Specificity Testing for NGT PCR-Based Detection Methods in the Context of the EU GMO Regulations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
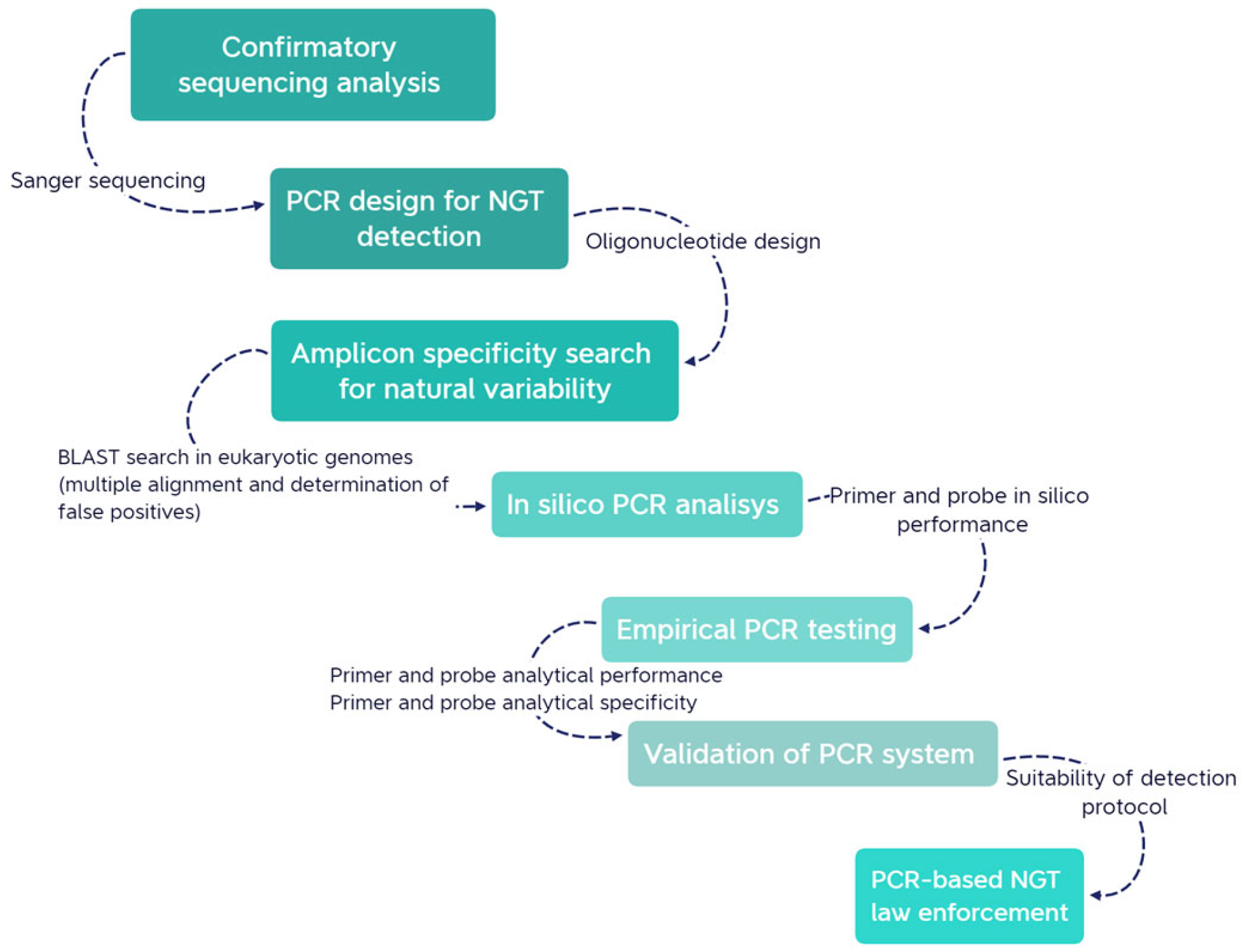
2.1. Overall Description of the Stepwise Approach
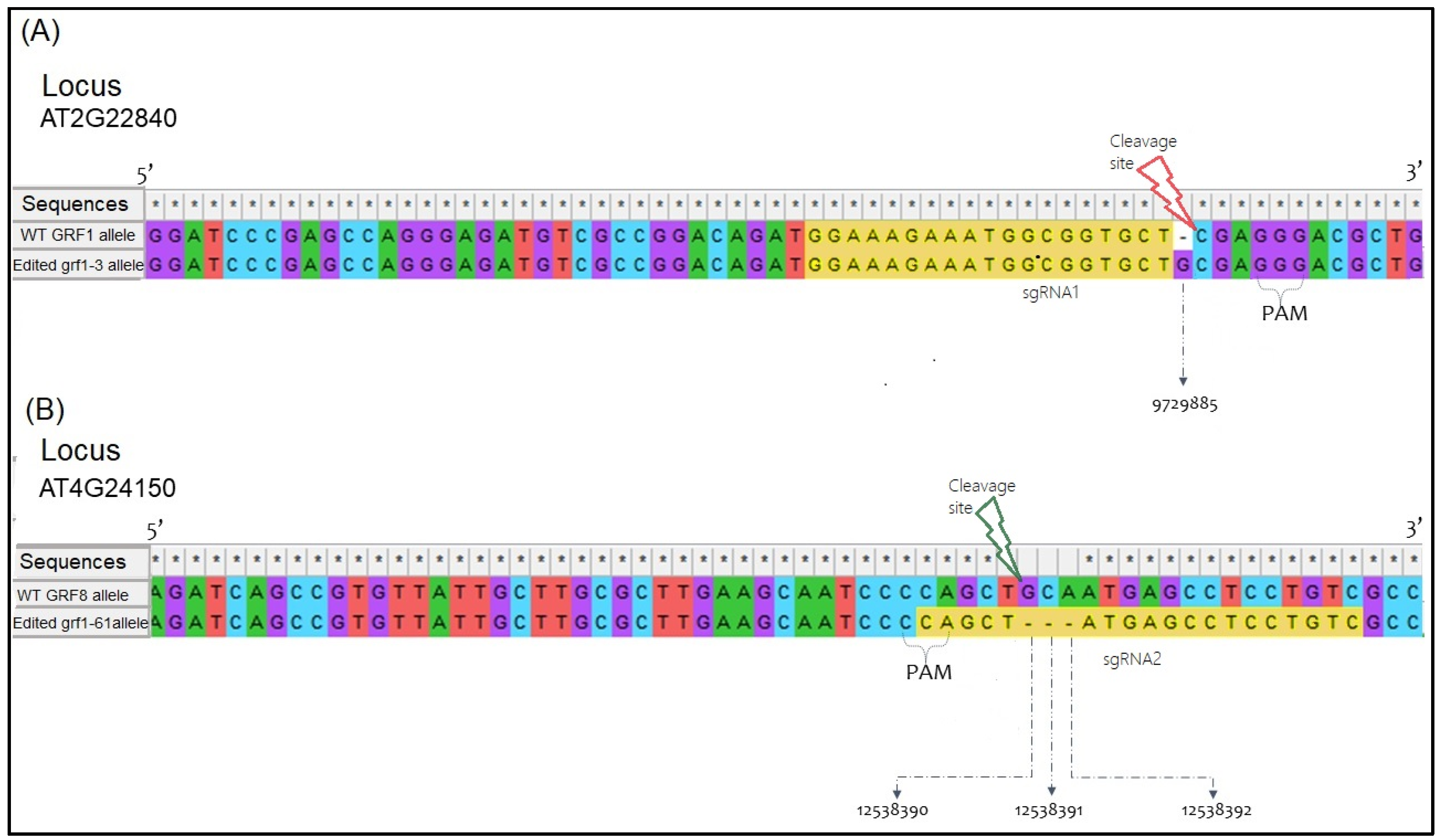
2.2. Confirmatory Sequencing Analysis of CRISPR-Cas9 Mutations
2.3. Amplicon Sequence Search for Natural Variants
2.4. RT-PCR Primer and Probe Design
2.5. In Silico PCR Testing
2.6. RT-qPCR Empirical Assay
3. Results
3.1. Sequence Confirmation of Mutated Alleles
3.2. In Silico Specificity Assessment
3.3. In Silico PCR Performance
3.4. Real-Time qPCR Performance and Empirical Primer Specificity Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Commission (EC). Science for Environment Policy Future Brief: Synthetic Biology and Biodiversity. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/science-environment-policy (accessed on 6 November 2022).
