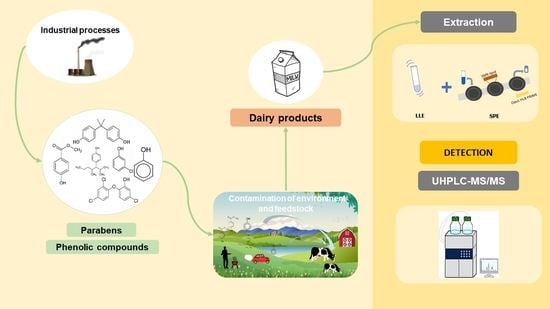
Determination of Parabens and Phenolic Compounds in Dairy Products through the Use of a Two-Step Continuous SPE System Including an Enhanced Matrix Removal Sorbent in Combination with UHPLC−MS/MS
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Analytes a | Samples | Sample Treatment b | Technique c | Analytical Figures of Merit d | Concentrations Found in Real Samples | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPA, parabens, and other plasticisers | Milk | MSPD | HPLC–MS/MS | LOQ 0.91–4.4 ng/kg RSD < 14% | BPA 1.8–59 ng/kg | [7] |
| BPF, BPE, BPB, BPA, and diglycidyl ether | Breast milk | SPE, QuEChERS | HPLC–FLD | LOD 57,000–78,000 ng/L RSD 1.0–14% R 57–88% | n.d. | [16] |
| BPA and BPF | Milk | SPE | HPLC–FLD | LOD 30 ng/L RSD 1.0–14.8% R 98–107% | BPF 1020–2690 ng/L | [17] |
| BPA, BPB, BPF, BPZ, BPS, and other bisphenol analogues | Yogurt | QuEChERS | CG–MS | LOQ 170 ng/kg | n.d. | [21] |
| Phenol, alkyphenols, chlorophenols, and bisphenols | Dairy products | SPE | CG/MS | LOD 6–63 ng /L RSD 2.4–11% R 85–108% | BPA 30–1400 ng/kg BPZ 96–1100 ng/kg BPF 270–950 ng/kg Nonylphenol 56–390 ng/kg 4-tert-Butylphenol 310–2100 ng/kg 3.4-Dimethylphenol 130–2300 ng/kg 4-Pentylphenol 190–990 ng/kg 2-Phenylphenol 320 ng/kg | [22] |
| 4-Chlorophenol, 4-tert-butylphenol, 4-tert-octylphenol, and other phenols | Milk | EA–SPME | GC–FID | LOD 1–30 ng/L RSD 3.8–12.4% R 88–119% | 4-tert-Butylphenol 850 ng/L 4-Chlorophenol n.d. 4-tert-Octylphenol n.d. | [23] |
| BPA, BPB, and other bisphenol analogues | Milk | QuEChERS | HPLC–FLD | LOD 1000–3100 ng/L RSD 9.1–16% R 86–99% | BPA 1374 ng/kg | [24] |
| BPA, BPF, BPS, and parabens | Breast milk | QuEChERS | HPLC–MS/MS | LOQ 100–250 ng/L RSD 5–16% R 83–115% | BPA 130–1 620 ng/L BPF 130–320 ng/L BPS 370 ng/L Parabens 130–4050 ng/L | [25] |
| BPA, nonylphenol, and 4-ter-octylphenol | Milk | MSPD | HPLC–MS/MS | LOD 50–100 ng/kg RSD 1.4–7.8% R 84–103% | BPA 490 ng/kg Nonylphenol 100 ng/kg 4-ter-Octylphenol 4240–17,600 ng/kg | [26] |
| BPA, BPB, BPF, BPS, and other bisphenol analogues | Breast milk and sweetened condensed milk | QuEChERS | HPLC–DAD/ HPLC–MS/MS | LOQ 100–250 ng/L RSD 8–17% R 35–102% | BPA 230–690 ng/L BPS 290–680 ng/L BPF 220–290 ng/L | [27] |
| Parabens, TCS, BPA, nonylphenol, 4-tert-octylphenol, and other phenols | Breast milk | SPE | CG/MS | LOD 1–9 ng /L RSD 4.4–7.0% R 86–104% | Phenols 550–5600 ng/L BPA 1400–2900 ng/L Parabens 15–8100 ng/L | [30] |
| BPA | Milk | DMSPE | HPLC–UV | LOD 3 050 ng/L RSD 9.1–16% R 86–99% | n.d.e | [34] |
| BPA, BPF, BPAF, and 4-chlorophenol | Milk | UA–DLLME | HPLC–UV | LOD 250–1000 ng/L RSD 0.67–13.7% R 83–119% | n.d. | [35] |
| BPA and BPS | Milk | LLE | PSI–MS | LOD 1500–4800 ng /L RSD 5.9–18.9% R 74–112% | BPA 77,600–150,800 ng/L BPS 60,000 ng/L | [36] |
| Nonylphenol, 4-tert-octylphenol and BPA | Dairy products | UA–DLLME | HPLC–FLD | LOD 10–40 ng/kg RSD 2.8–8.8% R 83–112% | BPA 800–128,700 ng/kg Nonylphenol 3500–36,700 ng/kg 4-tert-Octylphenol 300–29,500 ng/kg | [37] |
| BPA, BPB, BPF, BPZ, 4-tert-octylphenol, and nonylphenol | Milk | QuEChERS | UHPLC–MS/MS HPLC–FLD | LOD 200–1500 ng/L | BPA 500–5600 ng/L BPF 500–8700 ng/L | [38] |
| BPA, BPS, BPAF, BPF and parabens | Breast milk | QuEChERS | HPLC–MS/MS | LOD 10–200 ng/L RSD 1.0–7.9% R 77–100% | BPA 990–1910 ng/L BPS 60–200 ng/L BPAF 60–70 ng/L BPF n.d. Parabens 30–1520 ng/L | [39] |
| Parabens, phenol, alkylphenols, chlorophenols and bisphenols | Dairy products | Continuous SPE | HPLC–MS/MS | LOD 1–20 ng/kg RSD 2.0–11.4% R 91–105% | BPA 33–580 ng/kg BPZ 24–57 ng/kg Nonylphenol 34–210 ng/kg 4-tert-Butylphenol 21–220 ng/kg 4-Chlorophenol 50–160 ng/kg Pentachlorophenol 35–76 ng/kg Parabens 9–470 ng/kg | This work |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
2.2. Equipment
2.3. Sampling
2.4. Sample Treatment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sample Treatment Optimization
3.2. UHPLC−MS/MS Analysis
3.3. Validation of the Method
