Comparative Characterization of Volatile Compounds of Ningxiang Pig, Duroc and Their Crosses (Duroc × Ningxiang) by Using SPME-GC-MS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. E-Nose Analysis
2.2.1. Sample Pretreatment
2.2.2. E-Nose Parameter Setting
2.2.3. E-Nose Sensor Characteristics
2.3. GC-MS Analysis
2.3.1. Sample Pretreatment
2.3.2. GC-MS Conditions
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Volatile Flavors of Pork Characterized by E-Nose
3.2. Volatile Flavors of Pork Characterized by GC-MS
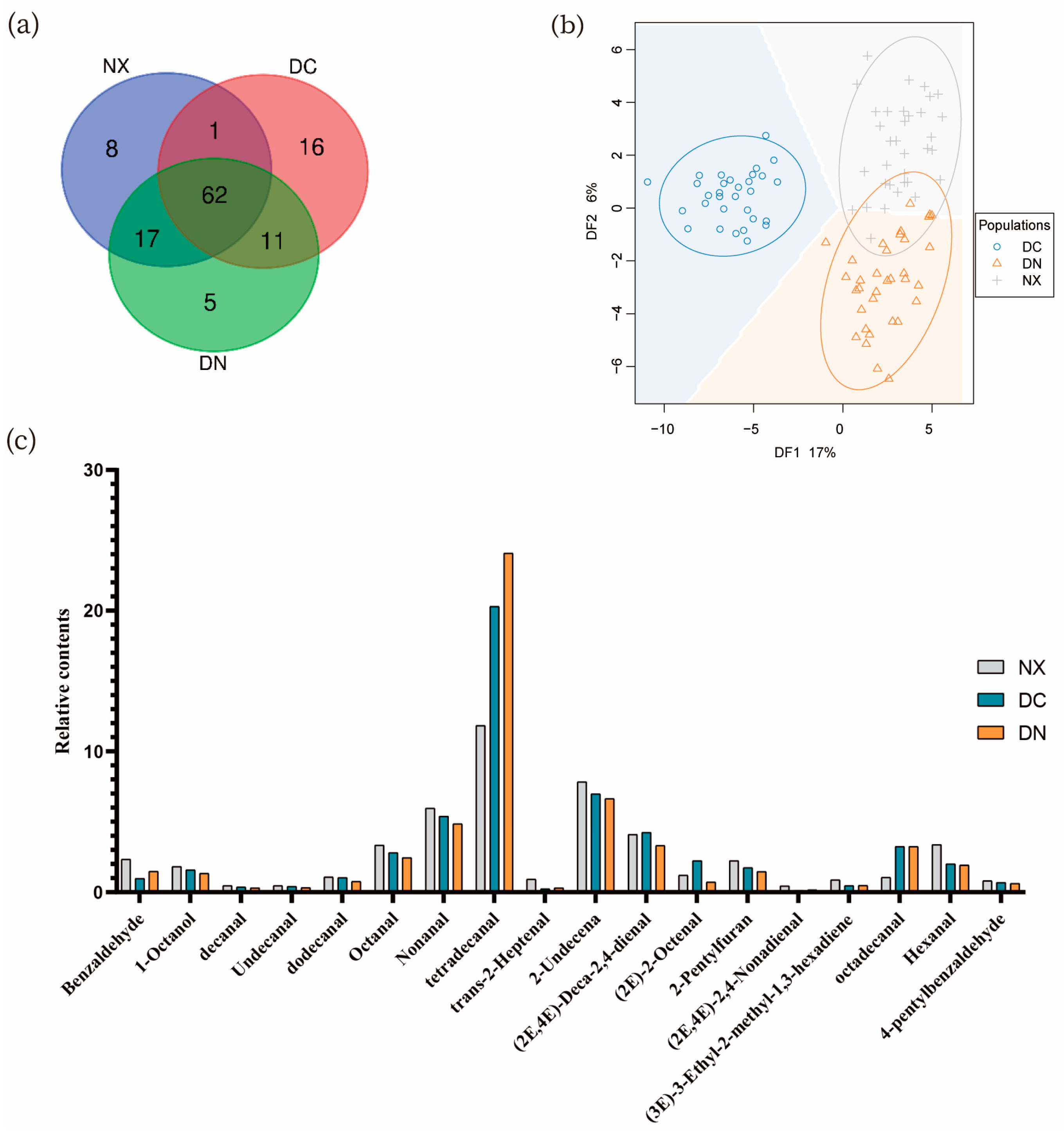
3.2.1. The Quantity of Volatile Substances
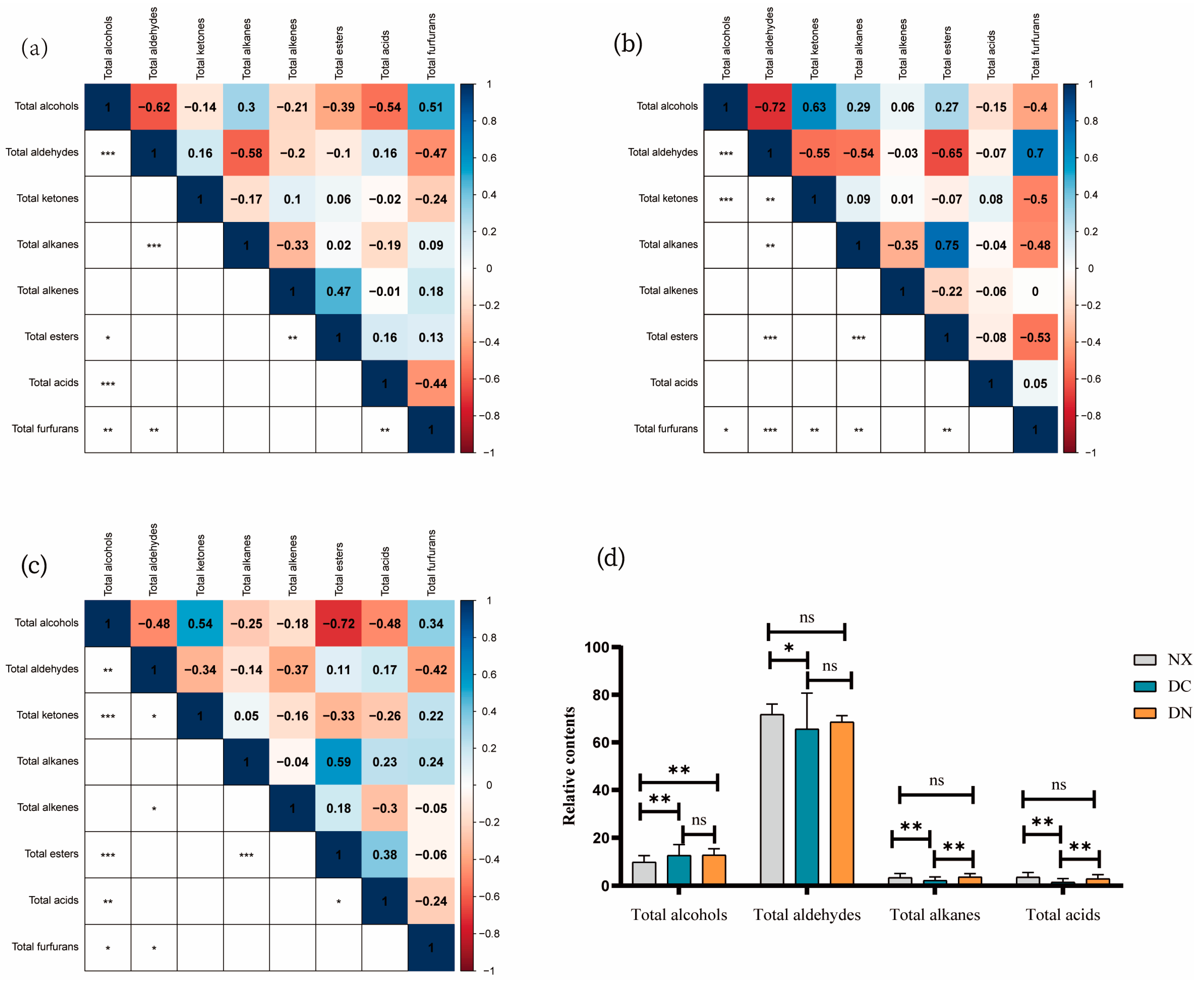
3.2.2. Correlation of Eight Major Volatile Flavors
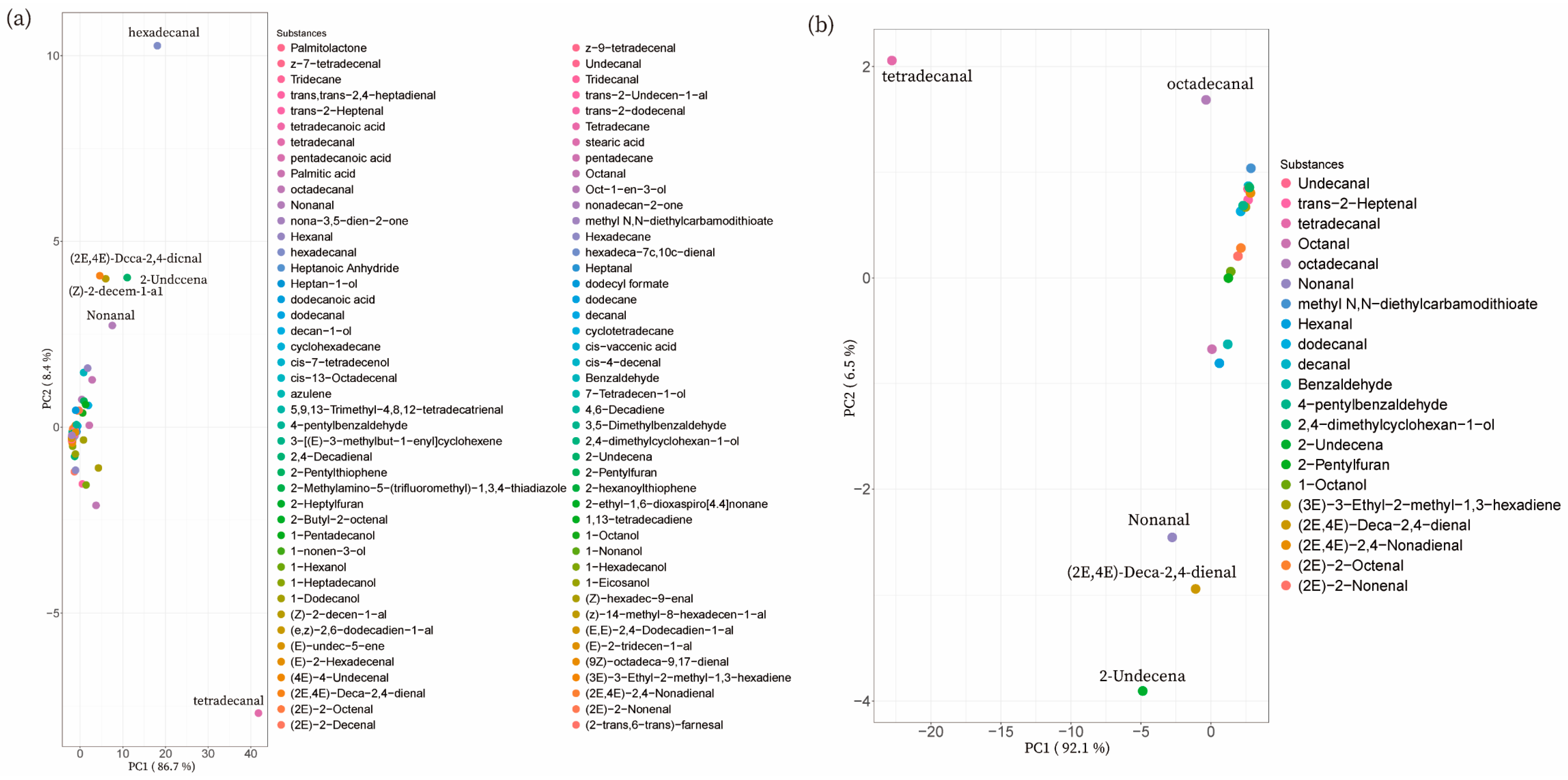
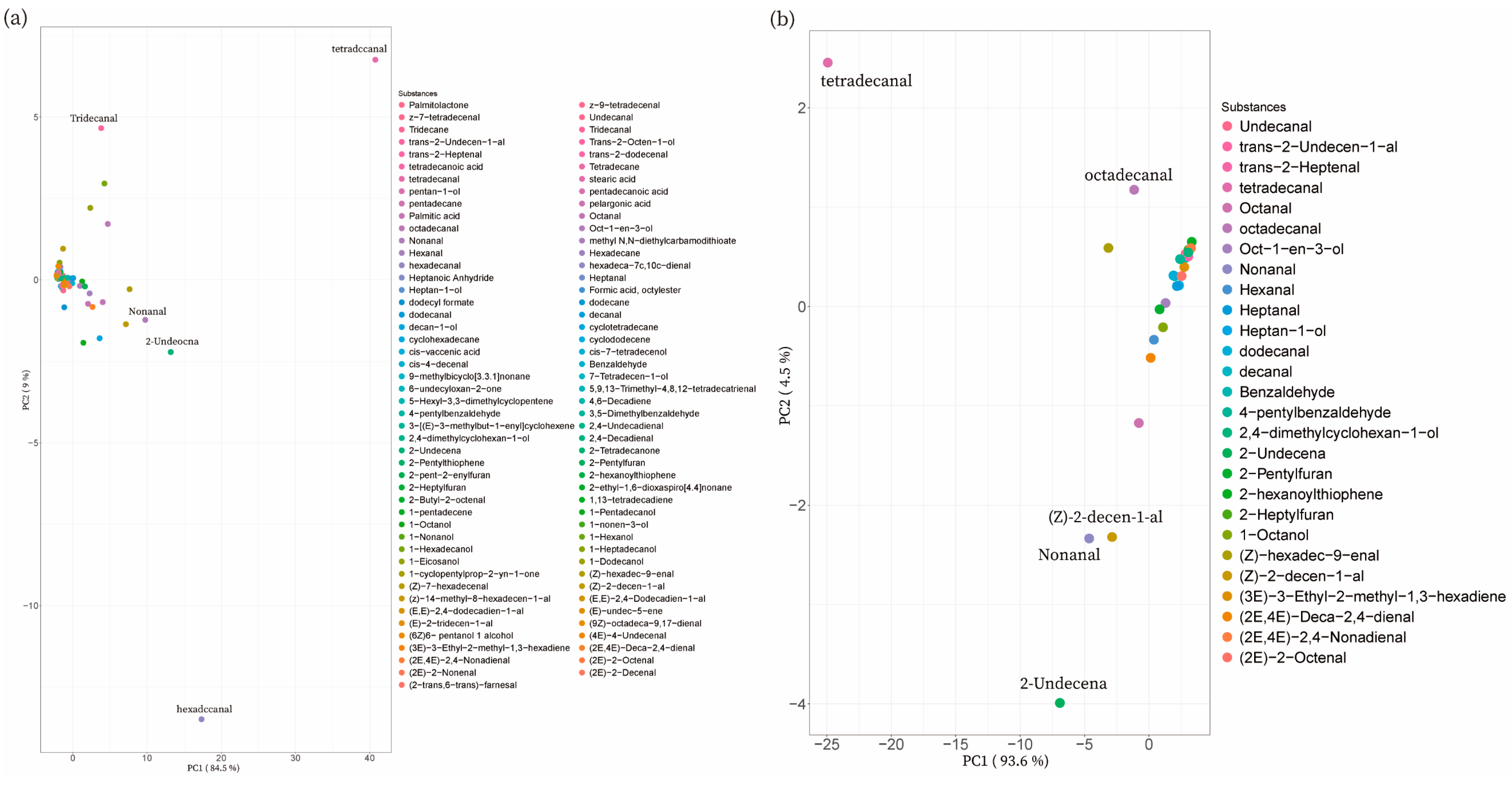
3.2.3. PCA of Volatile Flavors of Different Pork
3.3. Comparison of Volatile Flavor Compounds among Three Populations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Guo, T.; Jia, J.; Zhang, P.; Wang, L.; Xia, N.; Qian, Q.; Peng, H.; et al. Comparison of Nutrition and Flavor Characteristics of Five Breeds of Pork in China. Foods 2022, 11, 2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan-Clark, D.J.; Neale, E.P.; Charlton, K.E. Processed pork is the most frequently consumed type of pork in a survey of Australian children. Nutr. Res. 2013, 33, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtasik-Kalinowska, I.; Guzek, D.; Górska-Horczyczak, E.; Głąbska, D.; Brodowska, M.; Sun, D.-W.; Wierzbicka, A. Volatile compounds and fatty acids profile in Longissimus dorsi muscle from pigs fed with feed containing bioactive components. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 67, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.F.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Xiang, Q.R.; Feng, T. Analysis of the Effect of Vacuum Cooling on the Flavor of Sauce Beef Based on HS-SPME-GC-MS and GC-IMS Combined with Electron-ic Nose. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2021, 43, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beldarrain, L.R.; Morán, L.; Sentandreu, M.; Barron, L.J.R.; Aldai, N. Effect of ageing time on the volatile compounds from cooked horse meat. Meat Sci. 2022, 184, 108692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Lu, Y.; Lü, Y. Recent advances in the application of headspace gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2018, 36, 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirman, D.A.; Reich, R.F.; Kiss, A.; Heeren, R.M.A.; Yost, R.A. Quantitative MALDI Tandem Mass Spectrometric Imaging of Cocaine from Brain Tissue with a Deuterated Internal Standard. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Wang, J.; Wei, Z.; Deng, F.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, S. An optimization of the MOS electronic nose sensor array for the detection of Chinese pecan quality. J. Food Eng. 2017, 203, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yu, X.; Xu, L.; Gao, J.-M. Novel method for the producing area identification of Zhongning Goji berries by electronic nose. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zhang, M.; Adhikari, B. Advances of electronic nose and its application in fresh foods: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 2700–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevoli, C.; Cerretani, L.; Gori, A.; Caboni, M.F.; Toschi, T.G.; Fabbri, A. Classification of Pecorino cheeses using electronic nose combined with artificial neural network and comparison with GC–MS analysis of volatile compounds. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 1315–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, G.; Mores, N.; Penas, A.; Capuano, R.; Mondino, C.; Trové, A.; Macagno, F.; Zini, G.; Cattani, P.; Martinelli, E.; et al. Electronic Nose and Exhaled Breath NMR-based Metabolomics Applications in Airways Disease. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1610–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wu, X.-L.; Zeng, Q.; Li, H.; Ma, H.; Jiang, J.; Rosa, G.J.M.; Gianola, D.; Tait, R.G.T., Jr.; Bauck, S. Genomic mating as sustainable breeding for Chinese indigenous Ningxiang pigs. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Shibata, T.; Kadowaki, H.; Abe, H.; Toyoshima, T. Meat quality comparison of Berkshire, Duroc and crossbred pigs sired by Berkshire and Duroc. Meat Sci. 2003, 64, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Li, D.; Yin, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z. Flavour differences of cooked longissimus muscle from Chinese indigenous pig breeds and hybrid pig breed (Duroc × Landrace × Large White). Food Chem. 2008, 107, 1529–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Gao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, Y.; Zeng, Q.; He, X.; Xu, K.; He, J. Optimizing conditions of electronic nose for rapid detection of flavor substances in Ningxiang Pork. J. Food Process. Eng. 2021, 44, e13758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Yang, F.; Zhu, B.; Yin, S.; Fu, Y.; Li, Y.; Liao, Y.; Kang, M.