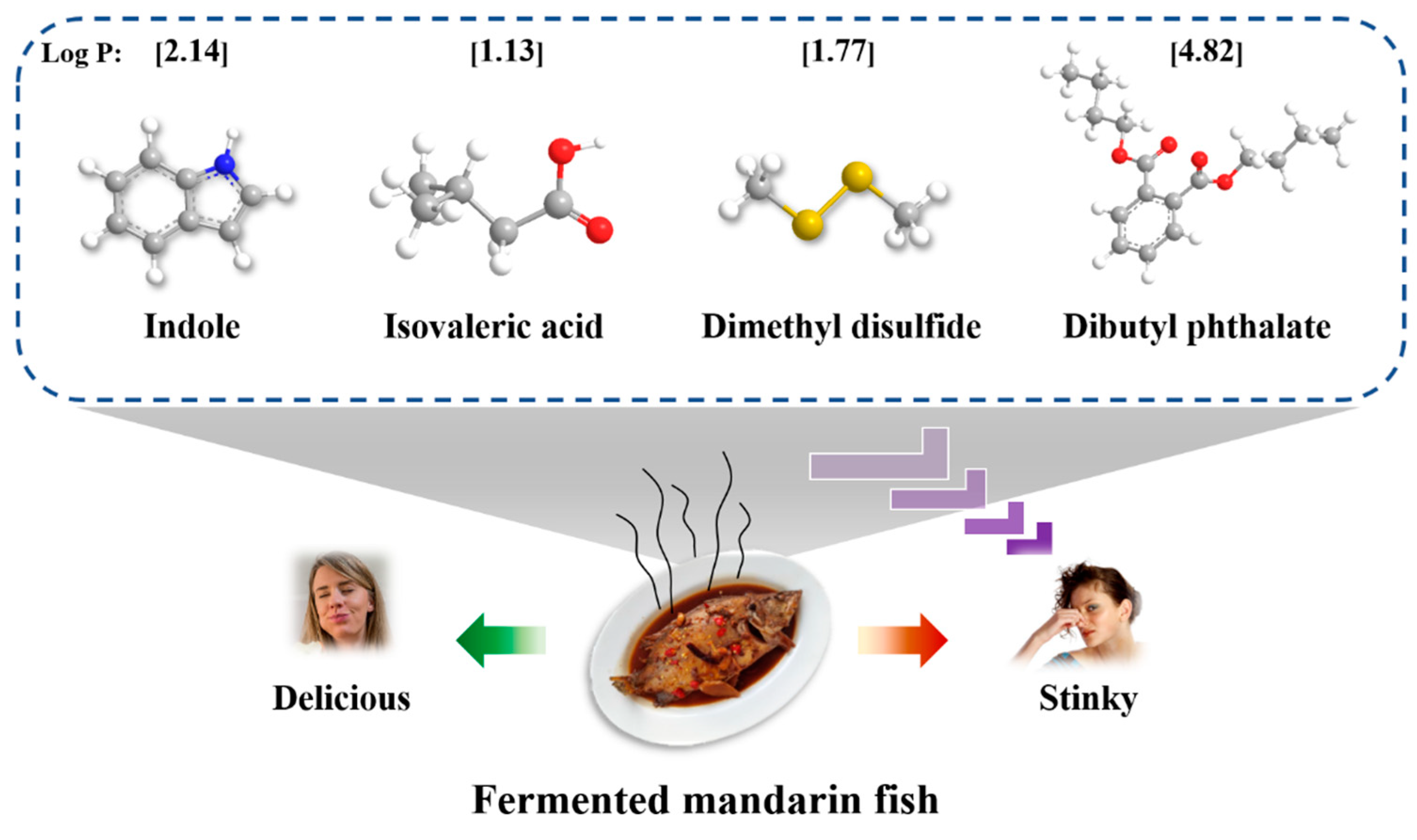
Comprehensive Multi-Spectroscopy and Molecular Docking Understanding of Interactions between Fermentation-Stinky Compounds and Mandarin Fish Myofibrillar Proteins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of MP Solution
2.3. Preparation of Fermentation-Stinky Standards and Bond-Disrupting Agent Solutions
2.4. SPME-GC-MS Analysis
2.4.1. Preparation of Samples for GC-MS
- (1)
- Different concentrations of fermentation-stinky compounds
- (2)
- Different bond-disrupting agents
2.4.2. GC-MS Parameters
2.5. Fluorescence Analysis
2.5.1. Preparation of Samples for Fluorescence Analysis
2.5.2. Fluorescence Quenching Spectra
2.5.3. Thermodynamic Stability of the MPs-Fermentation-Stinky Compound Complexes
2.5.4. Synchronous Fluorescence Spectra
2.6. Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectra
2.7. Molecular Docking
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
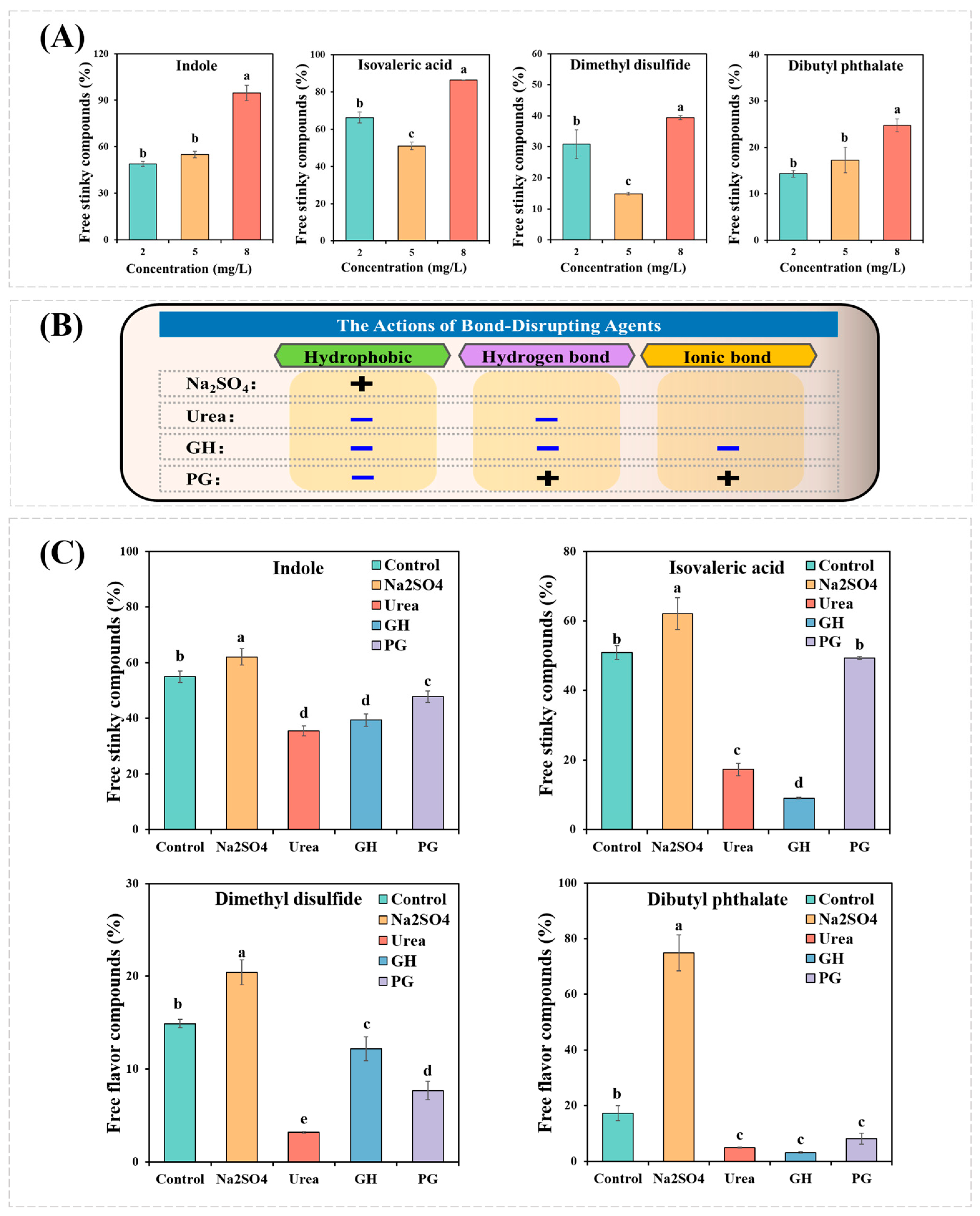
3.1. The Interactions between MPs and Fermentation-Stinky Compounds
3.2. Effects of Bond-Disrupting Agents on the Binding Capacity
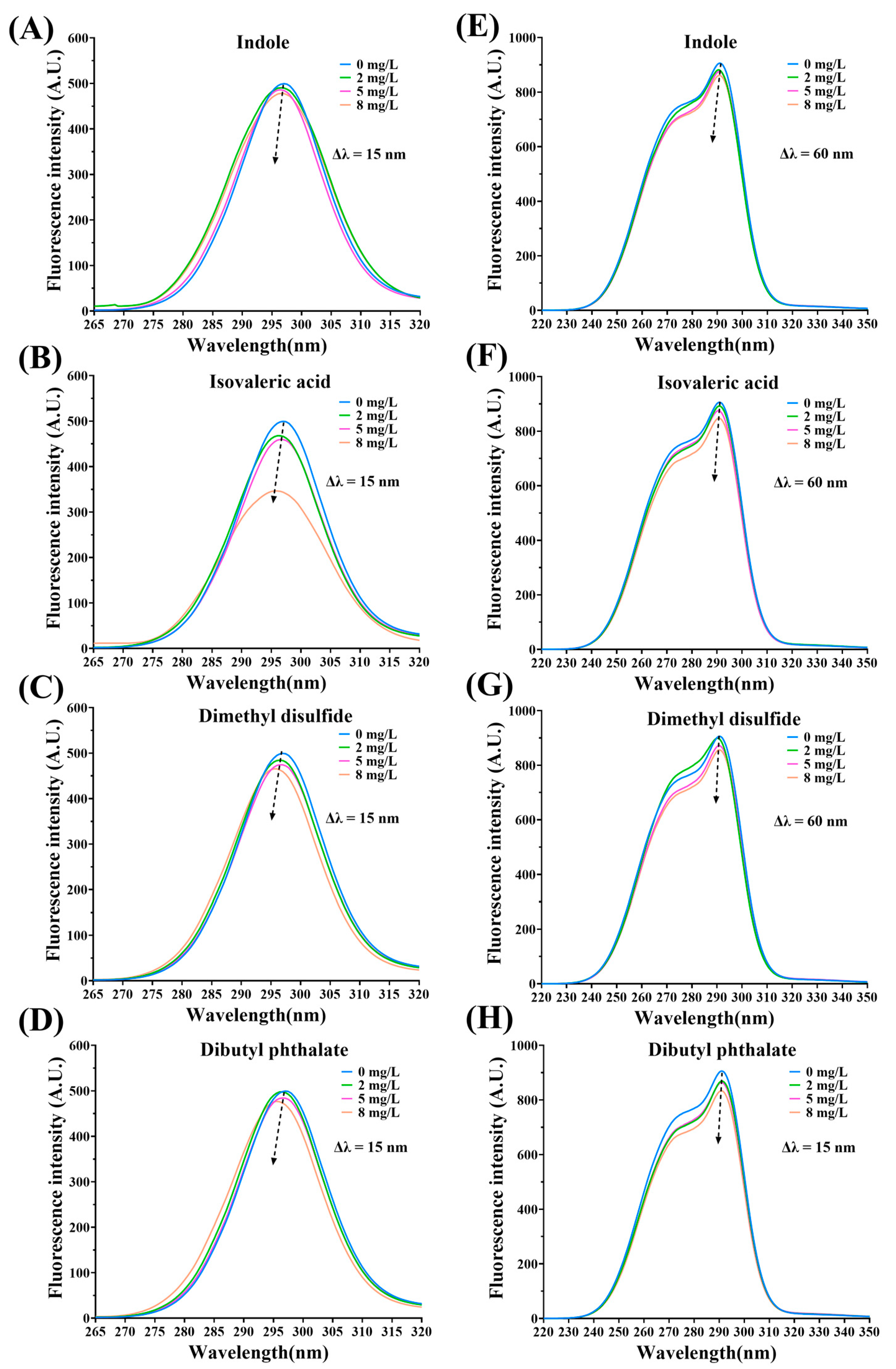
3.3. Fluorescence Quenching of MPs by Fermentation-Stinky Compounds
3.4. Thermodynamic Stability Analysis
3.5. Synchronous Fluorescence Spectra Analysis
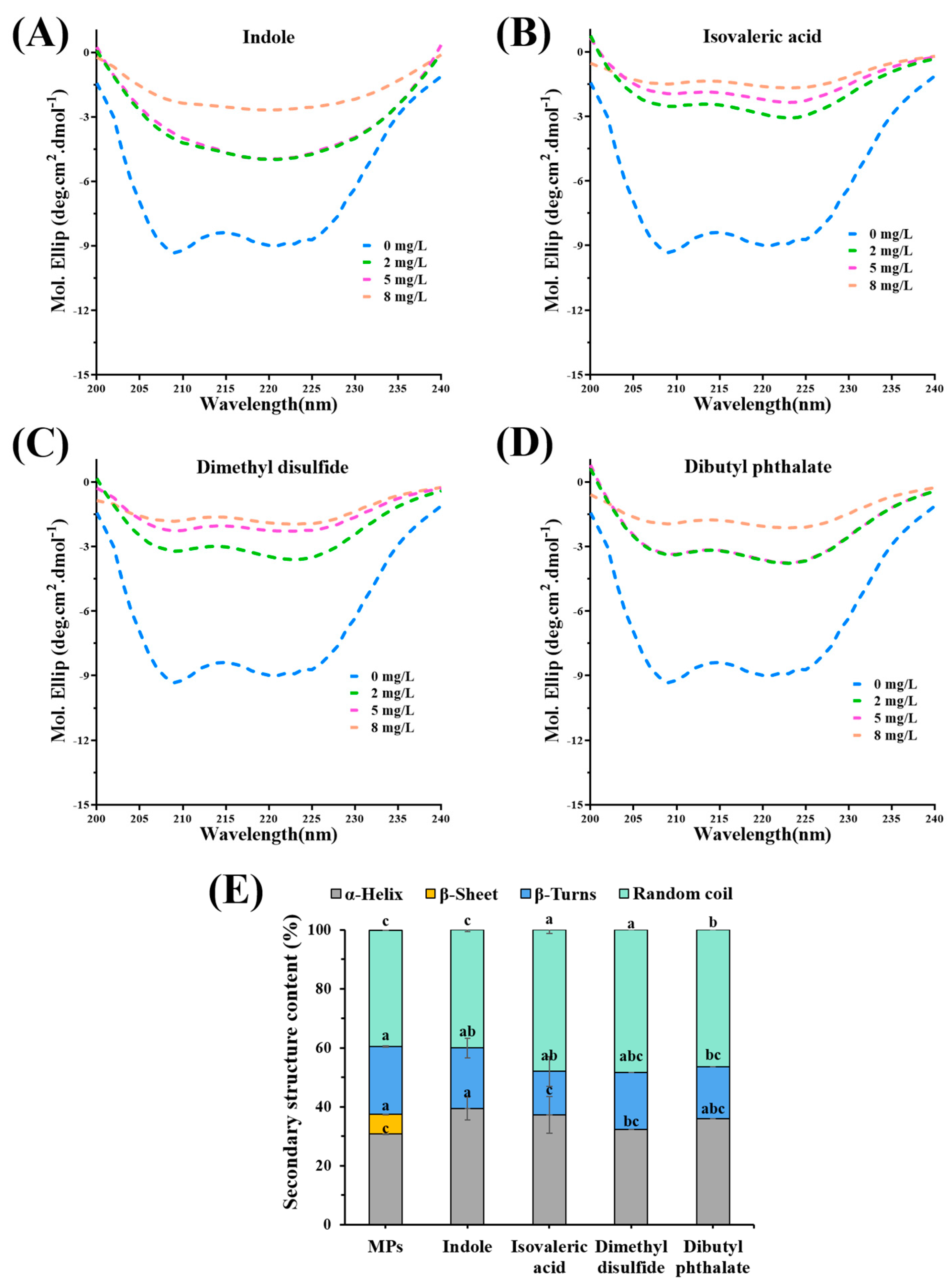
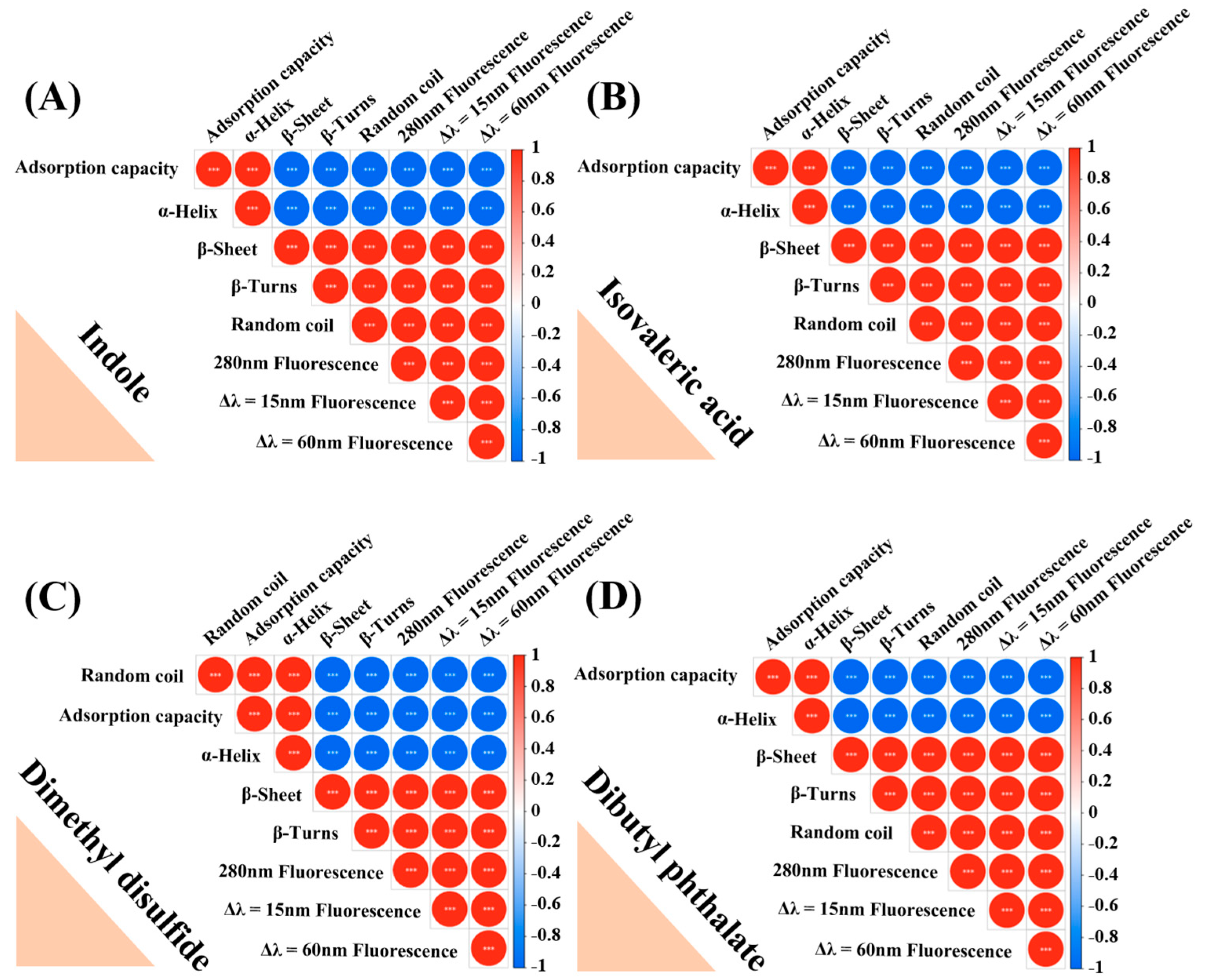
3.6. Change in the Secondary Structure of MPs
3.7. Analysis of the Binding Sites Based on Molecular Docking (MD)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.-N.; Han, H.-T.; Liu, C.-J.; Gao, Q.; Wang, X.-W.; Zhang, J.-W.; Tanokura, M.; Xue, Y.-L. Characterization of aroma-active compounds in Dongli by quantitative descriptive analysis, gas chromatography-triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry, and gas chromatography-olfactometry. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 4108–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-N.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Huang, X.-H.; Dong, M.; Dong, X.-P.; Zhou, D.-Y.; Zhu, B.-W.; Qin, L. Integrated volatolomics and metabolomics analysis reveals the characteristic flavor formation in Chouguiyu, a traditional fermented mandarin fish of China. Food Chem. 2023, 418, 135874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, S.; Lv, J.; Sun, Z.; Xu, W.; Ji, C.; Liang, H.; Li, S.; Yu, C.; Lin, X. Microbial succession and the changes of flavor and aroma in Chouguiyu, a traditional Chinese fermented fish. Food Biosci. 2020, 37, 100725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Li, P.; Chen, L.; Ma, J.-K.; Guo, H.-H.; Huang, X.-C.; Zhong, R.-M.; Jing, S.-Q.; Jiang, L.-W. The formation mechanisms of key flavor substances in stinky tofu brine based on metabolism of aromatic amino acids. Food Chem. 2022, 392, 133253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skåra, T.; Axelsson, L.; Stefánsson, G.; Ekstrand, B.; Hagen, H. Fermented and ripened fish products in the northern European countries. J. Ethn. Foods 2015, 2, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Tang, N.; Liu, R.; Gong, M.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, M. The relationship between flavor formation, lipid metabolism, and microorganisms in fermented fish products. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 5685–5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, S. Contribution of autochthonous microbiota succession to flavor formation during Chinese fermented mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi). Food Chem. 2021, 348, 