3.4. Application to Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food. Milk Month by Month. Catalog of Publications of the General State. 2021. Available online: https://www.mapa.gob.es/es/alimentacion/temas/consumo-tendencias/la-leche-mes-a-mes-agosto-2021_tcm30-581083.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2023).
- Vale, F.; Sousa, C.A.; Sousa, H.; Santos, L.; Simoes, M. Parabens as emerging contaminants: Environmental persistence, current practices and treatment processes. J. Clean. Produ. 2022, 347, 131244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Ma, N. Determination of organophosphorus in dairy products by graphitic carbon nitride combined molecularly imprinted microspheres with ultra performance liquid chromatography. Food Chem. 2022, 15, 100424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, W.; Guo, W.; Li, Y.; Jiang, R.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Li, Z. Simultaneous screening and analysis of 155 veterinary drugs in livestock foods using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem quadrupole linear-ion-trap mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.H.; Li, N.; Jiang, H.L.; Lin, J.M.; Zhao, R.S. Pretreatmetechniques and analytical methods for phenolic endocrine disrupting chemicals in food and environmental samples. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 119, 115592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Wang, Z.; Pan, Y.; Wang, H.; Sun, L.; Liu, L.; Zhong, W.J.; Zhang, W.B. Associations between mixed urinary phenols and parabens metabolites and bone mineral density: Four statistical models. Chemosphere 2023, 31, 137065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, L.; Quintanilla-López, J.E.; Fernández, M.A.; Gómara, B. Plasticisers and preservatives in commercial milk products: A comprehensive study on packages used in the Spanish market. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 128031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iribarne-Durán, L.M.; Serrano, L.; Peinado, F.M.; Peña-Caballero, M.; Hurtado, J.A.; Vela-Soria, F.; Fernández, M.F.; Freire, C.; Artacho-Cordóng, F.; Olea, N. Biomonitoring bisphenols, parabens, and benzophenones in breast milk from a human milk bank in Southern Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farajzadeh, M.A.; Nemati, M.; Altunay, N.; Tuzen, M.; Kaya, S.; Kheradmand, F. Experimental and density functional theory studies during a new solid phase extraction of phenolic compounds from wastewater samples prior to GC–MS determination. Microchem. J. 2022, 177, 107291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marazuela, M.D.; Klaiber, M.; Moreno-Gordaliza, E.; Barata, A.; Gómez-Gómez, M.M. Safety assessment of commercial antimicrobial food packaging: Triclosan and microplastics, a closer look. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 31, 100780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero-Casero, N.; Lunar, L.; Rubio, S. Analytical methods for the determination of mixtures of bisphenols and derivatives in human and environmental exposure sources and biological fluids. A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 908, 22–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Lei, M.; Li, J.; Zhao, K.; Liu, Y. Sensitive determination of bisphenol A, 4-nonylphenol and 4-octylphenol by magnetic solid phase extraction with Fe@MgAl-LDH magnetic nanoparticles from environmental water samples. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 182, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjei, J.K.; Ofori, A.; Megbenu, H.K.; Ahenguah, T.; Boateng, A.K.; Adjei, G.; Bentum, J.K.; Essumang, D.K. Health risk and source assessment of semi-volatile phenols, p-chloroaniline and plasticizers in plastic packaged (sachet) drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 149008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Bisphenol A: EFSA Draft Opinion Proposes Lowering the Tolerable Daily Intake. European Food Safety Agency. 2021. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/news/bisphenol-efsa-draft-opinion-proposes-lowering-tolerable-daily-intake (accessed on 30 June 2023).
