Molecular Barcoding: A Tool to Guarantee Correct Seafood Labelling and Quality and Preserve the Conservation of Endangered Species
Abstract
:1. Seafood Commerce and Fraud
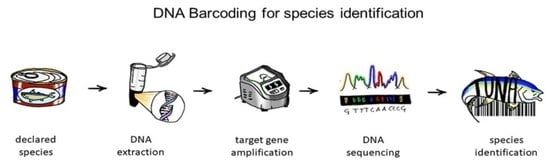
2. DNA Barcoding and Seafood Mislabelling
3. DNA Mini-Barcoding for Processed Seafood
4. The Impact of Seafood Frauds on Human Health
5. Implications for the Conservation of Endangered Species
6. DNA Barcode Regions
6.1. Cytochrome c Oxidase I (COI) Gene
6.2. Cytochrome b (cytb) Gene
6.3. 16S rDNA and 12S rDNA
6.4. Nuclear DNA
7. DNA Barcoding Databases
8. Evolution of Seafood Barcoding through the Genomic Era
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020|FAO. Available online: https://www.fao.org/family-farming/detail/en/c/1279714/ (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Lofstedt, A.; de Roos, B.; Fernandes, P.G. Less than Half of the European Dietary Recommendations for Fish Consumption Are Satisfied by National Seafood Supplies. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 4219–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, T.J.R.; Amaral, J.S.; Mafra, I. DNA Barcode Markers Applied to Seafood Authentication: An Updated Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 3904–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vindigni, G.; Pulvirenti, A.; Alaimo, S.; Monaco, C.; Spina, D.; Peri, I. Bioinformatics Approach to Mitigate Mislabelling in EU Seafood Market and Protect Consumer Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2021, 18, 7497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costello, C.; Cao, L.; Gelcich, S.; Cisneros-Mata, M.; Free, C.M.; Froehlich, H.E.; Golden, C.D.; Ishimura, G.; Maier, J.; Macadam-Somer, I.; et al. The Future of Food from the Sea. Nature 2020, 588, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marko, P.B.; Lee, S.C.; Rice, A.M.; Gramling, J.M.; Fitzhenry, T.M.; McAlister, J.S.; Harper, G.R.; Moran, A.L. Fisheries: Mislabelling of a Depleted Reef Fish. Nature 2004, 430, 309–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naylor, R.L.; Hardy, R.W.; Buschmann, A.H.; Bush, S.R.; Cao, L.; Klinger, D.H.; Little, D.C.; Lubchenco, J.; Shumway, S.E.; Troell, M. A 20-Year Retrospective Review of Global Aquaculture. Nature 2021, 591, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helyar, S.J.; Lloyd, H.A.D.; De Bruyn, M.; Leake, J.; Bennett, N.; Carvalho, G.R. Fish Product Mislabelling: Failings of Traceability in the Production Chain and Implications for Illegal, Unreported and Unregulated (IUU) Fishing. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acutis, P.L.; Cambiotti, V.; Riina, M.V.; Meistro, S.; Maurella, C.; Massaro, M.; Stacchini, P.; Gili, S.; Malandra, R.; Pezzolato, M.; et al. Detection of Fish Species Substitution Frauds in Italy: A Targeted National Monitoring Plan. Food Control 2019, 101, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuwen, S.P.J.; Van Velzen, M.J.M.; Swart, C.P.; Van Der Veen, I.; Traag, W.A.; De Boer, J. Halogenated Contaminants in Farmed Salmon, Trout, Tilapia, Pangasius, and Shrimp. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4009–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, P.; Armani, A.; Gianfaldoni, D.; Guidi, A. New Provisions for the Labelling of Fishery and Aquaculture Products: Difficulties in the Implementation of Regulation (EU) n. 1379/2013. Mar. Policy 2016, 71, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio, L.; González, I.; García, T.; Martín, R. Determination of Food Authenticity by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA). Food Control 2008, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolfe, M.; Primrose, S. Food Forensics: Using DNA Technology to Combat Misdescription and Fraud. Trends Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, B.G. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy in Food Analysis. Encycl. Anal. Chem. 2006, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Xing, R.R.; Zhou, M.Y.; Sun, R.X.; Han, J.X.; Zhang, J.K.; Zheng, W.J.; Chen, Y. Application of DNA Barcoding and Metabarcoding for Species Identification in Salmon Products. Food Addit. Contam. Part. A Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 2021, 38, 754–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawnay, N.; Ogden, R.; McEwing, R.; Carvalho, G.R.; Thorpe, R.S. Validation of the Barcoding Gene COI for Use in Forensic Genetic Species Identification. Forensic Sci. Int. 2007, 173, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, S.E.; Davidson, W. FINS (Forensically Informative Nucleotide Sequencing): A Procedure for Identifying the Animal Origin of Biological Specimens. Biotechniques 1992, 12, 408–411. [Google Scholar]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; DeWaard, J.R. Biological Identifications through DNA Barcodes. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nehal, N.; Choudhary, B.; Nagpure, A.; Gupta, R.K. DNA Barcoding: A Modern Age Tool for Detection of Adulteration in Food. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2021, 41, 767–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savolainen, V.; Cowan, R.S.; Vogler, A.P.; Roderick, G.K.; Lane, R. Towards Writing the Encyclopedia of Life: An Introduction to DNA Barcoding. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1805–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, W.J.; Erickson, D.L. DNA Barcodes: Genes, Genomics, and Bioinformatics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2761–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roe, A.D.; Sperling, F.A.H. Patterns of Evolution of Mitochondrial Cytochrome c Oxidase I and II DNA and Implications for DNA Barcoding. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 44, 325–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajibabaei, M.; Smith, M.A.; Janzen, D.H.; Rodriguez, J.J.; Whitfield, J.B.; Hebert, P.D.N. A Minimalist Barcode Can Identify a Specimen Whose DNA Is Degraded. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filonzi, L.; Chiesa, S.; Vaghi, M.; Nonnis Marzano, F. Molecular barcoding reveals mislabelling of commercial fish products in Italy. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imoto, J.M.; Saitoh, K.; Sasaki, T.; Yonezawa, T.; Adachi, J.; Kartavtsev, Y.P.; Miya, M.; Nishida, M.; Hanzawa, N. Phylogeny and Biogeography of Highly Diverged Freshwater Fish Species (Leuciscinae, Cyprinidae, Teleostei) Inferred from Mitochondrial Genome Analysis. Gene 2013, 514, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, R.D.; Zemlak, T.S.; Innes, B.H.; Last, P.R.; Hebert, P.D.N. DNA Barcoding Australia’s Fish Species. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1847–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, N.V.; Zemlak, T.S.; Hanner, R.H.; Hebert, P.D.N. Universal Primer Cocktails for Fish DNA Barcoding. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, D.C.; Neto, D.A.P.; Brasil, B.S.A.F.; Oliveira, D.A.A. DNA Barcoding Unveils a High Rate of Mislabelling in a Commercial Freshwater Catfish from Brazil. Mitochondrial DNA 2011, 22 (Suppl. S1), 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cline, E. Marketplace Substitution of Atlantic Salmon for Pacific Salmon in Washington State Detected by DNA Barcoding. Food Res. Int. 2012, 45, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, A.M.; Ferrito, V. DNA Barcoding Species Identification Unveils Mislabelling of Processed Flatfish Products in Southern Italy Markets. Fish. Res. 2015, 164, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naaum, A.M.; Hanner, R.H. An Introduction to DNA-Based Tools for Seafood Identification. In Seafood Authenticity and Traceability; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filonzi, L.; Vaghi, M.; Ardenghi, A.; Rontani, P.M.; Voccia, A.; Nonnis Marzano, F. Efficiency of DNA Mini-Barcoding to Assess Mislabelling in Commercial Fish Products in Italy: An Overview of the Last Decade. Foods 2021, 10, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokralla, S.; Hellberg, R.S.; Handy, S.M.; King, I.; Hajibabaei, M. A DNA Mini-barcoding system for authentication of processed fish products. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meusnier, I.; Singer, G.A.C.; Landry, J.F.; Hickey, D.A.; Hebert, P.D.N.; Hajibabaei, M. A Universal DNA Mini-Barcode for Biodiversity Analysis. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Armani, A.; Guardone, L.; La Castellana, R.; Gianfaldoni, D.; Guidi, A.; Castigliego, L. DNA Barcoding Reveals Commercial and Health Issues in Ethnic Seafood Sold on the Italian Market. Food Control 2015, 55, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chin, T.C.; Adibah, A.B.; Danial Hariz, Z.A.; Siti Azizah, M.N. Detection of Mislabelled Seafood Products in Malaysia by DNA Barcoding: Improving Transparency in Food Market. Food Control 2016, 64, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, B.; Raupach, M.J.; Knebelsberger, T. Full-Length and Mini-Length DNA Barcoding for the Identification of Seafood Commercially Traded in Germany. Food Control 2017, 73, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, S.; Ali, M.E.; Hossain, M.A.M.; Asing; Naquiah, N.; Zaidul, I.S.M. Universal Mini COI Barcode for the Identification of Fish Species in Processed Products. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, M.; Dhar, B.; Ghosh, S.K. Design of Character-Based DNA Barcode Motif for Species Identification: A Computational Approach and Its Validation in Fishes. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2017, 17, 1359–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollack, S.J.; Kawalek, M.D.; Williams-Hill, D.M.; Hellberg, R.S. Evaluation of DNA Barcoding Methodologies for the Identification of Fish Species in Cooked Products. Food Control 2018, 84, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spink, J.; Moyer, D.C. Defining the Public Health Threat of Food Fraud. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee on the Environment. Draft report on the food crisis, fraud in the food chain and the control thereof. In Public Health and Food Safety from European Parliament, 2091; EU Parliament Publisher: Strasbourg, France, 2013; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, X.; D’Amico, P.; Guardone, L.; Castigliego, L.; Guidi, A.; Gianfaldoni, D.; Armani, A. The Uncertainty of Seafood Labeling in China: A Case Study on Cod, Salmon and Tuna. Mar. Policy 2016, 68, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Yao, L.; Ying, X.; Lu, L.; Guardone, L.; Armani, A.; Guidi, A.; Xiong, X. Multiple Fish Species Identified from China’s Roasted Xue Yu Fillet Products Using DNA and Mini-DNA Barcoding: Implications on Human Health and Marine Sustainability. Food Control 2018, 88, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saoudi, M.; Abdelmouleh, A.; Kammoun, W.; Ellouze, F.; Jamoussi, K.; El Feki, A. Toxicity Assessment of the Puffer Fish Lagocephalus Lagocephalus from the Tunisian Coast. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2008, 331, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowenstein, J.H.; Amato, G.; Kolokotronis, S.O. The Real Maccoyii: Identifying Tuna Sushi with DNA Barcodes—Contrasting Characteristic Attributes and Genetic Distances. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zarza, M.C.P.; Gutiérrez, V.R.; Bravo, L. Lipid Composition of Two Purgative Fish: Ruvettus Pretiosus and Lepidocybium Flavobrunneum. Grasas Aceites 1993, 44, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tantillo, G.; Marchetti, P.; Mottola, A.; Terio, V.; Bottaro, M.; Bonerba, E.; Bozzo, G.; Di Pinto, A. Occurrence of mislabelling in prepared fishery products in Southern Italy. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2015, 4, 5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duarte, G.S.C.; Takemoto, R.M.; Yamaguchi, M.U.; de Matos, L.S.; Pavanelli, G.C. Evaluation of the Concentration of Heavy Metals in Fillets of Pangasius Hypophthalmus (Sauvage, 1878), Panga, Imported from Vietnam. Int. J. Dev. Res. 2019, 9, 30181–30186. [Google Scholar]
- IUCN. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2022-2. 2022. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 30 March 2023).
