beverage. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 42, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almanza-Rubio, J.L.; Gutiérrez-Méndez, N.; Leal-Ramos, M.Y.; Sepulveda, D.; Salmeron, I. Modification of the Textural and Rheological Properties of Cream Cheese Using Thermosonicated Milk. J. Food Eng. 2016, 168, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhankhar, P. Homogenization Fundamentals. J. Eng. 2014, 4, 2278–8719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.H.; Doraiswamy, L.K. Sonochemistry: Science and Engineering. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1999, 38, 1215–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Zill-e-Huma; Khan, M.K. Applications of Ultrasound in Food Technology: Processing, Preservation and Extraction. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 813–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudino, H.; Silva, E.K.; Gomes, A.; Guimarães, J.T.; Cunha, R.L.; Sant’Ana, A.S.; Meireles, M.A.A.; Cruz, A.G. Ultrasound Stabilization of Raw Milk: Microbial and Enzymatic Inactivation, Physicochemical Properties and Kinetic Stability. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 67, 105185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Butt, M.Z.; Aadil, R.M.; Inam-ur-Raheem, M.; Abdullah; Bekhit, A.E.-D.; Guimarães, J.T.; Balthazar, C.F.; Rocha, R.S.; Esmerino, E.A.; et al. Impact of Nonthermal Processing on Different Milk Enzymes. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2019, 72, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V.; Fernandez-Molina, J.J.; Swanson, B.G. Pulsed Electric Fields: A Novel Technology for Food Preservation. Agro Food Ind. Hi-Tech 2001, 12, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Buckow, R.; Ng, S.; Toepfl, S. Pulsed Electric Field Processing of Orange Juice: A Review on Microbial, Enzymatic, Nutritional, and Sensory Quality and Stability. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2013, 12, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monfort, S.; Gayán, E.; Saldaña, G.; Puértolas, E.; Condón, S.; Raso, J.; Álvarez, I. Inactivation of Salmonella Typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus by Pulsed Electric Fields in Liquid Whole Egg. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2010, 11, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Bremer, P.; Oey, I.; Everett, D.W. Bacterial Inactivation in Whole Milk Using Pulsed Electric Field Processing. Int. Dairy J. 2014, 35, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alirezalu, K.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Parniakov, O.; Barba, F.J.; Witt, J.; Toepfl, S.; Wiktor, A.; Lorenzo, J.M. Pulsed Electric Field and Mild Heating for Milk Processing: A Review on Recent Advances. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masotti, F.; Cattaneo, S.; Stuknytė, M.; De Noni, I. Current Insights into Non-Thermal Preservation Technologies Alternative to Conventional High-Temperature Short-Time Pasteurization of Drinking Milk. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Carøe, C.; Qin, Z.; Munk, D.M.E.; Crafack, M.; Petersen, M.A.; Ahrné, L. Comparative Study on Quality of Whole Milk Processed by High Hydrostatic Pressure or Thermal Pasteurization Treatment. LWT 2020, 127, 109370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, A.; Jamalian, J.; Farahnaky, A.; Mesbahi, G.; Moosavi-Nasab, M. The Effect of Microwave Pasteurization on Some Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Milk. Int. J. Food Eng. 2012, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.P.C.; Cavalcanti, R.N.; Couto, S.M.; Moraes, J.; Esmerino, E.A.; Silva, M.C.; Raices, R.S.L.; Gut, J.A.W.; Ramaswamy, H.S.; Tadini, C.C.; et al. Microwave Processing: Current Background and Effects on the Physicochemical and Microbiological Aspects of Dairy Products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschopoulou, E. Novel Processing Technology of Dairy Products. Foods 2021, 10, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Both, S.; Chemat, F.; Strube, J. Extraction of Polyphenols from Black Tea—Conventional and Ultrasound Assisted Extraction. Ultrasonics Sonochem. 