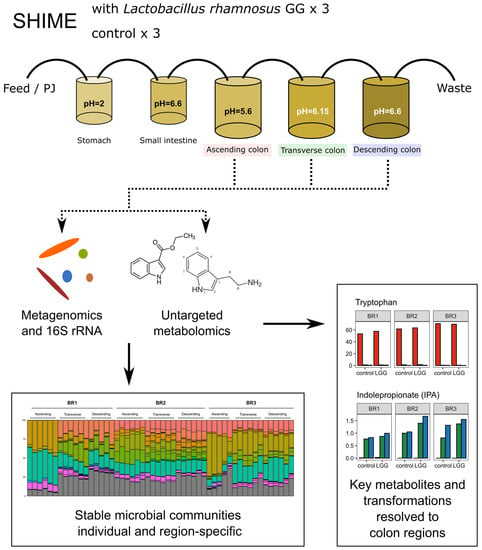
Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Strain GG (LGG) Regulate Gut Microbial Metabolites, an In Vitro Study Using Three Mature Human Gut Microbial Cultures in a Simulator of Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem (SHIME)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. SHIME Set Up and Operation
2.3. Metabolite Analysis
2.4. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
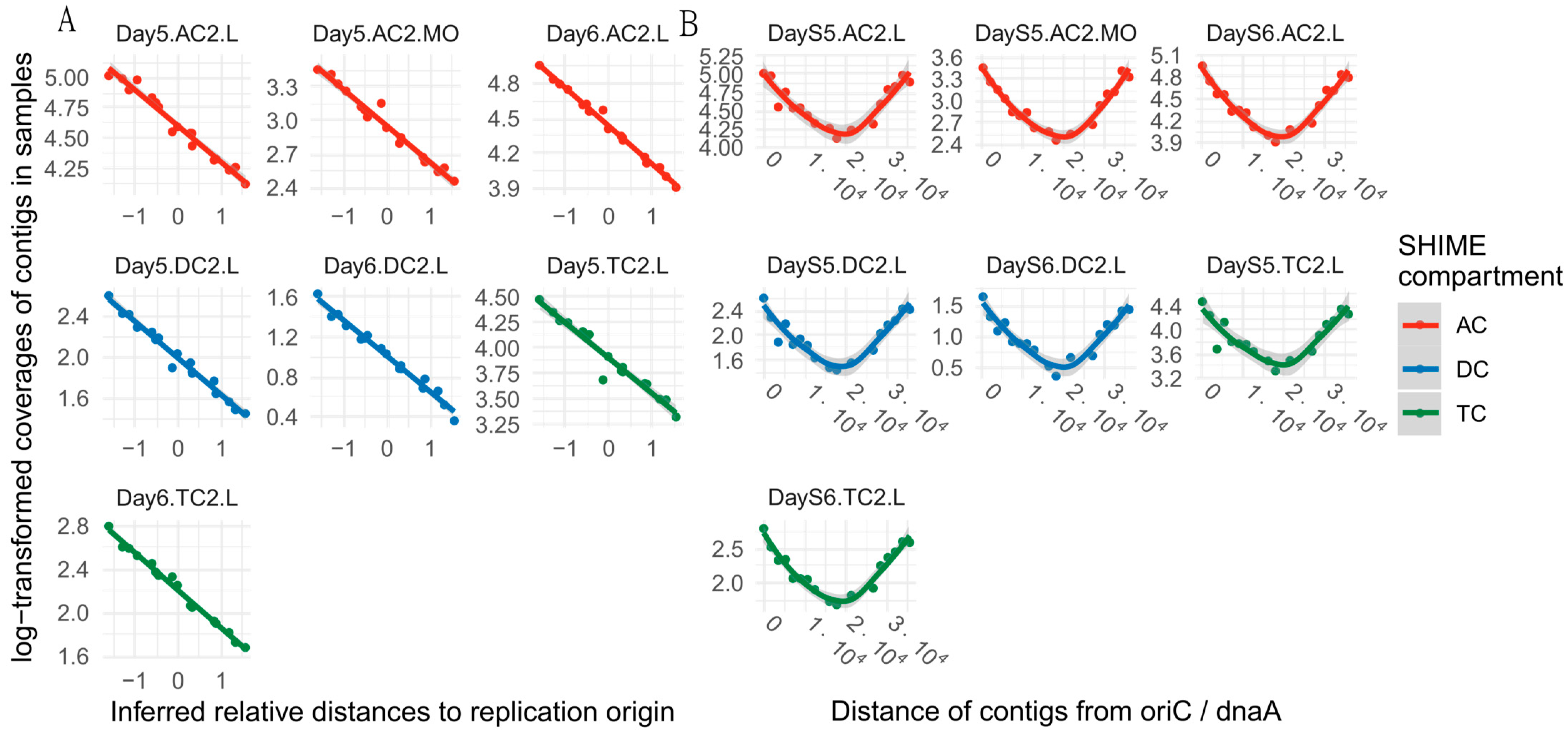
2.5. Peak-to-Trough Ratio Analysis
2.6. Bioinformatic and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. LGG Survival and Replication Subsection
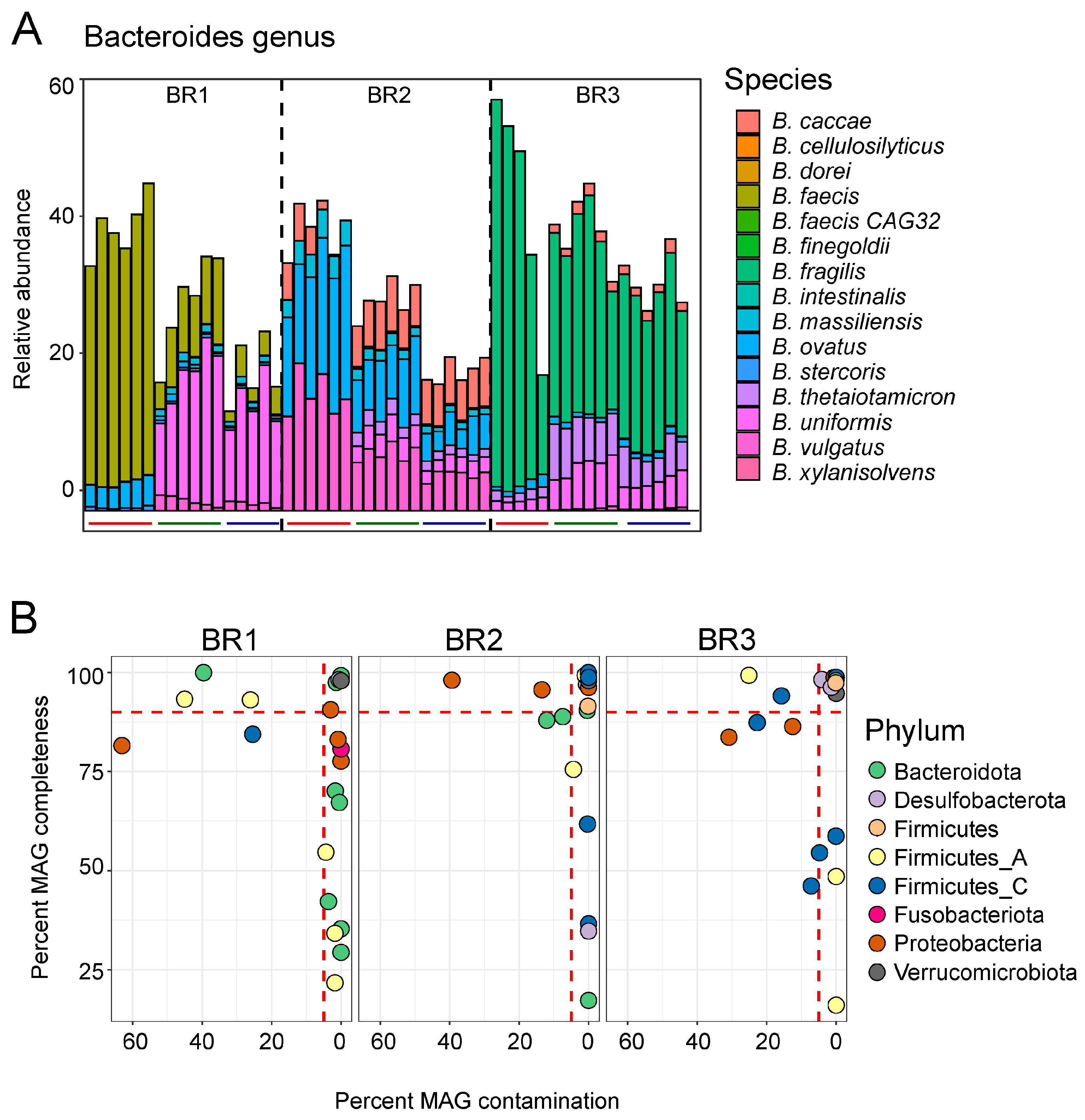
3.2. Shotgun Metagenomic Sequencing
3.3. Association of Microbiome and Metabolome
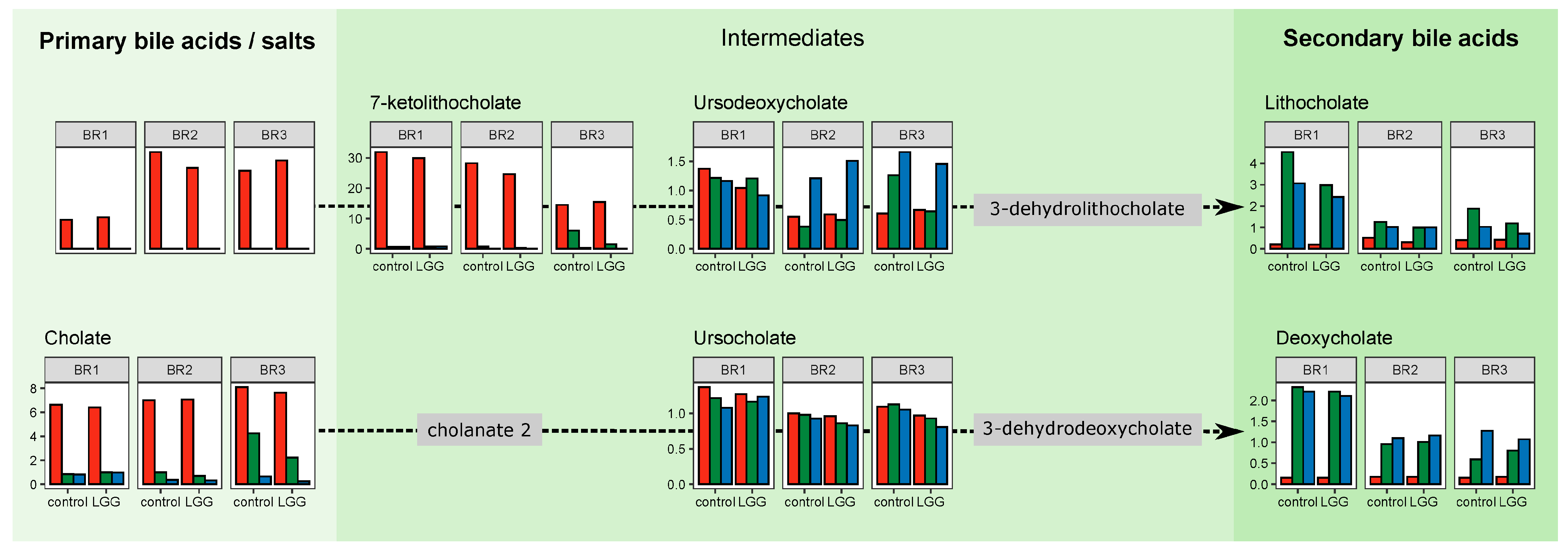
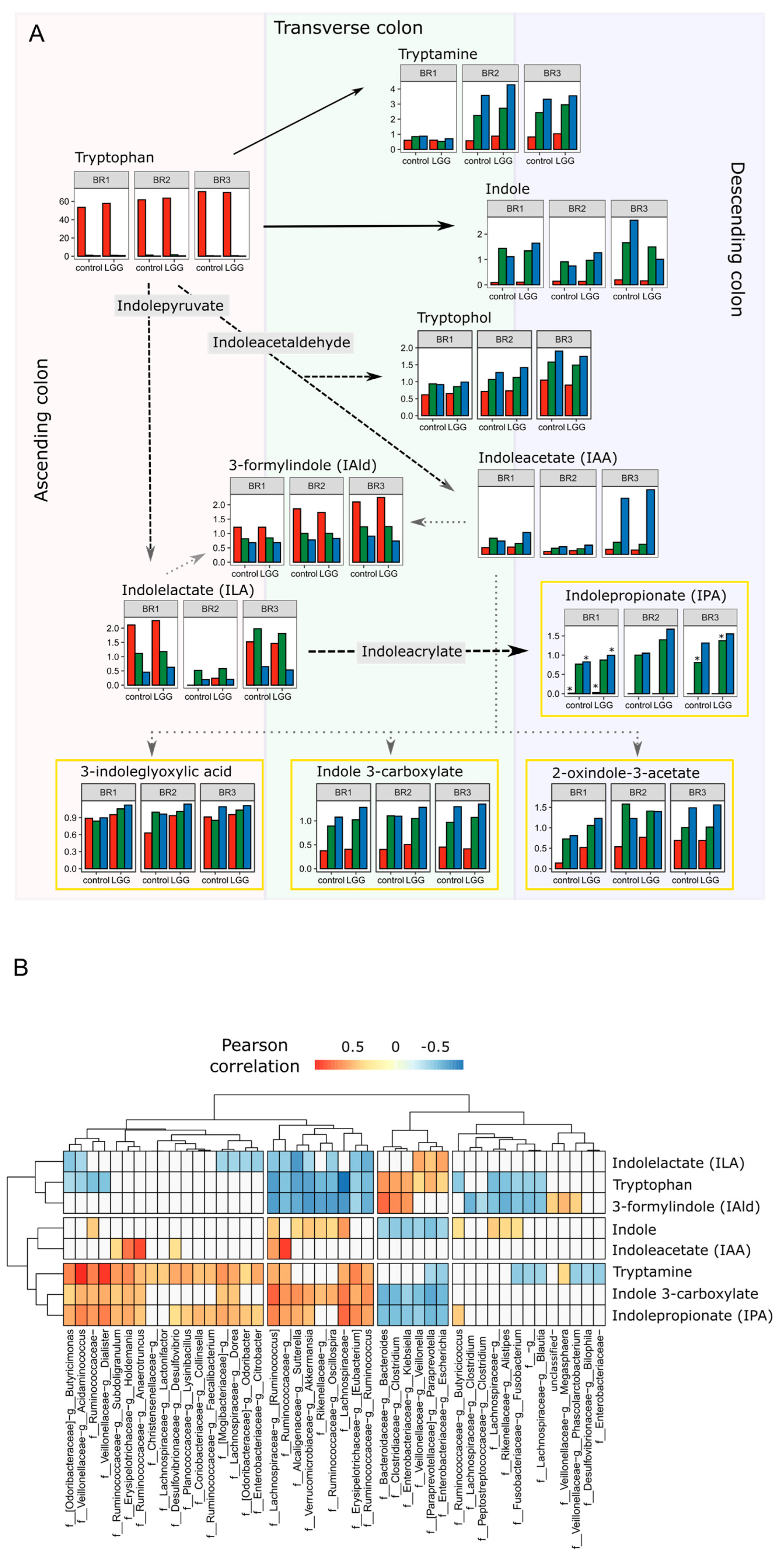
3.4. Spatial Resolution of Metabolite Transformations
3.5. Individual Metabolites and Pathways
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agus, A.; Clément, K.; Sokol, H. Gut microbiota-derived metabolites as central regulators in metabolic disorders. BMJ 2021, 70, 1174–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, W.; Zadeh, K.; Vekariya, R.; Ge, Y.; Mohamadzadeh, M. Tryptophan metabolism and gut-brain homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roger, H.M.; Licht, T.R. Microbial tryptophan catabolites in health and disease. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.S.; Davies, S.S. Microbial metabolism of dietary components to bioactive metabolites: Opportunities for new therapeutic interventions. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, F.; Pace, M.; Quartarone, G. Probiotics in digestive diseases: Focus on Lactobacillus GG. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2015, 61, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cameron, D.; Hock, Q.S.; Kadim, M.; Mohan, N.; Ryoo, E.; Sandhu, B.; Yamashiro, Y.; Jie, C.; Hoekstra, H.; Guarino, A. Probiotics for gastrointestinal disorders: Proposed recommendations for children of the Asia-Pacific region. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 7952–7964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Fasano, S.; Madayiputhiya, N.; Morin, N.P.; Nataro, J.; Fasano, A. Isolation, identification, and characterization of small bioactive peptides from Lactobacillus GG conditional media that exert both anti-Gram-negative and Gram-positive bactericidal activity. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2009, 49, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.H.; Yang, G.Y.; Liu, X.; Xia, B.; Hu, X.; Su, J.H.; Wang, J.F. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG affects microbiota and suppresses autophagy in the intestines of pigs challenged with salmonella infants. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segers, M.E.; Lebeer, S. Towards a better understanding of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG—Host interactions. Microb. Cell Fact. 2014, 13 (Suppl. S1), S1–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Polk, D.B. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG: An Updated Strategy to Use Microbial Products to Promote Health. Funct. Food Rev. 2012, 4, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, R.; Orlando, A.; Linsalata, M.; Cavallini, A.; Messa, C. Effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG on the cell growth and polyamine metabolism in HGC-27 human gastric cancer cells. Nutr. Cancer 2017, 59, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.-C.; Liu, J.-R. Effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG on Energy Metabolism, Leptin Resistance, and Gut Microbiota in Mice with Diet-Induced Obesity. Nutrients 2020, 9, 2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimura, N.; Li, Q.; Chu, E.S.H.; Lau, H.C.H.; Fong, W.; Liu, W.; Liang, C.; Nakatsu, G.; Su, A.C.Y.; Coker, O.O.; et al. Lactobacillus gallinarum modulates the gut microbiota and produces anti-cancer metabolites to protect against colorectal tumourigenesis. Gut Microbiota BMJ 2021, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Balasubramanian, I.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Nadler, I.; Singh, R.; Harlan, D.; Bumber, A.; He, Y.; Kerkhof, L.J.; Gao, N.; et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG modifies the metabolome of pathobionts in gnotobiotic mice. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capurso, L. Thirty years of Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GG, a review. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2019, 53, S1–S41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathipa-Mdakane, M.G.; Thantsha, M.S. Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus: A Suitable Candidate for the Construction of Novel Bioengineered Probiotic Strains for Targeted Pathogen Control. Foods 2022, 11, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Firrman, J.; Tanes, C.; Bittinger, K.; Thomas-Gahring, A.; Wu, G.D.; Van den Abbeele, P.; Tomasula, P.M. Establishing a mucosal gut microbial community in vitro using an artificial simulator. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firrman, J.; Liu, L.S.; Tanes, C.; Friedman, E.S.; Bittinger, K.; Daniel, S.; van den Abbeele, P.; Evans, B. Metabolic analysis of regionally distinct gut microbial communities using an in vitro platform. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 13056–13067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abellan-Schneyder, I.; Matchado, M.S.; Reitmeier, S.; Sommer, A.; Sewald, Z.; Baumbach, J.; List, M.; Neuhaus, K. Primer, Pipelines, Parameters: Issues in 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing. mSphere 2021, 6, e01202-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firrman, J.; Liu, L.; Mahalak, K.; Hu, W.; Bittinger, K.; Moustafa, A.; Narrowe, A.; Tomasula, P. An in-vitro analysis of how lactose modifies the gut microbiota structure and function of adults in a donor-independent manner. Front. Nutr. 2023, 9, 