- Ferrito, V.; Raffa, A.; Rossitto, L.; Federico, C.; Saccone, S.; Pappalardo, A.M. Swordfish or Shark Slice? A Rapid Response by COIBar–RFLP. Foods 2019, 8, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shehata, H.R.; Naaum, A.M.; Garduño, R.A.; Hanner, R. DNA Barcoding as a Regulatory Tool for Seafood Authentication in Canada. Food Control 2018, 92, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willette, D.A.; Simmonds, S.E.; Cheng, S.H.; Esteves, S.; Kane, T.L.; Nuetzel, H.; Pilaud, N.; Rachmawati, R.; Barber, P.H. Using DNA Barcoding to Track Seafood Mislabelling in Los Angeles Restaurants. Conserv. Biol. 2017, 31, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Fernandez, C.; Ardura, A.; Masiá, P.; Rodriguez, N.; Voces, L.; Fernandez-Raigoso, M.; Roca, A.; Machado-Schiaffino, G.; Dopico, E.; Garcia-Vazquez, E. Fraud in Highly Appreciated Fish Detected from DNA in Europe May Undermine the Development Goal of Sustainable Fishing in Africa. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufflocq, P.; Larraín, M.A.; Araneda, C. Species Substitution and Mislabelling in the Swordfish (Xiphias gladius) Market in Santiago, Chile: Implications in Shark Conservation. Food Control 2022, 133, 108607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, I.; Wainwright, B.J. DNA Barcoding Identifies Endangered Sharks in Pet Food Sold in Singapore. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almerón-Souza, F.; Sperb, C.; Castilho, C.L.; Figueiredo, P.I.C.C.; Gonçalves, L.T.; Machado, R.; Oliveira, L.R.; Valiati, V.H.; Fagundes, N.J.R. Molecular Identification of Shark Meat from Local Markets in Southern Brazil Based on DNA Barcoding: Evidence for Mislabelling and Trade of Endangered Species. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Staffen, C.F.; Staffen, M.D.; Becker, M.L.; Löfgren, S.E.; Muniz, Y.C.N.; de Freitas, R.H.A.; Marrero, A.R. DNA Barcoding Reveals the Mislabelling of Fish in a Popular Tourist Destination in Brazil. PeerJ 2017, 5, e4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbuto, M.; Galimberti, A.; Ferri, E.; Labra, M.; Malandra, R.; Galli, P.; Casiraghi, M. DNA barcoding reveals fraudulent substitutions in shark seafood products: The Italian case of “palombo” (Mustelus spp.). Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Ball, S.L.J.; Hebert, P.D.N.; Burian, S.K.; Webb, M. Biological Identifications of Mayflies (Ephemeroptera) Using DNA Barcodes. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2005, 24, 508–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajibabaei, M.; Singer, G.A.C.; Hebert, P.D.N.; Hickey, D.A. DNA Barcoding: How It Complements Taxonomy, Molecular Phylogenetics and Population Genetics. Trends Genet. 2007, 23, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clare, E.L.; Lim, B.K.; Engstrom, M.D.; Eger, J.L.; Hebert, P.D.N. DNA Barcoding of Neotropical Bats: Species Identification and Discovery within Guyana. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vences, M.; Thomas, M.; Bonett, R.M.; Vieites, D.R. Deciphering Amphibian Diversity through DNA Barcoding: Chances and Challenges. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1859–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Supikamolseni, A.; Ngaoburanawit, N.; Sumontha, M.; Chanhome, L.; Suntrarachun, S.; Peyachoknagul, S.; Srikulnath, K. Molecular Barcoding of Venomous Snakes and Species-Specific Multiplex PCR Assay to Identify Snake Groups for Which Antivenom Is Available in Thailand. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 13981–13997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rock, J.; Costa, F.O.; Walker, D.I.; North, A.W.; Hutchinson, W.F.; Carvalho, G.R. DNA Barcodes of Fish of the Scotia Sea, Antarctica Indicate Priority Groups for Taxonomic and Systematics Focus. Antarct. Sci. 2008, 20, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.H.K.; Shivji, M.S.; Hanner, R.H. Identifying Sharks with DNA Barcodes: Assessing the Utility of a Nucleotide Diagnostic Approach. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9 (Suppl. S1), 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, L.J.; Boilard, S.M.A.L.; Eagle, S.H.C.; Spall, J.L.; Shokralla, S.; Hajibabaei, M. DNA Barcodes for Everyday Life: Routine Authentication of Natural Health Products. Food Res. Int. 2012, 49, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, A.M.; Raffa, A.; Calogero, G.S.; Ferrito, V. Geographic Pattern of Sushi Product Misdescription in Italy-A Crosstalk between Citizen Science and DNA Barcoding. Foods 2021, 10, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.; Jessel, A.; Mariani, S. Seafood Mislabelling: Comparisons of Two Western European Case Studies Assist in Defining Influencing Factors, Mechanisms and Motives. Fish. Fish. 2012, 13, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bénard-Capelle, J.; Guillonneau, V.; Nouvian, C.; Fournier, N.; Loët, K.L.; Dettai, A. Fish Mislabelling in France: Substitution Rates and Retail Types. PeerJ 2015, 2, e714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muñoz-Colmenero, M.; Blanco, O.; Arias, V.; Martinez, J.L.; Garcia-Vazquez, E. DNA Authentication of Fish Products Reveals Mislabelling Associated with Seafood Processing. Fisheries 2016, 41, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoudi, S.; Karaiskou, N.; Avgeris, M.; Gkagkavouzis, K.; Tarantili, P.; Triantafyllidou, D.; Palilis, L.; Avramopoulou, V.; Tsikliras, A.; Barmperis, K.; et al. Seafood Mislabelling in Greek Market Using DNA Barcoding. Food Control 2020, 113, 107213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, D.J.; Rosado, D.; Xavier, R. DNA Barcoding Reveals Extensive Mislabelling in Seafood Sold in Portuguese Supermarkets. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2016, 25, 1375–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, H.; Fournier, N.; Hellemans, B.; Volckaert, F.A.M. Seafood Substitution and Mislabelling in Brussels’ Restaurants and Canteens. Food Control 2018, 85, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinacci, L.; Guidi, A.; Toto, A.; Guardone, L.; Giusti, A.; D’Amico, P.; Armani, A. DNA Barcoding for the Verification of Supplier’s Compliance in the Seafood Chain: How the Lab Can Support Companies in Ensuring Traceability. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2018, 7, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, M.