Application for Identifying the Origin and Predicting the Physiologically Active Ingredient Contents of Gastrodia elata Blume Using Visible–Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Machine Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Pre-Treatment
2.2. Acquisition of Vis-NIR Spectral Data
2.3. Determination of the Contents of Bioactive Components via HPLC
2.4. Chemometric Analysis
2.4.1. Partial Least Squares Regression (PLSR)/Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA)
2.4.2. K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN)
2.4.3. Support Vector Machine (SVM)/Support Vector Regression (SVR)
2.4.4. One-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Network (1D-CNN)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Statistical Analysis of Physiologically Active Ingredients Content Determined via the HPLC Method
3.2. Analysis Based on the Vis-NIR Method
3.2.1. Spectral Analysis of the G. elata Samples
3.2.2. Visual Analysis of Spectral Characteristics
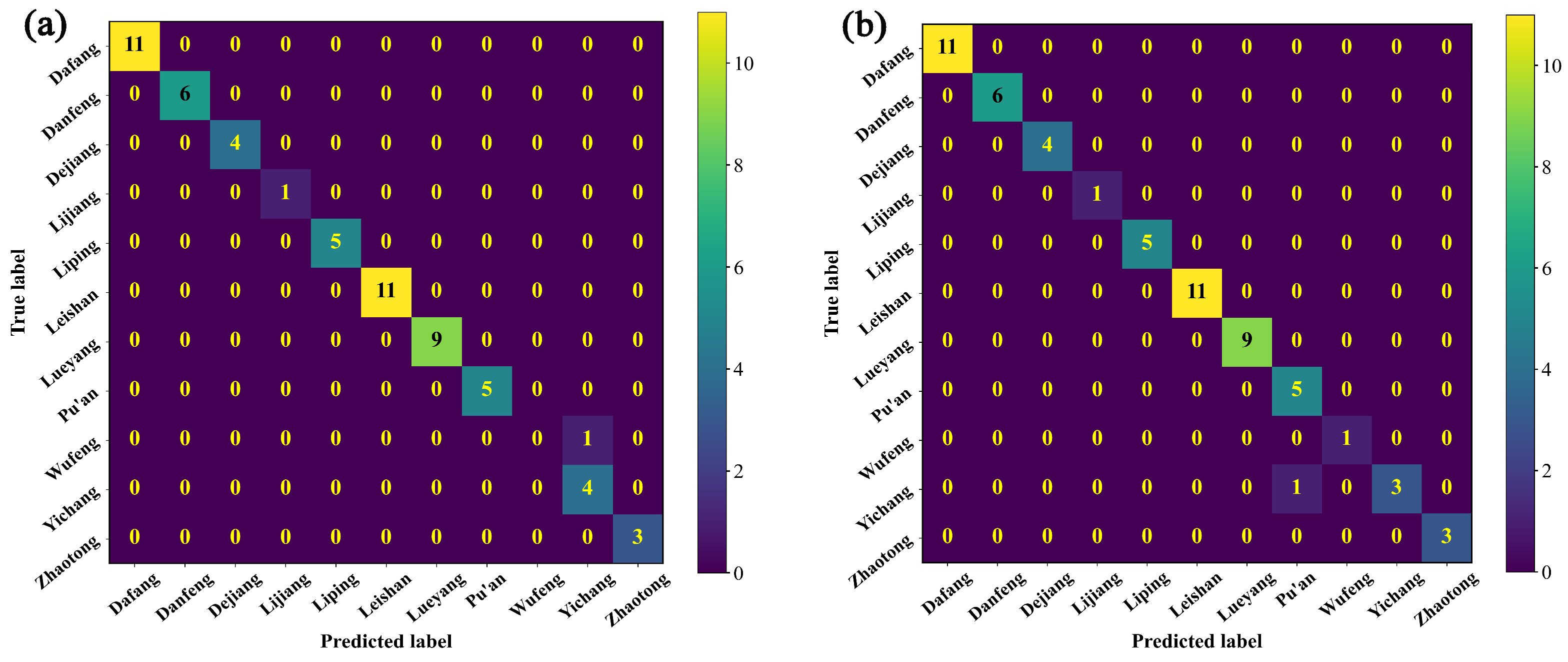
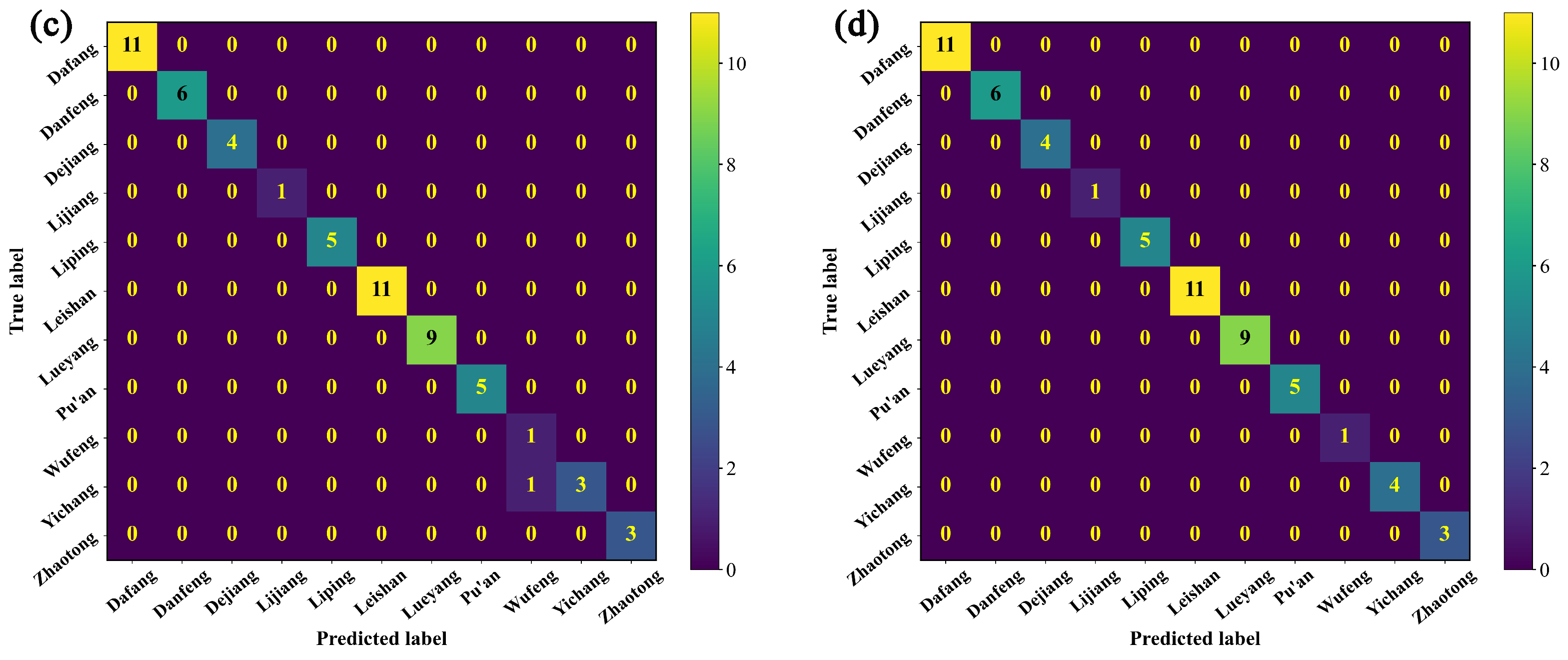
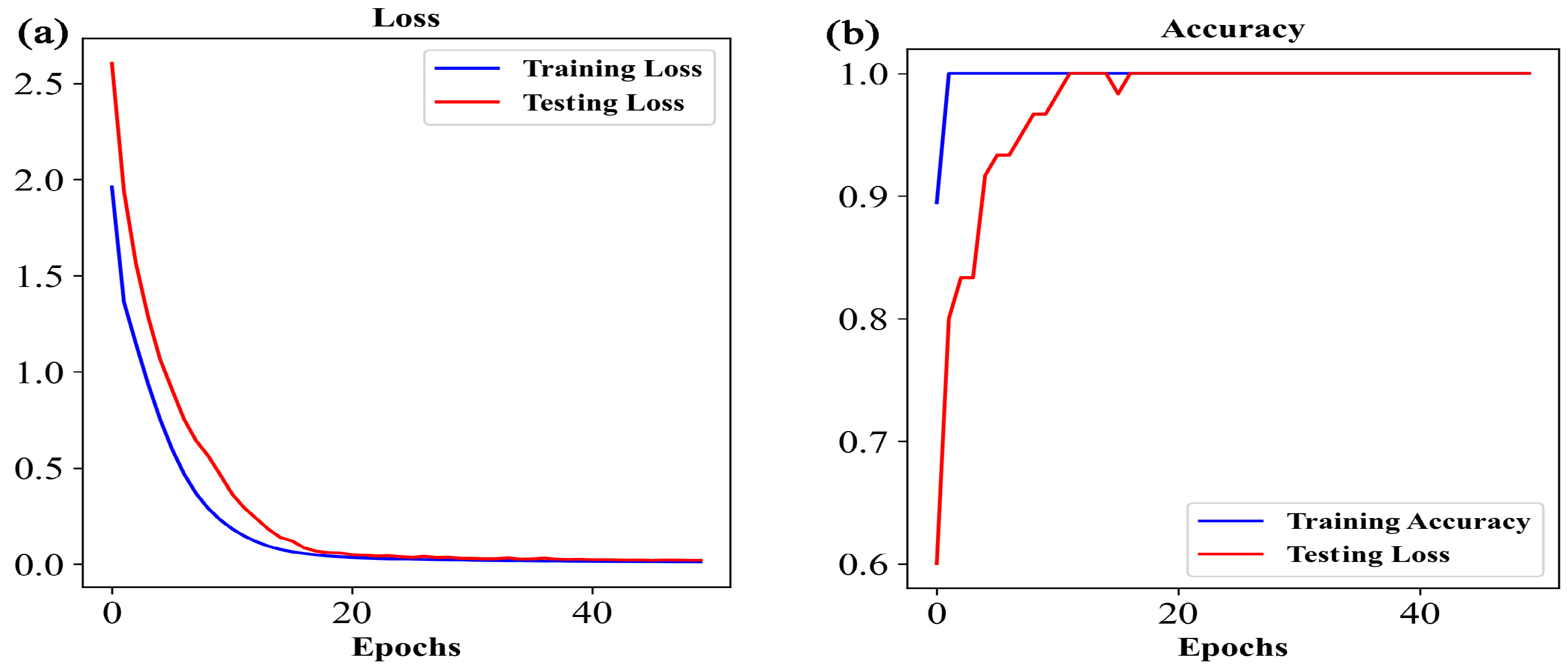
3.2.3. Identification of the Origin of G. elata Based on the Vis-NIR Data
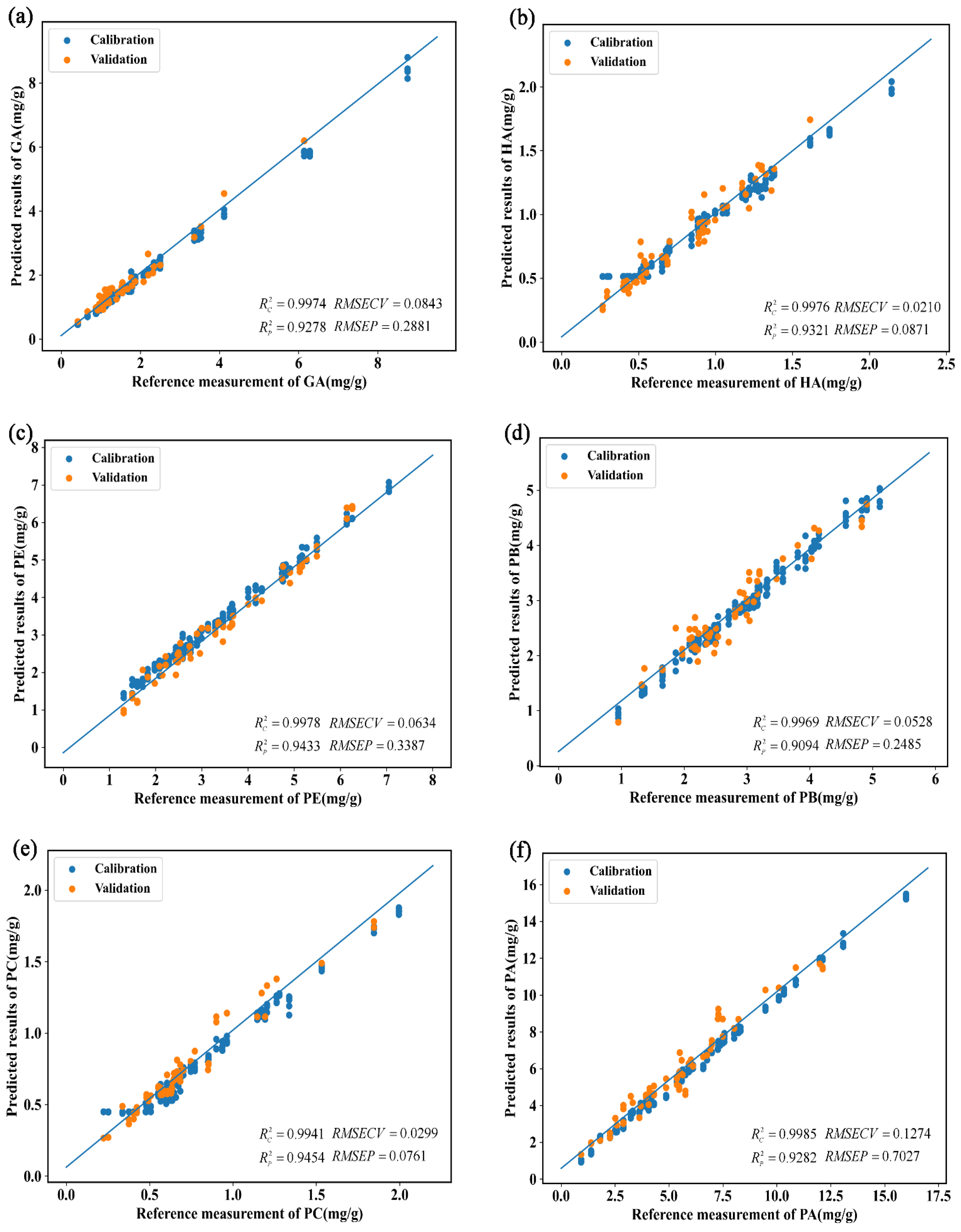
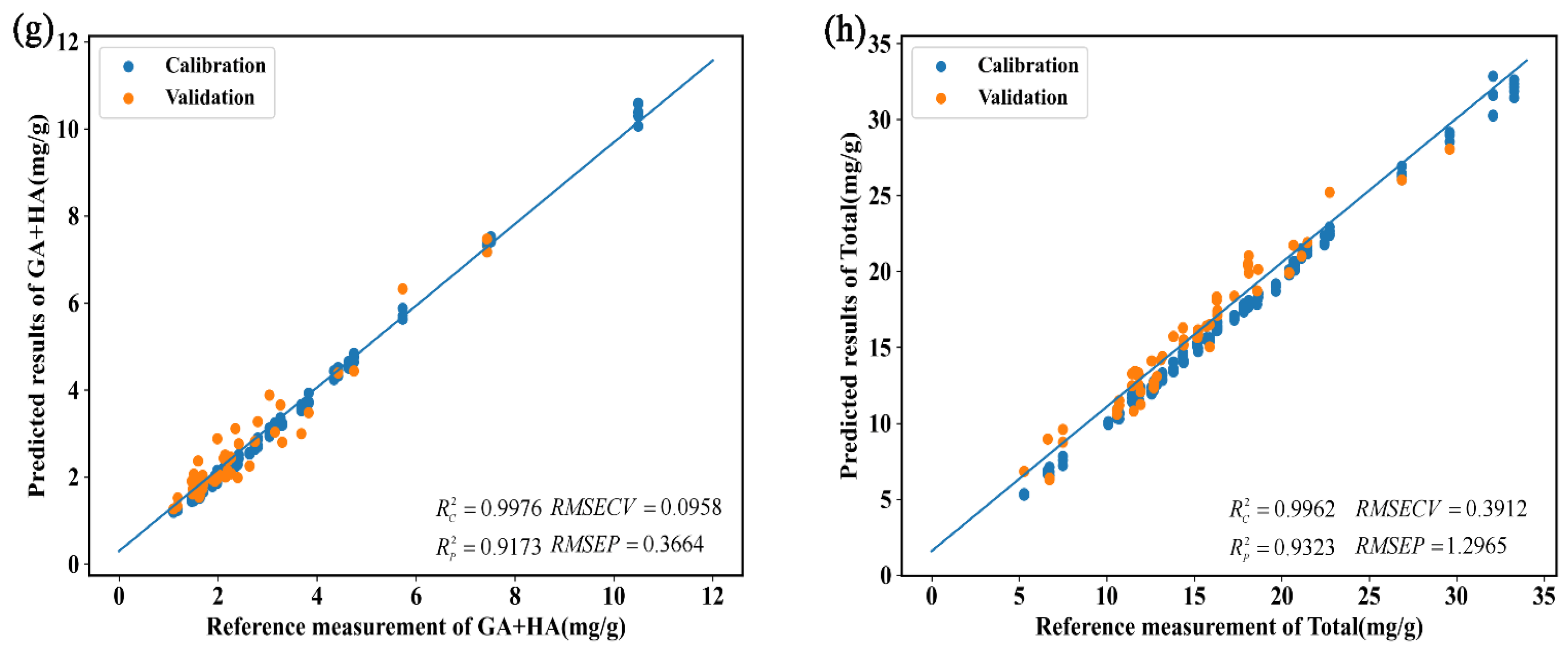
3.2.4. Prediction of Physiologically Active Ingredient Contents in G. elata Based on the Vis-NIR Method
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaswir, I.; Octavianti, F.; Lestari, W.; Hendri, R.; Ahmad, H. Fu1-Some characteristics and functional properties of Chunma (Gastrodia elata) as a food supplement: A short review. Int. Food Res. J. 2017, 24, S274–S280. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, J.; Wang, H.; Lu, C.; Liu, X.; Lu, G. Gastrodia elata blume ameliorates circadian rhythm disorder-induced mice memory impairment. Life Sci. Space Res. 2021, 31, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, J.; Chen, Z.; Guo, L.; Cui, X.; Xu, T.; Wan, F.; Zhou, T.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y. Evaluate how steaming and sulfur fumigation change the microstructure, physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of Gastrodia elata Bl. starch. Front. Nutr. 2023, 9, 1087453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Q.; Chen, C.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, B.; Zhao, S. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy for discrimination of Rhizoma gastrodiae (Tianma) from different producing areas. J. Mol. Struct. 2013, 1051, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elrasheid Tahir, H.; Adam Mariod, A.; Hashim, S.B.H.; Arslan, M.; Komla Mahunu, G.; Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Abdalla, I.I.H.; Zhou, X. Classification of Black Mahlab seeds (Monechma ciliatum) using GC–MS and FT-NIR and simultaneous prediction of their major volatile compounds using chemometrics. Food Chem. 2023, 408, 134948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Shi, Q.; Yan, S.; Fu, H.; Xie, S.; Lu, D. Chemometric Analysis of Elemental Fingerprints for GE Authentication of Multiple Geographical Origins. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2019, 2019, 2796502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Cui, X.; Xiong, Y. Quality Evaluation of Gastrodia Elata Tubers Based on HPLC Fingerprint Analyses and Quantitative Analysis of Multi-Components by Single Marker. Molecules 2019, 24, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Ji, D.; Su, L.; Zhang, F.; Tong, H.; Mao, C.; Lu, T. A simplified LC−MS/MS approach for simultaneous quantification and pharmacokinetics of five compounds in rats following oral administration of Gastrodia elata extract. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Guo, S.; Yao, W.; Shan, M.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ding, A. Quantitative analysis on 20 elements in Gastrodia elata from different regions by ICP-MS. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2017, 48, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, K.; Zhu, X.; Shi, Y.; Fu, J.; Wang, J.; Qian, J.; Ji, P. Exploit and Analysis of SNP Markers for Four Types of Gastrodias Based on SLAF Sequencing. Mol. Plant Breed. 2020, 18, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.; Lim, D.; Um, J.; Lim, C.; Hong, J.; Yoon, Y.; Ryu, Y.; Kim, H.; Cho, H.; Park, J.; et al. Evaluation of Four Different Analytical Tools to Determine the Regional Origin of Gastrodia elata and Rehmannia glutinosa on the Basis of Metabolomics Study. Molecules 2014, 19, 6294–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z. Transformation Mechanisms of Chemical Ingredients in Steaming Process of Gastrodia elata Blume. Molecules 2019, 24, 3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Y.; Chen, C.J.; Sun, H.Q.; Chen, L.J. Structural characterisation and ACE-inhibitory activities of polysaccharide from Gastrodia elata Blume. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 1721–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xiao, H.; Liang, X.; Wei, L. Identification of phenolics and nucleoside derivatives in Gastrodia elata by HPLC-UV-MS. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 1488–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Y.; Deng, X.; Wu, Q. Discrimination of Gastrodia elata from Different Geographical Origin for Quality Evaluation Using Newly-Build Near Infrared Spectrum Coupled with Multivariate Analysis. Molecules 2018, 23, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, W.; Wu, H.; Wang, T.; Dong, M.; Chen, L.; Yu, R. Fast identification of the geographical origin of Gastrodia elata using excitation-emission matrix fluorescence and chemometric methods. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 258, 119798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, L.; Zhong, S.; Liao, P.; Fan, Y.; Hu, C.; Qin, D. Study on a rapid quantitative analysis method for effective components in Gastrodia elata based on Near Infrared Spectroscopy. Her. Med. 2022, 41, 858–862. [Google Scholar]
