Multiscale Structural Insight into Dairy Products and Plant-Based Alternatives by Scattering and Imaging Techniques
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. ESEM
2.2. SAXS
3. Results and Discussion
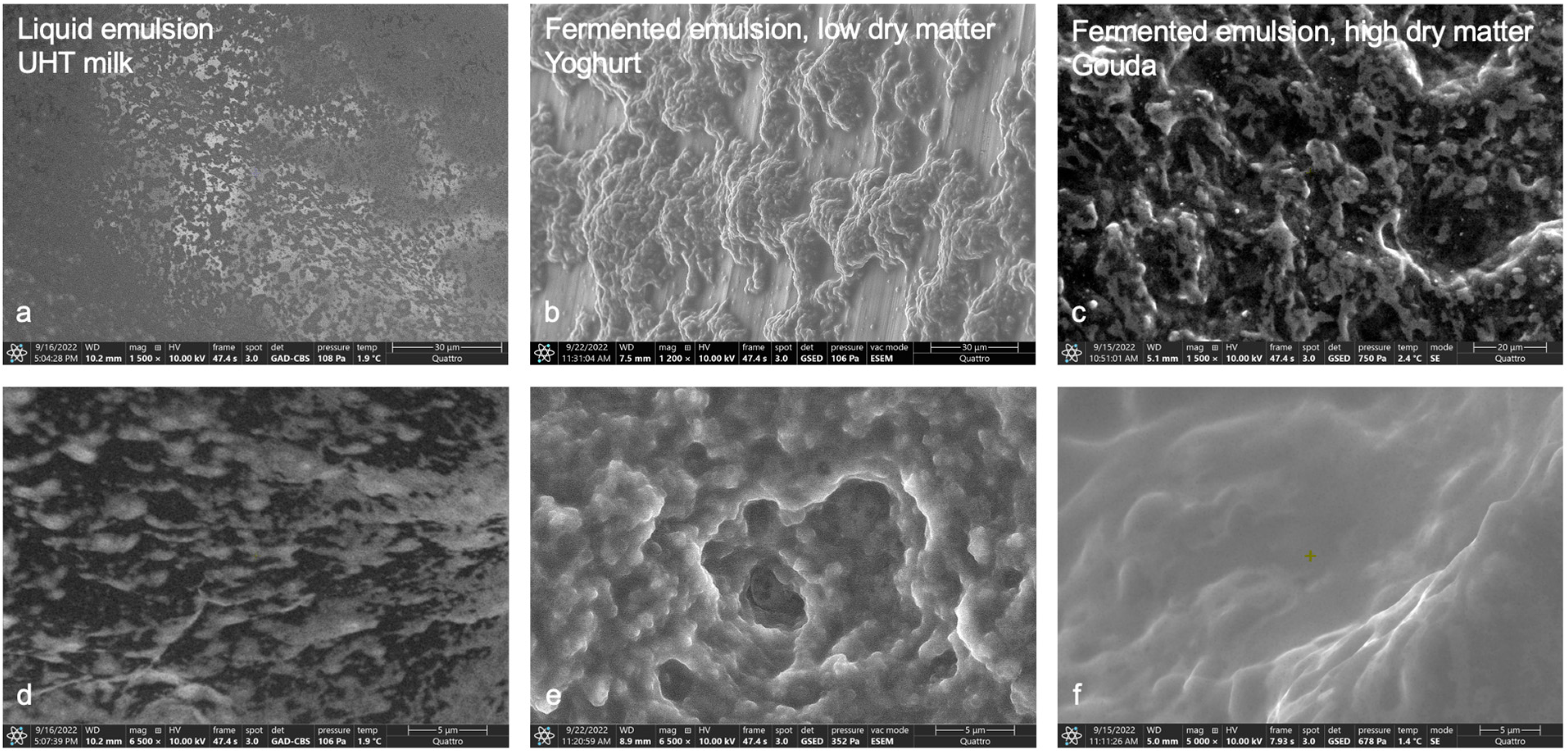
3.1. ESEM
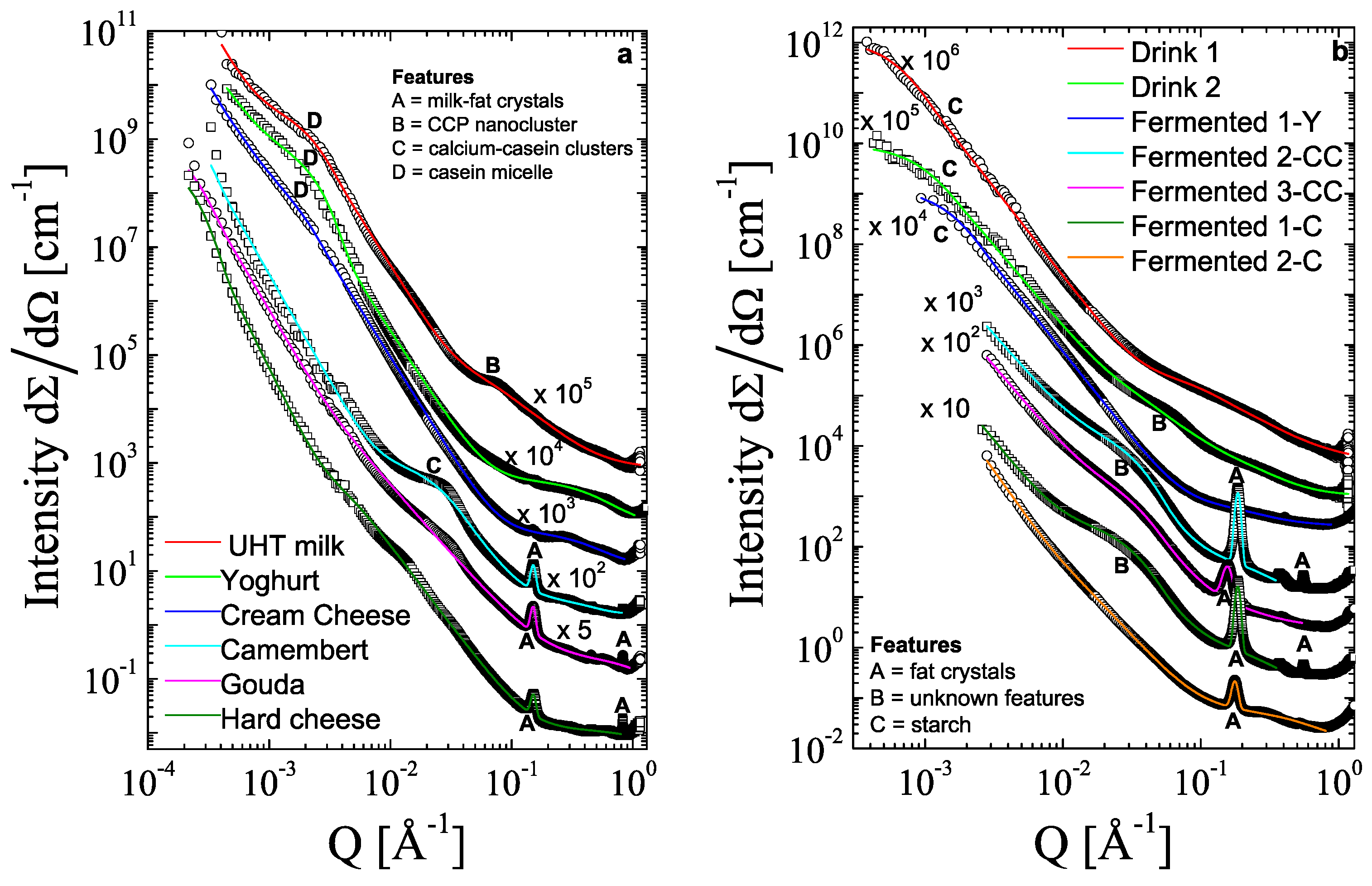
3.2. SAXS
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fischer, P.; Windhab, E.J. Rheology of Food Materials. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 16, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezger, T.G. The Rheology Handbook. For Users of Rotational and Oscillatory Rheometers, 4th ed.; Vincentz Network: Hanover, Germany, 2014; ISBN 9783866306509. [Google Scholar]
- Lawless, H.; Hildegarde, H. Sensory Evaluation of Food Flavors: Principles and Practices; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-1-4419-6487-8. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, E.P. Small-Angle X-ray and Neutron Scattering in Food Colloids. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 42, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kruif, C.G. Casein Micelle Interactions. Int. Dairy J. 1999, 9, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kruif, C.G. The Structure of Casein Micelles: A Review of Small-Angle Scattering Data. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2014, 47, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kruif, C.G.; Huppertz, T.; Urban, V.S.; Petukhov, A.V. Casein Micelles and Their Internal Structure. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 171–172, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingham, B.; Erlangga, G.D.; Smialowska, A.; Kirby, N.M.; Wang, C.; Matia-Merino, L.; Haverkamp, R.G.; Carr, A.J. Solving the Mystery of the Internal Structure of Casein Micelles. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 2723–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingham, B.; Smialowska, A.; Erlangga, G.D.; Matia-Merino, L.; Kirby, N.M.; Wang, C.; Haverkamp, R.G.; Carr, A.J. Revisiting the Interpretation of Casein Micelle SAXS Data. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 6937–6953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, L.; Raynes, J.K.; Leis, A.; Liu, L.H.; Williams, R.P.W. Probing the Internal and External Micelle Structures of Differently Sized Casein Micelles from Individual Cows Milk by Dynamic Light and Small-Angle X-ray Scattering. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 69, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C.; Cauty, C.; Guyomarc’h, F. Organization of Lipids in Milks, Infant Milk Formulas and Various Dairy Products: Role of Technological Processes and Potential Impacts. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2015, 95, 863–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C.; Bourgaux, C.; Lesieur, P.; Ollivon, M. Coupling of Time-Resolved Synchrotron X-ray Diffraction and DSC to Elucidate the Crystallisation Properties and Polymorphism of Triglycerides in Milk Fat Globules. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2007, 87, 459–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C.; Bourgaux, C.; Lesieur, P.; Bernadou, S.; Keller, G.; Ollivon, M. Thermal and Structural Behavior of Milk Fat 3. Influence of Cooling Rate and Droplet Size on Cream Crystallization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 254, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Valsecchi, J.; Oh, O.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.W.; Boue, F.; Lutton, E.; Busi, M.; Garvey, C.; Strobl, M. Quantitative Neutron Dark-Field Imaging of Milk: A Feasibility Study. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.N.; Brok, E.; Christiansen, M.V.; Ahrné, L. Casein Micelles in Milk as Sticky Spheres. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 9955–9963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingham, B.; Smialowska, A.; Kirby, N.M.; Wang, C.; Carr, A.J. A Structural Comparison of Casein Micelles in Cow, Goat and Sheep Milk Using X-Ray Scattering. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 3336–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, Z.; Otter, D.; Rehm, C.; Li, N.; Zhou, P.; Hemar, Y. Rheological and Structural Properties of Coagulated Milks Reconstituted in D2O: Comparison between Rennet and a Tamarillo Enzyme (Tamarillin). Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 79, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodini, I.; Lucas, A.; Tissier, J.P.; Corrieu, G. Physical Properties and Microstructure of Yoghurts Supplemented with Milk Protein Hydrolysates. Int. Dairy J. 2005, 15, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzeminski, A.; Großhable, K.; Hinrichs, J. Structural Properties of Stirred Yoghurt as Influenced by Whey Proteins. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 2134–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaneda, N.; Lee, Y. Microstructure of a Model Fresh Cheese and Bioaccessibility of Vitamin D3 Using in Vitro Digestion. Gels 2019, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bakry, M.; Sheehan, J. Analysing Cheese Microstructure: A Review of Recent Developments. J. Food Eng. 2014, 125, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brückner-Gühmann, M.; Vasil’eva, E.; Culetu, A.; Duta, D.; Sozer, N.; Drusch, S. Oat Protein Concentrate as Alternative Ingredient for Non-Dairy Yoghurt-Type Product. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 5852–5857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brückner-Gühmann, M.; Kratzsch, A.; Sozer, N.; Drusch, S. Oat Protein as Plant-Derived Gelling Agent: Properties and Potential of Modification. Future Foods 2021, 4, 100053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klost, M.; Brzeski, C.; Drusch, S. Effect of Protein Aggregation on Rheological Properties of Pea Protein Gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 106036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyash, M.M.; Sherkat, F.; Francis, P.; Williams, R.; Shah, N.P. The Effect of Sodium Chloride Substitution with Potassium Chloride on Texture Profile and Microstructure of Halloumi Cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noronha, N.; Duggan, E.; Ziegler, G.R.; O’Riordan, E.D.; O’Sullivan, M. Comparison of Microscopy Techniques for the Examination of the Microstructure of Starch-Containing Imitation Cheeses. Food Res. Int. 2008, 41, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monga, A.; Dev, M.J.; Singhal, R.S. Cottage Cheese from Blends of Fresh Green Peas (Pisum Sativum L.) and Dairy Milk (PEaneer): Preparation, Characterization, and Sensory Evaluation. LWT 2022, 160, 113263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaucage, G. Small-Angle Scattering from Polymeric Mass Fractals of Arbitrary Mass-Fractal Dimension. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1996, 29, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Dickinson, E. Sustainable Food-Grade Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by Plant-Based Particles. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 49, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, S.E.S.; Scheermeijer, R.; Ambühl, M.; Fernandez Farres, I. Novel Plant-Based Cream Cheese: A Tribology Perspective. J. Food Eng. 2022, 335, 111172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, L.; McClements, D.J. The Science of Plant-Based Foods: Approaches to Create Nutritious and Sustainable Plant-Based Cheese Analogs. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 118, 207–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, Y.H.; Drusch, S. (Eds.) Phase Transitions in Foods, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2016; ISBN 978-0-12-408086-7. [Google Scholar]
