The Interactional Characterization of Lentil Protein Isolate (LPI) with Cyanidin-3-O-Glucoside (C3G) and Their Effect on the Stability and Antioxidant Activity of C3G
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of LPI
2.3. Preparation of LPI-C3G Complexes
2.4. LPI-C3G Complex Particle Characteristics
2.5. Turbidity of the LPI-C3G Complexes
2.6. Foaming Performance of Complexes
2.7. Emulsifying Activity and Emulsion Stability
2.8. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.9. UV, Intrinsic Fluorescence, Synchronous Fluorescence, and Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.10. Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectroscopy
2.11. Surface Hydrophobicity
2.12. Differential Scanning Calorimeter (DSC)
2.13. Fluorescence Quenching Mechanism, Binding Constant, and Thermodynamic Parameters
2.14. Thermal and Oxidation Stability
2.15. Antioxidative Properties of the LPI-C3G Complexes
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
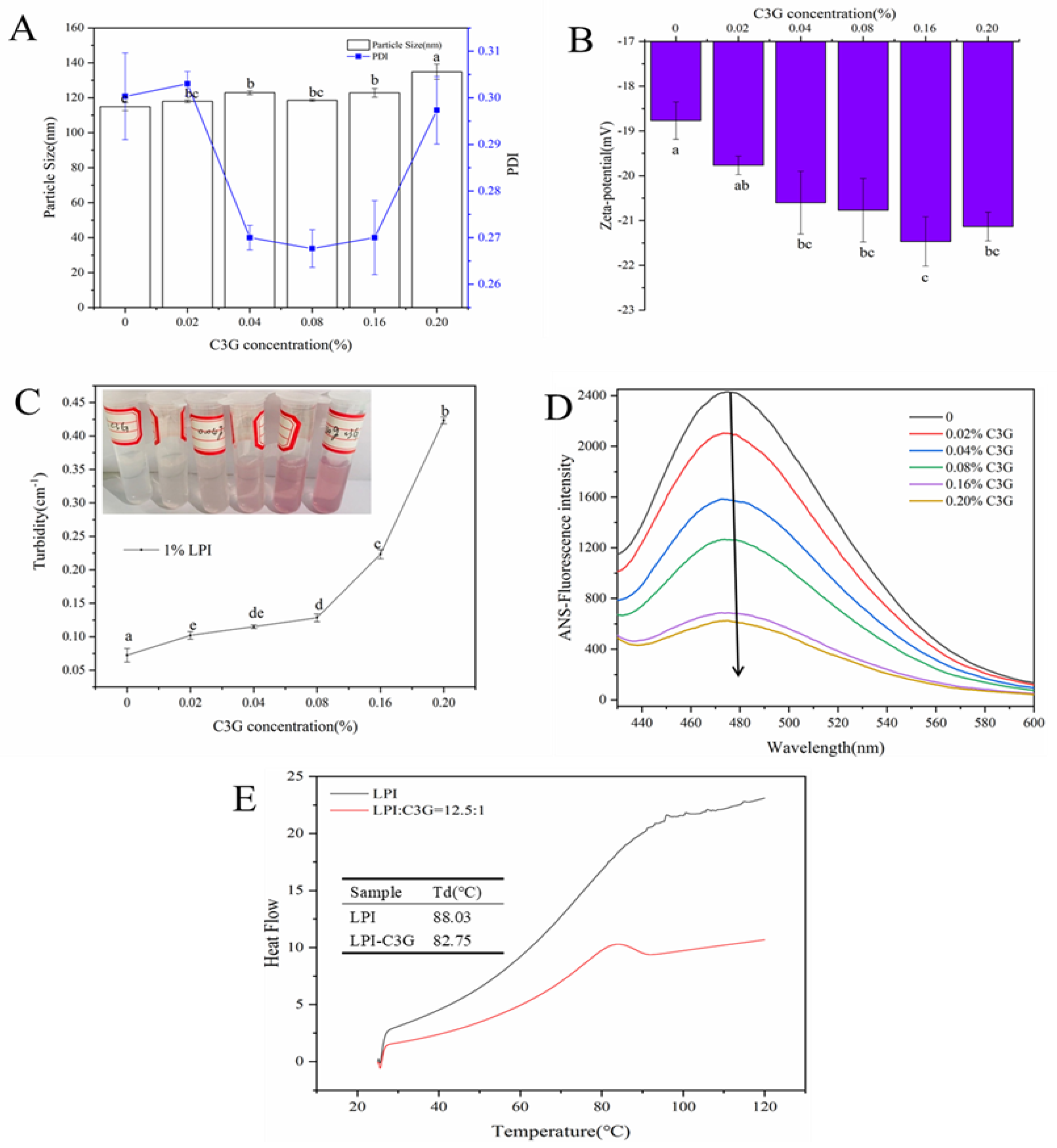
3.1. Physical Properties of LPI-C3G Complexes
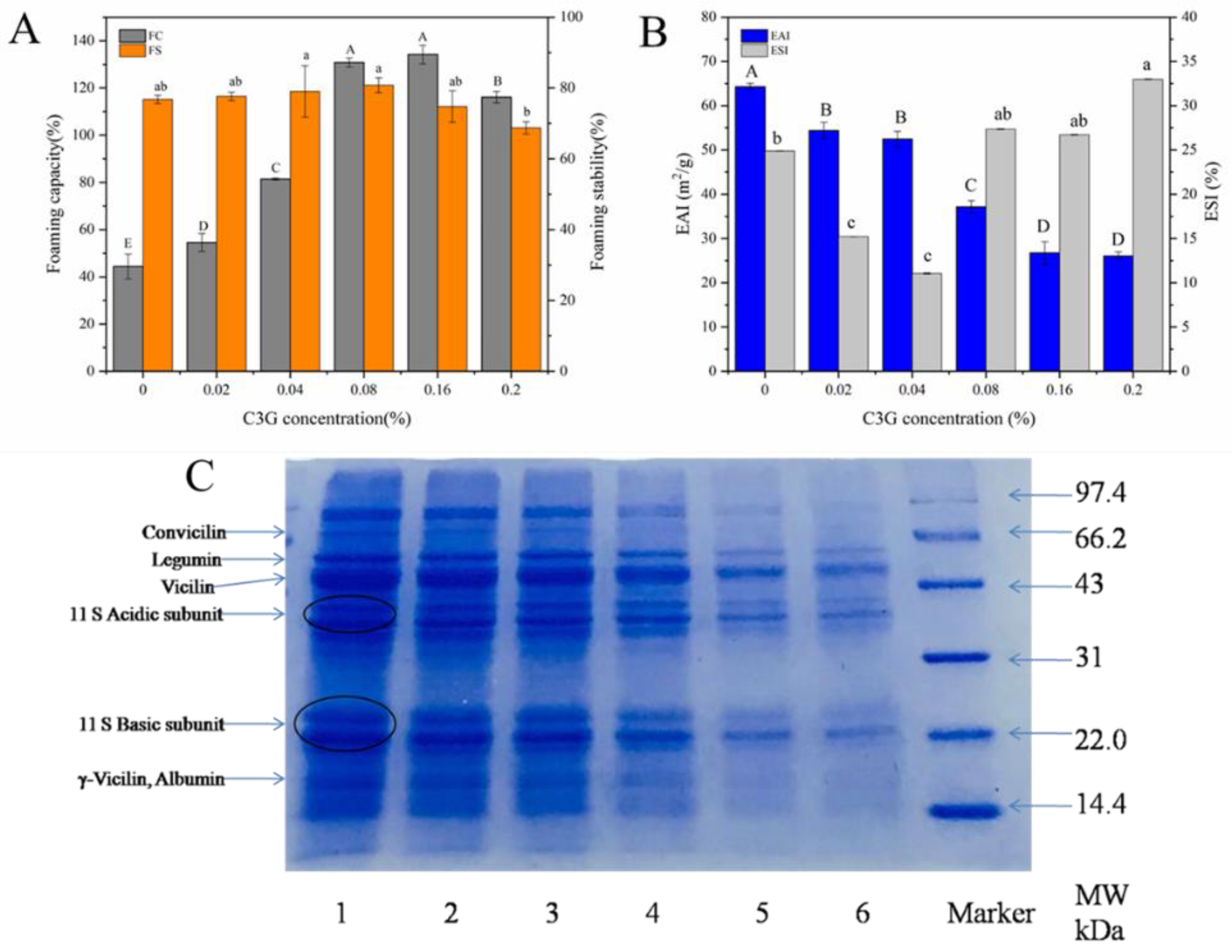
3.2. Functional Properties of LPI-C3G Complexes
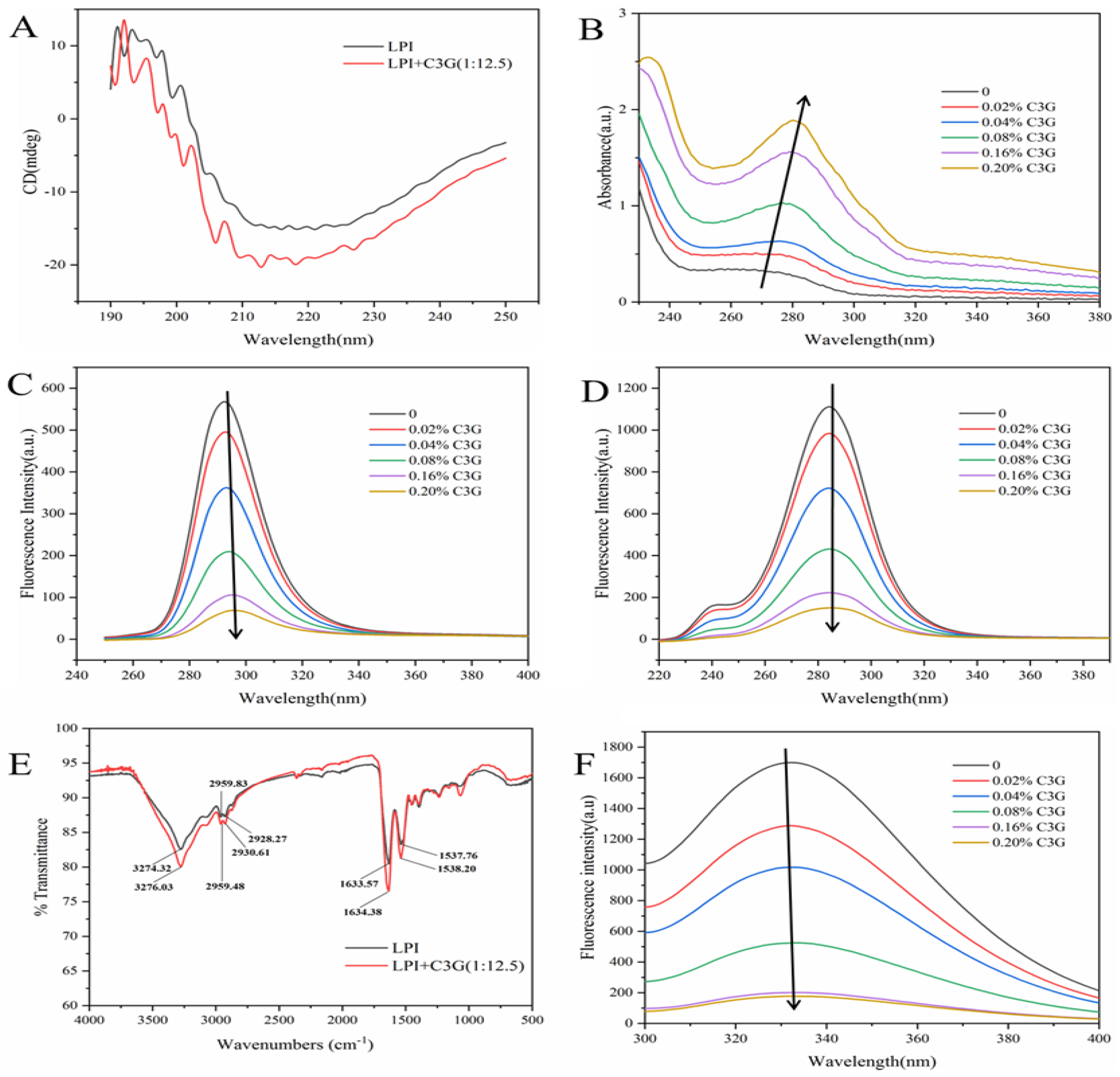
3.3. Effect of C3G on the Molecular Weight and Secondary Structure of LPI
3.4. UV–Vis Spectra of LPI-C3G Complexes
3.5. Synchronous Fluorescence Spectra of LPI-C3G Complexes
3.6. FTIR Spectra of LPI-C3G Complexes
3.7. Intrinsic Fluorescence Analysis
3.8. Fluorescence-Quenching Mechanism and Binding Constant
3.9. Thermodynamic Parameters and Binding Forces between LPI and C3G
3.10. Stability of C3G Influenced by LPI
3.11. Antioxidative Properties of LPI-C3G Complexes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lang, Y.; Gao, H.; Tian, J.; Shu, C.; Sun, R.; Li, B.; Meng, X. Protective effects of α-casein or β-casein on the stability and antioxidant capacity of blueberry anthocyanins and their interaction mechanism. LWT 2019, 115, 108434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Giusti, M.M. Anthocyanins: Natural Colorants with Health-Promoting Properties. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 1, 163–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, F.; Yang, P.; Wang, H.; Fernandes, I.; Mateus, N.; Liu, Y. Digestion and absorption of red grape and wine anthocyanins through the gastrointestinal tract. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 83, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeriglio, A.; Barreca, D.; Bellocco, E.; Trombetta, D. Chemistry, Pharmacology and Health Benefits of Anthocyanins. Phytother Res. 2016, 30, 1265–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, X.; Zhu, C.; Sun, J.; Tian, L.; Chen, W.; Bai, W. The target cells of anthocyanins in metabolic syndrome. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 921–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, R.L.; Wilkes, S.E.; Rogers, R.T.; Khanal, R.C.; Wu, X.; Howard, L.R. Purified blueberry anthocyanins and blueberry juice alter development of obesity in mice fed an obesogenic high-fat diet. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 3970–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, M.M.; Wrolstad, R.E. Acylated anthocyanins from edible sources and their applications in food systems. Biochem. Eng. J. 2003, 14, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; Rojanasasithara, T.; Mutilangi, W.; McClements, D.J. Enhanced stability of anthocyanin-based color in model beverage systems through whey protein isolate complexation. Food Res Int. 2015, 76 Pt 3, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Jiang, X.; Ma, X.; Sun, J.; Tian, L.; Vidyarthi, S.K.; Xu, J.; Pan, Z.; et al. A comprehensive review on innovative and advanced stabilization approaches of anthocyanin by modifying structure and controlling environmental factors. Food Chem. 2021, 366, 130611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Liu, J.-H.; Prasanna, G.; Jing, P. Spectrofluorimetric and molecular docking studies on the interaction of cyanidin-3-O-glucoside with whey protein, β-lactoglobulin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xie, Y. Interaction of Protein Isolate with Anthocyanin Extracted from Black Soybean and Its Effect on the Anthocyanin Stability. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 3140–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attaribo, T.; Jiang, X.; Huang, G.; Zhang, B.; Xin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Gui, Z. Studies on the interactional characterization of preheated silkworm pupae protein (SPP) with anthocyanins (C3G) and their effect on anthocyanin stability. Food Chem. 2020, 326, 126904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Yuan, D.; Wang, Q.; Hu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Cai, J.; Huang, Q.; Li, S.; Liu, G. Maillard-Reacted Whey Protein Isolates Enhance Thermal Stability of Anthocyanins over a Wide pH Range. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9556–9564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Belwal, T.; He, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, L.; Luo, Z. Interaction and binding mechanism of cyanidin-3-O-glucoside to ovalbumin in varying pH conditions: A spectroscopic and molecular docking study. Food Chem. 2020, 320, 126616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarpa-Parra, M. Lentil protein: A review of functional properties and food application. An overview of lentil protein functionality. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 892–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avramenko, N.A.; Chang, C.; Low, N.H.; Nickerson, M.T. Encapsulation of flaxseed oil within native and modified lentil protein-based microcapsules. Food Res. Int. 2016, 81, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, E.; Wismer, W.; Waduthanthri, K.; Babii, O.; Yang, J.; Chen, L. Application of Barley- and Lentil-Protein Concentrates in the Production of Protein-Enriched Doughnuts. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2018, 95, 1027–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarpa-Parra, M.; Wong, L.; Wismer, W.; Temelli, F.; Han, J.; Huang, W.; Eckhart, E.; Tian, Z.; Shi, K.; Sun, T.; et al. Quality characteristics of angel food cake and muffin using lentil protein as egg/milk replacer. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 1604–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primozic, M.; Duchek, A.; Nickerson, M.; Ghosh, S. Effect of lentil proteins isolate concentration on the formation, stability and rheological behavior of oil-in-water nanoemulsions. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Nickerson, M.T. Stability and in vitro release behaviour of encapsulated omega fatty acid-rich oils in lentil protein isolate-based microcapsules. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 69, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryee, F.N.A.; Nickerson, M.T. Formation of electrostatic complexes involving mixtures of lentil protein isolates and gum Arabic polysaccharides. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, K.; Courtet-Compondu, M.C.; Williamson, G.; Rezzi, S.; Kussmann, M.; Rytz, A. Non-covalent binding of proteins to polyphenols correlates with their amino acid sequence. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Dai, T.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Li, T.; Liu, C.; McClements, D.J. Protein-polyphenol functional ingredients: The foaming properties of lactoferrin are enhanced by forming complexes with procyanidin. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 128145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevkani, K.; Singh, N.; Kaur, A.; Rana, J.C. Structural and functional characterization of kidney bean and field pea protein isolates: A comparative study. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, S.; Feng, B.; Jiang, B.; Miao, M. Interaction between soybean protein and tea polyphenols under high pressure. Food Chem. 2019, 277, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Sun, H.; Qi, B.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L. Functional and conformational changes to soy proteins accompanying anthocyanins: Focus on covalent and non-covalent interactions. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Xu, M.; Zeng, M.; Qin, F.; Chen, J. Interactions of milk alpha- and beta-casein with malvidin-3-O-glucoside and their effects on the stability of grape skin anthocyanin extracts. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhu, H.; Xu, M.; Zeng, M.; Qin, F.; Chen, J. Complexation of bovine beta-lactoglobulin with malvidin-3-O-glucoside and its effect on the stability of grape skin anthocyanin extracts. Food Chem. 2016, 209, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, C.; Gao, X.; Chen, Y.; Santhanam, R.K.; Wang, C.; Xu, L.; Chen, H. Interaction characterization of preheated soy protein isolate with cyanidin-3-O-glucoside and their effects on the stability of black soybean seed coat anthocyanins extracts. Food Chem. 2019, 271, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobley, A.; Whitmore, L.; Wallace, B.A. DICHROWEB: An interactive website for the analysis of protein secondary structure from circular dichroism spectra. Bioinformatics 2002, 18, 211–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.; Chen, J.; Li, Q.; Li, P.; Hu, P.; Liu, C.; Li, T. Investigation the interaction between procyanidin dimer and alpha-amylase: Spectroscopic analyses and molecular docking simulation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parolia, S.; Maley, J.; Sammynaiken, R.; Green, R.; Nickerson, M.; Ghosh, S. Structure—Functionality of lentil protein-polyphenol conjugates. Food Chem. 2021, 367, 130603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, K.; Liu, L.; He, Z.; Xu, B.; Wu, X. Characterization of binding interactions of anthraquinones and bovine beta-lactoglobulin. Food Chem. 2019, 281, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Li, S.; Bi, H.; Gao, X. Interaction of cyanidin-3-O-glucoside with three proteins. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Xu, M.; Zeng, M.; Qin, F.; Chen, J. Preheated milk proteins improve the stability of grape skin anthocyanins extracts. Food Chem. 2016, 210, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, Q.; Hu, Z.; Cai, J.; Qin, X. Maillard-Reacted Whey Protein Isolates and Epigallocatechin Gallate Complex Enhance the Thermal Stability of the Pickering Emulsion Delivery of Curcumin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 5212–5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Wang, D. Formation of nanocomplexes comprising whey proteins and fucoxanthin: Characterization, spectroscopic analysis, and molecular docking. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.D.; Lin, Y.F.; Xu, X.; Meng, L.; Dong, M.S. Effect of non-covalent and covalent complexation of (-)-epigallocatechin gallate with soybean protein isolate on protein structure and in vitro digestion characteristics. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R.; Seijen ten-Hoorn, J.; Hazekamp, J.; Blijdenstein, T.B.J.; Velikov, K.P. Colloidal complexation of a macromolecule with a small molecular weight natural polyphenol: Implications in modulating polymer functionalities. Soft Matter. 2013, 9, 1428–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Hu, P.; Dai, T.; Li, P.; Ye, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, C. Comparing the binding interaction between beta-lactoglobulin and flavonoids with different structure by multi-spectroscopy analysis and molecular docking. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 201, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Gidley, M.J.; Warren, F.J. The mechanism of interactions between tea polyphenols and porcine pancreatic alpha-amylase: Analysis by inhibition kinetics, fluorescence quenching, differential scanning calorimetry and isothermal titration calorimetry. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1700324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, C.; Xiong, W.; Li, J.; Li, B. Comparison of binding interactions of cyanidin-3-O-glucoside to β-conglycinin and glycinin using multi-spectroscopic and thermodynamic methods. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 92, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.P.; Li, J.S.; Zha, D.Q.; Zhang, L.; Gao, P.; Yao, T.; Wu, X. Chlorogenic acid prevents diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation through modulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-kappa B pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 54, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boye, J.I.; Aksay, S.; Roufik, S.; Ribéreau, S.; Mondor, M.; Farnworth, E.; Rajamohamed, S. Comparison of the functional properties of pea, chickpea and lentil protein concentrates processed using ultrafiltration and isoelectric precipitation techniques. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primozic, M.; Duchek, A.; Nickerson, M.; Ghosh, S. Formation, stability and in vitro digestibility of nanoemulsions stabilized by high-pressure homogenized lentil proteins isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbana, C.; Boye, J.I. In vitro protein digestibility and physico-chemical properties of flours and protein concentrates from two varieties of lentil (Lens culinaris). Food Funct. 2013, 4, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Zhao, M.; Xia, N.; Teng, J.; Jia, C.; Wei, B.; Huang, L.; Chen, D. Interaction between plant phenolics and rice protein improved oxidative stabilities of emulsion. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 89, 102818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.; Chen, J.; McClements, D.J.; Hu, P.; Ye, X.; Liu, C.; Li, T. Protein-polyphenol interactions enhance the antioxidant capacity of phenolics: Analysis of rice glutelin-procyanidin dimer interactions. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, X.; McClements, D.J.; Zou, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, F. Co-encapsulation of Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) and Curcumin by Two Proteins-Based Nanoparticles: Role of EGCG. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13228–13236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Guo, Q.; Chen, Y.; Mao, L.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, F. Utilization of β-lactoglobulin-(−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) composite colloidal nanoparticles as stabilizers for lutein pickering emulsion. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 98, 105293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Zuo, H.; Shu, L. Comparison of the interaction between three anthocyanins and human serum albumins by spectroscopy. J. Lumin. 2014, 153, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samari, F.; Hemmateenejad, B.; Shamsipur, M.; Rashidi, M.; Samouei, H. Affinity of two novel five-coordinated anticancer Pt(II) complexes to human and bovine serum albumins: A spectroscopic approach. Inorg Chem. 2012, 51, 3454–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, P.D.; Subramanian, S. Thermodynamics of protein association reactions: Forces contributing to stability. Biochemistry 1981, 20, 3096–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Chen, J.; Moser, S.E.; Jones, O.G.; Ferruzzi, M.G. Interaction of β-casein with (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate assayed by fluorescence quenching: Effect of thermal processing temperature. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | α-Helix (%) | β-Sheet (%) | β-Turn (%) | Random Coil (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LPI | 9.13 ± 0.15 | 38.77 ± 0.23 | 22.77 ± 0.50 | 29.80 ± 0.85 |