129107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, X.; Wei, Y.; Huang, H. Comparison of the microbial community and flavor compounds in fermented mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi): Three typical types of Chinese fermented mandarin fish products. Food Res. Int. 2021, 144, 110365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhou, C.; Li, C.; Zhou, G. Effect of incubation temperature on the binding capacity of flavor compounds to myosin. Food Chem. 2021, 346, 128976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. Understanding interactions among aldehyde compounds and porcine myofibrillar proteins by spectroscopy and molecular dynamics simulations. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 349, 118190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Xia, X.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. Exploration of interaction between porcine myofibrillar proteins and selected ketones by GC–MS, multiple spectroscopy, and molecular docking approaches. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, P.; Feng, X.; Cheng, X.; Guan, Q.; Wang, J.; Qian, S.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; Ullah, N.; Zhu, B. Binding of aldehyde flavour compounds to beef myofibrillar proteins and the effect of nonenzymatic glycation with glucose and glucosamine. LWT 2021, 144, 111198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zheng, R.; Zuo, F.; Qian, C.; Yao, Z.; Dong, R.; Zhao, D.; Li, C. Influence of Proteolysis on the Binding Capacity of Flavor Compounds to Myofibrillar Proteins. Foods 2022, 11, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Huang, M.; Zhao, M.; Sun, W. Interactions of selected ketone flavours with porcine myofibrillar proteins: The role of molecular structure of flavour compounds. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 125060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Teng, F.; Huang, Z.; Lv, B.; Lv, X.; Babich, O.; Yu, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, L. Effects of material characteristics on the structural characteristics and flavor substances retention of meat analogs. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 105, 105752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kang, D.; Zhang, W.; Lorenzo, J.M. Recent advantage of interactions of protein-flavor in foods: Perspective of theoretical models, protein properties and extrinsic factors. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Dai, W.; Chong, Y.; Lyu, F.; Zhou, X.; Ding, Y. The binding of key fishy off-flavor compounds to silver carp proteins: A thermodynamic analysis. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 11292–11299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, Z.; Yu, C.; Prakash, S.; Dong, X. The synergistic effects of myofibrillar protein enrichment and homogenization on the quality of cod protein gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 127, 107468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guan, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. Elucidation of interaction mechanisms between myofibrillar proteins and ethyl octanoate by SPME-GC-MS, molecular docking and dynamics simulation. LWT 2022, 154, 112787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Mei, S.; Duan, R.; Geng, F.; Wu, W.; Li, X.; Cheng, L.; Wang, C. How black tea pigment theaflavin dyes chicken eggs: Binding affinity study of theaflavin with ovalbumin. Food Chem. 2020, 303, 125407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, P.H.C.; Coelho, Y.L.; da Silva, L.H.M.; Pinto, M.S.; Vidigal, M.C.T.; Pires, A.C.d.S. Influence of protein conformation and selected Hofmeister salts on bovine serum albumin/lutein complex formation. Food Chem. 2020, 305, 125463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhao, S.