Á.; Jiménez, E.; Viðarsson, J.R.; Ólafsson, K.; Ólafsdóttir, G.; Daníelsdóttir, A.K.; Pérez-Villareal, B. DNA Barcoding Revealing Mislabelling of Seafood in European Mass Caterings. Food Control 2018, 92, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.J.; Sampaio, I.; Santos, S. Re-visiting the occurrence of mislabelling in frozen “pescada-branca” (Cynoscion leiarchus and Plagioscion squamosissimus–Sciaenidae) sold in Brazil using DNA barcoding and octaplex PCR assay. Food Res. Int. 2021, 143, 110308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagalakshmi, K.; Annam, P.K.; Venkateshwarlu, G.; Pathakota, G.B.; Lakra, W.S. Mislabelling in Indian Seafood: An Investigation Using DNA Barcoding. Food Control 2016, 59, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Tinacci, L.; Acutis, P.L.; Riina, M.V.; Xu, Y.; Zeng, L.; Ying, X.; Chen, Z.; Guardone, L.; Chen, D.; et al. An Insight into the Chinese Traditional Seafood Market: Species Characterization of Cephalopod Products by DNA Barcoding and Phylogenetic Analysis Using COI and 16SrRNA Genes. Food Control 2017, 82, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neo, S.; Kibat, C.; Wainwright, B.J. Seafood Mislabelling in Singapore. Food Control 2022, 135, 108821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaksar, R.; Carlson, T.; Schaffner, D.W.; Ghorashi, M.; Best, D.; Jandhyala, S.; Traverso, J.; Amini, S. Unmasking Seafood Mislabelling in U.S. Markets: DNA Barcoding as a Unique Technology for Food Authentication and Quality Control. Food Control 2015, 56, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandamme, S.G.; Griffiths, A.M.; Taylor, S.A.; Di Muri, C.; Hankard, E.A.; Towne, J.A.; Watson, M.; Mariani, S. Sushi Barcoding in the UK: Another Kettle of Fish. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galal-Khallaf, A.; Ardura, A.; Mohammed-Geba, K.; Borrell, Y.J.; Garcia-Vazquez, E. DNA Barcoding Reveals a High Level of Mislabelling in Egyptian Fish Fillets. Food Control 2014, 46, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawthorn, D.M.; Duncan, J.; Kastern, C.; Francis, J.; Hoffman, L.C. Fish Species Substitution and Misnaming in South Africa: An Economic, Safety and Sustainability Conundrum Revisited. Food Chem. 2015, 185, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamendin, R.; Miller, K.; Ward, R.D. Labelling Accuracy in Tasmanian Seafood: An Investigation Using DNA Barcoding. Food Control 2015, 47, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.; Rothbart, A.; Frankham, G.; Johnson, R.N.; Neaves, L.E. Could Do Better! A High School Market Survey of Fish Labelling in Sydney, Australia, Using DNA Barcodes. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cawthorn, D.M.; Steinman, H.A.; Witthuhn, R.C. DNA Barcoding Reveals a High Incidence of Fish Species Misrepresentation and Substitution on the South African Market. Food Res. Int. 2012, 46, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munguia-Vega, A.; Terrazas-Tapia, R.; Dominguez-Contreras, J.F.; Reyna-Fabian, M.; Zapata-Morales, P. DNA Barcoding Reveals Global and Local Influences on Patterns of Mislabelling and Substitution in the Trade of Fish in Mexico. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0265960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariani, S.; Griffiths, A.M.; Velasco, A.; Kappel, K.; Jerome, M.; Perez-Martin, R.I.; Schroder, U.; Verrez-Bagnis, V.; Silva, H.; Vandamme, S.G.; et al. Low Mislabelling Rates Indicate Marked Improvements in European Seafood Market Operations. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2015, 13, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanner, R.; Floyd, R.; Bernard, A.; Collette, B.B.; Shivji, M. DNA Barcoding of Billfishes. Mitochondrial DNA 2011, 22, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.D.; Choi, T.J.; Kim, J.; An, H.E.; Park, Y.J.; Karagozlu, M.Z.; Kim, C.B. Assessment of Marine Fish Mislabelling in South Korea’s Markets by DNA Barcoding. Food Control 2019, 100, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitch, C.J.; Tabb, A.M.; Marquis, G.E.; Hellberg, R.S. Species Substitution and Mislabelling of Ceviche, Poke, and Sushi Dishes Sold in Orange County, California. Food Control 2022, 146, 109525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocher, T.D.; Thomas, W.K.; Meyer, A.; Edwards, S.V.; Paabo, S.; Villablanca, F.X.; Wilson, A.C. Dynamics of Mitochondrial DNA Evolution in Animals: Amplification and Sequencing with Conserved Primers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 6196–6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avise, J.C.; Ankney, C.D.; Nelson, W.S. Mitochondrial gene trees and the evolutionary relationship of mallard and black ducks. Evolution 1990, 44, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hedges, S.B. Molecular Evidence for the Origin of Birds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 2621–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, W.S. Inferring phylogenies from MtDNA variation: Mitochondrial-gene trees versus nuclear-gene trees. Evolution 1995, 49, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindell, D.P.; Sorenson, M.D.; Huddleston, C.J.; Miranda, H.C.; Knight, A.; Sawchuk, S.J.; Yuri, T. Phylogenetic Relationships among and within Select Avian Orders Based on Mitochondrial DNA. Avian Mol. Evol. Syst. 1997, 213–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposti, M.D.; De Vries, S.; Crimi, M.; Ghelli, A.; Patarnello, T.; Meyer, A. Mitochondrial Cytochrome b: Evolution and Structure of the Protein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1993, 1143, 243–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lau, C.H.; Drinkwater, R.D.; Yusoff, K.; Tan, S.G.; Hetzel, D.J.S.; Barker, J.S.F. Genetic Diversity of Asian Water Buffalo (Bubalus bubalis): Mitochondrial DNA D-Loop and Cytochrome b Sequence Variation. Anim. Genet. 1998, 29, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parson, W.; Pegoraro, K.; Niederstätter, H.; Föger, M.; Steinlechner, M. Species Identification by Means of the Cytochrome b Gene. Int. J. Legal. Med. 2000, 114, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevilla, R.G.; Diez, A.; Norén, M.; Mouchel, O.; Jérôme, M.; Verrez-Bagnis, V.; Van Pelt, H.; Favre-Krey, L.; Krey, G.; Bautista, J.M. Primers and Polymerase Chain Reaction Conditions for DNA Barcoding Teleost Fish Based on the Mitochondrial Cytochrome b and Nuclear Rhodopsin Genes. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kartavtsev, Y.P.; Jung, S.O.; Lee, Y.M.; Byeon, H.K.; Lee, J.S. Complete Mitochondrial Genome of the Bullhead Torrent Catfish, Liobagrus Obesus (Siluriformes, Amblycipididae): Genome Description and Phylogenetic Considerations Inferred from the Cyt b and 16S RRNA Genes. Gene 2007, 396, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartavtsev, Y.P.; Park, T.J.; Vinnikov, K.A.; Ivankov, V.N.; Sharina, S.N.; Lee, J.S. Cytochrome b (Cyt-b) Gene Sequence Analysis in Six Flatfish Species (Teleostei, Pleuronectidae), with Phylogenetic and Taxonomic Insights. Mar. Biol. 2007, 152, 757–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.D.; Holmes, B.H.; Yearsley, G.K. DNA Barcoding Reveals a Likely Second Species of Asian Sea Bass (Barramundi) (Lates calcarifer). J. Fish. Biol. 2008, 72, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesa, S.; Filonzi, L.; Vaghi, M.; Papa, R.; Marzano, F.N. Molecular Barcoding of an Atypical Cyprinid Population Assessed by Cytochrome B Gene Sequencing. Zoolog Sci. 2013, 30, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotelo, C.G.; Calo-Mata, P.; Chapela, M.J.; Pérez-Martín, R.I.; Rehbein, H.; Hold, G.L.; Russell, V.J.; Pryde, S.; Quinteiro, J.; Izquierdo, M.; et al. Identification of Flatfish (Pleuronectiforme) Species Using DNA-Based Techniques. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4562–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calo-Mata, P.; Sotelo, C.G.; Perez-Martin, R.I.; Rehbein, H.; Hold, G.L.; Russell, V.J.; Pryde, S.; Quinteiro, J.; Rey-Mendez, M.; Rosa, C.; et al. Identification of Gadoid Fish Species Using DNA-Based Techniques. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2003, 217, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, S.; Nohara, K.; Tanabe, T.; Itoh, T.; Tsuji, S.; Nishikawa, Y.; Uyeyanagi, S.; Uchikawa, K. Genetic and Morphological Identification of Larval and Small Juvenile Tunas (Pisces: Scombridae) Caught by a Midwater Trawl in the Western Pacific. Bull. Fish. Res. Agen. 2003, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Pepe, T.; Trotta, M.; Marco, I.D.I.; Cennamo, P.; Anastasio, A.; Cortesi, M.L. Mitochondrial Cytochrome b DNA Sequence Variations: An Approach to Fish Species Identification in Processed Fish Products. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teletchea, F.; Maudet, C.; Hänni, C. Food and Forensic Molecular Identification: Update and Challenges. Trends Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santaclara, F.J.; Espiñeira, M.; Cabado, A.G.; Aldasoro, A.; Gonzalez-Lavín, N.; Vieites, J.M. Development of a Method for the Genetic Identification of Mussel Species Belonging to Mytilus, Perna, Aulacomya, and Other Genera. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8461–8470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelini, E.; Cevenini, L.; Mezzanotte, L.; Simoni, P.; Baraldini, M.; De Laude, L.; Roda, A. One-Step Triplex-Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay for the Authentication of Yellowfin (Thunnus albacares), Bigeye (Thunnus obesus), and Skipjack (Katsuwonus pelamis) Tuna DNA from Fresh, Frozen, and Canned Tuna Samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 7638–7647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutarelli, A.; Amoroso, M.G.; De Roma, A.; Girardi, S.; Galiero, G.; Guarino, A.; Corrado, F. Italian Market Fish Species Identification and Commercial Frauds Revealing by DNA Sequencing. Food Control 2014, 37, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armani, A.; Castigliego, L.; Tinacci, L.; Gianfaldoni, D.; Guidi, A. Molecular Characterization of Icefish, (Salangidae Family), Using Direct Sequencing of Mitochondrial Cytochrome b Gene. Food Control 2011, 22, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, T.T.T.; Huong, N.T.; Hung, N.P.; Guiguen, Y. Species Identification Using DNA Barcoding on Processed Panga Catfish Products in Viet Nam Revealed Important Mislabelling. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 18, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutarelli, A.; Galiero, G.; Capuano, F.; Corrado, F. Species Identification by Means of Mitochondrial Cytochrome b DNA Sequencing in Processed Anchovy, Sardine and Tuna Products. Food Nutr. Sci. 2018, 09, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomes, G.; Correa, R.; Veneza, I.; da Silva, R.; da Silva, D.; Miranda, J.; Sampaio, I. Forensic Analysis Reveals Fraud in Fillets from the “Gurijuba” Sciades Parkeri (Ariidae—Siluriformes): A Vulnerable Fish in Brazilian Coastal Amazon. Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2019, 30, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, D.S.; Clemente, W.R.; Henning, F.; Solé-Cava, A.M. From Fish-Markets to Restaurants: Substitution Prevalence along the Flatfish Commercialization Chain in Brazil. Fish. Res 2021, 243, 106095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Tan, Z.; Wang, D.; Xue, L.; Guan, M.X.; Huang, T.; Li, R. Species Identification through Mitochondrial RRNA Genetic Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simons, A.M.; Mayden, R.L. Phylogenetic Relationships of the Western North American Phoxinins (Actinopterygii: Cyprinidae) as Inferred from Mitochondrial 12S and 16S Ribosomal RNA Sequences. Mol. Phylogenet Evol. 1998, 9, 308–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, M.; Das, D.K.; Dhara, A.; Swarup, D.; Yadav, M.P.; Gupta, P.K. Characterisation of Peacock (Pavo cristatus) Mitochondrial 12S RRNA Sequence and Its Use in Differentiation from Closely Related Poultry Species. Br. Poult. Sci. 2007, 48, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, T.; Umetsu, K.; Tian, W.; Osawa, M. Two Universal Primer Sets for Species Identification among Vertebrates. Int. J. Legal. Med. 2007, 121, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.R.; Patra, R.C.; Das, D.K.; Gupta, P.K.; Swarup, D.; Saini, M. Sequence Characterization and Polymerase Chain Reaction-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism of the Mitochondrial DNA 12S RRNA Gene Provides a Method for Species Identification of Indian Deer. Mitochondrial DNA 2008, 19, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascoal, A.; Barros-Velázquez, J.; Cepeda, A.; Gallardo, J.M.; Calo-Mata, P. A Polymerase Chain Reaction-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism Method Based on the Analysis of a 16S RRNA/TRNA(Val) Mitochondrial Region for Species Identification of Commercial Penaeid Shrimps (Crustacea: Decapoda: Penaeoidea) of Food Interest. Electrophoresis 2008, 29, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Jiang, J.; Xie, F.; Chen, X.; Dubois, A.; Liang, G.; Wagner, S. Molecular Phylogeny and Genetic Identification of Populations of Two Species of Feirana Frogs (Amphibia: Anura, Ranidae, Dicroglossinae, Paini) Endemic to China. Zoolog Sci. 2009, 26, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarri, C.; Stamatis, C.; Sarafidou, T.; Galara, I.; Godosopoulos, V.; Kolovos, M.; Liakou, C.; Tastsoglou, S.; Mamuris, Z. A New Set of 16S RRNA Universal Primers for Identification of Animal Species. Food Control 2014, 43, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Céspedes, A.; García, T.; Carrera, E.; González, I.; Fernández, A.; Asensio, L.; Hernández, P.E.; Martín, R. Genetic differentiation between sole (Solea solea) and Greenland halibut (Reinhardtius hippoglossoides) by PCR–RFLP analysis of a 12S rRNA gene fragment. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000, 80, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotta, M.; Schönhuth, S.; Pepe, T.; Cortesi, M.L.; Puyet, A.; Bautista, J.M. Multiplex PCR method for use in real-time PCR for identification of fish fillets from grouper (Epinephelus and Mycteroperca species) and common substitute species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 2039–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharrett, A.J.; Gray, A.K.; Heifetz, J. Identification of Rockfish (Sebastes spp.) by Restriction Site Analysis of the Mitochondrial ND-3/ND-4 and 12S/16S RRNA Gene Regions. Fish. Bull. 2001, 99, 49–62. [Google Scholar]