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) 2018/213 of 12 February 2018 on the use of bisphenol A in varnishes and coatings intended to come into contact with food and amending Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 as regards the use of that substance in plastic food contact. Off. J. Eur. Community 2018, L41, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Tuzimski, T.; Szubartowski, S. Application of d-SPE before spe and HPLC-FLD to analyze bisphenols in human breast milk samples. Molecules 2021, 26, 4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santonicola, S.; Albrizio, S.; Ferrante, M.C.; Mercogliano, R. Study on bisphenol F, a bisphenol A analogue, at a dairy company: Health hazard and risk assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 154, 112334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 of 14 January 2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food. Off. J. Eur. Community 2011, L12, 1–89. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Appendix A to 40 CFR, Part 423—126 Priority Pollutants; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. Available online: https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-40/chapter-I/subchapter-N/part-423/appendix-Appendix%20A%20to%20Part%20423 (accessed on 30 June 2023).
- USEPA. Contaminant Candidate List (CCL) and Regulatory Determination. Chemical Contaminants—CCL 4. Final CCL 4 Chemical Contaminants. 2022. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ccl/chemical-contaminants-ccl-4 (accessed on 30 June 2023).
- González, N.; Cunha, S.C.; Ferreira, R.; Fernandes, J.O.; Marqués, M.; Nadal, M.; Domingo, J.L. Concentrations of nine bisphenol analogues in food purchased from Catalonia (Spain): Comparison of canned and non-canned foodstuffs. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 136, 110992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios Colón, L.; Rascón, A.J.; Ballesteros, E. Simultaneous determination of phenolic pollutants in dairy products held in various types of packaging by gas chromatography−mass spectrometry. Food Control 2023, 146, 109564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Dang, X.; Dai, J.; Hu, Y.; Chen, H. Simultaneous detection of eight phenols in food contact materials after electrochemical assistance solid-phase microextraction based on amino functionalized carbon nanotube/polypyrrole composite. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1183, 338981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Yan, P.; Chu, M.; Gao, Y.Q.; Li, W.H.; Yang, X.L. A rapid and simple HPLC–FLD screening method with QuEChERS as the sample treatment for the simultaneous monitoring of nine bisphenols in milk. Food Chem. 2018, 244, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dualde, P.; Pardo, O.F.; Fernández, S.; Pastor, A.; Yusà, V. Determination of four parabens and bisphenols A, F and S in human breast milk using QuEChERS and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1114–1115, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, B.; Han, H.; Tu, X.; Huang, L. Analysis of alkylphenol and bisphenol A in eggs and milk by matrix solid phase dispersion extraction and liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 850, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuzimski, T.; Szubartowski, S. Method development for selected bisphenols analysis in sweetened condensed milk from a can and breast milk samples by HPLC–DAD and HPLC-QQQ-MS: Comparison of sorbents (Z-Sep, Z-Sep plus, PSA, C18, Chitin and EMR-lipid) for clean-up of QuEChERS extract. Molecules 2019, 24, 2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Bishop, A.M.; Needham, L.L.; Calafat, A.M. Automated on-line column-switching HPLC-MS/MS method with peak focusing for measuring parabens, triclosan, and other environmental phenols in human milk. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 622, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, N.; Xu, X.; Bao, T. Novel solid-phase extraction filter based on a zirconium meta-organic framework for determination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs residues. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1652, 462349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzouz, A.; Rascón, A.J.; Ballesteros, E. Simultaneous determination of parabens, alkylphenols, phenylphenols, bisphenol A and triclosan in human urine, blood and breast milk by continuous solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 119, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla-Fernández, D.; Moreno-González, D.; Beneito-Cambra, M.; Molina-Díaz, A. Critical assessment of two sample treatment methods for multiresidue determination of veterinary drugs in milk by UHPLC-MS/MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 1433–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Yuan, B.; Lyu, W.; Huang, Q.; Simon, J.E.; Wu, Q. Method development and validation for analysis of phenolic compounds in fatty complex matrices using enhanced matrix removal (EMR) lipid cleanup and UHPLC-QqQ-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Lukas, D. Multiresidue Analysis of Veterinary Drugs in Bovine Liver by LC/MS/MS Agilent Bond Elut Enhanced Matrix Removal—Lipid, Agilent Technologies Application Note. 2015. Available online: https://www.agilent.com/cs/library/applications/5991-6096EN.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2023).