| LPI-C3G | 7.80 ± 0.17 | 38.47 ± 0.35 | 22.57 ± 0.25 | 31.50 ± 0.20 |
| Complex | T (K) | Ksv (×104 M−1) | Kq (×1012 M−1·s−1) | R 2a | Ka (×106 M−1) | n | R 2b | (kJ·mol−1) | (kJ·mol−1) | (J·mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LPI-C3G | 298 | 4.83 ± 0.01 a | 4.83 ± 0.01 a | 0.9828 | 3.24 ± 0.01 a | 1.506 | 0.9916 | −37.11 | ||
| 308 | 4.76 ± 0.03 b | 4.76 ± 0.03 b | 0.9929 | 3.33 ± 0.04 b | 1.508 | 0.9913 | 4.61 | −38.51 | 140.01 | |
| 318 | 4.62 ± 0.02 c | 4.62 ± 0.02 c | 0.9867 | 3.63 ± 0.02 c | 1.532 | 0.9942 | −39.91 |
| Treatment | LPI Concentration (mg/mL) | C3G (mg/L) | C3G Degradation Rate (%) | FRAP Assay (mM FeSO4/g DW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated | 0.00 | |||
| Heated at 80 ℃ for 2 h | 0.00 | e | a | a |
| 0.05 | c | c | ab | |
| 0.10 | d | b | ab | |
| 0.15 | b | d | ab | |
| 0.20 | a | e | b | |
| Oxidized by 0.05 mg/mL H2O2 for 2 h | 0.00 | e | a | a |
| 0.05 | c | c | a | |
| 0.10 | d | b | ab | |
| 0.15 | b | d | ab | |
| 0.20 | a | e | b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, H.; Guo, F.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, L.; Sun, Y. The Interactional Characterization of Lentil Protein Isolate (LPI) with Cyanidin-3-O-Glucoside (C3G) and Their Effect on the Stability and Antioxidant Activity of C3G. Foods 2023, 12, 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12010104
Qian H, Guo F, Xiong H, Zhang H, Jiang L, Sun Y. The Interactional Characterization of Lentil Protein Isolate (LPI) with Cyanidin-3-O-Glucoside (C3G) and Their Effect on the Stability and Antioxidant Activity of C3G. Foods. 2023; 12(1):104. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12010104
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Hongxia, Fanghua Guo, Hua Xiong, Hua Zhang, Li Jiang, and Yong Sun. 2023. "The Interactional Characterization of Lentil Protein Isolate (LPI) with Cyanidin-3-O-Glucoside (C3G) and Their Effect on the Stability and Antioxidant Activity of C3G" Foods 12, no. 1: 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12010104
APA StyleQian, H., Guo, F., Xiong, H., Zhang, H., Jiang, L., & Sun, Y. (2023). The Interactional Characterization of Lentil Protein Isolate (LPI) with Cyanidin-3-O-Glucoside (C3G) and Their Effect on the Stability and Antioxidant Activity of C3G. Foods, 12(1), 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12010104