- Ríos-Reina, R.; Camiña, J.; Callejón, R.; Azcarate, S. Spectralprint techniques for wine and vinegar characterization, authentication and quality control: Advances and projections. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 134, 116121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Girolamo, A.; Cortese, M.; Cervellieri, S.; Lippolis, V.; Pascale, M.; Logrieco, A.; Suman, M. Tracing the Geographical Origin of Durum Wheat by FT-NIR Spectroscopy. Foods 2019, 8, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Chen, S.; Guo, X.; Shi, Z.; Zhao, X. Exploring the Potential of vis-NIR Spectroscopy as a Covariate in Soil Organic Matter Mapping. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckena, L.; Alksnis, R.; Erdberga, I.; Alsina, I.; Dubova, L.; Duma, M. Non-Destructive Quality Evaluation of 80 Tomato Varieties Using Vis-NIR Spectroscopy. Foods 2023, 12, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemi, C.; Mortensen, A.M.; Rautenberger, R.; Matsson, S.; Gorzsás, A.; Gentili, F.G. Rapid and accurate determination of protein content in North Atlantic seaweed by NIR and FTIR spectroscopies. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Bi, S.; Xu, R.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L. Hybrid lightweight Deep-learning model for Sensor-fusion basketball Shooting-posture recognition. Measurement 2022, 189, 110595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukey, N.; Yang, Z.; Li, B.; Zhang, G.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, W. Survey on Exact kNN Queries over High-Dimensional Data Space. Sensors 2023, 23, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, P.; Peng, P.; Khandelwal, M.; Qiu, Y. Performance Evaluation of Rockburst Prediction Based on PSO-SVM, HHO-SVM, and MFO-SVM Hybrid Models. Min. Metall. Explor. 2023, 40, 617–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Fu, C.; Pan, T. Modeling method and miniaturized wavelength strategy for near-infrared spectroscopic discriminant analysis of soy sauce brand identification. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 277, 121291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, H.; Shang, L.; Wu, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Yin, J. NIR spectroscopy combined with 1D-convolutional neural network for breast cancerization analysis and diagnosis. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 287, 121990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, K.; Nishigaki, T.; Andriamananjara, A.; Rakotonindrina, H.; Tsujimoto, Y.; Moritsuka, N.; Rabenarivo, M.; Razafimbelo, T. Using a One-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Network on Visible and Near-Infrared Spectroscopy to Improve Soil Phosphorus Prediction in Madagascar. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, P.; Ge, F.; Ruan, P.; Zhang, S. Quality characteristics of different parts of Gastrodia elata tuber based on simultaneous quantification of multiple index components. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2022, 53, 6337–6342. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Dai, L. PLS-DA and Vis-NIR spectroscopy based discrimination of abdominal tissues of female rabbits. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 271, 120887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, L.S.; Assis, C.; de Queiroz, M.E.L.R.; Neves, A.A.; de Oliveira, A.F. Building robust models for identification of adulteration in olive oil using FT-NIR, PLS-DA and variable selection. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, W.; Bei, Y. Medical Health Big Data Classification Based on KNN Classification Algorithm. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 28808–28819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Via, B.K.; Li, Y.; Wang, G. 35-BC Determination of Geographical Origin and Tree Species Using Vis-NIR and Chemometric Methods. For. Prod. J. 2022, 72, 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, C.; Pan, K.; Guo, Z.; Liu, J.; Xu, A.; Ma, H.; Pan, X. The Simultaneous Prediction of Soil Properties and Vegetation Coverage from Vis-NIR Hyperspectral Data with a One-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Network: A Laboratory Simulation Study. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed Alsumaidaee, Y.; Yaw, C.; Koh, S.; Tiong, S.; Chen, C.; Yusaf, T.; Abdalla, A.; Ali, K.; Raj, A. Detection of Corona Faults in Switchgear by Using 1D-CNN, LSTM, and 1D-CNN-LSTM Methods. Sensors 2023, 23, 3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, W.; Hu, B.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, H.; Sun, T.; Grattan, K.T.V. Automatic rock classification of LIBS combined with 1DCNN based on an improved Bayesian optimization. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, 10603–10614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Meng, X.; Xin, K.; Ju, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, C.; Hu, L. A comparative study on classification of edible vegetable oils by infrared, near infrared and fluorescence spectroscopy combined with chemometrics. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 288, 122120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, D.; Zhong, X. Current Situation of Protection of Chaotong Gastrodia elate, a National Geographical Symbol Product. Guizhou Agric. Sci. 2010, 38, 79–82. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L.; Pan, J.; He, Y.; Dou, X. Identification of pesticide varieties by detecting characteristics of Chlorella pyrenoidosa using Visible/Near infrared hyperspectral imaging and Raman microspectroscopy technology. Water Res. 2016, 104, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, W.; Yang, X.; Lu, G.; Deng, Y.; Yang, L. A rapid quality grade discrimination method for Gastrodia elata powderusing ATR-FTIR and chemometrics. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 264, 120189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melit Devassy, B.; George, S. Dimensionality reduction and visualisation of hyperspectral ink data using t-SNE. Forensic Sci. Int. 2020, 311, 110194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Kamruzzaman, M. Portable NIR spectroscopy and PLS based variable selection for adulteration detection in quinoa flour. Food Control 2022, 138, 108970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmawan, A.; Masithoh, R.E.; Amanah, H.Z. Development of PCA-MLP Model Based on Visible and Shortwave Near Infrared Spectroscopy for Authenticating Arabica Coffee Origins. Foods 2023, 12, 2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapcharoensuk, R.; Fhaykamta, C.; Anurak, W.; Chadwut, W.; Sitorus, A. Nondestructive Detection of Pesticide Residue (Chlorpyrifos) on Bok Choi (Brassica rapa subsp. Chinensis) Using a Portable NIR Spectrometer Coupled with a Machine Learning Approach. Foods 2023, 12, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, H.; Zhou, H.; Sui, Y.; Du, X.; Wang, W.; Dai, L.; Sui, F.; Huo, H.; Jiang, T. The rhizome of Gastrodia elata Blume—An ethnopharmacological review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 189, 361–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.L.; Zhang, P.; Liu, X. Tianma injection in the treatment of vertebral basilar artery insufficiency randomized parallel group study. J. Pract. Tradit. Chin. Intern. Med. 2014, 5, 44–46. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X. Clinical examination of treating vertigo with the Tianmasu injection. Clin. J. Chin. Med. 2012, 4, 86–87. [Google Scholar]

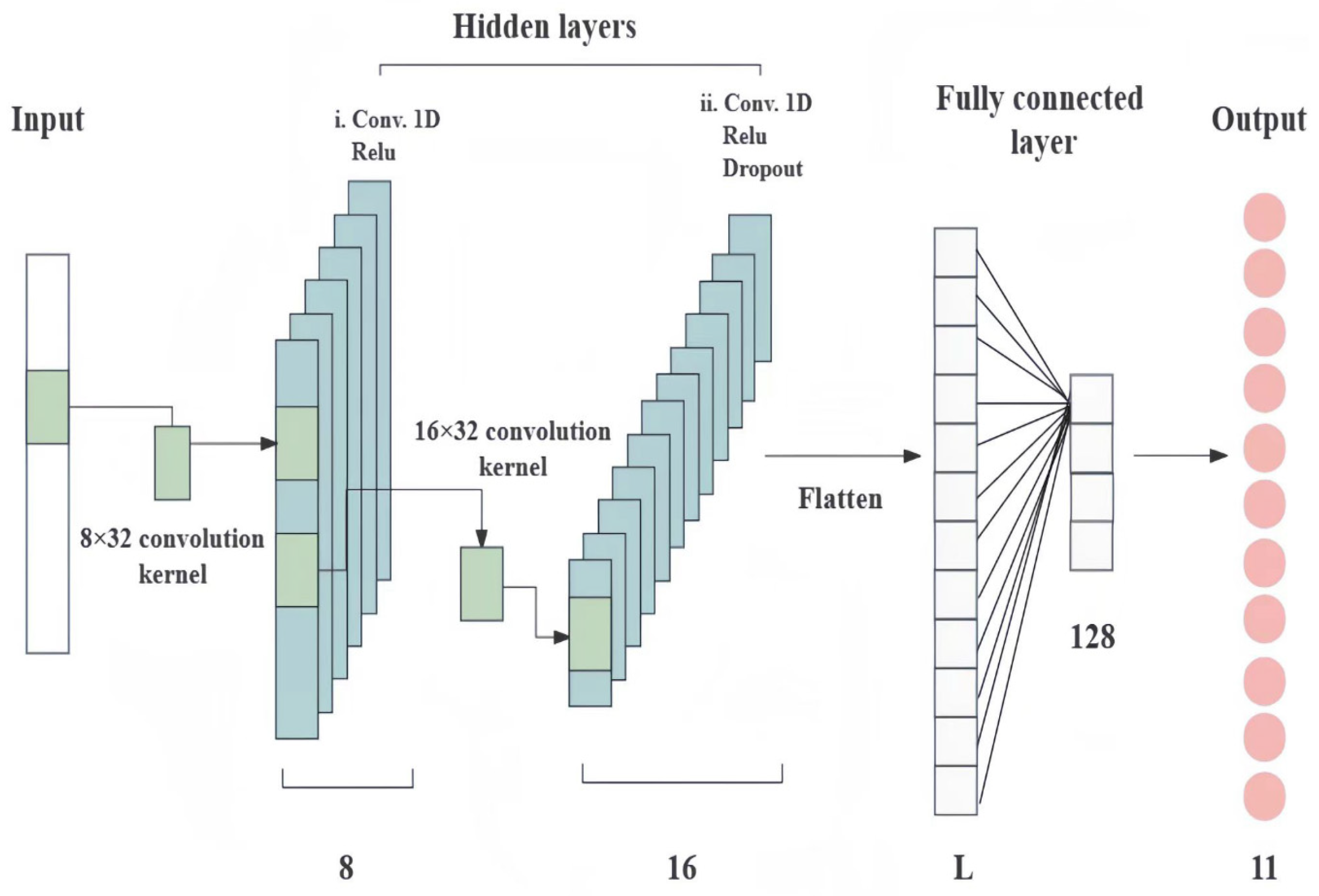
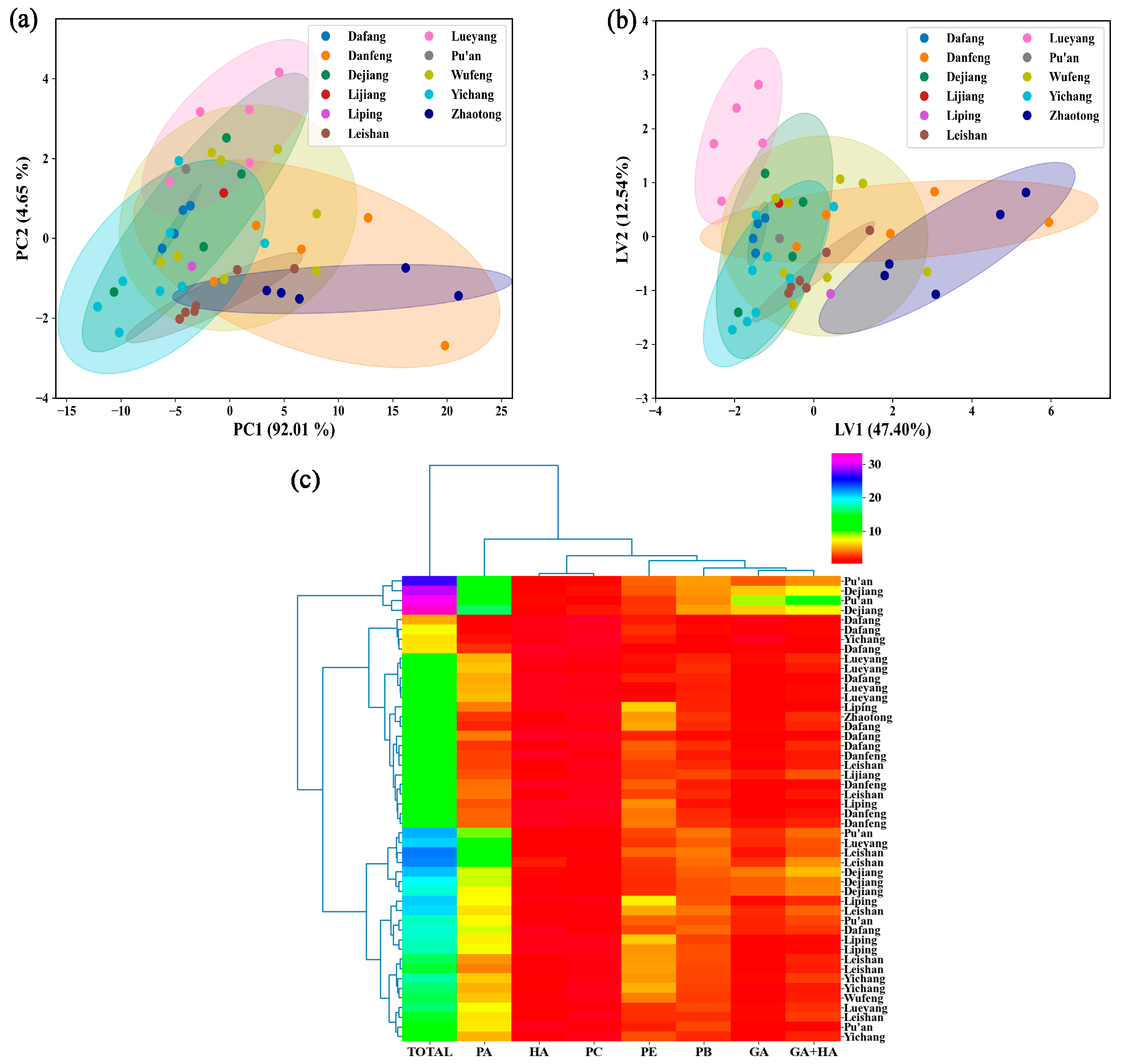
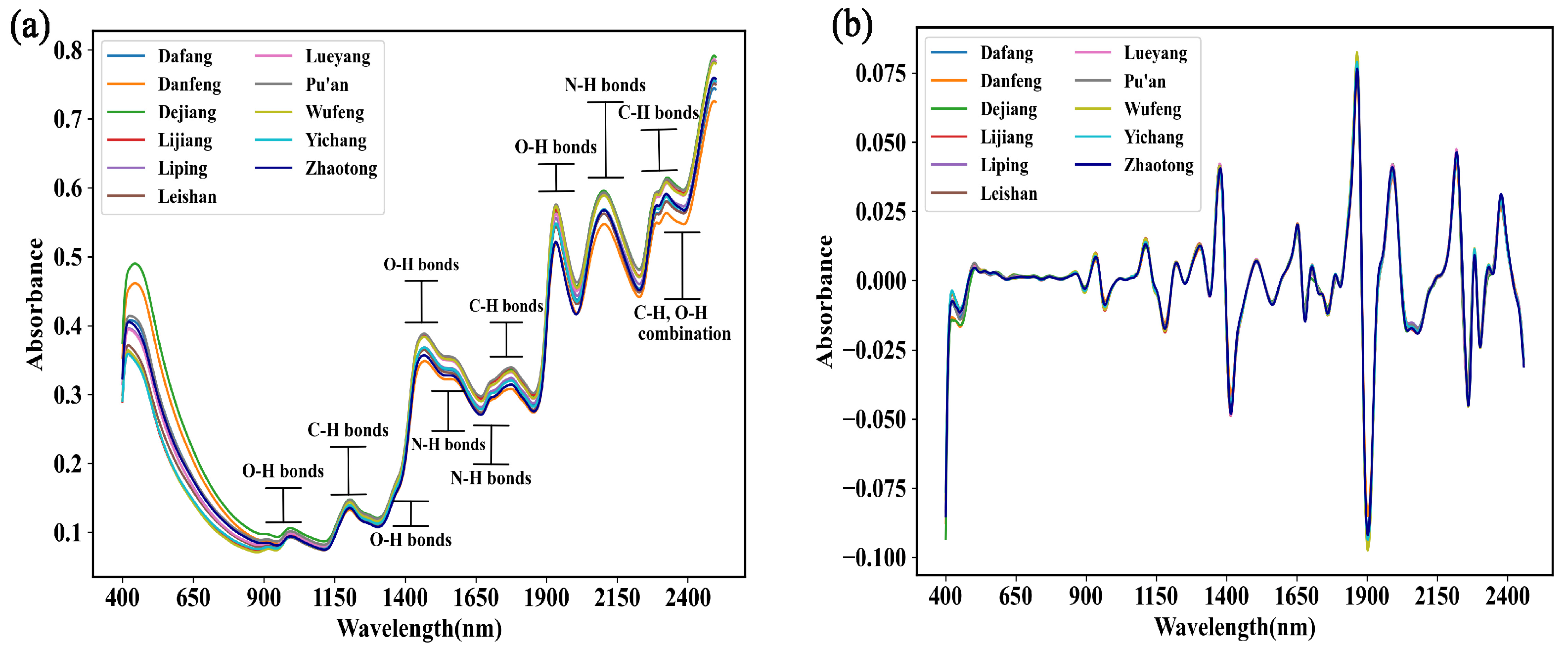
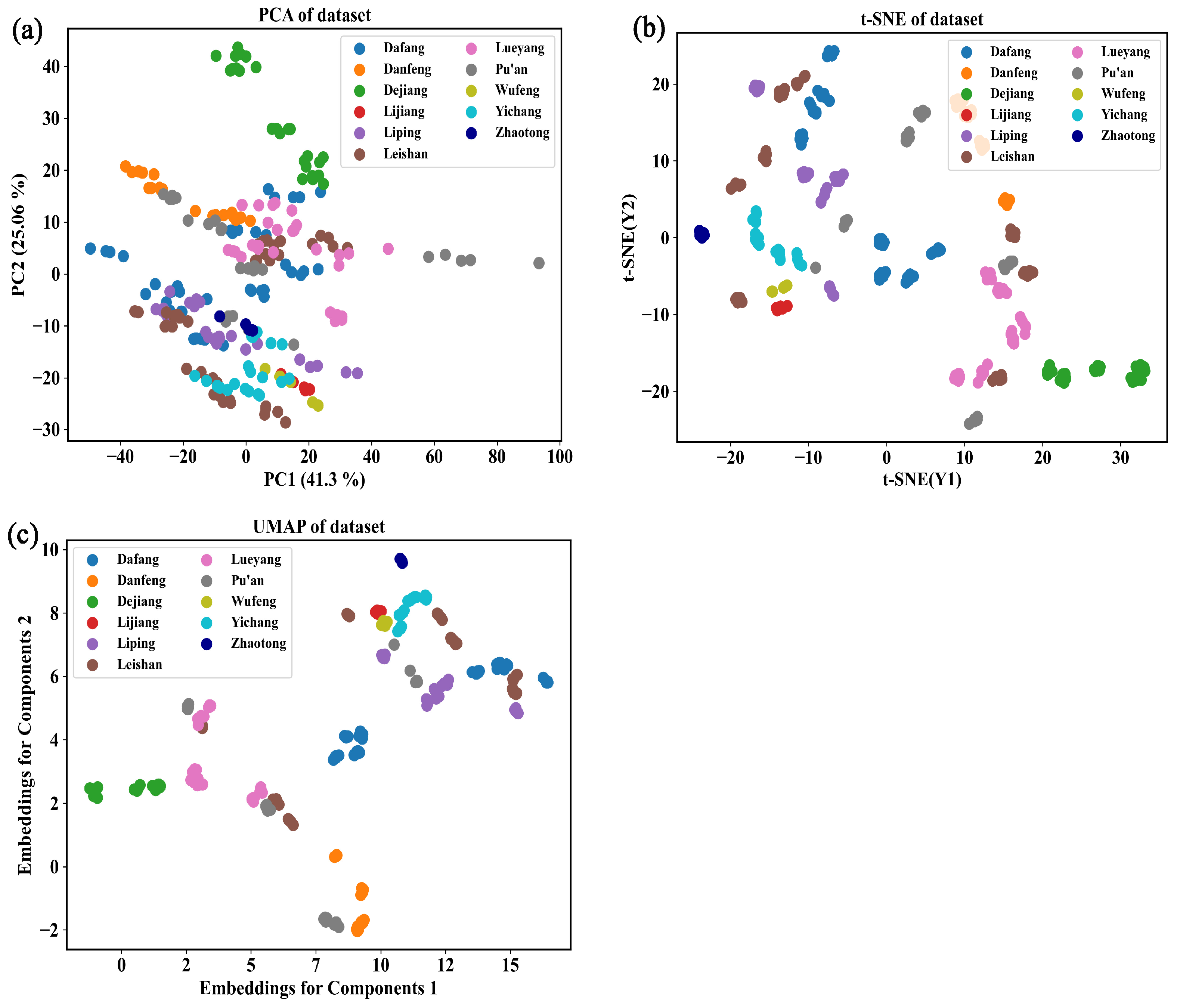
| City | Province | Number of Batches | Region (City) | Region (Province) | Number of Batches |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dejiang (DJ) | Guizhou | 25 | Zhaotong (ZT) | Yunnan | 5 |
| Dafang (DAF) | Guizhou | 40 | Yichang (YC) | Hubei | 20 |
| Leishan (LS) | Guizhou | 40 | Wufeng (WF) | Hubei | 5 |
| Pu’an (PUA) | Guizhou | 25 | Lueyang (LY) | Shaanxi | 30 |
| Liping (LP) | Guizhou | 25 | Danfeng (DF) | Shaanxi | 20 |
| Lijiang (LJ) | Yunnan | 5 |
| Network Layer | G. elata | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Input Shape | Output Shape | Hyperparameters | |
| Gaussian noise | (None, 1030) | (None, 1030) | t = 0.05 |
| Reshape | (None, 1030) | (None, 1030, 1) | |
| 1D convolution | (None, 1030, 1) | (None, 999, 8) | K = 8, s = 32, a = “ReLU” |
| 1D convolution | (None, 999, 8) | (None, 968, 16) | K = 16, s = 32, a = “ReLU” |
| Dropout | (None, 968, 16) | (None, 968, 16) | r = 0.5 |
| Flatten | (None, 968, 16) | (None, 15,488) | |
| Dense | (None, 15,488) | (None, 128) | d = 128, a = “ReLU” |
| Output | (None, 128) | (None, 11) | d =11, a = “Softmax” |
| Samples | SPXY Divided the Sample Set | Number of Samples | Min (mg/g) | Max (mg/g) | Mean (mg/g) | Std (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gastrodin (GA) | Training set | 180 | 0.4172 | 8.7501 | 2.0922 | 1.6732 |
| Testing set | 60 | 0.4172 | 6.1368 | 1.6160 | 1.0809 | |
| p-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol (HA) | Training set | 180 | 0.2654 | 2.1445 | 0.8901 | 0.4285 |
| Testing set | 60 | 0.2654 | 1.6148 | 0.7957 | 0.3369 | |
| Parishin E (PE) | Training set | 180 | 1.3070 | 7.0529 | 3.3809 | 1.3630 |
| Testing set | 60 | 1.3070 | 6.2551 | 3.5147 | 1.4350 | |
| Parishin B (PB) | Training set | 180 | 0.9511 | 5.1121 | 2.9258 | 0.9635 |
| Testing set | 60 | 0.9511 | 4.9068 | 2.6958 | 0.8327 | |
| Parishin C (PC) | Training set | 180 | 0.2227 | 1.9953 | 0.7953 | 0.3920 |
| Testing set | 60 | 0.2227 | 1.8459 | 0.7049 | 0.3285 | |
| Parishin A (PA) | Training set | 180 | 0.9179 | 15.9855 | 6.4430 | 3.3290 |
| Testing set | 60 | 0.9179 | 12.1205 | 5.3990 | 2.6437 | |
| GA + HA | Training set | 180 | 1.0952 | 10.4906 | 2.9512 | 1.9493 |