- Reyes-Gallardo, E.M.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M. Dispersive micro-solid phase extraction of bisphenol A from milk using magnetic nylon 6 composite and its final determination by HPLC-UV. Microchem. J. 2016, 124, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Sun, R.; Tao, Y.; Yan, Y. New low viscous hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for the ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction of endocrine-disrupting phenols in water, milk and beverage. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1662, 462728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuszewski, B.K.; Constanzer, M.L.; Chavez-Eng, C.M. Strategies for the assessment of matrix effect in quantitative bioanalytical methods based on HPLC-MS/MS. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 3019–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, T.; Zhao, X.E.; Zhu, S.; Qu, F.; Song, C.; You, J.; Suo, Y. Determination of bisphenol A, 4-octylphenol, and 4-nonylphenol in soft drinks and dairy products by ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with derivatization and high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 2757–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marco Pisciottano, I.; Guadagnuolo, G.; Busico, F.; Alessandroni, L.; Neri, B.; Vecchio, D.; Di Vuolo, G.; Cappelli, G.; Martucciello, A.; Gallo, P. Determination of 20 endocrine-disrupting compounds in the buffalo milk production chain and commercial bovine milk by UHPLC–MS/MS and HPLC–FLD. Animals 2022, 12, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czarczynska-Goslinska, B.; Grzeskowiak, T.; Frankowski, R.; Lulek, J.; Pieczak, J.; Zgoła-Grzeskowiak, A. Determination of bisphenols and parabens in breast milk and dietary risk assessment for Polish breastfed infants. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2021, 98, 103839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz Hornillos, M.; Yoldi Bienzobas, G. Leche y derivados. In Alimentos Composición y Propiedades; Astiasarán, I., Anchía, J.A., Hernández, M., Eds.; McGraw-Hill–Interamericana de España, S.A.U: Madrid, Spain, 2003; pp. 69–108. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, C.; Kannan, K. Concentrations and profiles of bisphenol A and other bisphenol analogues in foodstuffs from the United States and their implications for human exposure. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 4655–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Almeida Soares, D.; Pereira, I.; Sousa, J.C.P.; Bernardo, R.A.; Simas, R.C.; Vaz, B.G.; Chaves, A.R. Bisphenol determination in UHT milk and packaging by paper spray ionization mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2023, 400, 134014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Compounds | tR a | Precursor (m/z) | Quantification Peak (m/z) | Collision Energy (V) | Confirmation Peak (m/z) | Collision Energy (V) | RF Lens (V) | LOD b (ng/kg) | Linearity (ng/kg) | r2 c | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parabens | Methylparaben | 4.63 | 152.2 | 93.0 | 21.0 | 137.0 | 14.1 | 56.0 | 1.0 | 3.3–20,000 | 0.997 |
| Ethylparaben | 6.57 | 166.2 | 93.0 | 22.6 | 138.0 | 14.0 | 50.0 | 1.0 | 3.4–20,000 | 0.996 | |
| Isopropylparaben | 9.48 | 179.3 | 93.0 | 21.6 | 137.0 | 14.3 | 49.6 | 1.0 | 3.3–20,000 | 0.994 | |
