Preparation and Characterization of Food-Grade Pickering Emulsions Stabilized with Chitosan-Phytic Acid-Cyclodextrin Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of CS-PA-CD Nanoparticles
2.2.1. Preparation of Phytic Acid Modified β-Cyclodextrin
2.2.2. Preparation of CS-PA-CD Nanoparticles
2.3. Characterization of CS-PA-CD Nanoparticles
2.3.1. Physical Properties of CS-PA-CD Nanoparticles
2.3.2. Particle Size of CS-PA-CD Nanoparticles
2.4. Preparation of Pickering Emulsions
2.5. Droplet Size and Zeta Potential Measurements of Pickering Emulsions
2.6. Microscopy Analysis of Pickering Emulsions
2.7. Rheological Measurements of Pickering Emulsions
2.8. Assessment of Emulsions Stability to Different Influencing Factors
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of CS-PA-CD Nanoparticles
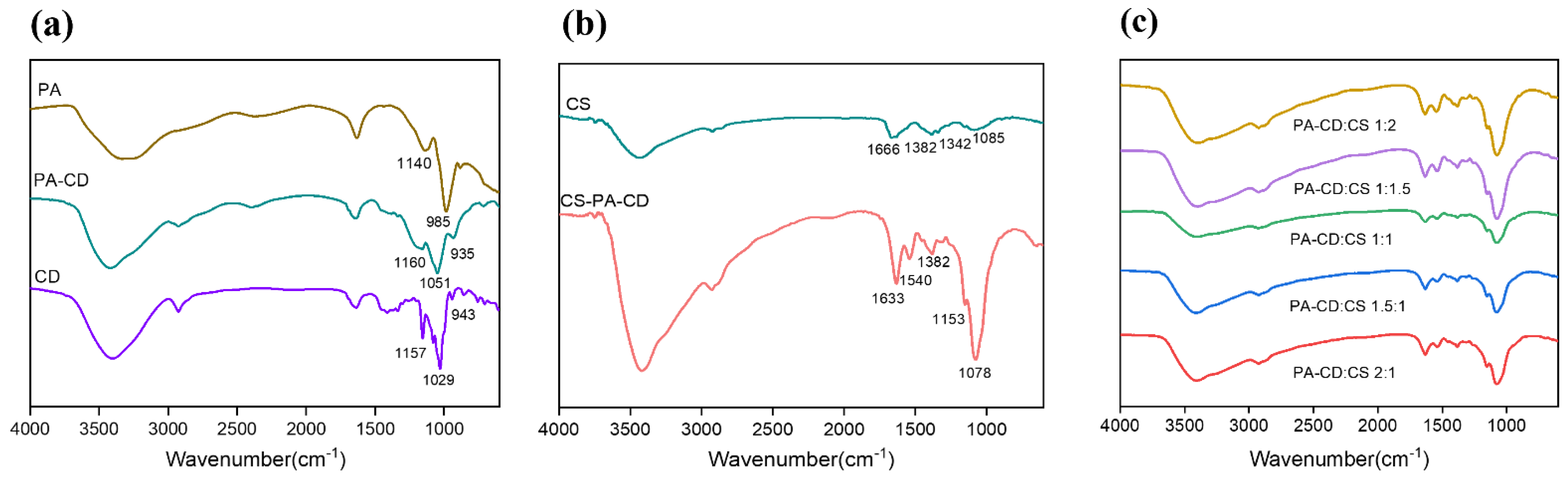
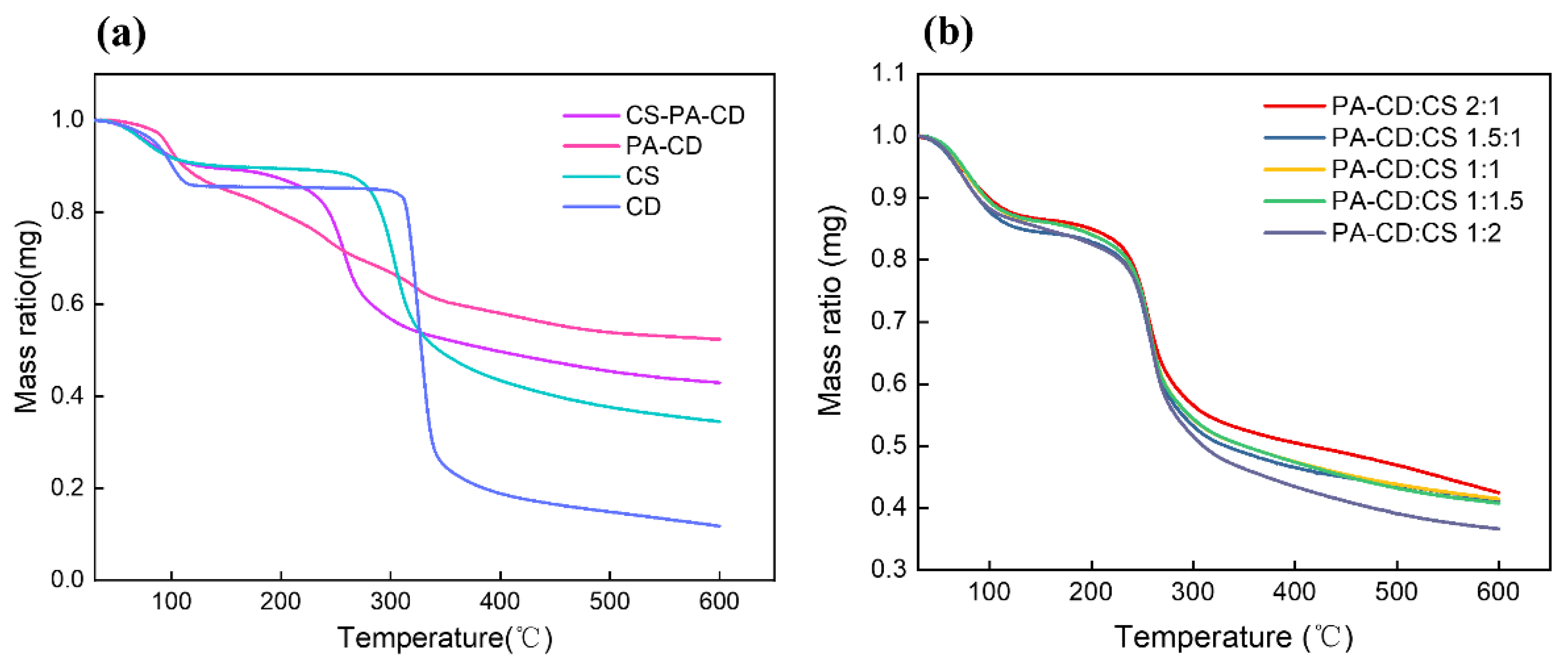
3.1.1. Physical Properties of CS-PA-CD Nanoparticles
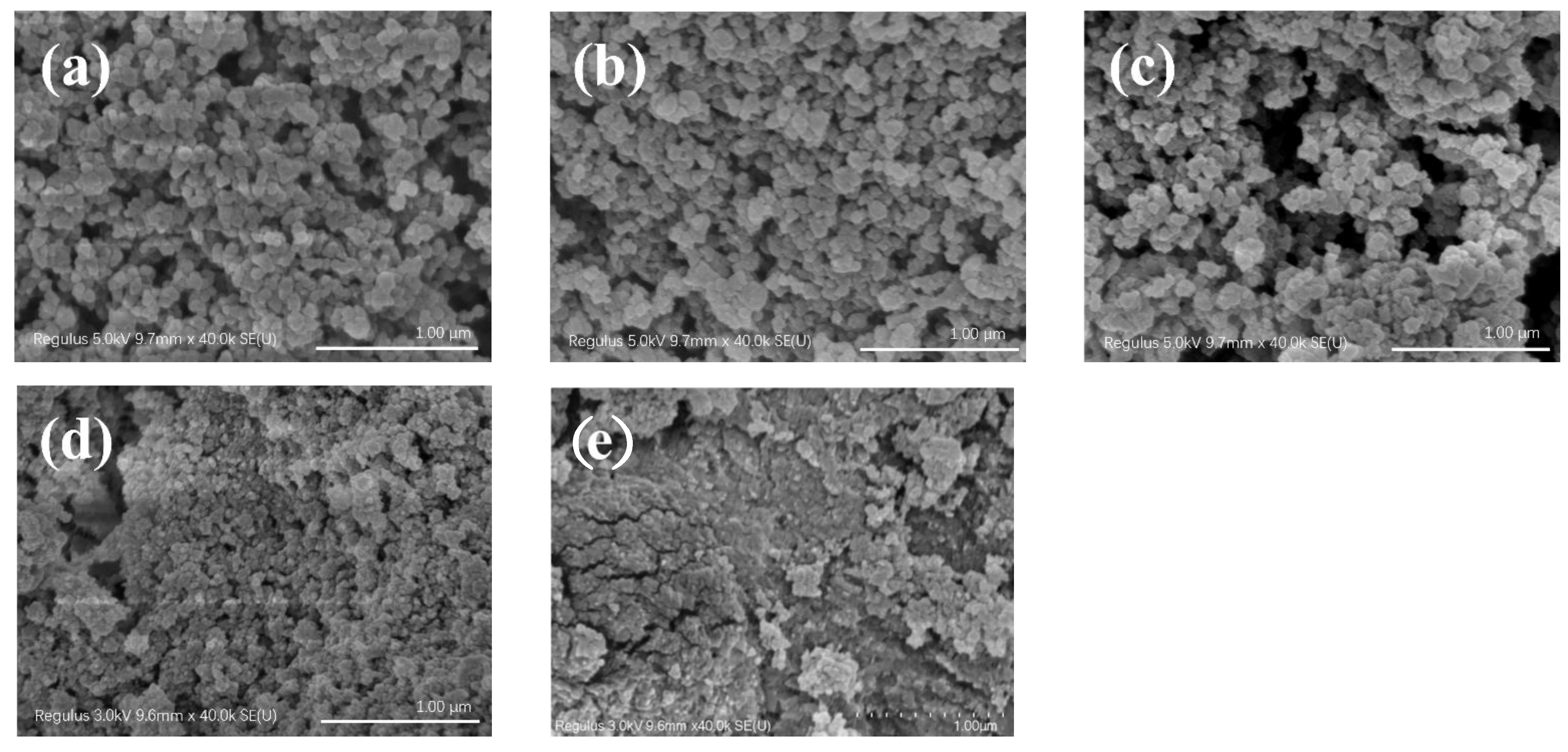
3.1.2. Average Size and Morphology of CS-PA-CD Nanoparticles
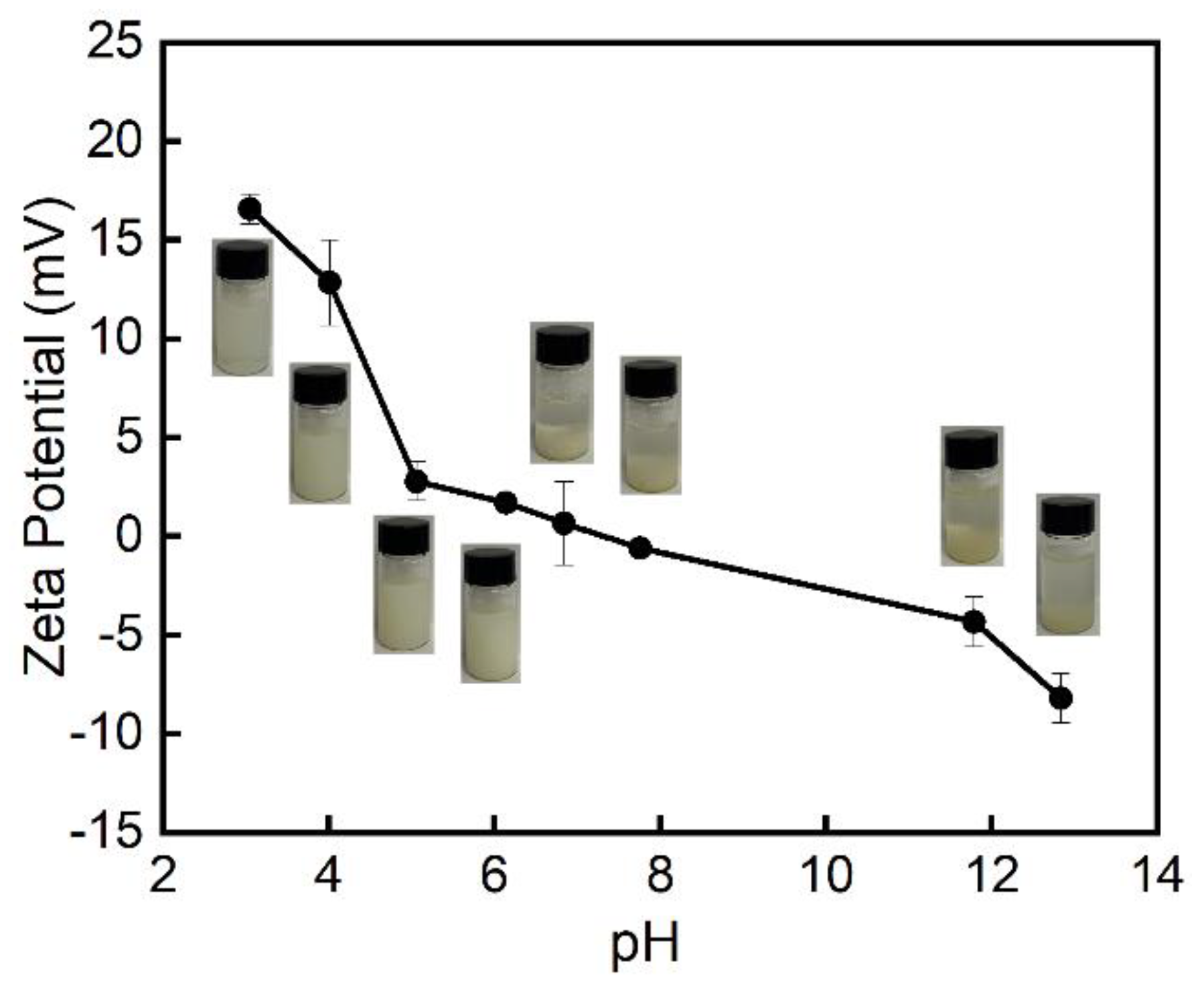
3.1.3. Zeta Potential on Different pH Values
3.2. Characterization of Pickering Emulsions Stabilized with CS-PA-CD Nanoparticles
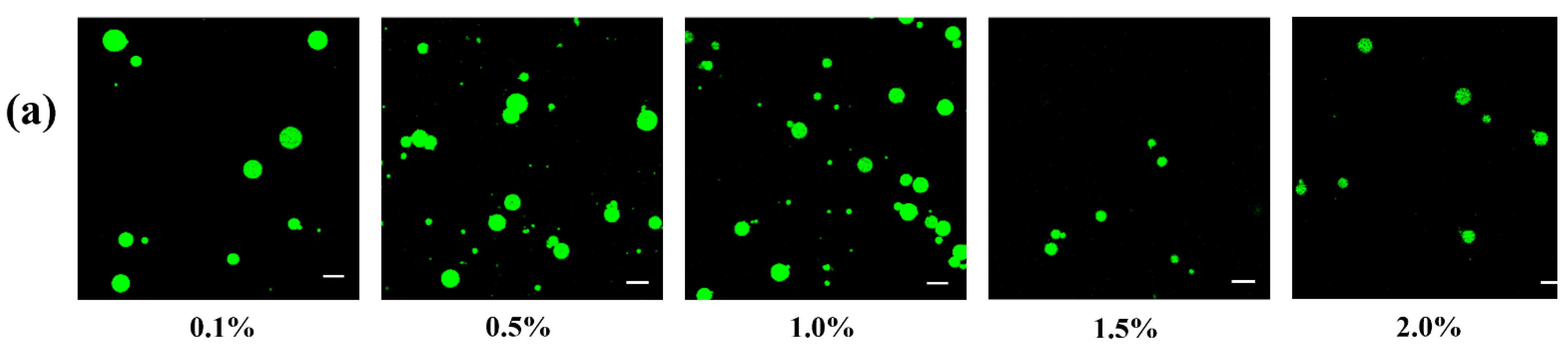
3.2.1. Appearance and Droplet Size of Pickering Emulsions
3.2.2. Rheological Properties of Pickering Emulsions
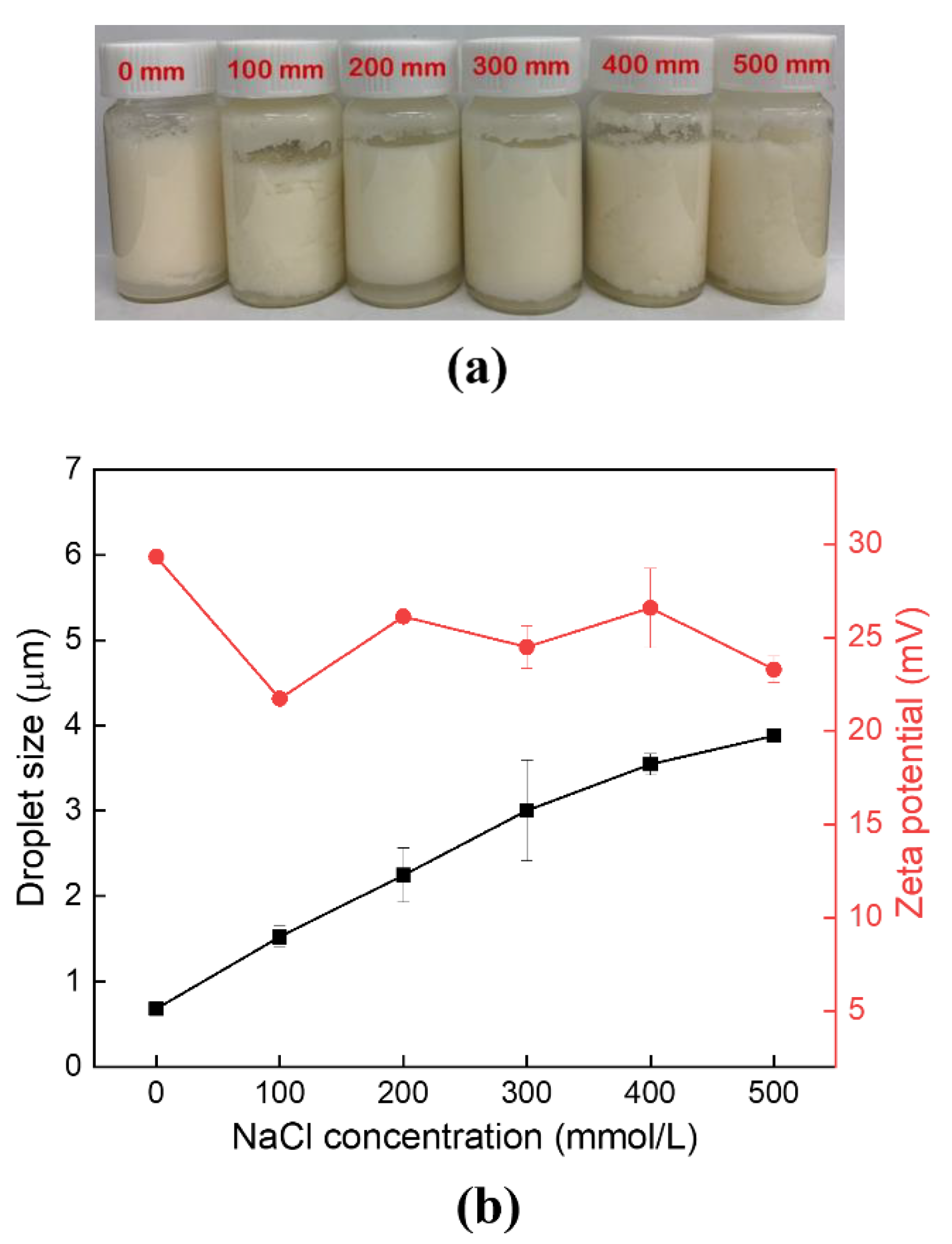
3.3. Effects of Ionic Strength on Pickering Emulsions Stability
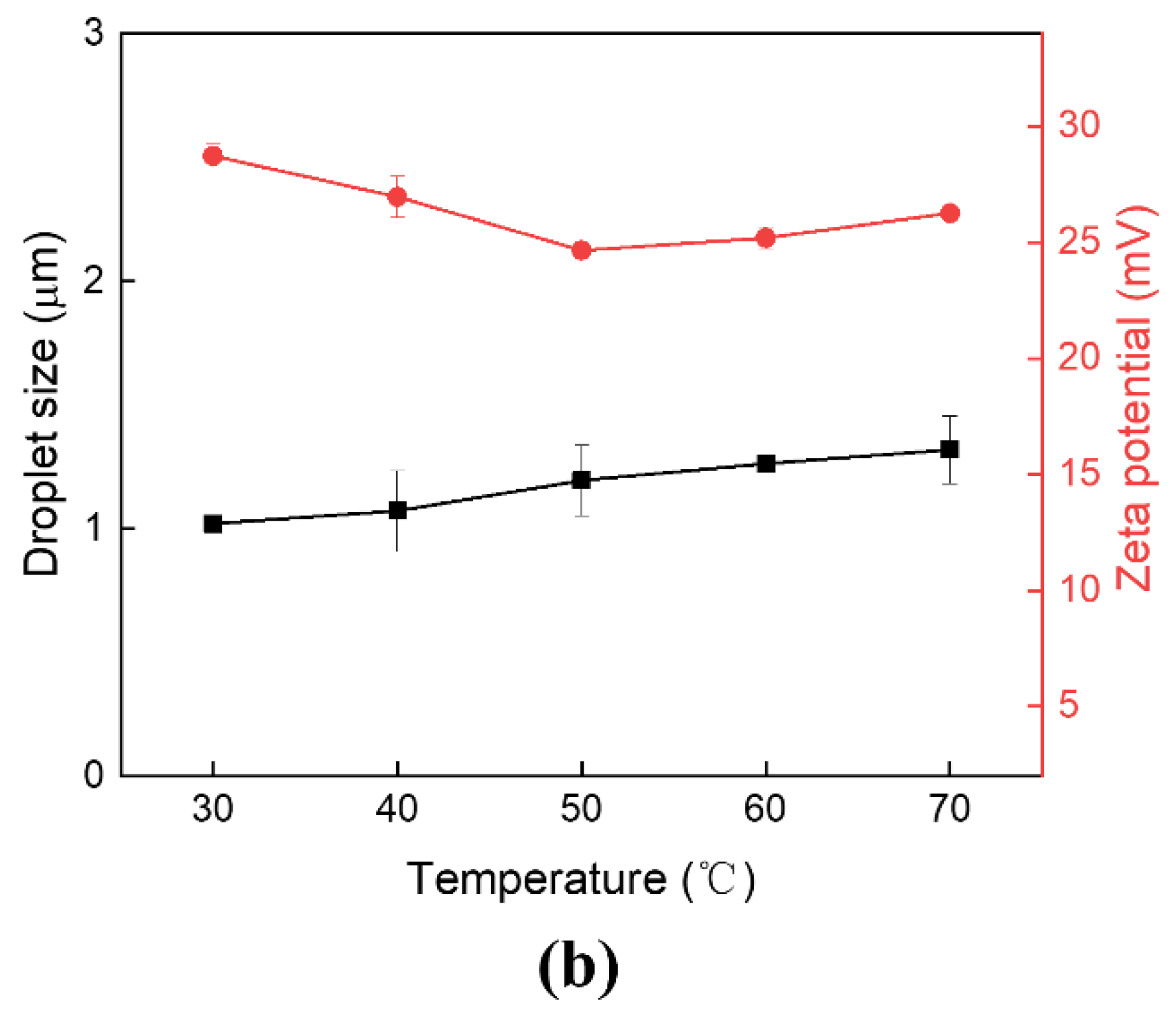
3.4. Effects of Temperature on Pickering Emulsions Stability
3.5. Effects of pH Value on Pickering Emulsions Stability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharkawy, A.; Barreiro, M.F.; Rodrigues, A.E. Chitosan-based Pickering emulsions and their applications: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 250, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashki, S.; Asgarpour, K.; Tarrahimofrad, H.; Hashemipour, M.; Ebrahimi, M.S.; Fathizadeh, H.; Khorshidi, A.; Khan, H.; Marzhoseyni, Z.; Salavati-Niasari, M.; et al. Chitosan-based nanoparticles against bacterial infections. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakshi, P.S.; Selvakumar, D.; Kadirvelu, K.; Kumar, N.S. Chitosan as an environment friendly biomaterial—a review on recent modifications and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Farias, B.S.; Sant’Anna Cadaval Junior, T.R.; de Almeida Pinto, L.A. Chitosan-functionalized nanofibers: A comprehensive review on challenge’s and prospects for food applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, Y.; Bolzinger, M.-A. Emulsions stabilized with solid nanoparticles: Pickering emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 439, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Biopolymer-based particles as stabilizing agents for emulsions and foams. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 68, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenxi, W.; McClements, D.J.; Aiquan, J.; Jinpeng, W.; Zhengyu, J.; Chao, Q. Resistant starch and its nanoparticles: Recent advances in their green synthesis and application as functional food ingredients and bioactive delivery systems. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 119, 90–100. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.Y.; Zou, S.W.; Wei, Z.J.; Tong, Z. Simple, Reversible Emulsion System Switched by pH on the Basis of Chitosan without Any Hydrophobic Modification. Langmuir 2012, 28, 11017–11024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwangi, W.W.; Ho, K.W.; Tey, B.T.; Chan, E.S. Effects of environmental factors on the physical stability of pickering-emulsions stabilized by chitosan particles. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 60, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, B.R.; Li, Y.; Jin, W.P.; An, Y.P.; He, L.; Li, Z.S.; Xu, W.; Li, B. Preparation and optimization of Pickering emulsion stabilized by chitosan-tripolyphosphate nanoparticles for curcumin encapsulation. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atarian, M.; Rajaei, A.; Tabatabaei, M.; Mohsenifar, A.; Bodaghi, H. Formulation of Pickering sunflower oil-in-water emulsion stabilized by chitosan-stearic acid nanogel and studying its oxidative stability. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 210, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, R.S.; Rajaei, A. Potential Pickering emulsion stabilized with chitosan-stearic acid nanogels incorporating clove essential oil to produce fish-oil-enriched mayonnaise. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 241, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; McClements, D.J.; Zhu, Y.; Zou, L.; Zhou, W.; Liu, W. Fabrication of OSA Starch/Chitosan Polysaccharide-Based High Internal Phase Emulsion via Altering Interfacial Behaviors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 10937–10946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Zi-Ling, W.; Jun-You, Z.; Shou-Wei, Y.; Chuan-He, T.; Lei-Yan, W.; Xiao-Quan, Y. Development of antioxidant Pickering high internal phase emulsions (HIPEs) stabilized by protein/polysaccharide hybrid particles as potential alternative for PHOs. Food Chem. 2017, 231, 122–130. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.L.; Hao, H.; Zhang, C.G.; Yang, R.C.; Sun, M.Y.; Wong, C.P.; Xu, Y. Bioadhesive hydrocaffeic acid modified chitosan colloidal particles using as particulate emulsifiers. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2019, 40, 1559–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.Y.; Thoo, Y.Y.; Young, D.J.; Siow, L.F. Stability and recovery of cyclodextrin encapsulated catechin in various food matrices. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, W.F.; Rogach, A.L.; Wong, W.T. Chemistry and engineering of cyclodextrins for molecular imaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 6379–6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kfoury, M.; Auezova, L.; Greige-Gerges, H.; Fourmentin, S. Promising applications of cyclodextrins in food: Improvement of essential oils retention, controlled release and antiradical activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 131, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.Y.; Xiao, Z.B.; Zhou, R.J.; Zhu, Y.L. Study of production and pyrolysis characteristics of sweet orange flavor-beta-cyclodextrin inclusion complex. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 105, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.; Cheng, C.Y.; Cui, B. Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by Cyclodextrin Nanoparticles: A Review. Starch Stärke 2021, 73, 2100077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.W.; Yen, M.W.; Wang, A.J.E.; Chu, I.M. Effect of oil structure on cyclodextrin-based Pickering emulsions for bupivacaine topical application. Colloid Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 161, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davarpanah, L.; Vahabzadeh, F. Formation of oil-in-water (O/W) pickering emulsions via complexation between beta-cyclodextrin and selected organic solvents. Starch Starke 2012, 64, 898–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Chen, W.J.; Chen, W.X.; Yun, Y.H.; Zhong, Q.P.; Fu, X.; Chen, H.M.; Liu, G. Preparation and Characterization of a Modified-beta-Cyclodextrin/beta-Carotene Inclusion Complex and Its Application in Pickering Emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 12875–12884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, M.; Hashizaki, K.; Taguchi, H.; Saito, Y. Emulsifying Ability of -Cyclodextrins for Common Oils. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2010, 31, 1648–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.K.; Luo, Z.G.; Lu, X.X.; Peng, X.C. Modulation of Cyclodextrin Particle Amphiphilic Properties to Stabilize Pickering Emulsion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Wang, J.P.; Qin, Y.; Fan, H.R.; Xu, X.M.; Jin, Z.Y. Green Synthesis of Cyclodextrin-Based Metal Organic Frameworks through the Seed-Mediated Method for the Encapsulation of Hydrophobic Molecules. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 4244–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Qin, Y.; Xu, X.; Jin, Z. Novel Approach with Controlled Nucleation and Growth for Green Synthesis of Size-Controlled Cyclodextrin-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks Based on Short-Chain Starch Nanoparticles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9785–9793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jingou, J.; Shilei, H.; Weiqi, L.; Danjun, W.; Tengfei, W.; Yi, X. Preparation, characterization of hydrophilic and hydrophobic drug in combine loaded chitosan/cyclodextrin nanoparticles and in vitro release study. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 83, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Antoniou, J.; Li, Y.; Majeed, H.; Liang, R.; Ma, Y.; Ma, J.G.; Zhong, F. Chitosan/sulfobutylether-beta-cyclodextrin nanoparticles as a potential approach for tea polyphenol encapsulation. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 57, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Mo, G.J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Huang, C. Fabrication and characterization of TPP-beta-cyclodextrin/chitosan supramolecular nanoparticles for delivery dual bioactive compounds. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 343, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Z.C.; Qian, J.; Han, J.H.; Deng, X.Y.; Shen, J.L.; Li, G.W.; Xie, Y. Comparison of three water-soluble polyphosphate tripolyphosphate, phytic acid, and sodium hexametaphosphate as crosslinking agents in chitosan nanoparticle formulation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 230, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oatway, L.; Vasanthan, T.; Helm, J.H. Phytic acid. Food Rev. Int. 2001, 17, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Qiu, C.; McClements, D.J.; Qin, Y.; Fan, L.P.; Xu, X.M.; Wang, J.P.; Jin, Z.Y. Simple Strategy Preparing Cyclodextrin Carboxylate as a Highly Effective Carrier for Bioactive Compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 11006–11014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martel, B.; Ruffin, D.; Weltrowski, M.; Lekchiri, Y.; Morcellet, M. Water-soluble polvmers and gels from the polycondensation between cyclodextrins and poly(carboxylic acid)s: A study of the preparation parameters. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 97, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qiu, C.; Zhan, C.; McClements, D.J.; Qin, Y.; Jiao, A.; Jin, Z.; Wang, J. Green Preparation of Robust Hydrophobic beta-Cyclodextrin/Chitosan Sponges for Efficient Removal of Oil from Water. Langmuir 2021, 37, 14380–14389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Xie, Q.T.; Zhu, J.; Pan, Y.; Meng, R.; Zhang, B.; Chen, H.Q.; Jin, Z.Y. Chitosan hydrochloride/carboxymethyl starch complex nanogels as novel Pickering stabilizers: Physical stability and rheological properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.F.; Chen, C.J.; Shi, P.P.; Yue, L.Z. Determination of melamine in milk based on beta-cyclodextrin modified carbon nanoparticles via host-guest recognition. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, E.F.; de Barros-Alexandrino, T.T.; Assis, O.B.G.; Cruz, A.; Quiles, A.; Hernando, I.; Nicoletti, V.R. Chitosan and crosslinked chitosan nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and their role as Pickering emulsifiers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 250, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.Y.; Zhong, C.; Hu, H.B.; Jin, Y.; Chen, Y.Z.; Lou, K.Y.; Gao, F. Cyclodextrin/chitosan nanoparticles for oral ovalbumin delivery: Preparation, characterization and intestinal mucosal immunity in mice. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 14, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, Z. Thermal and conductivity studies of chitosan acetate-based polymer electrolytes. Ionics 2005, 11, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thitisomboon, W.; Opaprakasit, P.; Jaikaew, N.; Boonyarattanakalin, S. Characterizations of modified cassava starch with long chain fatty acid chlorides obtained from esterification under low reaction temperature and its PLA blending. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A Pure Appl. Chem. 2018, 55, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Gao, H.Y.; Zhang, J.; Qin, Y.; Wang, D.Y. Phytic Acid Intercalated Graphene Oxide for Anticorrosive Reinforcement of Waterborne Epoxy Resin Coating. Polymers 2019, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiokias, S.; Gordon, M.H.; Oreopoulou, V. Effects of composition and processing variables on the oxidative stability of protein-based and oil-in-water food emulsions. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kibici, D.; Kahveci, D. Effect of Emulsifier Type, Maltodextrin, and beta-Cyclodextrin on Physical and Oxidative Stability of Oil-In-Water Emulsions. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Su, Z.W.; Meng, X.H.; Zhang, X.Y.; Kennedy, J.F.; Liu, B.J. Fabrication and characterization of Pickering emulsion stabilized by soy protein isolate-chitosan nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Qiu, C.; Jin, Z.; Qin, Y.; Zhan, C.; Xu, X.; Wang, J. Pickering emulsions with enhanced storage stabilities by using hybrid beta-cyclodextrin/short linear glucan nanoparticles as stabilizers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Wang, J.; Qin, Y.; Xu, X.; Jin, Z. Characterization and Mechanisms of Novel Emulsions and Nanoemulsion Gels Stabilized by Edible Cyclodextrin-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks and Glycyrrhizic Acid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shengju, G.; Liu, X.; Man, L.; Jing, L.; Jie, Y.; Ranran, C.; Caifeng, L.; Qingjie, S. Characterizations of Pickering emulsions stabilized by starch nanoparticles: Influence of starch variety and particle size. Food Chem. 2017, 234, 339–347. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, D.; Xinyu, Z.; Yang, W.; Cuixia, S.; Like, M.; McClements, D.J.; Yanxiang, G. Composite zein—propylene glycol alginate particles prepared using solvent evaporation: Characterization and application as Pickering emulsion stabilizers. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 85, 281–290. [Google Scholar]







