Geographical Indication Characteristics of Aroma and Phenolic Acids of the Changping Strawberry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materialsand Chemicals
2.2. Aroma Analysis
2.2.1. Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction (HS–SPME)
2.2.2. Gas Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Analysis (GC–MS/MS)
2.3. Phenolic Acid Analysis
2.3.1. Phenolic Acid Extraction
2.3.2. Ultrahigh-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC)–MS/MS
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
2.4.2. Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA)
2.4.3. Orthogonal Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis (OPLS–DA)
2.4.4. Differential Metabolite Identification
2.4.5. KEGG Annotation and Enrichment Analysis
2.4.6. Fisher Discriminant Analysis (FDA)
3. Results
3.1. Volatile Profile of Strawberry Samples
3.1.1. Comparison of Volatile Compounds and Relative Content
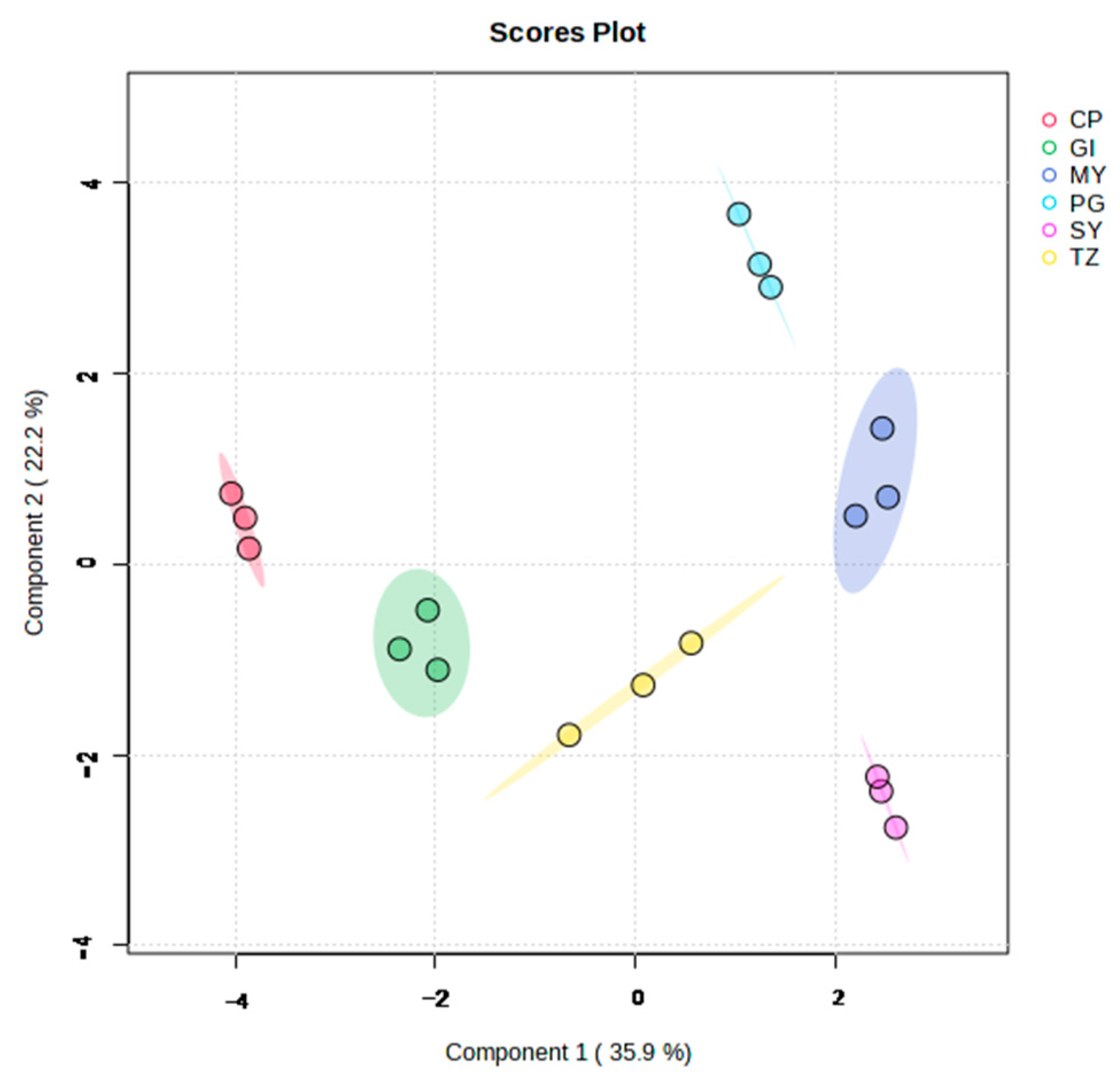
3.1.2. Diversity in Volatile Compound Profiles among Different Groups
3.1.3. OPLS–DA Models of Volatile Compounds between GI and Other Groups
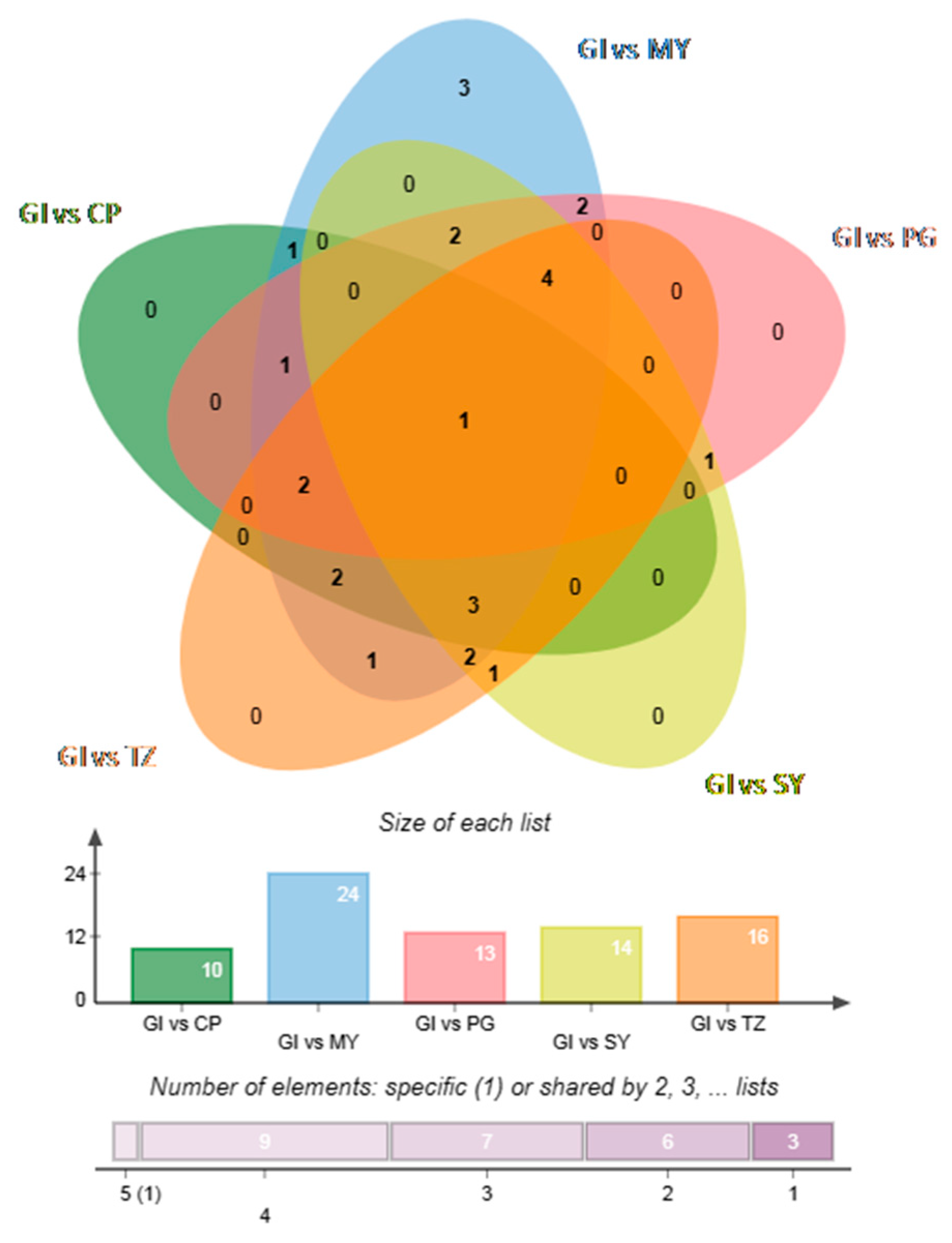
3.1.4. Determination of Volatile Differential Metabolites and Characteristic Markers
3.1.5. Functional Annotation and Enrichment Analysis of KEGG Differential Metabolite
3.2. Characterization of Phenolic Acids in Strawberry Samples
3.2.1. Quality Analysis of Phenolic Acids
3.2.2. PCA and HCA Results of Total Samples Based on Phenolic Acids
3.2.3. OPLS–DA Models of Phenolic Acids between GI Group and Other Groups
3.2.4. Determination of Phenolic Acids and Characteristic Markers
3.3. Classification of Strawberry Samples from Six Groups Based on Three Characteristic Markers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z.; Ma, Z.; Xu, M.; Chen, J.; Zhao, X. Geographical indication characteristics, uniqueproduction methods and industrial development measures of Zhuanbu strawberry. Asian Agric. Res. 2021, 13, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Wang, Z.; Lu, X. Set up a model of geographical indication for the agricultural industry in the suburbs of Beijing. Farmers’ Dly. 2022, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Liu, T.J.; Luo, H.F.; Liu, S.C. The transcriptional landscape of cultivated strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa) and its diploid ancestor (Fragaria vesca) during fruit development. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 1540–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Han, Y.; Li, L.; Rakariyatham, K.; Wu, X.; Gao, Z.; Xiao, H. Protective effects of non-extractable phenolics from strawberry against inflammation and colon cancer in vitro. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, Y.; Barbey, C.R.; Chandra, S.; Bai, J.; Fan, Z.; Plotto, A.; Pillet, J.; Folta, K.M.; Whitaker, V.M.; Lee, S. Genomic characterization of the fruity aroma gene, FaFAD1, reveals a gene dosage effect on gamma-decalactone production in strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa). Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 639345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.W.; Ban, Z.J.; Lu, H.Y.; Li, D.; Poverenov, E.; Luo, Z.S.; Li, L. The aroma volatile repertoire in strawberry fruit: A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 4395–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Sun, R.; Wang, G.; Chang, L.; Sun, J.; Zhong, C.; Dong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ulrich, D. A comparative analysis on fruit characteristic aroma compounds in eight strawberry varieties (strains). J. Fruit Sci. 2018, 35, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Palma, C.; Úbeda, C.; Gil, M.; Ramos, P.; Castro, R.I.; Morales-Quintana, L. Comparative study of the volatile organic compounds of four strawberry cultivars and it relation to alcohol acyltransferase enzymatic activity. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 251, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Taher, F.; Nemzer, B. Identification of aroma compounds in freeze-dried strawberries and raspberries by HS-SPME-GC-MS. J. Food Res. 2020, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Ni, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Gao, H. Characteristic-aroma-component-based evaluation and classification of strawberry varieties by aroma type. Molecules 2021, 26, 6219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.L.; Zhang, Y.T.; Dong, J.; Sun, R.; Sun, J.; Zhong, C.F.; Zhang, H.L.; Zheng, S.Q.; Wang, G.X. Volatile components in three strawberry cultivars with white flesh. Acta Hortic. 2021, 1309, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogay, G.; Ürün, İ.; Attar, Ş.H.; Kafkas, S.; Kafkas, N.E. Identification of volatile compounds of Turkish local strawberry genotypes using various extraction techniques by GC/MS. Acta Hortic. 2021, 1309, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Hasing, T.; Johnson, T.S.; Garner, D.M.; Schwieterman, M.L.; Barbey, C.R.; Colquhoun, T.A.; Sims, C.A.; Resende, M.F.R.; Whitaker, V.M. Strawberry sweetness and consumer preference are enhanced by specific volatile compounds. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubrow, G.A.; Forero, D.P.; Peterson, D.G. Identification of volatile compounds correlated with consumer acceptability of strawberry preserves: Untargeted GC-MS analysis. Food Chem. 2022, 378, 132043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żary-Sikorska, E.; Kosmala, M.; Milala, J.; Fotschki, B.; Ognik, K.; Juśkiewicz, J. Concentrations of blood serum and urinal ellagitannin metabolites depend largely on the post-intake time and duration of strawberry phenolics ingestion in rats. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2019, 69, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes, L.; Martínez-Ferri, E.; Soria, C.; Ariza, M.T. Bioavailability of phenolic compounds in strawberry, raspberry and blueberry: Insights for breeding programs. Food Biosci. 