| Butylparaben | 9.66 | 197.0 | 129.1 | 11.7 | 178.1 | 12.5 | 51.8 | 1.1 | 3.6–20,000 | 0.996 | |
| Propylparaben | 10.11 | 180.2 | 93.0 | 23.3 | 92.0 | 23.8 | 53.8 | 1.1 | 3.6–20,000 | 0.995 | |
| Isobutylparaben | 15.29 | 193.2 | 92.0 | 24.8 | 137.1 | 15.7 | 51.3 | 10 | 34–20,000 | 0.997 | |
| Benzylparaben | 16.42 | 227.1 | 92.0 | 24.1 | 136.1 | 14.9 | 50.1 | 1.0 | 3.3–20,000 | 0.998 | |
| Phenols | Pentylphenol | 0.74 | 165.0 | 96.9 | 10.3 | 78.9 | 26.7 | 37.4 | 1.1 | 3.5–20,000 | 0.997 |
| 4-Chloro-3-methylphenol | 0.97 | 141.0 | 35.0 | 19.1 | 105.0 | 16.7 | 62.4 | 10 | 34–20,000 | 0.994 | |
| 4-tert-Octylphenol | 1.15 | 209.1 | 96.9 | 15.0 | 78.9 | 34.1 | 65.8 | 10 | 35–20,000 | 0.994 | |
| Phenol | 1.27 | 91.1 | 45.0 | 10.3 | 89.4 | 55.0 | 206.5 | 10 | 34–20,000 | 0.999 | |
| 4-tert-Butylphenol | 1.48 | 147.1 | 61.9 | 11.4 | 46.0 | 45.2 | 35.7 | 1.1 | 3.5–20,000 | 0.995 | |
| Nonylphenol | 1.59 | 219.1 | 172.9 | 10.3 | 171.0 | 19.9 | 80.9 | 1.1 | 3.6–20,000 | 0.998 | |
| 2-tert-Butyl-4-methylphenol | 1.69 | 147.1 | 61.9 | 13.9 | 89.0 | 12.8 | 30.0 | 1.0 | 3.3–20,000 | 0.997 | |
| Bisphenol F | 1.82 | 198.0 | 130.1 | 10.3 | 171.1 | 10.8 | 30.0 | 10 | 34–20,000 | 0.994 | |
| 3.4-Dimethylphenol | 3.44 | 121.0 | 77.0 | 13.1 | 91.9 | 23.5 | 52.8 | 20 | 65–20,000 | 0.995 | |
| 2.5-Dimethylphenol | 3.66 | 121.0 | 76.9 | 10.9 | 91.9 | 25.8 | 49.8 | 10 | 33–20,000 | 0.997 | |
| 4-Phenylphenol | 4.19 | 169.0 | 19.2 | 32.6 | 69.0 | 54.1 | 38.7 | 1.0 | 3.3–20,000 | 0.995 | |
| 2-Phenylphenol | 4.36 | 169.1 | 19.3 | 41.9 | 150.9 | 13.8 | 48.3 | 1.1 | 3.6–20,000 | 0.997 | |
| Bisphenol S | 4.51 | 249.1 | 108.0 | 28.0 | 92.0 | 35.3 | 109.1 | 1.0 | 3.4–20,000 | 0.997 | |
| 4-Chlorophenol | 7.11 | 127.0 | 35.1 | 19.3 | 91.0 | 17.6 | 60.4 | 7.0 | 23–20,000 | 0.994 | |
| 4-Hexylphenol | 16.74 | 177.1 | 148.0 | 16.0 | 149.1 | 16.8 | 158.8 | 10 | 34–20,000 | 0.995 | |
| Bisphenol A | 16.89 | 221.1 | 205.2 | 30.2 | 164.0 | 25.2 | 115.8 | 5.1 | 17–20,000 | 0.996 | |
| Bisphenol B | 19.08 | 241.1 | 225.0 | 10.2 | 223.0 | 10.2 | 68.6 | 5.0 | 16–20,000 | 0.994 | |
| 4-Heptylphenol | 19.54 | 195.3 | 179.1 | 19.9 | 167.0 | 16.0 | 78.7 | 7.0 | 23–20,000 | 0.996 | |
| Bisphenol Z | 20.48 | 267.1 | 173.1 | 27.0 | 223.0 | 32.6 | 100.7 | 5.0 | 17–20,000 | 0.994 | |
| Pentachlorophenol | 25.8 | 264.8 | 35.0 | 55.0 | 97.0 | 27.4 | 125.4 | 10 | 34–20,000 | 0.994 | |
| Triclosan | 25.36 | 289.0 | 35.04 | 10.3 | 37.1 | 10.2 | 45.1 | 1.0 | 3.3–20,000 | 0.996 | |
| Triphenylphosphate (IS) | 27.54 | 337.3 | 96.9 | 32.7 | 79.9 | 46.5 | 122.9 | ||||
| Compounds | RSD (%) a | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milk | Yogurt | Custard | Milkshake | Cream | Cheese | Butter | Margarine | ||||||||||
| Intraday | Interday | Intraday | Interday | Intraday | Interday | Intraday | Interday | Intraday | Interday | Intraday | Interday | Intraday | Interday | Intraday | Interday | ||
| Parabens | Methylparaben | 5.11 | 8.22 | 5.31 | 10.21 | 5.05 | 10.16 | 5.06 | 9.03 | 2.55 | 9.75 | 4.26 | 9.26 | 4.01 | 7.12 | 2.36 | 7.42 |
| Ethylparaben | 4.26 | 9.33 | 4.43 | 11.15 | 5.06 | 8.03 | 3.83 | 7.23 | 2.13 | 7.98 | 5.62 | 7.32 | 5.25 | 8.92 | 4.53 | 8.54 | |
| Isopropylparaben | 5.13 | 11.10 | 5.55 | 9.08 | 6.88 | 9.39 | 5.19 | 9.77 | 8.26 | 9.28 | 3.13 | 5.52 | 4.37 | 11.44 | 6.06 | 10.23 | |