-m.; Liu, Y.-m.; Yang, H.; Xiong, S.-b.; Xie, B.-j.; Qin, L.-h. Effect of pH on the gel properties and secondary structure of fish myosin. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.D.; Arntfield, S.D. Molecular forces involved in heat-induced pea protein gelation: Effects of various reagents on the rheological properties of salt-extracted pea protein gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 28, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Cai, M.-j.; Cheng, J.-h.; Sun, D.-W. Effects of constant power microwave on the adsorption behaviour of myofibril protein to aldehyde flavour compounds. Food Chem. 2021, 336, 127728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Gao, M.; Wang, H.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. Probing the interaction between selected furan derivatives and porcine myofibrillar proteins by spectroscopic and molecular docking approaches. Food Chem. 2022, 397, 133776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrens, F. Calculation of partition coefficient and hydrophobic moment of the secondary structure of lysozyme. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 908, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xia, X.; Yin, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. Investigation of molecular mechanisms of interaction between myofibrillar proteins and 1-heptanol by multiple spectroscopy and molecular docking methods. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; You, J.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, S.; Yin, T.; Huang, Q. Capacity of myofibrillar protein to adsorb characteristic fishy-odor compounds: Effects of concentration, temperature, ionic strength, pH and yeast glucan addition. Food Chem. 2021, 363, 130304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yu, Y.; Saleh, A.S.; Yang, X.; Ma, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z. Understanding interactions among flavor compounds from spices and myofibrillar proteins by multi-spectroscopy and molecular docking simulation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 229, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Kang, S.; Tian, J.; Li, M.; Liang, X.; Yang, M.; Zheng, Y.; Pi, Y.; Cao, X.; Liu, Y. Interaction of xylitol with whey proteins: Multi-spectroscopic techniques and docking studies. Food Chem. 2020, 326, 126804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Compound | T (K) | Ksv (103M−1) | Kq (1011M−1s−1) | Ka (104M−1) | n | ΔH (kJ·mol−1) | ΔS (J·mol−1 K−1) | ΔG (kJ·mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indole | 293 | 9.6 | 9.6 | 2.57 × 10³ | 1.1077 | −512.42 | −1607.01 | −41.57 |
| 303 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 3.51 | 0.5650 | −25.50 | |||
| 313 | 2.2 | 2.2 | 2.05 | 0.4609 | −24.18 | |||
| Isovaleric acid | 293 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 6.18 | 0.6915 | −79.89 | −257.51 | −4.44 |
| 303 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 2.15 | 0.5010 | −1.86 | |||
| 313 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 3.06 × 108 | 2.4453 | −47.60 | |||
| Dimethyl disulfide | 293 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 6.30 | 0.9650 | −275.50 | −905.81 | −10.10 |
| 303 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.53 | 0.4711 | −1.04 | |||
