Effects of Fertilizer on the Quality and Traceability of Tibet highland Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.): A Diagnosis Using Nutrients and Mineral Elements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Sampling Information
2.2. Preparation of Samples
2.3. Determination of Nutrients
2.3.1. Starch Content
2.3.2. Crude Protein Content
2.3.3. Crude Fiber Content
2.3.4. β-Glucan Contents
2.3.5. Total Flavonoid Contents
2.4. Element Analysis
2.4.1. Phosphorus Content
2.4.2. Contents of Other Mineral Elements
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Differences in the Nutrient and Mineral Element Contents between Unfertilized and Fertilized Highland Barley Samples
3.2. Differences in Nutrient and Mineral Element Contents in Highland Barley Samples from Different Regions
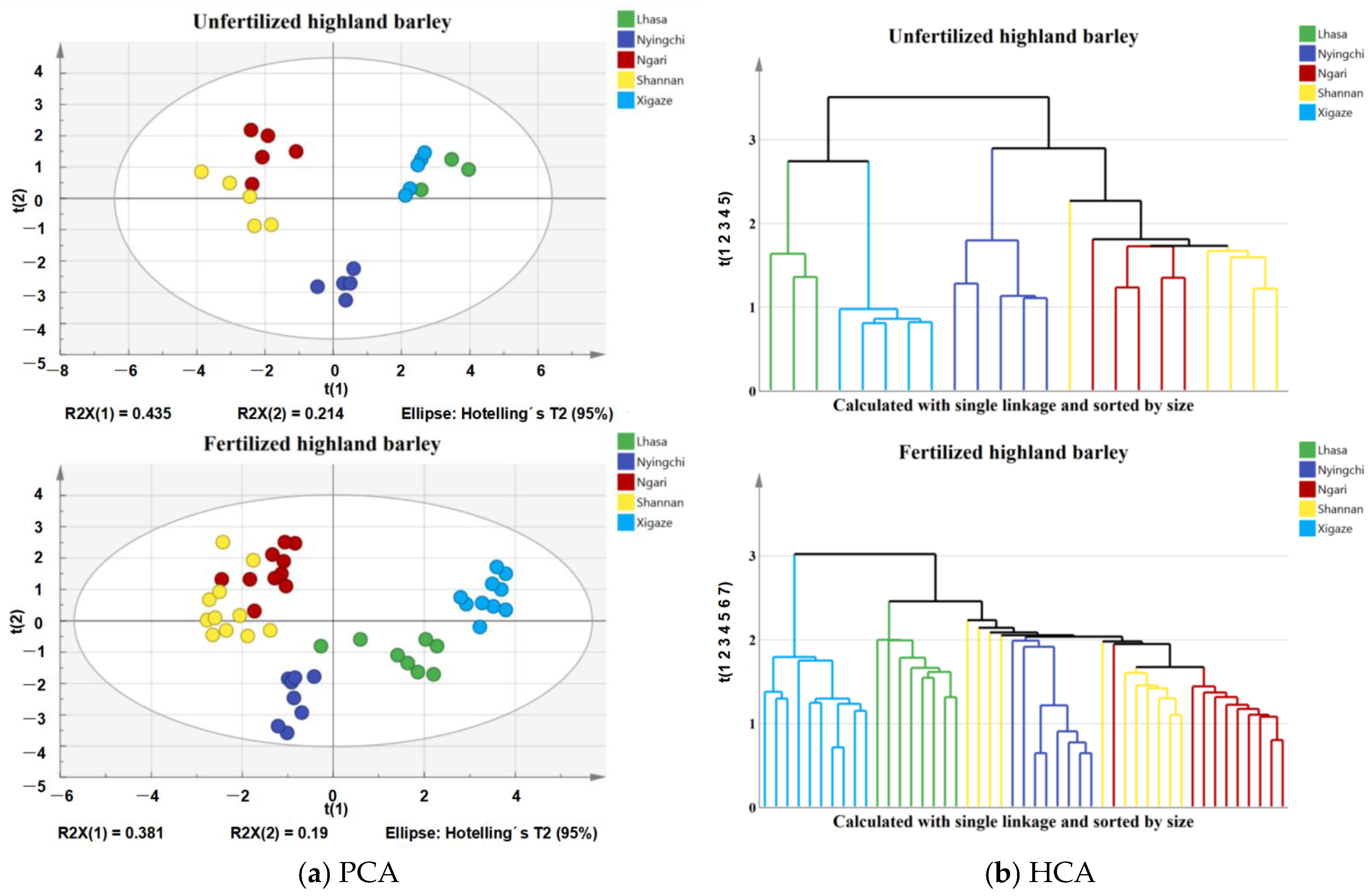
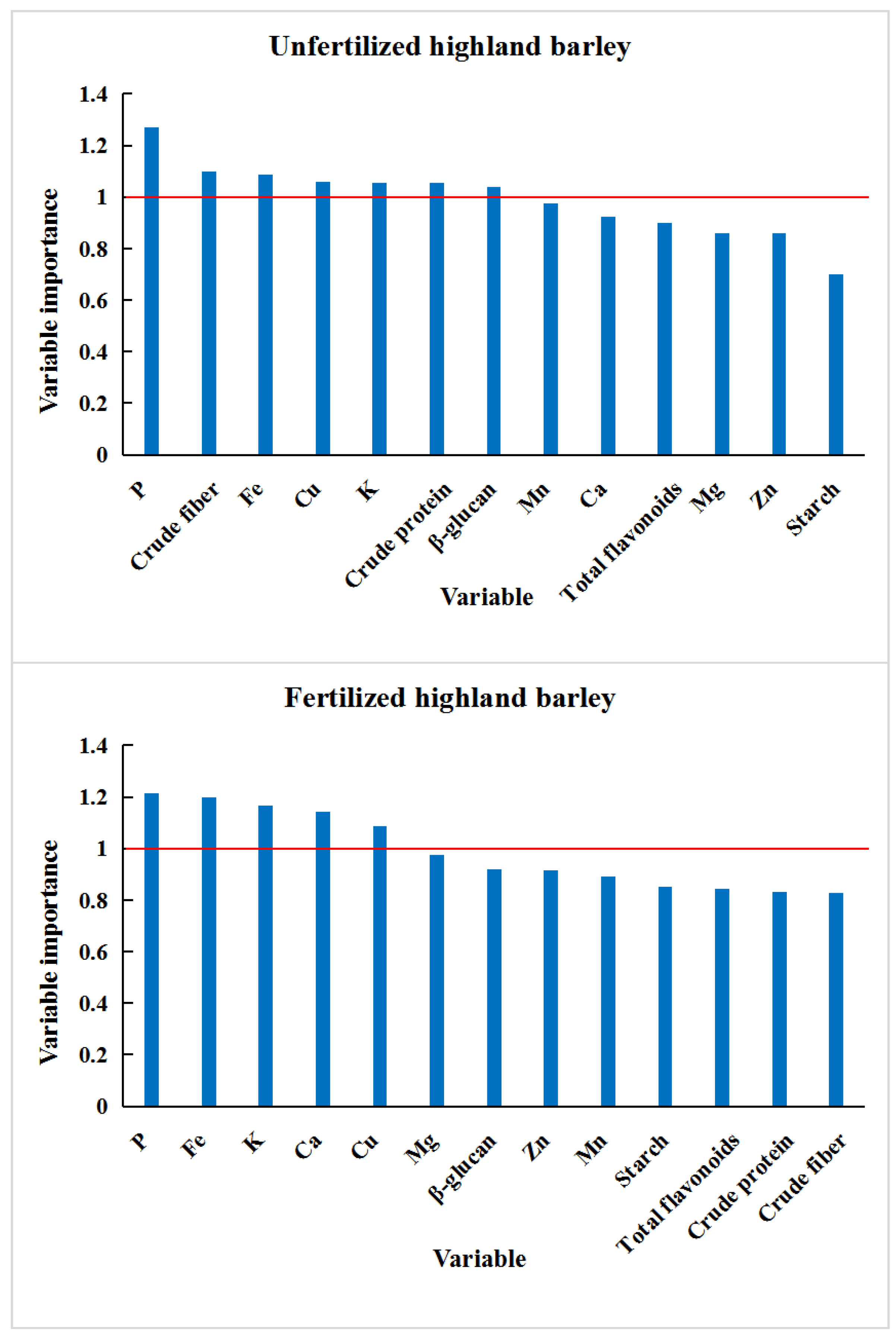
3.3. Chemometric Analysis of Highland Barley Samples from Different Regions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhong, Z.; Shen, Z.; Fu, G. Response of soil respiration to experimental warming in a highland barley of the Tibet. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Shen, Y.B.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, L.L.; Wang, L.; Qian, H.F.; Qi, X.G. In vitro and in vivo antioxidant activity of polyphenols extracted from black highland barley. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Gao, J.; Du, Y.; Chang, M.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y. Research progress on food processing of highland barley. Food Res. Dev. 2021, 42, 201–210. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Tan, B.; Liu, M.; Tian, X.; Liu, X. Research Progress and Prospect of Bioactive Components in Whole Grain. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 12, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Bonoli, M.; Verardo, V.; Marconi, E.; Caboni, M.F. Phenols in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) flour: Comparative spectrophotometric study among extraction methods of free and bound phenolic compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 5195–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohyama, N.; Ono, H.; Yanagisawa, T. Changes in anthocyanins in the grains of purple waxy hull-less barley during seed maturation and after harvest. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 5770–5774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebenhandl, S.; Grausgruber, H.; Pellegrini, N.; Del Rio, D.; Fogliano, V.; Pernice, R.; Berghofer, E. Phytochemical profile of main antioxidants in different fractions of purple and blue wheat, and black barley. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8541–8547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.-X.; Jin, C.; Wu, L.