| Butylparaben | 5.25 | 11.28 | 4.23 | 9.17 | 5.20 | 9.40 | 3.43 | 6.29 | 6.28 | 9.58 | 4.22 | 9.13 | 4.28 | 10.58 | 5.27 | 10.44 | |
| Propylparaben | 5.06 | 9.35 | 6.12 | 10.35 | 4.18 | 9.84 | 3.81 | 6.27 | 3.29 | 7.33 | 2.03 | 8.57 | 6.64 | 6.35 | 6.69 | 9.65 | |
| Isobutylparaben | 4.27 | 8.63 | 5.46 | 10.42 | 3.36 | 8.42 | 5.73 | 8.88 | 8.48 | 10.1 | 3.65 | 6.56 | 3.46 | 7.72 | 8.50 | 10.16 | |
| Benzylparaben | 3.19 | 9.46 | 5.88 | 9.44 | 4.32 | 8.03 | 6.52 | 9.06 | 5.55 | 9.08 | 4.42 | 9.04 | 4.56 | 6.96 | 4.04 | 6.34 | |
| Phenols | Pentylphenol | 3.00 | 7.78 | 7.20 | 9.46 | 3.54 | 10.04 | 5.06 | 10.03 | 4.23 | 9.17 | 5.82 | 11.02 | 5.83 | 7.38 | 6.68 | 8.43 |
| 4-Chloro-3-methylphenol | 5.34 | 9.50 | 4.25 | 8.58 | 4.07 | 10.15 | 2.82 | 9.52 | 6.12 | 10.35 | 5.25 | 7.24 | 5.62 | 8.54 | 4.52 | 8.06 | |
| 4-tert-Octylphenol | 4.16 | 8.44 | 2.13 | 7.40 | 6.48 | 9.35 | 8.07 | 10.44 | 5.46 | 10.42 | 6.52 | 8.33 | 5.75 | 8.94 | 3.06 | 8.03 | |
| Phenol | 3.42 | 7.65 | 5.52 | 9.06 | 4.27 | 10.13 | 5.08 | 8.32 | 7.26 | 11.03 | 3.21 | 7.75 | 3.06 | 6.25 | 2.82 | 9.82 | |
| 4-tert-Butylphenol | 5.15 | 11.16 | 5.06 | 10.03 | 3.33 | 9.23 | 2.24 | 9.66 | 4.28 | 9.44 | 4.27 | 8.24 | 7.52 | 9.18 | 7.07 | 9.44 | |
| Nonylphenol | 7.06 | 10.23 | 4.82 | 9.82 | 4.66 | 7.55 | 3.55 | 9.63 | 5.35 | 9.38 | 4.17 | 9.12 | 5.54 | 10.07 | 4.01 | 7.10 | |
| 2-tert-Butylphenol | 5.27 | 10.44 | 7.07 | 9.44 | 7.91 | 10.25 | 4.05 | 6.01 | 4.20 | 8.17 | 5.07 | 7.02 | 7.36 | 9.25 | 4.25 | 8.99 | |
| Bisphenol F | 4.69 | 9.65 | 4.08 | 8.22 | 4.12 | 8.02 | 3.06 | 8.03 | 2.93 | 7.89 | 4.56 | 6.45 | 3.12 | 6.32 | 5.37 | 11.04 | |
| 3,4-Dimehylphenol | 7.50 | 10.16 | 4.24 | 9.66 | 6.32 | 9.33 | 4.75 | 9.95 | 3.05 | 8.53 | 3.04 | 6.34 | 4.23 | 6.64 | 6.28 | 10.38 | |
| 2,5-Dimethylphenol | 3.56 | 7.76 | 3.55 | 9.13 | 7.84 | 10.07 | 9.41 | 7.91 | 5.27 | 10.26 | 4.68 | 9.43 | 4.45 | 6.87 | 7.64 | 6.33 | |
| 4-Phenylphenol | 5.23 | 10.31 | 6.13 | 9.21 | 6.86 | 8.25 | 8.02 | 4.12 | 6.38 | 10.39 | 4.75 | 5.24 | 3.32 | 7.02 | 4.46 | 8.70 | |
| 2-Phenylphenol | 4.45 | 9.22 | 7.26 | 11.03 | 4.12 | 7.32 | 9.06 | 6.32 | 5.20 | 11.40 | 3.37 | 7.25 | 3.55 | 9.74 | 5.56 | 7.95 | |
| Bisphenol S | 5.27 | 10.26 | 4.28 | 9.44 | 4.13 | 9.64 | 3.12 | 7.32 | 4.01 | 7.11 | 2.61 | 5.24 | 4.32 | 6.64 | 4.18 | 9.84 | |
| 4-Chlorophenol | 6.38 | 10.39 | 5.29 | 10.77 | 6.32 | 9.33 | 7.13 | 9.64 | 3.25 | 7.99 | 4.32 | 8.03 | 2.58 | 7.54 | 3.36 | 8.42 | |
| 4-Hexylphenol | 5.20 | 11.40 | 3.48 | 5.29 | 4.37 | 9.44 | 6.06 | 10.23 | 5.38 | 11.54 | 5.54 | 10.04 | 4.78 | 10.96 | 5.34 | 9.50 | |
| Bisphenol A | 4.18 | 8.84 | 3.86 | 6.27 | 3.28 | 10.58 | 9.82 | 4.66 | 5.98 | 9.38 | 5.07 | 10.15 | 7.63 | 9.68 | 7.26 | 11.03 | |
| Bisphenol B | 2.36 | 7.42 | 4.73 | 8.86 | 4.08 | 8.22 | 4.12 | 8.02 | 4.24 | 9.66 | 3.48 | 9.35 | 4.96 | 8.02 | 4.28 | 9.44 | |
| 4-Heptylphenol | 4.53 | 8.54 | 4.32 | 7.22 | 3.36 | 6.76 | 3.05 | 9.03 | 3.55 | 9.13 | 5.27 | 10.13 | 5.88 | 9.03 | 2.36 | 7.42 | |
| Bisphenol Z | 4.66 | 9.65 | 6.23 | 8.41 | 4.18 | 8.84 | 3.86 | 6.27 | 4.12 | 7.32 | 3.33 | 9.23 | 4.24 | 8.85 | 5.20 | 11.40 | |
| Pentachlorophenol | 4.48 | 9.27 | 3.44 | 5.58 | 2.61 | 4.24 | 4.32 | 6.64 | 3.18 | 8.84 | 8.91 | 11.30 | 5.85 | 7.23 | 6.38 | 10.39 | |