| 313 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.60 | 0.4555 | −1.15 | |||
| Dibutyl phthalate | 293 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 1.02 × 105 | 1.2105 | −390.19 | −1235.80 | −28.10 |
| 303 | 9.9 | 9.9 | 6.40 × 102 | 0.9438 | −15.74 | |||
| 313 | 16.1 | 16.1 | 1.36 × 104 | 5.1350 | −23.19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.-N.; Zhao, H.-L.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Zhou, D.-Y.; Qin, L.; Huang, X.-H. Comprehensive Multi-Spectroscopy and Molecular Docking Understanding of Interactions between Fermentation-Stinky Compounds and Mandarin Fish Myofibrillar Proteins. Foods 2023, 12, 2054. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12102054
Chen J-N, Zhao H-L, Zhang Y-Y, Zhou D-Y, Qin L, Huang X-H. Comprehensive Multi-Spectroscopy and Molecular Docking Understanding of Interactions between Fermentation-Stinky Compounds and Mandarin Fish Myofibrillar Proteins. Foods. 2023; 12(10):2054. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12102054
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jia-Nan, Hui-Lin Zhao, Yu-Ying Zhang, Da-Yong Zhou, Lei Qin, and Xu-Hui Huang. 2023. "Comprehensive Multi-Spectroscopy and Molecular Docking Understanding of Interactions between Fermentation-Stinky Compounds and Mandarin Fish Myofibrillar Proteins" Foods 12, no. 10: 2054. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12102054
APA StyleChen, J.-N., Zhao, H.-L., Zhang, Y.-Y., Zhou, D.-Y., Qin, L., & Huang, X.-H. (2023). Comprehensive Multi-Spectroscopy and Molecular Docking Understanding of Interactions between Fermentation-Stinky Compounds and Mandarin Fish Myofibrillar Proteins. Foods, 12(10), 2054. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12102054









