Modification of the Structural and Functional Characteristics of Mung Bean Globin Polyphenol Complexes: Exploration under Heat Treatment Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Preparation of Mung Bean Globulin
2.4. Protein Purity Determination
2.5. Preparation of the Protein–Polyphenol Complex
2.6. Protein–Polyphenol Binding Rate and Mass Ratio
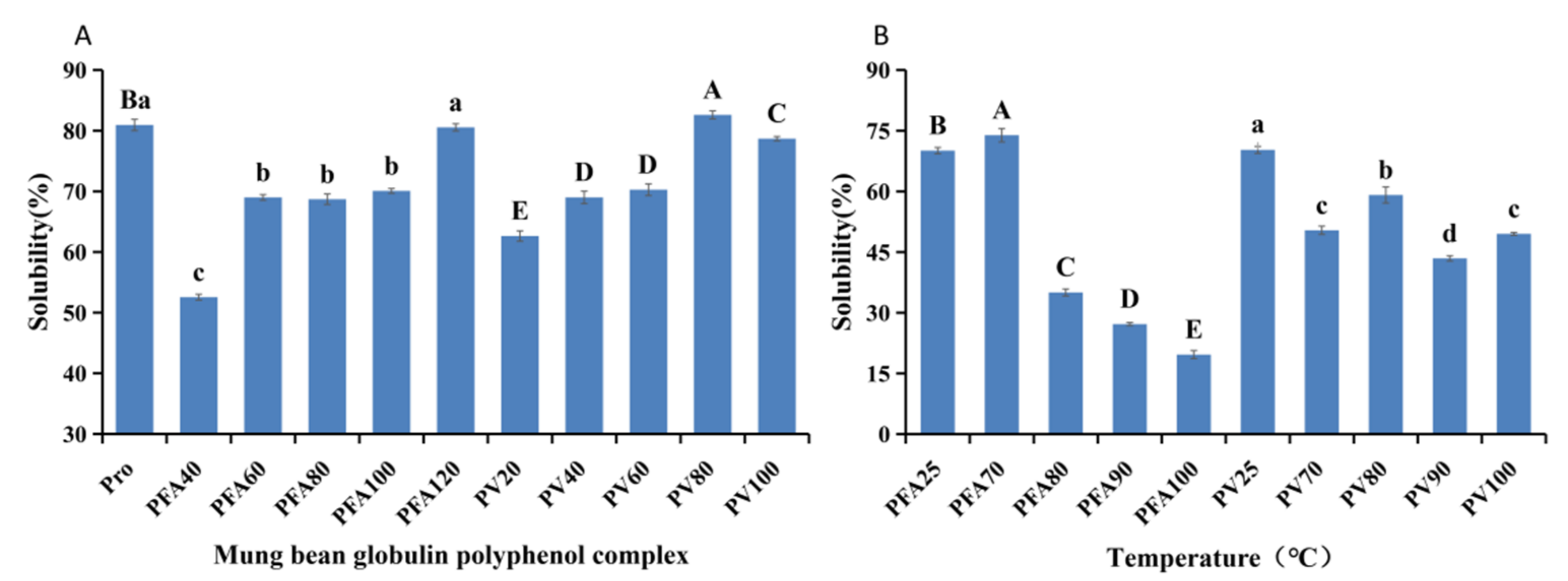
2.7. Solubility Properties
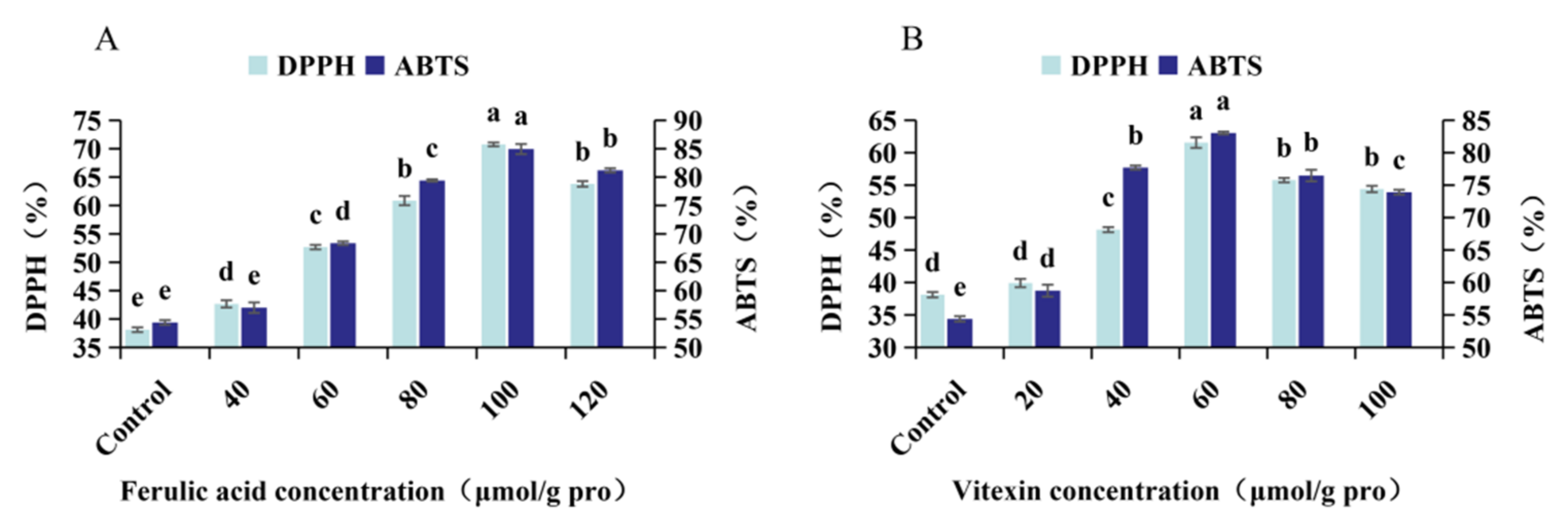
2.8. Determination of DPPH Free Radical Scavenging Activity
2.9. Determination of ABTS+ Free Radical Scavenging Activity
2.10. Ferric-Reducing Antioxidant Power
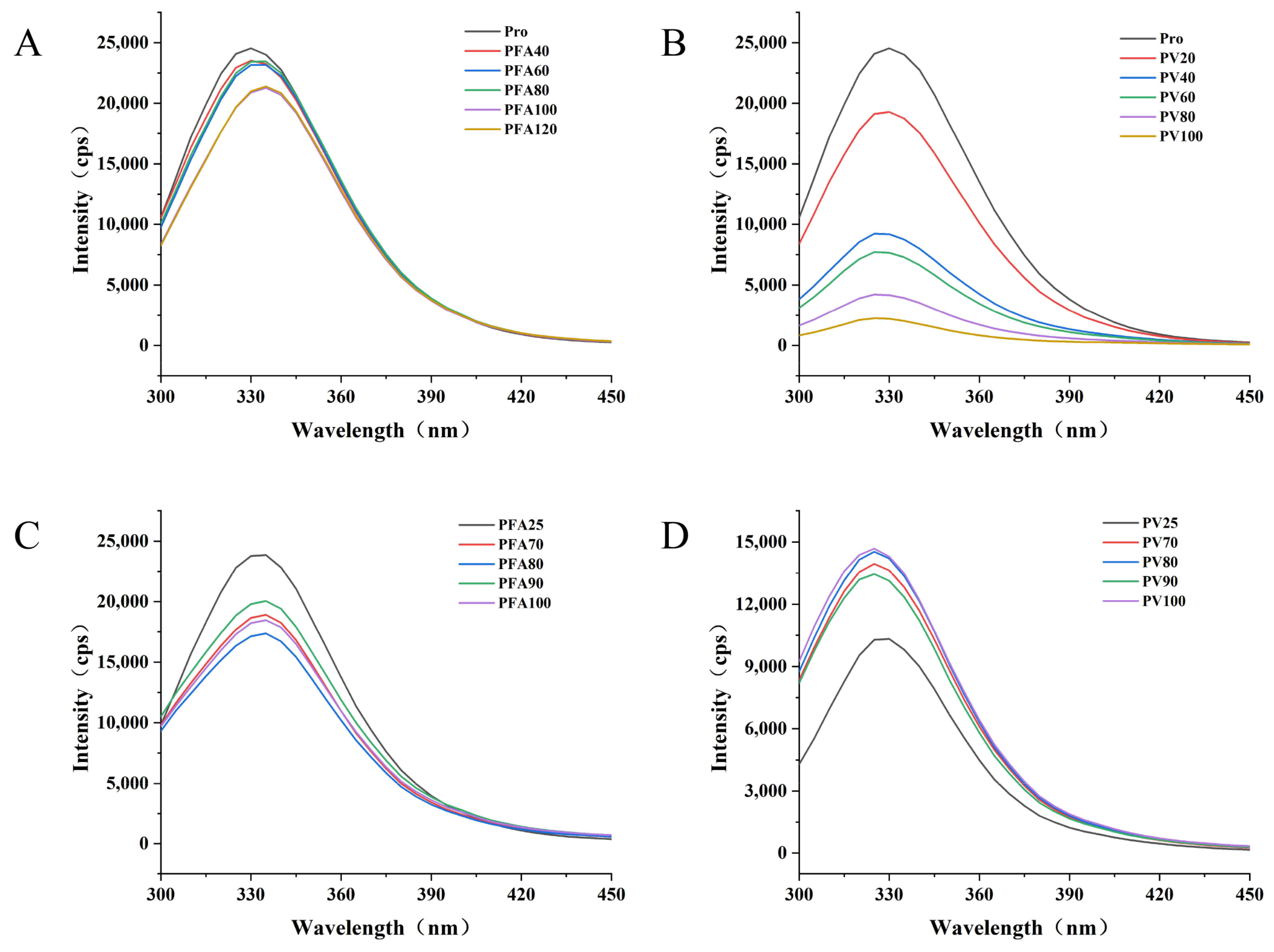
2.11. Fluorescence Spectrometry
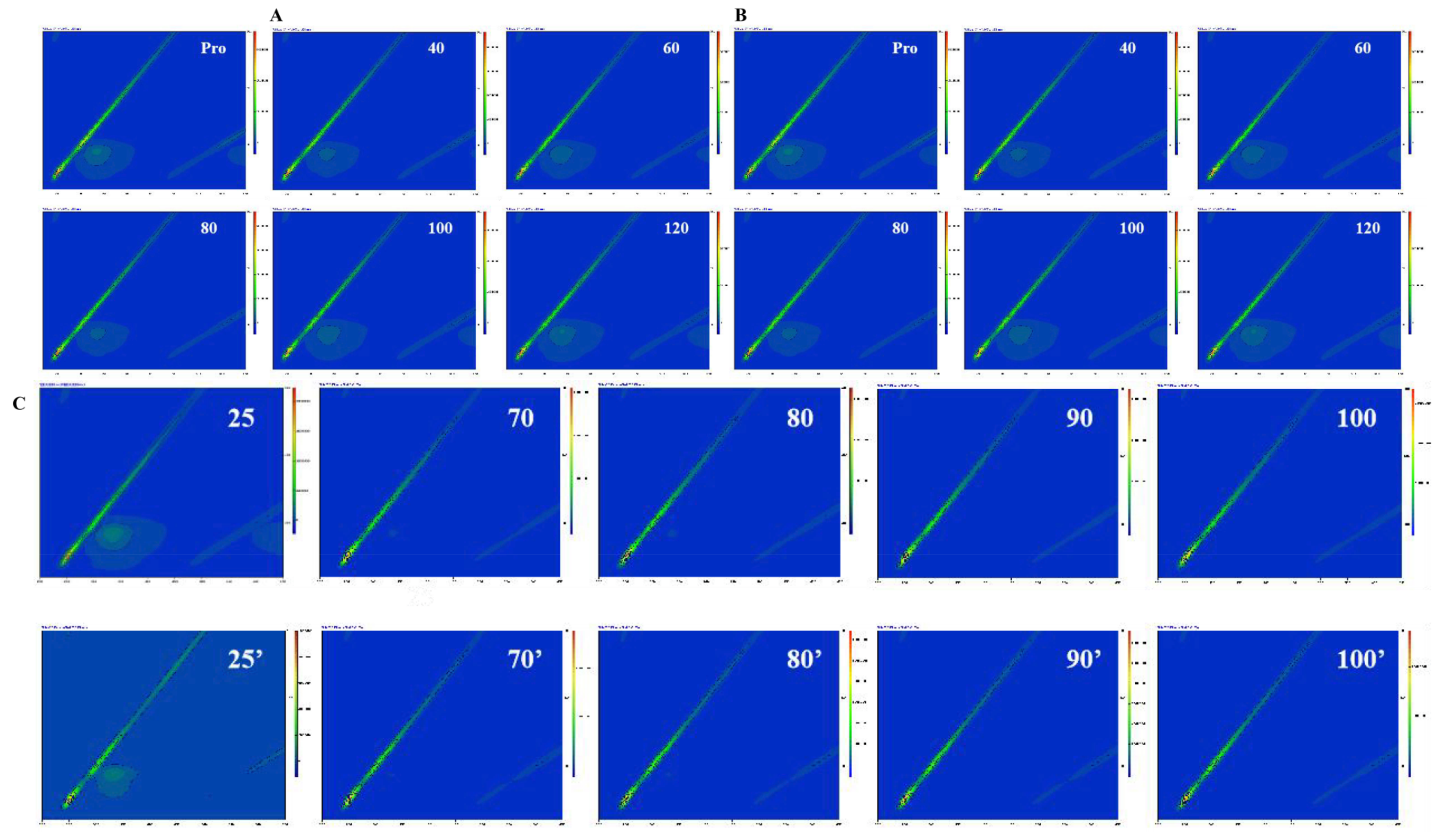
2.12. Fluorescence Quenching Mechanism
2.13. Calculation of the Binding Constant and Binding Site
2.14. Thermodynamic Parameters and Force Type
2.15. Fourier Infrared Spectrum Analysis
2.16. SDS–PAGE Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
2.17. Particle Size Distribution and ζ Potential
2.18. Determination of Surface Hydrophobicity
2.19. Data Statistics and Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Binding Amount
3.2. Antioxidant Activity
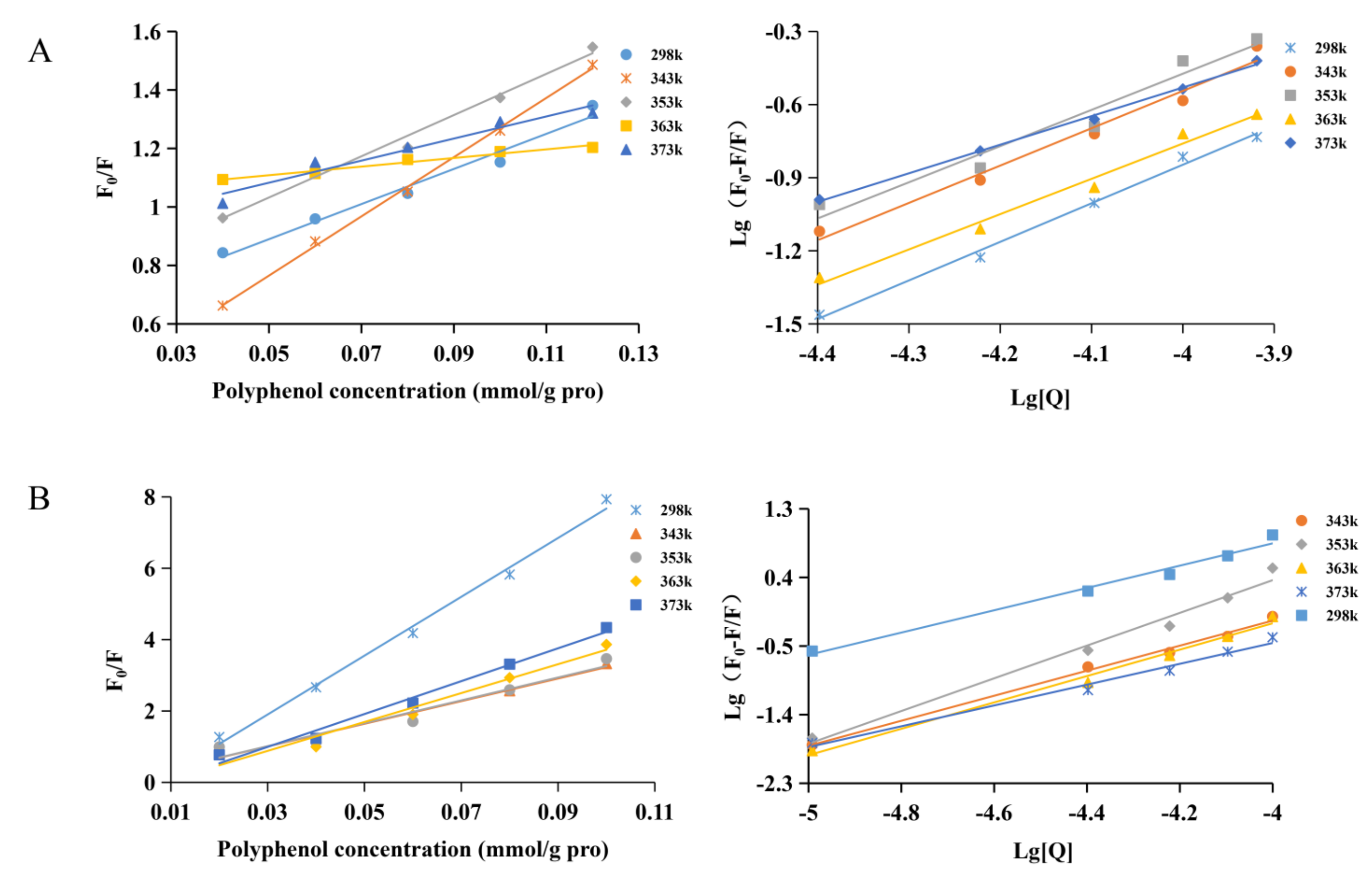
3.3. Fluorescence Spectrum
3.4. Quenching Mechanism
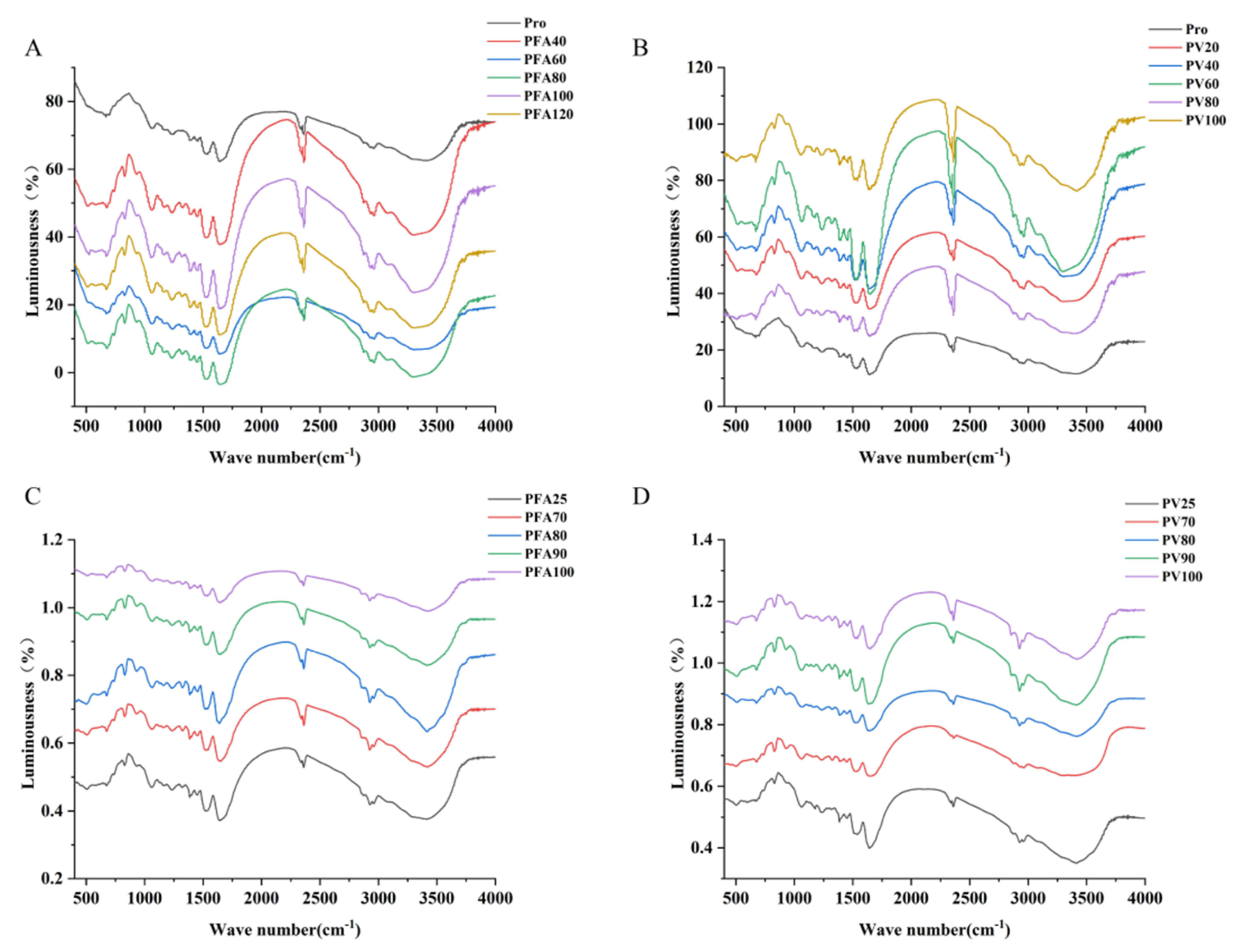
3.5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
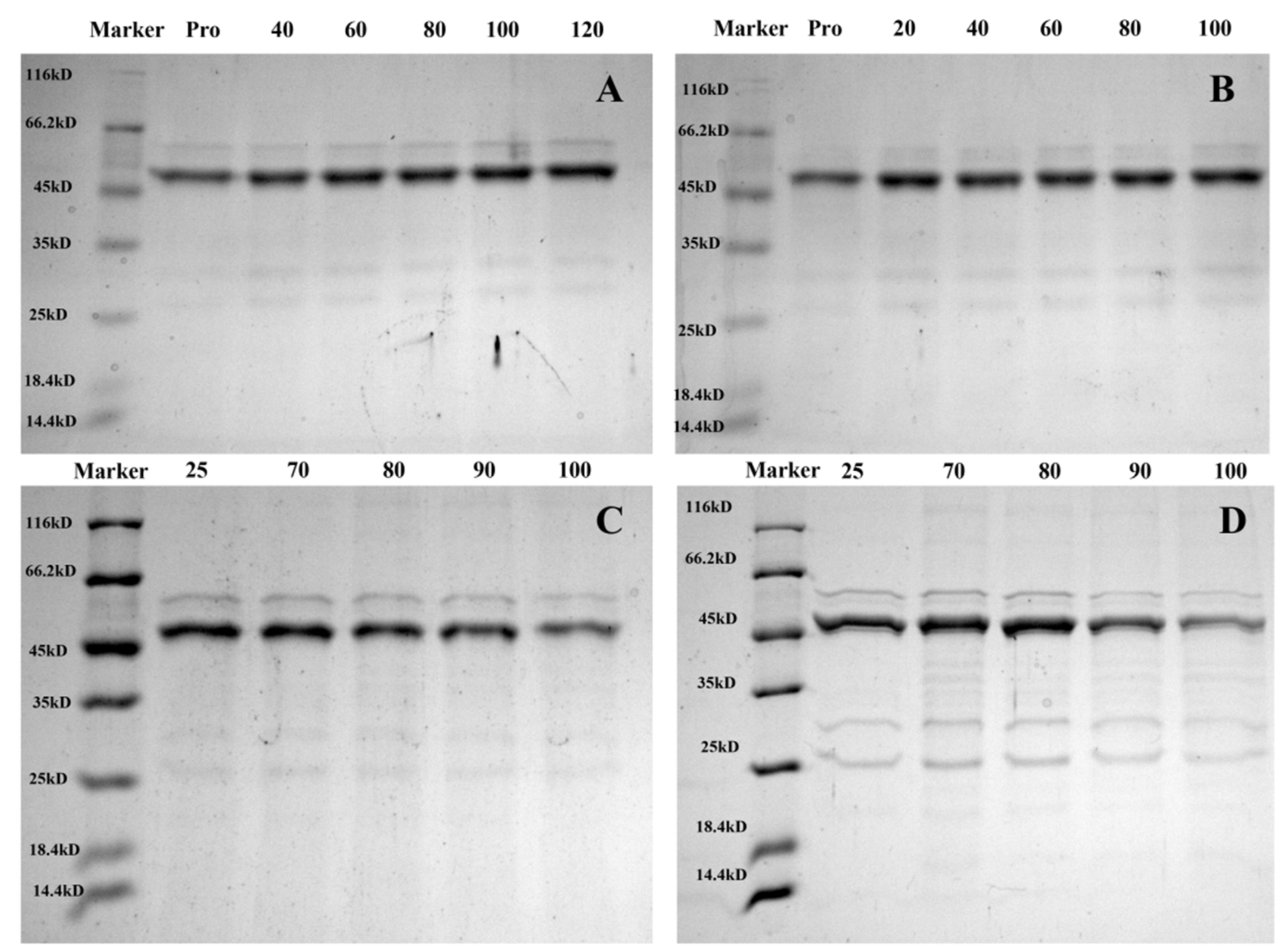
3.6. SDS–PAGE
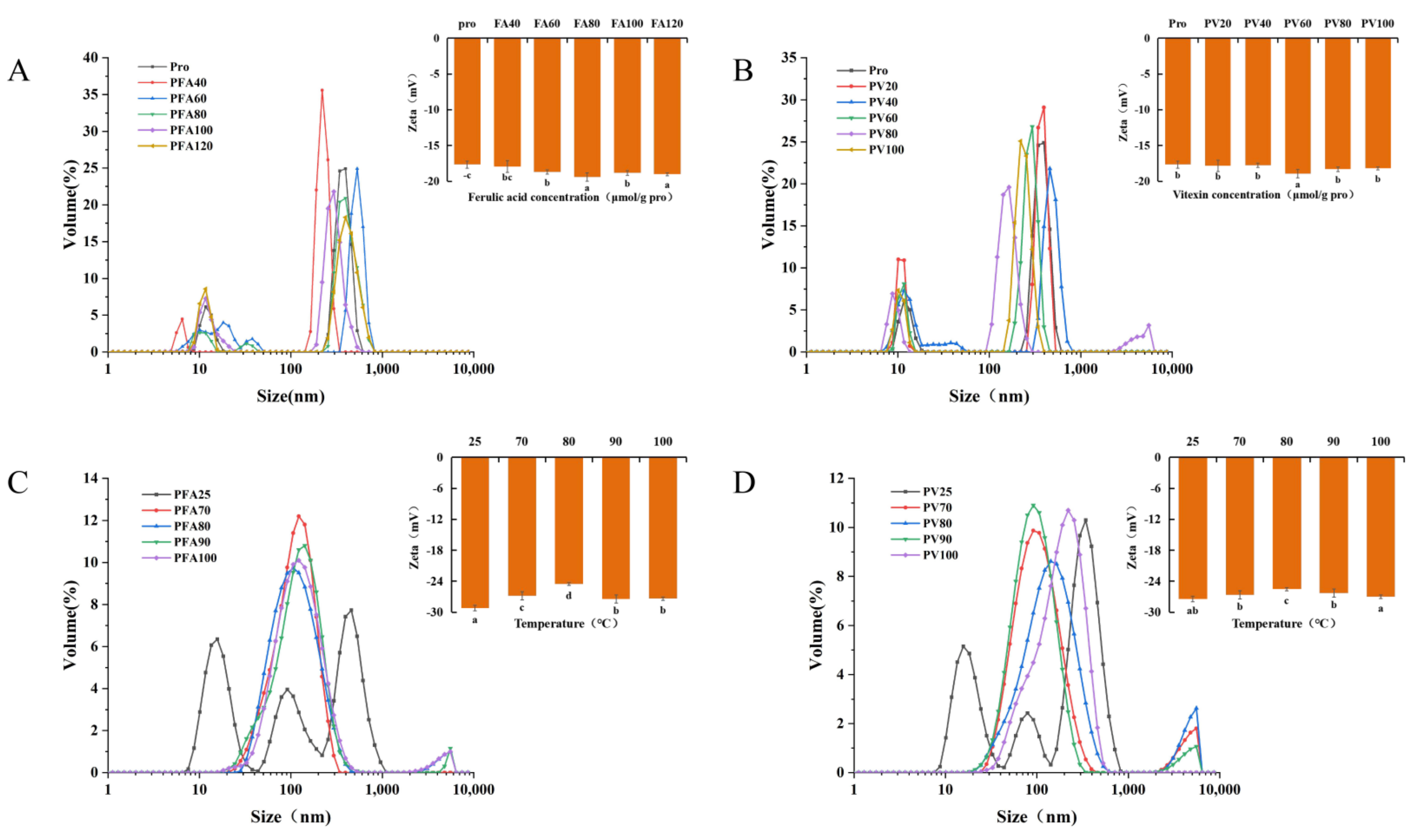
3.7. Particle Size and ζ Potential
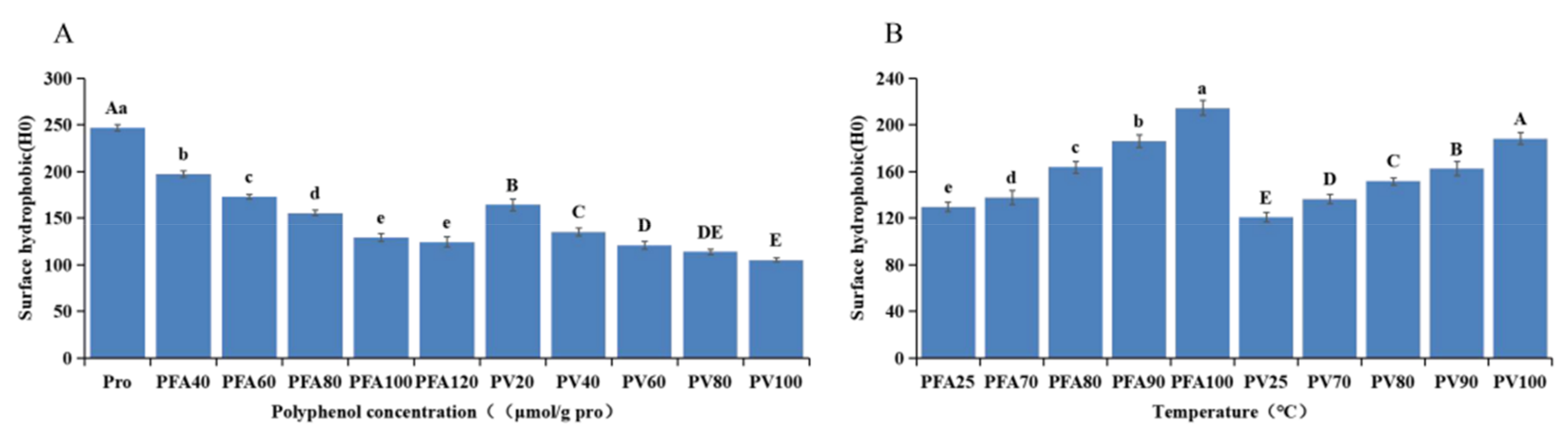
3.8. Surface Hydrophobicity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, Z.Y.; Chen, Z.Z.; Zhang, Y.Y. Novel food-grade pickering emulsions stabilized by tea water-insoluble protein nanoparticles from tea residues. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 96, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, N.; Yang, J.X. Protein/polysaccharide intramolecular electrostatic complex as superior food-grade foaming agent. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkaczewska, J.; Borawska-Dziadkiewicz, J.; Kulawik, P.; Duda, I.; Morawska, M.; Mickowska, B. The effects of hydrolysis condition on the antioxidant activity of protein hydrolysate from Cyprinus carpio skin gelatin. LWT 2020, 117, 108616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.; Chen, J.; McClements, D.J.; Hu, P.; Ye, X.; Liu, C.; Li, T. Protein-polyphenol interactions enhance the antioxidant capacity of phenolics: Analysis of rice glutelin-procyanidin dimer interactions. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, W.N.; McClements, D.J.; Maqsood, S. Whey protein-polyphenol conjugates and complexes: Production, characterization, and applications. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Z.; Cheng, Z.Z.; Wang, Y.B. Dietary protein phenolic interactions, characterization, biochemical-physiological consequences, and potential food applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2021, 61, 3589–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Qu, Y.Z.; Gao, Y.R.; Wu, R.N.; Wu, J.R. Recent advances in understanding the biological activities and applications of polyphenol-protein complexes. Food Sci. 2022, 43, 258–266. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.J.; Lu, M.W.; Mao, Z. Modulation of interfacial phenolic antioxidant distribution in Pickering emulsions via interactions between zeimnanoparticles and gallic acid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Yu, S.J.; Shi, C. Amyloid-polyphenol hybrid nanofilaments mitigate colitis and regulate gut microbial dysbiosis. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 2760–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdal, T.; Capanoglu, E.; Altay, F. A review on protein-phenolic interactions and associated changes. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 954–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohn, S. Possibilities and limitations in the analysis of covalent interactions between phenolic compounds and proteins. Food Res. Int. 2014, 65, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.M.; Zhao, J.R.; Wu, F.F.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, X.H. The non-covalent interacting forces and scavenging activities to three free radicals involved in the caseinate-flavonol (kaempferol and quercetin) complexes. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 16, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Dai, T.; Tan, Y.; Fu, G.; Wan, Y.; Liu, C.; McClements, D.J. Fabrication of pea protein-tannic acid complexes: Impact on formation, stability, and digestion of flaxseed oil emulsions. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhao, J.; Dai, T.; McClements, D.J.; Liu, C. The effect of whey protein-puerarin interactions on the formation and performance of protein hydrogels. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.J.; Liu, D.H.; Li, Y.C. Effect of preparation methods on the structural and functional properties of whey protein isolate-chlorogenic acid conjugates. Food Sci. 2021, 42, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Rawelhm, R.S.; Kruse, H.P. Structural changes induced in bovine serum albumin by covalent attachment of chlorogenic acid. Food Chem. 2002, 78, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Xiong, Y.L. Thermosonication-induced structural changes and solution properties of mung bean protein. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2019, 62, 104908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.M.; Li, R.N.; Tang, J.; Hou, D.Z.; Lu, J. Nutritional Components and Health Functions of Mung Bean and its Application in the Development of Plant-based Food. Grain Oil Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 30, 6–23+12. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.Q.; Ce, Y.Y.; Gunaraten, A. Phenolic profiles, antioxidant activities, and antiproliferative activities of different mung bean (Vigna radiata) varieties from Sri Lanka. Food Biosic. 2020, 37, 100705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.Z.; Yousaf, L.; Xue, Y. Mung bean (Vigna radiata L.); bioactive polyphenols, polysaccharides, peptides, and health benefits. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giusti, F.; Caprioli, G.; Ricciutelli, M.; Torregiani, E.; Vittori, S.; Sagratini, G. Analysis of 17 polyphenolic compounds in organic and conventional legumes by high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection (hplc-dad) and evaluation of their antioxidant activity. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 69, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.H. Studies on Nutritional Quality, Polyphenol Composition and Functional Activity of Different Varieties of Mung Bean; Nanjing University of Finance and Economics: Nanjing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Das, M.C.; Sandhu, P.; Gupta, P. Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation by Vitexin: A combinatorial study with azithromycin and gentamicin. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Qin, P.Z.; Han, X. Evaluation of antioxidant and antibacterial properties of extracts from Trollius chinensis Bunge. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 240, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Z.; Yang, X.N.; Zhang, Y. Research progress of ferulic acid in food and agriculture. Grain Process. 2019, 44, 41–43. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H. Study on Interaction between Mung Bean Protein and Vitexin; Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University: Daqing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Sheng, Y.N.; Feng, Y.C. Changes in structural and functional properties of globulin-polyphenol complexes in mung beans: Exploration under different interaction ratios and heat treatment conditions. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 57, 1920–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, C.Y.; Sheng, Y.N.; Feng, Y.C.; Fu, T.X.; Li, X. Effects of processing methods on structure and functional properties of mung bean protein. Food Sci. 2019, 40, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, N. Study on Extraction and Functional Properties of Mung Bean (Vigna radiata) Protein; Tianjin University of Commerce: Tianjin, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cw, A.; Ti, A.; Jing, Q.A. Effects of lactic acid fermentation-based biotransformation on phenolic profiles, antioxidant capacity and flavor volatiles of apple juice. LWT 2020, 122, 109064. [Google Scholar]
- Lahouar, L.; El, A.A.; Ghrairi, F. Phytochemical content and antioxidant properties of diverse varieties of whole barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) grown in Tunisia. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.N.; Peng, S.Y.; Yan, H.; Yin, C.H. Production and antioxidant activities of carotenoids from Rhodopseudomonas palustris. Chem. Progress 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xe, W.L.; Huang, Y.; Xiang, Y.Z. Insights into the binding mechanism of polyphenols and fish myofibrillar proteins explored using multi-spectroscopic methods. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2020, 13, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Huang, X.; Peng, Q. Physicochemical properties of peanut protein isolate-glucomannan conjugates prepared by ultrasonic treatment. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2014, 21, 1722–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulhattin, Y.; Ramazan, T.; Zeynep, S. Fungal fermentation inducing improved nutritional qualities associated with altered secondary protein structure of soybean meal determined by FTIR spectroscopy. Measurement 2020, 161, 107895. [Google Scholar]
- Sara, N.T.; Bahareh, E.; Mostafa, S.N.; Mohammadreza, A.; Ehsan, A. Physico-chemical and antioxidant properties of barberry juice powder and its efervescent tablets. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2021, 8, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Bohin, M.C.; Vincken, J.P.; Westpha, L.H. Interaction o-flavan-3-ol derivatives and different caseins determined by more than proline content and number of proline repeats. Food Chem. 2014, 158, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, A.L.; Bean, S.R.; Tilley, M. Interaction mechanisms of condensed tannins (proanthocyanidins) with wheat gluten proteins. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.X. Inhibitory Effect of Flaxseed Gum on Catechin-Myofibrin Interaction and Emulsifying Gel Properties; Bohai University: Tianjin, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Seyoum, A.; Asresk, E.F.K. Structure-radical scavenging activity relationships of lavonoids. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 2058–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ma, Y.T.; Feng, Y.C.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhang, D.J. Potential effects of mung bean protein and a mung bean protein-polyphenol complex on oxidative stress levels and intestinal microflora in aging mice. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Progress on factors influencing polyphenol-protein interaction and functional characteristics thereof. J. Henan Univ. Technol. 2012, 33, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.G.; Ma, C.C.; Gao, Y.X. Food-grade covalent complexes and their application as nutraceutical delivery systems: A review. Compr. Rve Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 76–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.P.; Peng, N.; Chang, C.H. Fabrication of surface-active antioxidant food biopolymers: Conjugation of catechin polymers to egg white proteins. Food Biophys. 2017, 12, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.F.; Chi, Z.P.; Wang, X.G.; Li, M.D. Study on functional characteristics and antioxidant activity of soybean protein polyphenols during processing. China Food Addit. 2022, 33, 122–128. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Xiong, Y.L. Chlorogenic Acid-Mediated Gel Formation of Oxidatively Stressed Myofibrillar Protein. Food Chem. 2015, 180, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, H. Effects of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate on the functional and structural properties of soybean protein isolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 2306–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X. Interaction of Green Tea Polyphenols, Theaflavins and Proteins and Their Effects on the Formation of Tea Cheese; Southwest University: Chongqing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.H.; Hao, M.H.; Sun, Q.F. Comparative studies of interaction of β-lactoglobulin with three polyphenols. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Xie, Y.L.; Fan, T.T. Interaction between anthocyanins and wheat protein and its effect on protein structure. Food Sci. 2019, 40, 60–63. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Liang, H.S.; Zhao, J.Y.; Dai, Y.L.; Wan, C.Y.; Zhou, B. Preparation and characterization of zein polyphenol interaction and complex. Food Sci. 2022, 43, 8–17. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.J.; Mu, H.B.; Liu, Z.M.; Lu, M.; Hang, F.; Chen, J.; Zeng, M.M.; Qin, F.; He, Z.Y. Effect of preheat treatment of milk proteins on their interactions with cyanidin-3-O-glucoside. Food Res. Int. 2018, 107, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakis, C.D.; Hasni, I.; Bourassa, P. Milk β-lactoglobulin complexes with tea polyphenols. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.H.; Lang, S.B.; Peng, T. Influence of phenolic compounds on physicochemical and functional properties of protein isolate from Cinamomumm camphora seed kernel. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 102, 105612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Ma, M.; Zhang, H. Progressive study of the effect of superfine green tea, soluble tea, and tea polyphenols on the physico-chemical and structural properties of wheat gluten in noodle system. Food Chem. 2020, 308, 125676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, T.; Lu, Y. Effect of chlorogenic acid covalent conjugation on the allergenicity digestibility and functional properties of whey protein. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 125024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawel, H.M.; Kroll, J.; Rohn, S. Reactions of phenolic substances with lysozyme-Physicochemical characterisation and proteolytic digestion of the derivatives. Food Chem. 2001, 72, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.B.; Tao, Y.; Miao, X. Changes in functional properties of protein polyphenol complexes during kidney bean processing. J. Chin. Cereals Oils 2021, 36, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.Z.; Chen, S.; Li, Y.; Wu, C.J.; Wang, Z.J.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Qi, B.K.; Sui, X.N.; Chen, F.H.; Xu, Z.G. Effects of Complexation with Anthocyanin on the Structural and Functional Properties of Denatured Soybean Protein. Food Sci. 2018, 39, 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Sun, L.; Liu, L. Study on the mechanism of mulberry polyphenols inhibiting oxidation of beef myofibrillar protein. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Luo, X.X.; Chi, Y.F. Effects of black rice anthocyanin on the structural and interfacial properties of soy 7S/11S protein. Food Ferment. Ind. 2023, 49, 166–173. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.D.; Lin, Y.F.; Xu, X.; Meng, L.; Dong, M.S. Effect of non-covalent and covalent complexation of (-)-epigallocatechin gallate with soybean protein isolate on protein structure and in vitro digestion characteristics. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Sarteshnizi, R.A.; Udenigwe, C.C. Recent advances in protein-polyphenol interactions focusing on structural properties related to antioxidant activities. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2022, 45, 100840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Wei, Y.; Rui, F.; Fang, Y.; Gao, Y. Evaluation of structural and functional properties of protein-EGCG complexes and their ability of stabilizing a model β-carotene emulsion. Food Hydrocolloid. 