-J.; Wu, X.-Q.; Zhang, Y. Tibetan Hull-less Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) as a Potential Source of Antioxidants. Cereal Chem. 2012, 89, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-J.; Hyun, J.-N.; Kim, J.-A.; Park, J.-C.; Kim, M.-Y.; Kim, J.-G.; Lee, S.-J.; Chun, S.-C.; Chung, I.-M. Relationship between phenolic compounds, anthocyanins content and antioxidant activity in colored barley germplasm. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 4802–4809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blotevogel, S.; Schreck, E.; Laplanche, C.; Besson, P.; Saurin, N.; Audry, S.; Viers, J.; Oliva, P. Soil chemistry and meteorological conditions influence the elemental profiles of West European wines. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 125033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Fang, Y.; Shen, F.; Mao, B.; Zou, Y.; Li, P.; Pei, F.; Hu, Q. Multiangle discrimination of geographical origin of rice based on analysis of mineral elements and characteristic volatile components. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 2088–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalvez, A.; Armenta, S.; de la Guardia, M. Geographical traceability of “Arros de Valencia” rice grain based on mineral element composition. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 1254–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, C.N.; Monteiro, L.R.; Freire, B.M.; Franco, D.F.; de Souza, R.O.; dos Reis Ferreira, C.S.; Centeno da Silva, J.J.; Batista, B.L. Mineral profile exploratory analysis for rice grains traceability. Food Chem. 2019, 300, 125145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Du, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, K. Study on Response of Sensitive Area of Main Crops to Climate Change in Tibet Area. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2019, 35, 1484–1489. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Qu, H.; Qiu, C.; Yu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, T.; Lha, C. Effect of Location and Variety on the Nutritional Quality of Tibetan Hulless Barley. J. Triticeae Crops 2017, 37, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Zhao, S.; Qie, M.; Wu, X.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, Y. Study on the origin traceability of Tibet highland barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) based on its nutrients and mineral elements. Food Chem. 2021, 346, 128928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanelli, D.; Goodwin, I.; Jones, R. Minimal nitrogen and water use in horticulture: Effects on quality and content of selected nutrients. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1833–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ballesta, M.; López-Pérez, L.; Hernández, M.; López-Berenguer, C.; Fernández-García, N.; Carvajal, M. Agricultural practices for enhanced human health. Phytochem. Rev. 2008, 7, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajid, K.; Ahmad, K.; Khan, Z.I.; Nadeem, M.; Bashir, H.; Chen, F.; Ugulu, I. Effect of Organic Manure and Mineral Fertilizers on Bioaccumulation and Translocation of Trace Metals in Maize. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 104, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Zhang, C.; Zuo, F.; Zheng, L.; Li, D.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, D. Effects of fertilizers and pesticides on the mineral elements used for the geographical origin traceability of rice. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2019, 83, 103276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Wei, Y.; Yang, X.E.; Feng, Y.; Wu, C. Effects of different nitrogen fertilizer levels on concentrations of Fe, Mn, Cu and Zn and grain quality in rice (Oryza sativa). Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2007, 21, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zheng, D.; Hao, B.; Hou, F.; Yao, L.; Shao, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Z. Effects of Nitrogen on Micronutrient Concentration and Accumulation in Grains of Wheat. Acat Agric. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2009, 18, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Z.I.; Nisar, A.; Ugulu, I.; Ahmad, K.; Wajid, K.; Bashir, H.; Dogan, Y. Determination of Cadmium Concentrations of Vegetables Grown in Soil Irrigated with Wastewater: Evaluation of Health Risk to the Public. Egypt. J. Bot. 2019, 59, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlken, S.; Kirchner, G. Environmental processes affecting plant root uptake of radioactive trace elements and variability of transfer factor data: A review. J. Environ. Radioact. 2002, 58, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, D.V.; Steponkus, P.L. Plasma Membrane Lipid Alterations Associated with Cold Acclimation of Winter Rye Seedlings (Secale cereale L. cv Puma). Plant Physiol. 1987, 83, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsen, E.T.; Orcutt, D.M. Physiology of Plants under Stress. Abiotic Factors; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Dang, B.; Yang, X.; Wu, K.; Chi, D. Evaluation of Nutritional Quality of Different Hulless Barleys. J. Triticeae Crops 2016, 36, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar]