| Triclosan | 5.00 | 10.16 | 5.36 | 9.63 | 4.13 | 9.64 | 4.05 | 9.05 | 4.05 | 9.51 | 3.12 | 8.22 | 5.16 | 10.41 | 5.20 | 11.40 | |
| Compounds | Recoveries (% ± SD, n = 3) a | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milk | Yogurt | Cheese | Milkshake | Cream | Custard | Butter | Margarine | ||
| Parabens | Methylparaben | 102 ± 8 | 100 ± 9 | 91 ± 8 | 95 ± 6 | 95 ± 7 | 95 ± 7 | 94 ± 6 | 91 ± 9 |
| Ethylparaben | 103 ± 8 | 91 ± 6 | 95 ± 7 | 102 ± 7 | 102 ± 6 | 96 ± 9 | 98 ± 5 | 91 ± 9 | |
| Isopropylparaben | 95 ± 7 | 97 ± 5 | 95 ± 10 | 101 ± 6 | 101 ± 6 | 101 ± 9 | 104 ± 8 | 98 ± 10 | |
| Butylparaben | 100 ± 9 | 99 ± 4 | 99 ± 10 | 101 ± 10 | 104 ± 7 | 93 ± 6 | 100 ± 5 | 99 ± 5 | |
| Propylparaben | 104 ± 5 | 101 ± 6 | 95 ± 9 | 99 ± 9 | 99 ± 9 | 95 ± 6 | 104 ± 7 | 95 ± 9 | |
| Isobutylparaben | 96 ± 7 | 104 ± 7 | 105 ± 7 | 103 ± 9 | 99 ± 8 | 96 ± 11 | 99 ± 9 | 105 ± 7 | |
| Benzylparaben | 105 ± 6 | 105 ± 8 | 102 ± 8 | 91 ± 9 | 103 ± 6 | 95 ± 6 | 105 ± 5 | 100 ± 8 | |
| Phenols | Pentylphenol | 103 ± 9 | 103 ± 5 | 101 ± 6 | 99 ± 9 | 98 ± 8 | 101 ± 6 | 100 ± 8 | 96 ± 11 |
| 4-Chloro-3-methylphenol | 96 ± 6 | 93 ± 6 | 100 ± 5 | 101 ± 10 | 100 ± 8 | 94 ± 7 | 103 ± 8 | 96 ± 11 | |
| 4-tert-Octylphenol | 102 ± 7 | 92 ± 7 | 100 ± 5 | 96 ± 11 | 104 ± 8 | 95 ± 6 | 101 ± 8 | 106 ± 6 | |
| Phenol | 103 ± 9 | 97 ± 7 | 91 ± 8 | 100 ± 8 | 96 ± 6 | 95 ± 6 | 100 ± 7 | 103 ± 5 | |
| 4-tert-Butylphenol | 101 ± 6 | 98 ± 8 | 97 ± 9 | 104 ± 8 | 94 ± 7 | 91 ± 9 | 103 ± 6 | 91 ± 8 | |
| Nonylphenol | 100 ± 8 | 91 ± 9 | 94 ± 7 | 102 ± 7 | 95 ± 6 | 96 ± 11 | 102 ± 7 | 104 ± 8 | |
| 2-tert-Butylphenol | 104 ± 8 | 91 ± 9 | 95 ± 6 | 96 ± 6 | 100 ± 7 | 96 ± 6 | 103 ± 6 | 102 ± 7 | |
| Bisphenol F | 96 ± 11 | 99 ± 9 | 101 ± 6 | 96 ± 7 | 104 ± 7 | 96 ± 9 | 98 ± 8 | 97 ± 9 | |
| 3,4-Dimethylphenol | 105 ± 7 | 99 ± 8 | 101 ± 10 | 101 ± 9 | 91 ± 8 | 98 ± 5 | 93 ± 7 | 94 ± 7 | |
| 2,5-Dimethylphenol | 99 ± 8 | 103 ± 8 | 96 ± 9 | 98 ± 5 | 99 ± 5 | 104 ± 8 | 99 ± 9 | 98 ± 5 | |
| 4-Phenylphenol | 102 ± 7 | 102 ± 7 | 101 ± 8 | 103 ± 9 | 102 ± 6 | 98 ± 5 | 96 ± 6 | 99 ± 9 | |
| 2-Phenylphenol | 100 ± 7 | 96 ± 6 | 95 ± 6 | 103 ± 8 | 98 ± 5 | 99 ± 9 | 98 ± 8 | 96 ± 11 | |
| Bisphenol S | 98 ± 10 | 101 ± 9 | 106 ± 6 | 102 ± 7 | 95 ± 6 | 101 ± 8 | 94 ± 6 | 99 ± 9 | |
| 4-Chlorophenol | 99 ± 5 | 100 ± 7 | 103 ± 5 | 98 ± 5 | 99 ± 9 | 95 ± 6 | 102 ± 9 | 94 ± 7 | |
| 4-Hexylphenol | 102 ± 6 | 105 ± 8 | 96 ± 8 | 104 ± 8 | 96 ± 11 | 96 ± 6 | 102 ± 9 | 95 ± 6 | |
| Bisphenol A | 96 ± 9 | 101 ± 9 | 97 ± 7 | 98 ± 5 | 105 ± 7 | 98 ± 10 | 95 ± 7 | 100 ± 5 | |
| Bisphenol B | 101 ± 9 | 95 ± 7 | 97 ± 7 | 104 ± 8 | 98 ± 10 | 98 ± 5 | 105 ± 7 | 91 ± 8 | |
| 4-Heptylphenol | 96 ± 9 | 102 ± 6 | 97 ± 6 | 97 ± 5 | 95 ± 10 | 104 ± 8 | 98 ± 5 | 103 ± 9 | |
| Bisphenol Z | 95 ± 6 | 95 ± 8 | 103 ± 6 | 99 ± 4 | 99 ± 10 | 97 ± 9 | 105 ± 10 | 96 ± 11 | |
| Pentachlorophenol | 99 ± 9 | 95 ± 8 | 99 ± 8 | 99 ± 8 | 103 ± 5 | 94 ± 7 | 97 ± 8 | 105 ± 7 | |
| Triclosan | 102 ± 5 | 97 ± 9 | 90 ± 8 | 102 ± 7 | 96 ± 8 | 104 ± 8 | 91 ± 9 | 104 ± 8 | |
| Milk | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skimmed Cow’s Milk b | Semi-Skimmed Cow’s Milk | Semi-Skimmed Goat’S Milk | Semi-Skimmed Sheep’s Milk | Whole Cow’s Milk | ||||||||||||
| Detected compounds | Sample (Packaging Material) | 1 (MC) c | 2 (MC) | 3 (MC) | 4 (HDPE) | 1 (MC) | 2 (MC) | 3 (HDPE) | 4 (PET) | 1 (MC) | 2 (MC) | 1 (MC) | 1 (MC) | 2 e (MC) | 3 (PET) | 4 (HDPE) |