2015, 45, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Gao, X.; Hao, M.; Tang, L. Comparison of binding interaction between beta-lactoglobulin and three common polyphenols using multi-spectroscopy and modeling methods. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.D.; Yu, Z.L.; Zeng, W.C. Structural and functional modifications of myofibrillar protein by natural phenolic compounds and their application in pork meatball. Food Res. Int. 2021, 148, 110593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Temperature (°C) | PV | PFA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DPPH (%) | ABTS (%) | FRAP (μmol TE/g) | DPPH (%) | ABTS (%) | FRAP (μmol TE/g) | |
| 25 | 64.04 ± 0.93 a | 83.13 ± 0.75 a | 72.13 ± 0.734 a | 77.29 ± 2.01 a | 82.69 ± 1.27 a | 80.46 ± 1.24 a |
| 70 | 52.53 ± 1.04 b | 73.66 ± 0.69 d | 40.56 ± 1.026 c | 52.14 ± 1.16 c | 74.18 ± 1.53 b | 59.27 ± 0.95 c |
| 80 | 47.17 ± 0.69 c | 76.34 ± 1.04 c | 45.72 ± 2.113 bc | 43.76 ± 0.96 d | 67.01 ± 0.94 d | 53.24 ± 0.87 d |
| 90 | 51.75 ± 1.43 b | 77.61 ± 2.078 b | 47.13 ± 1.314 b | 54.78 ± 1.04 bc | 70.52 ± 1.24 c | 61.33 ± 2.02 b |
| 100 | 52.73 ± 0.46 b | 78.28 ± 1.623 b | 48.66 ± 0.463 b | 57.6 ± 0.83 b | 71.87 ± 2.02 c | 62.55 ± 1.73 b |
| Sample | T/K | KSV/(×103 L/mol) | Kq/[×1012/(mol·s)] | KA/(×104 L/mol) | R2 | n | ΔH/(kJ/mol) | ΔG/(kJ/mol) | ΔS/[J/(mol·K)] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFA | 298 | 4.21 | 4.21 | 4.19 | 0.9926 | 1.37 | - | - | - |
| 343 | 2.61 | 2.61 | 32.97 | 0.9964 | 1.52 | 0.67 | −2.64 | 47.25 | |
| 353 | 3.73 | 3.73 | 29.27 | 0.9973 | 1.48 | 0.59 | −2.62 | 40.04 | |
| 363 | 1.89 | 1.89 | 19.40 | 0.9934 | 1.51 | 0.44 | −2.53 | 33.02 | |
| 373 | 2.91 | 2.91 | 10.79 | 0.9955 | 1.38 | 0.26 | −2.41 | 26.71 | |
| PV | 298 | 36.40 | 36.40 | 499.80 | 0.9961 | 1.47 | - | - | - |
| 343 | 5.86 | 5.86 | 251.65 | 0.9946 | 1.64 | −0.22 | −2.21 | 40.58 | |
| 353 | 6.80 | 6.80 | 150.18 | 0.9981 | 1.58 | −0.36 | −2.12 | 32.41 | |
| 363 | 5.06 | 5.06 | 520.60 | 0.9927 | 1.73 | 0.01 | −3.21 | 35.85 | |
| 373 | 7.04 | 7.04 | 775.35 | 0.9956 | 1.78 | 0.12 | −3.30 | 34.19 |
| Group | Sample | β-Sheet/% | α-Helix/% | Random Coil/% | β-Turn/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pro | 47.14 ± 0.12 Bc | 23.85 ± 0.12 Aa | 9.15 ± 0.17 Bc | 19.85 ± 0.11 Aa | |
| Ratio (μmol/g pro) | PFA40 | 49.15 ± 0.09 ab | 23.68 ± 0.08 ab | 10.71 ± 0.22 b | 16.46 ± 0.14 b |
| PFA60 | 49.31 ± 0.15 a | 23.66 ± 0.11 ab | 10.84 ± 0.26 b | 16.19 ± 0.10 bc | |
| PFA80 | 49.12 ± 0.17 ab | 23.68 ± 0.19 ab | 10.69 ± 0.07 b | 16.51 ± 0.06 bc | |