- Lausanne, D.; Qiang, X. Research reports of situations about analysis and exploitation of specific nutrients in barley. Tibet Sci. Technol. 2001, 100, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, A.; Smith, D.L. Flavonoids in Agriculture: Chemistry and Roles in, Biotic and Abiotic Stress Responses, and Microbial Associations. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Nunes, L.; Wang, Y.J.; Williams, P.N.; Zheng, M.Z.; Zhang, Q.F.; Zhu, Y.G. Profiling the ionome of rice and its use in discriminating geographical origins at the regional scale. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A.; Pendias, H.K. Trace elements in soils and plants. In Food Chains and Human Nutrition; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1984; pp. 273–315. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Xin, S.; Bu, N.; Ma, L.; Li, X. Research Advance on Effect of Drought Stress on Mineral Elements of Plant. Biotechnol. Bull. 2013, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Q.; Liu, H.; Long, X.; Liu, Z.; Niu, D.; Gao, Y. Effects of salt stress on ionic absorption and distribution of rapeseed seedlings. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 2010, 32, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, L.; Li, Y. State-of-the-art review of the impact of climatic change on bioavailability of mineral elements in crops. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Hoegy, P.; Fangmeier, A. Effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 on grain quality of wheat. J. Cereal Sci. 2008, 48, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loladze, I. Rising atmospheric CO2 and human nutrition: Toward globally imbalanced plant stoichiometry? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2002, 17, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Chen, X.; Wu, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z. Study of Pu′er Raw Materials Grade Classification by PCA and PLS-DA. J. Tea Sci. 2015, 35, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Patras, A.; Brunton, N.P.; Downey, G.; Rawson, A.; Warriner, K.; Gernigon, G. Application of principal component and hierarchical cluster analysis to classify fruits and vegetables commonly consumed in Ireland based on in vitro antioxidant activity. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2011, 24, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Region | Fertilized or Not | Number | Altitude (m) | East Longitude | North Latitude | Yearly Rainfall (mm) | Yearly Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lhasa | Unfertilized | 3 | 3600 | 90.90 | 29.38 | 444.8 | 7.5 |
| Fertilized | 8 | ||||||
| Nyingchi | Unfertilized | 5 | 2700 | 95.56 | 30.28 | 977 | 8.5 |
| Fertilized | 8 | ||||||
| Ngari | Unfertilized | 5 | 3900 | 81.17 | 30.29 | 172.8 | 3 |
| Fertilized | 10 | ||||||
| Shannan | Unfertilized | 5 | 4000 | 91.88 | 28.97 | 293.1 | 8.2 |
| Fertilized | 11 | ||||||
| Xigaze | Unfertilized | 5 | 4006 | 89.56 | 28.94 | 304.3 | 5 |
| Fertilized | 10 |
