Relationship between Molecular Structure and Heat-Induced Gel Properties of Duck Myofibrillar Proteins Affected by the Addition of Pea Protein Isolate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Heat-Induced Mixed-Protein Gels
2.3. Color Measurement
2.4. Water-Holding Capacity
2.5. Gel-Penetration Test
2.6. Low Field NMR Measurements
2.7. Raman Spectroscopy Measurements
2.8. Dynamic Rheological Measurements
2.9. Microstructural Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Gel Color
3.2. Gel WHC
3.3. Gel-Penetration Test
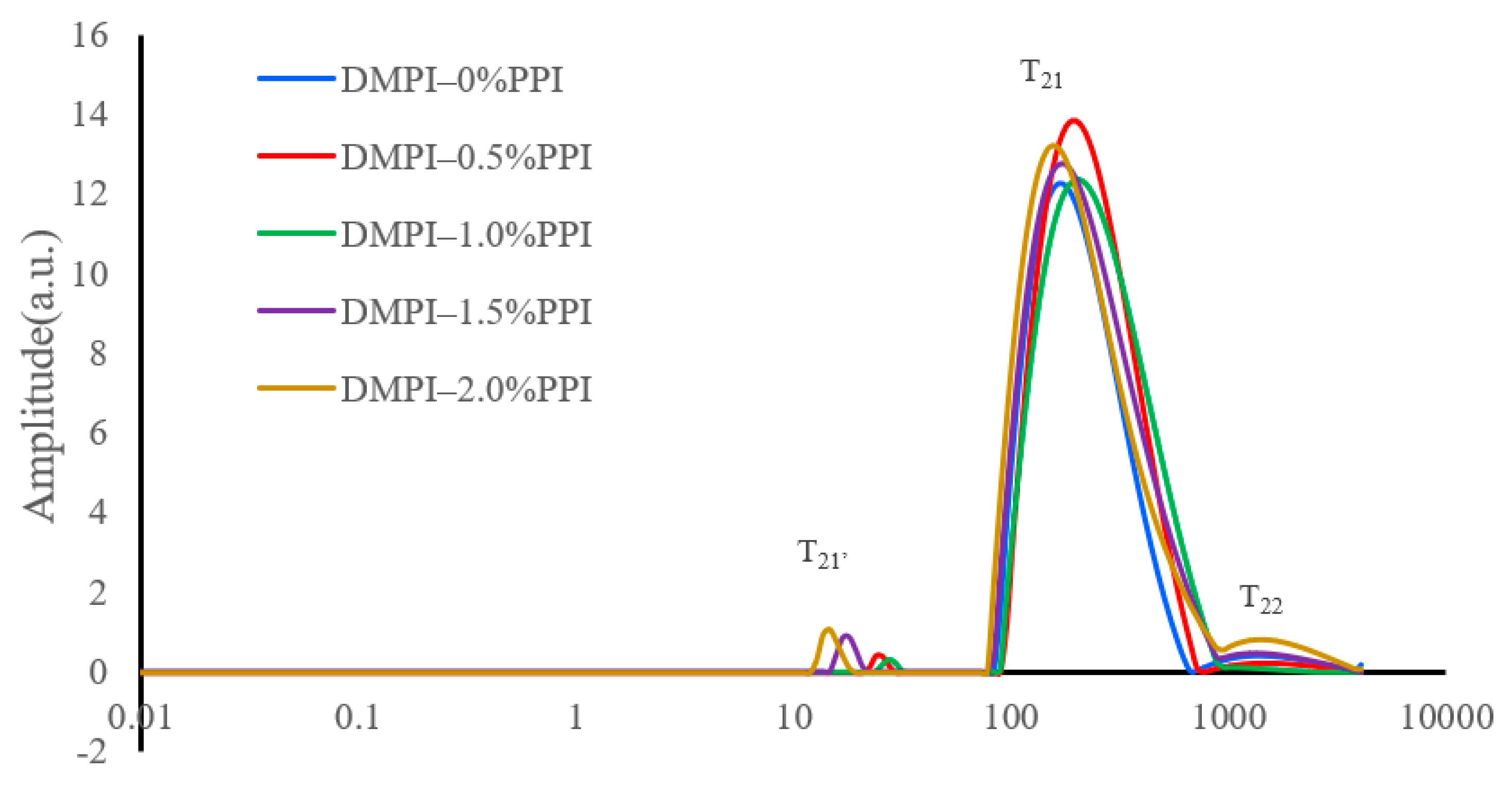
3.4. NMR Analysis
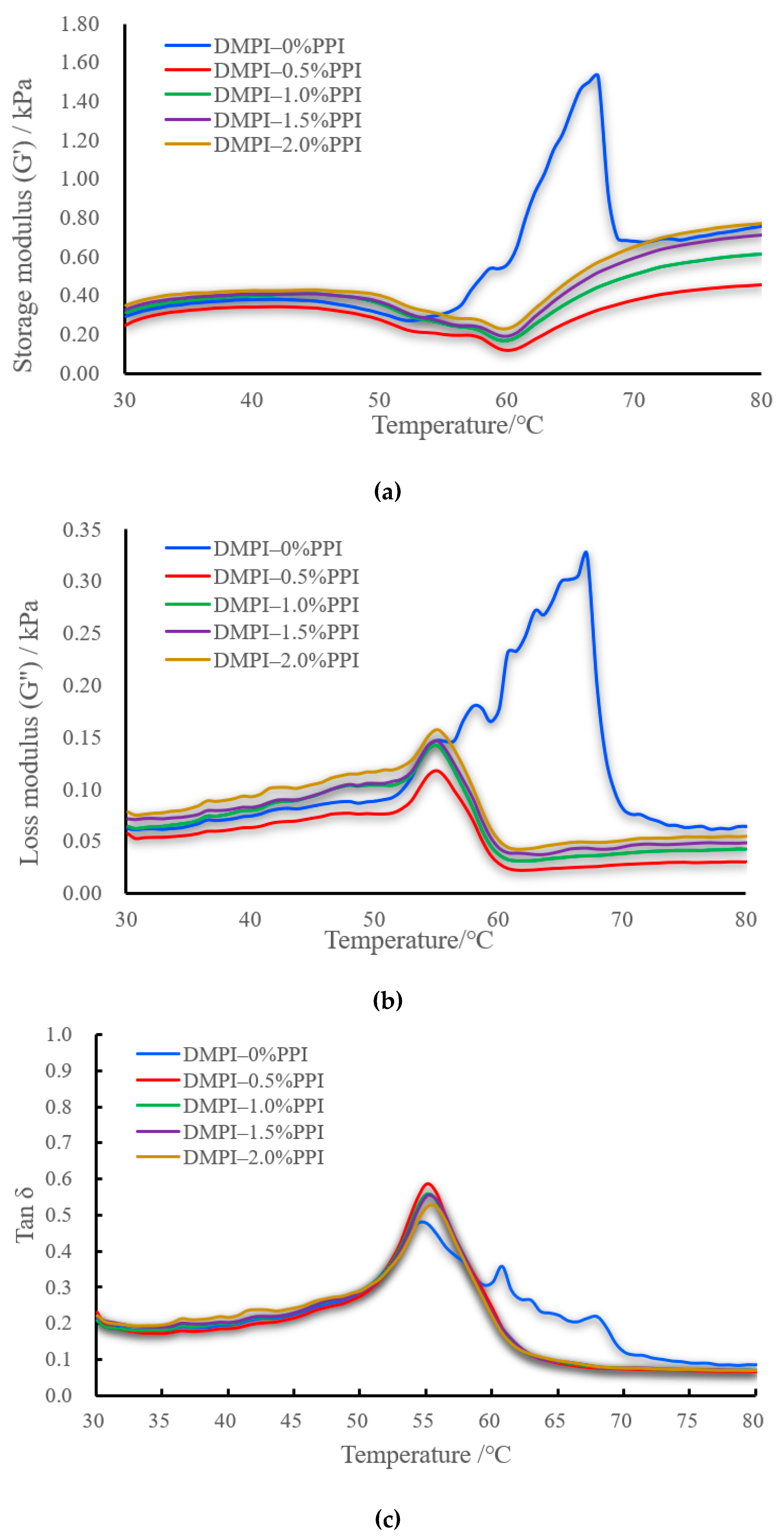
3.5. Rheological Properties Analysis
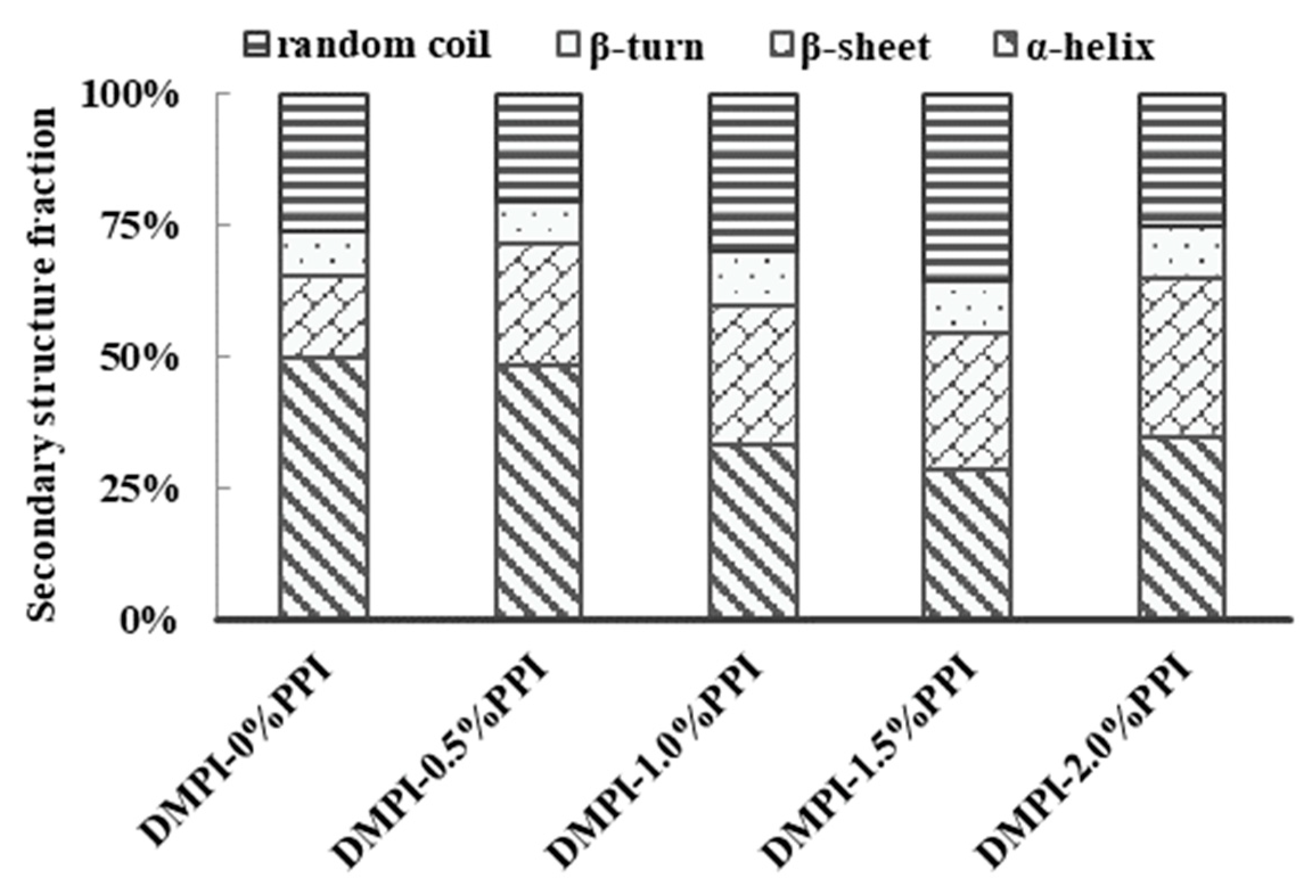
3.6. Changes in the Protein Secondary Structures
3.7. Principal Component Analysis
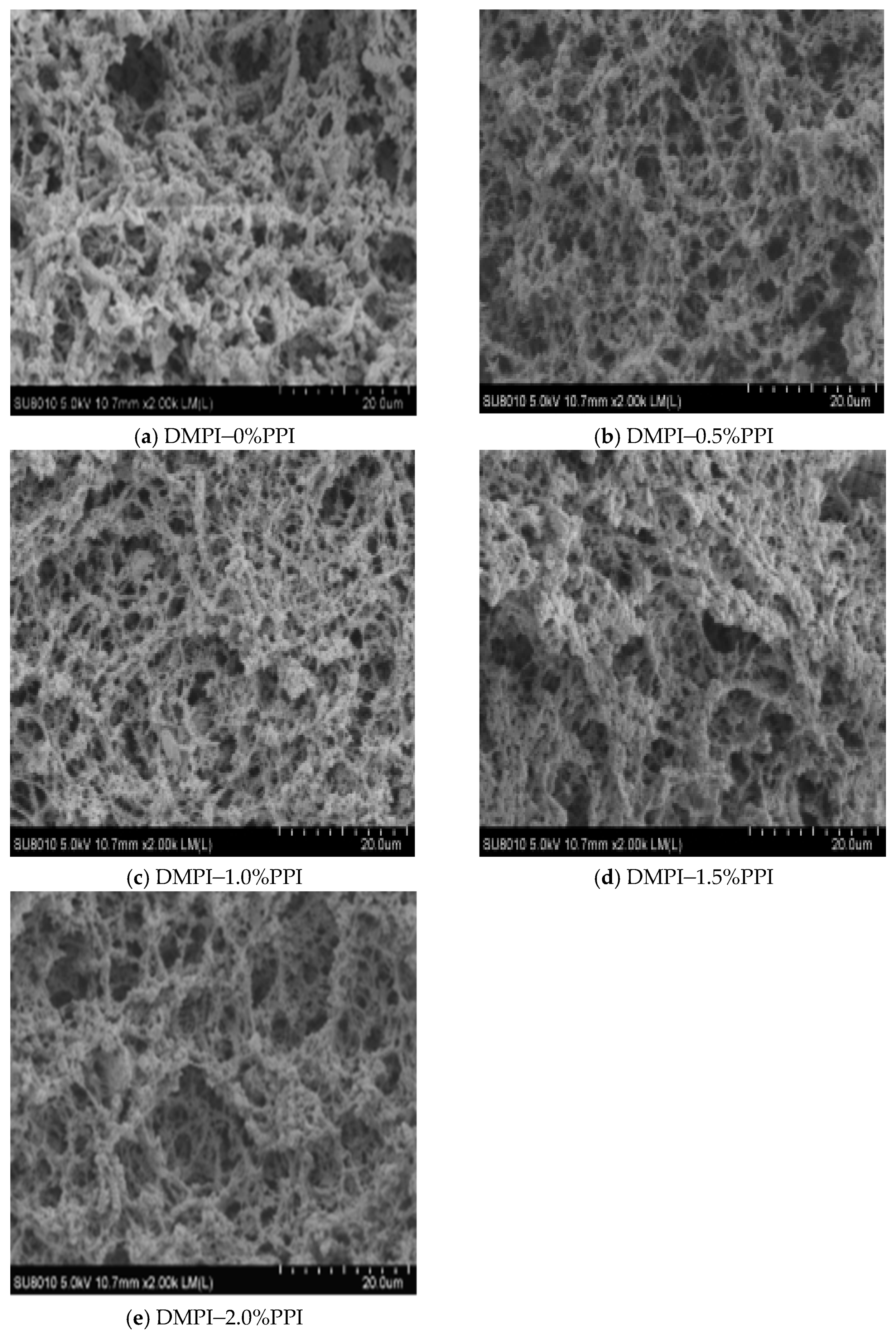
3.8. Microstructure of the Gels
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biswas, S.; Banerjee, R.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Patra, G.; Das, A.K.; Das, S.K. Technological investigation into duck meat and its products—A potential alternative to chicken. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2019, 75, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Naveena, B.M.; Jo, C.; Sakata, R.; Zhou, G.; Banerjee, R.; Nishiumi, T. Technological demands of meat processing—An Asian perspective. Meat Sci. 2017, 132, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAfee, A.J.; McSorley, E.M.; Cuskelly, G.J.; Moss, B.W.; Wallace, J.M.W.; Bonham, M.P.; Fearon, A.M. Red meat consumption: An overview of the risks and benefits. Meat Sci. 2010, 84, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, G.E.D.A.; Silva-Queiroz-Monici, K.; Reis, S.M.P.M.; Oliveira, A.C.D. Chemical composition, dietary fibre and resistant starch contents of raw and cooked pea, common bean, chickpea and lentil legumes. Food Chem. 2004, 94, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu-Ansah, Y.J.; McCurdy, S.M. Pea proteins: A review of chemistry, technology of production, and utilization. Food Rev. Int. 1991, 7, 103–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shand, P.J.; Ya, H.; Pietrasik, Z.; Wanasundara, P.K.J.P.D.P. Physicochemical and textural properties of heat-induced pea protein isolate gels. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, A.C.Y.; Can Karaca, A.; Tyler, R.T.; Nickerson, M.T. Pea protein isolates: Structure, extraction, and functionality. Food Rev. Int. 2018, 34, 126–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudra, M.N.; Chowdhury, L.M. Methionine content of cereals and legumes. Nature 1950, 166, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravelle, A.J.; Marangoni, A.G.; Barbut, S. Insight into the mechanism of myofibrillar protein gel stability: Influencing texture and microstructure using a model hydrophilic filler. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 60, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świątecka, D.; Narbad, A.; Ridgway, K.P.; Kostyra, H. The study on the impact of glycated pea proteins on human intestinal bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 145, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccord, A.; Smyth, A.B.; O’neill, E.E. Heat-induced gelation properties of salt-soluble muscle proteins as affected by non-meat proteins. J. Food Sci. 1998, 63, 580–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wu, Z.; Xu, X.; Liu, P. Effect of peanut protein isolate on functional properties of chicken salt-soluble proteins from breast and thigh muscles during heat-induced gelation. Meat Sci. 2012, 91, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.; Xiong, Y.L.; Alderton, A.L. Concentration effects of hydroxyl radical oxidizing systems on biochemical properties of porcine muscle myofibrillar protein. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.Y.; Watanabe, K.; Maruyama, Y. Relation between the ATP-breakdown in ice-stored Alaska pollack meat and the quality of frozen surimi. Bull. Tokai Reg. Fish. Res. Lab. 1973, 75, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kocher, P.N.; Foegeding, E.A. Microcentrifuge-based method for measuring water-holding of protein gels. J. Food Sci. 1993, 58, 1040–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhou, G. Insight into the mechanism of physicochemical influence by three polysaccharides on myofibrillar protein gelation. Carbohyd. Polym. 