Nondestructive Detection of Pesticide Residue (Chlorpyrifos) on Bok Choi (Brassica rapa subsp. Chinensis) Using a Portable NIR Spectrometer Coupled with a Machine Learning Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. NIR Spectra Data Collection
2.3. Determination of the Real Value of Pesticide Residue
2.4. Machine Learning Process
2.4.1. Data Preprocessing
2.4.2. Modeling and Evaluation of Model Performance
2.4.3. Validation of Model with Unknown Sample
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spectra of Samples
3.2. Results of Real Chlorpyrifos Residue Value
3.3. Principal Componant Analysis
3.4. Classification of Vegetables with Machine Learning
3.5. X-Loading and Regression Coefficient
3.6. Validation of Model with Unknown Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sankom, A.; Mahakarnchanakul, W.; Rittiron, R.; Sajjaanantakul, T.; Thongket, T. Detection of Profenofos in Chinese Kale, Cabbage, and Chili Spur Pepper Using Fourier Transform Near-Infrared and Fourier Transform Mid-Infrared Spectroscopies. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 26404–26415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Public Health Food Safety. Available online: http://bqsf.dmsc.moph.go.th/bqsfWeb/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/Food-safety-report-63.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Naksen, W.; Surat, H.; Zhen-Lin, X.; Natthapol, K.; Tanyaporn, K.; Tippawan, P.; Vanvimol, P. Health Risk Assessment from Organophosphate Insecticides Residues in Commonly Consumed Vegetables of Local Markets, Northern Thailand. J. Health Res. 2023, 37, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapbamrer, R.; Hongsibsong, S. Organophosphorus pesticide residues in vegetables from farms, markets, and a supermarket around Kwan Phayao Lake of Northern Thailand. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 67, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanwimolruk, S.; Phopin, K.; Boonpangrak, S.; Prachayasittikul, V. Food safety in Thailand 4: Comparison of pesticide residues found in three commonly consumed vegetables purchased from local markets and supermarkets in Thailand. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silipunyo, T.; Hongsibsong, S.; Phalaraksh, C.; Laoyang, S.; Kerdnoi, T.; Patarasiriwong, V.; Prapamontol, T. Determination of organophosphate pesticides residues in fruits, vegetables and health risk assessment among consumers in Chiang Mai Province, Northern Thailand. Res. J. Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 11, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Shen, T.; He, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.; Liu, F. Detection of chlorpyrifos and carbendazim residues in the cabbage using visible/near-infrared spectroscopy combined with chemometrics. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 257, 119759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. Thai FDA Announced Ban of Paraquat and Chlorpyrifos on Imported Food Products. Available online: https://www.fas.usda.gov/data/thailand-thai-fda-announced-ban-paraquat-and-chlorpyrifos-imported-food-products (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Cho, S.K.; Abd El-Aty, A.M.; Rahman, M.M.; Choi, J.H.; Shim, J.H. Simultaneous multi-determination and transfer of eight pesticide residues from green tea leaves to infusion using gas chromatography. Food Chem. 2014, 165, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, E.; Kobara, Y.; Baba, K.; Eun, H. Determination of Seven Neonicotinoid Insecticides in Cucumber and Eggplant by Water-Based Extraction and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Lett. 2015, 48, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Sun, M.; Li, M. A survey of determination for organophosphorus pesticide residue in agricultural products. Adv. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 5, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, T.M.P.; Stellari, A. Review: NIR Spectroscopy as a Suitable Tool for the Investigation of the Horticultural Field. Agronomy 2019, 9, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, A.; Arazuri, S.; García, I.; Mangado, J.; Jarén, C. A review of the application of near-infrared spectroscopy for the analysis of potatoes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 5413–5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, G. Mid and near infrared spectroscopy. In Analytical Techniques in the Pharmaceutical Sciences; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 61–138. [Google Scholar]
- Ngo, V.D.; Hoang, L.T.A.; Pham, V.C.; Ngo, V.H.; Tran, P.H. Estimation of pesticide residues on leafy vegetables using a developed handheld spectrometer. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 12, 8163–8173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarloo, A.S.; Sharabiani, V.R.; Gilandeh, Y.A.; Taghinezhad, E.; Szymanek, M. Evaluation of different models for non-destructive detection of tomato pesticide residues based on near-infrared spectroscopy. Sensors 2021, 21, 3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazarloo, A.S.; Sharabiani, V.R.; Gilandeh, Y.A.; Taghinezhad, E.; Szymanek, M.; Sprawka, M. Feasibility of using VIS/NIR spectroscopy and multivariate analysis for pesticide residue detection in tomatoes. Processes 2021, 9, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Ma, B.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Li, C. Nondestructive identification of pesticide residues on the Hami melon surface using deep feature fusion by Vis/NIR spectroscopy and 1D-CNN. J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 44, e13602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Ge, X.; Wu, X.; Dai, C.; Yang, N. Identification of pesticide residues in lettuce leaves based on near infrared transmission spectroscopy. J. Food Process Eng. 2018, 41, e12816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, B.; Mohajerani, E.; Jamshidi, J.; Minaei, S.; Sharifi, A. Non-destructive detection of pesticide residues in cucumber using visible/near-infrared spectroscopy. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Exposure Risk Assess. 2015, 32, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, B.; Mohajerani, E.; Jamshidi, J. Developing a Vis/NIR spectroscopic system for fast and non-destructive pesticide residue monitoring in agricultural product. Measurement 2016, 89, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Cai, J.; Li, J.; Liu, M. Application of particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm to determine dichlorvos residue on the surface of navel orange with Vis-NIR spectroscopy. Procedia Eng. 2012, 29, 4124–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.T.; Flores-Rojas, K.; Guerrero, J.E.; Garrido-Varo, A.; Pérez-Marín, D. Measurement of pesticide residues in peppers by near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Wang, H.; Yong, W.; Zhang, F.; Sun, L.; Yang, M.