| Index | Fertilized or Not | Lhasa | Nyingchi | Ngari | Shannan | Xigaze |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Starch (%) | Unfertilized | 49.86 ± 0.96 b | 48.59 ± 2.35 ab | 46.74 ± 1.56 a | 46.36 ± 1.79 a | 49.82 ± 0.84 b |
| Fertilized | 48.76 ± 1.65 b | 45.73 ± 1.69 a | 46.29 ± 1.65 a | 45.34 ± 1.59 a | 48.78 ± 1.01 b | |
| p-Value | 0.31 | 0.02 | 0.62 | 0.27 | 0.08 | |
| Crude protein (%) | Unfertilized | 10.58 ± 1.37 b | 9.90 ± 2.95 ab | 7.59 ± 1.61 a | 10.21 ± 0.84 ab | 8.63 ± 0.99 ab |
| Fertilized | 9.88 ± 2.80 ab | 11.55 ± 1.79 b | 8.72 ± 1.70 a | 11.01 ± 2.32 b | 9.60 ± 1.04 ab | |
| p-Value | 0.70 | 0.32 | 0.24 | 0.33 | 0.13 | |
| Crude fiber (%) | Unfertilized | 2.80 ± 0.35 a | 4.11 ± 0.22 d | 3.17 ± 0.30 b | 3.69 ± 0.12 c | 3.27 ± 0.22 b |
| Fertilized | 3.39 ± 0.51 bc | 3.58 ± 0.40 c | 2.92 ± 0.55 a | 3.54 ± 0.30 c | 3.12 ± 0.29 ab | |
| p-Value | 0.10 | 0.03 | 0.36 | 0.20 | 0.39 | |
| β-glucan (%) | Unfertilized | 5.51 ± 0.09 c | 4.61 ± 0.43 ab | 5.27 ± 0.35 bc | 5.01 ± 0.78 abc | 4.49 ± 0.31 a |
| Fertilized | 4.43 ± 0.41 a | 4.60 ± 0.29 ab | 4.73 ± 0.34 abc | 5.04 ± 0.38 c | 4.84 ± 0.38 bc | |
| p-Value | 0 | 0.79 | 0.01 | 0.92 | 0.05 | |
| Total flavonoids (%) | Unfertilized | 0.20 ± 0.03 | 0.18 ± 0.02 | 0.27 ± 0.08 | 0.22 ± 0.06 | 0.27 ± 0.08 |
| Fertilized | 0.22 ± 0.05 ab | 0.19 ± 0.02 a | 0.25 ± 0.07 b | 0.21 ± 0.04 a | 0.23 ± 0.04 ab | |
| p-Value | 0.58 | 0.25 | 0.73 | 0.48 | 0.21 | |
| P (mg/kg) | Unfertilized | 4320.79 ± 206.71 b | 4957.91 ± 351.29 c | 3713.41 ± 526.56 a | 3729.91 ± 138.73 a | 3328.63 ± 348.55 a |
| Fertilized | 4113.58 ± 359.54 c | 5350.46 ± 433.62 d | 3592.10 ± 371.05 b | 3953.70 ± 567.47 bc | 3171.35 ± 275.91 a | |
| p-Value | 0.38 | 0.05 | 0.61 | 0.41 | 0.21 | |
| Ca (mg/kg) | Unfertilized | 471.63 ± 104.42 c | 41.59 ± 11.68 ab | 90.84 ± 34.36 b | 17.93 ± 8.27 a | 425.81 ± 50.36 c |
| Fertilized | 101.70 ± 55.05 c | 18.79 ± 9.61 a | 89.71 ± 29.31 bc | 35.07 ± 10.63 ab | 595.75 ± 125.75 d | |
| p-Value | 0 | 0 | 0.95 | 0.01 | 0 | |
| Cu (mg/kg) | Unfertilized | 3.66 ± 0.59 a | 3.20 ± 0.39 a | 59.25 ± 10.47 c | 38.78 ± 21.12 b | 5.97 ± 0.75 a |
| Fertilized | 3.54 ± 0.42 a | 3.25 ± 0.69 a | 59.44 ± 11.03 c | 40.81 ± 10.83 b | 5.79 ± 1.26 a | |
| p-Value | 0.71 | 0.67 | 0.97 | 0.80 | 0.78 | |
| Fe (mg/kg) | Unfertilized | 130.75 ± 22.81 abc | 64.82 ± 12.48 a | 154.02 ± 53.09 bc | 196.84 ± 76.02 c | 86.57 ± 26.91 ab |
| Fertilized | 178.60 ± 54.47 bc | 67.81 ± 17.74 a | 123.38 ± 32.25 ab | 208.76 ± 134.25 c | 130.15 ± 66.68 ab | |
| p-Value | 0.19 | 0.47 | 0.18 | 0.86 | 0.06 | |
| K (mg/kg) | Unfertilized | 8631.61 ± 293.48 d | 5069.77 ± 524.57 c | 3711.78 ± 393.96 b | 2110.28 ± 175.98 a | 5343.72 ± 324.24 c |
| Fertilized | 6107.49 ± 636.79 e | 4458.54 ± 447.79 c | 3633.97 ± 408.66 b | 2534.69 ± 282.32 a | 5456.81 ± 388.93 d | |
| p-Value | 0 | 0.10 | 0.73 | 0.01 | 0.60 | |