2020, 37, 100680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariza, M.T.; Reboredo-Rodriguez, P.; Cervantes, L.; Soria, C.; Martinez-Ferri, E.; Gonzalez-Barreiro, C.; Cancho-Grande, B.; Battino, M.; Simal-Gandara, J. Bioaccessibility and potential bioavailability of phenolic compounds from achenes as a new target for strawberry breeding programs. Food Chem. 2018, 248, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milosavljevic, D.M.; Mutavdzic, D.R.; Radotic, K.; Milivojevic, J.M.; Maksimovic, V.M.; Dragisic Maksimovic, J.J. Phenolic profiling of 12 strawberry cultivars using different spectroscopic methods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 4346–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Zhao, Q.; Xu, D.; Jin, Y.; Wu, F.; Jin, Z.; Xu, X. Volatile compounds in Chinese steamed bread influenced by fermentation time, yeast level and steaming time. LWT 2021, 141, 110861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, C.N.; Qin, D.D.; Cai, H.L.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.H.; Li, W.J.; Yang, P.X.; Wu, H.L. Flavor compounds in Ning black tea by QDA and GC-MS combined with PLSR. Food Ferment. Ind. 2021, 47, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ma, S.; Wang, M.; Feng, X.Y. Characterization of free, conjugated, and bound phenolic acids in seven commonly consumed vegetables. Molecules 2017, 22, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caridi, F.; Mottese, A.F.; Messina, M.; D’Agostino, M. Fatty acids evaluation by principal component analysis for the traceability of Sicilian and Calabrian olive oils. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2021, 17, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhandy, D.; Yulia, M. Rapid authentication of stingless bees (Heterotrigonaitama) honey by UV spectroscopy and hierarchical cluster analysis. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1024, 012064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M. KEGG for taxonomy-based analysis of pathways and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D587–D592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmatuzzaman Rana, M.; Babor, M.; Sabuz, A.A. Traceability of sweeteners in soy yogurt using linear discriminant analysis of physicochemical and sensory parameters. J. Agric. Food Res. 2021, 5, 100155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Bakain, R.Z.; Al-Degs, Y.S.; Cizdziel, J.V.; Elsohly, M.A. Linear discriminant analysis based on gas chromatographic measurements for geographical prediction of USA medical domestic cannabis. Acta Chromatogr. 2021, 33, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouelenein, D.; Mustafa, A.M.; Angeloni, S.; Borsetta, G.; Vittori, S.; Maggi, F.; Sagratini, G.; Caprioli, G. Influence of freezing and different drying methods on volatile profiles of strawberry and analysis of volatile compounds of strawberry commercial jams. Molecules 2021, 26, 4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Quintana, L.; Ramos, P. Chilean strawberry (Fragaria chiloensis): An integrative and comprehensive review. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, R.J.; Agyemang, D.; Curto, N.L.; Yusuf, A.; Chen, M.Z.; Janczuk, A.J. In-depth analysis of Ciflorette strawberries (Fragaria × ananassa ‘Ciflorette’) by multidimensional gas chromatography and gas chromatography-olfactometry. Flavour Fragr. J. 2015, 30, 302–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, D.; Kecke, S.; Olbricht, K. What Do We Know about the Chemistry of Strawberry Aroma? J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 3291–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Plotto, A.; Baldwin, E.; Rouseff, R. Evaluation