1040744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firrman, J.; Mahalak, K.; Bobokalonov, J.; Liu, L.; Lee, J.; Bittinger, K.; Mattei, L.; Gadaingan, R.; Narrowe, A.; Lemons, J. The prebiotic effects of lemon pectin are dependent on molecular weight and degree of esterification. Foods 2023, 11, 3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Hofstaedter, C.E.; Zhao, C.; Mattei, L.; Tanes, C.; Clarke, E.; Lauder, A.; Sherrill-Mix, S.; Chehoud, C.; Kelsen, J.; et al. Optimizing methods and dodging pitfalls in microbiome research. Microbiome 2017, 5, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2020, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, D.; Price, M.N.; Goodrich, J.; Nawrocki, E.P.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Probst, A.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R.; Hugenholtz, P. An improved Greengenes taxonomy with explicit ranks for ecological and evolutionary analyses of bacteria and archaea. ISME J. 2012, 6, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2—Approximately Maximum-Likelihood Trees for Large Alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanes, C.; Bittinger, K.; Gao, Y.; Friedman, E.S.; Nessel, L.; Paladhi, U.R.; Chau, L.; Panfen, E.; Fischbach, M.A.; Braun, J.; et al. Role of dietary fiber in the recovery of the human gut microbiome and its metabolome. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 394–407.