- Frick, B.; Richter, D.; Ritter, C.L. Structural Changes near the Glass Transition-Neutron Diffraction on a Simple Polymer. Europhys. Lett. 1989, 9, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, G. Predictions of the Shear Modulus of Cheese, a Soft Matter Approach. Appl. Rheol. 2019, 29, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olakanmi, S.; Karunakaran, C.; Jayas, D. Applications of X-Ray Micro-Computed Tomography and Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering Techniques in Food Systems: A Concise Review. J. Food Eng. 2023, 342, 111355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, C.; Arendt, E.K. Proteins in Oats; Their Synthesis and Changes during Germination: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 52, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinsella, J.E. Functional Properties of Soy Proteins. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1979, 56, 242–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyagawa, Y.; Shintani, K.; Katsuki, K.; Nakagawa, K.; Adachi, S. Thermal and Structural Changes of Rapeseed Oil during Isothermal Storage at Low Temperature. Food Struct. 2017, 11, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Pan, Q.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, L. Rapid Determination of Phospholipid Content of Vegetable Oils by FTIR Spectroscopy Combined with Partial Least-Square Regression. Food Chem. 2014, 147, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Category | Product | Fat (%), of Which Is Saturated | Carbohydrates (%), of Which Is Sugar | Protein (%) | Salt (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid emulsion | UHT milk | 3.5, 2.4 | 4.8, 4.8 | 3.3 | 0.1 |
| Fermented emulsion, low dry matter | Yogurt | 3.5, 2.4 | 5.1, 5.1 | 4.4 | 0.2 |
| Cream cheese | 17.0, 11.0 | 3.0, 3.0 | 8.5 | 0.3 | |
| Fermented emulsion, high dry matter | Camembert | 32.0, 22.0 | 0.5, 0.5 | 17.0 | 1.4 |
| Gouda | 28.0, 18.8 | 0.5, 0.5 | 23.5 | 1.5 | |
| Hard cheese | 29.7, 19.6 | 0.0, 0.0 | 32.4 | 1.6 | |
| Liquid emulsion | Drink 1 | 3.5, 0.4 | 5.7, 0.0 | 0.7 | 0.1 |
| Drink 2 | 3.0, 0.3 | 7.1, 3.4 | 1.1 | 0.1 | |
| Fermented emulsion, low dry matter | Fermented 1-Y | 1.9, 0.4 | 3.4, 1.0 | 3.8 | 0.3 |
| Fermented 2-CC | 23.0, 21.0 | 8.0, 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.2 | |
| Fermented 3-CC | 20.0, 8.0 | 9.8, 3.6 | 3.2 | 0.7 | |
| Fermented emulsion, high dry matter | Fermented 1-C | 29.0, 26.0 | 11.0, 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.7 |
| Fermented 2-C | 19.0, 17.0 | 24.0, 0.5 | 0.5 | 1.9 |