-L.; Wu, Y.-N.; Chu, X.-G. The effects of washing and cooking on chlorpyrifos and its toxic metabolites in vegetables. Food Control 2011, 22, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongsibsong, S.; Prapamontol, T.; Xu, T.; Hammock, B.D.; Wang, H.; Chen, Z.-J.; Xu, Z.-L. Monitoring of the organophosphate pesticide chlorpyrifos in vegetable samples from local markets in Northern Thailand by developed immunoassay. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2020, 17, 4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foong, S.Y.; Ma, N.L.; Lam, S.S.; Peng, W.; Low, F.; Lee, B.H.; Alstrup, A.K.; Sonne, C. A recent global review of hazardous chlorpyrifos pesticide in fruit and vegetables: Prevalence, remediation and actions needed. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Hsiung, C.; Smith, V. Investigation of Direct Model Transferability Using Miniature Near-Infrared Spectrometers. Molecules 2019, 24, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harshit, D.; Charmy, K.; Nrupesh, P. Organophosphorus pesticides determination by novel HPLC and spectrophotometric method. Food Chem. 2017, 230, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xie, L.; Ying, Y. Factors influencing near infrared spectroscopy analysis of agro-products: A review. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2019, 6, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinnan, Å.; Van Den Berg, F.; Engelsen, S.B. Review of the most common pre-processing techniques for near-infrared spectra. TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 1201–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pornchaloempong, P.; Sharma, S.; Phanomsophon, T.; Srisawat, K.; Inta, W.; Sirisomboon, P.; Prinyawiwatkul, W.; Nakawajana, N.; Lapcharoensuk, R.; Teerachaichayut, S. Non-Destructive Quality Evaluation of Tropical Fruit (Mango and Mangosteen) Purée Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Partial Least Squares Regression. Agriculture 2022, 12, 2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saechua, W.; Sharma, S.; Nakawajana, N.; Leepaitoon, K.; Chunsri, R.; Posom, J.; Roeksukrungrueang, C.; Siritechavong, T.; Phanomsophon, T.; Sirisomboon, P.; et al. Integrating vis-swnir spectrometer in a conveyor system for in-line measurement of dry matter content and soluble solids content of durian pulp. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 181, 111640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapcharoensuk, R.; Sirisomboon, P. Eating quality of cooked rice determination using Fourier transform near infrared spectroscopy. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2014, 7, 1450003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Rutledge, D.N.; Roger, J.-M.; Wali, K.; Khan, H.A. Chemometric pre-processing can negatively affect the performance of near-infrared spectroscopy models for fruit quality prediction. Talanta 2021, 229, 122303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, Y.; Yuan, K.; Xiao, W.; Wu, J.; Shi, C.; Xia, J.; Chu, G.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, G. A local pre-processing method for near-infrared spectra, combined with spectral segmentation and standard normal variate transformation. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 909, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasisi, A.; Attoh-Okine, N. Principal components analysis and track quality index: A machine learning approach. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2018, 91, 230–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Qu, N.; Wang, B.; Chi, Y.Z.; Ren, Y.L. Simultaneous determination of two active components in compound aspirin tablets using principal component artificial neural networks (PC-ANNs) on NIR spectroscopy. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 32, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanmohammadi, M.; Garmarudi, A.B.; Ghasemi, K.; Garrigues, S.; de la Guardia, M. Artificial neural network for quantitative determination of total protein in yogurt by infrared spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2009, 91, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoplac, I.; Avila-George, H.; Vargas, L.; Robert, P.; Castro, W. Determination of the superficial citral content on microparticles: An application of NIR spectroscopy coupled with chemometric tools. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Tian, G.; Qiu, Y.; Qu, H. Rapid quantification of active pharmaceutical ingredient for sugar-free Yangwei granules in commercial production using FT-NIR spectroscopy based on machine learning techniques. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 245, 118878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurinjak Tušek, A.; Jurina, T.; Čulo, I.; Valinger, D.; Gajdoš Kljusurić, J.; Benković, M. Application of NIRs coupled with PLS and ANN modelling to predict average droplet size in oil-in-water emulsions prepared with different microfluidic devices. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 270, 120860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, N.; Kang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, R.; Ning, J.; Ding, H.; Sheng, X.; Zhou, D. Rapid identification of geographical origin of sea cucumbers Apostichopus japonicus using FT-NIR coupled with light gradient boosting machine. Food Control 2021, 124, 107883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.; Kim, Y.; Han, H.-J.; Son, W.C.; Hong, Z.-Y.; Sohn, I.; Shim, J.; Hwang, C. Predicting Successes and Failures of Clinical Trials With Outer Product–Based Convolutional Neural Network. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 670670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krstinić, D.; Braović, M.; Šerić, L.; Božić-Štulić, D. Multi-label classifier performance evaluation with confusion matrix. Comput. Sci. Inf. Syst. 2020, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapcharoensuk, R.; Nakawajana, N. Identification of syrup type using fourier transform-near infrared spectroscopy with multivariate classification methods. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2018, 11, 1750019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, B.; Li, H.; Shen, M.; Tian, S.; Zhang, H.; Ren, X.; Xing, L.; Zhao, J. Determination of bagged ‘Fuji’apple maturity by visible and near-infrared spectroscopy combined with a machine learning algorithm. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2020, 111, 103529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.H.; Guindo, M.L.; Chen, R.; Liu, F. Geographic origin discrimination of millet using Vis-NIR spectroscopy combined with machine learning techniques. Foods 2021, 10, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morellos, A.; Tziotzios, G.; Orfanidou, C.; Pantazi, X.E.; Sarantaris, C.; Maliogka, V.; Alexandridis, T.K.; Moshou, D. Non-destructive early detection and quantitative severity stage classification of Tomato Chlorosis Virus (ToCV) infection in young tomato plants using vis–NIR Spectroscopy. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, S.A.; Strümke, I.; Thambawita, V.; Hammou, M.; Riegler, M.A.; Halvorsen, P.; Parasa, S. On evaluation metrics for medical applications of artificial intelligence. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, B.G.; Fearn, T.; Hindle, P.H. Practical NIR Spectroscopy with Applications in Food and Beverage Analysis; Longman Scientific and Technical: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Conzen, J. Multivariate Calibration: A Practical Guide for Developing Methods in the Quantitative Analytical Chemistry; BrukerOptik GmbH: Ettlingen, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, M.; Suyama, H.; Sato, T.; Amano, T.; Ogawa, N. Discrimination of Plastics Using a Portable near Infrared Spectrometer. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 2002, 10, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, F.S.; Armstrong, P.R.; Maghirang, E.B.; Yaptenco, K.F.; Scully, E.D.; Arthur, F.H.; Brabec, D.L.; Adviento-Borbe, A.D.; Suministrado, D.C. NIR Spectroscopy Detects Chlorpyrifos-Methyl Pesticide Residue in Rough, Brown, and Milled Rice. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2020, 36, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Ma, S.; Wu, T. Individual wheat kernels vigor assessment based on NIR spectroscopy coupled with machine learning methodologies. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2020, 105, 103213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.; Rurik, M.; Gurk, S.; Kohlbacher, O.; Fischer, M. Food monitoring: Screening of the geographical origin of white asparagus using FT-NIR and machine learning. Food Control 2019, 104, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Wu, J. A Method for Determining Organophosphorus Pesticide Concentration Based on Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Trans. ASABE 2011, 54, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janik, L.J.; Cozzolino, D.; Dambergs, R.; Cynkar, W.; Gishen, M. The prediction of total anthocyanin concentration in red-grape homogenates using visible-near-infrared spectroscopy and artificial neural networks. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 594, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
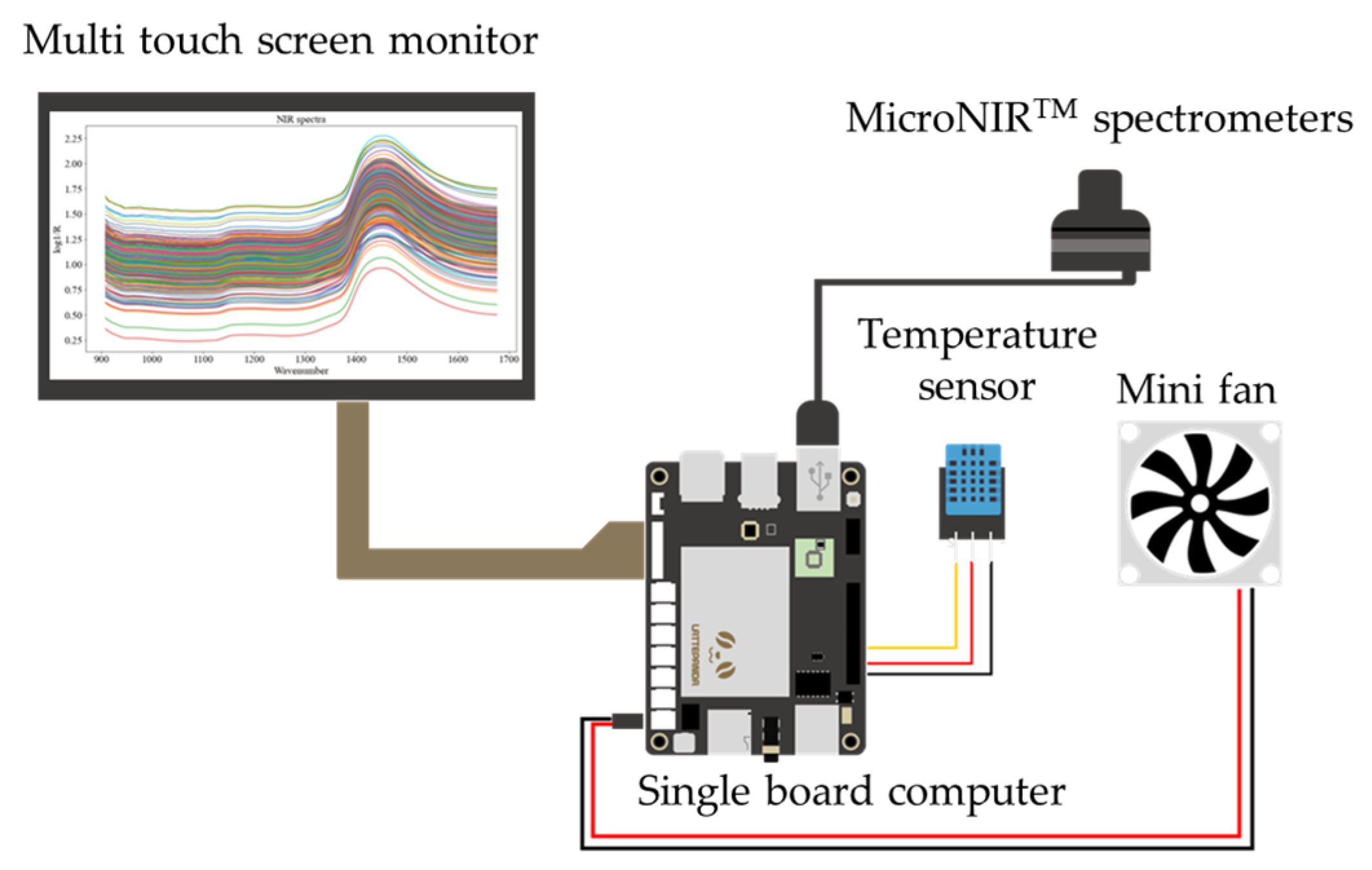

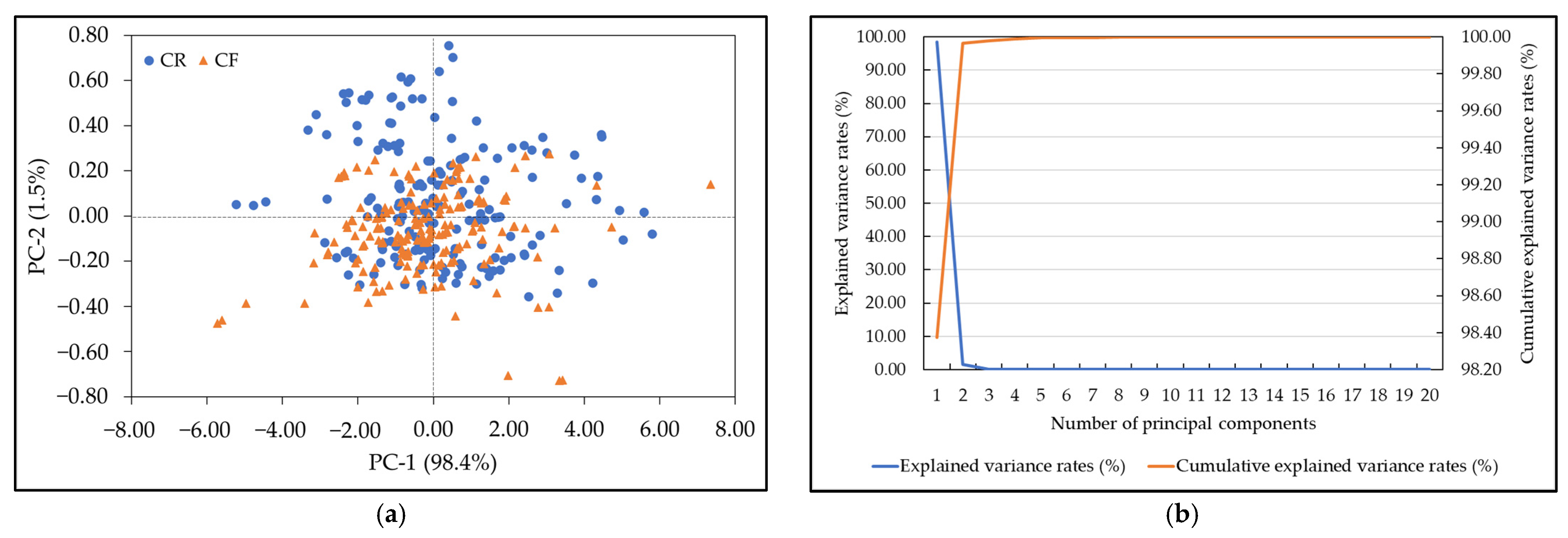
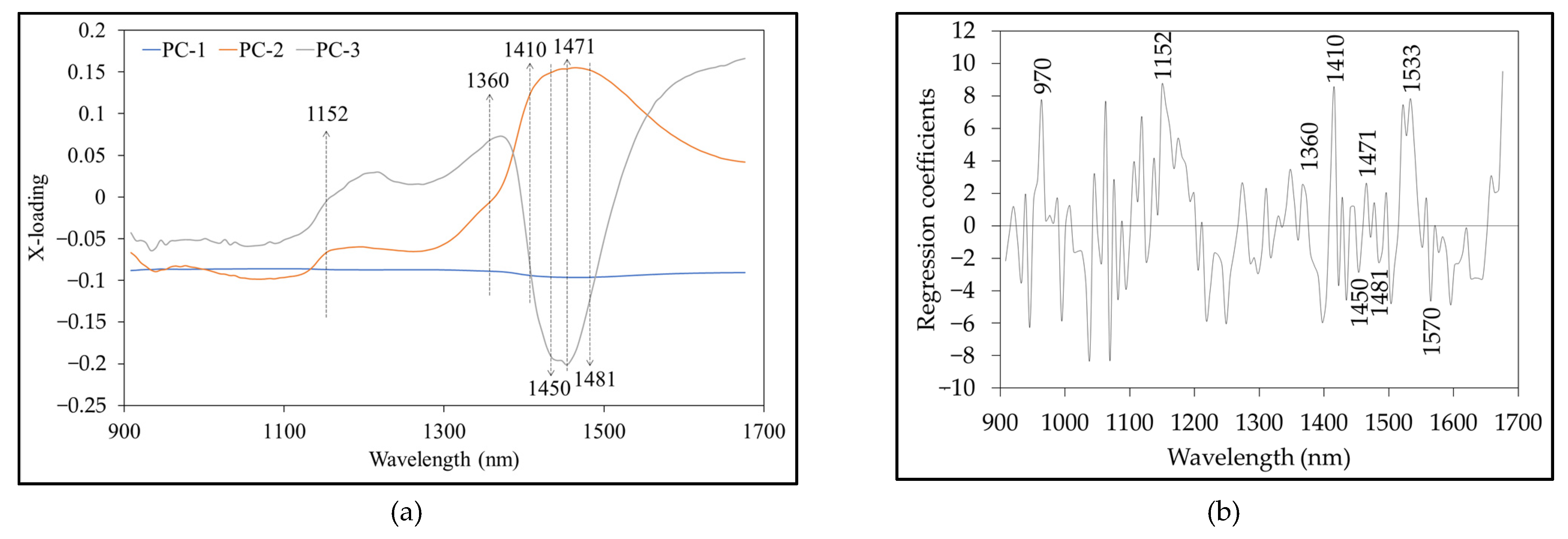
| Agro-Products (Source) | Residue | Wavelength (nm) | Pesticide Residue Range (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lettuce, Oriental mustard, Bok choy [15] | Indoxacarb, chlorantraniliprole, emamectin benzoate | 340–840 | <0.01–0.56 |
| Chinese kale, cabbage, green chili spur pepper [1] | Profenofos | 800–2500 | 0.53–106.28 |
| Cabbage [7] | Chlorpyrifos, carbendazim | 350–2500 | 0.1–100 |
| Tomato [16,17] | Profenofos | 350–1100 | 0.0–42.9 |