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, E.L.; Taylor, L.J.; Zhao, C.; Connell, A.; Lee, J.J.; Fett, B.; Bushman, F.D.; Bittinger, K. An extensible pipeline for analyzing metagenomic sequencing experiments. Microbiome 2019, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, H. Quantifying and comparing bacterial growth dynamics in multiple metagenomic samples. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 1041–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, N.A.; Fass, J.N. Sickle: A Sliding-Window, Adaptive, Quality-Based Trimming Tool for FastQ Files (Version 1.33) [Software]. 2011. Available online: https://github.com/najoshi/sickle (accessed on 13 November 2018).
- Beghini, F.; McIver, L.J.; Blanco-Míguez, A.; Dubois, L.; Asnicar, F.; Maharjan, S.; Mailyan, A.; Manghi, P.; Scholz, M.; Thomas, A.M.; et al. Integrating taxonomic, functional, and strain-level profiling of diverse microbial communities with bioBakery 3. eLife 2021, 10, e65088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.W. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.D.; Li, F.; Kirton, E.; Thomas, A.; Egan, R.; An, H.; Wang, Z. MetaBAT 2: An adaptive binning algorithm for robust and efficient genome reconstruction from metagenome assemblies. Peer J. 2019, 26, e7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM: Assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaumeil, P.A.; Mussig, A.J.; Hugenholtz, P.; Parks, D.H. GTDB-Tk: A toolkit to classify genomes with the Genome Taxonomy Database. Bioinformatics 2019, 15, 1925–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 18 April 2022).