- Grohmann, L.; Keilwagen, J.; Duensing, N.; Dagand, E.; Hartung, F.; Wilhelm, R.; Bendiek, J.; Sprink, T. Detection and identification of genome editing in plants: Challenges and opportunities. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprink, T.; Eriksson, D.; Schiemann, J.; Hartung, F. Regulatory hurdles for genome editing: Process- vs. product-based approaches in different regulatory contexts. Plant Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 1493–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broll, H.; Braeuning, A.; Lampen, A. European Court of Justice decision for genome editing: Consequences on food/feed risk assessment and detection. Food Control 2019, 104, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metje-Sprink, J.; Sprink, T.; Hartung, F. Genome-edited plants in the field. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2020, 61, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaj, T.; Gersbach, C.A.; Barbas, C.F. ZFN, TALEN, and CRISPR/Cas-based methods for genome engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osakabe, Y.; Osakabe, K. Genome editing with engineered nucleases in plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Network of GMO Laboratories Detection of Food and Feed Plant Products Obtained by New Mutagenesis Techniques. Available online: https://gmo-crl.jrc.ec.europa.eu/doc/JRC116289-GE-report-ENGL.pdf (accessed on 6 November 2022).
- European Network of GMO Laboratories. ENGL-Definition of Minimum Performance Requirements for Analytical Methods of GMO Testing. Available online: https://gmo-crl.jrc.ec.europa.eu/doc/MPR%20Report%20Application%2020_10_2015.pdf (accessed on 6 November 2022).
- Araki, M.; Nojima, K.; Ishii, T. Caution required for handling genome editing technology. Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraiture, M.A.; Guiderdoni, E.; Meunier, A.C.; Papazova, N.; Roosens, N. ddPCR strategy to detect a gene-edited plant carrying a single variation point: Technical feasibility and interpretation issues. Food Control 2021, 137, 108904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grohmann, L.; Barbante, A.; Eriksson, R.; Gatto, F.; Georgieva, T.; Huber, I.; Hulin, J.; Köppel, R.; Marchesi, U.; Marmin, L.; et al. Guidance Document on Multiplex Real-Time PCR Methods; EUR 30708 EN; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2021; ISBN 978-92-76-37820-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidner, C.; Edelmann, S.; Moor, D.; Lieske, K.; Savini, C.; Jacchia, S.; Sacco, M.G.; Mazzara, M.; Lamke, J.; Eckermann-Mann, K.N.; et al. Assessment of the Real-Time PCR Method Claiming to be Specific for Detection and Quantification of the First Commercialised Genome-Edited Plant. Food Anal. Methods 2022, 15, 2107–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, S.; Yan, X.; Si, N.; Gao, H.; Li, Y.; Zhai, S.; Xiao, F.; Wu, G.; et al. An editing-site-specific pcr method for detection and quantification of cao1-edited rice. Foods 2021, 10, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, J.; Astin, C.P.; Bauer, O.; Blash, K.J.; Bowen, N.M.; Chukwudinma, N.J.; DiNofrio, A.S.; Faletti, D.O.; Ghulam, A.M.; Gusinde-Duffy, C.M.; et al. CRISPR/Cas9 mutagenesis of the Arabidopsis GROWTH-REGULATING FACTOR (GRF) gene family. Front. Genome Ed. 2023, 5, 1251557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozen, S.; Skaletsky, H. Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods Mol. Biol. 2000, 132, 365–386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Untergasser, A.; Nijveen, H.; Rao, X.; Bisseling, T.; Geurts, R.; Leunissen, J. Primer3Plus, an enhanced web interface to Primer3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robledo, R.; Beggs, W.R.; Bender, P. TaqMan genotyping of insertion/deletion polymorphisms. Methods Mol. Biol. 2005, 311, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE Guidelines: Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Hasi, A.; Wang, Z. Structural and functional analysis of a bidirectional promoter from gossypium hirsutum in arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Coulouris, G.; Zaretskaya, I.; Cutctache, I.; Rozen, S.; Madden, T.L. Primer-BLAST: A tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Xue, D.; Chuai, G.; Gao, Y.; Zhanh, G.; Liu, Q. Benchmarking and integrating genome-wide CRISPR off-target detection and prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 11370–11379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.D.; Karimi, M.; Impens, L.; Van Lerberge, E.; Coussens, G.; Aesaert, S.; Rombaut, D.; Holtappels, D.; Ibrahim, H.M.M.; Van Montagu, M.; et al. Efficient CRISPR-mediated base editing in Agrobacterium spp. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2013338118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Yiqin, H.L.Y.; Chen, L.; Yongxing, Z.; Cai, S.; Dongfang, M.; Junliang, Y. Genome-wide analysis of growth-regulating factors (GRFs) in Triticum aestivum. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidbakhshfard, M.A.; Sebastian, P.; Ushio, F.; Bernd, M.R. Growth-regulating factors (GRFs): A small transcription factor family with important functions in plant biology. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 998–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.Z.; Henry, I.M.; Lynagh, P.G.; Comai, L.; Cahoon, E.B.; Weeks, D.P. Significant enhancement of fatty acid composition in seeds of the allohexaploid, Camelina sativa, using CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morineau, C.; Bellec, Y.; Tellier, F.; Gissot, L.; Kelemen, Z.; Nogué, F.; Faure, J.D. Selective gene dosage by CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing in hexaploid Camelina sativa. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuzaki, A.; Ogawa, T.; Koizuka, C.; Kaneko, K.; Inaba, M.; Imamura, J.; Koizuka, N. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing of the fatty acid desaturase 2 gene in Brassica napus. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 131, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pröbsting, M.; Schenke, D.; Hossain, R.; Häder, C.; Thurau, T.; Wighardt, L.; Schuster, A.; Zhou, Z.; Ye, W.; Rietz, S.; et al. Loss of function of CRT1a (calreticulin) reduces plant susceptibility to Verticillium longisporum in both Arabidopsis thaliana and oilseed rape (Brassica napus). Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 2328–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Court of Justice C-528/16-Judgement of 25 July 2018 on New Mutagenesis Techniques. Available online: http://curia.europa.eu/juris/document/document.jsf?text=&docid=204387&pageIndex=0&doclang=EN&mode=lst&dir=&occ=first&part=1&cid=138460 (accessed on 16 May 2020).