2020, 229, 115449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alix, A.J.P.; Pedanou, G.; Berjot, M. Fast determination of the quantitative secondary structure of proteins by using some parameters of the Raman Amide I band. J. Mol. Struct. 1988, 174, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhu, B.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, Y. Interfacial structural role of pH-shifting processed pea protein in the oxidative stability of oil/water emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borderías, A.J.; Tovar, C.A.; Domínguez-Timón, F.; Díaz, M.T.; Moreno, H.M. Characterization of healthier mixed surimi gels obtained through partial substitution of myofibrillar proteins by pea protein isolates. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 107, 105976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, P.; Miao, S.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, B. Curdlan enhances the structure of myosin gel model. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 2123–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Dong, X.; Li, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Du, M.; Zhang, J.; Bai, Y. Effect of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) protein isolate on the heat-induced gelation properties of pork myofibrillar protein. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 2108–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Hao, X.; Xiong, G.; Ge, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, G.; Yue, X. Interaction between carrageenan/soy protein isolates and salt-soluble meat protein. Food Bioprod. Process. 2016, 100, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Li, Q.; Zha, X.; Pan, L.; Luo, J. Effects of calcium or sodium ions on the properties of whey protein isolate-lotus root amylopectin composite gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, F.; Li, P.; Chen, C. Effect of resistant corn starch on the thermal gelling properties of chicken breast myosin. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 96, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Dang, Y.; Cao, J.; Pan, D.; Guo, Y.; He, J. Water-insoluble dietary fibers from oats enhance gel properties of duck myofibrillar proteins. Food Chem. 2021, 344, 128690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Guo, H.; Li, Y.; Song, J.; Ren, F. The effects of calcium chloride on the gel properties of porcine myosin–κ-carrageenan mixtures. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Damodaran, S. Thermal gelation of globular proteins: Influence of protein conformation on gel strength. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1991, 39, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Zheng, B.; Guo, Z. Effects of high pressure processing on gelation properties and molecular forces of myosin containing deacetylated konjac glucomannan. Food Chem. 2019, 291, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.K.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Xu, J.L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.H. Physicochemical properties of Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide and its interactions with myofibrillar protein. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2017, 11, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Xiong, Y.L. Extreme pH treatments enhance the structure-reinforcement role of soy protein isolate and its emulsions in pork myofibrillar protein gels in the presence of microbial transglutaminase. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Li, Y.; Han, J.; Liu, Q.; Kong, B. Gelation and rheological properties of myofibrillar proteins influenced by the addition of soybean protein isolates subjected to an acidic pH treatment combined with a mild heating. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 70, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Xu, P.; Zhou, C.; Wang, Y. Effects of L-Arginine on water holding capacity and texture of heat-induced gel of salt-soluble proteins from breast muscle. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trout, G.R. Techniques for measuring water-binding capacity in muscle foods—A review of methodology. Meat Sci. 1988, 23, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Wang, P.