| Testing set | 60 | 1.0952 | 7.4369 | 2.4284 | 1.2823 | |
| Total | Training set | 180 | 5.2818 | 33.2749 | 16.4603 | 6.3342 |
| Testing set | 60 | 5.2818 | 29.5875 | 14.5303 | 5.0405 |
| Region of Origin | Gastrodin (GA) | p-Hydroxybenzyl Alcohol (HA) | Parishin E (PE) | Parishin B (PB) | Parishin C (PC) | Parishin A (PA) | GA + HA | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dafang (DaF) | 1.5117 | 0.3898 | 3.7303 | 2.2392 | 0.6245 | 3.5280 | 1.9015 | 12.0235 |
| Pu’an (PA) | 3.5800 | 1.1643 | 2.9929 | 3.9372 | 1.1369 | 9.7448 | 4.7443 | 22.5561 |
| Yingchang (YC) | 1.0361 | 0.9661 | 3.8818 | 2.4010 | 0.4814 | 4.7407 | 2.0021 | 13.5071 |
| Wufeng (WF) | 1.2197 | 0.8885 | 4.2984 | 2.7102 | 0.5647 | 6.0205 | 2.1082 | 15.7020 |
| Lijiang (LJ) | 2.0826 | 1.2167 | 2.7562 | 3.0411 | 0.6751 | 3.3120 | 3.2993 | 13.0837 |
| Zhaotong (ZT) | 1.3222 | 1.1378 | 4.9121 | 2.5771 | 0.5723 | 2.6593 | 2.4600 | 13.1809 |
| Lueyang (LY) | 1.5378 | 0.6945 | 1.9492 | 2.6026 | 0.7956 | 6.7290 | 2.2323 | 14.3087 |
| Liping (LP) | 1.1844 | 0.5356 | 5.8001 | 2.6807 | 0.4926 | 5.8463 | 1.7200 | 16.5397 |
| Leishan (LS) | 1.5864 | 1.2674 | 3.7008 | 3.1863 | 0.7102 | 6.3293 | 2.8538 | 16.7804 |
| Danfeng (DF) | 1.2382 | 0.5367 | 2.7307 | 2.0601 | 0.5670 | 3.4004 | 1.7749 | 10.5331 |
| Dejiang (DJ) | 4.7040 | 1.1842 | 2.6924 | 3.9674 | 1.5170 | 10.3782 | 5.8882 | 24.4433 |
| Mean | 1.9094 | 0.9074 | 3.5859 | 2.8548 | 0.7398 | 5.6989 | 2.8168 | 15.6962 |
| CV% | 61.06 | 35.09 | 31.23 | 22.05 | 42.74 | 44.98 | 47.8204 | 27.4375 |
| Data Augmentation | Pre-Processing | Modeling Method | Acc_Train | Acc_Test | Precision | Recall Rate | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Raw | PLS-DA | 0.7833 | 0.8167 | 0.7995 | 0.8167 | 0.8031 |
| KNN | 0.7555 | 0.8167 | 0.8417 | 0.8167 | 0.8064 | ||
| SVM | 0.4167 | 0.4500 | 0.4366 | 0.4500 | 0.3750 | ||
| 1D-CNN | 0.2611 | 0.2500 | 0.1131 | 0.2500 | 0.1392 | ||
| Normalization | PLS-DA | 0.8889 | 0.9167 | 0.9102 | 0.9167 | 0.9085 | |
| KNN | 1.0000 | 0.5167 | 0.5060 | 0.5167 | 0.5062 | ||
| SVM | 0.8278 | 0.6500 | 0.7211 | 0.6500 | 0.6579 | ||
| 1D-CNN | 1.0000 | 0.9167 | 0.9142 | 0.9167 | 0.9067 | ||
| SD + Normalization | PLS-DA | 0.9429 | 0.9556 | 0.9500 | 0.9440 | 0.9500 | |
| KNN | 0.9944 | 0.9667 | 0.9542 | 0.9667 | 0.9583 | ||
| SVM | 0.9611 | 0.9833 | 0.9847 | 0.9833 | 0.9828 | ||
| 1D-CNN | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| Yes | Raw | PLS-DA | 0.7125 | 0.7167 | 0.6845 | 0.7167 | 0.6706 |
| KNN | 0.8292 | 0.7167 | 0.8539 | 0.7167 | 0.7170 | ||
| SVM | 0.3833 | 0.4500 | 0.2933 | 0.4500 | 0.3241 | ||
| 1D-CNN | 0.3951 | 0.4667 | 0.3495 | 0.4667 | 0.3641 | ||
| Normalization | PLS-DA | 0.9667 | 0.9167 | 0.9117 | 0.9167 | 0.9096 | |
| KNN | 1.0000 | 0.7167 | 0.7409 | 0.7167 | 0.7121 | ||
| SVM | 0.8625 | 0.8833 | 0.9012 | 0.8833 | 0.8718 | ||
| 1D-CNN | 1.0000 | 0.9833 | 0.9847 | 0.9833 | 0.9833 | ||
| SD + Normalization | PLS-DA | 0.9764 | 0.9833 | 0.9701 | 0.9833 | 0.9759 | |
| KNN | 1.0000 | 0.9833 | 0.9861 | 0.9833 | 0.9829 | ||
| SVM | 1.0000 | 0.9833 | 0.9917 | 0.9833 | 0.9849 | ||