- Huang, M.M.; Arheim, N.; Goodman, M.F. Extension of base mispairs by Taq DNA polymerase: Implications for single. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 1992, 20, 4567–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayyadevare, S.; Thaden, J.; Shmookler, R.; Robert, J. Discrimination of primer 3′-nucleotide mismatch by Taq DNA polymerase during polymerase chain reaction. Anal. Biochem. 2000, 284, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guertler, P.; Pallarz, S.; Belter, A.; Eckermann, K.N.; Grohmann, L. Detection of commercialized plant products derived from new genomic techniques (NGT)—Practical examples and current perspectives. Food Control 2023, 152, 109869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhalliyil, P.; Ilves, H.; Kazakov, S.A.; Howard, S.J.; Johnston, B.H.; Fagan, J. A Real-Time Quantitative PCR Method Specific for Detection and Quantification of the First Commercialized Genome-Edited Plant. Foods 2020, 9, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broccanello, C.; Chiodi, C.; Funk, A.; McGrath, J.M.; Panella, L.; Stevanato, P. Comparison of three PCR-based assays for SNP genotyping in plants. Plant Methods 2018, 14, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/i6030e/i6030e.pdf (accessed on 6 November 2022).
- Fraiture, M.-A.; D’aes, J.; Guiderdoni, E.; Meunier, A.-C.; Delcourt, T.; Hoffman, S.; Vandermassen, E.; De Keersmaecker, S.C.J.; Vanneste, K.; Roosens, N.H.C. Targeted High-Throughput Sequencing Enables the Detection of Single Nucleotide Vari-ations in CRISPR/Cas9 Gene-Edited Organisms. Foods 2023, 12, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sequence Number | Hits | Accession | BLAST against the Query grf1-3 | (MSA) Mismatches (bp) or Gaps against Each Accession | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Query Cover | Per. Ident | Forward | Probe | Reverse | |||
| 1 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 2 | LR782543.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 2 | LR699746.2 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 2 | LR699771.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 2 | LR699766.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 2 | LR699761.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 2 | LR699756.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 2 | LR699751.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 8 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 2 | LR215053.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 9 | Arabidopsis thaliana growth-regulating factor 1 (GRF1), mRNA | NM_127849.4 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 10 | Arabidopsis thaliana chromosome 2 | CP116281.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 11 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 2 | OX298798.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 12 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 2 | OX298803.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 13 | Arabidopsis thaliana ecotype 1254 chromosome 2 sequence | CP086755.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 14 | Arabidopsis thaliana ecotype 5856 chromosome 2 sequence | CP086750.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 15 | Arabidopsis thaliana ecotype 6021 chromosome 2 sequence | CP086745.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 16 | Arabidopsis thaliana ecotype 6024 chromosome 2 sequence | CP086740.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 17 | Arabidopsis thaliana ecotype 9412 chromosome 2 sequence | CP086735.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 18 | Arabidopsis thaliana ecotype 9470 chromosome 2 sequence | CP086730.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 19 | Arabidopsis thaliana chromosome 2 | CP087127.2 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 20 | Arabidopsis thaliana isolate t2t_salk_col chromosome 2 | CP096025.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 21 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 2 | OW119597.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 22 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 2 | LR881467.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 23 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 2 | LR797808.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 24 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 2 | LR797803.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 25 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 2 | LR797798.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 26 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 2 | LR797793.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 27 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 2 | LR797788.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 28 | Arabidopsis thaliana chromosome 2 | CP002685.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 29 | Arabidopsis thaliana At2g22840 mRNA for hypothetical protein, partial cds, clone: RAAt2g22840 | AB493560.