of volatiles from two subtropical strawberry cultivars using GC–Olfactometry, GC-MS odor activity values, and Sensory Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 12569–12577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohloff, J. Impact of agricultural and environmental factors on strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) aroma—A review. Eur. J. Plant Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 5, 17–34. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Feng, H.; Xie, X.; Hao, F.; Zhang, L.; Fang, C. Volatile constituents and ellagic acid formation in strawberry fruits of selected cultivars. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prat, L.; Espinoza, M.I.; Agosin, E.; Silva, H. Identification of volatile compounds associated with the aroma of white strawberries (Fragaria chiloensis). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, A.H.; Pillet, J.; Plotto, A.; Bai, J.; Whitaker, V.M.; Folta, K.M. Identification of a strawberry flavor gene candidate using an integrated genetic-genomic-analytical chemistry approach. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Sevilla, J.F.; Cruz-Rus, E.; Valpuesta, V.; Botella, M.A.; Amaya, I. Deciphering gamma-decalactone biosynthesis in strawberry fruit using a combination of genetic mapping, RNA-Seq and eQTL analyses. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Sun, P.; Chen, L.; Gao, S.; Shao, W.; Li, J. Comparative analysis of fruit volatiles and related gene expression between the wild strawberry Fragaria pentaphylla and cultivated Fragaria × ananassa. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 244, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wein, M.; Lavid, N.; Lunkenbein, S.; Lewinsohn, E.; Schwab, W.; Kaldenhoff, R. Isolation, cloning and expression of a multifunctional O-methyltransferase capable of forming 2,5-dimethyl-4-methoxy-3(2H)-furanone, one of the key aroma compounds in strawberry fruits. Plant J. 2002, 31, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hadi, M.A.; Zhang, F.J.; Wu, F.F.; Zhou, C.H.; Tao, J. Advances in fruit aroma volatile research. Molecules 2013, 18, 8200–8229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Loftus, H.; McAinch, A.J.; Su, X.Q. Blueberry as a source of bioactive compounds for the treatment of obesity, type 2 diabetes and chronic inflammation. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 30, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.M.; Angeloni, S.; Abouelenein, D.; Acquaticci, L.; Xiao, J.; Sagratini, G.; Maggi, F.; Vittori, S.; Caprioli, G. A new HPLC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of 36 polyphenols in blueberry, strawberry and their commercial products and determination of antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2022, 367, 130743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha Filho, M.; Araujo Filho, R.N.; Cunha, A.L.X.; Piscoya, V.C.; Moreira, G.R.; Lima, I.d.S.; Da Silva, R.D.; Pimentel, R.M.d.M.; Lima, D.d.S.; Marinho Junior, J.L.; et al. Use of multivariate statistical methods for classification of olive oil. J. Environ. Anal. Prog. 2021, 6, 035–043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrama, L.; Valderrama, P.; Carasek, E. A semi-quantitative model through PLS-DA in the evaluation of carbendazim in grape juices. Food Chem. 2022, 368, 130742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.