| 1D-CNN | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| Number | Components | Spectral Pre-Processing | Modeling Method | MRECV | RMSECV | MREP | RMSEP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gastrodin (GA) | SD | PLSR | 0.9770 | 0.1277 | 0.2530 | 0.6794 | 0.3868 | 0.6069 |
| KNN | 0.8835 | 0.1968 | 0.5696 | 0.8995 | 0.1964 | 0.3398 | |||
| SVR | 0.9974 | 0.0549 | 0.0851 | 0.8869 | 0.2360 | 0.3604 | |||
| 1D-CNN | 0.9867 | 0.0707 | 0.1924 | 0.8913 | 0.1920 | 0.3535 | |||
| SD + augmentation | PLSR | 0.9749 | 0.1323 | 0.2642 | 0.6775 | 0.3864 | 0.6086 | ||
| KNN | 0.9247 | 0.1722 | 0.4577 | 0.9202 | 0.1714 | 0.3027 | |||
| SVR | 0.9985 | 0.0385 | 0.0644 | 0.8863 | 0.2243 | 0.3615 | |||
| 1D-CNN | 0.9974 | 0.0328 | 0.0843 | 0.9278 | 0.1396 | 0.2881 | |||
| 2 | p-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol
(HA) | SD | PLSR | 0.9179 | 0.1463 | 0.1224 | 0.6796 | 0.2459 | 0.1918 |
| KNN | 0.941 | 0.0952 | 0.1038 | 0.89 | 0.1207 | 0.1108 | |||
| SVR | 0.9644 | 0.1094 | 0.0806 | 0.8749 | 0.1596 | 0.1182 | |||
| 1D-CNN | 0.9744 | 0.072 | 0.0684 | 0.919 | 0.1184 | 0.0951 | |||
| SD + augmentation | PLSR | 0.9346 | 0.1270 | 0.1093 | 0.6715 | 0.2602 | 0.1915 | ||
| KNN | 0.8761 | 0.1143 | 0.1505 | 0.9274 | 0.0891 | 0.09 | |||
| SVR | 0.9746 | 0.0926 | 0.0681 | 0.8972 | 0.1412 | 0.1071 | |||
| 1D-CNN | 0.9976 | 0.0201 | 0.021 | 0.9321 | 0.0884 | 0.0871 | |||
| 3 | Parishin E
(PE) | SD | PLSR | 0.856 | 0.1468 | 0.5158 | 0.8862 | 0.1196 | 0.4801 |
| KNN | 0.8810 | 0.1153 | 0.4689 | 0.8858 | 0.1143 | 0.4810 | |||
| SVR | 0.8499 | 0.1183 | 0.5267 | 0.8800 | 0.1228 | 0.4930 | |||
| 1D-CNN | 0.9971 | 0.018 | 0.0735 | 0.8963 | 0.1166 | 0.4583 | |||
| SD + augmentation | PLSR | 0.8522 | 0.1479 | 0.5226 | 0.885 | 0.1197 | 0.4825 | ||
| KNN | 0.9381 | 0.0763 | 0.3382 | 0.9241 | 0.0902 | 0.3919 | |||
| SVR | 0.9972 | 0.0218 | 0.0725 | 0.9405 | 0.0831 | 0.3471 | |||
| 1D-CNN | 0.9978 | 0.0164 | 0.0634 | 0.9433 | 0.0839 | 0.3387 | |||
| 4 | Parishin B (PB) | SD | PLSR | 0.801 | 0.1409 | 0.4286 | 0.6413 | 0.1704 | 0.4945 |
| KNN | 0.9166 | 0.0867 | 0.2775 | 0.8345 | 0.1139 | 0.3359 | |||
| SVR | 0.9907 | 0.0328 | 0.0925 | 0.9066 | 0.0849 | 0.2523 | |||
| 1D-CNN | 0.9788 | 0.0388 | 0.1396 | 0.8978 | 0.0812 | 0.2639 | |||
| SD + augmentation | PLSR | 0.7998 | 0.141 | 0.4299 | 0.6408 | 0.1710 | 0.4949 | ||
| KNN | 0.826 | 0.1021 | 0.4008 | 0.8623 | 0.0776 | 0.3064 | |||
| SVR | 0.9951 | 0.0228 | 0.0670 | 0.9243 | 0.0752 | 0.2271 | |||
| 1D-CNN | 0.9969 | 0.0151 | 0.0528 | 0.9094 | 0.0788 | 0.2485 | |||
| 5 | Parishin C
(PC) | SD | PLSR | 0.8844 | 0.164 | 0.1329 | 0.7178 | 0.2076 | 0.1731 |
| KNN | 0.9589 | 0.0926 | 0.0792 | 0.9087 | 0.1216 | 0.0984 | |||
| SVR | 0.9572 | 0.1219 | 0.0808 | 0.8514 | 0.1901 | 0.1256 | |||
| 1D-CNN | 0.985 | 0.0601 | 0.0478 | 0.9304 | 0.1176 | 0.0859 | |||
| SD + augmentation | PLSR | 0.8709 | 0.1762 | 0.1405 | 0.7201 | 0.2141 | 0.1723 | ||
| KNN | 0.9119 | 0.1031 | 0.116 | 0.9373 | 0.0885 | 0.0816 | |||
| SVR | 0.9691 | 0.1001 | 0.0688 | 0.8691 | 0.1712 | 0.1179 | |||
| 1D-CNN | 0.9941 | 0.0335 | 0.0299 | 0.9454 | 0.0887 | 0.0761 | |||
| 6 | Parishin A
(PA) | SD | PLSR | 0.8934 | 0.2027 | 1.0839 | 0.6216 | 0.3181 | 1.6127 |
| KNN | 0.9359 | 0.1334 | 0.8402 | 0.8439 | 0.2031 | 1.0358 | |||
