Inhibition of Fungal Growth and Aflatoxin B1 Synthesis in Aspergillus flavus by Plasma-Activated Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup and Methods
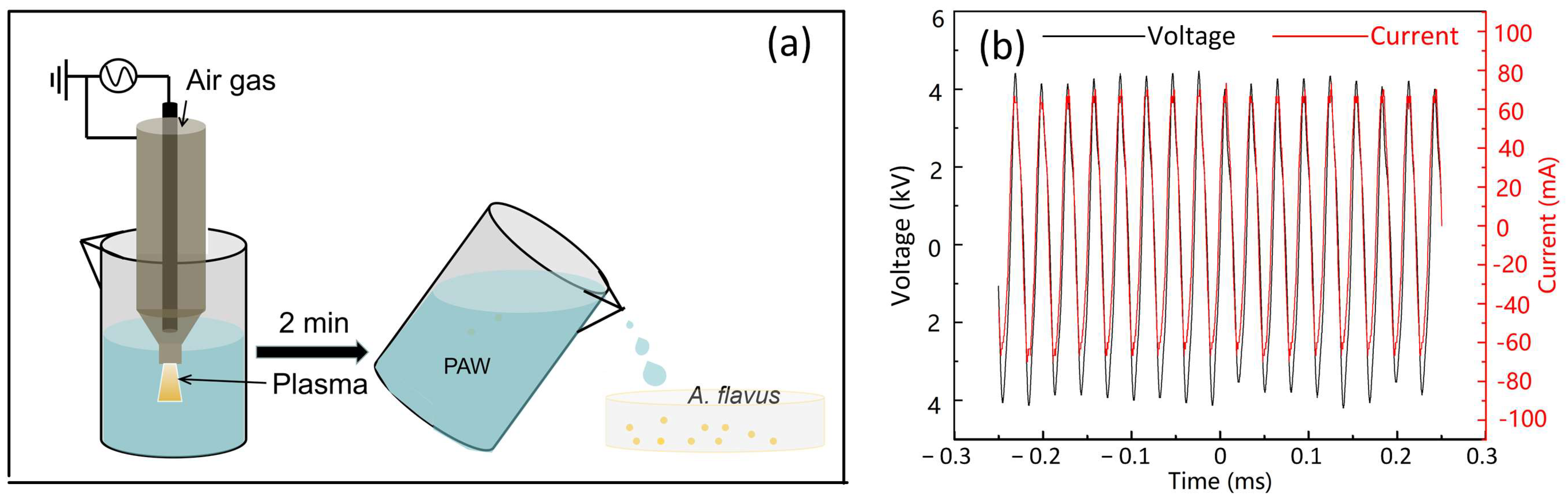
2.1. The Preparation of PAW
2.2. Measurements of Optical Emission Spectra
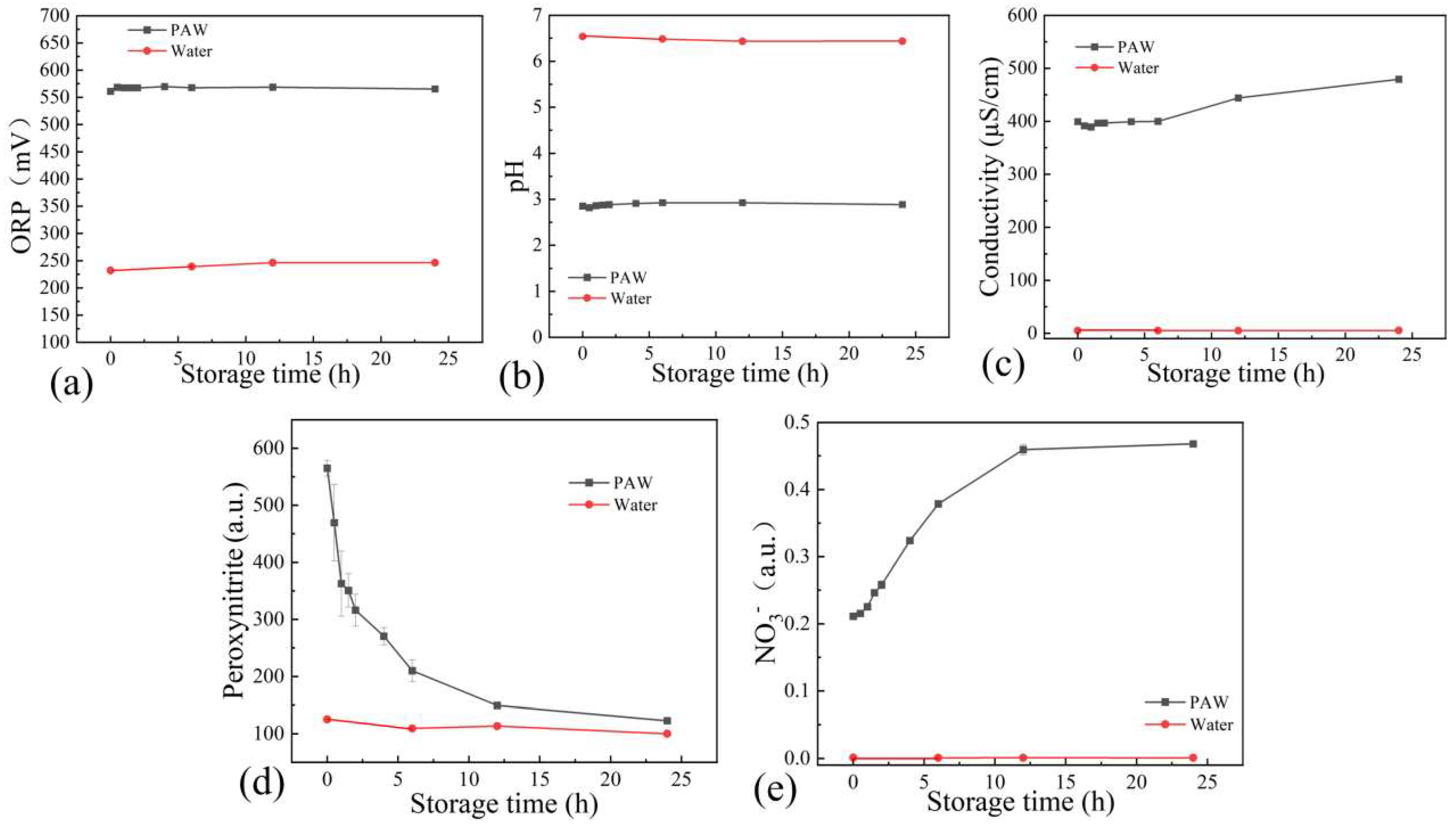
2.3. Measurements of pH, ORP, Electrical Conductivity, and ONOO− in PAW
2.4. The Culture of A. flavus Spores and Mycelium
2.5. Detection of A. flavus Inactivation Efficiency
2.6. Detection of Cell Membrane Integrity, Intracellular RNS and Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
2.7. Determination of AFB1 Concentration
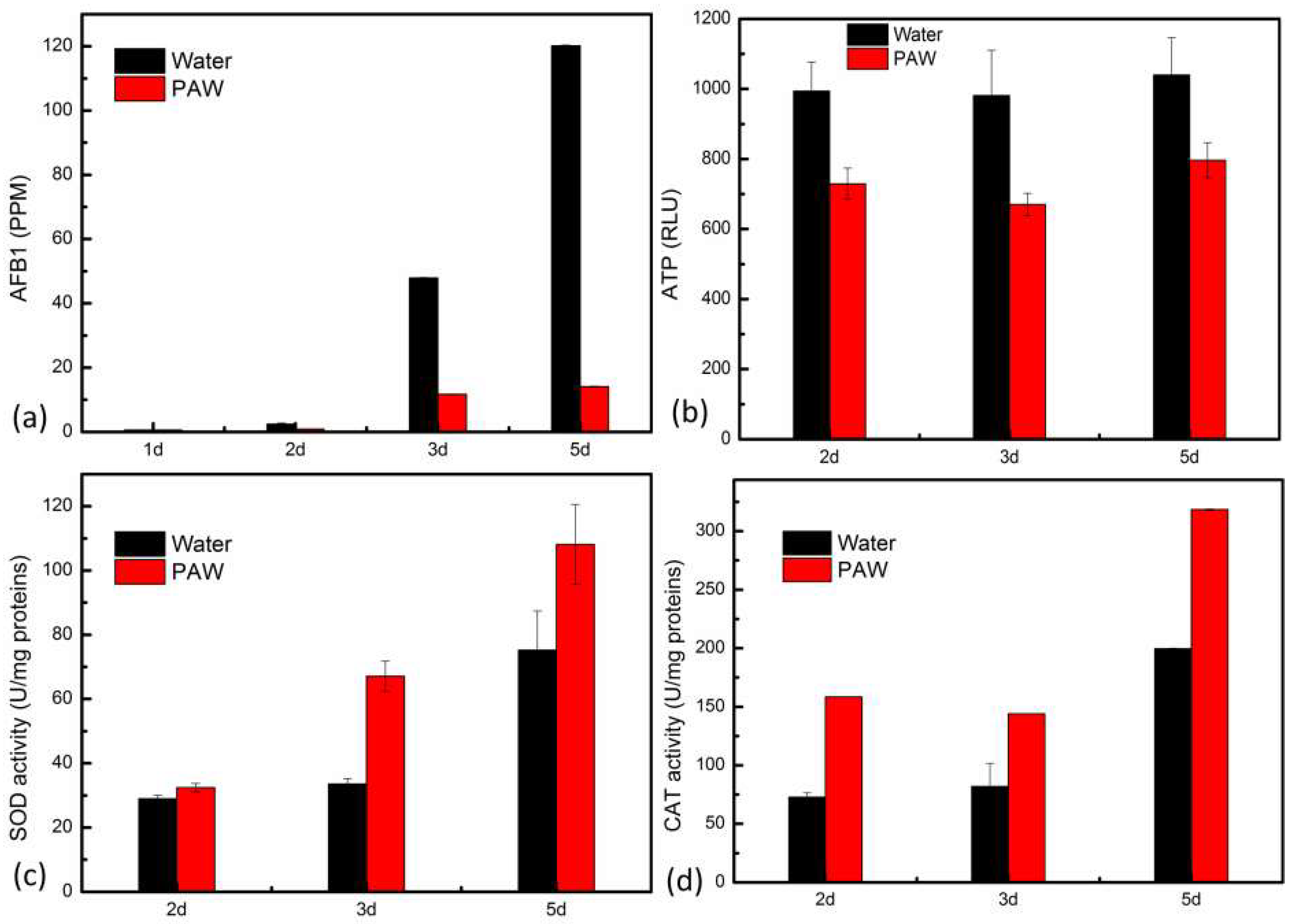
2.8. Determination of SOD Activity, CAT Activity, and ATP Content
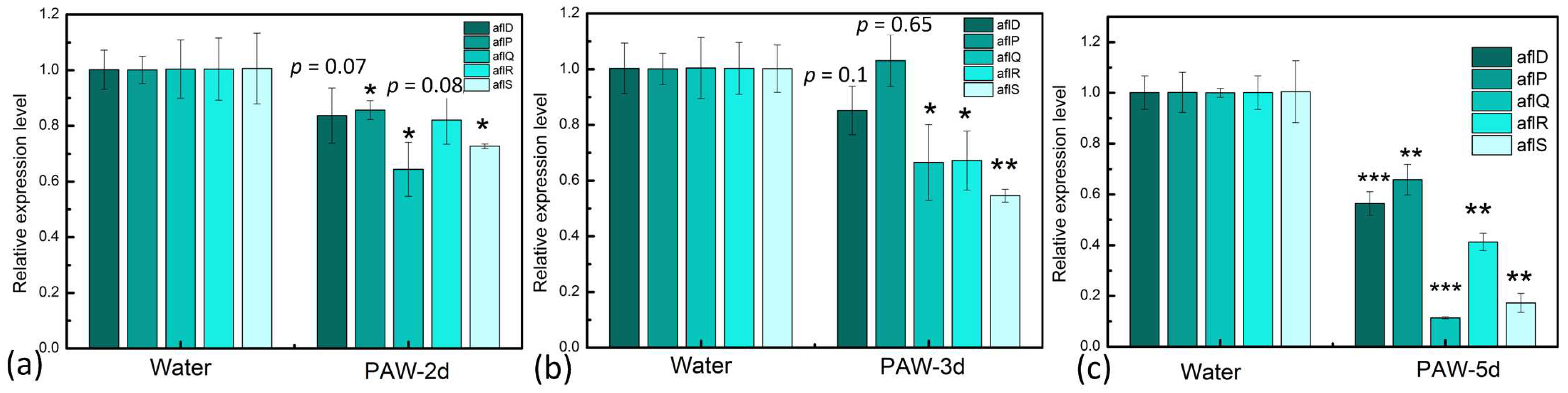
2.9. Detection of the Gene Expression Level
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The OES of Plasma Jet
3.2. Physicochemical Properties of PAW
3.3. The Inactivation of A. flavus by PAW
3.4. The Antifungal Mechanism of A. flavus by PAW
3.5. The Inhibition of AFB1 Synthesis by PAW
3.6. Inhibition of Key Genes Expression of AFB1 Synthesis in A. flavus by PAW
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Misra, N.N.; Yadav, B.; Roopesh, M.S.; Jo, C. Cold Plasma for Effective Fungal and Mycotoxin Control in Foods: Mechanisms, Inactivation Effects, and Applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, L.C.; Appleton, H.J.; Shi, H.; Keener, K.; Mellata, M. High voltage atmospheric cold plasma treatment inactivates Aspergillus flavus spores and deoxynivalenol toxin. Food Microbiol. 2021, 95, 103669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.M.; Patel, A.K.; Chiu, Y.C.; Hou, C.Y.; Kuo, C.H.; Dong, C.D.; Chen, H.L. The application of novel rotary plasma jets to inhibit the aflatoxin-producing Aspergillus flavus and the spoilage fungus, Aspergillus niger on peanuts. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 78, 102994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, K.; Liu, H.J.; Li, L.T. Product Identification and Safety Evaluation of Aflatoxin B1 Decontaminated by Electrolyzed Oxidizing Water. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9770–9778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, M.; Calvo, T.; Prieto, M.; Múgica-Vidal, R.; Muro-Fraguas, I.; Alba-Elías, F.; Alvarez-Ordóñez, A. A review on non-thermal atmospheric plasma for food preservation: Mode of action, determinants of effectiveness, and applications. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hojnik, N.; Modic, M.; Ni, Y.; Filipič, G.; Cvelbar, U.; Walsh, J.L. Effective Fungal Spore Inactivation with an Environmentally Friendly Approach Based on Atmospheric Pressure Air Plasma. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1893–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, C.; Ni, G.; Lan, Y.; Meng, Y.; Xia, W.; Chu, P.K. Preferential production of reactive species and bactericidal efficacy of gas-liquid plasma discharge. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasan, B.G.; Boyaci, I.H.; Mutlu, M. Inactivation of aflatoxigenic fungi (Aspergillus spp.) on granular food model, maize, in an atmospheric pressure fluidized bed plasma system. Food Control. 2016, 70, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasan, B.G.; Mutlu, M.; Boyaci, I.H. Decontamination of Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus spores on hazelnuts via atmospheric pressure fluidized bed plasma reactor. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 216, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasan, B.G.; Boyaci, I.H.; Mutlu, M. Nonthermal plasma treatment of Aspergillus spp. spores on hazelnuts in an atmospheric pressure fluidized bed plasma system: Impact of process parameters and surveillance of the residual viability of spores. J. Food Eng. 2017, 196, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, Y.; Thirumdas, R.; Sarangapani, C.; Deshmukh, R.R.; Annapure, U.S. Influence of cold plasma on fungal growth and aflatoxins production on groundnuts. Food Control. 2017, 77, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mošovská, S.; Medvecká, V.; Gregová, M.; Tomeková, J.; Valík, Ľ.; Mikulajová, A.; Zahoranová, A. Plasma inactivation of Aspergillus flavus on hazelnut surface in a diffuse barrier discharge using different working gases. Food Control 2019, 104, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herianto, S.; Hou, C.Y.; Lin, C.M.; Chen, H.L. Nonthermal plasma-activated water: A comprehensive review of this new tool for enhanced food safety and quality. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 583–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wu, S.; Dang, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Fang, J.; Han, P.; Zhang, J. Reduction of phoxim pesticide residues from grapes by atmospheric pressure non-thermal air plasma activated water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 377, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.; Fridman, G.; Fridman, A.; Joshi, S. Biological responses of Bacillus stratosphericus to Floating Electrode-Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma Treatment. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 2039–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhou, R.; Prasad, K.; Fang, Z.; Speight, R.; Bazaka, K.; Ostrikov, K. Cold atmospheric plasma activated water as a prospective disinfectant: The crucial role of peroxynitrite. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 5276–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhou, R.; Wang, P.; Xian, Y.; Mai-Prochnow, A.; Lu, X.P.; Cullen, P.J.; Ostrikov, K.; Bazaka, K. Plasma-activated water: Generation, origin of reactive species and biological applications. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 303001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, J.; Xie, H.; Jiang, J.; Li, C.; Li, W.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Lin, F. Inactivation effects of plasma-activated water on Fusarium graminearum. Food Control 2022, 134, 108683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Yao, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Qi, Y.; Gou, L.; Xi, W.; Liu, D.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Plasma-activated water: An alternative disinfectant for S protein inactivation to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 421, 127742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Wang, G.; Tian, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, J.; Fang, J. Non-thermal plasma-activated water inactivation of food-borne pathogen on fresh produce. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukes, P.; Dolezalova, E.; Sisrova, I.; Clupek, M. Aqueous-phase chemistry and bactericidal effects from an air discharge plasma in contact with water: Evidence for the formation of peroxynitrite through a pseudo-second-order post-discharge reaction of H2O2and HNO2. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2014, 23, 5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balazinski, M.; Schmidt-Bleker, A.; Winter, J.; von Woedtke, T. Peroxynitrous Acid Generated In Situ from Acidified H2O2 and NaNO2. A Suitable Novel Antimicrobial Agent? Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herianto, S.; Arcega, R.D.; Hou, C.Y.; Chao, H.R.; Lee, C.C.; Lin, C.M.; Mahmudiono, T.; Chen, H.L. Chemical decontamination of foods using non-thermal plasma-activated water. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarabová, B.; Lukeš, P.; Hammer, M.U.; Jablonowski, H.; von Woedtke, T.; Reuter, S.; Machala, Z. Fluorescence measurements of peroxynitrite/peroxynitrous acid in cold air plasma treated aqueous solutions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 8883–8896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, H.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fang, J. Assessment of the Physicochemical Properties and Biological Effects of Water Activated by Non-thermal Plasma Above and Beneath the Water Surface. Plasma Process. Polym. 2015, 12, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, N.H.; Qari, S.H.; Matar, S.; Hamad, N.A.; Dessoky, E.S.; Elshaer, M.M.; Sobhy, S.; Abdelkhalek, A.; Zakaria, H.M.; Heflish, A.A.; et al. Licorice, Doum, and Banana Peel Extracts Inhibit Aspergillus flavus Growth and Suppress Metabolic Pathway of Aflatoxin B1 Production. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Cui, D.; Du, M.; Wang, J.; Ma, R.; Jiao, Z. Evaluating the roles of OH radicals, H2O2, ORP and pH in the inactivation of yeast cells on a tissue model by surface micro-discharge plasma. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2019, 52, 395201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Joh, H.M.; Chung, T.H. Production of intracellular reactive oxygen species and change of cell viability induced by atmospheric pressure plasma in normal and cancer cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 153705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qi, Y.; Guo, L.; Huang, L.; Yao, Z.; Yang, L.; Li, G.; Chen, J.; Yan, J.; Niyazi, G.; et al. The bactericidal effects of plasma-activated saline prepared by the combination of surface discharge plasma and plasma jet. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2021, 54, 385202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Guo, L.; Yao, Z.; Xi, W.; Zhao, Y.; Lv, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, D. Nitrox surface discharge used for water activation: The reactive species and their correlation to the bactericidal effect. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2022, 55, 265203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Haute, S.; Zhou, B.; Luo, Y.; Sampers, I.; Vanhaverbeke, M.; Millner, P. The use of redox potential to estimate free chlorine in fresh produce washing operations: Possibilities and limitations. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 156, 110957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Los, A.; Ziuzina, D.; Boehm, D.; Cullen, P.J.; Bourke, P. Inactivation Efficacies and Mechanisms of Gas Plasma and Plasma-Activated Water against Aspergillus flavus Spores and Biofilms: A Comparative Study. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e02619-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, C.; Ischiropoulos, H.; Radi, R. Peroxynitrite: Biochemistry, pathophysiology and development of therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 662–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Du, M.; Wang, Y.; Ju, S.; Ma, R.; Jiao, Z. Subcellular mechanism of microbial inactivation during water disinfection by cold atmospheric-pressure plasma. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncada, S.; Bolanos, J.P. Nitric oxide, cell bioenergetics and neurodegeneration. J. Neurochem. 2006, 97, 1676–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán, B.; Mathur, A.; Duchen, M.R.; Erusalimsky, J.D.; Moncada, S. The effect of nitric oxide on cell respiration: A key to understanding its role in cell survival or death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 14602–14607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Liu, D.; Ding, T. Nonthermal Plasma Induces the Viable-but-Nonculturable State in Staphylococcus aureus via Metabolic Suppression and the Oxidative Stress Response. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e02216-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Shang, H.; Ma, R.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, X.; Ju, S.; Zhao, W.; Sun, H.; Zhuang, J.; et al. Effective inhibition of fungal growth, deoxynivalenol biosynthesis and pathogenicity in cereal pathogen Fusarium spp. by cold atmospheric plasma. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 437, 135307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, L.; Ma, X.; Liu, Y.; Shan, J.; Ma, K.; Xing, F. Comprehensive Transcriptome and Proteome Analyses Reveal the Modulation of Aflatoxin Production by Aspergillus flavus on Different Crop Substrates. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverberi, M.; Fabbri, A.A.; Zjalic, S.; Ricelli, A.; Punelli, F.; Fanelli, C. Antioxidant enzymes stimulation in Aspergillus parasiticus by Lentinula edodes inhibits aflatoxin production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 69, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grintzalis, K.; Vernardis, S.I.; Klapa, M.I.; Georgiou, C.D. Role of Oxidative Stress in Sclerotial Differentiation and Aflatoxin B1 Biosynthesis in Aspergillus flavus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5561–5571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caceres, I.; El Khoury, R.; Bailly, S.; Oswald, I.P.; Puel, O.; Bailly, J.D. Piperine inhibits aflatoxin B1 production in Aspergillus flavus by modulating fungal oxidative stress response. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2017, 107, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Shang, B.; Wang, L.; Lu, Z.; Liu, Y. Cinnamaldehyde inhibits fungal growth and aflatoxin B1 biosynthesis by modulating the oxidative stress response of Aspergillus flavus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 1355–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, T.E.; Yu, J.; Fedorova, N.; Bhatnagar, D.; Payne, G.A.; Nierman, W.C.; Bennett, J.W. Potential of Aspergillus flavus genomics for applications in biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, Q.; Xu, H.; Zhuang, J.; Cui, D.; Ma, R.; Jiao, Z. Inhibition of Fungal Growth and Aflatoxin B1 Synthesis in Aspergillus flavus by Plasma-Activated Water. Foods 2023, 12, 2490. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12132490
Yao Q, Xu H, Zhuang J, Cui D, Ma R, Jiao Z. Inhibition of Fungal Growth and Aflatoxin B1 Synthesis in Aspergillus flavus by Plasma-Activated Water. Foods. 2023; 12(13):2490. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12132490
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Qihuan, Hangbo Xu, Jie Zhuang, Dongjie Cui, Ruonan Ma, and Zhen Jiao. 2023. "Inhibition of Fungal Growth and Aflatoxin B1 Synthesis in Aspergillus flavus by Plasma-Activated Water" Foods 12, no. 13: 2490. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12132490
APA StyleYao, Q., Xu, H., Zhuang, J., Cui, D., Ma, R., & Jiao, Z. (2023). Inhibition of Fungal Growth and Aflatoxin B1 Synthesis in Aspergillus flavus by Plasma-Activated Water. Foods, 12(13), 2490. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12132490