| Melon [18] | Chlorothalonil, imidacloprid, pyraclostrobin | 348–1141 | 1.0 |
| Lettuce leaves [19] | Fenvalerate, chlorpyrifos | 950–1650 | 1.0–10 |
| Cucumber [20,21] | Diazinon | 450–1000 | 0.0–32 |
| Oranges [22] | Dichlorvos | 350–1800 | 1.0–1.25 |
| Peppers [23] | Mixed pesticides | 400–1700 | 0.01–1.05 |
| Model | Hyperparameter | Tuning Range |
|---|---|---|
| PLS-DA | n_components | 1–20 |
| SVM | kernel degree gamma | linear, poly, rbf, sigmoid 2–7 0.001–0.09 |
| ANN | activation hidden layer sizes learning rate learning rate initial | identity, logistic, tanh, relu 100, 110, 120, (100, 100), (110, 110), (120, 120), (100, 110, 100), (110, 120, 110) constant, invscaling, adaptive 0.001, 0.01, 0.1 |
| PC-ANN (PCs = 20) | activation hidden layer sizes learning rate learning rate initial | identity, logistic, tanh, relu 10, 11, 12, (10, 10), (11, 11), (12, 12), (10, 11, 10), (11, 12, 11) constant, invscaling, adaptive 0.001, 0.01, 0.1 |
| Sample | Sample Group | Max (mg/kg) | Min (mg/kg) | Mean (mg/kg) | SD (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | Chlorpyrifos-free (CF) (n = 60) | n.d. * | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Chlorpyrifos residues (CR) (n = 60) | 2.184 | 0.011 | 1.120 | 0.532 | |
| Unknown | Chlorpyrifos-free (CF) (n = 15) | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Chlorpyrifos residues (CR) (n = 25) | 1.596 | 0.022 | 1.385 | 0.410 |
| Model | Preprocessing | Training | Testing | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | ||
| PLS-DA | RS | 0.99 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.99 |
| SGS | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 0.97 | |
| MN | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 0.97 | |
| SNV&D | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 0.97 | |
| BC | 0.99 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.99 | |
| MSC | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 0.97 | |
| D1 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.96 | |
| D2 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.93 | 0.90 | 0.97 | 0.94 | |
| SVM | RS | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| SGS | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.99 | |
| MN | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | |
| SNV&D | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | |
| BC | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| MSC | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | |
| D1 | 0.51 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.47 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| D2 | 0.51 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.47 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| ANN | RS | 0.73 | 0.88 | 0.52 | 0.65 | 0.81 | 1.00 | 0.63 | 0.77 |
| SGS | 0.61 | 0.63 | 0.50 | 0.56 | 0.61 | 0.71 | 0.45 | 0.55 | |
| MN | 0.54 | 1.00 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 0.05 | 0.10 | |
| SNV&D | 0.67 | 1.00 | 0.33 | 0.50 | 0.64 | 1.00 | 0.32 | 0.48 | |
| BC | 0.61 | 0.60 | 0.65 | 0.62 | 0.71 | 0.73 | 0.71 | 0.72 | |
| MSC | 0.69 | 1.00 | 0.30 | 0.46 | 0.66 | 1.00 | 0.24 | 0.46 | |
| D1 | 0.84 | 0.90 | 0.77 | 0.83 | 0.92 | 0.97 | 0.87 | 0.92 | |
| D2 | 0.87 | 0.81 | 0.96 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.85 | 0.96 | 0.88 | |