| Nonylphenol | - d | - | - | - | - | - | 130 ± 10 | 34 ± 3 | 210 ± 20 | - | 53 ± 4 | - | - | - | - | |
| 4-tert-butylphenol | 170 ± 10 | - | - | - | 81 ± 6 | 220 ± 20 | 110 ± 10 | 21 ± 1 | 220 ± 20 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Ethylparaben | 80 ± 6 | 63 ± 3 | 47 ± 4 | - | 33 ± 2 | - | - | - | 470 ± 40 | 300 ± 30 | 210 ± 20 | 300 ± 20 | - | - | - | |
| 4-Chlorophenol | 160 ± 10 | 110 ± 10 | 60 ± 5 | - | 50 ± 4 | - | - | - | 130 ± 10 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Propylparaben | - | - | - | - | - | 10 ± 1 | - | 9 ± 0.8 | 33 ± 3 | 24 ± 2 | 23 ± 2 | 30 ± 2 | - | - | - | |
| Benzyl-paraben | - | - | - | - | 31 ± 3 | 24 ± 2 | - | 33 ± 1 | 98 ± 9 | 90 ± 6 | 86 ± 6 | 130 ± 10 | - | - | - | |
| Bisphenol A | 130 ± 10 | 33 ± 3 | - | - | 67 ± 5 | - | - | - | 64 ± 5 | 99 ± 8 | 170 ± 10 | 580 ± 50 | 260 ± 20 | 190 ± 10 | 290 ± 20 | |
| Bisphenol Z | 33 ± 3 | 44 ± 4 | 41 ± 4 | 25 ± 2 | 35 ± 3 | 34 ± 3 | 24 ± 2 | 36 ± 3 | 57 ± 5 | 47 ± 4 | 45 ± 4 | 42 ± 3 | - | - | - | |
| Pentachlorophenol | - | - | - | - | - | 40 ± 3 | 35 ± 3 | 55 ± 5 | 40 ± 2 | - | 76 ± 6 | - | - | - | - | |
| Dairy Products | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milkshake | Yogurt | Cheese | Butter | Margarine | Cream | ||||||||||||
| Sheep | Cow | Cow | Sheep | ||||||||||||||
| Detected compounds | Sample (packaging material) | 1 (PET) | 2 (HDPE) | 3 (MC) | 1 (Glass) | 2 (Glass) | 3 (PS) | 4 (Glass) | 1 (PS) | 2 (PS) | 3 (PS) | 1 (PS) | 2 (PS) | 1 (PS) | 2 (PS) | 1 (MC) | 2 (MC) |
| Nonylphenol | - d | - | - | 43 ± 3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 98 ± 8 | 99 ± 7 | 49 ± 4 | - | - | |
| Bisphenol A | 360 ± 20 | 420 ± 40 | 370 ± 30 | - | - | 58 ± 5 | - | - | 150 ± 10 | - | 140 ± 10 | 50 ± 5 | 170 ± 10 | 160 ± 10 | 260 ± 20 | 450 ± 40 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palacios Colón, L.; Rascón, A.J.; Ballesteros, E. Determination of Parabens and Phenolic Compounds in Dairy Products through the Use of a Two-Step Continuous SPE System Including an Enhanced Matrix Removal Sorbent in Combination with UHPLC−MS/MS. Foods 2023, 12, 2909. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152909
Palacios Colón L, Rascón AJ, Ballesteros E. Determination of Parabens and Phenolic Compounds in Dairy Products through the Use of a Two-Step Continuous SPE System Including an Enhanced Matrix Removal Sorbent in Combination with UHPLC−MS/MS. Foods. 2023; 12(15):2909. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152909
Chicago/Turabian StylePalacios Colón, Laura, Andrés J. Rascón, and Evaristo Ballesteros. 2023. "Determination of Parabens and Phenolic Compounds in Dairy Products through the Use of a Two-Step Continuous SPE System Including an Enhanced Matrix Removal Sorbent in Combination with UHPLC−MS/MS" Foods 12, no. 15: 2909. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152909
APA StylePalacios Colón, L., Rascón, A. J., & Ballesteros, E. (2023). Determination of Parabens and Phenolic Compounds in Dairy Products through the Use of a Two-Step Continuous SPE System Including an Enhanced Matrix Removal Sorbent in Combination with UHPLC−MS/MS. Foods, 12(15), 2909. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152909