| Product | Size 1 [nm] | Exponent | Size 2 [nm] | Exponent | Size 3 [nm] | Exponent | Size 4 (Periodic) [nm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UHT milk | >1000 | 4 fix | 96 ± 1.7 | 3.59 ± 0.01 | 2.34 ± 0.07 | 1.99 ± 0.02 | -- |
| Yogurt | >1000 | 3.33 ± 0.01 | 95.1 ± 1.6 | 5.23 ± 0.01 | 0.37 ± 0.04 | 1.9 ± 1.0 | -- |
| Cream cheese | >1000 | 3.50 ± 0.02 | 123 ± 4 | 3.71 ± 0.05 | 0.39 ± 0.01 | 2.4 ± 0.3 | -- |
| Camembert | >1000 | 4 fix | 7.7 ± 0.1 | 3.17 ± 0.03 | 0.39 ± 0.02 | large | 4.18 ± 0.01 |
| Gouda | >1000 | 3.82 ± 0.01 | 40 ± 3 | 2.39 ± 0.01 | 0.15 ± 0.03 | large | 4.19 ± 0.01 |
| Hard cheese | >1000 | 4.59 ± 0.01 | 40.4 ± 0.9 | 2.93 ± 0.01 | 0.17 ± 0.17 | small | 4.17 ± 0.01 |
| Drink 1 | 321 ± 8 | 3.51 ± 0.01 | 1.68 ± 0.05 | 1.72 ± 0.03 | -- | -- | -- |
| Drink 2 | 197 ± 4 | 3.22 ± 0.02 | 4.8 ± 0.5 | 2.3 ± 0.2 | 0.61 ± 0.06 | 2.5 ± 0.2 | -- |
| Fermented1-Y | 130 ± 1 | 3.44 ± 0.01 | -- | -- | 0.71 ± 0.01 | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 4.03 ± 0.01 |
| Fermented2-CC | >100 | 3.10 ± 0.06 | 6.4 ± 0.1 | 4.2 ± 0.1 | 0.66 ± 0.06 | 2 fix | 3.38 ± 0.01 |
| Fermented3-CC | >100 | 3.22 ± 0.02 | 6.39 ± 0.06 | 3.62 ± 0.02 | 0.71 ± 0.04 | 2 fix | 4.03 ± 0.01 |
| Fermented1-C | >100 | 3.40 ± 0.06 | 6.6 ± 0.1 | 3.74 ± 0.04 | 0.72 ± 0.06 | 2 fix | 3.39 ± 0.01 |
| Fermented2-C | >100 | 3.89 ± 0.05 | 13.3 ± 0.7 | 2.79 ± 0.02 | 0.311 ± 0.003 | 2 fix | 3.55 ± 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heiden-Hecht, T.; Wu, B.; Appavou, M.-S.; Förster, S.; Frielinghaus, H.; Holderer, O. Multiscale Structural Insight into Dairy Products and Plant-Based Alternatives by Scattering and Imaging Techniques. Foods 2023, 12, 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12102021
Heiden-Hecht T, Wu B, Appavou M-S, Förster S, Frielinghaus H, Holderer O. Multiscale Structural Insight into Dairy Products and Plant-Based Alternatives by Scattering and Imaging Techniques. Foods. 2023; 12(10):2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12102021
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeiden-Hecht, Theresia, Baohu Wu, Marie-Sousai Appavou, Stephan Förster, Henrich Frielinghaus, and Olaf Holderer. 2023. "Multiscale Structural Insight into Dairy Products and Plant-Based Alternatives by Scattering and Imaging Techniques" Foods 12, no. 10: 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12102021
APA StyleHeiden-Hecht, T., Wu, B., Appavou, M.-S., Förster, S., Frielinghaus, H., & Holderer, O. (2023). Multiscale Structural Insight into Dairy Products and Plant-Based Alternatives by Scattering and Imaging Techniques. Foods, 12(10), 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12102021










