A High-Luminescence Biomimetic Nanosensor Based on N, S-GQDs-Embedded Zinc-Based Metal–Organic Framework@Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Sensitive Detection of Octopamine in Fermented Foods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Instruments
2.2. Synthesis of ZIF-8, N, S-GQDs and the N, S-GQDs@ZIF-8@MIP Composite
2.3. Fluorescence Measurement
2.4. Pretreatment of Samples
3. Results and Discussion
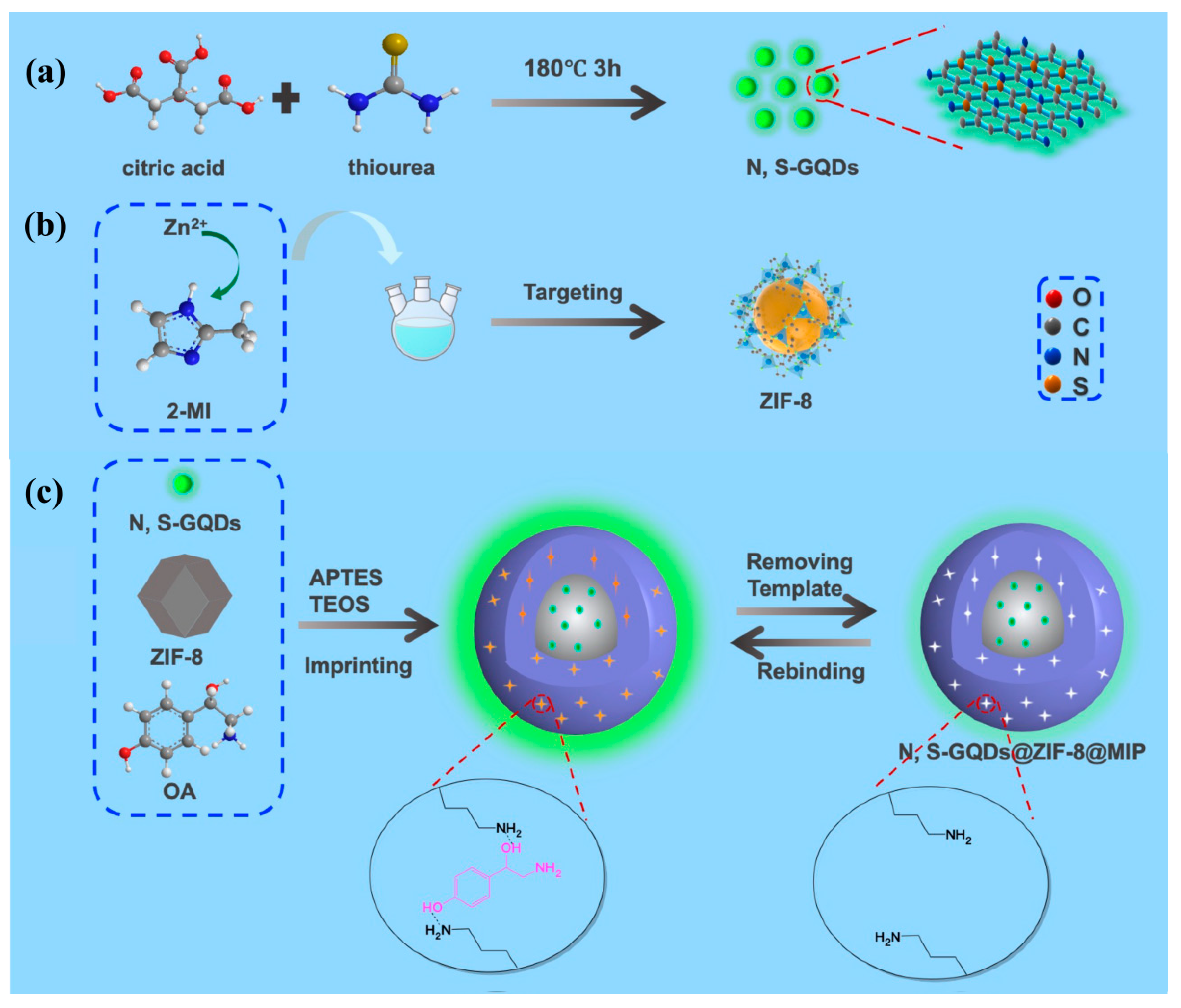
3.1. Preparation of N, S-GQDs, ZIF-8 and N, S-GQDs@ZIF-8@MIP
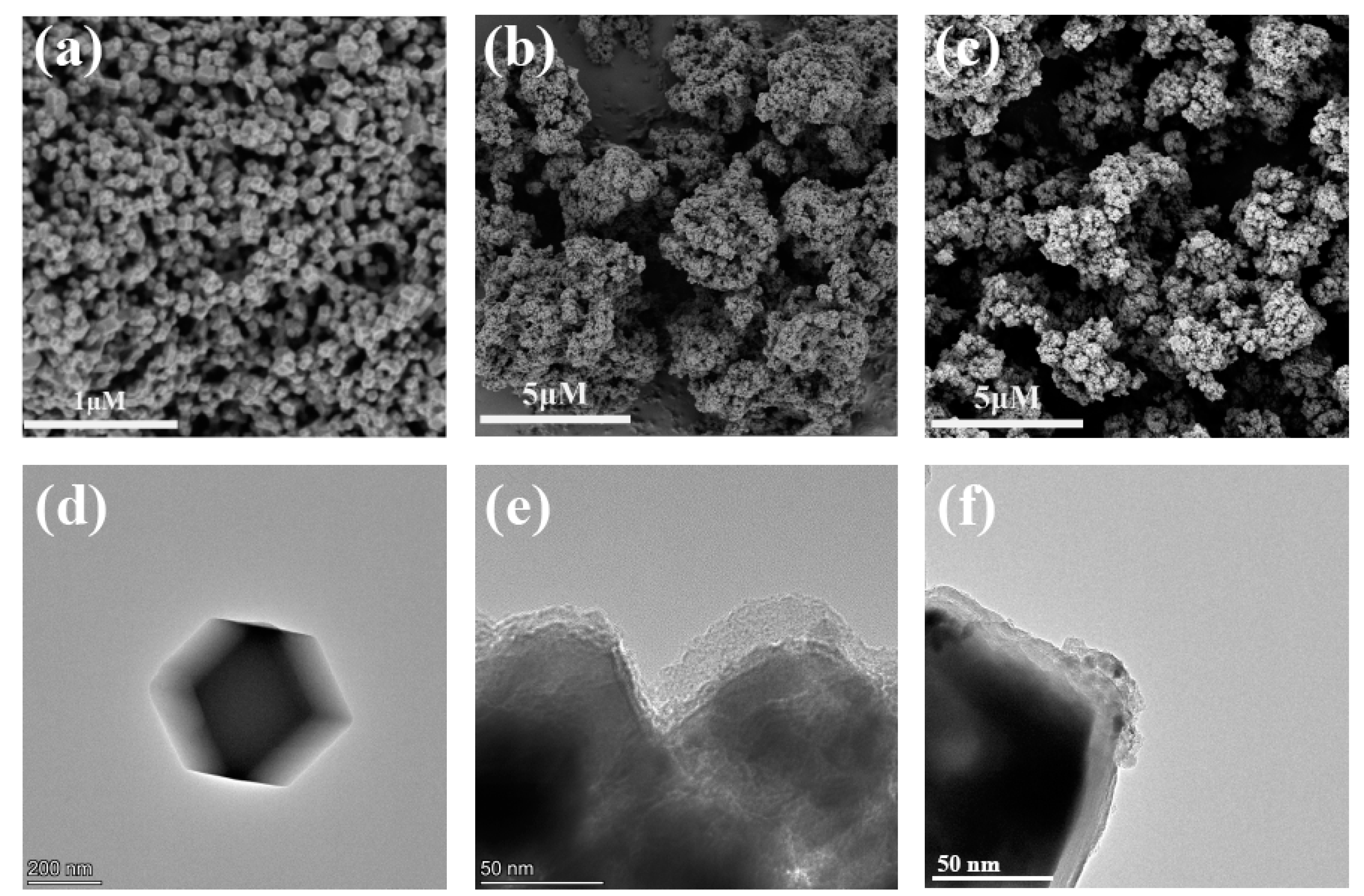
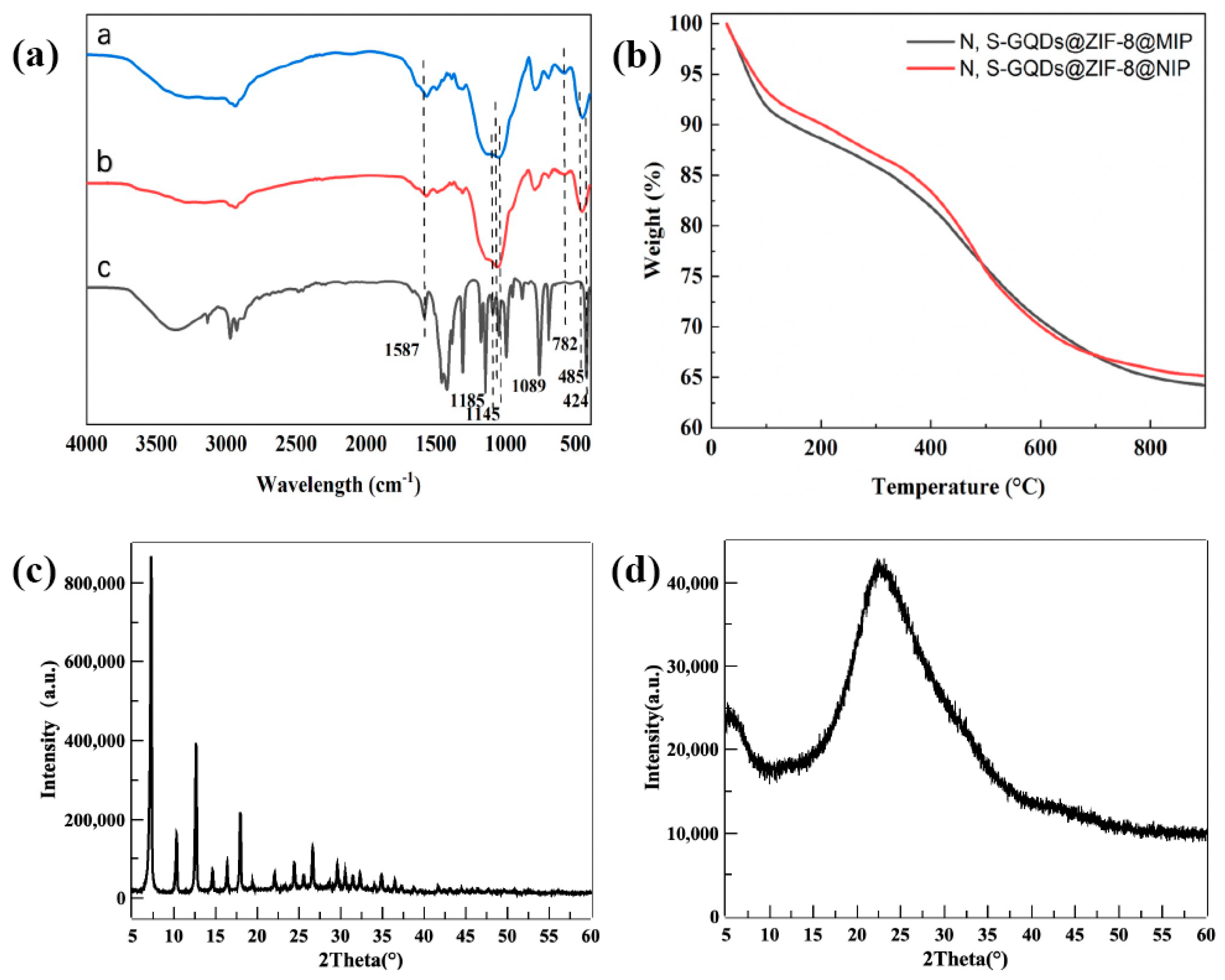
3.2. Characterization of Materials
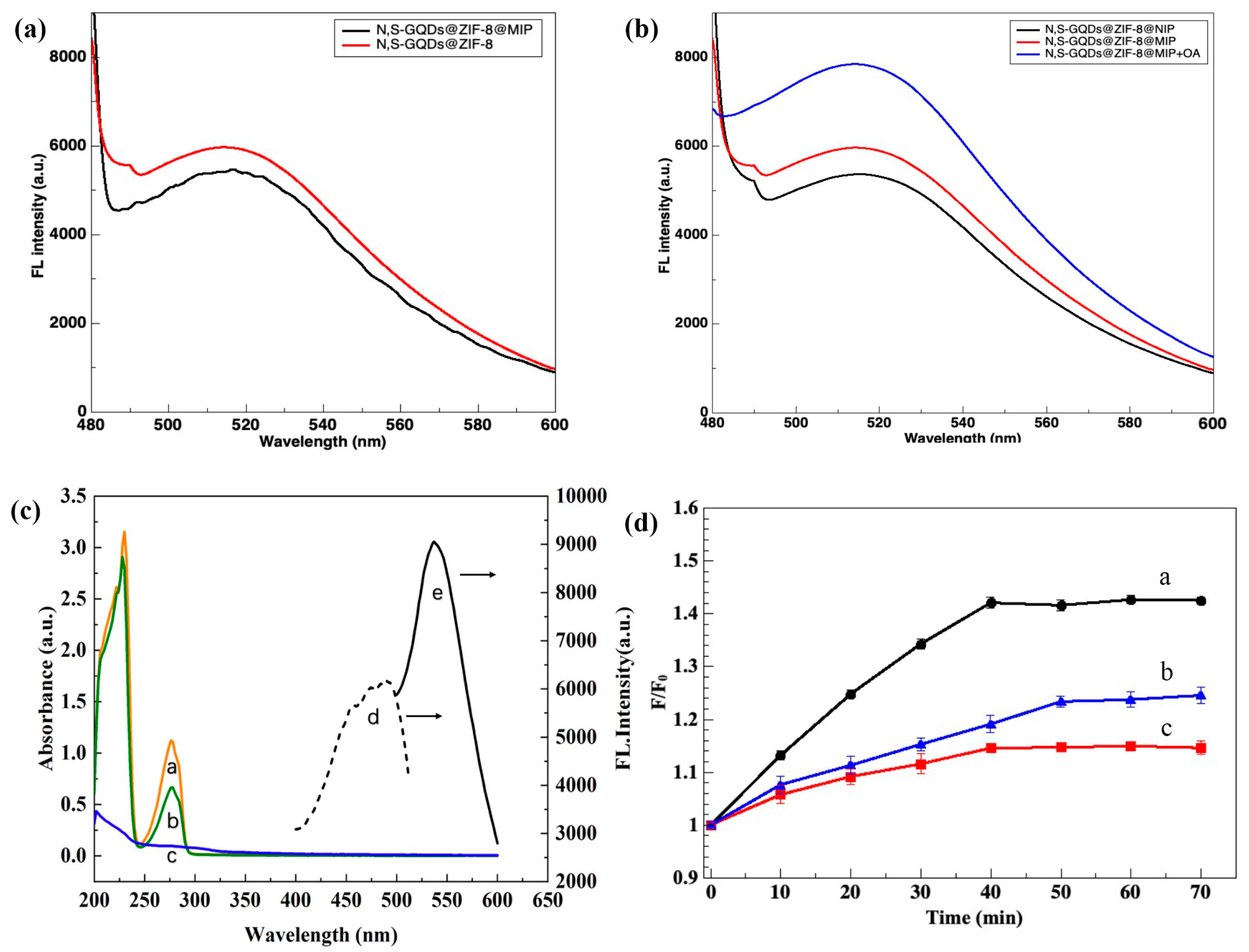
3.3. Photoluminescence Properties and Kinetic Absorption of N, S-GQDs@ZIF-8@MIP
3.4. Establishment of Fluorescence Sensing Detection for OA
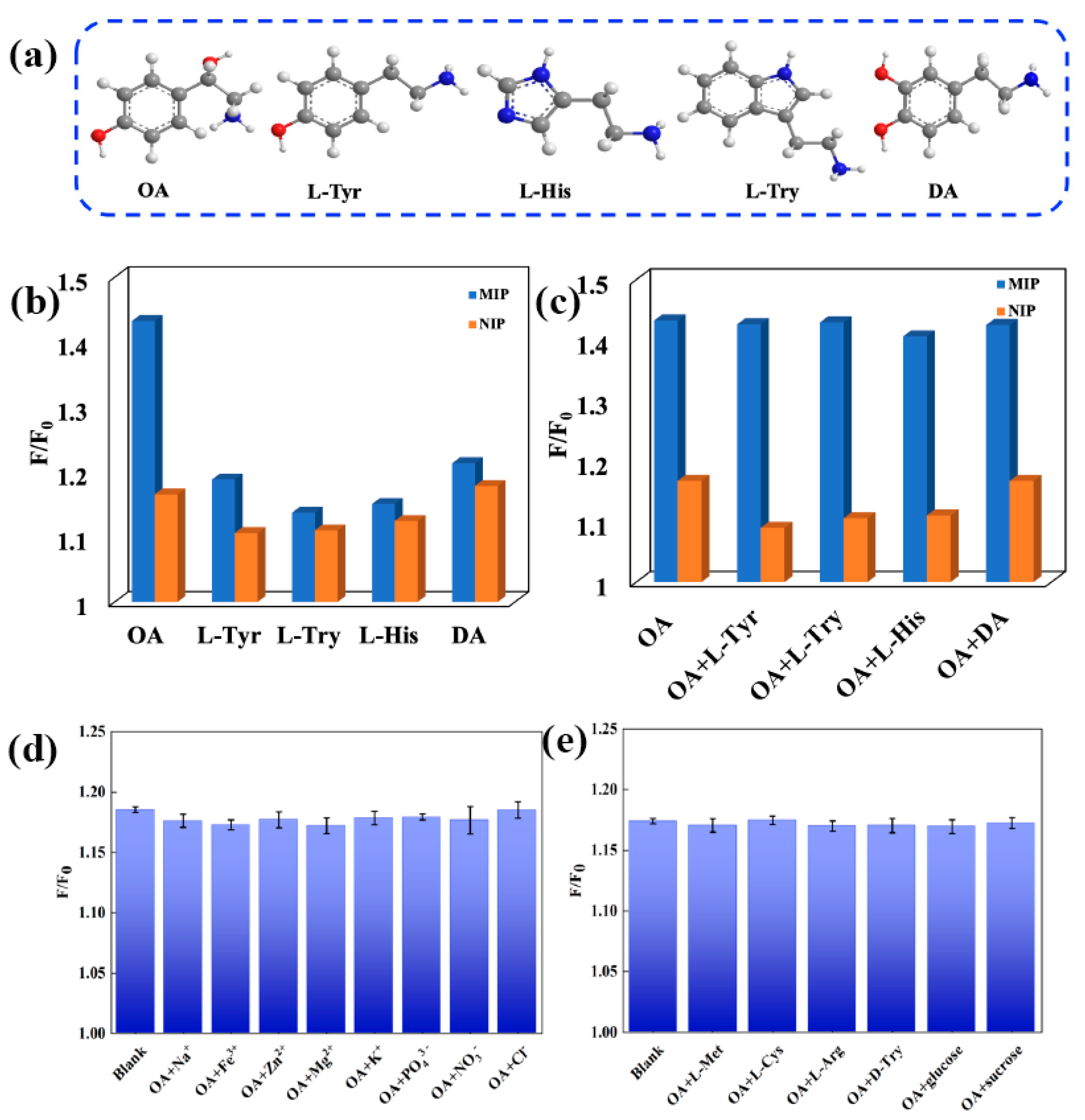
3.5. Selectivity of N, S-GQDs@ZIF-8@MIP
3.6. OA Detection in Real Samples
3.7. Method Performance Comparison
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tofalo, R.; Perpetuini, G.; Schirone, M.; Suzzi, G. Biogenic Amines: Toxicology and Health Effect. Encycl. Food Health 2015, 71, 424–429. [Google Scholar]
- Elias, D.O.; Land, B.R.; Mason, A.C.; Hoy, R.R. Measuring and quantifying dynamic visual signals in jumping spiders. J. Comp. Physiol. A Sens. Neural Behav. Physiol. 2006, 192, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wójcik, W.; Łukasiewicz, M.; Puppel, K. Biogenic amines: Formation, action and toxicity—A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 101, 2634–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thevis, M.; Koch, A.; Sigmund, G.; Thomas, A.; Schänzer, W. Analysis of octopamine in human doping control samples. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2011, 26, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wei, Q.; Gao, Y.; Guo, L.; Al-Ghanim, K.A.; Mahboob, S.; Zhang, X. An Easily Fabricated Electrochemical Sensor Based on a Graphene-Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode for Determination of Octopamine and Tyramine. Sensors 2016, 16, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moczko, E.; Díaz, R.; Rivas, B.; García, C.; Pereira, E.; Piletsky, S.; Cáceres, C. Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles Assay (MINA) in Pseudo ELISA: An Alternative to Detect and Quantify Octopamine in Water and Human Urine Samples. Polymers 2019, 11, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pyakurel, P.; Champaloux, E.P.; Venton, B.J. Fast-Scan Cyclic Voltammetry (FSCV) Detection of Endogenous Octopamine in Drosophila melanogaster Ventral Nerve Cord. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 1112–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pawar, R.S.; Sagi, S.; Leontyev, D. Analysis of bitter orange dietary supplements for natural and synthetic phenethylamines by LC–MS/MS. Drug Test. Anal. 2020, 12, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H.; Kim, C. Colorimetric detection of iron and fluorescence detection of zinc and cadmium by a chemosensor containing a bio-friendly octopamine. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2018, 17, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Chaudhary, N.; Srivastava, R.; Sharma, G.D.; Bhardwaj, R.; Chand, S. Luminscent Graphene Quantum Dots for Organic Photovoltaic Devices. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 9960–9963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Guo, S. Chemically doped fluorescent carbon and graphene quantum dots for bioimaging, sensor, catalytic and photoelectronic applications. Nanoscale 2015, 8, 2532–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, S.; Yadav, R.M.; Narayanan, T.N.; Shelke, M.V.; Vajtai, R.; Ajayan, P.M.; Pillai, V.K. Synthesis of N, F and S Co-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 11515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, D.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X.; Haddad, R.E.; Fan, H.; Sun, Z. Formation mechanism and optimization of highly luminescent N-doped graphene quantum dots. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Lau, S.P.; Tang, L.; Ji, R.; Yang, P. Sulphur doping: A facile approach to tune the electronic structure and optical properties of graphene quantum dots. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 5323–5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhu, J.; Fan, L.; Li, X. Sulfur-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots as a Novel Fluorescent Probe for Highly Selective and Sensitive Detection of Fe3+. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 10201–10207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Hai, X.; Chen, X.-W.; Wang, J.-H. Simultaneously fabrication of free and solidified N, S-doped graphene quantum dots via a facile solvent-free synthesis route for fluorescent detection. Talanta 2017, 168, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghi, O.M.; Li, G.; Li, H. Selective binding and removal of guests in a microporous metal–organic framework. Nature 1995, 378, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.; Forrest, K.A.; Franz, D.M.; Space, B. Experimental and theoretical investigations of the gas adsorption sites in rht-metal–organic frameworks. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 4646–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, G.; Chen, C.; Chai, Z.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Wang, X. Metal–organic framework-based materials: Superior adsorbents for the capture of toxic and radioactive metal ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2322–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altintas, C.; Avci, G.; Daglar, H.; Azar, A.N.V.; Velioglu, S.; Erucar, I.; Keskin, S. Database for CO2 Separation Performances of MOFs Based on Computational Materials Screening. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 17257–17268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Pan, Z.; Ye, B.; Xu, M. Determination of Malachite Green in Fish by a Modified MOF-Based Electrochemical Sensor. Food Anal. Methods 2019, 12, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.-L.; Xu, Q. Metal-organic framework composites. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5468–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.P.; Subudhi, S.; Parida, K. Inter-MOF hybrid (IMOFH): A concise analysis on emerging core–shell based hierarchical and multifunctional nanoporous materials. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 434, 213786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Fang, G.; Liu, J.; Pan, M.; Wang, R.; Wang, S. One-pot synthesis of nanoscale carbon dots-embedded metal–organic frameworks at room temperature for enhanced chemical sensing. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 15880–15887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Lu, W.; Wu, X.; Li, J. Molecular imprinting: Perspectives and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2137–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.I.; Shaikh, H.; Mustafa, G.; Bhanger, M.I. Recent Applications of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in Analytical Chemistry. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2018, 48, 179–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, M.; Płotka-Wasylka, J.; Morrison, C.; Wieczorek, P.P.; Namiesnik, J.; Marć, M. Application of molecularly imprinted polymers in analytical chiral separations and analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 102, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caoa, Y.; Hua, X.; Zhaoa, T.; Maoa, Y.; Fanga, G.; Wangab, S. A core-shell molecularly imprinted optical sensor based on the upconversion nanoparticles decorated with Zinc-based metal-organic framework for selective and rapid detection of octopamine. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2020, 326, 128838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Cao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Qi, Y.; Fang, G.; Wang, S. A molecularly imprinted fluorescence nanosensor based on upconversion metal–organic frameworks for alpha-cypermethrin specific recognition. Mikrochim. Acta 2020, 187, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, H.; Liu, X.; Xie, Z. Three Colors Emission from S.N. Co-doped Graphene Quantum Dots for Visible Light H2Production and Bioimaging. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2015, 3, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hai, X.; Xia, C.; Chen, X.-W.; Wang, J.