Composition of Minerals and Volatile Organic Components of Non-Centrifugal Cane Sugars from Japan and ASEAN Countries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Standards and Reagents
2.3. Mineral Composition Analysis
2.4. Volatile Composition Analysis
2.5. MS-e-nose Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
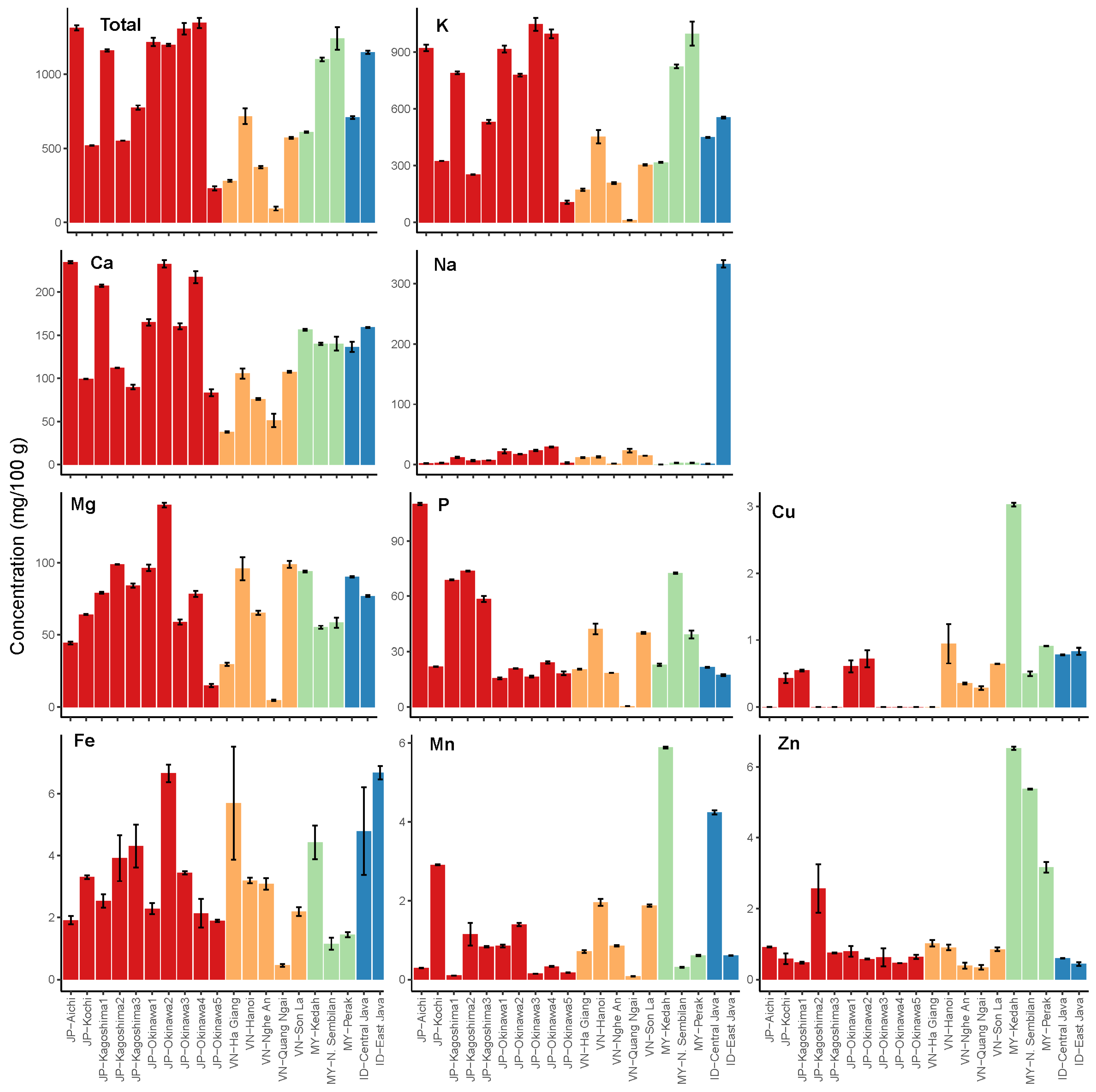
3.1. Mineral Composition
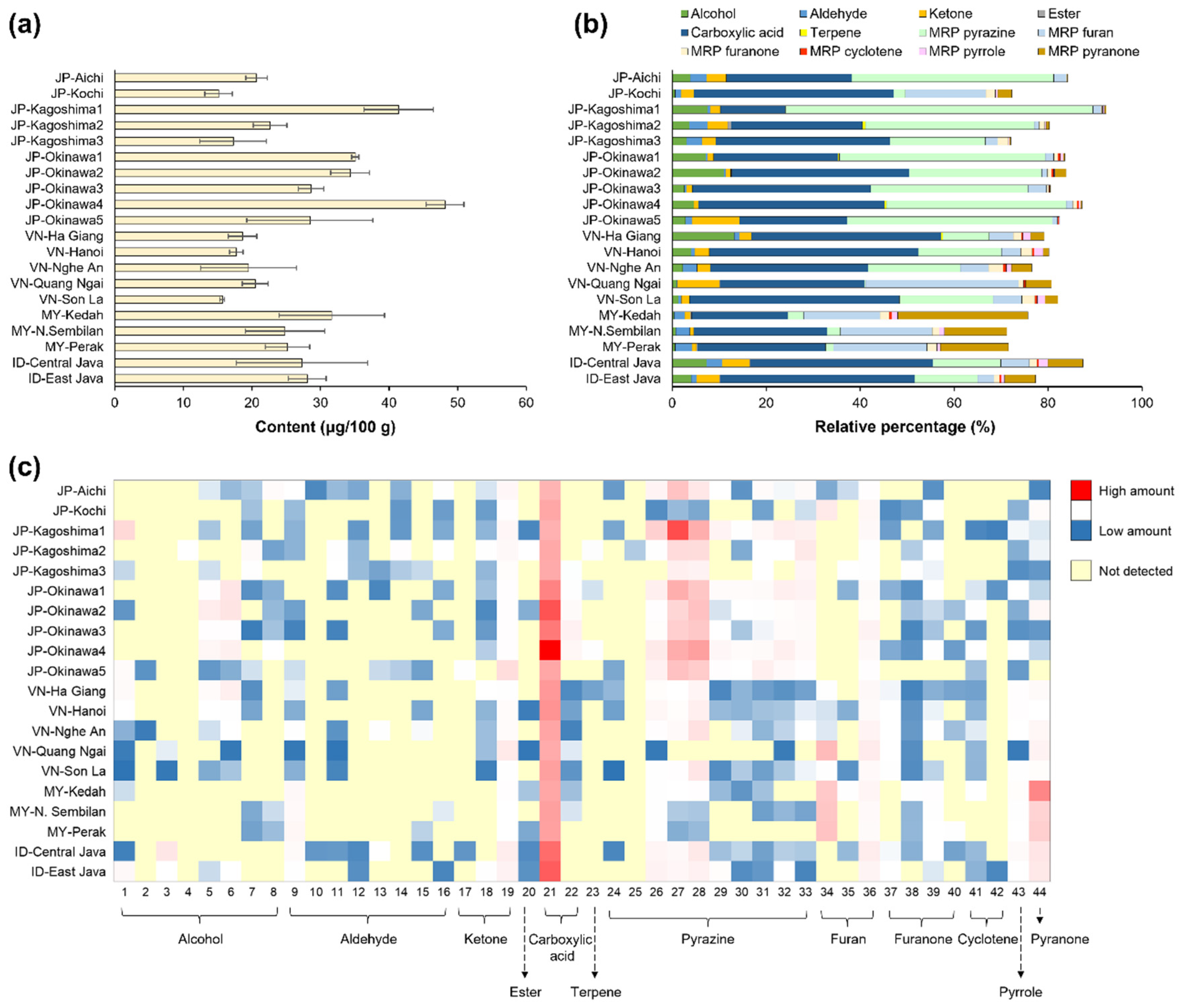
3.2. Volatile Organic Components (VOCs)
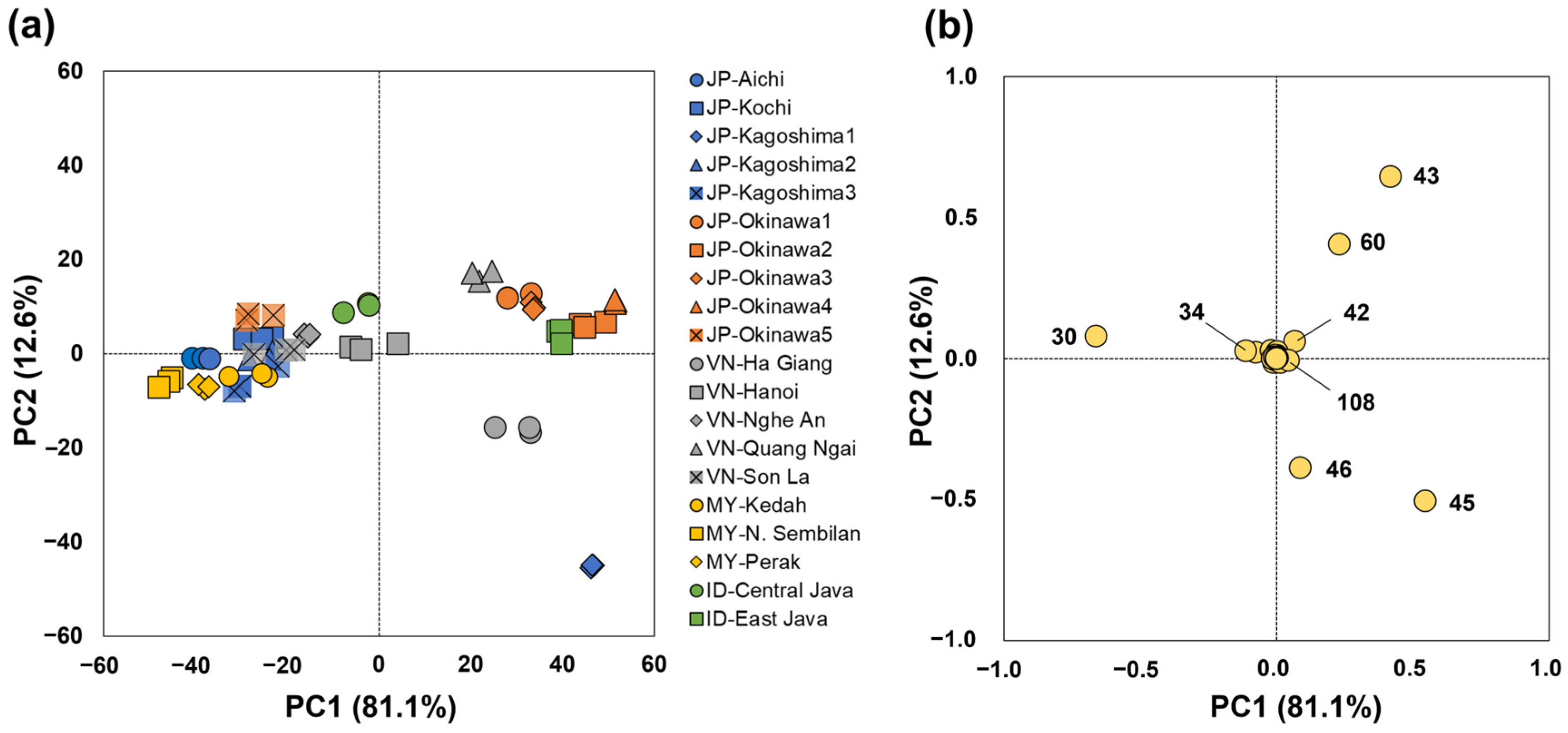
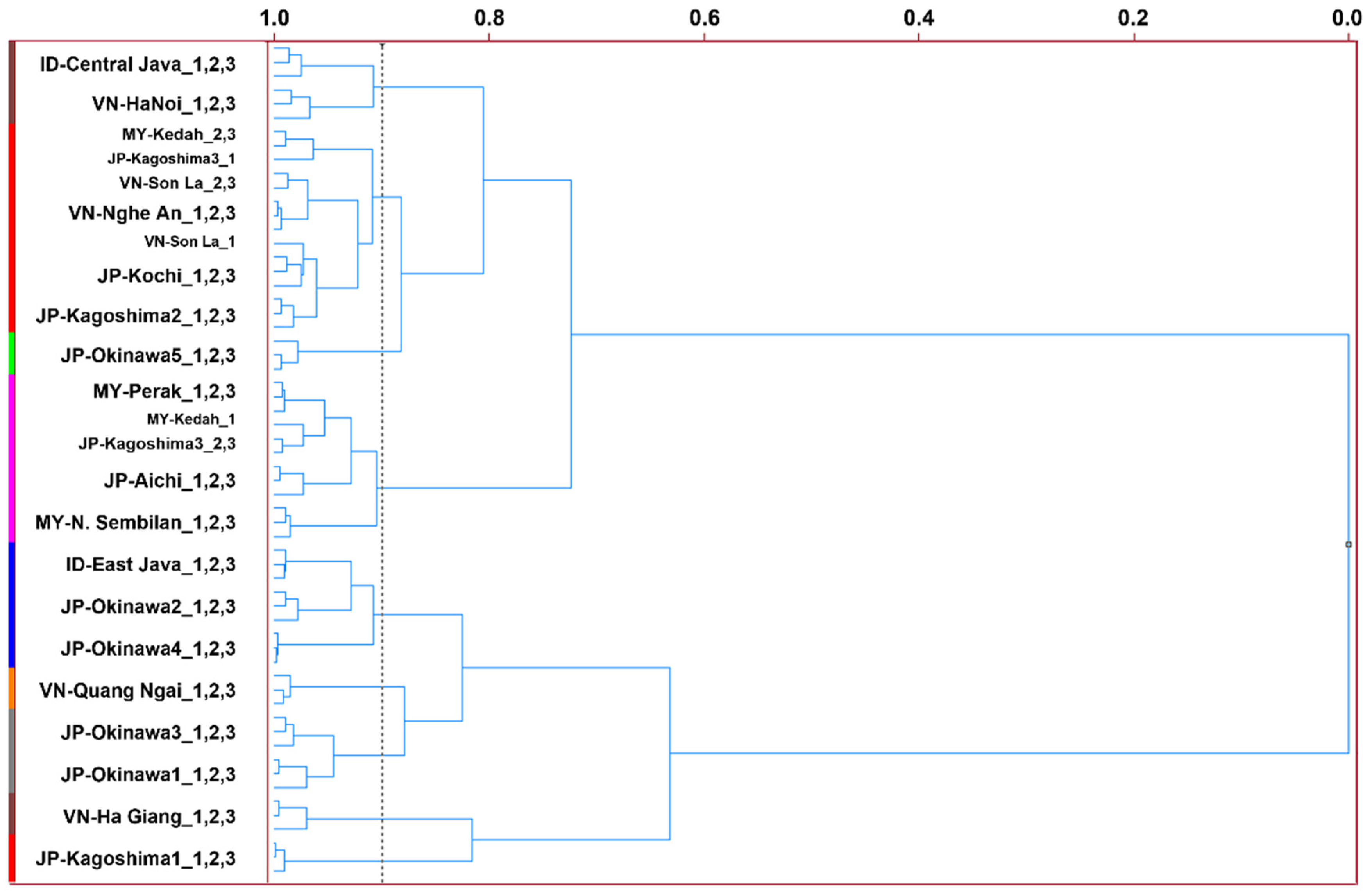
3.3. MS-e-Nose Profiles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weerawatanakorn, M.; Asikin, Y.; Kamchonemenukool, S.; Tamaki, H.; Takara, K.; Wada, K. Physicochemical, antioxidant, volatile component, and mass spectrometry-based electronic nose analyses differentiated unrefined non-centrifugal cane, palm, and coconut sugars. Food Meas. 2021, 15, 1563–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipčev, B.; Šimurina, O.; Dapčević Hadnađev, T.; Jevtić-Mučibabić, R.; Filipović, V.; Lončar, B. Effect of liquid (native) and dry molasses originating from sugar beet on physical and textural properties of gluten-free biscuit and biscuit dough. J. Texture Stud. 2015, 46, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidan, D.; Azlan, A. Non-centrifugal sugar (NCS) and health: A review on functional components and health benefits. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffé, W.R. Health effects of non-centrifugal sugar (NCS): A review. Sugar Tech. 2012, 14, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez, F.; Espitia, J.; Mendieta, O.; Escobar, S.; Rodríguez, J. Non-centrifugal cane sugar processing: A review on recent advances and the influence of process variables on qualities attributes of final products. J. Food Eng. 2019, 255, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Ramalingam, S.; Jo, I.G.; Kwon, Y.S.; Bahuguna, A.; Oh, Y.S.; Kwon, O.J.; Kim, M. Comparative study of the physicochemical, nutritional, and antioxidant properties of some commercial refined and non-centrifugal