| PC-ANN (PCs = 20) | RS | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| SGS | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.96 | |
| MN | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 1.00 | 0.97 | |
| SNV&D | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.89 | 1.00 | 0.94 | |
| BC | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | |
| MSC | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 1.00 | 0.97 | |
| D1 | 0.51 | 0.51 | 1.00 | 0.67 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 1.00 | 0.64 | |
| D2 | 0.49 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.53 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Model | Preprocessing | Hyperparameter |
|---|---|---|
| PLS-DA | RS | n_components = 11 |
| SVM | RS | kernel = poly, degree = 6, gamma = 1 |
| ANN | D1 | activation = identity, hidden layer sizes = 100, learning rate = invscaling, learning rate initial = 0.001 |
| PC-ANN (PCs = 20) | RS | activation = relu, hidden layer sizes = (11, 11), learning rate = adaptive, learning rate initial = 0.1 |
| Wavelength (nm) | Bond Vibration/Functional Group (Structure) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 970 | O-H str. second overtone (H2O) | [51,52] |
| 1152 | C-H str. second overtone (CH3) | [51,52] |
| 1360 | 2 × C-H str. + C-H def. (CH3) | [51] |
| 1410 | 2 × C-H str. + C-H def. (CH3) | [51,53,54] |
| 1450 | O-H str. first overtone (H2O) | [51,52] |
| 1471 | N-H str. first overtone (CONHR) | [51] |
| 1481 | N-H str. first overtone (CONH2) | [51] |
| 1533 | C-H str. first overtone (C=H) | [51] |
| 1570 | N-H str. first overtone (-CONH-) | [51] |
| Model | Processing Spectra | Independent Validation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | ||
| PLS-DA | RS | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| SVM | RS | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| ANN | D1 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 1.0 | 0.5 |
| PC-ANN (PCs = 20) | RS | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lapcharoensuk, R.; Fhaykamta, C.; Anurak, W.; Chadwut, W.; Sitorus, A. Nondestructive Detection of Pesticide Residue (Chlorpyrifos) on Bok Choi (Brassica rapa subsp. Chinensis) Using a Portable NIR Spectrometer Coupled with a Machine Learning Approach. Foods 2023, 12, 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12050955
Lapcharoensuk R, Fhaykamta C, Anurak W, Chadwut W, Sitorus A. Nondestructive Detection of Pesticide Residue (Chlorpyrifos) on Bok Choi (Brassica rapa subsp. Chinensis) Using a Portable NIR Spectrometer Coupled with a Machine Learning Approach. Foods. 2023; 12(5):955. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12050955
Chicago/Turabian StyleLapcharoensuk, Ravipat, Chawisa Fhaykamta, Watcharaporn Anurak, Wasita Chadwut, and Agustami Sitorus. 2023. "Nondestructive Detection of Pesticide Residue (Chlorpyrifos) on Bok Choi (Brassica rapa subsp. Chinensis) Using a Portable NIR Spectrometer Coupled with a Machine Learning Approach" Foods 12, no. 5: 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12050955
APA StyleLapcharoensuk, R., Fhaykamta, C., Anurak, W., Chadwut, W., & Sitorus, A. (2023). Nondestructive Detection of Pesticide Residue (Chlorpyrifos) on Bok Choi (Brassica rapa subsp. Chinensis) Using a Portable NIR Spectrometer Coupled with a Machine Learning Approach. Foods, 12(5), 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12050955