| CS Concentration (m/v) | Acetic Acid (v/v) | PA-CD Concentration (m/v) | PA-CD:CS Ratio | Reacting Solution:Ethanol (v:v) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0% | 2% | 1.0% | 1:1 | 1:10 |
| PA-CD:CS Mass Ratio | Particle Size (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2:1 | 434.2 ± 2.5 e | 0.220 ± 0.027 ab | +15.25 ± 3.81 c |
| 1.5:1 | 481.2 ± 3.0 d | 0.211 ± 0.011 b | +11.18 ± 1.38 d |
| 1:1 | 504.9 ± 11.6 c | 0.210 ± 0.010 b | +15.48 ± 1.25 c |
| 1:1.5 | 612.4 ± 11.1 b | 0.247 ± 0.027 a | +21.44 ± 2.00 b |
| 1:2 | 811.1 ± 7.0 a | 0.219 ± 0.005 ab | +26.81 ± 1.84 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, J.; Li, X.; Qiu, C.; McClements, D.J.; Jiao, A.; Wang, J.; Jin, Z. Preparation and Characterization of Food-Grade Pickering Emulsions Stabilized with Chitosan-Phytic Acid-Cyclodextrin Nanoparticles. Foods 2022, 11, 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11030450
Lu J, Li X, Qiu C, McClements DJ, Jiao A, Wang J, Jin Z. Preparation and Characterization of Food-Grade Pickering Emulsions Stabilized with Chitosan-Phytic Acid-Cyclodextrin Nanoparticles. Foods. 2022; 11(3):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11030450
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Jiaxin, Xiaojing Li, Chao Qiu, David Julian McClements, Aiquan Jiao, Jinpeng Wang, and Zhengyu Jin. 2022. "Preparation and Characterization of Food-Grade Pickering Emulsions Stabilized with Chitosan-Phytic Acid-Cyclodextrin Nanoparticles" Foods 11, no. 3: 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11030450
APA StyleLu, J., Li, X., Qiu, C., McClements, D. J., Jiao, A., Wang, J., & Jin, Z. (2022). Preparation and Characterization of Food-Grade Pickering Emulsions Stabilized with Chitosan-Phytic Acid-Cyclodextrin Nanoparticles. Foods, 11(3), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11030450