| PFA100 | 48.86 ± 0.06 b | 23.7 ± 0.15 a | 10.49 ± 0.15 b | 16.95 ± 0.17 b | |
| PFA120 | 49.6 ± 0.23 a | 23.64 ± 0.24 b | 11.06 ± 0.18 a | 15.7 ± 0.21 c | |
| PV20 | 49.44 ± 0.07 A | 23.65 ± 0.29 A | 10.94 ± 0.11 A | 15.96 ± 0.28 C | |
| PV40 | 49.54 ± 0.16 A | 23.64 ± 0.18 A | 11.02 ± 0.09 A | 15.79 ± 0.14 C | |
| PV60 | 49.48 ± 0.24 A | 23.82 ± 0.24 A | 9.42 ± 0.18 B | 17.28 ± 0.17 B | |
| PV80 | 49.18 ± 0.19 A | 23.68 ± 0.16 A | 10.73 ± 0.21 A | 16.42 ± 0.16 BC | |
| PV100 | 49.37 ± 0.27 A | 23.66 ± 0.19 A | 10.88 ± 0.16 A | 16.09 ± 0.23 C | |
| Temperature (°C) | PFA25 | 48.86 ± 0.13 d | 23.7 ± 0.14 a | 10.49 ± 0.23 a | 16.95 ± 0.22 bc |
| PFA70 | 49.97 ± 0.15 cd | 22.72 ± 0.16 bc | 9.04 ± 0.28 bc | 18.27 ± 0.14 a | |
| PFA80 | 53.23 ± 0.26 a | 21.66 ± 0.23 c | 9.53 ± 0.19 b | 15.59 ± 0.09 c | |
| PFA90 | 52.12 ± 0.21 b | 21.74 ± 0.05 c | 8.65 ± 0.16 c | 17.49 ± 0.26 b | |
| PFA100 | 50.82 ± 0.08 c | 23.03 ± 0.11 ab | 10.69 ± 0.21 a | 15.47 ± 0.17 c | |
| PV25 | 49.48 ± 0.24 A | 23.82 ± 0.24 A | 9.42 ± 0.18 B | 17.28 ± 0.17 C | |
| PV70 | 47.18 ± 0.13 B | 20.98 ± 0.19 B | 10.23 ± 0.29 A | 21.6 ± 0.12 A | |
| PV80 | 47.27 ± 0.24 B | 21.02 ± 0.24 B | 10.37 ± 0.14 A | 21.35 ± 0.25 A | |
| PV90 | 47.19 ± 0.27 B | 20.99 ± 0.11 B | 10.25 ± 0.16 A | 21.56 ± 0.21 A | |
| PV100 | 47.47 ± 0.09 B | 21.09 ± 0.17 B | 10.68 ± 0.19 A | 20.77 ± 0.08 B |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Zhang, S.; Feng, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C. Modification of the Structural and Functional Characteristics of Mung Bean Globin Polyphenol Complexes: Exploration under Heat Treatment Conditions. Foods 2023, 12, 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112091
Ma Y, Zhang S, Feng Y, Wang H, Liu Y, Wang C. Modification of the Structural and Functional Characteristics of Mung Bean Globin Polyphenol Complexes: Exploration under Heat Treatment Conditions. Foods. 2023; 12(11):2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112091
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yantao, Shu Zhang, Yuchao Feng, Haoyu Wang, Yuhang Liu, and Changyuan Wang. 2023. "Modification of the Structural and Functional Characteristics of Mung Bean Globin Polyphenol Complexes: Exploration under Heat Treatment Conditions" Foods 12, no. 11: 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112091
APA StyleMa, Y., Zhang, S., Feng, Y., Wang, H., Liu, Y., & Wang, C. (2023). Modification of the Structural and Functional Characteristics of Mung Bean Globin Polyphenol Complexes: Exploration under Heat Treatment Conditions. Foods, 12(11), 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112091