| Mg (mg/kg) | Unfertilized | 990.28 ± 212.95 c | 391.12 ± 43.59 b | 218.25 ± 14.07 a | 157.45 ± 19.79 a | 896.54 ± 39.05 c |
| Fertilized | 495.02 ± 51.02 c | 309.03 ± 65.62 b | 216.62 ± 39.03 a | 183.46 ± 28.48 a | 979.50 ± 48.02 d | |
| p-Value | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.91 | 0.09 | 0 | |
| Mn (mg/kg) | Unfertilized | 10.82 ± 1.07 c | 4.33 ± 0.95 b | 4.87 ± 1.06 b | 2.03 ± 0.10 a | 10.00 ± 1.34 c |
| Fertilized | 7.94 ± 1.09 c | 3.84 ± 0.65 ab | 4.56 ± 1.73 b | 2.90 ± 0.75 a | 12.41 ± 1.80 d | |
| p-Value | 0 | 0.27 | 0.73 | 0.02 | 0 | |
| Zn (mg/kg) | Unfertilized | 26.23 ± 1.92 a | 28.80 ± 4.14 a | 52.22 ± 6.25 b | 48.08 ± 7.50 b | 29.20 ± 2.96 a |
| Fertilized | 25.06 ± 7.56 a | 32.23 ± 4.62 b | 46.69 ± 8.89 c | 44.03 ± 7.47 c | 27.53 ± 3.60 ab | |
| p-Value | 0.80 | 0.15 | 0.24 | 0.33 | 0.32 |
| Samples | Region | Lhasa | Nyingchi | Ngari | Shannan | Xigaze | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unfertilized highland barley | Original classification (%) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Cross-validation (%) | 66.7 | 100 | 100 | 80 | 80 | 87.0 | |
| Fertilized highland barley | Original classification (%) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Cross-validation (%) | 100 | 100 | 80 | 81.8 | 100 | 91.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, S.; Qiu, C.; Zhang, T.; Hu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, X.; Ma, Y.; Qie, M.; Chen, C. Effects of Fertilizer on the Quality and Traceability of Tibet highland Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.): A Diagnosis Using Nutrients and Mineral Elements. Foods 2022, 11, 3397. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11213397
Zhao S, Qiu C, Zhang T, Hu X, Zhao Y, Cheng X, Ma Y, Qie M, Chen C. Effects of Fertilizer on the Quality and Traceability of Tibet highland Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.): A Diagnosis Using Nutrients and Mineral Elements. Foods. 2022; 11(21):3397. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11213397
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Shanshan, Cheng Qiu, Tangwei Zhang, Xiangyu Hu, Yan Zhao, Xiyu Cheng, Yuxuan Ma, Mengjie Qie, and Chang Chen. 2022. "Effects of Fertilizer on the Quality and Traceability of Tibet highland Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.): A Diagnosis Using Nutrients and Mineral Elements" Foods 11, no. 21: 3397. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11213397
APA StyleZhao, S., Qiu, C., Zhang, T., Hu, X., Zhao, Y., Cheng, X., Ma, Y., Qie, M., & Chen, C. (2022). Effects of Fertilizer on the Quality and Traceability of Tibet highland Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.): A Diagnosis Using Nutrients and Mineral Elements. Foods, 11(21), 3397. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11213397