-H. Preparation of Excitation-Independent Photoluminescent Graphene Quantum Dots with Visible-Light Excitation/Emission for Cell Imaging. Chem. A Eur. J. 2013, 19, 15918–15923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.; Zheng, M.; Du, P.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, D.; Tan, H.; Zhao, Z.; Xie, Z.; Sun, Z. Highly luminescent S, N co-doped graphene quantum dots with broad visible absorption bands for visible light photocatalysts. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 12272–12277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhou, S.; Xiao, L.; Yuan, Q.; Gan, W. Time-efficient syntheses of nitrogen and sulfur co-doped graphene quantum dots with tunable luminescence and their sensing applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 36554–36560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravillon, J.; Münzer, S.; Lohmeier, S.-J.; Feldhoff, A.; Huber, K.; Wiebcke, M. Rapid Room-Temperature Synthesis and Characterization of Nanocrystals of a Prototypical Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 1410–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wang, T.; An, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Li, G.; Wu, X.; Su, Z.; Wang, C. Carbon nanodots@zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 nanoparticles for simultaneous pH-responsive drug delivery and fluorescence imaging. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 3259–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Feng, W.; Liang, K.; Chen, C.; Cai, C. A novel fluorescence molecularly imprinted sensor for Japanese encephalitis virus detection based on metal organic frameworks and passivation-enhanced selectivity. Talanta 2020, 212, 120744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Analytical Methods Committee Recommendations for the definition, estimation and use of the detection limit. Analyst 1987, 112, 199–204. [CrossRef]