-W.; Yin, X.-L.; Peng, T.-Q.; Pan, Y.; Cui, H.-N.; Li, Z.-Q.; Sun, W.; Ding, B.; Hu, X.-C.; Zhang, Z.-H.; et al. Geographical origin identification and chemical markers screening of Chinese green tea using two-dimensional fingerprints technique coupled with multivariate chemometric methods. Food Control 2022, 135, 108795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, D.; He, Y.; Cao, J.; Li, X. Identification of the age of white tea using proton transfer reaction time-of-flight mass spectrometry (PTR-TOF-MS) coupled with multivariate analysis. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 36, e9215(3). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Tao, H.; Song, J.; Xu, C.; Sun, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H. Composition differences and quality characteristics of Pu’an black tea with different grades. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2022, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Ma, H.; Li, R.; Yang, S.; Qiao, R.; Zhong, P. Metabolic analysis of aroma components in two interspecific hybrids from the cross of F. ananassa Duch. and Fragaria nilgerrensis Schlecht. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2021, 54, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, P.; Hu, H.W.; Cui, A.H.; Tang, H.J.; Liu, Y.G. HS-GC-IMS with PCA to analyze volatile flavor compounds of honey peach packaged with different preservation methods during storage. LWT 2021, 149, 111963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, A.S.; Ranadheera, C.S.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Warner, R.; Ajlouni, S. Using biological metabolites as biomarkers to predict safety and quality of whole and minimally processed spinach. Food Chem. 2022, 375, 131870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gießel, J.M.; Loesche, A.; Hoenke, S.; Csuk, R. In search of new cinnamic acid derived flavours and fragrances. Results Chem. 2019, 1, 100010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, L.; Wang, X.; Hao, J.; Zhu, N.; Wang, M. Geographical Indication Characteristics of Aroma and Phenolic Acids of the Changping Strawberry. Foods 2023, 12, 3889. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12213889
Wu L, Wang X, Hao J, Zhu N, Wang M. Geographical Indication Characteristics of Aroma and Phenolic Acids of the Changping Strawberry. Foods. 2023; 12(21):3889. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12213889
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Linxia, Xinlu Wang, Jianqiang Hao, Ning Zhu, and Meng Wang. 2023. "Geographical Indication Characteristics of Aroma and Phenolic Acids of the Changping Strawberry" Foods 12, no. 21: 3889. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12213889
APA StyleWu, L., Wang, X., Hao, J., Zhu, N., & Wang, M. (2023). Geographical Indication Characteristics of Aroma and Phenolic Acids of the Changping Strawberry. Foods, 12(21), 3889. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12213889