| SVR | 0.9904 | 0.0494 | 0.3244 | 0.8955 | 0.1967 | 0.8474 | |||
| 1D-CNN | 0.9950 | 0.0379 | 0.2358 | 0.9448 | 0.1215 | 0.6159 | |||
| SD + augmentation | PLSR | 0.8985 | 0.1922 | 1.0577 | 0.6228 | 0.3160 | 1.6101 | ||
| KNN | 0.9089 | 0.1362 | 1.0018 | 0.9269 | 0.1079 | 0.7086 | |||
| SVR | 0.9990 | 0.0204 | 0.1032 | 0.9078 | 0.1690 | 0.7959 | |||
| 1D-CNN | 0.9985 | 0.0247 | 0.1274 | 0.9282 | 0.1329 | 0.7027 | |||
| 7 | GA + HA | SD | PLSR | 0.9741 | 0.1089 | 0.3129 | 0.6699 | 0.2989 | 0.7321 |
| KNN | 0.9191 | 0.1465 | 0.5530 | 0.8946 | 0.1486 | 0.4136 | |||
| SVR | 0.9976 | 0.0351 | 0.0942 | 0.9037 | 0.1618 | 0.3954 | |||
| 1D-CNN | 0.9970 | 0.0298 | 0.1047 | 0.9015 | 0.1216 | 0.3999 | |||
| SD + augmentation | PLSR | 0.9704 | 0.1132 | 0.3344 | 0.6718 | 0.2994 | 0.7300 | ||
| KNN | 0.9483 | 0.1202 | 0.4420 | 0.9141 | 0.1331 | 0.3733 | |||
| SVR | 0.9988 | 0.0251 | 0.0667 | 0.8990 | 0.1584 | 0.4048 | |||
| 1D-CNN | 0.9976 | 0.0254 | 0.0958 | 0.9173 | 0.1006 | 0.3664 | |||
| 8 | Total | SD | PLSR | 0.8928 | 0.1257 | 2.0679 | 0.6419 | 0.1830 | 2.9827 |
| KNN | 0.9388 | 0.0872 | 1.5628 | 0.8649 | 0.1156 | 1.8318 | |||
| SVR | 0.9370 | 0.0863 | 1.5851 | 0.8485 | 0.1314 | 1.9400 | |||
| 1D-CNN | 0.9991 | 0.0097 | 0.1926 | 0.9136 | 0.0861 | 1.4653 | |||
| SD + augmentation | PLSR | 0.8897 | 0.1272 | 2.0975 | 0.6435 | 0.1826 | 2.9757 | ||
| KNN | 0.9789 | 0.0375 | 0.9175 | 0.9261 | 0.0775 | 1.3547 | |||
| SVR | 0.9983 | 0.0137 | 0.2580 | 0.9301 | 0.0864 | 1.3180 | |||
| 1D-CNN | 0.9962 | 0.0202 | 0.3912 | 0.9323 | 0.0794 | 1.2965 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, J.; Zhou, X.; Xie, B.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Ge, F.; Huang, F. Application for Identifying the Origin and Predicting the Physiologically Active Ingredient Contents of Gastrodia elata Blume Using Visible–Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Machine Learning. Foods 2023, 12, 4061. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12224061
Ma J, Zhou X, Xie B, Wang C, Chen J, Zhu Y, Wang H, Ge F, Huang F. Application for Identifying the Origin and Predicting the Physiologically Active Ingredient Contents of Gastrodia elata Blume Using Visible–Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Machine Learning. Foods. 2023; 12(22):4061. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12224061
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Jinfang, Xue Zhou, Baiheng Xie, Caiyun Wang, Jiaze Chen, Yanliu Zhu, Hui Wang, Fahuan Ge, and Furong Huang. 2023. "Application for Identifying the Origin and Predicting the Physiologically Active Ingredient Contents of Gastrodia elata Blume Using Visible–Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Machine Learning" Foods 12, no. 22: 4061. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12224061
APA StyleMa, J., Zhou, X., Xie, B., Wang, C., Chen, J., Zhu, Y., Wang, H., Ge, F., & Huang, F. (2023). Application for Identifying the Origin and Predicting the Physiologically Active Ingredient Contents of Gastrodia elata Blume Using Visible–Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Machine Learning. Foods, 12(22), 4061. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12224061