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 30 | Arabidopsis thaliana isolate CS906 GRL1 (GRL1) gene, partial cds | EU550462.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 31 | Arabidopsis thaliana isolate CS902 GRL1 (GRL1) gene, partial cds | EU550456.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 32 | Arabidopsis thaliana isolate CS6799 GRL1 (GRL1) gene, partial cds | EU550455.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 33 | Arabidopsis thaliana isolate CS901 GRL1 (GRL1) gene, partial cds | EU550445.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 34 | Arabidopsis thaliana transcription activator (GRF1) mRNA, complete cds | AY102634.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 35 | Arabidopsis thaliana chromosome 2 clone T20K9 map CIC06C07, complete sequence | AC004786.3 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 36 | Arabidopsis thaliana Full-length cDNA Complete sequence from clone GSLTPGH12ZD08 of Hormone-Treated Callus of strain col-0 of Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) | BX820248.1 | 100% | 99.24% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 37 | PREDICTED: Arabidopsis xampl subsp. xampl growth-regulating factor 1 (LOC9316532), mRNA | XM_002878592.2 | 100% | 98.47% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 38 | PREDICTED: Camelina sativa growth-regulating factor 1-like (LOC104713726), mRNA | XM_010430916.2 | 100% | 98.47% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 39 | PREDICTED: Camelina sativa growth-regulating factor 1 (LOC104751923), mRNA | XM_010473979.2 | 100% | 98.47% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 40 | PREDICTED: Camelina sativa growth-regulating factor 1-like (LOC104704976), mRNA | XM_010420970.1 | 100% | 98.47% | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 41 | Camelina hispida cultivar hispida voucher DAO 902780 chromosome 2 | CP094632.1 | 100% | 97.71% | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 42 | Arabidopsis arenosa genome assembly, chromosome: 4 | LR999454.1 | 100% | 97.71% | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 43 | Raphanus sativus genome assembly, chromosome: 6 | LR778315.1 | 98% | 96.12% | 1 | 0 | 2 (gap) |
| 44 | PREDICTED: Raphanus sativus growth-regulating factor 1 (LOC108836427), mRNA | XM_018609585.1 | 98% | 96.12% | 1 | 0 | 2 (gap) |
| 45 | PREDICTED: Brassica rapa growth-regulating factor 1 (LOC103858395), mRNA | XM_009135745.3 | 100% | 95.42% | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 46 | Brassica oleracea HDEM genome, scaffold: C3 | LR031872.1 | 100% | 95.42% | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 47 | Brassica rapa genome, scaffold: A03 | LR031572.1 | 100% | 95.42% | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 48 | PREDICTED: Capsella rubella growth-regulating factor 1 (LOC17887921), mRNA | XM_006293922.2 | 100% | 95.42% | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 49 | PREDICTED: Brassica napus growth-regulating factor 1-like (LOC125584397), mRNA | XM_048752816.1 | 100% | 95.42% | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 50 | PREDICTED: Brassica napus growth-regulating factor 1 (LOC106389497), mRNA | XM_013829762.3 | 100% | 95.42% | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 51 | Brassica rapa genome assembly, chromosome: A03 | LS974619.2 | 100% | 95.42% | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 52 | Brassica napus genome assembly, chromosome: C03 | HG994367.1 | 100% | 95.42% | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 53 | Brassica napus genome assembly, chromosome: A03 | HG994357.1 | 100% | 95.42% | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 54 | Brassica rapa subsp. Pekinensis growth-regulating xamp 1 mRNA, partial cds | JN698986.1 | 100% | 95.42% | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 55 | PREDICTED: Brassica oleracea var. oleracea growth-regulating factor 1 (LOC106328366), mRNA | XM_013766798.1 | 100% | 94.66% | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 56 | PREDICTED: Eutrema salsugineum growth-regulating factor 1 (LOC18021800), mRNA | XM_006404687.2 | 100% | 93.89% | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 57 | Arabis alpina genome assembly, chromosome: 6 | LT669793.1 | 93% | 95.90% | 1 | 2 | 9 (gap) |
| Sequence Number | Description | Accession | BLAST against the Query grf8-61 | (MSA) Mismatches (bp) or Gaps against Each Accession | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Query Cover | Per. Ident | Forward | Probe | Reverse | |||