| Samples | Added (mg L−1) | N, S-GQDs@ZIF-8@MIP | HPLC-UV | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Found (mg L−1) (n = 3) | Recovery% (Mean ± SD) (n = 3) | RSD% (n = 3) | Found (mg L−1) (n = 3) | Recovery % (Mean ± SD) (n = 3) | RSD% (n = 3) | ||
| white vinegar | 0.00 | ND a | - | - | ND a | - | - |
| 1.00 | 0.87 | 86.86 ± 2.31 | 2.66 | 0.80 | 80.38 ± 3.96 | 4.93 | |
| 5.00 | 4.68 | 93.58 ± 1.64 | 1.75 | 4.30 | 85.90 ± 1.04 | 1.22 | |
| 9.00 | 8.00 | 88.92 ± 2.46 | 2.77 | 7.27 | 80.75 ± 2.60 | 3.23 | |
| wine | 0.00 | ND a | - | - | ND a | - | - |
| 1.00 | 0.91 | 91.08 ± 1.68 | 1.84 | 0.84 | 84.48 ± 2.24 | 2.65 | |
| 5.00 | 4.54 | 90.90 ± 4.13 | 4.54 | 4.36 | 87.17 ± 1.81 | 2.09 | |
| 9.00 | 8.29 | 92.07 ± 2.66 | 2.89 | 7.41 | 82.31 ± 2.36 | 2.87 | |
| Methods | Detector | LOD (mg L−1) | Linear Range (mg L−1) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Advantages | Limitations | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical | octopamine tyramine | 0.153 0.041 | 0.0153–6.12 0.013–0.034 | 98.5–104.7 102.2–103.1 | 5.9–6.1 5.6–6.4 | fast sensitive | The scope of use is limited | [5] |
| ELISA | octopamine | 0.59 | 2.259–15.3 | 96.2–106.4 | - | high reproducibility | Low sensitivity and specificity | [6] |
| FSCV | octopamine | 0.336 | - | - | - | sensitive | Low accuracy, easily disturbed | [7] |
| HPLC | synephrine octopamine | 0.033 0.092 | 0.2–1.2 0.2–1.2 | 98.2–101.5 | 1.5–2.5 | wide range of applications | Costly, complex preprocessing | [8] |