2014, 21, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altin, O.; Skipnes, D.; Skåra, T.; Erdogdu, F. A Computational Study for the Effects of Sample Movement and Cavity Geometry in Industrial Scale Continuous Microwave Systems during Heating and Thawing Processes. IFSET 2022, 77, 102953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosnes, J.T.; Skipnes, D. Minimal Heat Processing Applied in Fish Processing. In Trends in Fish Processing Technologies; Borda, D., Nicolau, A.I., Raspor, P., Eds.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2017; p. 44, ISBN 978-1-315-12046-1. [Google Scholar]
- Abesinghe, A.M.N.L.; Vidanarachchi, J.K.; Islam, N.; Prakash, S.; Silva, K.F.S.T.; Bhandari, B.; Karim, M.A. Effects of Ultrasonication on the Physicochemical Properties of Milk Fat Globules of Bubalus bubalis (Water Buffalo) under Processing Conditions: A Comparison with Shear-Homogenization. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 59, 102237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregersen, S.B.; Wiking, L.; Hammershøj, M. Acceleration of Acid Gel Formation by High Intensity Ultrasound Is Linked to Whey Protein Denaturation and Formation of Functional Milk Fat Globule-Protein Complexes. J. Food Eng. 2019, 254, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floury, J.; Desrumaux, A.; Lardières, J. Effect of High-Pressure Homogenization on Droplet Size Distributions and Rheological Properties of Model Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2000, 1, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutariya, S.G.; Huppertz, T.; Patel, H.A. Influence of Milk Pre-Heating Conditions on Casein–Whey Protein Interactions and Skim Milk Concentrate Viscosity. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 69, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favé, G.; Coste, T.C.; Armand, M. Physicochemical Properties of Lipids: New Strategies to Manage Fatty Acid Bioavailability. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2004, 50, 815–831. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Boeren, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, P.; Hettinga, K. Ultrasonication Retains More Milk Fat Globule Membrane Proteins Compared to Equivalent Shear-Homogenization. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 70, 102703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez-Aguirre, D.; Mawson, R.; Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V. Microstructure of Fat Globules in Whole Milk after Thermosonication Treatment. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, E325–E332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Oey, I.; Everett, D.W. Interfacial Properties and Transmission Electron Microscopy Revealing Damage to the Milk Fat Globule System after Pulsed Electric Field Treatment. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 47, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna-Hernandez, S.O.; Escobedo-Avellaneda, Z.; García-García, R.; Rostro-Alanis, M.d.J.; Welti-Chanes, J. High Hydrostatic Pressure Induced Changes in the Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Milk and Dairy Products: A Review. Foods 2021, 10, 1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, A.; Anema, S.; Singh, H. High-Pressure–Induced Interactions Between Milk Fat Globule Membrane Proteins and Skim Milk Proteins in Whole Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 4013–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.; Nadeem, M.; Qureshi, T.M.; Leong, T.S.H.; Gamlath, C.J.; Martin, G.J.O.; Ashokkumar, M. Effects of High Pressure, Microwave and Ultrasound Processing on Proteins and Enzyme Activity in Dairy Systems—A Review. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 57, 102192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.; Zhao, W.; Li, X.; Ge, W.; Muhammad, Z.; Wang, H.; Du, L. Study on Microwave-Accelerated Casein Protein Grafted with Glucose and β-Cyclodextrin to Improve the Gel Properties. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 1429–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iuliana, C.; Rodica, C.; Sorina, R.; Oana, M. Impact of Microwaves on the Physico-Chemical Characteristics of Cow Milk. Rom. Rep. Phys. 2015, 67, 423–430. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Ren, F. Effects of Size and Stability of Native Fat Globules on the Formation of Milk Gel Induced by Rennet. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ménard, O.; Ahmad, S.; Rousseau, F.; Briard-Bion, V.; Gaucheron, F.; Lopez, C. Buffalo vs. Cow Milk Fat Globules: Size Distribution, Zeta-Potential, Compositions in Total Fatty Acids and in Polar Lipids from the Milk Fat Globule Membrane. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegu, K.; Arya, S.S. Comparative Assessment of HTST, Hydrodynamic Cavitation and Ultrasonication on Physico-Chemical Properties, Microstructure, Microbial and Enzyme Inactivation of Raw Milk. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 69, 102640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratakos, A.C.; Inguglia, E.S.; Linton, M.; Tollerton, J.; Murphy, L.; Corcionivoschi, N.; Koidis, A.; Tiwari, B.K. Effect of High Pressure Processing on the Safety, Shelf Life and Quality of Raw Milk. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 52, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Amezquita, L.E.; Primo-Mora, A.R.; Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V.; Sepulveda, D.R. Effect of Nonthermal Technologies on the Native Size Distribution of Fat Globules in Bovine Cheese-Making Milk. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2009, 10, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSweeney, P.L.H.; McNamara, J.P. (Eds.) Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Mokrzycki, W.S.; Maciej, T. Colour Difference Δ E-A Survey. Mach. Graph. Vis. 2011, 20.4, 383–411. [Google Scholar]
- Harte, F.; Luedecke, L.; Swanson, B.; Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V. Low-Fat Set Yogurt Made from Milk Subjected to Combinations of High Hydrostatic Pressure and Thermal Processing. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 1074–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAuley, C.M.; Singh, T.K.; Haro-Maza, J.F.; Williams, R.; Buckow, R. Microbiological and Physicochemical Stability of Raw, Pasteurised or Pulsed Electric Field-Treated Milk. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 38, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clare, D.A.; Bang, W.S.; Cartwright, G.; Drake, M.A.; Coronel, P.; Simunovic, J. Comparison of Sensory, Microbiological, and Biochemical Parameters of Microwave versus Indirect UHT Fluid Skim Milk during Storage. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 4172–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalac, S.; Alvarez, V.; Ji, T.; Zhang, Q.H. Inactivation of Selected Microorganisms and Properties of Pulsed Electric Field Processed Milk. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2003, 27, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, B.Y.; Simpson, M.V.; Ngadi, M.O.; Simpson, B.K. Flow Behaviour and Viscosity of Reconstituted Skimmed Milk Treated with Pulsed Electric Field. Biosyst. Eng. 2011, 109, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thum, C.; Ozturk, G.; McNabb, W.C.; Roy, N.C.; Leite Nobrega de Moura Bell, J.M. Effects of Microwave Processing Conditions on Microbial Safety and Antimicrobial Proteins in Bovine Milk. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, e14348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, Q.-A.; Buffa, M.; Guamis, B.; Saldo, J. Factors Affecting Bacterial Inactivation during High Hydrostatic Pressure Processing of Foods: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, G.; Munk, D.M.E.; Qin, Z.; Petersen, M.A.; Cardoso, D.R.; Otte, J.; Ahrné, L. Cycled High Hydrostatic Pressure Processing of Whole and Skimmed Milk: Effects on Physicochemical Properties. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 63, 102378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delso, C.; Martínez, J.M.; Cebrián, G.; Condón, S.; Raso, J.; Álvarez, I. Microbial Inactivation by Pulsed Electric Fields. In Pulsed Electric Fields Technology for the Food Industry: Fundamentals and Applications; Raso, J., Heinz, V., Alvarez, I., Toepfl, S., Eds.; Food Engineering Series; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 169–207. ISBN 978-3-030-70586-2. [Google Scholar]