- Applewhite, L.; Rasmussen, R.; Morrissey, M. Species Identification of Seafood. The Seafood Industry: Species, Products, Processing, and Safety, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 193–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Der Heyden, S.; Barendse, J.; Seebregts, A.J.; Matthee, C.A. Misleading the Masses: Detection of Mislabelled and Substituted Frozen Fish Products in South Africa. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2010, 67, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melo Palmeira, C.A.; da Silva Rodrigues-Filho, L.F.; de Luna Sales, J.B.; Vallinoto, M.; Schneider, H.; Sampaio, I. Commercialization of a Critically Endangered Species (Largetooth sawfish, Pristis perotteti) in Fish Markets of Northern Brazil: Authenticity by DNA Analysis. Food Control 2013, 34, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lea-Charris, E.; Castro, L.R.; Villamizar, N. DNA Barcoding Reveals Fraud in Commercial Common Snook (Centropomus undecimalis) Products in Santa Marta, Colombia. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horreo, J.L.; Fitze, P.S.; Jiménez-Valverde, A.; Noriega, J.A.; Pelaez, M.L. Amplification of 16S RDna Reveals Important Fish Mislabelling in Madrid Restaurants. Food Control 2019, 96, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrondo, M.; López, S.; Aparicio-Valencia, A.; Fueyo, A.; Quintanilla-García, P.; Arias, A.; Borrell, Y.J. Almost Never You Get What You Pay for: Widespread Mislabelling of Commercial “Zamburiñas” in Northern Spain. Food Control 2021, 120, 107541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.M.; Uddin, S.M.K.; Chowdhury, Z.Z.; Sultana, S.; Johan, M.R.; Rohman, A.; Ali, M.E. Universal Mitochondrial 16S RRNA Biomarker for Mini-Barcode to Identify Fish Species in Malaysian Fish Products. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2019, 36, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, R.R.; Hu, R.R.; Han, J.X.; Deng, T.T.; Chen, Y. DNA barcoding and mini-barcoding in authenticating processed animal-derived food: A case study involving the Chinese market. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.H.; Kao, Y.T.; Huang, T.T.; Wang, Y.C. Product Authentication Using Two Mitochondrial Markers Reveals Inconsistent Labeling and Substitution of Canned Tuna Products in the Taiwanese Market. Foods 2021, 10, 2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helgoe, J.; Oswald, K.J.; Quattro, J.M. A Comprehensive Analysis of the Mislabelling of Atlantic Cod (Gadus morhua) Products in Spain. Fish. Res. 2020, 222, 105400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Sakurai, S.; Matsuda, Y. Rat 5S rDNA spacer sequences and chromosomal assignment of the genes to the extreme terminal region of chromosome 19. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 1996, 72, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.A.; García, T.; González, I.; Asensio, L.; Fernández, A.; Lobo, E.; Hernández, P.E.; Martín, R. Identification of goose (Anser anser) and mule duck (Anas platyrhynchos × Cairina moschata) foie gras by multiplex polymerase chain reaction amplification of the 5S RDNA gene. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 2717–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranishi, F. Rapid PCR-RFLP Method for Discrimination of Imported and Domestic Mackerel. Mar. Biotechnol. 2005, 7, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, E.; García, T.; Céspedes, A.; González, I.; Fernández, A.; Asensio, L.M.; Hernández, P.E.; Martín, R. Differentiation of Smoked Salmo Salar, Oncorhynchus Mykiss and Brama Raii Using the Nuclear Marker 5S RDNA. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 35, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, S.C.; Magnussen, J.E.; Abercrombie, D.L.; McAllister, M.K.; Shivji, M.S. Identification of Shark Species Composition and Proportion in the Hong Kong Shark Fin Market Based on Molecular Genetics and Trade Records. Conserv. Biol. 2006, 20, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán, P.; Garcia-Vazquez, E. Identification of Highly Prized Commercial Fish Using a PCR-Based Methodology. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 2006, 34, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, J.; Garcia-Vazquez, E. Genetic identification of nine hake species for detection of commercial fraud. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 2792–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllidis, A.; Karaiskou, N.; Perez, J.; Martinez, J.L.; Roca, A.; Lopez, B.; Garcia-Vazquez, E. Fish Allergy Risk Derived from Ambiguous Vernacular Fish Names: Forensic DNA-Based Detection in Greek Markets. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 2214–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigerio, J.; Gorini, T.; Palumbo, C.; De Mattia, F.; Labra, M.; Mezzasalma, V. A Fast and Simple DNA Mini-Barcoding and RPA Assay Coupled with Lateral Flow Assay for Fresh and Canned Mackerel Authentication. Food Anal. Methods 2022, 16, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, B.; Ning, Y.; Brenner, S. Late Changes in Spliceosomal Introns Define Clades in Vertebrate Evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 10267–10271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdullah, A.; Rehbein, H. DNA Barcoding for the Species Identification of Commercially Important Fishery Products in Indonesian Markets. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.; Rehbein, H. Authentication of Raw and Processed Tuna from Indonesian Markets Using DNA Barcoding, Nuclear Gene and Character-Based Approach. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2014, 239, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.; Rehbein, H. The Differentiation of Tuna (Family: Scombridae) Products through the PCR-Based Analysis of the Cytochrome b Gene and Parvalbumin Introns. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinbunga, S.; Pripue, P.; Khamnamtong, N.; Puanglarp, N.; Tassanakajon, A.; Jarayabhand, P.; Aoki, T.; Menasveta, P. Genetic diversity and molecular markers of the tropical abalone (Haliotis asinina) in Thailand. Mar. Biotechnol. 2003, 5, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meistertzheim, A.L.; Héritier, L.; Lejart, M. High-Resolution Melting of 18S RDNA Sequences (18S-HRM) for Discrimination of Bivalve’s Species at Early Juvenile Stage: Application to a Spat Survey. Mar. Biol. 2017, 164, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hanner, R. Molecular Approach to the Identification of Fish in the South China Sea. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novotny, A.; Jan, K.M.G.; Dierking, J.; Winder, M. Niche Partitioning between Planktivorous Fish in the Pelagic Baltic Sea Assessed by DNA Metabarcoding, QPCR and Microscopy. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Peer, Y.; Caers, A.; De Rijk, P.; De Wachter, R. Database on the Structure of Small Ribosomal Subunit RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998, 26, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beebee, T.; Rowe, G. An Introduction to Molecular Ecology; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Corse, E.; Costedoat, C.; Chappaz, R.; Pech, N.; Martin, J.F.; Gilles, A. A PCR-Based Method for Diet Analysis in Freshwater Organisms Using 18S RDNA Barcoding on Faeces. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, J.L.; Galetti, P.M. DNA Barcode and Evolutionary Relationship within Laemolyta Cope 1872 (Characiformes: Anostomidae) through Molecular Analyses. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2015, 93, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Tang, W.; Liu, Q.; Wang, D.; Ding, S. Genetic Diversity within Grouper Species and a Method for Interspecific Hybrid Identification Using DNA Barcoding and RYR3 Marker. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018, 121, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimberti, A.; De Mattia, F.; Losa, A.; Bruni, I.; Federici, S.; Casiraghi, M.; Martellos, S.; Labra, M. DNA Barcoding as a New Tool for Food Traceability. Food Res. Int. 2013, 50, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, L.F. The Current Status of DNA Barcoding Technology for Species Identification in Fish Value Chains. Food Policy 2015, 54, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, M.; Sharma, A.R.; Patra, B.C.; Sharma, G.; Seo, E.M.; Nam, J.S.; Chakraborty, C.; Lee, S.S. DNA Barcoding to Fishes: Current Status and Future Directions. Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 2016, 27, 2744–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M. A Simple Method for Estimating Evolutionary Rates of Base Substitutions through Comparative Studies of Nucleotide Sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellberg, R.S.; Morrissey, M.T. Advances in DNA-Based Techniques for the Detection of Seafood Species Substitution on the Commercial Market. J. Lab. Autom. 2011, 16, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, D.A.; Cavanaugh, M.; Clark, K.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Lipman, D.J.; Ostell, J.; Sayers, E.W. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D37–D42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidartondo, M.I.; Bruns, T.D.; Blackwell, M.; Edwards, I.; Taylor, A.F.S.; Bianchinotti, M.V.; Padamsee, M.; Callac, P.; Lima, N.; White, M.M.; et al. Preserving Accuracy in GenBank. Science 2018, 319, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Shen, X.; Chen, X.; Xiang, D.; Murphy, R.W.; Shen, Y. Detection of Potential Problematic Cytb Gene Sequences of Fishes in GenBank. Front. Genet. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D.N. Bold: The Barcode of Life Data System (http://www.barcodinglife.org). Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cipriani, P.; Smaldone, G.; Acerra, V.; D’Angelo, L.; Anastasio, A.; Bellisario, B.; Palma, G.; Nascetti, G.; Mattiucci, S. Genetic Identification and Distribution of the Parasitic Larvae of Anisakis pegreffii and Anisakis simplex (s. s.) in European Hake Merluccius Merluccius from the Tyrrhenian Sea and Spanish Atlantic Coast: Implications for Food Safety. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 198, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, S.R.; Mammel, M.K.; Lacher, D.W.; Elkins, C.A. Application of Metagenomic Sequencing to Food Safety: Detection of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia Coli on Fresh Bagged Spinach. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 8183–8191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, L.L.; Peatman, E.; Lu, J.; Kucuktas, H.; He, S.; Zhou, C.; Na-nakorn, U.; Liu, Z. DNA Barcoding of Catfish: Species Authentication and Phylogenetic Assessment. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.; Hanner, R.; Steinke, D. Five Years of FISH-BOL: Brief Status Report. Mitochondrial DNA 2011, 22, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- International Barcode of Life—Illuminate Biodiversity. Available online: https://ibol.org/ (accessed on 26 March 2023).
- FishTrace–Home—European Commission. Available online: https://fishtrace.jrc.ec.europa.eu/ (accessed on 26 March 2023).
- Zanzi, A.; Martinsohn, J.T. FishTrace: A Genetic Catalogue of European Fishes. Database 2017, 2017, bax075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- AquaGene. Available online: https://www.aquagene.org/ (accessed on 26 March 2023).
- Coissac, E.; Hollingsworth, P.M.; Lavergne, S.; Taberlet, P. From barcodes to genomes: Extending the concept of DNA barcoding. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franco, C.M.; Ambrosio, R.L.; Cepeda, A.; Anastasio, A. Fish Intended for Human Consumption: From DNA Barcoding to a next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)-Based Approach. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 42, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, E.; Jimenez, E.; Pardo, M.A.; Helyar, S.J. The Future of NGS (Next Generation Sequencing) Analysis in Testing Food Authenticity. Food Control 2019, 101, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, E.S.; Lee, M.N.; Kim, E.M.; Nam, B.H.; Noh, J.K.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Kang, J.H. Discrimination of Raw Material Species in Mixed Seafood Products (Surimi) Using the next Generation Sequencing Method. Food Biosci. 2021, 41, 100786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappel, K.; Haase, I.; Käppel, C.; Sotelo, C.G.; Schröder, U. Species Identification in Mixed Tuna Samples with Next-Generation Sequencing Targeting Two Short Cytochrome b Gene Fragments. Food Chem. 2017, 234, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carvalho, D.C.; Palhares, R.M.; Drummond, M.G.; Gadanho, M. Food Metagenomics: Next Generation Sequencing Identifies Species Mixtures and Mislabelling within Highly Processed Cod Products. Food Control 2017, 80, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, A.; Armani, A.; Sotelo, C.G. Advances in the Analysis of Complex Food Matrices: Species Identification in Surimi-Based Products Using Next Generation Sequencing Technologies. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paracchini, V.; Petrillo, M.; Lievens, A.; Puertas Gallardo, A.; Martinsohn, J.T.; Hofherr, J.; Maquet, A.; Silva, A.P.B.; Kagkli, D.M.; Querci, M.; et al. Novel Nuclear Barcode Regions for the Identification of Flatfish Species. Food Control 2017, 79, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paracchini, V.; Petrillo, M.; Lievens, A.; Kagkli, D.M.; Angers-Loustau, A. Nuclear DNA Barcodes for Cod Identification in Mildly-Treated and Processed Food Products. Food Addit. Contam. Part. A Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 2019, 36, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prosser, S.W.J.; Dewaard, J.R.; Miller, S.E.; Hebert, P.D.N. DNA Barcodes from Century-Old Type Specimens Using next-Generation Sequencing. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2016, 16, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, C.R.; Oliva-Teles, A.; Tavares, F. Gut Microbiota Dynamics in Carnivorous European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Fed Plant-based Diets. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascolo, C.; Ceruso, M.; Sordino, P.; Palma, G.; Anastasio, A.; Pepe, T. Comparison of Mitochondrial DNA Enrichment and Sequencing Methods from Fish Tissue. Food Chem. 2019, 294, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| mtDNA | nDNA | |
|---|---|---|
| High number of copies of mtDNA | Useful when occur hybridization and introgression | |
| Advantages | Matrilinear inheritance | |
| Low variability within species and greater differentiation between | ||
| Disadvantages | Nomenclature difficulties in differentiating closely related species | Subjected to recombination |
| Single copy genes present in each cell |
| Reference | Collected Sample | Species Discovered | Global “Red List” | World Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| “Caçao” fish | Carcharhinus brachyurus | VU | Brazil | |
| “Caçao” fish | Galeorhinus galeus | CR | Brazil | |
| “Caçao” fish | Gymnura altavela | EN | Brazil | |
| “Caçao” fish | Myliobatis goodei | VU | Brazil | |
| “Caçao” fish | Narcine brasiliensis | NT | Brazil | |
| “Caçao” fish | Prionace glauca | NT | Brazil | |
| “Caçao” fish | Pseudobatos horkelii | CR | Brazil | |
| Almeròn-Souza F. et al., 2018 [57] | “Caçao” fish | Rhizoprionodon lalandii | VU | Brazil |
| “Caçao” fish | Rhizoprionodon porosus | VU | Brazil | |
| “Caçao” fish | Sphyrna lewini | CR | Brazil | |
| “Caçao” fish | Sphyrna zygaena | VU | Brazil | |
| “Caçao” fish | Squalus mitsukurii | EN | Brazil | |
| “Caçao” fish | Squatina occulta | CR | Brazil | |
| “Caçao” fish | Xiphias gladius | NT | Brazil | |
| “Caçao” fish | Zapteryx brevirostris | EN | Brazil | |
| Engraulis encrasicolus | Thunnus albacares | LC | Europe | |
| Engraulis encrasicolus | Thunnus alalunga | LC | Europe | |
| Thunnus alalunga | Thunnus thynnus | LC | Africa | |
| Blanco-Fernandez C. et al., 2021 [54] | Thunnus alalunga | Thunnus obesus | VU | Africa |
| Merluccius capensis | Gadus morhua | VU | Africa | |
| Katsowomus pelamis | Thunnus thynnus | LC | Italy | |
| Filonzi L. et al., 2021 [32] | Katsowomus pelamis | Thunnus maccoyii | EN | Italy |
| Lamna nasus | Isurus oxyrinchus | EN | Italy | |
| Lowenstein J.H. et al., 2009 [46] | Thunnus sp. | Thunnus thynnus | LC | USA |
| Thunnus sp. | Thunnus maccoyii | EN | USA | |
| Dufflocq P. et al., 2022 [55] | Xiphias gladius | Isurus oxyrinchus | EN | Chile |
| Xiphias gladius | Lamna nasus | VU | Chile | |
| Ferrito V. et al., 2019 [51] | Xiphias gladius | Mustelus mustelus | EN | Italy |
| Xiphias gladius | Oxyntus centrina | EN | Italy | |
| Conger sp. | Micropogonias furnieri | LC | Brazil | |
| Salmo salar | Thunnus alalunga | NT | Brazil | |
| Thunnus sp. | Seriola zonata | LC | Brazil | |
| Thunnus sp. | Lepidocybium flavobrunneum | LC | Brazil | |
| Thunnus sp. | Salmo salar | LC | Brazil | |
| Thunnus sp. | Seriola lalandii | LC | Brazil | |
| “White fish” | Thunnus obesus | VU | Brazil | |
| “White fish” | Salmo salar | LC | Brazil | |
| Staffen C.F. et al., 2017 [58] | Peprilus paru | Micropogonias furnieri | LC | Brazil |
| Micropogonias undulatus | Prionace glauca | NT | Brazil | |
| Lepidocybium flavobrunneum | Ruvettus pretiosus | LC | Brazil | |
| Flounder gen. | Isopisthus parvipinnis | LC | Brazil | |
| Flounder gen. | Micropogonias furnieri | LC | Brazil | |
| Epinephelus sp. | Micropogonias furnieri | LC | Brazil | |
| Molva sp. | Micropogonias furnieri | LC | Brazil | |
| Pangasius pangasius | Micropogonias furnieri | LC | Brazil | |
| Salmo salar | Seriola zonata | LC | Brazil | |
| Salmo salar | Prionace glauca | NT | Brazil | |
| Salmo salar | Micropogonias furnieri | LC | Brazil | |
| Carcharias taurus | Prionace glauca | NT | Brazil | |
| Xiphias gladius | Trichiurus lepturus | LC | Brazil | |
| Cynoscion regalis | Isopisthus parvipinnis | LC | Brazil | |
| Barbuto M. et al., 2010 [59] | Mustelus mustelus | Squalus acanthias | VU | Italy |
| Mustelus mustelus | Prionace glauca | NT | Italy | |
| Mustelus mustelus | Galeorhinus galeus | CR | Italy | |
| Mustelus mustelus | Alopias superciliosus | VU | Italy | |
| Mustelus mustelus | Isurus oxyrinchus | EN | Italy |
| Database | Molecular Markers | Taxa | N° of Sequences | World Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GenBank | All | All | 239 milions | All |
| BOLD | COI, ITS, rbcL, matK | Animal, Plants, Fungi, Protists | 11 milions | All |
| FISH-BOL | COI | Freshwater and Marine Species | Not Available | All |
| Fish-Trace | cytb, rhodopsin | Marine Species | Not Available | Europe |
| Aquagene | COI, cytb, MYH6, rhodopsin | Marine Species | 1383 | Central Eastern Atlantic |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Filonzi, L.; Ardenghi, A.; Rontani, P.M.; Voccia, A.; Ferrari, C.; Papa, R.; Bellin, N.; Nonnis Marzano, F. Molecular Barcoding: A Tool to Guarantee Correct Seafood Labelling and Quality and Preserve the Conservation of Endangered Species. Foods 2023, 12, 2420. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12122420
Filonzi L, Ardenghi A, Rontani PM, Voccia A, Ferrari C, Papa R, Bellin N, Nonnis Marzano F. Molecular Barcoding: A Tool to Guarantee Correct Seafood Labelling and Quality and Preserve the Conservation of Endangered Species. Foods. 2023; 12(12):2420. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12122420
Chicago/Turabian StyleFilonzi, Laura, Alessia Ardenghi, Pietro Maria Rontani, Andrea Voccia, Claudio Ferrari, Riccardo Papa, Nicolò Bellin, and Francesco Nonnis Marzano. 2023. "Molecular Barcoding: A Tool to Guarantee Correct Seafood Labelling and Quality and Preserve the Conservation of Endangered Species" Foods 12, no. 12: 2420. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12122420
APA StyleFilonzi, L., Ardenghi, A., Rontani, P. M., Voccia, A., Ferrari, C., Papa, R., Bellin, N., & Nonnis Marzano, F. (2023). Molecular Barcoding: A Tool to Guarantee Correct Seafood Labelling and Quality and Preserve the Conservation of Endangered Species. Foods, 12(12), 2420. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12122420