| Fluorescence (UCNPs@ZIF-8@MIP) | octopamine | 0.081 | 0.1–10 | 81.75–90.63 | 2.56–5.13 | simple preprocessing | UCNP synthesis conditions were complex | [28] |
| Fluorescence (N,S-GQDs@ZIF-8@MIP) | octopamine | 0.062 | 0.1–10 | 86.86–93.58 | 1.75–4.54 | fast, sensitive, high detection limits | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Yuan, G.; Hu, X.; Zhang, J.; Fang, G. A High-Luminescence Biomimetic Nanosensor Based on N, S-GQDs-Embedded Zinc-Based Metal–Organic Framework@Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Sensitive Detection of Octopamine in Fermented Foods. Foods 2022, 11, 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11091348
Guo Y, Yuan G, Hu X, Zhang J, Fang G. A High-Luminescence Biomimetic Nanosensor Based on N, S-GQDs-Embedded Zinc-Based Metal–Organic Framework@Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Sensitive Detection of Octopamine in Fermented Foods. Foods. 2022; 11(9):1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11091348
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Ying, Guanqing Yuan, Xuelian Hu, Jinni Zhang, and Guozhen Fang. 2022. "A High-Luminescence Biomimetic Nanosensor Based on N, S-GQDs-Embedded Zinc-Based Metal–Organic Framework@Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Sensitive Detection of Octopamine in Fermented Foods" Foods 11, no. 9: 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11091348
APA StyleGuo, Y., Yuan, G., Hu, X., Zhang, J., & Fang, G. (2022). A High-Luminescence Biomimetic Nanosensor Based on N, S-GQDs-Embedded Zinc-Based Metal–Organic Framework@Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Sensitive Detection of Octopamine in Fermented Foods. Foods, 11(9), 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11091348