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. Low-field NMR study of heat-induced gelation of pork myofibrillar proteins and its relationship with microstructural characteristics. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, J.; Koehler, P. Study of the thermal denaturation of selected proteins of whey and egg by low resolution NMR. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 38, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Ma, J.; Yang, K.; Sun, W. Effects of radio frequency heating on water distribution and structural properties of grass carp myofibrillar protein gel. Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, S.; Wang, Q. Rheological properties of pea protein isolate-amylose/amylopectin mixtures and the application in the high-moisture extruded meat substitutes. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 117, 106732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.D.; Arntfield, S.D. Gelation properties of myofibrillar/pea protein mixtures induced by transglutaminase crosslinking. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 27, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Peng, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Li, M.; Xu, H. Gel properties and formation mechanism of soy protein isolate gels improved by wheat bran cellulose. Food Chem. 2020, 324, 126876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, J.; Tang, X.; Zhou, G. Rheological and Microstructural Properties of Porcine Myofibrillar Protein–Lipid Emulsion Composite Gels. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouraoui, M.; Nakai, S.; Li-Chan, E. In situ investigation of protein structure in Pacific whiting surimi and gels using Raman spectroscopy. Food Res. Int. 1997, 30, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.L.; Han, M.Y.; Fei, Y.; Zhou, G.H. Raman spectroscopic study of heat-induced gelation of pork myofibrillar proteins and its relationship with textural characteristic. Meat Sci. 2011, 87, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, X.; Wang, L.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, G. Insight into the mechanism of myofibrillar protein gel influenced by konjac glucomannan: Moisture stability and phase separation behavior. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 127941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, G.R.; Foegeding, E.A. The Gelation of Proteins. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Kinsella, J.E., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 203–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, X.; Guan, H.; Zhao, X.; Diao, X.; Kong, B. Physicochemical and structural properties of composite gels prepared with myofibrillar protein and lard diacylglycerols. Meat Sci. 2016, 121, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, P.; Yang, Z.; Du, F.; Li, Z.; Wu, C.; Fang, A.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. Molecular dynamics simulation exploration of the interaction between curcumin and myosin combined with the results of spectroscopy techniques. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Gu, Y.; Yu, X.; Gao, F.; Wang, R. Relationship between Molecular Structure and Heat-Induced Gel Properties of Duck Myofibrillar Proteins Affected by the Addition of Pea Protein Isolate. Foods 2022, 11, 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11071040
Zhu X, Zhang J, Liu S, Gu Y, Yu X, Gao F, Wang R. Relationship between Molecular Structure and Heat-Induced Gel Properties of Duck Myofibrillar Proteins Affected by the Addition of Pea Protein Isolate. Foods. 2022; 11(7):1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11071040
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Xueshen, Jiaxin Zhang, Shaohua Liu, Ying Gu, Xiaobo Yu, Feng Gao, and Renlei Wang. 2022. "Relationship between Molecular Structure and Heat-Induced Gel Properties of Duck Myofibrillar Proteins Affected by the Addition of Pea Protein Isolate" Foods 11, no. 7: 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11071040
APA StyleZhu, X., Zhang, J., Liu, S., Gu, Y., Yu, X., Gao, F., & Wang, R. (2022). Relationship between Molecular Structure and Heat-Induced Gel Properties of Duck Myofibrillar Proteins Affected by the Addition of Pea Protein Isolate. Foods, 11(7), 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11071040