- Alander, M.; Korpela, R.; Saxelin, M.; Vilpponen-Salmela, T.; Mattila-Sandholm, T.; von Wright, A. Recovery of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG from human colonic biopsies. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1997, 24, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, A.J.; Yaya, A.M.A.; Ng, S.; Chandrashekhar, K.; Roach, J.; Magness, S.T.; Azcarate-Peril, M.A. Lumen and mucosa-associated Lactobacillus rhamnosus from the intestinal tract of organ donors. Gut Microbiome 2020, 1, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalak, K.K.; Firrman, J.; Lee, J.J.; Bittinger, K.; Nuñez, A.; Mattei, L.M.; Zhang, H.; Fett, B.; Bobokalonov, J.; Arango-Argoty, G.; et al. Triclosan treatment has robust, yet reversible impact on human gut microbial composition in vitro. PLoS ONE 2020, 16, e0234046. [Google Scholar]
- Mahalak, K.K.; Firrman, J.; Bobokalonov, J.; Narrowe, A.B.; Bittinger, K.; Daniel, S.; Tanes, C.; Mattei, L.M.; Zeng, W.B.; Soares, J.W.; et al. The probiotic Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus strain GG (LGG) persists in an in vitro model of the gut microbiome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negatu, D.A.; Gengenbacher, M.; Dartois, V.; Dick, T. Indole propionic acid, an unusual antibiotic produced by the gut microbiota, with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 11, 575586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhang, F.; Zhong, S.; Sun, Y.; Huo, J.; Zhu, J.; Wu, C. The gut microbiota-produced indole-3-propionic acid confers the antihyperlipidemic effect of mulberry-derived 1-deoxynojirimycin. mSystems 2020, 5, e00313–e00320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konopelski, P.; Mogilnick, I. Biological effects of indole-3-propionic acid, a gut microbiota-derive metabolite, and Its precursor tryptophan in mammals’ health and disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodd, D.; Spitzer, M.H.; Van Treuren, W.; Merrill, B.D.; Hryckowian, A.J.; Higginbottom, S.K.; Le, A.; Cowan, T.M.; Nolan, G.P.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. A gut bacterial pathway metabolizes aromatic amino acids into nine circulating metabolites. Nat. Lett. 2017, 551, 648–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Narrowe, A.B.; Firrman, J.A.; Mahalak, K.K.; Bobokalonov, J.T.; Lemons, J.M.S.; Bittinger, K.; Daniel, S.; Tanes, C.; Mattei, L.; et al. Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Strain GG (LGG) Regulate Gut Microbial Metabolites, an In Vitro Study Using Three Mature Human Gut Microbial Cultures in a Simulator of Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem (SHIME). Foods 2023, 12, 2105. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112105
Liu L, Narrowe AB, Firrman JA, Mahalak KK, Bobokalonov JT, Lemons JMS, Bittinger K, Daniel S, Tanes C, Mattei L, et al. Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Strain GG (LGG) Regulate Gut Microbial Metabolites, an In Vitro Study Using Three Mature Human Gut Microbial Cultures in a Simulator of Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem (SHIME). Foods. 2023; 12(11):2105. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112105
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, LinShu, Adrienne B. Narrowe, Jenni A. Firrman, Karley K. Mahalak, Jamshed T. Bobokalonov, Johanna M. S. Lemons, Kyle Bittinger, Scott Daniel, Ceylan Tanes, Lisa Mattei, and et al. 2023. "Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Strain GG (LGG) Regulate Gut Microbial Metabolites, an In Vitro Study Using Three Mature Human Gut Microbial Cultures in a Simulator of Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem (SHIME)" Foods 12, no. 11: 2105. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112105
APA StyleLiu, L., Narrowe, A. B., Firrman, J. A., Mahalak, K. K., Bobokalonov, J. T., Lemons, J. M. S., Bittinger, K., Daniel, S., Tanes, C., Mattei, L., Friedman, E. S., Soares, J. W., Kobori, M., Zeng, W.-B., & Tomasula, P. M. (2023). Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Strain GG (LGG) Regulate Gut Microbial Metabolites, an In Vitro Study Using Three Mature Human Gut Microbial Cultures in a Simulator of Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem (SHIME). Foods, 12(11), 2105. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112105