| 1 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 4 | LR782545.1 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 2 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 4 | LR699748.2 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 3 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 4 | LR699773.1 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 4 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 4 | LR699768.1 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 5 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 4 | LR699758.1 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 6 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 4 | LR699753.1 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 7 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 4 | LR215055.1 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 8 | Arabidopsis thaliana chromosome 4 | CP116283.1 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 9 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 4 | OX298800.1 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 10 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 4 | OX298805.1 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 11 | Arabidopsis thaliana ecotype 1254 chromosome 4 sequence | CP086757.1 | 98% | 99.20% | 0 | 0 | 4 (gaps) 1 mismatch |
| 12 | Arabidopsis thaliana ecotype 5856 chromosome 4 sequence | CP086752.1 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 13 | Arabidopsis thaliana ecotype 6021 chromosome 4 sequence | CP086747.1 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 14 | Arabidopsis thaliana ecotype 6024 chromosome 4 sequence | CP086742.1 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 15 | Arabidopsis thaliana ecotype 9412 chromosome 4 sequence | CP086737.1 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 16 | Arabidopsis thaliana ecotype 9470 chromosome 4 sequence | CP086732.1 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 17 | Arabidopsis thaliana chromosome 4 | CP087129.2 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 18 | Arabidopsis thaliana isolate t2t_salk_col chromosome 4 | CP096027.1 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 19 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 4 | OW119599.1 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 20 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 4 | LR881469.1 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 21 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 4 | LR797810.1 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 22 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 4 | LR797805.1 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 23 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 4 | LR797800.1 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 24 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 4 | LR797795.1 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 25 | Arabidopsis thaliana chromosome 4 | CP002687.1 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 26 | Arabidopsis thaliana DNA chromosome 4, contig xample No. 61 | AL161561.2 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 27 | Arabidopsis thaliana DNA chromosome 4, BAC clone T19F6, partial sequence (ESSA xample) | AL109619.1 | 96% | 100.00% | 0 | 0 | 5 (gaps) |
| 28 | Arabidopsis thaliana chromosome IV BAC T19F6 genomic sequence, complete sequence | AC002343.1 | 98% | 99.20% | 0 | 0 | 4 (gaps) 1 mismatch |
| 29 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 4 | LR699763.1 | 96% | 97.54% | 0 | 2 | 5 (gaps) |
| 30 | Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly, chromosome: 4 | LR797790.1 | 96% | 97.54% | 0 | 2 | 5 (gaps) |
| 31 | Arabidopsis thaliana growth-regulating factor 8 (GRF8), partial mRNA | NM_118547.2 | 83% | 100.00% | |||
| Total of Mismatches | Number/Hits Analyzed | Sequences Corresponding Perfectly to the Primer | Number of BLAST Hits Recovered | Possible Discrimination between the grf1-3 Genotype and Other Lines |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 39 | 0 | 57 | Low |
| 2 | 17 | 0 | ||
| 3 | 1 | 0 |
| Total of Mismatches | Number/Hits Analyzed | Sequences Corresponding Perfectly to the Primers | Number of BLAST Hits Recovered | Possible Discrimination between the grf8-3 Genotype and Other Lines |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | High |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zanatta, C.B.; Hoepers, A.M.; Nodari, R.O.; Agapito-Tenfen, S.Z. Specificity Testing for NGT PCR-Based Detection Methods in the Context of the EU GMO Regulations. Foods 2023, 12, 4298. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12234298
Zanatta CB, Hoepers AM, Nodari RO, Agapito-Tenfen SZ. Specificity Testing for NGT PCR-Based Detection Methods in the Context of the EU GMO Regulations. Foods. 2023; 12(23):4298. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12234298
Chicago/Turabian StyleZanatta, Caroline Bedin, Aline Martins Hoepers, Rubens Onofre Nodari, and Sarah Zanon Agapito-Tenfen. 2023. "Specificity Testing for NGT PCR-Based Detection Methods in the Context of the EU GMO Regulations" Foods 12, no. 23: 4298. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12234298
APA StyleZanatta, C. B., Hoepers, A. M., Nodari, R. O., & Agapito-Tenfen, S. Z. (2023). Specificity Testing for NGT PCR-Based Detection Methods in the Context of the EU GMO Regulations. Foods, 12(23), 4298. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12234298