- Saldaña, G.; Puértolas, E.; Monfort, S.; Raso, J.; Álvarez, I. Defining Treatment Conditions for Pulsed Electric Field Pasteurization of Apple Juice. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 151, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckow, R.; Chandry, P.S.; Ng, S.Y.; McAuley, C.M.; Swanson, B.G. Opportunities and Challenges in Pulsed Electric Field Processing of Dairy Products. Int. Dairy J. 2014, 34, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda, D.R.; Góngora-Nieto, M.M.; Guerrero, J.A.; Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V. Shelf Life of Whole Milk Processed by Pulsed Electric Fields in Combination with PEF-Generated Heat. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 42, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Days | 0 | 7 | 14 | 21 | 28 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw | −11.4 ± 0.8 aA | −12.1 ± 0.3 aA | |||
| US | −17.5 ± 1.2 aC | −20.1 ± 0.8 abB | −19.1 ± 1.0 bB | ||
| Commercial | −14.6 ± 1.0 aB | −14.7 ± 1.2 aB | −14.4 ± 1.1 aA | −14.6 ± 1.0 aA | −15.3 ± 1.0 aA |
| US + PEF | −18.5 ± 1.3 aCD | −20.2 ± 0.8 aB | −19.9 ± 0.7 aB | −19.3 ± 1.2 aB | −19.4 ± 0.7 aB |
| US + MW | −20.1 ± 1.1 aD | −20.2 ± 0.3 aB | −19.4 ± 1.2 aB | −18.9 ± 1.0 aB | −18.5 ± 1.0 aB |
| US + HPP | −19.7 ± 1.2 aD | −20.5 ± 0.7 aB | −19.7 ± 0.9 aB | −18.7 ± 1.0 aB | −19.2 ± 0.7 aB |
| Days | 0 | 7 | 14 | 21 | 28 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K-index | |||||
| Raw | 0.030 ± 0.007 A | ||||
| US | 0.024 ± 0.005 aAC | 0.058 ± 0.013 aA | 0.042 ± 0.013 aA | ||
| Commercial | 0.046 ± 0.003 aB | 0.023 ± 0.000 aB | 0.028 ± 0.010 aA | 0.027 ± 0.009 aA | 0.019 ± 0.000 aA |
| US + HPP | 0.026 ± 0.003 aAC | 0.032 ± 0.010 aAB | 0.019 ± 0.001 aA | 0.038 ± 0.008 aA | 0.030 ± 0.010 aA |
| US + MW | 0.040 ± 0.009 aAB | 0.036 ± 0.019 aAB | 0.042 ± 0.016 aA | 0.048 ± 0.011 aA | 0.022 ± 0.001 aA |
| US + PEF | 0.028 ± 0.002 aAC | 0.034 ± 0.009 aAB | 0.040 ± 0.09 aA | 0.038 ± 0.008 aA | 0.034 ± 0.015 aA |
| n-value | |||||
| Raw | 0.689 ± 0.036 A | ||||
| US | 0.732 ± 0.028 aA | 0.618 ± 0.029 abA | 0.670 ± 0.026 bA | ||
| Commercial | 0.627 ± 0.021 aAB | 0.736 ± 0.009 bA | 0.713 ± 0.047 bA | 0.717 ± 0.037 bA | 0.758 ± 0.000 bA |
| US + HPP | 0.724 ± 0.018 aAC | 0.701 ± 0.047 aA | 0.773 ± 0.001 aA | 0.695 ± 0.037 aA | 0.719 ± 0.046 aA |
| US + MW | 0.643 ± 0.037 aA | 0.698 ± 0.076 aA | 0.661 ± 0.045 aA | 0.675 ± 0.035 aA | 0.735 ± 0.015 aA |
| US + PEF | 0.704 ± 0.002 aA | 0.690 ± 0.038 aA | 0.684 ± 0.031 aA | 0.702 ± 0.028 aA | 0.718 ± 0.048 aA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Astráin-Redín, L.; Skipnes, D.; Cebrián, G.; Álvarez-Lanzarote, I.; Rode, T.M. Effect of the Application of Ultrasound to Homogenize Milk and the Subsequent Pasteurization by Pulsed Electric Field, High Hydrostatic Pressure, and Microwaves. Foods 2023, 12, 1457. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12071457
Astráin-Redín L, Skipnes D, Cebrián G, Álvarez-Lanzarote I, Rode TM. Effect of the Application of Ultrasound to Homogenize Milk and the Subsequent Pasteurization by Pulsed Electric Field, High Hydrostatic Pressure, and Microwaves. Foods. 2023; 12(7):1457. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12071457
Chicago/Turabian StyleAstráin-Redín, Leire, Dagbjørn Skipnes, Guillermo Cebrián, Ignacio Álvarez-Lanzarote, and Tone Mari Rode. 2023. "Effect of the Application of Ultrasound to Homogenize Milk and the Subsequent Pasteurization by Pulsed Electric Field, High Hydrostatic Pressure, and Microwaves" Foods 12, no. 7: 1457. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12071457
APA StyleAstráin-Redín, L., Skipnes, D., Cebrián, G., Álvarez-Lanzarote, I., & Rode, T. M. (2023). Effect of the Application of Ultrasound to Homogenize Milk and the Subsequent Pasteurization by Pulsed Electric Field, High Hydrostatic Pressure, and Microwaves. Foods, 12(7), 1457. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12071457