sugars. Food Res. Int. 2018, 109, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flórez-Martínez, D.H.; Contreras-Pedraza, C.A.; Escobar-Parra, S.; Rodríguez-Cortina, J. Key drivers for non-centrifugal sugar cane research, technological development, and market linkage: A technological roadmap approach for Colombia. Sugar Tech. 2022, 25, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asikin, Y.; Takahara, W.; Takahashi, M.; Hirose, N.; Ito, S.; Wada, K. Compositional and electronic discrimination analyses of taste and aroma profiles of non-centrifugal cane brown sugars. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 1844–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honig, V.; Procházka, P.; Obergruber, M.; Roubík, H. Nutrient effect on the taste of mineral waters: Evidence from Europe. Foods 2020, 9, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintaes, K.D.; Diez-Garcia, R.W. The importance of minerals in the human diet. In Handbook of Mineral Elements in Food; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Asikin, Y.; Hirose, N.; Tamaki, H.; Ito, S.; Oku, H.; Wada, K. Effects of different drying–solidification processes on physical properties, volatile fraction, and antioxidant activity of non-centrifugal cane brown sugar. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 66, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.; Song, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, B.; Che, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S. Analysis of aroma components from sugarcane to non-centrifugal cane sugar using GC-O-MS. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 32276–32289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera-Gutiérrez, T.; García-Muñoz, M.C.; Otálvaro-Alvarez, A.M.; Mendieta-Menjura, O. Effect of processing technology and sugarcane varieties on the quality properties of unrefined non-centrifugal sugar. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asikin, Y.; Kamiya, A.; Mizu, M.; Takara, K.; Tamaki, H.; Wada, K. Changes in the physicochemical characteristics, including flavour components and Maillard reaction products, of non-centrifugal cane brown sugar during storage. Food Chem. 2014, 149, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez Viejo, C.; Tongson, E.; Fuentes, S. Integrating a low-cost electronic nose and machine learning modelling to assess coffee aroma profile and intensity. Sensors 2021, 21, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakubu, H.G.; Kovacs, Z.; Toth, T.; Bazar, G. Trends in artificial aroma sensing by means of electronic nose technologies to advance dairy production—A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Xu, J. Applications of electronic nose (e-nose) and electronic tongue (e-tongue) in food quality-related properties determination: A review. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2020, 4, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saevels, S.; Lammertyn, J.; Berna, A.Z.; Veraverbeke, E.A.; Di Natale, C.; Nicolaï, B.M. An electronic nose and a mass spectrometry-based electronic nose for assessing apple quality during shelf life. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2004, 31, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, M.R.F.; Machado, M.C.; Lisboa, M.T.; Vieira, M.A.; Zimmer, T.B.R.; Otero, D.M.; Zambiazi, R.C. Physicochemical characterization and antioxidant activity of refined and unrefined sugarcane products from Southern Brazil. Sugar Tech. 2022, 25, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azlan, A.; Khoo, H.E.; Sajak, A.A.B.; Aizan Abdul Kadir, N.A.; Yusof, B.N.M.; Mahmood, Z.; Sultana, S. Antioxidant activity, nutritional and physicochemical characteristics, and toxicity of minimally refined brown sugar and other sugars. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 5048–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Rivera, N.; Olvera-Vargas, L.A. Innovations for sustainable production of traditional and artisan unrefined non-centrifugal cane sugar in Mexico. In Innovations and Traditions for Sustainable Development; Leal Filho, W., Krasnov, E.V., Gaeva, D.V., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 313–330. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, P.; Chavanpatil, V.; Shah, N.G.; Mahajani, S.M. Scientific understanding of the traditional practices followed in India for the production of non-centrifugal sugar. Sugar Tech. 2021, 23, 1393–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, S.; Ahmad, S. Instrumental neutron activation analysis of different products from the sugarcane industry in Pakistan Part 1: Essential elements for nutritional adequacy. J. AOAC Int. 2008, 91, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, H. Production and processing of brown sugar. J. Cook. Sci. 2020, 53, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-Y.; Chen, X.-W.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Yen, G.-C.; Lin, J.-A. Authentication of dark brown sugars from different processing using three-dimensional fluorescence spectroscopy. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 150, 111959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, R.; Singh, P.; Ali, O.M.; Abdel Latef, A.A.H.; Laing, A.M.; Hossain, A. Yield and quality of ratoon sugarcane are improved by applying potassium under irrigation to potassium deficient soils. Agronomy. 2021, 11, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawati, E.; Karimah, R.N.; Suryana, A.L.; Destarianto, P.; Oktafa, H. The effect of sodium metabisulfite concentration and drying time on the quality of coconut sugar. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 672, 012069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaavya, R.; Pandiselvam, R.; Kothakota, A.; Banuu Priya, E.P.; Arun Prasath, V. Sugarcane juice preservation: A critical review of the state of the art and way forward. Sugar Tech. 2019, 21, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paravisini, L.; Soldavini, A.; Peterson, J.; Simons, C.T.; Peterson, D.G. Impact of bitter tastant sub-qualities on retronasal coffee aroma perception. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.; Crusciol, C.A.C.; McCray, J.M.; Nascimento, C.A.C.; Martello, J.M.; de Siqueira, G.F.; Tarumoto, M.B. Magnesium as a promoter of technological quality in sugarcane. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 20, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, R.T.X.; Korndörfer, G.H.; Brem Soares, R.A.; Fontoura, P.R. Phosphate fertilizers for sugarcane used at pre-planting (phosphorus fertilizer application). J. Plant Nutr. 2015, 38, 1444–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Srivastava, S.; Solomon, S.; Shrivastava, A.K.; Chandra, A. Impact of excess zinc on growth parameters, cell division, nutrient accumulation, photosynthetic pigments and oxidative stress of sugarcane (Saccharum spp.). Acta Physiol. Plant. 2010, 32, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.K.; Appel, L.J.; Brands, M.; Howard, B.V.; Lefevre, M.; Lustig, R.H.; Sacks, F.; Steffen, L.M.; Wylie-Rosett, J. American Heart Association Nutrition Committee of the Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism and the Council on Epidemiology and Prevention. Dietary sugars intake and cardiovascular health: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2009, 120, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, S.; Nagai, Y.; Hirata, A. Classification of various types of sugar products by mineral composition. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2021, 27, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, S.; Nagai, Y.; Hirata, A. Relationship between evaluation of taste sensing system and component analysis in sugar products. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2020, 26, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destro, T.M.; Prates, D.d.F.; Watanabe, L.S.; Garcia, S.; Biz, G.; Spinosa, W.A. Organic brown sugar and jaboticaba pulp influence on water kefir fermentation. Ciênc. Agrotec. 2019, 43, e005619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.-X.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Qin, L.; Chen, C.; Liu, Y.; Yu, H.-Y. Evaluating taste contribution of brown sugar in chicken seasoning using taste compounds, sensory evaluation, and electronic tongue. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, M.; Linforth, R.S.T.; Taylor, A.J. Simultaneous real-time measurements of mastication, swallowing, nasal airflow, and aroma release. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 5052–5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starowicz, M.; Zieliński, H. How Maillard reaction influences sensorial properties (color, flavor and texture) of food products? Food Rev. Int. 2019, 35, 707–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, P.; Xu, D.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y. Aroma patterns of Beijing rice vinegar and their potential biomarker for traditional Chinese cereal vinegars. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 398–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, V.; Mall, A.K.; Solomon, S.; Ansari, M.I. Post-harvest biology and recent advances of storage technologies in sugarcane. Biotechnol. Rep. 2022, 33, e00705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Song, C.; Ho, C.T.; Wan, X. Contribution of l-theanine to the formation of 2,5-dimethylpyrazine, a key roasted peanutty flavor in Oolong tea during manufacturing processes. Food Chem. 2018, 263, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tang, X.-Y.; Wu, C.-J.; Yu, S.-J. Formation of 2,3-dihydro-3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyl-4(H)-pyran-4-One (DDMP) in glucose-amino acids Maillard reaction by dry-heating in comparison to wet-heating. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 105, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutzach, I.; Chatonnet, P.; Henry, R.; Dubourdieu, D. Identification of volatile compounds with a “toasty” aroma in heated oak used in barrelmaking. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 2217–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sun, H.; Ma, G.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L.; Pei, H.; Li, X.; Gao, L. Insights into flavor and key influencing factors of Maillard reaction products: A recent update. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 973677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerny, C.; Briffod, M. Effect of pH on the Maillard reaction of [13C5]xylose, cysteine, and thiamin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 1552–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, W. Natural 4-hydroxy-2,5-dimethyl-3(2H)-furanone (Furaneol®). Molecules 2013, 18, 6936–6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Westbrook, C.K.; Cool, T.A.; Hansen, N.; Kohse-Höinghaus, K. The effect of carbon–carbon double bonds on the combustion chemistry of small fatty acid esters. Z. Phys. Chem. 2011, 225, 1293–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwabie, N.M.; Schade, G.W.; Custer, T.G.; Linke, S.; Hinz, T. Abundances and flux estimates of volatile organic compounds from a dairy cowshed in Germany. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ayustaningwarno, F.; Asikin, Y.; Amano, R.; Vu, N.T.; Hajar-Azhari, S.; Anjani, G.; Takara, K.; Wada, K. Composition of Minerals and Volatile Organic Components of Non-Centrifugal Cane Sugars from Japan and ASEAN Countries. Foods 2023, 12, 1406. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12071406
Ayustaningwarno F, Asikin Y, Amano R, Vu NT, Hajar-Azhari S, Anjani G, Takara K, Wada K. Composition of Minerals and Volatile Organic Components of Non-Centrifugal Cane Sugars from Japan and ASEAN Countries. Foods. 2023; 12(7):1406. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12071406
Chicago/Turabian StyleAyustaningwarno, Fitriyono, Yonathan Asikin, Ryo Amano, Nam Tuan Vu, Siti Hajar-Azhari, Gemala Anjani, Kensaku Takara, and Koji Wada. 2023. "Composition of Minerals and Volatile Organic Components of Non-Centrifugal Cane Sugars from Japan and ASEAN Countries" Foods 12, no. 7: 1406. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12071406
APA StyleAyustaningwarno, F., Asikin, Y., Amano, R., Vu, N. T., Hajar-Azhari, S., Anjani, G., Takara, K., & Wada, K. (2023). Composition of Minerals and Volatile Organic Components of Non-Centrifugal Cane Sugars from Japan and ASEAN Countries. Foods, 12(7), 1406. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12071406