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.; et al. Optimization of HS-SPME-GC-MS for the Determination of Volatile Flavor Compounds in Ningxiang Pork. Foods 2023, 12, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Han, W.; Ge, W.-C.; Lin, Y. Chemical composition of the volatile oil from Zanthoxylum avicennae and antimicrobial activities and cytotoxicity. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2014, 10, S164–S170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohart, F.; Gautier, B.; Singh, A.; Lê Cao, K.-A. mixOmics: An R package for ‘omics feature selection and multiple data integration. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schober, P.; Boer, C.; Schwarte, L.A. Correlation Coefficients: Appropriate Use and Interpretation. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 126, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ba, H.; Amna, T.; Hwang, I. Significant influence of particular unsaturated fatty acids and pH on the volatile compounds in meat-like model systems. Meat Sci. 2013, 94, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashmaa, D.E.A. Meat Quality and Volatile Flavor Traits of Duroc, Berkshire and Yorksire Breeds. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2011, 31, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Cui, H.; Yuan, X.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Ding, J.; Xiang, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; et al. Identification of the main aroma compounds in Chinese local chicken high-quality meat. Food Chem. 2021, 359, 129930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, A.K.; Albrecht, F.; Hahne, F.; Jordan, P.; Fraatz, M.A.; Ley, J.P.; Geissler, T.; Schrader, J.; Zorn, H.; Buchhaupt, M. Biotechnological Production of Odor-Active Methyl-Branched Aldehydes by a Novel α-Dioxygenase from Crocosphaera subtropica. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 10432–10440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, A. A metabolomics-based approach investigates volatile flavor formation and characteristic compounds of the Dahe black pig dry-cured ham. Meat Sci. 2019, 158, 107904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, M.R.; Estévez, M.; Morcuende, D.; Cava, R. Effect of the Type of Frying Culinary Fat on Volatile Compounds Isolated in Fried Pork Loin Chops by Using SPME-GC-MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 7637–7643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Zargar-Shoshtari, K.; Pow-Sang, J.M. Biomarkers for prostate cancer: Present challenges and future opportunities. Futur. Sci. OA 2016, 2, FSO72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, H.C.; Yoo, S.S.; Oh, S.J.; Kim, H.S.; Chin, K.B. Evaluation of Fermented Sausages Manufactured with Reduced-fat and Functional Starter Cultures on Physicochemical, Functional and Flavor Characteristics. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2014, 34, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.D.; Zhou, F.Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Z.L.; Zhang, C.J.; Zhang, H. Comparative Study on Volatile Flavor Components of Three Kinds of Braised Pork Meats. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2019, 40, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippolis, V.; Ferrara, M.; Cervellieri, S.; Damascelli, A.; Epifani, F.; Pascale, M.; Perrone, G. Rapid prediction of ochratoxin A-producing strains of Penicillium on dry-cured meat by MOS-based electronic nose. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 218, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Sowndhararajan, K.; Choi, H.J.; Park, S.J.; Kim, S. Olfactory Stimulation Effect of Aldehydes, Nonanal, and Decanal on the Human Electroencephalographic Activity, According to Nostril Variation. Biomedicines 2019, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Liu, D.-Y.; Zhou, G.-H.; Xu, X.-L. Characteristic Flavor of Traditional Soup Made by Stewing Chinese Yellow-Feather Chickens. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 2031–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Shen, Q.; Pan, T.; Hui, T.; Ma, J. Characterization of Key Aroma Compounds in Beijing Roasted Duck by Gas Chromatography–Olfactometry–Mass Spectrometry, Odor-Activity Values, and Aroma-Recombination Experiments. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 5847–5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Wang, P.; Zhan, P.; Tian, H. Characterization of key aroma compounds in stewed mutton (goat meat) added with thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.) based on the combination of instrumental analysis and sensory verification. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biller, E.; Boselli, E.; Obiedziński, M.; Karpiński, P.; Waszkiewicz-Robak, B. The profile of volatile compounds in the outer and inner parts of broiled pork neck is strongly influenced by the acetic-acid marination conditions. Meat Sci. 2016, 121, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takakura, Y.; Osanai, H.; Masuzawa, T.; Wakabayashi, H.; Nishimura, T. Characterization of the key aroma compounds in pork soup stock by using an aroma extract dilution analysis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zheng, Y.; You, M.; Song, H.; Zou, T. Characterization of key aroma-active compounds in four commercial egg flavor Sachimas with differing egg content. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e13040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, J.; Sun, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, C.; Fu, L. High-throughput sequencing-based characterization of the predominant microbial community associated with characteristic flavor formation in Jinhua Ham. Food Microbiol. 2021, 94, 103643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Dong, K.; Wang, Q.; Huang, X.; Wang, G.; An, F.; Luo, Z.; Luo, P. Changes in volatile flavor of yak meat during oxidation based on multi-omics. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
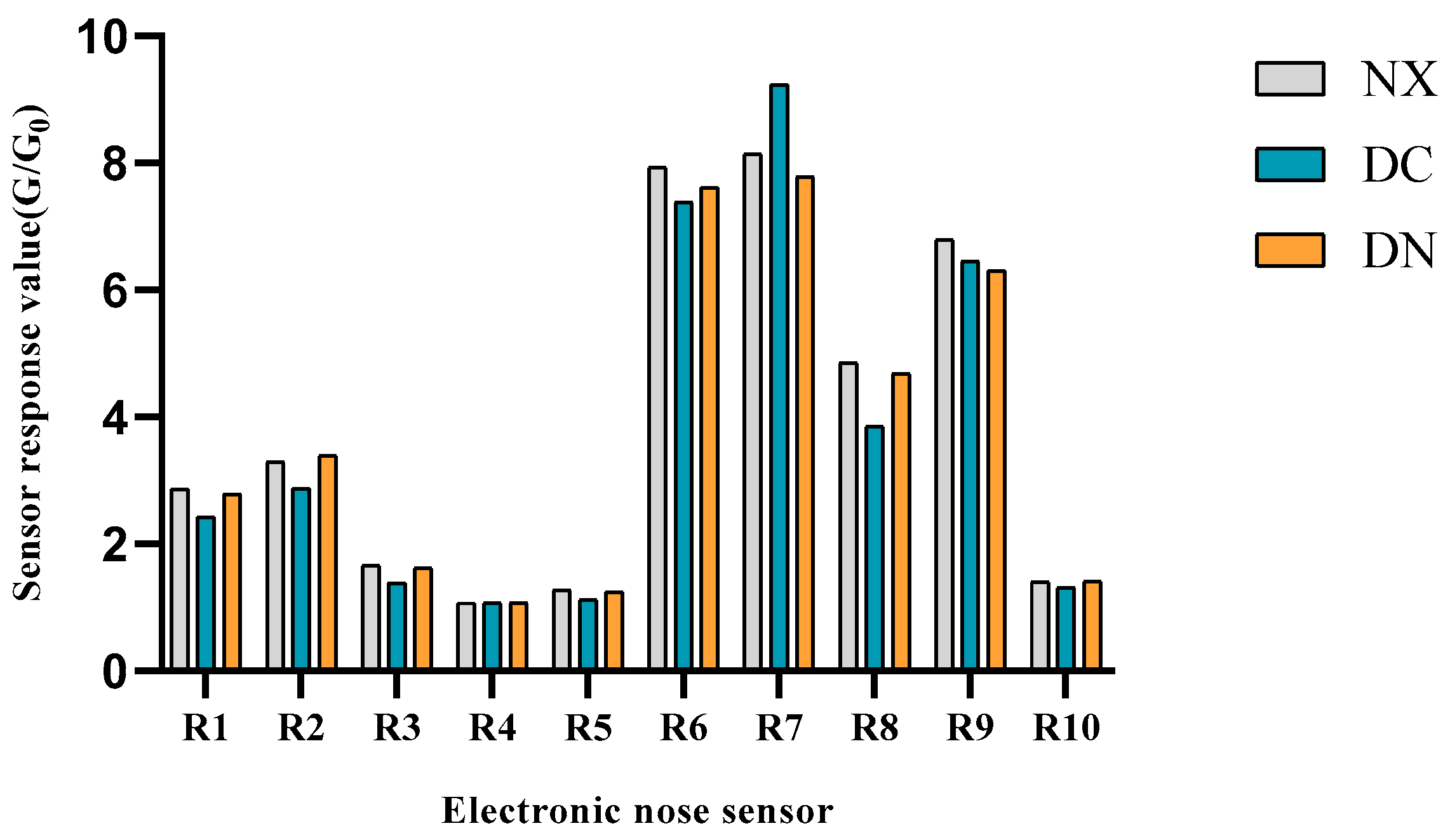

| NO | Sensor | Sensitive Substance |
|---|---|---|
| R1 | W1C | Aromatic component |
| R2 | W5S | Oxynitride |
| R3 | W3C | Ammonia, aromatic compound |
| R4 | W6S | Selective to hydrogen |
| R5 | W5C | Alkane and aromatic compound |
| R6 | W1S | Sensitive to methyl |
| R7 | W1W | Inorganic sulfur compound |
| R8 | W2S | Ethanol, aromatic compound |
| R9 | W2W | Organosulfur compound |
| R10 | W3S | Long chain alkane |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, B.; Gao, H.; Yang, F.; Li, Y.; Yang, Q.; Liao, Y.; Guo, H.; Xu, K.; Tang, Z.; Gao, N.; et al. Comparative Characterization of Volatile Compounds of Ningxiang Pig, Duroc and Their Crosses (Duroc × Ningxiang) by Using SPME-GC-MS. Foods 2023, 12, 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12051059
Zhu B, Gao H, Yang F, Li Y, Yang Q, Liao Y, Guo H, Xu K, Tang Z, Gao N, et al. Comparative Characterization of Volatile Compounds of Ningxiang Pig, Duroc and Their Crosses (Duroc × Ningxiang) by Using SPME-GC-MS. Foods. 2023; 12(5):1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12051059
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Bangqiang, Hu Gao, Fang Yang, Yiyang Li, Qiaoyue Yang, Yinchang Liao, Haimin Guo, Kang Xu, Zhiqiang Tang, Ning Gao, and et al. 2023. "Comparative Characterization of Volatile Compounds of Ningxiang Pig, Duroc and Their Crosses (Duroc × Ningxiang) by Using SPME-GC-MS" Foods 12, no. 5: 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12051059
APA StyleZhu, B., Gao, H., Yang, F., Li, Y., Yang, Q., Liao, Y., Guo, H., Xu, K., Tang, Z., Gao, N., Zhang, Y., & He, J. (2023). Comparative Characterization of Volatile Compounds of Ningxiang Pig, Duroc and Their Crosses (Duroc × Ningxiang) by Using SPME-GC-MS. Foods, 12(5), 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12051059






